Sport in Tokelau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tokelau (; ; known previously as the Union Islands, and, until 1976, known officially as the Tokelau Islands) is a
 The first European to sight Atafu was Commodore
The first European to sight Atafu was Commodore 
 According to the US Central Intelligence Agency's
According to the US Central Intelligence Agency's
File:Nukunonu Lagoon20070716.jpg, Nukunonu Lagoon in Tokelau.
File:Atafu street dawn 20070715.jpg, Atafu street at dawn
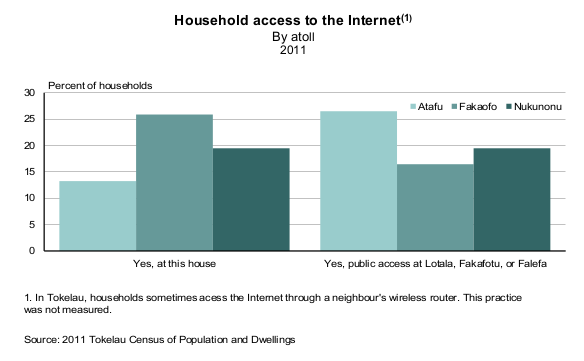 Tokelau has increased its GDP by more than 10% through registrations of domain names under its
Tokelau has increased its GDP by more than 10% through registrations of domain names under its
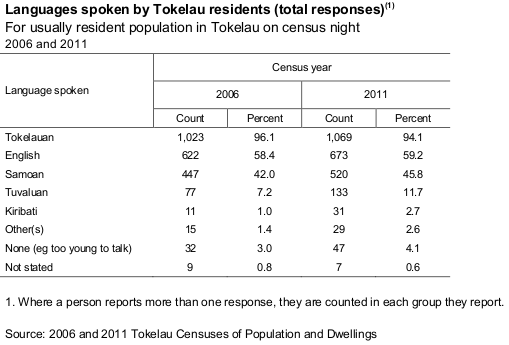 According to the 2016 Tokelau Census, Tokelau has a '' de jure'' usually resident population of 1,499 people. The census shows a 6.2% increase in the de jure usually resident population between 2011 and 2016.
The nationals of Tokelau are called Tokelauans, and the major ethnic group is Polynesian; it has no recorded minority groups. About 84% of inhabitants are of wholly or partly Tokelauan ethnicity; people of Samoan ethnicity make up 6.7% of the population, and Tuvaluans 2.8%. The main language—spoken by over 90% of inhabitants—is Tokelauan, but almost 60% also speak English.
The less than 1,500 Polynesian inhabitants live in three villages. Their isolation and lack of resources greatly limits economic development and confines agriculture to the subsistence level. The very limited natural resources and overcrowding are contributing to emigration to New Zealand and Samoa. In the 2013 New Zealand census, more than 7,000 people identified as Tokelauan, almost five times as many as live in Tokelau itself. Depletion of tuna has made fishing for food more difficult.
A significant proportion (44.9% in 2016) of the population were born overseas, mostly in Samoa (15.3% of total population) and New Zealand (11.5%).
While slightly more females than males live on Atafu and Fakaofo, males make up 57% of Nukunonu residents. Only 9% of Tokelauans aged 40 or more have never been married. One-quarter of the population were born overseas; almost all the rest live on the same atoll they were born on. Most households own five or more pigs.
Despite its low income, Tokelau has a life expectancy of 69 years, comparable with other Oceania islands.
According to the 2016 Tokelau Census, Tokelau has a '' de jure'' usually resident population of 1,499 people. The census shows a 6.2% increase in the de jure usually resident population between 2011 and 2016.
The nationals of Tokelau are called Tokelauans, and the major ethnic group is Polynesian; it has no recorded minority groups. About 84% of inhabitants are of wholly or partly Tokelauan ethnicity; people of Samoan ethnicity make up 6.7% of the population, and Tuvaluans 2.8%. The main language—spoken by over 90% of inhabitants—is Tokelauan, but almost 60% also speak English.
The less than 1,500 Polynesian inhabitants live in three villages. Their isolation and lack of resources greatly limits economic development and confines agriculture to the subsistence level. The very limited natural resources and overcrowding are contributing to emigration to New Zealand and Samoa. In the 2013 New Zealand census, more than 7,000 people identified as Tokelauan, almost five times as many as live in Tokelau itself. Depletion of tuna has made fishing for food more difficult.
A significant proportion (44.9% in 2016) of the population were born overseas, mostly in Samoa (15.3% of total population) and New Zealand (11.5%).
While slightly more females than males live on Atafu and Fakaofo, males make up 57% of Nukunonu residents. Only 9% of Tokelauans aged 40 or more have never been married. One-quarter of the population were born overseas; almost all the rest live on the same atoll they were born on. Most households own five or more pigs.
Despite its low income, Tokelau has a life expectancy of 69 years, comparable with other Oceania islands.
 Tokelau is predominantly
Tokelau is predominantly
 Each atoll has a school and hospital. The health services have a Director of Health in Apia and a Chief Clinical Advisor who moves from atoll to atoll as required to assist the doctors attached to each hospital. In 2007 there was not always a doctor on each island and locums were appointed to fill the gaps.
Many Tokelauan youth travel to New Zealand to further their education and Tokelau is most populated around the Christmas season, with students returning home and then heading off for another year of study.
Each atoll has a school and hospital. The health services have a Director of Health in Apia and a Chief Clinical Advisor who moves from atoll to atoll as required to assist the doctors attached to each hospital. In 2007 there was not always a doctor on each island and locums were appointed to fill the gaps.
Many Tokelauan youth travel to New Zealand to further their education and Tokelau is most populated around the Christmas season, with students returning home and then heading off for another year of study.
 Due to its small size, Tokelau is unaffiliated to most international sports organisations, and rarely takes part in international events. The only significant international competition Tokelau takes part in is the Pacific Games. Tokelau won its first-ever gold medals at the
Due to its small size, Tokelau is unaffiliated to most international sports organisations, and rarely takes part in international events. The only significant international competition Tokelau takes part in is the Pacific Games. Tokelau won its first-ever gold medals at the
International Table Tennis Federation, 7 October 2010 Tokelau was due to take part, for the first time, in the
Rec.Sport.Soccer Statistics Foundation, 29 July 2010.
 Tokelau has a radio telephone service between the islands and to Samoa. In 1997, a government-regulated telephone service (TeleTok) with three satellite earth stations was established. Each atoll has a radio-broadcast station that broadcasts shipping and weather reports and every household has a radio or access to one. News is disseminated through the government
Tokelau has a radio telephone service between the islands and to Samoa. In 1997, a government-regulated telephone service (TeleTok) with three satellite earth stations was established. Each atoll has a radio-broadcast station that broadcasts shipping and weather reports and every household has a radio or access to one. News is disseminated through the government
Tokelau
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Tokelau
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * *
Tokelau Council of Ongoing Government
executive branch of the government
The Administrator of Tokelau
Tokelau website of the NZ Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade
Fakaofo
Nukunonu
{{Authority control 1948 establishments in Oceania Atolls of New Zealand British Western Pacific Territories Dependent territories of New Zealand English-speaking countries and territories Geography of Polynesia Island countries States and territories established in 1948
dependent territory
A dependent territory, dependent area, or dependency (sometimes referred as an external territory) is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a sovereign state, yet remains politically outside the controlli ...
of New Zealand in the southern Pacific Ocean. It consists of three tropical coral atolls: Atafu
Atafu, formerly known as the Duke of York Group, is a group of 52 coral islets within Tokelau in the south Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. With a land area of , it is the smallest of the three islands that constitute Tokelau. It is an atoll and su ...
, Nukunonu, and Fakaofo
Fakaofo, formerly known as Bowditch Island, is a South Pacific Ocean atoll located in the Tokelau Group. The actual land area is only about 3 km2 (1.1 sq mi), consisting of islets on a coral reef surrounding a central lagoon of some 45 k ...
. They have a combined land area of . The capital rotates yearly among the three atolls. In addition to these three, Swains Island
Swains Island (; Tokelauan: ''Olohega'' ; Samoan: ''Olosega'' ) is a remote coral atoll in the Tokelau Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. The island is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute between Tokelau and the United States, whi ...
, which forms part of the same archipelago, is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute; it is currently administered by the United States as part of American Samoa. Tokelau lies north of the Samoan Islands, east of Tuvalu, south of the Phoenix Islands, southwest of the more distant Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands (in Gilbertese, ''Aono Raina'') are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawa ...
, and northwest of the Cook Islands.
Tokelau has a population of approximately 1,500 people; it has the fourth-smallest population of any sovereign state or dependency in the world. As of the 2016 census, around 45% of its residents had been born overseas, mostly in Samoa or New Zealand. The populace has a life expectancy of 69, which is comparable to that of other Oceanian island nations. Approximately 94% of the population speak Tokelauan as their first language. Tokelau has the smallest economy of any sovereign nation, although it is a leader in renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
, being the first 100% solar-power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic ...
ed nation in the world.
Tokelau is officially referred to as a '' nation'' by both the New Zealand government and the Tokelauan government. It is a free and democratic nation with elections every three years. However, in 2007, the United Nations General Assembly included Tokelau on its list of non-self-governing territories. Its inclusion on this list is controversial, as Tokelauans have twice narrowly voted against further self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
, and the islands' small population makes the viability of self-government challenging. The basis of Tokelau's legislative, administrative and judicial systems is the Tokelau Islands Act 1948
The constitutional history of Tokelau comprises several acts and amendments. Tokelau comprises the three Pacific atolls of Atafu, Nukunonu, and Fakaofo. The constitutional history of the atoll group dates to its earliest human settlement of at le ...
, which has been amended several times. Since 1993, the territory has annually elected its own head of government, the ''Ulu-o-Tokelau''. Before 1993, the administrator of Tokelau
The Administrator of Tokelau is an official of the New Zealand Government, responsible for supervising the government of the dependent territory of Tokelau.
Powers and functions
Certain of the Administrator's powers and functions are set f ...
was the highest official in the government and the territory was directly administered by a New Zealand government department.
Etymology
is a word meaning "north wind" in the nativeTokelau language
Tokelauan is a Polynesian language spoken in Tokelau and on Swains Island (or Olohega) in American Samoa. It is closely related to Tuvaluan and is related to Samoan and other Polynesian languages. Tokelauan has a co-official status with Englis ...
. The Tokelau islands were named the ''Union Islands'' and ''Union Group'' by European explorers at an earlier time. ''Tokelau Islands'' was adopted as the islands’ official name in 1946. The name was officially shortened to ''Tokelau'' on 9 December 1976.
History
Pre-history
Archaeological evidence indicates that the atolls of Tokelau –Atafu
Atafu, formerly known as the Duke of York Group, is a group of 52 coral islets within Tokelau in the south Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. With a land area of , it is the smallest of the three islands that constitute Tokelau. It is an atoll and su ...
, Nukunonu, and Fakaofo
Fakaofo, formerly known as Bowditch Island, is a South Pacific Ocean atoll located in the Tokelau Group. The actual land area is only about 3 km2 (1.1 sq mi), consisting of islets on a coral reef surrounding a central lagoon of some 45 k ...
– were settled about 1,000 years ago from Samoa and may have been a gateway into Eastern Polynesia. The inhabitants embrace Polynesian mythology and the local god, Tui Tokelau. Over time, they developed distinctive musical
Musical is the adjective of music.
Musical may also refer to:
* Musical theatre, a performance art that combines songs, spoken dialogue, acting and dance
* Musical film and television, a genre of film and television that incorporates into the narr ...
and art forms. The three atolls have historically functioned separately politically, while maintaining social and linguistic cohesion. Tokelauan society has been governed by chiefly clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, meaning ...
s, and there have been occasional skirmishes and wars between the atolls, as well as inter-marriage. Fakaofo, the "chiefly island", held some dominion over Atafu and Nukunonu after the dispersal of Atafu. Life on the atolls was historically subsistence-based, with a diet that relied mainly on fish and coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
.
Contact with other cultures
 The first European to sight Atafu was Commodore
The first European to sight Atafu was Commodore John Byron
Vice-Admiral John Byron (8 November 1723 – 1 April 1786) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer. He earned the nickname "Foul-Weather Jack" in the press because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sa ...
, on 24 June 1765. He called the island "Duke of York's Island". Parties from his expedition who ventured ashore reported that there were no signs of current or previous inhabitants.MacGregor, 30 Captain Edward Edwards, having learned of Byron's discovery, visited Atafu on 6 June 1791 in search of the ''Bounty'' mutineers. They found no inhabitants, but saw that there were houses containing canoes and fishing gear, which suggested to them that the island was being used as a temporary residence by fishing parties from other, nearby islands. On 12 June 1791, Edwards sailed farther south, and sighted Nukunonu, naming it "Duke of Clarence's Island". A landing party that went ashore was unable to make contact with the inhabitants, but saw "''morai''s", burying places, and canoes with "stages in their middle" sailing across the island's lagoons.
On 29 October 1825, August R. Strong of the USS ''Dolphin'' and his crew arrived at the atoll Nukunonu. He wrote: Upon examination, we found they had removed all the women and children from the settlement, which was quite small, and put them in canoes lying off a rock in the lagoon. They would frequently come near the shore, but when we approached they would pull off with great noise and precipitation.On 14 February 1835, Captain Smith, of the United States
whaling ship
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japa ...
the ''General Jackson'', wrote of having sighted Fakaofo, which he chose to call "D'Wolf's Island". On 25 January 1841, the United States Exploring Expedition visited Atafu, and discovered a small population living on the island. The residents appeared to be there only temporarily, because there was no chief among them, and they had the kind of double canoes that were typically used for inter-island travel. They appeared to have interacted with foreigners in the past, because they expressed a desire to engage in barter with the expedition crew, and they possessed items that were apparently of foreign origin: blue beads and a plane-iron. A few days later, French explorer Captain Morvan sighted Fakaofo. The American expedition reached Nukunonu on 28 January 1841, but did not record any information about inhabitants. On 29 January 1841, the expedition sighted Fakaofo and named it "Bowditch". The Fakaofo islanders were found to be similar in appearance and behavior to the Atafu islanders.
Missionaries preached Christianity in Tokelau
The vast majority of people in Tokelau are Christians and Christianity plays a significant role in the Tokelauan way of life.
History
Missionaries preached Christianity in Tokelau from 1845 to the 1860s. French Roman Catholic missionaries on Wall ...
from 1845 to the 1870s. French Catholic missionaries on Wallis Island (also known as 'Uvea) and missionaries of the Protestant London Missionary Society in Samoa used native teachers to convert the Tokelauans. Atafu was converted to Protestantism by the London Missionary Society, Nukunonu was converted to Catholicism and Fakaofo was converted to both denominations. The Rev. Samuel James Whitmee, of the London Missionary Society, visited Tokelau in 1870.
Helped by Swains Island
Swains Island (; Tokelauan: ''Olohega'' ; Samoan: ''Olosega'' ) is a remote coral atoll in the Tokelau Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. The island is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute between Tokelau and the United States, whi ...
-based Eli Jennings senior, Peruvian "blackbird" slave traders arrived in 1863 and kidnapped nearly all (253) of the able-bodied men to work as labourers, depopulating the atolls. The Tokelauan men died of dysentery and smallpox, and very few returned. With that loss, the system of governance became based on the "Taupulega", or "Councils of Elders", on which individual families on each atoll were represented. During that time, Polynesian immigrants settled, followed by American, Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
, French, Portuguese and German beachcombers
''The Beachcombers'' is a Canadian comedy-drama television series that ran on CBC Television from October 1, 1972, to December 12, 1990. With over 350 episodes, it is one of the longest-running dramatic series ever made for English-language Canad ...
, marrying local women and repopulating the atolls.
Between 1856 and 1979, the United States claimed that it held sovereignty over the island and the other Tokelauan atolls. In 1979, the U.S. conceded that Tokelau was under New Zealand sovereignty, and a maritime boundary between Tokelau and American Samoa was established by the Treaty of Tokehega.

Tropical cyclones
Cyclone Percy
Cyclone Percy was the seventh named storm of the 2004–05 South Pacific cyclone season and the fourth and final severe tropical cyclone to form during the 2004–05 South Pacific cyclone season. Cyclone Percy originated as a tropical disturbance ...
struck and severely damaged Tokelau in late February and early March 2005. Forecasters underestimated the cyclone's strength and the length of time it would be in vicinity to Tokelau. It coincided with a spring tide which put most of the area of the two villages on Fakaofo and Nukunonu under a metre of seawater. The cyclone also caused major erosion on several islets of all three atolls, damaging roads and bridges and disrupting electric power and telecommunications systems. The cyclone did significant and widespread damage to food crops including bananas, coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
s and pandanus
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with some 750 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. The greatest number of species are found in Madagascar and Malaysia. Common names ...
. It did not seriously injure anyone but villagers lost significant amounts of property.
No significant land is more than above high water of ordinary tides. This means Tokelau is particularly vulnerable to any possible sea level rises.
Time zone
Until December 2011, Tokelau was 11 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). At midnight 29 December 2011 Tokelau shifted to UTC+13:00 in response to Samoa's decision to switch sides of the International Dateline. This brought Tokelau closer to New Zealand time (and in the process omitted 30 December). Many sources claim that Tokelau is 14 hours ahead of UTC (UTC−10 before the 2011 date switch), but the correct time zone offset is UTC+13:00.Government
In 1877, the islands were included under the protection of the United Kingdom by an Order in Council that claimed jurisdiction over all unclaimedPacific Islands
Collectively called the Pacific Islands, the islands in the Pacific Ocean are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of se ...
. Commander C. F. Oldham on HMS ''Egeria'' landed at each of the three atolls in June 1889 and officially raised the Union Flag, declaring the group a British protectorate. In conformity with desire expressed by "the Native government" they were annexed by the United Kingdom and included in the Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
by the Tokelau Islands (Union Islands) Order in Council, 1916.''Commonwealth and Colonial Law'' by Kenneth Roberts-Wray, London, Stevens, 1966. P. 894 The annexation took place on 29 February 1916. From the point in time that the islands were annexed, their people had the status of British subjects
The term "British subject" has several different meanings depending on the time period. Before 1949, it referred to almost all subjects of the British Empire (including the United Kingdom, Dominions, and colonies, but excluding protectorates ...
. Tokelau was removed from the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony
The Gilbert and Ellice Islands (GEIC as a colony) in the Pacific Ocean were part of the British Empire from 1892 to 1976. They were a protectorate from 1892 to 12 January 1916, and then a colony until 1 January 1976. The history of the colony w ...
and placed under the jurisdiction of the Governor-General of New Zealand
The governor-general of New Zealand ( mi, te kāwana tianara o Aotearoa) is the viceregal representative of the monarch of New Zealand, currently King Charles III. As the King is concurrently the monarch of 14 other Commonwealth realms and li ...
in 1925, two Orders in Council being made for the purpose on the same day. This step meant that New Zealand took over administration of Tokelau from the British on 11 February 1926.''Tokelau: A history of Government – The constitutional history and legal development of Tokelau''; Compiled and recorded for the Tokelau Law Team by Tony Angelo and Talei Pasikale, 2008 At this point, Tokelau was still a territory under the sovereignty of the United Kingdom but administered by New Zealand.
The Union Islands (Revocation) Order in Council, 1948 after reciting the agreement by the governments of the United Kingdom and New Zealand that the islands should become part of New Zealand, revoked the Union Islands (No. 2) Order in Council, 1925, with effect from a date fixed by the Governor-General of New Zealand after he was satisfied that the New Zealand Parliament had provided for the incorporation of the islands with New Zealand, as it did by the ''Tokelau Islands Act 1948''. Tokelau formally became part of New Zealand on 1 January 1949.
The Dominion of New Zealand
The Dominion of New Zealand was the historical successor to the Colony of New Zealand. It was a constitutional monarchy with a high level of self-government within the British Empire.
New Zealand became a separate British Crown colony in 184 ...
, of which Tokelau formerly was a part, has since been superseded by the Realm of New Zealand, of which Tokelau remains a part. Defence is the responsibility of New Zealand. When the ''British Nationality and New Zealand Citizenship Act 1948'' came into effect on 1 January 1949, Tokelauans who were British subjects gained New Zealand citizenship
New Zealand nationality law details the conditions by which a person holds New Zealand nationality. The primary law governing nationality requirements is the Citizenship Act 1977, which came into force on 1 January 1978. Regulations apply to t ...
; a status they still hold.
Villages are entitled to enact their own laws regulating their daily lives and New Zealand law only applies where it has been extended by specific enactment. Serious crime is rare and there are no prisons, and offenders are publicly rebuked, fined or made to work.
Politics
The head of state is , the in right of New Zealand, who also reigns over the otherCommonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
s. The is represented in the territory by the Administrator
Administrator or admin may refer to:
Job roles Computing and internet
* Database administrator, a person who is responsible for the environmental aspects of a database
* Forum administrator, one who oversees discussions on an Internet forum
* N ...
– currently Don Higgins. The current head of government is Siopili Perez, who presides over the Council for the Ongoing Government of Tokelau
The Council for the Ongoing Government of Tokelau is the executive body in Tokelau. It serves as the governing organization for Tokelau when the General Fono is not in session. The council has six members, consisting of the ''faipule'' (leader) ...
, which functions as a cabinet. The Council consists of the ''faipule'' (leader) and ''pulenuku'' (village mayor) of each of the three atolls. The administrator is appointed by the minister of Foreign Affairs and Trade of New Zealand, and the role of head of government rotates between the three ''faipule'' for a one-year term.
The Tokelau Amendment Act of 1996 confers legislative power on the General Fono
The General Fono is the parliament of Tokelau. It has 20 members (15 before 2008), representing the 3 atolls. Elections are held every three years.
Tokelau is a de facto non-partisan democracy since both village and Fono elections are made witho ...
, a unicameral body. The number of seats each atoll receives in the Fono is determined by population – at present, Fakaofo and Atafu each have seven and Nukunonu has six. ''Faipule'' and ''pulenuku'' also sit in the Fono.
On 11 November 2004, Tokelau and New Zealand took steps to formulate a treaty that would turn Tokelau from a non-self-governing territory to a self-governing state in free association with New Zealand. Besides the treaty, a United Nations-sponsored referendum on self-determination took place, with the three islands voting on successive days starting 13 February 2006. (Tokelauans in Apia, Samoa, voted on 11 February.) Out of 581 votes cast, 349 were for Free Association, being short of the two-thirds majority required for the measure to pass. The referendum was profiled (somewhat light-heartedly) in the 1 May 2006 issue of '' The New Yorker'' magazine. A repeat referendum took place on 20–24 October 2007, again narrowly failing to approve self-government. This time the vote was short by just 16 votes or 3%.
In May 2008, the United Nations' Secretary General Ban Ki-moon
Ban Ki-moon (; ; born 13 June 1944) is a South Korean politician and diplomat who served as the eighth secretary-general of the United Nations between 2007 and 2016. Prior to his appointment as secretary-general, Ban was his country's Minister ...
urged colonial powers "to complete the decolonization process in every one of the remaining 16 non-self-governing territories
Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter defines a non-self-governing territory (NSGT) as a territory "whose people have not yet attained a full measure of self-government". In practice, an NSGT is a territory deemed by the United Nations Gener ...
", including Tokelau. This led '' The New Zealand Herald'' to comment that the United Nations was "apparently frustrated by two failed attempts to get Tokelau to vote for independence". In April 2008, speaking as leader of the National Party, future New Zealand Prime Minister John Key stated that New Zealand had "imposed two referenda on the people of the Tokelau Islands", and questioned "the accepted wisdom that small states should undergo a de-colonisation process".
Geography
Tokelau includes three atolls in the South Pacific Ocean between longitudes 171° and 173° W and between latitudes 8° and 10° S, about midway between Hawaii and New Zealand. From Atafu in the north to Fakaofo in the south, Tokelau extends for less than 200 km. The atolls lie about north of Samoa. The atolls areAtafu
Atafu, formerly known as the Duke of York Group, is a group of 52 coral islets within Tokelau in the south Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. With a land area of , it is the smallest of the three islands that constitute Tokelau. It is an atoll and su ...
, Nukunonu, both in a group of islands once called the Duke of Clarence Group, and Fakaofo
Fakaofo, formerly known as Bowditch Island, is a South Pacific Ocean atoll located in the Tokelau Group. The actual land area is only about 3 km2 (1.1 sq mi), consisting of islets on a coral reef surrounding a central lagoon of some 45 k ...
, once Bowditch Island. Their combined land area is . The atolls each have a number of coral islands, where the villages
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
are situated. The highest point of Tokelau is just above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. There are no ports or harbours for large vessels, however, all three atolls have a jetty to and from which supplies and passengers are shipped. Tokelau lies in the Pacific tropical cyclone belt. A fourth island that is culturally, historically, and geographically, but not politically, part of the Tokelau chain is Swains Island
Swains Island (; Tokelauan: ''Olohega'' ; Samoan: ''Olosega'' ) is a remote coral atoll in the Tokelau Islands in the South Pacific Ocean. The island is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute between Tokelau and the United States, whi ...
(Olohega), under United States control since about 1900 and administered as part of American Samoa since 1925.
Swains Island was claimed by the United States pursuant to the Guano Islands Act, as were the other three islands of Tokelau; the latter three claims were ceded to Tokelau by treaty in 1979. In the draft constitution of Tokelau subject to the Tokelauan self-determination referendum in 2006, Olohega (Swains Island) was also claimed as a part of Tokelau, though the claim was surrendered in the same 1979 treaty. This established a clearly defined boundary between American Samoa and Tokelau.
Tokelau's claim to Swains is generally comparable to the Marshall Islands' claim to US-administered Wake Island, but the re-emergence of this somewhat dormant issue has been an unintended result of the United Nations' recent efforts to promote decolonisation in Tokelau. Tokelauans have proven somewhat reluctant to push their national identity in the political realm: recent decolonisation moves have mainly been driven from outside for ideological reasons. But at the same time, Tokelauans are reluctant to disown their common cultural identity with Swains Islanders who speak their language.
Environment
Tokelau is located in the Western Polynesian tropical moist forests ecoregion. Most of the original vegetation has been replaced bycoconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
plantations, some of which have been abandoned and became scrubby forests. The atolls of Tokelau provide habitat for 38 indigenous plant species, over 150 insect species and 10 land crab species. One of the greatest threats to biodiversity is posed by introduced mammalian predators such as the Polynesian Rat.
In 2011 Tokelau declared its entire exclusive economic zone of a shark sanctuary.
Economy
list of countries by GDP (PPP)
GDP (PPP) means gross domestic product based on purchasing power parity.
This article includes a list of countries by their forecast estimated GDP (PPP). Countries are sorted by GDP (PPP) forecast estimates from financial and statistical ...
Tokelau has the smallest economy in the world. Tokelau has an annual purchasing power of about US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
1,000 (€
The euro sign () is the currency sign used for the euro, the official currency of the eurozone and unilaterally adopted by Kosovo and Montenegro. The design was presented to the public by the European Commission on 12 December 1996. It consists o ...
674) per capita. The government is almost entirely dependent on subsidies from New Zealand. It has annual revenues of less than US$500,000 (€336,995) against expenditures of some US$2.8 million (€1.9 million). The deficit is made up by aid from New Zealand.
Tokelau annually exports around US$100,000 (€67,000) of stamps, copra and woven and carved handicrafts and imports over US$300,000 (€202,000) of foodstuffs, building materials, and fuel to, and from, New Zealand. New Zealand also pays directly for the cost of medical and education services. Local industries include small-scale enterprises for copra production, wood work, plaited craft goods, stamps, coins, and fishing. Agriculture and livestock produces coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
s, copra, breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family (Moraceae) believed to be a domesticated descendant of ''Artocarpus camansi'' originating in New Guinea, the Maluku Islands, and the Philippi ...
, papaya
The papaya (, ), papaw, () or pawpaw () is the plant species ''Carica papaya'', one of the 21 accepted species in the genus ''Carica'' of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and ...
s, bananas, fig
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Moraceae. Native to the Mediterranean and western Asia, it has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world ...
s, pigs, poultry and a few goats. Many Tokelauans live in New Zealand and support their families in Tokelau through remittance
A remittance is a non-commercial transfer of money by a foreign worker, a member of a diaspora community, or a citizen with familial ties abroad, for household income in their home country or homeland. Money sent home by migrants competes wit ...
s.
Solar power
The goal of 100% renewable electricity was met on 7 November 2012, according to theForeign Affairs Minister of New Zealand
The Minister of Foreign Affairs is a senior member of the New Zealand Government heading the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade and responsible for relations with foreign countries.
The current Minister of Foreign Affairs is Nanaia Mahuta. ...
, Murray McCully. Previously electricity was generated using diesel generators and was only available about 16 hours/day.
Three solar power stations with a total generation capacity of 930kWp were installed to provide 100% of current electrical demand from photovoltaics, with lead acid battery backup able to store around 8MWh. The first power station was completed in August 2012. In total, 4,032 solar panels are used and 1,344 batteries weighing each. The systems are designed to withstand winds of . By 2011, Tokelau's electricity was 93% generated by photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
s, with the remainder generated from coconut oil
frameless , right , alt = A cracked coconut and a bottle of coconut oil
Coconut oil (or coconut butter) is an edible oil derived from the wick, meat, and milk of the coconut palm fruit. Coconut oil is a white solid fat; in warmer climates duri ...
. As of 2019, increased demand and degradation of batteries had led to increased need for backup power. Plans were made for an additional 210 kW of PV and close to 2MWh of lithium-ion battery capacity.
Internet domain name
 Tokelau has increased its GDP by more than 10% through registrations of domain names under its
Tokelau has increased its GDP by more than 10% through registrations of domain names under its top-level domain
A top-level domain (TLD) is one of the domains at the highest level in the hierarchical Domain Name System of the Internet after the root domain. The top-level domain names are installed in the root zone of the name space. For all domains in ...
, .tk
.tk is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Tokelau, a territory of New Zealand in the South Pacific. It can be registered on the company Freenom.
Overview
Tokelau allows any individual to register domain names. Users and smal ...
. Registrations can be either free, in which case the user owns only usage rights and not the domain itself, or paid, which grants full rights. Free domains are pointed to Tokelau name servers, which redirects the domain via HTML frames
In the context of a web browser, a frame is a part of a web page or browser window which displays content independent of its container, with the ability to load content independently. The HTML or media elements shown in a frame may come from a ...
to a specified address or to a specified A or NS record, and the redirection of up to 250 email addresses to an external address (not at a .tk domain).
In September 2003 Fakaofo
Fakaofo, formerly known as Bowditch Island, is a South Pacific Ocean atoll located in the Tokelau Group. The actual land area is only about 3 km2 (1.1 sq mi), consisting of islets on a coral reef surrounding a central lagoon of some 45 k ...
became the first part of Tokelau with a high-speed Internet connection. Foundation Tokelau financed the project. Tokelau gives most domain names under its authority away to anyone for free to gain publicity for the territory. This has allowed the nation to gain enhanced telecommunications technologies, such as more computers and Internet access for Tokelauan residents. By 2012, there were about 120 computers, mostly laptops, and 1/6th of the economy consists of income from .tk domain names.
According to a 2016 analysis of domain name registration performed by the .uk
.uk is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for the United Kingdom. It was first registered in July 1985, seven months after the original generic top-level domains such as .com and the first country code after .us.
, it is the fift ...
registrar Nominet
Nominet UK is currently delegated by IANA to be the manager of the .uk domain name. Nominet directly manages registrations directly under .uk, and some of the second level domains .co.uk, .org.uk, .sch.uk, .me.uk, .net.uk, .ltd.uk and .plc.uk.
...
using data from ZookNIC, tk domains are the "world's largest country-code domain ... almost as large as second and third place holders China (.cn
.cn is the country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for the People's Republic of China introduced on 28 November 1990. Domain name administration in mainland China is managed through a branch of the Ministry of Industry and Information. The registr ...
) and Germany (.de
.de is the country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for the Federal Republic of Germany. DENIC (the Network Information Centre responsible for .de domains) does not require specific second-level domains, and there are no official ccSLDs under .d ...
) combined".
Demography
 According to the 2016 Tokelau Census, Tokelau has a '' de jure'' usually resident population of 1,499 people. The census shows a 6.2% increase in the de jure usually resident population between 2011 and 2016.
The nationals of Tokelau are called Tokelauans, and the major ethnic group is Polynesian; it has no recorded minority groups. About 84% of inhabitants are of wholly or partly Tokelauan ethnicity; people of Samoan ethnicity make up 6.7% of the population, and Tuvaluans 2.8%. The main language—spoken by over 90% of inhabitants—is Tokelauan, but almost 60% also speak English.
The less than 1,500 Polynesian inhabitants live in three villages. Their isolation and lack of resources greatly limits economic development and confines agriculture to the subsistence level. The very limited natural resources and overcrowding are contributing to emigration to New Zealand and Samoa. In the 2013 New Zealand census, more than 7,000 people identified as Tokelauan, almost five times as many as live in Tokelau itself. Depletion of tuna has made fishing for food more difficult.
A significant proportion (44.9% in 2016) of the population were born overseas, mostly in Samoa (15.3% of total population) and New Zealand (11.5%).
While slightly more females than males live on Atafu and Fakaofo, males make up 57% of Nukunonu residents. Only 9% of Tokelauans aged 40 or more have never been married. One-quarter of the population were born overseas; almost all the rest live on the same atoll they were born on. Most households own five or more pigs.
Despite its low income, Tokelau has a life expectancy of 69 years, comparable with other Oceania islands.
According to the 2016 Tokelau Census, Tokelau has a '' de jure'' usually resident population of 1,499 people. The census shows a 6.2% increase in the de jure usually resident population between 2011 and 2016.
The nationals of Tokelau are called Tokelauans, and the major ethnic group is Polynesian; it has no recorded minority groups. About 84% of inhabitants are of wholly or partly Tokelauan ethnicity; people of Samoan ethnicity make up 6.7% of the population, and Tuvaluans 2.8%. The main language—spoken by over 90% of inhabitants—is Tokelauan, but almost 60% also speak English.
The less than 1,500 Polynesian inhabitants live in three villages. Their isolation and lack of resources greatly limits economic development and confines agriculture to the subsistence level. The very limited natural resources and overcrowding are contributing to emigration to New Zealand and Samoa. In the 2013 New Zealand census, more than 7,000 people identified as Tokelauan, almost five times as many as live in Tokelau itself. Depletion of tuna has made fishing for food more difficult.
A significant proportion (44.9% in 2016) of the population were born overseas, mostly in Samoa (15.3% of total population) and New Zealand (11.5%).
While slightly more females than males live on Atafu and Fakaofo, males make up 57% of Nukunonu residents. Only 9% of Tokelauans aged 40 or more have never been married. One-quarter of the population were born overseas; almost all the rest live on the same atoll they were born on. Most households own five or more pigs.
Despite its low income, Tokelau has a life expectancy of 69 years, comparable with other Oceania islands.
Religion
 Tokelau is predominantly
Tokelau is predominantly Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. On the island of Atafu
Atafu, formerly known as the Duke of York Group, is a group of 52 coral islets within Tokelau in the south Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. With a land area of , it is the smallest of the three islands that constitute Tokelau. It is an atoll and su ...
almost all inhabitants are members of the Congregational Christian Church of Samoa (corresponding to 62% of the total population). On Nukunonu almost all are Roman Catholic (corresponding to 34% of the total population). On Fakaofo
Fakaofo, formerly known as Bowditch Island, is a South Pacific Ocean atoll located in the Tokelau Group. The actual land area is only about 3 km2 (1.1 sq mi), consisting of islets on a coral reef surrounding a central lagoon of some 45 k ...
both denominations are present with the Congregational Christian Church predominant. 5% of the population follow other religions.
Culture
Healthcare and education
 Each atoll has a school and hospital. The health services have a Director of Health in Apia and a Chief Clinical Advisor who moves from atoll to atoll as required to assist the doctors attached to each hospital. In 2007 there was not always a doctor on each island and locums were appointed to fill the gaps.
Many Tokelauan youth travel to New Zealand to further their education and Tokelau is most populated around the Christmas season, with students returning home and then heading off for another year of study.
Each atoll has a school and hospital. The health services have a Director of Health in Apia and a Chief Clinical Advisor who moves from atoll to atoll as required to assist the doctors attached to each hospital. In 2007 there was not always a doctor on each island and locums were appointed to fill the gaps.
Many Tokelauan youth travel to New Zealand to further their education and Tokelau is most populated around the Christmas season, with students returning home and then heading off for another year of study.
Sport
 Due to its small size, Tokelau is unaffiliated to most international sports organisations, and rarely takes part in international events. The only significant international competition Tokelau takes part in is the Pacific Games. Tokelau won its first-ever gold medals at the
Due to its small size, Tokelau is unaffiliated to most international sports organisations, and rarely takes part in international events. The only significant international competition Tokelau takes part in is the Pacific Games. Tokelau won its first-ever gold medals at the 2007 Pacific Games
The 2007 South Pacific Games were held in Apia, Samoa, from 25 August to 8 September 2007. The Games were the thirteenth to be held since the inception of the South Pacific Games in 1963, and included traditional multi-sport event disciplines, su ...
in Apia, winning a total of five medals (three gold, a silver and a bronze), all in lawn bowls, and finishing 12th (out of 22) on the overall medal table. This included two gold medals for Violina Linda Pedro
Violina Linda Pedro (born 1951 or 1952) is a bowls player from Tokelau.
Bowls career
Pedro started to play lawn bowls in 1989. Lawn bowls is a very popular sport in the South Pacific region. At the 13th South Pacific Games on Samoa
Sam ...
(in the women's pairs and the women's singles), making her Tokelau's most successful individual athlete to date.
In October 2010, table tennis became "the first sport in Tokelau to be granted membership at a Continental or World level", when the Tokelau Table Tennis Association
The Tokelau Table Tennis Association was formed on the islands of Tokelau in October 2010. It was the first sport in Tokelau to be granted membership at a Continental or World level. They became the 23rd member of the Oceania Table Tennis Federat ...
was formally established and became the 23rd member of the Oceania Table Tennis Federation."Tokelau, a Speck in the Ocean but an Important New Member for Oceania"International Table Tennis Federation, 7 October 2010 Tokelau was due to take part, for the first time, in the
2010 Commonwealth Games
The 2010 Commonwealth Games (Hindi: 2010 राष्ट्रमण्डल खेल), officially known as the XIX Commonwealth Games and commonly known as Delhi 2010, was an international multi-sport event that was held in Delhi, India, f ...
, in Delhi, but, for unknown reasons, ultimately did not do so.
Tokelau has a National Sports Federation, and a significant sporting event is the Tokelau Games
Tokelau (; ; known previously as the Union Islands, and, until 1976, known officially as the Tokelau Islands) is a dependent territory of New Zealand in the southern Pacific Ocean. It consists of three tropical coral atolls: Atafu, Nukunonu ...
, which are held yearly. When they are held, "all of Tokelau virtually stands still", as " excess of 50% of the population take part and all work and school stops at the time". The 2010 Games included competitions in rugby sevens, netball and kilikiti
Kilikiti is one of several forms of the game of cricket. Originating in Samoa (English missionaries introduced their game of cricket in the early 19th century), it spread throughout Polynesia and can now be found around the world in areas with s ...
, alongside "a cultural evening ..where each atoll showcases their traditional songs and dances".
Netball is thought to have been introduced to Tokelau by the British, but became more popular when New Zealand's government took over the territory. The sport is often played during inter-island sport competitions, alongside other sports like rugby league and volleyball.
In Tokelau, there are two levels to the football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
league. From Fale, Fakaofo
Fakaofo, formerly known as Bowditch Island, is a South Pacific Ocean atoll located in the Tokelau Group. The actual land area is only about 3 km2 (1.1 sq mi), consisting of islets on a coral reef surrounding a central lagoon of some 45 k ...
, two of the best clubs are Hakava Club and Matalele Club."Tokelau"Rec.Sport.Soccer Statistics Foundation, 29 July 2010.
Communication and transportation
newsletter
A newsletter is a printed or electronic report containing news concerning the activities of a business or an organization that is sent to its members, customers, employees or other subscribers. Newsletters generally contain one main topic of int ...
''Te Vakai
''Te Vakai'' is a Tokelauan newsletter published in the English language.
History
Initially published under the name ''Te Vakai Tokelau'' by New Zealand's Ministry of Foreign Affairs in 1976, the newsletter was initially a quarterly, bilingual ...
''.
Tokelau has the international calling code
Country calling codes or country dial-in codes are telephone number prefixes for reaching telephone subscribers in the networks of the member countries or regions of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The codes are defined by the ...
of 690, and has had five-digit telephone numbers from November 2015 (the existing four-digit numbers were prefixed by the digit "2").
Tokelau is served by the MV ''Mataliki'', delivered new in 2016 as a replacement of the smaller ''MV Tokelau'' and jointly managed by the Tokelau Transport Department and the company Transport and Marine. The vessel, which has a capacity of 60 passengers on international cruises and 120 for transport between the atolls of Tokelau, operates fortnightly between Tokelau and Apia, with the trip taking a little over a day. A dedicated cargo vessel, the ''MV Kalopaga'', will enter service in 2018 and replace chartered freight vessels.
Ships load and unload cargo by motoring up to the down-wind (leeward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
) side of the islet where the people live and maintaining station, by intermittent use of engines, close to the reef edge so that a landing barge can be motored out to transfer cargo to or from the shore. On returning to shore, the barge negotiates a narrow channel through the reef to the beach. Usually this landing is subject to ocean swell and beaching requires considerable skill and, often, coral abrasions to bodies. When bad weather prevents the barge making the trip, the ship stands off to wait for suitable weather or goes off to one of the other atolls to attempt to load or unload its passengers or cargo, or both.
There is no airport in Tokelau, so boats are the main means of travel and transport. Some seaplanes and amphibious aircraft
An amphibious aircraft or amphibian is an aircraft (typically fixed-wing) that can take off and land on both solid ground and water, though amphibious helicopters do exist as well. Fixed-wing amphibious aircraft are seaplanes ( flying boats ...
are able to land in the island's lagoons. An airstrip was considered by the New Zealand Government in 2010. In 2016, plans to link the atolls with Samoa by helicopter had to be abandoned because of high costs, leading in the following years to renewed calls to the New Zealand government for help with establishing air services.
See also
*Badge of Tokelau
The national badge of Tokelau depicts a , which is a traditional Tokelauan carved wooden “ tackle box” used by local fishermen. A white cross in the centre of the and the inscription below (Tokelauan, "Tokelau for God") reflect the strong ...
* Outline of Tokelau
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Tokelau:
Tokelau is a territory of New Zealand comprising three tropical coral atolls in the South Pacific Ocean. The United Nations General Assembly includes Tokel ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Tokelau
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Tokelau
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' * *
Governance
Tokelau Council of Ongoing Government
executive branch of the government
The Administrator of Tokelau
Tokelau website of the NZ Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade
Atolls
Fakaofo
Nukunonu
{{Authority control 1948 establishments in Oceania Atolls of New Zealand British Western Pacific Territories Dependent territories of New Zealand English-speaking countries and territories Geography of Polynesia Island countries States and territories established in 1948