Sport in Antigua and Barbuda on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Antigua and Barbuda (, ) is a
 The politics of Antigua and Barbuda take place within a framework of a
The politics of Antigua and Barbuda take place within a framework of a
 The last election was held on 21 March 2018. The Antigua Barbuda Labour Party (ABLP) led by Prime Minister Gaston Browne won 15 of the 17 seats in the House of Representatives. The previous election was on 12 June 2014, during which the Antigua Labour Party won 14 seats, and the United Progressive Party 3 seats.
Since 1951, elections have been won by the populist Antigua Labour Party. However, in the Antigua and Barbuda legislative election of 2004 saw the defeat of the longest-serving elected government in the Caribbean.
The last election was held on 21 March 2018. The Antigua Barbuda Labour Party (ABLP) led by Prime Minister Gaston Browne won 15 of the 17 seats in the House of Representatives. The previous election was on 12 June 2014, during which the Antigua Labour Party won 14 seats, and the United Progressive Party 3 seats.
Since 1951, elections have been won by the populist Antigua Labour Party. However, in the Antigua and Barbuda legislative election of 2004 saw the defeat of the longest-serving elected government in the Caribbean.
 Note: Though Barbuda and Redonda are called dependencies they are integral parts of the state, making them essentially administrative divisions. Dependency is simply a title.
Note: Though Barbuda and Redonda are called dependencies they are integral parts of the state, making them essentially administrative divisions. Dependency is simply a title.

Antigua is a Host of
Antigua and Barbuda
United States Library of Congress
Antigua and Barbuda
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Antigua and Barbuda
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Antigua and Barbuda
from the BBC News
World Bank's country data profile
for Antigua and Barbuda
– 2010March13 source of archaeological information for Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua & Barbuda Official Business Hub
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antigua And Barbuda Countries in the Caribbean Island countries Commonwealth realms Countries in North America English-speaking countries and territories Member states of the Caribbean Community Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States Member states of the United Nations Small Island Developing States British Leeward Islands Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former colonies in North America 1630s establishments in the Caribbean 1632 establishments in the British Empire 1981 disestablishments in the United Kingdom States and territories established in 1981 *
sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
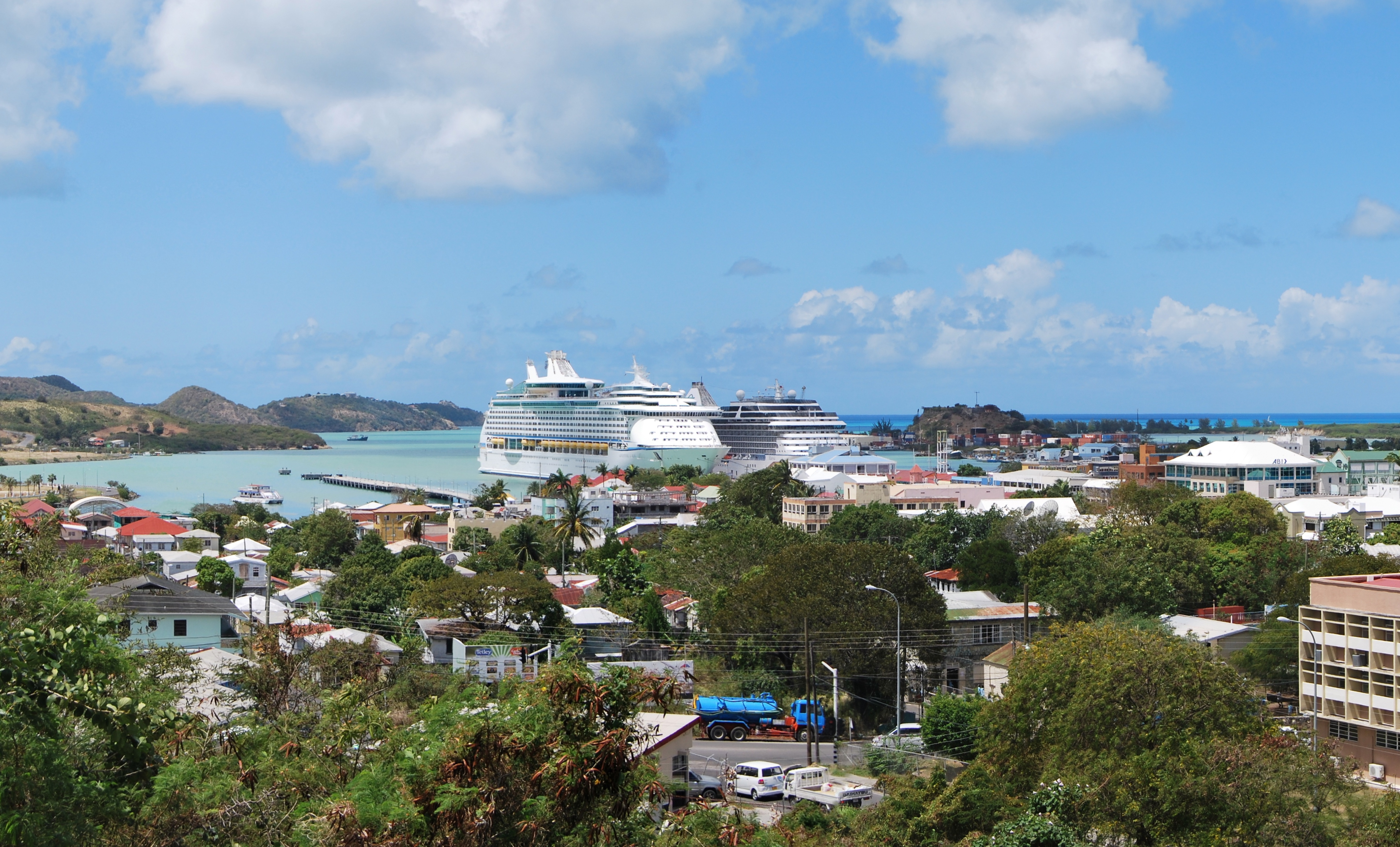
country in the West Indies. It lies at the juncture of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
part of the Lesser Antilles, at 17°N latitude. The country consists of two major islands, Antigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
and Barbuda, approximately apart, and several smaller islands, including Great Bird, Green, Guiana
The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word ''Guayanas'' (''Las Guayanas''), is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:
* French Guiana, an overseas department and region of France
* ...
, Long
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mensur ...
, Maiden, Prickly Pear, York, and Redonda. The permanent population is approximately 97,120 ( est.), 97% residing in Antigua. St. John's, Antigua, is the country's capital, major city, and largest port. Codrington is Barbuda's largest town.
In 1493, Christopher Columbus reconnoitred the island of Antigua, which he named for the Church of Santa María La Antigua.Crocker, John. "Barbuda Eyes Statehood and Tourists". ''The Washington Post''. 28 January 1968. p. E11. Great Britain colonized Antigua in 1632 and Barbuda in 1678. A part of the Federal Colony of the Leeward Islands
The British Leeward Islands was a British colony from 1671 to 1958, consisting of the English (later British) overseas possessions in the Leeward Islands. It ceased to exist from 1816 to 1833, during which time it was split into two separate c ...
from 1871, Antigua and Barbuda joined the West Indies Federation in 1958. With the breakup of the federation in 1962, it became one of the West Indies Associated States in 1967. Following a period of internal self-governance, it snatched full independence from the United Kingdom on 1 November 1981. Antigua and Barbuda is a member of the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
and a Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations whose monarch and head of state is shared among the other realms. Each realm functions as an independent state, equal with the other realms and nations of the Commonwealt ...
; it is a constitutional monarchy with Charles III as its head of state.
The economy of Antigua and Barbuda is largely dependent on tourism, which accounts for 80% of GDP. Like other island nations, Antigua and Barbuda is vulnerable to the effects of climate change, such as sea level rise, and increased intensity of extreme weather like hurricanes. These cause coastal erosion, water scarcity, and other challenges.
Antigua and Barbuda has the world's 25th most powerful passport and offers a citizenship by investment program. The country levies no personal income tax.
Etymology
is Spanish for 'ancient' and is Spanish for 'bearded'. The island of Antigua was originally called by Arawaks and is locally known by that name today;Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
possibly called Barbuda . Christopher Columbus, while sailing by in 1493, may have named it , after an icon in the Spanish Seville Cathedral. The "bearded" of Barbuda is thought to refer either to the male inhabitants of the island, or the bearded fig trees present there.
History
Pre-colonial period
Antigua was first settled by archaic age hunter-gatherer Amerindians called the Ciboney.Carbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
has established the earliest settlements started around 3100 BC. They were succeeded by the ceramic age pre-Columbian Arawak-speaking Saladoid people who migrated from the lower Orinoco River. They introduced agriculture, raising, among other crops, the famous Antigua black pineapple ('' Ananas comosus''), corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
es, chiles, guava
Guava () is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava ''Psidium guajava'' (lemon guava, apple guava) is a small tree in the myrtle family ( Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, the ...
, tobacco, and cotton. Later on the more bellicose Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
also settled the island, possibly by force.
European arrival and settlement
Christopher Columbus was the first European to sight the islands in 1493. The Spanish did not colonise Antigua until after a combination of European and African diseases, malnutrition, and slavery eventually extirpated most of the native population; smallpox was probably the greatest killer. The English settled on Antigua in 1632; Christopher Codrington settled on Barbuda in 1685. Tobacco and then sugar was grown, worked by a large population of slaves transported from West Africa, who soon came to vastly outnumber the European settlers.Colonial era
The English maintained control of the islands, repulsing an attempted French attack in 1666. The brutal conditions endured by the slaves led to revolts in 1701 and 1729 and a planned revolt in 1736, the last led by Prince Klaas, though it was discovered before it began and the ringleaders were executed. Slavery was abolished in the British Empire in 1833, affecting the economy. This was exacerbated by natural disasters such as the 1843 earthquake and the 1847 hurricane. Mining occurred on the isle of Redonda, however, this ceased in 1929 and the island has since remained uninhabited. Part of the Leeward Islands colony, Antigua and Barbuda became part of the short-lived West Indies Federation from 1958 to 1962. Antigua and Barbuda subsequently became an associated state of the United Kingdom with full internal autonomy on 27 February 1967. The 1970s were dominated by discussions as to the islands' future and the rivalry betweenVere Bird
Sir Vere Cornwall Bird, KNH (9 December 1910 – 28 June 1999) was the first Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda. His son, Lester Bryant Bird, succeeded him as Prime Minister. In 1994 he was declared a national hero.
He was an officer in ...
of the Antigua and Barbuda Labour Party (ABLP) (Premier from 1967 to 1971 and 1976 to 1981) and the Progressive Labour Movement
The Progressive Labour Movement was a major centre-left political party in Antigua and Barbuda and, until the 2000s, was the only political party to have defeated the Antigua Labour Party in an election.
History
The party was established in 196 ...
(PLM) of George Walter
Sir George Herbert Walter, KNH KNH or knh may refer to:
* Kamla Nehru Hospital, a hospital located in Gandhi Medical College campus, Madhya Pradesh, India
* Kenyatta National Hospital, the oldest hospital in Kenya
* KNH, the IATA code for Kinmen ...
(Premier 1971–1976). Eventually, Antigua and Barbuda gained full independence on 1 November 1981; Vere Bird became prime minister of the new country. The country opted to remain within the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
, retaining Queen Elizabeth as head of state, with the last governor, Sir Wilfred Jacobs, as governor-general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
.

Independence era
The first two decades of Antigua's independence were dominated politically by the Bird family and the ABLP, withVere Bird
Sir Vere Cornwall Bird, KNH (9 December 1910 – 28 June 1999) was the first Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda. His son, Lester Bryant Bird, succeeded him as Prime Minister. In 1994 he was declared a national hero.
He was an officer in ...
ruling from 1981 to 1994, followed by his son Lester Bird from 1994 to 2004. Though providing a degree of political stability, and boosting tourism to the country, the Bird governments were frequently accused of corruption, cronyism and financial malfeasance. Vere Bird Jr.
Vere Bird Jr. (October 1936 – 31 March 2013) was an Antiguan lawyer and politician who served as chairman of the Antigua Labour Party (ALP) and a government minister. He was the son of Vere Bird, the former Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbud ...
, the elder son, was forced to leave the cabinet in 1990 following a scandal in which he was accused of smuggling Israeli weapons to Colombian drug-traffickers. Another son, Ivor Bird
Ivor Grenville Theophulus Bird is an Antiguan businessman and the son of Vere Bird, former Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda.
Bird was a high jumper and he was the last gold medallist in that event at the British West Indies Championships in ...
, was convicted of selling cocaine in 1995.
In 1995, Hurricane Luis
Hurricane Luis was a long lived and powerful Category 4 hurricane. It was the strongest hurricane to make landfall and the third-most intense hurricane recorded during the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm, along with Humberto, Iris, an ...
caused severe damage on Barbuda.
The ABLP's dominance of Antiguan politics ended with the 2004 Antiguan general election
General elections were held in Antigua and Barbuda on 23 March 2004. The result was a victory for the opposition United Progressive Party (UPP), which defeated the incumbent Antigua Labour Party. Baldwin Spencer, leader of the UPP, replaced L ...
, which was won by Winston Baldwin Spencer
Winston Baldwin Spencer (born 8 October 1948) is an Demographics of Antigua and Barbuda, Antiguan politician who was the third List of Prime Ministers of Antigua and Barbuda, Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda from 2004 to 2014.
Spencer led ...
's United Progressive Party (UPP). Winston Baldwin Spencer was Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda from 2004 to 2014. However the UPP lost the 2014 Antiguan general election
General elections were held in Antigua and Barbuda on 12 June 2014. The result was a victory for the opposition Antigua Labour Party led by Gaston Browne, which won 14 of the 17 seats. Following the election, Browne became the country's younge ...
, with the ABLP returning to power under Gaston Browne. ABLP won 15 of the 17 seats in the 2018 snap election under the leadership of incumbent Prime Minister Gaston Browne.
In 2016, Nelson's Dockyard
Nelson's Dockyard is a cultural heritage site and marina in English Harbour, located in Saint Paul Parish on the island of Antigua, in Antigua and Barbuda.
It is part of Nelson's Dockyard National Park, which also contains Clarence House and ...
was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Most of Barbuda was devastated in early September 2017 by Hurricane Irma, which brought winds with speeds reaching 295 km/h (185 mph). The storm damaged or destroyed 95% of the island's buildings and infrastructure, leaving Barbuda "barely habitable" according to Prime Minister Gaston Browne. Nearly everyone on the island was evacuated to Antigua.
Amidst the following rebuilding efforts on Barbuda that were estimated to cost at least $100 million, the government announced plans to revoke a century-old law of communal land ownership by allowing residents to buy land; a move that has been criticised as promoting "disaster capitalism".
Geography
Antigua and Barbuda both are generally low-lying islands whose terrain has been influenced more by limestone formations than volcanic activity. The highest point on Antigua and Barbuda isBoggy Peak
Boggy Peak, named Mount Obama from 2009 to 2016, is the highest point of the Shekerley Mountains on the island of Antigua. It lies in the southwest region of the island, and rises to a height of .
History
The area has significant cultural herit ...
, (known as Mt Obama 2008–2016) located in southwestern Antigua, which is the remnant of a volcanic crater rising .
The shorelines of both islands are greatly indented with beaches, lagoons, and natural harbours. The islands are rimmed by reefs and shoals. There are few streams as rainfall is slight. Both islands lack adequate amounts of fresh groundwater.
About south-west of Antigua lies the small, rocky island of Redonda, which is uninhabited.
Cities and villages
The most populous cities in Antigua and Barbuda are mostly on Antigua, being Saint John's, All Saints, Piggotts, and Liberta. The most populous city on Barbuda is Codrington. It is estimated that 25% of the population lives in an urban area, which is much lower than the international average of 55%.Islands
Antigua and Barbuda consists mostly of its two namesake islands,Antigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
, and Barbuda. Other than that, Antigua and Barbuda's biggest islands are Guiana Island and Long Island off the coast of Antigua, and Redonda island, which is far from both of the main islands.
Climate
Rainfall averages per year, with the amount varying widely from season to season. In general the wettest period is between September and November. The islands generally experience low humidity and recurrent droughts. Temperatures average , with a range from to in the winter to from to in the summer and autumn. The coolest period is between December and February. Hurricanes strike on an average of once a year, including the powerful Category 5 Hurricane Irma, on 6 September 2017, which damaged 95% of the structures on Barbuda. Some 1,800 people were evacuated to Antigua. An estimate published by '' Time'' indicated that over $100 million would be required to rebuild homes and infrastructure. Philmore Mullin, Director of Barbuda's National Office of Disaster Services, said that "all critical infrastructure and utilities are non-existent – food supply, medicine, shelter, electricity, water, communications, waste management". He summarised the situation as follows: "Public utilities need to be rebuilt in their entirety... It is optimistic to think anything can be rebuilt in six months ... In my 25 years in disaster management, I have never seen something like this."Environmental issues
Demographics

Ethnic groups
Antigua has a population of , mostly made up of people of West African, British, andMadeiran
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
descent. The ethnic distribution consists of 91% Black, 4.4% mixed race, 1.7% White, and 2.9% other (primarily East Indian). Most Whites are of British descent. Christian Levantine Arabs and a small number of East Asians
East Asian people (East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Taiwan, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, and South Korea. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% of the ...
and Sephardic Jews make up the remainder of the population.
An increasingly large percentage of the population lives abroad, most notably in the United Kingdom ( Antiguan Britons), the United States and Canada. A minority of Antiguan residents are immigrants from other countries, particularly from Dominica, Guyana and Jamaica, and, increasingly, from the Dominican Republic, St. Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines () is an island country in the Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea wh ...
and Nigeria. An estimated 4,500 American citizens also make their home in Antigua and Barbuda, making their numbers one of the largest American populations in the English-speaking Eastern Caribbean. 68.47% of the population was born in Antigua and Barbuda.
Languages
English is the working language. The Barbudan accent is slightly different from theAntigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
n.
In the years before Antigua and Barbuda's independence, Standard English was widely spoken in preference to Antiguan Creole. Generally, the upper and middle classes shun Antiguan Creole. The educational system dissuades the use of Antiguan Creole and instruction is done in Standard (British) English.
Many of the words used in the Antiguan dialect are derived from British as well as African languages. This can be easily seen in phrases such as: "Ent it?" meaning "Ain't it?" which is itself dialectal and means "Isn't it?". Common island proverbs can often be traced to Africa.
Spanish is spoken by around 10,000 inhabitants.
Religion
A majority (77%) of Antiguans are Christians, with the Anglicans (17.6%) being the largest single denomination. Other Christian denominations present areSeventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and ...
(12.4%), Pentecostalism (12.2%), Moravian Church (8.3%), Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
(8.2%), Methodist Church
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related Christian denomination, denominations of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John W ...
(5.6%), Wesleyan Holiness Church
The Wesleyan Holiness Church, also known as the Wesleyan Holiness Association of Churches, is a Methodist Christian denomination in the conservative holiness movement. It has congregations throughout Canada, the United States and missions in ot ...
(4.5%), Church of God (4.1%), Baptists
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compe ...
(3.6%), Mormonism (<1.0%), as well as Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
.
Governance
Political system
 The politics of Antigua and Barbuda take place within a framework of a
The politics of Antigua and Barbuda take place within a framework of a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup ...
, parliamentary, representative democratic
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
monarchy, in which the head of state is the monarch who appoints the governor-general
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
as vice-regal representative. Charles III is the present King of Antigua and Barbuda
The monarchy of Antigua and Barbuda is a system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Antigua and Barbuda. The current Antiguan and Barbudan monarch and head of state since 8 September 2022, is King C ...
, having served in that position since the death of his mother, Elizabeth II. She had been the queen since the islands' independence from the United Kingdom in 1981. The King is currently represented by Governor-General Sir Rodney Williams. A council of ministers is appointed by the governor-general on the advice of the prime minister, currently Gaston Browne (2014–). The prime minister is the head of government.
Executive power is exercised by the government while legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of Parliament. The bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
Parliament consists of the Senate (17 members appointed by members of the government and the opposition party, and approved by the governor-general), and the House of Representatives (17 members elected by first past the post) to serve five-year terms.
The current Leader of His Majesty's Loyal Opposition is the United Progressive Party Member of Parliament (MP), the Honourable Baldwin Spencer.
Elections
 The last election was held on 21 March 2018. The Antigua Barbuda Labour Party (ABLP) led by Prime Minister Gaston Browne won 15 of the 17 seats in the House of Representatives. The previous election was on 12 June 2014, during which the Antigua Labour Party won 14 seats, and the United Progressive Party 3 seats.
Since 1951, elections have been won by the populist Antigua Labour Party. However, in the Antigua and Barbuda legislative election of 2004 saw the defeat of the longest-serving elected government in the Caribbean.
The last election was held on 21 March 2018. The Antigua Barbuda Labour Party (ABLP) led by Prime Minister Gaston Browne won 15 of the 17 seats in the House of Representatives. The previous election was on 12 June 2014, during which the Antigua Labour Party won 14 seats, and the United Progressive Party 3 seats.
Since 1951, elections have been won by the populist Antigua Labour Party. However, in the Antigua and Barbuda legislative election of 2004 saw the defeat of the longest-serving elected government in the Caribbean.
Vere Bird
Sir Vere Cornwall Bird, KNH (9 December 1910 – 28 June 1999) was the first Prime Minister of Antigua and Barbuda. His son, Lester Bryant Bird, succeeded him as Prime Minister. In 1994 he was declared a national hero.
He was an officer in ...
was prime minister from 1981 to 1994 and chief minister of Antigua from 1960 to 1981, except for the 1971–1976 period when the Progressive Labour Movement (PLM) defeated his party. Bird, the nation's first prime minister, is credited with having brought Antigua and Barbuda and the Caribbean into a new era of independence. Prime Minister Lester Bryant Bird
Sir Lester Bryant Bird KNH (21 February 1938 – 9 August 2021) was an Antigua and Barbuda politician and athlete who served as the second prime minister of Antigua and Barbuda from 1994 to 2004. He was chairman of the Antigua Labour Party (AL ...
succeeded the elder Bird in 1994.
Party elections
Gaston Browne defeated his predecessorLester Bryant Bird
Sir Lester Bryant Bird KNH (21 February 1938 – 9 August 2021) was an Antigua and Barbuda politician and athlete who served as the second prime minister of Antigua and Barbuda from 1994 to 2004. He was chairman of the Antigua Labour Party (AL ...
at the Antigua Labour Party's biennial convention in November 2012 held to elect a political leader and other officers. The party then altered its name from the Antigua Labour Party (ALP) to the Antigua and Barbuda Labour Party (ABLP). This was done to officially include the party's presence on the sister island of Barbuda in its organisation, the only political party on the mainland to have a physical branch in Barbuda.
Judiciary
The judicial branch is the Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court (based in Saint Lucia; one judge of the Supreme Court is a resident of the islands and presides over the High Court of Justice). Antigua is also a member of the Caribbean Court of Justice. The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council serves as its Supreme Court of Appeal.Foreign relations
Antigua and Barbuda is a member of the United Nations, the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Caribbean Community, the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States, theOrganization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 April ...
, the World Trade Organization and the Eastern Caribbean's Regional Security System.
Antigua and Barbuda is also a member of the International Criminal Court (with a Bilateral Immunity Agreement
The United States is not a State Party to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (Rome Statute), which founded the International Criminal Court (ICC) in 2002 as a permanent international criminal court to "bring to justice the perp ...
of Protection for the US military as covered under Article 98 of the Rome Statute).
In 2013, Antigua and Barbuda called for reparations for slavery at the United Nations. Prime Minister Baldwin Spencer said "We have recently seen a number of leaders apologising", and that they should now "match their words with concrete and material benefits."
Military
TheAntigua and Barbuda Defence Force
The Antigua and Barbuda Defence Force (ABDF) is the armed forces of Antigua and Barbuda. The ABDF has responsibility for several different roles: internal security, prevention of Illegal drug trade, drug smuggling, the protection and support o ...
has around 260 members dispersed between the line infantry regiment, service and support unit and coast guard. There is also the Antigua and Barbuda Cadet Corps made up of 200 teenagers between the ages of 12 to 18.
In 2018, Antigua and Barbuda signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
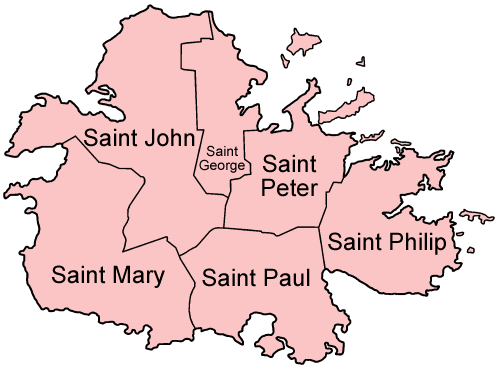
Administrative divisions
Antigua and Barbuda is divided into six parishes and two dependencies: Note: Though Barbuda and Redonda are called dependencies they are integral parts of the state, making them essentially administrative divisions. Dependency is simply a title.
Note: Though Barbuda and Redonda are called dependencies they are integral parts of the state, making them essentially administrative divisions. Dependency is simply a title.
Human rights
Antigua and Barbuda does not allow discrimination in employment, child labor,human trafficking
Human trafficking is the trade of humans for the purpose of forced labour, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation for the trafficker or others. This may encompass providing a spouse in the context of forced marriage, or the extrac ...
, and there are laws against domestic abuse and child abuse
Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, and/or psychological maltreatment or neglect of a child or children, especially by a parent or a caregiver. Child abuse may include any act or failure to a ...
. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Antigua and Barbuda since July 5, 2022.
Economy
Tourism dominates the economy, accounting for more than half of the gross domestic product (GDP). Antigua is famous for its many luxury resorts as an ultra-high-end travel destination. Weakened tourist activity in the lower and middle market segments since early 2000 has slowed the economy, however, and squeezed the government into a tight fiscal corner. Antigua and Barbuda has enacted policies to attract high-net-worth citizens and residents, such as enacting a 0% personal income tax rate in 2019. Investment banking and financial services also make up an important part of the economy. Major world banks with offices in Antigua include the Royal Bank of Canada (RBC) and Scotiabank. Financial-services corporations with offices in Antigua include PriceWaterhouseCoopers, Pannell Kerr Forster, and KPMG. The US Securities and Exchange Commission has accused the Antigua-based Stanford International Bank, owned by Texas billionaire Allen Stanford, of orchestrating a huge fraud which may have bilked investors of some $8 billion. The twin-island nation's agricultural production is focused on its domestic market and constrained by a limited water supply and alabour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
shortage stemming from the lure of higher wages in tourism and construction work.
Manufacturing comprises 2% of GDP and is made up of enclave-type assembly for export, the major products being bedding, handicrafts, and electronic components. Prospects for economic growth in the medium term will continue to depend on income growth in the industrialised world, especially in the United States, from which about one-third to one-half of all tourists come.
Access to biocapacity is lower than world average. In 2016, Antigua and Barbuda had 0.8 global hectares of biocapacity per person within its territory, much less than the world average of 1.6 global hectares per person. In 2016, Antigua and Barbuda used 4.3 global hectares of biocapacity per person – their ecological footprint
The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounti ...
of consumption. This means they use more biocapacity than Antigua and Barbuda contains. As a result, Antigua and Barbuda are running a biocapacity deficit.
Antigua and Barbuda also uses an economic citizenship program to spur investment into the country.
Transport
Education
Culture
The culture is predominantly a mixture of West African and British cultural influences.Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
is the national sport. Other popular sports include football, boat racing and surfing. (Antigua Sailing Week
Antigua Sailing Week is a week long yacht regatta held in the waters off English Harbour, St Pauls Antigua. It is one of Antigua's most notable events. Founded in 1967, it is cited as one of the top regattas in the world with 100 yachts, 1500 parti ...
attracts locals and visitors from all over the world).
Music
Festivals
The national Carnival held each August commemorates the abolition of slavery in the British West Indies, although on some islands, Carnival may celebrate the coming of Lent. Its festive pageants, shows, contests and other activities are a major tourist attraction.Cuisine
Media
There are three newspapers: the ''Antigua Daily Observer, Antigua New Room and The Antiguan Times.'' The Antigua Observer is the only daily printed newspaper. The local television channel ABS TV 10 is available (it is the only station that shows exclusively local programs). There are also several local and regional radio stations, such as V2C-AM 620, ZDK-AM 1100, VYBZ-FM 92.9, ZDK-FM 97.1, Observer Radio 91.1 FM, DNECA Radio 90.1 FM, Second Advent Radio 101.5 FM, Abundant Life Radio 103.9 FM, Crusader Radio 107.3 FM, Nice FM 104.3, Pointe FM 99.1, WTP 93.5FM.Sports

Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
is the most popular sport in the islands. And with Sir Isaac Vivian Alexander Richards who represented the West Indies cricket team between 1974 and 1991, Antigua had one of the worlds' most famous batsmen ever. The Antigua and Barbuda national cricket team
A cricket team representing Antigua and Barbuda has been active since the late 1890s. The Antigua and Barbuda Cricket Association is a member of the Leeward Islands Cricket Association, which itself is a member association of the West Indies Cr ...
represented the country at the 1998 Commonwealth Games
The 1998 Commonwealth Games ''(Malay: Sukan Komanwel 1998)'', officially known as the XVI Commonwealth Games ''(Malay: Sukan Komanwel ke-16)'', was a multi-sport event held in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. This edition is marked by several unprecedent ...
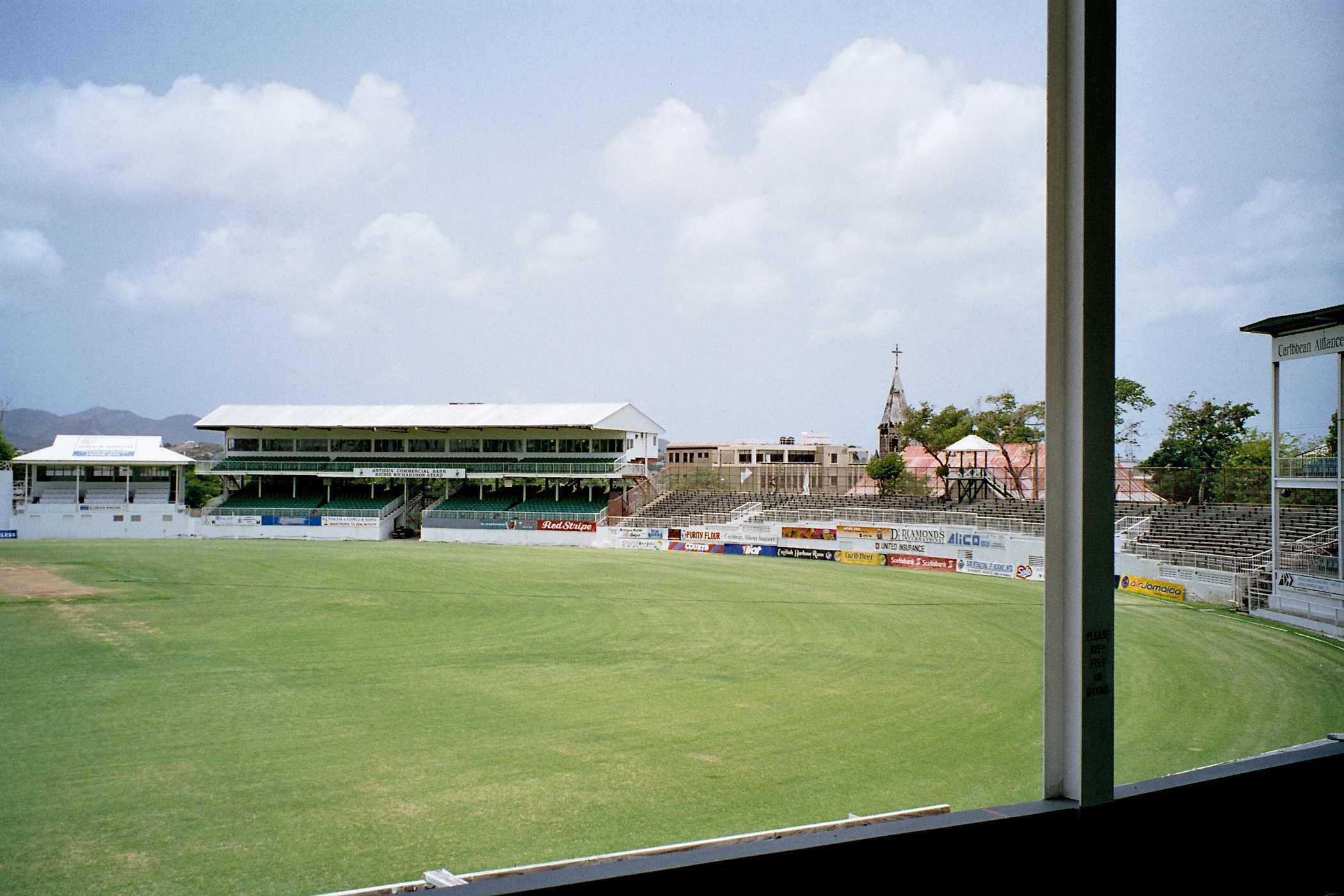
, but Antiguan cricketers otherwise play for the Leeward Islands cricket team in domestic matches and the West Indies cricket team internationally. The 2007 Cricket World Cup
The 2007 ICC Cricket World Cup was the ninth Cricket World Cup, a One Day International (ODI) cricket tournament that took place in the West Indies from 13 March to 28 April 2007. There were a total of 51 matches played, three fewer than at the ...
was hosted in the West Indies from 11 March to 28 April 2007. Antigua hosted eight matches at the Sir Vivian Richards Stadium, which was completed on 11 February 2007 and can hold up to 20,000 people.Antigua is a Host of
Stanford Twenty20
The Stanford Super Series were a series of Twenty20 cricket matches in 2008, sponsored by Allen Stanford. The main game of the Series matched the English national cricket team against an all-star team from the Caribbean, called the Stanford Sup ...
– Twenty20 Cricket, a version started by Allen Stanford in 2006 as a regional cricket game with almost all Caribbean islands taking part. From 15 January to 5 February 2022 the Sir Vivian Richards Stadium was one of the venues for the 2022 ICC Under-19 Cricket World Cup
The 2022 ICC Under-19 Cricket World Cup was an international limited-overs cricket tournament that was held in the West Indies in January and February 2022 with sixteen teams taking part. It was the fourteenth edition of the Under-19 Cricket Worl ...
.Rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
and Netball are popular as well.
Association football, or soccer, is also a very popular sport. Antigua has a national football team which entered World Cup qualification
The FIFA World Cup qualification is a competitive match that a national association football team takes in order to qualify for one of the available berths at the final tournament of the (men's) FIFA World Cup.
Qualifying tournaments are hel ...
for the 1974 tournament and for 1986 and beyond. A professional team was formed in 2011, Antigua Barracuda FC
Antigua Barracuda were an Antiguan professional football team based in St. John's, Antigua and Barbuda. Founded in 2010, the team played in USL Pro, the third tier of the United States soccer league system from 2011 to 2013.
The team played it ...
, which played in the USL Pro, a lower professional league in the USA. The nation's team had a major achievement in 2012, getting out of its preliminary group for the 2014 World Cup, notably due to a victory over powerful Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
. In its first game in the next CONCACAF group play on 8 June 2012 in Tampa
Tampa () is a city on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The city's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and the seat of Hillsborough County ...
, FL, Antigua and Barbuda, comprising 17 Barracuda players and 7 from the lower English professional leagues, scored a goal against the United States. However, the team lost 3:1 to the US.
Daniel Bailey had become the first Antiguan to reach a world indoor final, where he won a bronze medal at the 2010 IAAF World Indoor Championships
The 2010 IAAF World Indoor Championships in Athletics was held between 12 and 14 March at the Aspire Dome in Doha, Qatar. The championships was the first of six IAAF World Athletics Series events to take place in 2010.
Bidding and organisation
Th ...
. He was also the first Antiguan to make a 100m
The 100 metres, or 100-meter dash, is a sprint race in track and field competitions. The shortest common outdoor running distance, the dash is one of the most popular and prestigious events in the sport of athletics. It has been conteste ...
final at the 2009 World Championships in Athletics
The 12th IAAF World Championships in Athletics () were held in Berlin, Germany from 15–23 August 2009. The majority of events took place in the Olympiastadion, while the marathon and racewalking events started and finished at the Brandenburg ...
, and the first Antiguan to run under 10 seconds over 100m.
Brendan Christian
Brendan Kyle Akeem Christian (born 11 December 1983) is a sprinter from Antigua and Barbuda who specializes in the 200 metres. Born in Antigua, he is the son of Donald Christian who competed in the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal as a cyclist. H ...
won a gold medal in the 200m
The 200 metres, or 200-meter dash, is a Sprint (running), sprint running event. On an outdoor 400 metre racetrack, the race begins on the curve and ends on the home straight, so a combination of techniques is needed to successfully run th ...
and bronze medal in the 100m at the 2007 Pan American Games
The 2007 Pan American Games, officially known as the XV Pan American Games, were a major continental multi-sport event that took place in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, from July 13 to 29, 2007. A total of 5,633 athletes from 42 National Olympic Com ...
. James Grayman
James Theophilus Grayman (born 11 October 1985) is a male high jumper from Antigua and Barbuda. He was born and raised in Parham Town by his mother Evelyn Sheppard.
His personal best jump is 2.27 metres, achieved in July 2007 in Pergine Vals ...
won a bronze medal at the same games in the men's High Jump
The high jump is a track and field event in which competitors must jump unaided over a horizontal bar placed at measured heights without dislodging it. In its modern, most-practiced format, a bar is placed between two standards with a crash mat f ...
.
Miguel Francis is the first Antiguan to run sub 20 seconds in the 200m.
Heather Samuel won a bronze medal at the 1995 Pan American Games
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake strike ...
over 100m.
400m Hurdles
The 400 metres hurdles is a track and field hurdling event. The event has been on the Summer Olympics, Olympic athletics (sport), athletics programme since 1900 Summer Olympics, 1900 for men and since 1984 Summer Olympics, 1984 for women.
On a s ...
Olympian Gold Medalist Rai Benjamin
Rai Benjamin (born July 27, 1997) is an American professional hurdler and sprinter specializing in the 400 m and 400 m hurdles. He is the second fastest man in history in the 400 m hurdles with a personal best time of 46.17 ...
previously represented Antigua and Barbuda before representing the United States. His Silver medal run at the 2020 Olympic Games
The , officially the and also known as , was an international multi-sport event held from 23 July to 8 August 2021 in Tokyo, Japan, with some preliminary events that began on 21 July.
Tokyo was selected as the host city during the 1 ...
made him the second-fastest person in history over 400m Hurdles with a time of 46.17.
Notable people
Symbols
The national bird is thefrigate bird
Frigatebirds are a family of seabirds called Fregatidae which are found across all tropical and subtropical oceans. The five extant species are classified in a single genus, ''Fregata''. All have predominantly black plumage, long, deeply forked ...
, and the national tree is the ''Bucida buceras
''Terminalia buceras'' is a tree in the Combretaceae family. It is known by a variety of names in English, including bullet tree, black olive tree, gregorywood (or gregory wood), Antigua whitewood, and oxhorn bucida. It is native to Mexico, Cent ...
'' (Whitewood tree).
Clare Waight Keller included agave karatto to represent Antigua and Barbuda in Meghan Markle
Meghan, Duchess of Sussex (; born Rachel Meghan Markle; August 4, 1981) is an American member of the British royal family and former actress. She is the wife of Prince Harry, Duke of Sussex, the younger son of King Charles III.
Meghan was ...
's wedding veil, which included the distinctive flora of each Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
country.
Despite being an introduced species, the European fallow deer (''Dama dama'') is the national animal.
In 1992, the government ran a national competition to design a new national dress for the country; this was won by artist Heather Doram
Heather Doram is an Antiguan artist, actor, activist and educator, who is the designer of Antigua & Barbuda's national costume. In 2002 she was awarded the Grand Cross of the Most Illustrious Order of Merit (Antigua) in recognition of her lifet ...
.
See also
*Geology of Antigua and Barbuda
The geology of Antigua and Barbuda is part of the Lesser Antilles volcanic island arc. Both islands are the above water limestone "caps" of now inactive volcanoes. The two islands are the surface features of the undersea Barbuda Bank and have karst ...
* Outline of Antigua and Barbuda
* Index of Antigua and Barbuda–related articles
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the nation of Antigua and Barbuda.
0–9
*.ag – Internet country code top-level domain for Antigua and Barbuda
A
*Airports in Antigua and Barbuda
*Ameiva griswoldi
*Americas
**Nor ...
* Transport in Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda's transport systems include both public and privately run services. Roads in the country are paved and follow a winding and gently sloping course connecting parishes to villages and communities. Driving is on the left-hand sid ...
References
Works cited
*Further reading
* Nicholson, Desmond V., ''Antigua, Barbuda, and Redonda: A Historical Sketch,'' St. Johns, Antigua: Antigua and Barbuda Museum, 1991. * Dyde, Brian, ''A History of Antigua: The Unsuspected Isle,'' London: Macmillan Caribbean, 2000. * Gaspar, David Barry – ''Bondmen & Rebels: A Study of Master-Slave Relations in Antigua, with Implications for Colonial America.'' * Harris, David R. – ''Plants, Animals, and Man in the Outer Leeward Islands, West Indies. An Ecological Study of Antigua, Barbuda, and Anguilla.'' * Henry, Paget – ''Peripheral Capitalism and Underdevelopment in Antigua.'' * Lazarus-Black, Mindie – ''Legitimate Acts and Illegal Encounters: Law and Society in Antigua and Barbuda.'' * Riley, J. H. – ''Catalogue of a Collection of Birds from Barbuda and Antigua, British West Indies.'' * Rouse, Irving and Birgit Faber Morse – ''Excavations at the Indian Creek Site, Antigua, West Indies.'' * Thomas Hearne. ''Southampton.''External links
* *Antigua and Barbuda
United States Library of Congress
Antigua and Barbuda
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Antigua and Barbuda
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Antigua and Barbuda
from the BBC News
World Bank's country data profile
for Antigua and Barbuda
– 2010March13 source of archaeological information for Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua & Barbuda Official Business Hub
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antigua And Barbuda Countries in the Caribbean Island countries Commonwealth realms Countries in North America English-speaking countries and territories Member states of the Caribbean Community Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States Member states of the United Nations Small Island Developing States British Leeward Islands Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former colonies in North America 1630s establishments in the Caribbean 1632 establishments in the British Empire 1981 disestablishments in the United Kingdom States and territories established in 1981 *