Spontaneous vaginal birth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A vaginal delivery is the
A vaginal delivery is the

 A vaginal delivery is the
A vaginal delivery is the birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
of offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by a single organism or, in the case of sexual reproduction, two organisms. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny in a more general way. This ca ...
in mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
(babies
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to ...
in humans) through the vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
(also called the "birth canal"). It is the most common method of childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glob ...
worldwide. It is considered the preferred method of delivery, with lower morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
and mortality than Caesarean sections (C-sections).
Epidemiology
United States
70% of births in the United States in 2019 were vaginal deliveries.Global
80% of births globally in 2021 were vaginal deliveries, with rates varying from 95% in sub-Saharan Africa to 45% in the Caribbean.Benefits of vaginal delivery
Mother
Benefits for the mother include * Avoiding surgery and resulting quicker recovery time and shorter hospital admission * Quicker onset of lactation * Decreased complications in future pregnancies, includingplacenta previa
Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated wi ...
Infant
Benefits for the infant include: * Develop microbiota from exposure to the gut bacteria from the mother's gut, while the microbiota of babies born by caesarean section have more bacteria associated with hospital environments. * Decreased infant respiratory conditions, includinginfant respiratory distress syndrome
Infantile respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS), also called respiratory distress syndrome of newborn, or increasingly surfactant deficiency disorder (SDD), and previously called hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a syndrome in premature infants ...
, transient tachypnea of the newborn, and respiratory-related NICU
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as kn ...
admissions
* Improved immune function, possibly due to the infant's exposure to normal vaginal and gut bacteria during vaginal birth
Types of vaginal delivery
Different types of vaginal deliveries have different terms: * A ''spontaneous vaginal delivery'' (''SVD'') occurs when a pregnant woman goes intolabor
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the la ...
without the use of drugs or techniques to induce labor and delivers their baby without forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Fo ...
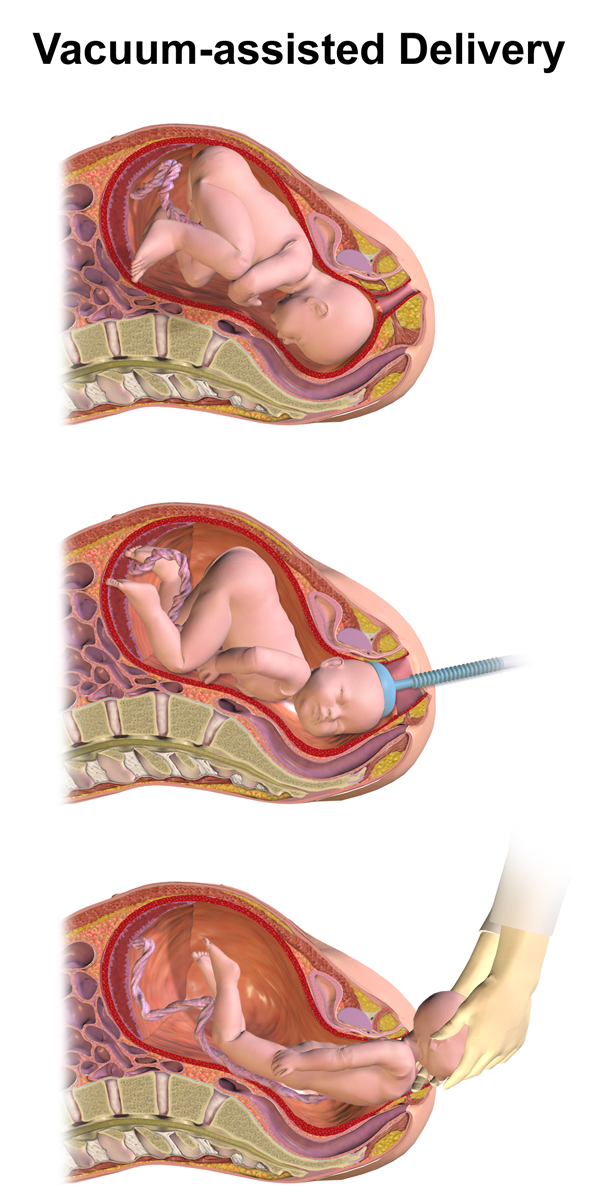
, vacuum extraction
Vacuum extraction (VE), also known as ventouse, is a method to assist delivery of a baby using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labor if it has not progressed adequately. It may be an alternative to a forceps delivery and caes ...
, or a cesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
.
*An ''induced vaginal delivery'' is a delivery involving labor induction
Labor induction is the process or treatment that stimulates childbirth and delivery. Inducing (starting) labor can be accomplished with pharmaceutical or non-pharmaceutical methods. In Western countries, it is estimated that one-quarter of pregnan ...
, where drugs or manual techniques are used to initiate labor. Vaginal delivery can be either spontaneous or induced.
* An ''assisted vaginal delivery'' (''AVD'') or ''instrumental vaginal delivery'' occurs when a pregnant woman requires the use of special instruments such as forceps or a vacuum extractor to deliver her baby vaginally. It is usually performed when the pregnancy does not progress during the second stage of labor. If the goal is to avoid the adverse effects of pushing that a cardiac patient may experience, it may also be performed in this case. Both spontaneous and induced vaginal delivery can be assisted. Examples of instruments to assist delivery include obstretical forcepts and vacuum extraction with a vacuum cup device.
A ''normal vaginal delivery'' (''NVD'') is defined as any vaginal delivery, assisted or unassisted.
Stages of labor
Labor is characterized by uterine contractions which push the fetus through thebirth canal
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hyme ...
and results in delivery. Labor is divided into three stages.
# ''First stage of labor'' starts with the onset of contractions and finishes when the cervix is fully dilated at 10 cm. This stage can further be divided into latent and active labor. The latent phase is defined by cervical dilation of 0 to 6 cm. The active phase is defined by cervical dilation of 6 cm to 10 cm.
# ''Second stage of labor'' starts when the cervix is dilated to 10 cm and finishes with the birth of the fetus. This is stage is characterized by strong contractions and active pushing by the mother. It can last from 20 minutes to 2 hours.
# ''Third stage of labor'' starts after the birth of the fetus and is finished when the placenta is delivered. It can last from 5 to 30 minutes.
Risks and complications of vaginal delivery
Complications of vaginal delivery can be grouped into the following criteria; failure to progress, abnormal fetal heart rate tracing, intrapartum hemorrhage, and post-partum hemorrhage. ''Failure to progress'' occurs when the labor process slows or stops entirely, indicated by slowed cervical dilation. Factors that place a woman's pregnancy at higher risk include advanced maternal age, Premature Rupture of Membranes (PROM
A promenade dance, commonly called a prom, is a dance party for high school students. It may be offered in semi-formal black tie or informal suit for boys, and evening gowns for girls. This event is typically held near the end of the school y ...
) and induction of labor. Oxytocin, a uterotonic agent, can be administered to augment labor. Cesarean section is also commonly considered when the pregnancy fails to progress. With a cesarean section, there is a higher chance that the uterus will become infected or that thromboembolic
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thro ...
complications will occur. There is also a higher chance of death.
''Abnormal fetal heart tracing'' suggests that the fetus's heart rate has slowed during labor due to head compression, cord compression, hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the bod ...
or anemia. Uterine tachysystole, the most common adverse effect of oxytocin (usually as a result of a problematic dosage), can result in nonreassuring fetal heart tracing. It can usually be reversed when oxytocin infusion is decreased or stopped. If the abnormal fetal heart rate persists, and uterine tachysystole continues, tocolytic
Tocolytics (also called anti-contraction medications or labor suppressants) are medications used to suppress premature labor (from Greek τόκος ''tókos'', "childbirth", and λύσις ''lúsis'', "loosening"). Preterm birth accounts for 70% ...
remedies, such as terbutaline
Terbutaline, sold under the brand names Bricanyl and Marex among others, is a β2 adrenergic receptor agonist, used as a "reliever" inhaler in the management of asthma symptoms and as a tocolytic (anti-contraction medication) to delay preterm ...
, may be used. Afterward, if beneficial and uterine tone has returned to baseline and fetal status is stable, oxytocin as a labor augmenting agent may be resumed. The persistence of an abnormal fetal heart rate may also indicate that a cesarean section is necessary.
'' Intrapartum hemorrhage'' is characterized by the presence of copious blood during labor. The bleeding may be due to placental abruption, uterine rupture, placenta accrete, undiagnosed placenta previa, or vasa previa. Cesarean section is indicated.
'' Post-partum hemorrhage'' is defined by the loss of at least 1,000 mL of blood accompanied with symptoms of hypovolemia within 24 hours after delivery. Typically, the first symptom is excessive bleeding accompanied by tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ( ...
. Significant loss of blood may also result in hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
, nausea, dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
, and chest pain. It is estimated that between 3% to 5% of women giving birth vaginally will experience post-partum hemorrhage. Risk factors include fetal macrosomia
Large for gestational age (LGA) is a term used to describe infants that are born with an abnormally high weight, specifically in the 90th percentile or above, compared to other babies of the same developmental age. Macrosomia is a similar term tha ...
, pre-eclampsia, and prolonged labor. Prevention consists of administering oxytocin (Pitocin
Synthetic oxytocin, sold under the brand name Pitocin among others, is a medication made from the peptide '' oxytocin''. As a medication, it is used to cause contraction of the uterus to start labor, increase the speed of labor, and to stop ...
) at delivery and early umbilical cord clamping. Post-partum hemorrhage is usually attributed to uterus atony, when the uterus fails to contract after delivering the baby.
As a result of discrepancies in diagnostic criteria and human variability
Human variability, or human variation, is the range of possible values for any characteristic, physical or mental, of human beings.
Frequently debated areas of variability include cognitive ability, personality, physical appearance ( body sh ...
, there is wide variation in data on maternal and fetal death associated with poor progress.
Contraindications to vaginal delivery
Spontaneous vaginal delivery at term is the preferred outcome of pregnancy, and according to the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics, will be recommended if there are no evidence-based clinical indications forcesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
. However, there are some contraindications for vaginal delivery that would result in conversion to cesarean delivery. The decision to switch to cesarean delivery is made by the health care provider and mother, and is sometimes delayed until the mother is in labor.
''Breech birth
A breech birth is when a baby is born bottom first instead of head first, as is normal. Around 3–5% of pregnant women at term (37–40 weeks pregnant) have a breech baby. Due to their higher than average rate of possible complications for the ...
'' presentations occur when the fetus' buttocks or lower extremities are poised to deliver before the fetus' upper extremities or head. The three types of breech positions are footling breech, frank breech, and complete breech. These births occur in 3% to 4% of all term pregnancies. They usually result in cesarean sections because it is more difficult to deliver the baby through the birth canal and there is a lack of expertise in vaginal breech delivery and therefore fewer vaginal breech deliveries performed. It is also associated with cord prolapse and an elevated risk for birth defects of breech babies. Controversy and debate surround the topic due to different views on the preferred route of delivery when breech presentation occurs. Some health professionals believe that vaginal breech delivery can be a safe alternative to planned cesarean in certain instances.
''Complete placenta previa
Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated wi ...
'' occurs when the placenta covers the opening of the cervix. If placenta previa is present at the time of delivery, vaginal delivery is contraindicated because the placenta is blocking the fetus’ passageway to the vaginal canal.
'' Herpes simplex virus with active genital lesions or prodromal symptoms'' is a contraindication for vaginal delivery so as to avoid mother-fetal transfer of HSV lesions.
''Untreated human immunodeficiency virus (HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
) infection'' is a contraindication for vaginal delivery to avoid mother-fetal transfer of human immunodeficiency virus.
See also
*Home birth
A home birth is a birth that takes place in a residence rather than in a hospital or a birthing center. They may be attended by a midwife, or lay attendant with experience in managing home births. Home birth was, until the advent of modern medic ...
*Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour and delivery, is the ending of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births glob ...
*Caesarian section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or ...
*Silent birth Silent birth, sometimes known as quiet birth, is a birthing procedure advised by L. Ron Hubbard and advocated by Scientologists in which "everyone attending the birth should refrain from spoken words as much as possible" and where "... chatty doctor ...
References