Sodium phosphate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


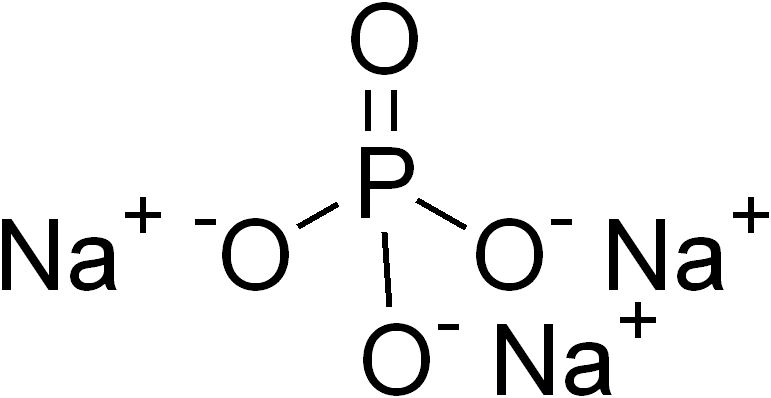 Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of
Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of


 Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of
Sodium phosphate is a generic term for a variety of salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
s of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
(Na+) and phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
(PO43−). Phosphate also forms families or condensed anions including di-, tri-, tetra-, and polyphosphates. Most of these salts are known in both anhydrous (water-free) and hydrated forms. The hydrates are more common than the anhydrous forms.
Uses
Sodium phosphates have many applications in food and for water treatment. For example, sodium phosphates are often used as emulsifiers (as inprocessed cheese
Processed cheese (also known as process cheese, cheese food, prepared cheese, cheese product, or plastic cheese) is a food product made from cheese and unfermented dairy ingredients mixed with emulsifiers. Additional ingredients, such as vegeta ...
), thickening agent
A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering the ...
s, and leavening agent
In cooking, a leavening agent () or raising agent, also called a leaven () or leavener, is any one of a number of substances used in doughs and batters that cause a foaming action (gas bubbles) that lightens and softens the mixture. An altern ...
s for baked goods. They are also used to control pH of processed foods. They are also used in medicine for constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel movement ...
and to prepare the bowel for medical procedures. Moreover, they are used in detergents for softening water, and as an efficient anti rust solution.
Adverse effects
Sodium phosphates are popular in commerce in part because they are inexpensive and because they are nontoxic at normal levels of consumption. However, oral sodium phosphates when taken at high doses for bowel preparation for colonoscopy may in some individuals carry a risk of kidney injury under the form of phosphate nephropathy. There are several oral phosphate formulations which are prepared extemporaneously. Oral phosphate prep drugs have been withdrawn in the United States, although evidence of causality is equivocal. Since safe and effective replacements for phosphate purgatives are available, several medical authorities have recommended general disuse of oral phosphates.Monophosphates
Three families of sodium monophosphates are common, those derived from orthophosphate (PO43−), hydrogen phosphate (HPO42−), and dihydrogenphosphate (H2PO4−). Some of the most well known salts are shown in the table.Di- and polyphosphates
In addition to these phosphates, sodium forms a number of useful salts withpyrophosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among othe ...
s (also called diphosphates), triphosphates and high polymers. Of these salts, those of the diphosphates are particularly common commercially.
Beyond the diphosphates, sodium salts are known triphosphates, e.g. sodium triphosphate
Sodium triphosphate (STP), also sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), or tripolyphosphate (TPP),
and tetraphosphates. The cyclic polyphosphates, called metaphosphates, include the trimer sodium trimetaphosphate
Sodium trimetaphosphate (also STMP), with formula Na3P3O9, is one of the metaphosphates of sodium. It has the formula but the hexahydrate is also well known. It is the sodium salt of trimetaphosphoric acid. It is a colourless solid that finds ...
and the tetramer, Na3P3O9 and Na4P4O12, respectively.
Polymeric sodium phosphates are formed upon heating mixtures of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4, which induces a condensation reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a ...
. The specific polyphosphate generated depends on the details of the heating and annealing. One derivative is the glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching ...
y (i.e., amorphous) Graham's salt. It is a linear polyphosphate the average formula NaO(NaPO3)Na2. Crystalline high molecular weight polyphosphates include Kurrol's salt and Maddrell's salt (CAS#10361-03-2). These species have the formula aPO3sub>n aPO3(OH)sub>2 where n can be as great as 2000. In terms of their structures, these polymers consist of PO3− "monomers", with the chains are terminated by protonated phosphates.
References
External links
* * {{Phosphates Phosphates Sodium compounds Edible thickening agents