Sigma Octantis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sigma Octantis is a solitary star in the
 ''σ Octantis'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Octantis'') is the star's Bayer designation.
As the southern hemisphere's pole star it bore the name ''Polaris Australis'', first applied in the 1700s. In 2016, the IAU organized a
''σ Octantis'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Octantis'') is the star's Bayer designation.
As the southern hemisphere's pole star it bore the name ''Polaris Australis'', first applied in the 1700s. In 2016, the IAU organized a
 At magnitude +5.42, Sigma Octantis is barely visible to the naked eye, making it unusable for navigation, especially by comparison with the much brighter and more easily visible Polaris.
Because of this, the constellation
At magnitude +5.42, Sigma Octantis is barely visible to the naked eye, making it unusable for navigation, especially by comparison with the much brighter and more easily visible Polaris.
Because of this, the constellation
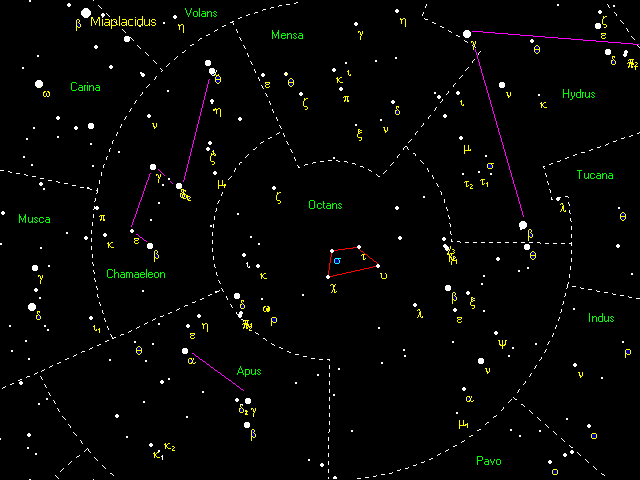
Octans
Octans () is a faint constellation located in the deep Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for the eighth part of a circle, but it is named after the octant, a navigational instrument. Devised by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1752 ...
constellation that forms the pole star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
of the Southern Hemisphere. Its name is also written as σ Octantis, abbreviated as Sigma Oct or σ Oct, and it is officially named Polaris Australis (). The star is positioned one degree away from the southern celestial pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers a ...
of the Southern Hemisphere, lying nearly opposite to the North Star
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris ( Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude tha ...
.
Located approximately from Earth, it is classified as a subgiant
A subgiant is a star that is brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as giant stars. The term subgiant is applied both to a particular spectral luminosity class and to a stage in the evolution ...
with a spectral type
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
of F0 III. Sigma Octantis has an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's ...
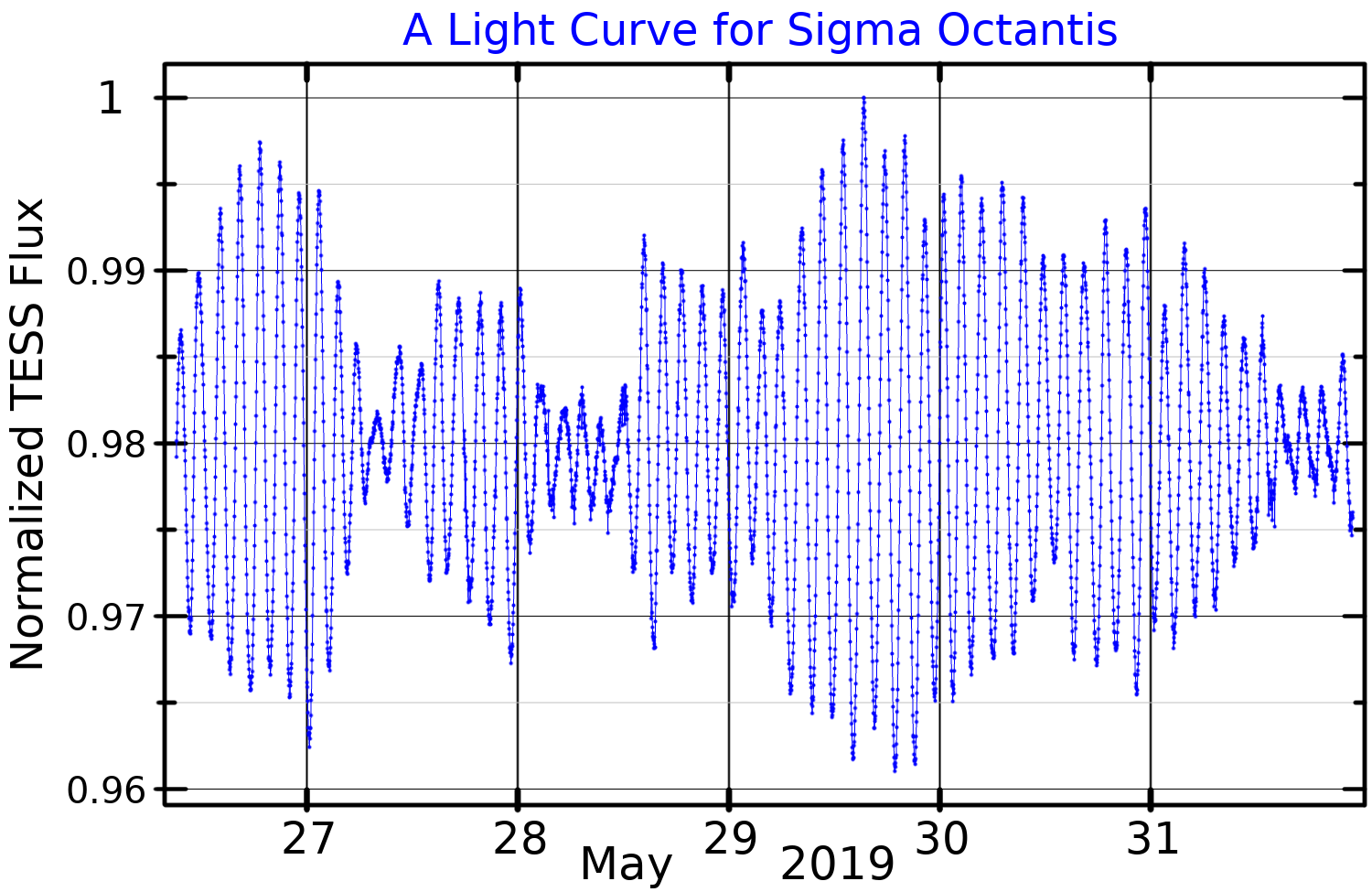
of 5.5, but is slightly variable and is classified as a Delta Scuti variable
A Delta Scuti variable (sometimes termed dwarf cepheid when the V-band amplitude is larger than 0.3 mag.) is a subclass of young pulsating star.
These variables as well as classical cepheids are important standard candles and have been used to es ...
.
Nomenclature
 ''σ Octantis'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Octantis'') is the star's Bayer designation.
As the southern hemisphere's pole star it bore the name ''Polaris Australis'', first applied in the 1700s. In 2016, the IAU organized a
''σ Octantis'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Octantis'') is the star's Bayer designation.
As the southern hemisphere's pole star it bore the name ''Polaris Australis'', first applied in the 1700s. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education ...
(WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Polaris Australis'' for this star on 5 September 2017 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. It is the southernmost named star.
Properties
With a spectral class of F0IV, Sigma Octantis appears to be asubgiant
A subgiant is a star that is brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as giant stars. The term subgiant is applied both to a particular spectral luminosity class and to a stage in the evolution ...
, although it has also been classified as F0III. Evolutionary models place it at the very end of its main sequence life with an age of about 900 million years. It has expanded somewhat to a size 4.4 that of the Sun and emits 44 times as much electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) li ...
from its photosphere at an effective temperature of .
Sigma Octantis is a Delta Scuti variable
A Delta Scuti variable (sometimes termed dwarf cepheid when the V-band amplitude is larger than 0.3 mag.) is a subclass of young pulsating star.
These variables as well as classical cepheids are important standard candles and have been used to es ...
, varying by about 0.03 magnitudes every 2.33 hours. It is thought to pulsate only in the fundamental mode.
Southern pole star
Sigma Octantis is the current southernpole star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
, whose counterpart is Polaris, the current North Star. To an observer in the southern hemisphere, Sigma Octantis appears almost motionless and all the other stars in the Southern sky appear to rotate around it. It is part of a small "half hexagon" shape. It is slightly more than a degree away from the true south pole, and the south celestial pole is moving away from it due to precession of the equinoxes
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In partic ...
.
Crux
Crux () is a constellation of the southern sky that is centred on four bright stars in a cross-shaped asterism commonly known as the Southern Cross. It lies on the southern end of the Milky Way's visible band. The name ''Crux'' is Latin for ...
is often preferred for determining the position of the South Celestial Pole.
Once Sigma Octantis' approximate position has been determined, either by the major stars in Octans
Octans () is a faint constellation located in the deep Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for the eighth part of a circle, but it is named after the octant, a navigational instrument. Devised by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1752 ...
or using the Southern Cross (Crux) method, it can be positively verified using an asterism: Sigma, Chi, Tau
Tau (uppercase Τ, lowercase τ, or \boldsymbol\tau; el, ταυ ) is the 19th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless dental or alveolar plosive . In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 300.
The name in English ...
, and Upsilon Octantis are all stars of around magnitude 5.6, and form the distinctive shape of a trapezoid
A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezoid () in American and Canadian English. In British and other forms of English, it is called a trapezium ().
A trapezoid is necessarily a convex quadrilateral in Eu ...
.
In astrometrics
Sigma Octantis was used as a reference to measure the magnitudes of stars in the southern hemisphere for the 1908 Revised Harvard Photometry catalogue. The Pole Star and Lambda Ursae Minoris were used for the northern hemisphere. It was then noted that "Neither of these stars appears to vary perceptibly" but that, due to the procedures used "if they did, the variation would have no effect on the final measures."In culture
Sigma Octantis is the dimmest star to be represented on a national flag. It appears on theflag of Brazil
The national flag of Brazil ( pt, bandeira do Brasil), is a blue disc depicting a starry sky (which includes the Southern Cross) spanned by a curved band inscribed with the national motto "''Ordem e Progresso''" ("Order and Progress"), within a ...
, symbolising the Brazilian Federal District.
See also
*Polar alignment
Polar alignment is the act of aligning the rotational axis of a telescope's equatorial mount or a sundial's gnomon with a celestial pole to parallel Earth's axis.
Alignment methods
The method to use differs depending on whether the alignment ...
* Polaris
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sigma Octantis Delta Scuti variables F-type subgiants Southern pole stars Polaris Australis Octantis, Sigma Octans Durchmusterung objects 177482 104382 7228