|
Lambda Ursae Minoris
Lambda Ursae Minoris (λ UMi, λ Ursae Minoris) is a star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is an M-type red giant with an apparent magnitude of +6.38 and is approximately 880 light years from Earth. Lambda Ursae Minoris is an asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star, a star that has exhausted its core hydrogen and helium and is now fusing material in shells outside its core. AGB stars are often unstable and tend to pulsate, and Lambda Ursae Minoris is classified as a semiregular variable star and its brightness varies by about 0.1 magnitudes. Its variability was discovered from Hipparcos astrometry and it was entered into the General Catalogue of Variable Stars in 1999. This star was used from 1882 as a reference to measure the magnitudes of stars in the northern hemisphere for the 1908 Revised Harvard Photometry catalogue. Sigma Octantis was used for the southern hemisphere. It was then noted that "Neither of these stars appears to vary perceptibly" but that, due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Years
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bright Star Catalogue Objects
Bright may refer to: Common meanings *Bright, an adjective meaning giving off or reflecting illumination; see Brightness *Bright, an adjective meaning someone with intelligence People * Bright (surname) * Bright (given name) *Bright, the stage name of Thai actor/musician Vachirawit Chiva-aree Places Australia * Bright, Victoria, a town * Electoral district of Bright in South Australia Canada * Bright Parish, New Brunswick Northern Ireland *Bright, County Down, a village and parish in County Down United States *Bright, Indiana, a census-designated place * Bright, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Bright, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Music *Bright (American band), an experimental pop group from Brooklyn, New York ** ''Bright'' (Bright (American band) album), the eponymous debut from the aforementioned group *Bright (Japanese band), a dance vocal band from Japan ** ''Bright'' (Bright (Japanese band) album) * "Bright" (song), a song b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiregular Variable Stars
In astronomy, a semiregular variable star, a type of variable star, is a giant or supergiant of intermediate and late (cooler) spectral type showing considerable periodicity in its light changes, accompanied or sometimes interrupted by various irregularities. Periods lie in the range from 20 to more than 2000 days, while the shapes of the light curves may be rather different and variable with each cycle. The amplitudes may be from several hundredths to several magnitudes (usually 1-2 magnitudes in the V filter). Classification The semiregular variable stars have been sub-divided into four categories for many decades, with a fifth related group defined more recently. The original definitions of the four main groups were formalised in 1958 at the tenth general assembly of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) has updated the definitions with some additional information and provided newer reference stars where old examples such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M-type Giants
Type M or M type may refer to: Science and technology * Type M, a xD-Picture Card * Type M, a name for the 15 amp BS 546 electrical plug * Vaio Type M, a kind of Vaio computer from Sony * M-type asteroid * m-type filter, an electronic filter * M-type star * M-types, an implementation of inductive type Other uses * Audi Type M, a 1920s car * Beretta 92FS Compact Type M, a pistol * MG M-type, a sports car See also * M class (other) M class or M-class may refer to: Military * M-class cruiser, a planned German light cruiser class * M-class destroyer, several classes of destroyer ** Admiralty M-class destroyer, a class of British destroyers built 1913–1916 and served in Worl ... * Class M (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Minor (constellation)
Ursa Minor (Latin: 'Lesser Bear', contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the North American name, Little Dipper: seven stars with four in its bowl like its partner the Big Dipper. Ursa Minor was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, because of Polaris being the north pole star. Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging in apparent magnitude from 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Objects
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceuticals; consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer and dyer Friedrich Weskott. As was common in this era, the company was established as a dyestuffs producer. The versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand their business into other areas, and in 1899 Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. In 1904 Bayer received a trademark for the "Bayer Cross" logo, which was subsequently stamped onto each aspirin tablet, creating an iconic product that is still sold by Bayer. Other commonly known produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim Kaler
James Bailey "Jim" Kaler (December 29, 1938 — November 26, 2022) was an American astronomer and science writer. After elementary and high-school education in Albany, New York, Kaler earned his A.B. at the University of Michigan in 1960. He attended graduate school at the University of Michigan (1960–61), at Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel (Germany, 1961–62), and UCLA (1962–64), where he also obtained his Ph.D. in Astronomy 1964. His thesis advisor was Lawrence H. Aller. Professional career Kaler started his professional career with appointments as a research and teaching assistant at the University of Michigan from 1958 to summer 1960. In 1961 he worked as an astronomer with the United States Naval Observatory. In 1964 he was appointed as an assistant professor of Astronomy by the University of Illinois, and promoted to associate professor in 1968 and to a full professor position in 1976 (all at University of Illinois). Since 1995 he is Campus Honors Faculty. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
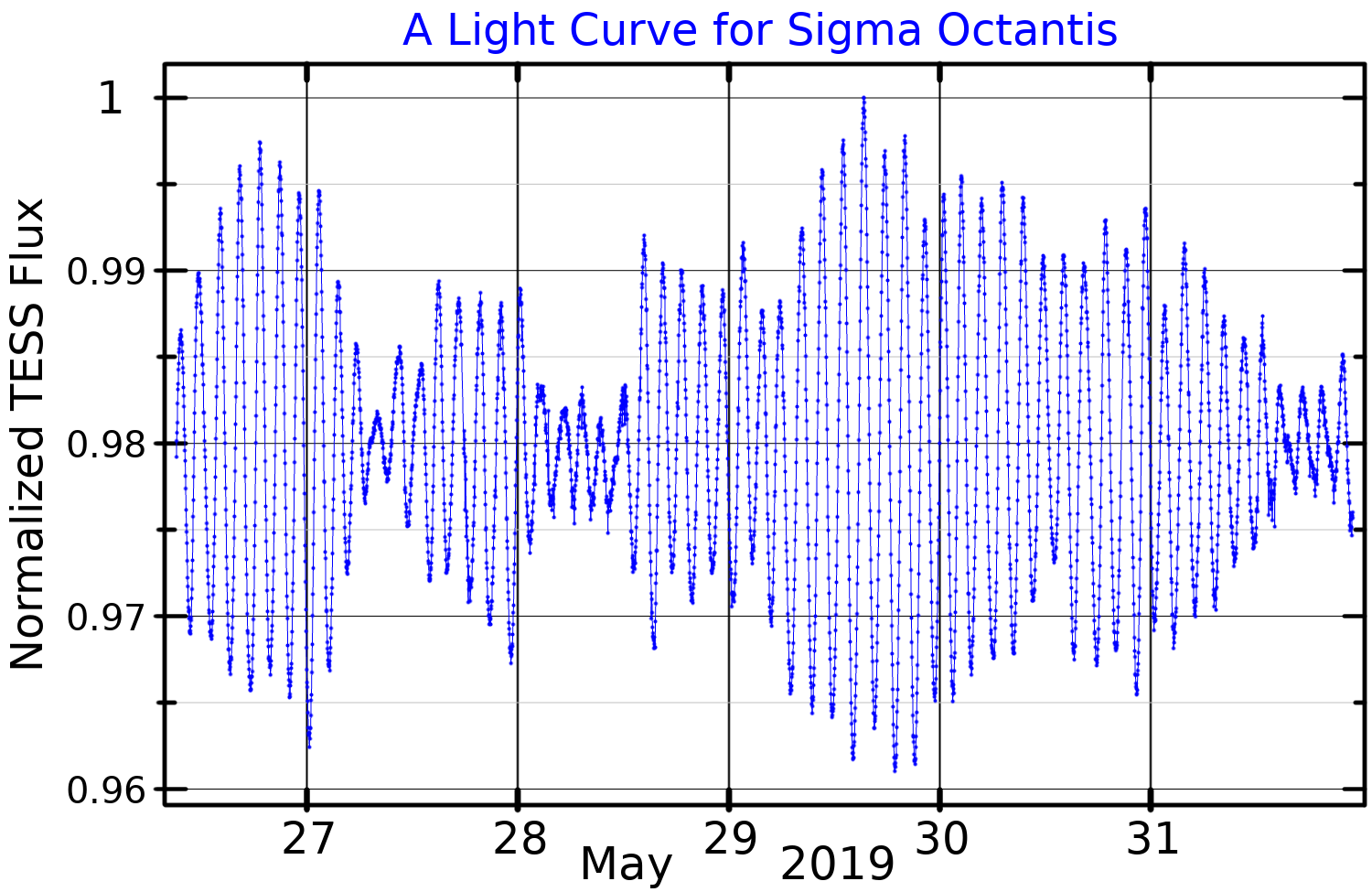
Sigma Octantis
Sigma Octantis is a solitary star in the Octans constellation that forms the pole star of the Southern Hemisphere. Its name is also written as σ Octantis, abbreviated as Sigma Oct or σ Oct, and it is officially named Polaris Australis (). The star is positioned one degree away from the southern celestial pole of the Southern Hemisphere, lying nearly opposite to the North Star. Located approximately from Earth, it is classified as a subgiant with a spectral type of F0 III. Sigma Octantis has an apparent magnitude of 5.5, but is slightly variable and is classified as a Delta Scuti variable. Nomenclature ''σ Octantis'' ( Latinised to ''Sigma Octantis'') is the star's Bayer designation. As the southern hemisphere's pole star it bore the name ''Polaris Australis'', first applied in the 1700s. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Polaris Australis'' for thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Revised Photometry Catalogue
The Bright Star Catalogue, also known as the Yale Catalogue of Bright Stars, Yale Bright Star Catalogue, or just YBS, is a star catalogue that lists all stars of stellar magnitude 6.5 or brighter, which is roughly every star visible to the naked eye from Earth. The catalog lists 9,110 objects, of which 9,095 are stars, 11 are novae or supernovae (which were "bright stars" only at the time when they were at their peak), and four are non-stellar objects which are the globular clusters 47 Tucanae (designated HR 95) and NGC 2808 (HR 3671), and the open clusters NGC 2281 (HR 2496) and Messier 67 (HR 3515). The catalogue is fixed in number of entries, but its data is maintained, and it is appended with a comments section about the objects that has been steadily enhanced. The abbreviation for the catalog as a whole is BS or YBS but all citations of stars it indexes use HR before the catalog number, a homage to the catalog's direct predecessor, published in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Catalogue Of Variable Stars
The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) is a list of variable stars. Its first edition, containing 10,820 stars, was published in 1948 by the Academy of Sciences of the USSR and edited by B. V. Kukarkin and P. P. Parenago. Second and third editions were published in 1958 and 1968; the fourth edition, in three volumes, was published 1985–1987. It contained 28,435 stars. A fourth volume of the fourth edition containing reference tables was later published, as well as a fifth volume containing variable stars outside the Galaxy. The last edition (GCVS v5.1) based on data compiled in 2015 gathers 52,011 variable stars. The most up-to-date version of the GCVS is available at the GCVS website. It contains improved coordinates for the variable stars in the printed fourth edition of the GCVS, as well as variable stars discovered too recently to be included in the fourth edition. An older version of the GCVS dating from 2004 is available from the VizieR service at the Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |