Saturnian system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The moons of Saturn are numerous and diverse, ranging from tiny

moonlet
A moonlet, minor moon, minor natural satellite, or minor satellite is a particularly small natural satellite orbiting a planet, dwarf planet, or other minor planet.
Up until 1995, moonlets were only hypothetical components of Saturn's F-ring ...
s only tens of meters across to enormous Titan, which is larger than the planet Mercury. Saturn has 83 moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
with confirmed orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
s that are not embedded in its rings
Ring may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
:(hence) to initiate a telephone connection
Arts, entertainment and media Film and ...
—of which only 13 have diameters greater than 50 kilometers—as well as dense rings that contain millions of embedded moonlets and innumerable smaller ring particles. Seven Saturnian moons are large enough to have collapsed into a relaxed, ellipsoidal shape, though only one or two of those, Titan and possibly Rhea, are currently in hydrostatic equilibrium
In fluid mechanics, hydrostatic equilibrium (hydrostatic balance, hydrostasy) is the condition of a fluid or plastic solid at rest, which occurs when external forces, such as gravity, are balanced by a pressure-gradient force. In the planetary ...
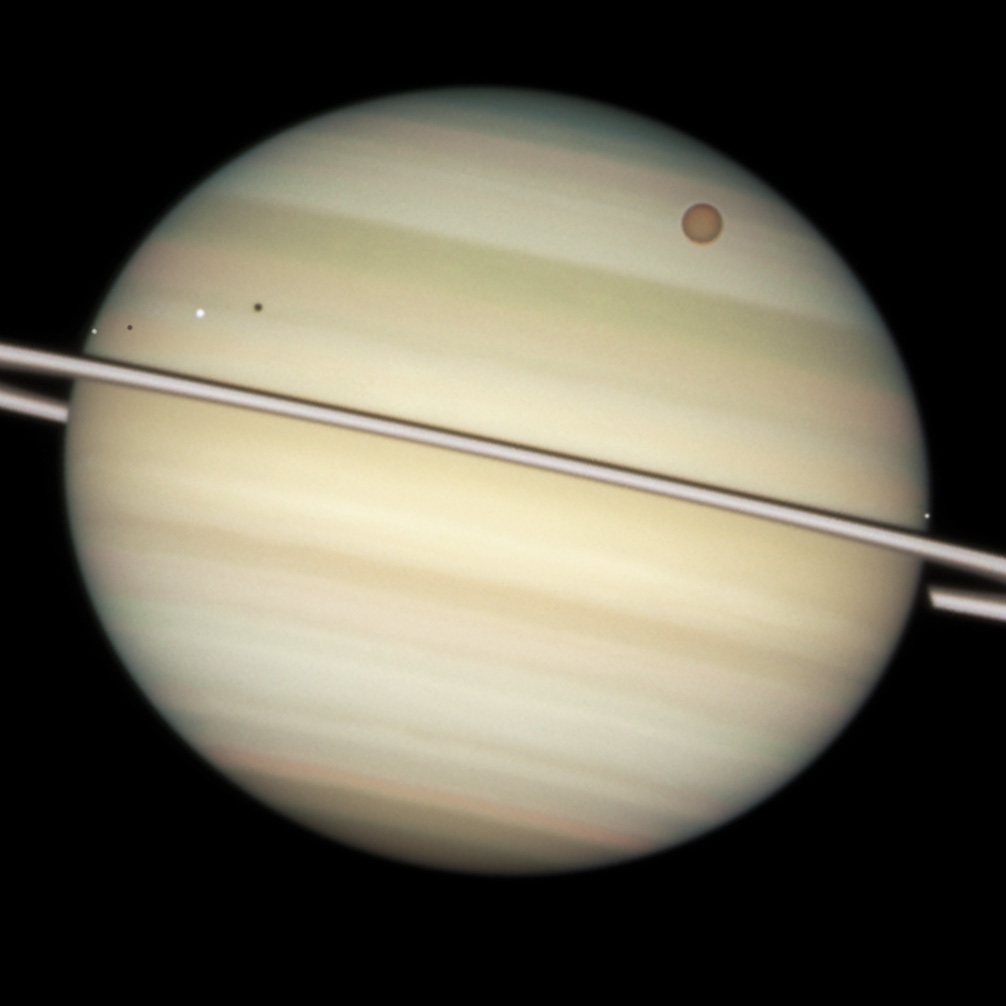
. Particularly notable among Saturn's moons are Titan, the second-largest
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (o ...
moon in the Solar System (after Jupiter's Ganymede), with a nitrogen-rich Earth-like atmosphere and a landscape featuring dry river networks and hydrocarbon lakes, Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn (19th largest in the Solar System). It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Enceladus is mostly covered by fresh, clean ice, making it one of the most refle ...
, which emits jets of gas and dust from its south-polar region, and Iapetus, with its contrasting black and white hemispheres.
Twenty-four of Saturn's moons are ''regular satellites''; they have prograde orbit
Retrograde motion in astronomy is, in general, orbital or rotational motion of an object in the direction opposite the rotation of its primary, that is, the central object (right figure). It may also describe other motions such as precession or ...
s not greatly inclined to Saturn's equatorial plane. They include the seven major satellites, four small moons that exist in a trojan
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 189 ...
orbit with larger moons, two mutually co-orbital moons and two moons that act as shepherds
A shepherd or sheepherder is a person who tends, herds, feeds, or guards flocks of sheep. ''Shepherd'' derives from Old English ''sceaphierde (''sceap'' 'sheep' + ''hierde'' 'herder'). ''Shepherding is one of the world's oldest occupations, i ...
of Saturn's F Ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entir ...
. Two other known regular satellites orbit within gaps in Saturn's rings. The relatively large Hyperion is locked in a resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied Periodic function, periodic force (or a Fourier analysis, Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system ...
with Titan. The remaining regular moons orbit near the outer edge of the A Ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entirel ...
, within the G Ring G Ring may refer to:
* Rings of Saturn#G Ring, a planetary ring system around Saturn.
* G-ring
In commutative algebra, a G-ring or Grothendieck ring is a Noetherian ring such that the map of any of its local rings to the completion is regular ( ...
and between the major moons Mimas and Enceladus. The regular satellites are traditionally named after Titans
In Greek mythology, the Titans ( grc, οἱ Τῑτᾶνες, ''hoi Tītânes'', , ''ho Tītân'') were the pre-Olympian gods. According to the ''Theogony'' of Hesiod, they were the twelve children of the primordial parents Uranus (Sky) and Gai ...
and Titanesses or other figures associated with the mythological Saturn.
The remaining fifty-nine, with mean diameters ranging from 4 to 213 km, are ''irregular satellites'', whose orbits are much farther from Saturn, have high inclinations, and are mixed between prograde and retrograde. These moons are probably captured minor planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''mino ...
s, or debris
Debris (, ) is rubble, wreckage, ruins, litter and discarded garbage/refuse/trash, scattered remains of something destroyed, or, as in geology, large rock fragments left by a melting glacier, etc. Depending on context, ''debris'' can refer to ...
from the breakup of such bodies after they were captured, creating collisional families. The irregular satellites have been classified by their orbital characteristics into the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
, Norse, and Gallic groups, and their names are chosen from the corresponding mythologies (with the Gallic group corresponding to Celtic mythology). The sole exception is Phoebe, the ninth moon of Saturn and largest irregular, discovered at the end of the 19th century; it is part of the Norse group but named for a Greek Titaness.
The rings of Saturn are made up of objects ranging in size from microscopic to moonlet
A moonlet, minor moon, minor natural satellite, or minor satellite is a particularly small natural satellite orbiting a planet, dwarf planet, or other minor planet.
Up until 1995, moonlets were only hypothetical components of Saturn's F-ring ...
s hundreds of meters across, each in its own orbit around Saturn. Thus a precise number of Saturnian moons cannot be given, because there is no objective boundary between the countless small anonymous objects that form Saturn's ring system and the larger objects that have been named as moons. Over 150 moonlets embedded in the rings have been detected by the disturbance they create in the surrounding ring material, though this is thought to be only a small sample of the total population of such objects.
There are still twenty unnamed moons (), of which all but one is irregular. If named, they will receive names from Gallic, Norse and Inuit mythology
Inuit religion is the shared spiritual beliefs and practices of the Inuit, an Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous people from Alaska, northern Canada, parts of Siberia and Greenland. Their religion shares many similarities with some Al ...
based on the orbital groups of the moons.
Discovery

Early observations
Before the advent of telescopic photography, eight moons of Saturn were discovered by direct observation usingoptical telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through elect ...
s. Saturn's largest moon, Titan, was discovered in 1655 by Christiaan Huygens using a objective lens
In optical engineering, the objective is the optical element that gathers light from the object being observed and focuses the light rays to produce a real image. Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elem ...
on a refracting telescope
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and a ...
of his own design. Tethys, Dione, Rhea and Iapetus (the "Sidera Lodoicea
Sidera Lodoicea is the name given by the astronomer Giovanni Domenico Cassini to the four moons of Saturn discovered by him in the years 1671, 1672, and 1684 and published in his ''Découverte de deux nouvelles planètes autour de Saturne'' in 16 ...
") were discovered between 1671 and 1684 by Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian (naturalised French) mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the ...
. Mimas and Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn (19th largest in the Solar System). It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Enceladus is mostly covered by fresh, clean ice, making it one of the most refle ...
were discovered in 1789 by William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel (; german: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline ...
. Hyperion was discovered in 1848 by W. C. Bond, G. P. Bond and William Lassell
William Lassell (18 June 1799 – 5 October 1880) was an English merchant and astronomer.long-exposure photographic plates made possible the discovery of additional moons. The first to be discovered in this manner, Phoebe, was found in 1899 by
 Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital
Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital 
 In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the
In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the

 Shepherd satellites are small moons that orbit within, or just beyond, a planet's
Shepherd satellites are small moons that orbit within, or just beyond, a planet's
 The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
* Mimas is the smallest and least massive of the inner round moons, although its mass is sufficient to alter the orbit of Methone. It is noticeably ovoid-shaped, having been made shorter at the poles and longer at the equator (by about 20 km) by the effects of Saturn's gravity. Mimas has a large
The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
* Mimas is the smallest and least massive of the inner round moons, although its mass is sufficient to alter the orbit of Methone. It is noticeably ovoid-shaped, having been made shorter at the poles and longer at the equator (by about 20 km) by the effects of Saturn's gravity. Mimas has a large


Saturn Moons
* * * *
at ''
(2017-05-17) by Emily Lakdawalla with images giving comparative sizes of the moons * Tilmann Denk
Outer Moons of Saturn
{{DEFAULTSORT:Moons Of Saturn Lists of moons
W. H. Pickering
William Henry Pickering (February 15, 1858 – January 16, 1938) was an American astronomer. Pickering constructed and established several observatories or astronomical observation stations, notably including Percival Lowell's Flagstaff Obser ...
. In 1966 the tenth satellite of Saturn was discovered by Audouin Dollfus, when the rings were observed edge-on near an equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and se ...
. It was later named Janus. A few years later it was realized that all observations of 1966 could only be explained if another satellite had been present and that it had an orbit similar to that of Janus. This object is now known as Epimetheus
In Greek mythology, Epimetheus (; grc-gre, Ἐπιμηθεύς, , afterthought) was the brother of Prometheus (traditionally interpreted as "foresight", literally "fore-thinker"), a pair of Titans who "acted as representatives of mankind". They ...
, the eleventh moon of Saturn. It shares the same orbit with Janus—the only known example of co-orbitals in the Solar System. In 1980, three additional Saturnian moons were discovered from the ground and later confirmed by the '' Voyager'' probes. They are trojan moon
In astronomy, a co-orbital configuration is a configuration of two or more astronomical objects (such as asteroids, moons, or planets) orbiting at the same, or very similar, distance from their primary, i.e. they are in a 1:1 mean-motion resonance ...
s of Dione ( Helene) and Tethys ( Telesto and Calypso).
Observations by spacecraft
The study of the outer planets has since been revolutionized by the use of unmanned space probes. The arrival of the '' Voyager'' spacecraft at Saturn in 1980–1981 resulted in the discovery of three additional moons –Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
, Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning " forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titan god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technology, kn ...
and Pandora, bringing the total to 17. In addition, Epimetheus was confirmed as distinct from Janus. In 1990, Pan was discovered in archival ''Voyager'' images.
The '' Cassini'' mission, which arrived at Saturn in the summer of 2004, initially discovered three small inner moons including Methone and Pallene between Mimas and Enceladus as well as the second trojan moon of Dione – Polydeuces. It also observed three suspected but unconfirmed moons in the F Ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entir ...
. In Cassini scientists announced that the structure of Saturn's rings
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entire ...
indicates the presence of several more moons orbiting within the rings, although only one, Daphnis
In Greek mythology, Daphnis (; grc, Δάφνις, from , ''daphne'', "Bay Laurel") was a Sicilian shepherd who was said to be the inventor of pastoral poetry.
Family
According to tradition, he was the son of Hermes and a nymph, despite which ...
, had been visually confirmed at the time. In 2007 Anthe was announced. In 2008 it was reported that ''Cassini'' observations of a depletion of energetic electrons in Saturn's magnetosphere near Rhea might be the signature of a tenuous ring system around Saturn's second largest moon. In , Aegaeon, a moonlet within the G Ring, was announced. In July of the same year, S/2009 S 1
S/2009 S 1 is a moonlet embedded in the outer part of Saturn's B Ring, orbiting away from the planet. The moonlet was discovered by the ''Cassini'' Imaging Team during the Saturnian equinox event on 26 July 2009, when the ''Cassini'' spacecraft ...
, the first moonlet within the B Ring, was observed. In April 2014, the possible beginning of a new moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, within the A Ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entirel ...
, was reported. ( related image)
Outer moons
 Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital
Study of Saturn's moons has also been aided by advances in telescope instrumentation, primarily the introduction of digital charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
s which replaced photographic plates. For the 20th century, Phoebe stood alone among Saturn's known moons with its highly irregular orbit. Then in 2000, three dozen additional irregular moons have been discovered using ground-based telescopes. A survey starting in late 2000 and conducted using three medium-size telescopes found thirteen new moons orbiting Saturn at a great distance, in eccentric orbits, which are highly inclined to both the equator of Saturn and the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
. They are probably fragments of larger bodies captured by Saturn's gravitational pull. In 2005, astronomers using the Mauna Kea Observatory
The Mauna Kea Observatories (MKO) are a group of independent astronomical research facilities and large telescope observatories that are located at the summit of Mauna Kea on the Big Island of Hawaiʻi, United States. The facilities are locate ...
announced the discovery of twelve more small outer moons, in 2006, astronomers using the Subaru 8.2 m telescope reported the discovery of nine more irregular moons, in , Tarqeq (S/2007 S 1) was announced and in May of the same year S/2007 S 2 and S/2007 S 3 were reported. In 2019, twenty new irregular satellites of Saturn were reported, resulting in Saturn overtaking Jupiter as the planet with the most known moons for the first time since 2000. Yet another was reported in 2021, after a survey for Saturnian moons took place in 2019.
Naming
The modern names for Saturnian moons were suggested by John Herschel in 1847. He proposed to name them after mythological figures associated with the Roman titan of time, Saturn (equated to the Greek Cronus). In particular, the then known seven satellites were named afterTitans
In Greek mythology, the Titans ( grc, οἱ Τῑτᾶνες, ''hoi Tītânes'', , ''ho Tītân'') were the pre-Olympian gods. According to the ''Theogony'' of Hesiod, they were the twelve children of the primordial parents Uranus (Sky) and Gai ...
, Titanesses and Giants
A giant is a being of human appearance, sometimes of prodigious size and strength, common in folklore.
Giant(s) or The Giant(s) may also refer to:
Mythology and religion
*Giants (Greek mythology)
*Jötunn, a Germanic term often translated as 'gi ...
—brothers and sisters of Cronus. In 1848, Lassell proposed that the eighth satellite of Saturn be named Hyperion after another Titan. When in the 20th century the names of Titans were exhausted, the moons were named after different characters of the Greco-Roman mythology
Classical mythology, Greco-Roman mythology, or Greek and Roman mythology is both the body of and the study of myths from the ancient Greeks and ancient Romans as they are used or transformed by cultural reception. Along with philosophy and poli ...
or giants from other mythologies. All the irregular moons (except Phoebe, discovered about a century before the others) are named after Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
and Gallic gods and after Norse ice giants.
Some asteroids share the same names as moons of Saturn: 55 Pandora, 106 Dione
Dione ( minor planet designation: 106 Dione) is a large main-belt asteroid. It probably has a composition similar to 1 Ceres. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on October 10, 1868, and named after Dione, a Titaness in Greek mythology who was ...
, 577 Rhea, 1809 Prometheus, 1810 Epimetheus, and 4450 Pan
4450 Pan ('' prov. designation:'' ) is a highly eccentric asteroid and contact binary, classified as a potentially hazardous asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 1.1 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 25 S ...
. In addition, three more asteroids would share the names of Saturnian moons but for spelling differences made permanent by the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
(IAU): Calypso and asteroid 53 Kalypso; Helene and asteroid 101 Helena
Helena (minor planet designation: 101 Helena) is a large, rocky main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by Canadian-American astronomer J. C. Watson on August 15, 1868, and was named after Helen of Troy in Greek mythology.
This object is orbitin ...
; and Gunnlod and asteroid 657 Gunlöd.
Sizes
Saturn's satellite system is very lopsided: one moon, Titan, comprises more than 96% of the mass in orbit around the planet. The six otherplanemo
A planetary-mass object (PMO), planemo, or planetary body is by geophysical definition of celestial objects any celestial object massive enough to achieve hydrostatic equilibrium (to be rounded under its own gravity), but not enough to sustain ...
( ellipsoidal) moons constitute roughly 4% of the mass, and the remaining 76 small moons, together with the rings, comprise only 0.04%.
Orbital groups
Although the boundaries may be somewhat vague, Saturn's moons can be divided into ten groups according to their orbital characteristics. Many of them, such as Pan andDaphnis
In Greek mythology, Daphnis (; grc, Δάφνις, from , ''daphne'', "Bay Laurel") was a Sicilian shepherd who was said to be the inventor of pastoral poetry.
Family
According to tradition, he was the son of Hermes and a nymph, despite which ...
, orbit within Saturn's ring system and have orbital periods only slightly longer than the planet's rotation period. The innermost moons and most regular satellites all have mean orbital inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Earth ...
s ranging from less than a degree to about 1.5 degrees (except Iapetus, which has an inclination of 7.57 degrees) and small orbital eccentricities. On the other hand, irregular satellites in the outermost regions of Saturn's moon system, in particular the Norse group
The Norse group is a large group of retrograde irregular satellites of Saturn. Their semi-major axes range between 12 and 24 Gm, their inclinations between 136° and 175° and their eccentricities between 0.13 and 0.77. Unlike for the Inuit ...
, have orbital radii of millions of kilometers and orbital periods lasting several years. The moons of the Norse group also orbit in the opposite direction to Saturn's rotation.
Ring moonlets
During late July 2009, amoonlet
A moonlet, minor moon, minor natural satellite, or minor satellite is a particularly small natural satellite orbiting a planet, dwarf planet, or other minor planet.
Up until 1995, moonlets were only hypothetical components of Saturn's F-ring ...
, S/2009 S 1
S/2009 S 1 is a moonlet embedded in the outer part of Saturn's B Ring, orbiting away from the planet. The moonlet was discovered by the ''Cassini'' Imaging Team during the Saturnian equinox event on 26 July 2009, when the ''Cassini'' spacecraft ...
, was discovered in the B Ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entirel ...
, 480 km from the outer edge of the ring, by the shadow it cast. It is estimated to be 300 m in diameter. Unlike the A Ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entirel ...
moonlets (see below), it does not induce a 'propeller' feature, probably due to the density of the B Ring.
In 2006, four tiny moonlets were found in ''Cassini'' images of the A Ring. Before this discovery only two larger moons had been known within gaps in the A Ring: Pan and Daphnis. These are large enough to clear continuous gaps in the ring. In contrast, a moonlet is only massive enough to clear two small—about 10 km across—partial gaps in the immediate vicinity of the moonlet itself creating a structure shaped like an airplane propeller. The moonlets themselves are tiny, ranging from about 40 to 500 meters in diameter, and are too small to be seen directly.
 In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the
In 2007, the discovery of 150 more moonlets revealed that they (with the exception of two that have been seen outside the Encke gap
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entirel ...
) are confined to three narrow bands in the A Ring between 126,750 and 132,000 km from Saturn's center. Each band is about a thousand kilometers wide, which is less than 1% the width of Saturn's rings. This region is relatively free from the disturbances caused by resonances with larger satellites, although other areas of the A Ring without disturbances are apparently free of moonlets. The moonlets were probably formed from the breakup of a larger satellite. It is estimated that the A Ring contains 7,000–8,000 propellers larger than 0.8 km in size and millions larger than 0.25 km. In April 2014, NASA scientists reported the possible consolidation of a new moon within the A Ring, implying that Saturn's present moons may have formed in a similar process in the past when Saturn's ring system was much more massive.
Similar moonlets may reside in the F Ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entir ...
. There, "jets" of material may be due to collisions, initiated by perturbations from the nearby small moon Prometheus, of these moonlets with the core of the F Ring. One of the largest F Ring moonlets may be the as-yet unconfirmed object S/2004 S 6. The F Ring also contains transient "fans" which are thought to result from even smaller moonlets, about 1 km in diameter, orbiting near the F Ring core.
One of the recently discovered moons, Aegaeon, resides within the bright arc of G Ring G Ring may refer to:
* Rings of Saturn#G Ring, a planetary ring system around Saturn.
* G-ring
In commutative algebra, a G-ring or Grothendieck ring is a Noetherian ring such that the map of any of its local rings to the completion is regular ( ...
and is trapped in the 7:6 mean-motion resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied Periodic function, periodic force (or a Fourier analysis, Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system ...
with Mimas. This means that it makes exactly seven revolutions around Saturn while Mimas makes exactly six. The moon is the largest among the population of bodies that are sources of dust in this ring.
Ring shepherds

 Shepherd satellites are small moons that orbit within, or just beyond, a planet's
Shepherd satellites are small moons that orbit within, or just beyond, a planet's ring system
A ring system is a disc or ring, orbiting an astronomical object, that is composed of solid material such as dust and moonlets, and is a common component of satellite systems around giant planets. A ring system around a planet is also known as ...
. They have the effect of sculpting the rings: giving them sharp edges, and creating gaps between them. Saturn's shepherd moons are Pan (Encke gap
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entirel ...
), Daphnis
In Greek mythology, Daphnis (; grc, Δάφνις, from , ''daphne'', "Bay Laurel") was a Sicilian shepherd who was said to be the inventor of pastoral poetry.
Family
According to tradition, he was the son of Hermes and a nymph, despite which ...
(Keeler gap
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost ent ...
), Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
(A Ring), Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning " forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titan god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technology, kn ...
(F Ring) and Pandora (F Ring). These moons together with co-orbitals (see below) probably formed as a result of accretion of the friable ring material on preexisting denser cores. The cores with sizes from one-third to one-half the present-day moons may be themselves collisional shards formed when a parental satellite of the rings disintegrated.
Co-orbitals
Janus andEpimetheus
In Greek mythology, Epimetheus (; grc-gre, Ἐπιμηθεύς, , afterthought) was the brother of Prometheus (traditionally interpreted as "foresight", literally "fore-thinker"), a pair of Titans who "acted as representatives of mankind". They ...
are called co-orbital moons. They are of roughly equal size, with Janus being slightly larger than Epimetheus. Janus and Epimetheus have orbits with only a few kilometers difference in semi-major axis, close enough that they would collide if they attempted to pass each other. Instead of colliding, their gravitational interaction causes them to swap orbits every four years.
Inner large
 The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
* Mimas is the smallest and least massive of the inner round moons, although its mass is sufficient to alter the orbit of Methone. It is noticeably ovoid-shaped, having been made shorter at the poles and longer at the equator (by about 20 km) by the effects of Saturn's gravity. Mimas has a large
The innermost large moons of Saturn orbit within its tenuous E Ring, along with three smaller moons of the Alkyonides group.
* Mimas is the smallest and least massive of the inner round moons, although its mass is sufficient to alter the orbit of Methone. It is noticeably ovoid-shaped, having been made shorter at the poles and longer at the equator (by about 20 km) by the effects of Saturn's gravity. Mimas has a large impact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
one-third its diameter, Herschel, situated on its leading hemisphere. Mimas has no known past or present geologic activity, and its surface is dominated by impact craters. The only tectonic features known are a few arcuate and linear troughs, which probably formed when Mimas was shattered by the Herschel impact.
* Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn (19th largest in the Solar System). It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Enceladus is mostly covered by fresh, clean ice, making it one of the most refle ...
is one of the smallest of Saturn's moons that is spherical in shape—only Mimas is smaller—yet is the only small Saturnian moon that is currently endogenously active, and the smallest known body in the Solar System that is geologically active today. Its surface is morphologically diverse; it includes ancient heavily cratered terrain as well as younger smooth areas with few impact craters. Many plains on Enceladus are fractured and intersected by systems of lineament ''See also Line (geometry)''
A lineament is a linear feature in a landscape which is an expression of an underlying geological structure such as a fault. Typically a lineament will appear as a fault-aligned valley, a series of fault or fold-ali ...
s. The area around its south pole was found by ''Cassini'' to be unusually warm and cut by a system of fractures about 130 km long called "tiger stripes", some of which emit jets of water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
and dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ho ...
. These jets form a large plume off its south pole, which replenishes Saturn's E ring and serves as the main source of ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s in the magnetosphere of Saturn. The gas and dust are released with a rate of more than 100 kg/s. Enceladus may have liquid water underneath the south-polar surface. The source of the energy for this cryovolcanism
A cryovolcano (sometimes informally called an ice volcano) is a type of volcano that erupts volatiles such as water, ammonia or methane into an extremely cold environment that is at or below their freezing point. The process of formation is know ...
is thought to be a 2:1 mean-motion resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relationsh ...
with Dione. The pure ice on the surface makes Enceladus one of the brightest known objects in the Solar System—its geometrical albedo
In astronomy, the geometric albedo of a celestial body is the ratio of its actual brightness as seen from the light source (i.e. at zero phase angle (astronomy), phase angle) to that of an ''idealized'' flat, fully reflecting, diffuse reflection, d ...
is more than 140%.
* Tethys is the third largest of Saturn's inner moons. Its most prominent features are a large (400 km diameter) impact crater named Odysseus on its leading hemisphere and a vast canyon system named Ithaca Chasma
Ithaca Chasma is a valley (graben) of Saturn's moon Tethys, named after the island of Ithaca, in Greece. It is up to wide, deep and long, running approximately three-quarters of the way around Tethys' circumference, making it one of the long ...
extending at least 270° around Tethys. The Ithaca Chasma is concentric with Odysseus, and these two features may be related. Tethys appears to have no current geological activity. A heavily cratered hilly terrain occupies the majority of its surface, while a smaller and smoother plains region lies on the hemisphere opposite to that of Odysseus. The plains contain fewer craters and are apparently younger. A sharp boundary separates them from the cratered terrain. There is also a system of extensional troughs radiating away from Odysseus. The density of Tethys (0.985 g/cm3) is less than that of water, indicating that it is made mainly of water ice with only a small fraction of rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
.
* Dione is the second-largest inner moon of Saturn. It has a higher density than the geologically dead Rhea, the largest inner moon, but lower than that of active Enceladus. While the majority of Dione's surface is heavily cratered old terrain, this moon is also covered with an extensive network of troughs and lineaments, indicating that in the past it had global tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
activity. The troughs and lineaments are especially prominent on the trailing hemisphere, where several intersecting sets of fractures form what is called "wispy terrain". The cratered plains have a few large impact craters reaching 250 km in diameter. Smooth plains with low impact-crater counts are also present on a small fraction of its surface. They were probably tectonically resurfaced relatively later in the geological history of Dione. At two locations within smooth plains strange landforms (depressions) resembling oblong impact craters have been identified, both of which lie at the centers of radiating networks of cracks and troughs; these features may be cryovolcanic in origin. Dione may be geologically active even now, although on a scale much smaller than the cryovolcanism of Enceladus. This follows from Cassini magnetic measurements that show Dione is a net source of plasma in the magnetosphere of Saturn, much like Enceladus.
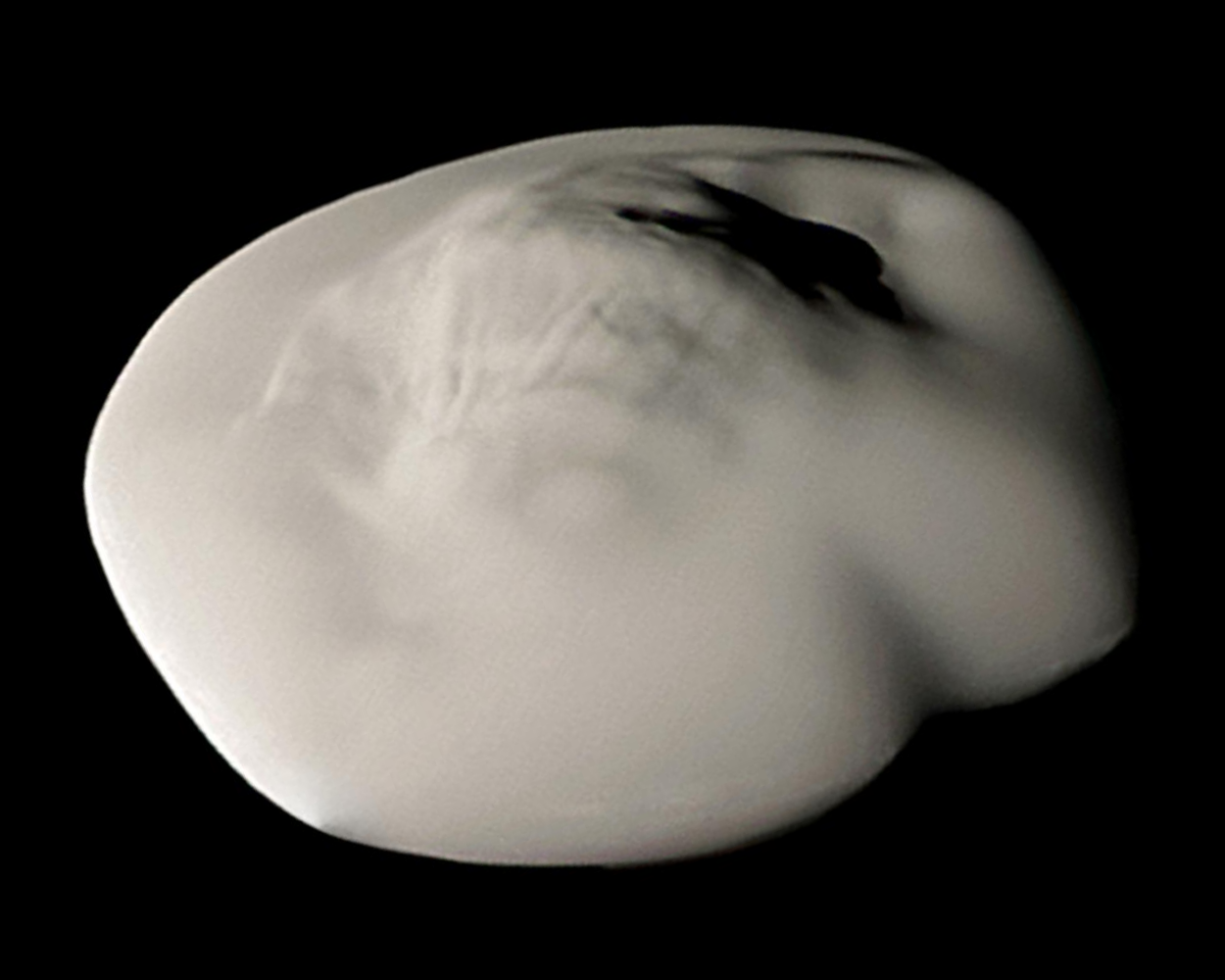
Alkyonides
Three small moons orbit between Mimas and Enceladus: Methone, Anthe, and Pallene. Named after theAlkyonides The Alcyonides (, ''Alkyonides'') were, in Greek mythology, the seven daughters of the giant Alcyoneus.
Names
These sisters were identified individually as, Alkippe, Anthe, Asteria, Drimo, Methone, Pallene and Phthonia ( Phosthonia or Ch ...
of Greek mythology, they are some of the smallest moons in the Saturn system. Anthe and Methone have very faint ring arcs along their orbits, whereas Pallene has a faint complete ring. Of these three moons, only Methone has been photographed at close range, showing it to be egg-shaped with very few or no craters.
Trojan
Trojan moons are a unique feature only known from the Saturnian system. A trojan body orbits at either the leading L4 or trailing L5 Lagrange point of a much larger object, such as a large moon or planet. Tethys has two trojan moons, Telesto (leading) and Calypso (trailing), and Dione also has two, Helene (leading) and Polydeuces (trailing). Helene is by far the largest trojan moon, while Polydeuces is the smallest and has the most chaotic orbit. These moons are coated with dusty material that has smoothed out their surfaces.Outer large
These moons all orbit beyond the E Ring. They are: * Rhea is the second-largest of Saturn's moons. It is even slightly larger thanOberon
Oberon () is a king of the fairies in medieval and Renaissance literature. He is best known as a character in William Shakespeare's play ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'', in which he is King of the Fairies and spouse of Titania, Queen of the Fairi ...
, the second-largest moon of Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
. In 2005 ''Cassini'' detected a depletion of electrons in the plasma wake of Rhea, which forms when the co-rotating plasma of Saturn's magnetosphere is absorbed by the moon. The depletion was hypothesized to be caused by the presence of dust-sized particles concentrated in a few faint equatorial rings. Such a ring system would make Rhea the only moon in the Solar System known to have rings. Subsequent targeted observations of the putative ring plane from several angles by ''Cassinis narrow-angle camera turned up no evidence of the expected ring material, leaving the origin of the plasma observations unresolved. Otherwise Rhea has rather a typical heavily cratered surface, with the exceptions of a few large Dione-type fractures (wispy terrain) on the trailing hemisphere and a very faint "line" of material at the equator that may have been deposited by material deorbiting from present or former rings. Rhea also has two very large impact basins on its anti-Saturnian hemisphere, which are about 400 and 500 km across. The first, Tirawa, is roughly comparable to the Odysseus basin on Tethys. There is also a 48 km-diameter impact crater called Inktomi at 112°W that is prominent because of an extended system of bright rays
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (gra ...
, which may be one of the youngest craters on the inner moons of Saturn. No evidence of any endogenic activity has been discovered on the surface of Rhea.
* Titan, at 5,149 km diameter, is the second largest moon in the Solar System and Saturn's largest. Out of all the large moons, Titan is the only one with a dense (surface pressure of 1.5 atm), cold atmosphere, primarily made of nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
with a small fraction of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ea ...
. The dense atmosphere frequently produces bright white convective clouds, especially over the south pole region. On June 6, 2013, scientists at the IAA-CSIC reported the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. ...
in the upper atmosphere Upper atmosphere is a collective term that refers to various layers of the atmosphere of the Earth above the troposphere and corresponding regions of the atmospheres of other planets, and includes:
* The mesosphere, which on Earth lies between th ...
of Titan. On June 23, 2014, NASA claimed to have strong evidence that nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
in the atmosphere of Titan
The atmosphere of Titan is the dense layer of gases surrounding Titan, the largest moon of Saturn. It is the only thick atmosphere of a natural satellite in the Solar System. Titan's lower atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (94.2%), ...
came from materials in the Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
, associated with comets
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ar ...
, and not from the materials that formed Saturn in earlier times. The surface of Titan, which is difficult to observe due to persistent atmospheric haze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon in which dust, smoke, and other dry particulates suspended in air obscure visibility and the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classificati ...
, shows only a few impact craters and is probably very young. It contains a pattern of light and dark regions, flow channels and possibly cryovolcanos. Some dark regions are covered by longitudinal dune fields shaped by tidal winds, where sand is made of frozen water or hydrocarbons. Titan is the only body in the Solar System beside Earth with bodies of liquid on its surface, in the form of methane–ethane lakes in Titan's north and south polar regions. The largest lake, Kraken Mare
Kraken Mare is the largest known body of liquid on the surface of Saturn's moon Titan. It was discovered by the space probe '' Cassini'' in 2006, and was named in 2008 after the Kraken, a legendary sea monster. It covers an area slightly bigger ...
, is larger than the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
. Like Europa and Ganymede, it is believed that Titan has a subsurface ocean made of water mixed with ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
, which can erupt to the surface of the moon and lead to cryovolcanism. On July 2, 2014, NASA reported the ocean inside Titan may be "as salty as the Earth's Dead Sea".
* Hyperion is Titan's nearest neighbor in the Saturn system. The two moons are locked in a 4:3 mean-motion resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relationsh ...
with each other, meaning that while Titan makes four revolutions around Saturn, Hyperion makes exactly three. With an average diameter of about 270 km, Hyperion is smaller and lighter than Mimas. It has an extremely irregular shape, and a very odd, tan-colored icy surface resembling a sponge, though its interior may be partially porous as well. The average density of about 0.55 g/cm3 indicates that the porosity exceeds 40% even assuming it has a purely icy composition. The surface of Hyperion is covered with numerous impact craters—those with diameters 2–10 km are especially abundant. It is the only moon besides the small moons of Pluto
The dwarf planet Pluto has five natural satellites. In order of distance from Pluto, they are Charon, Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra. Charon, the largest, is mutually tidally locked with Pluto, and is massive enough that Pluto–Charon is some ...
known to have a chaotic rotation, which means Hyperion has no well-defined poles or equator. While on short timescales the satellite approximately rotates around its long axis at a rate of 72–75° per day, on longer timescales its axis of rotation (spin vector) wanders chaotically across the sky. This makes the rotational behavior of Hyperion essentially unpredictable.
* Iapetus is the third-largest of Saturn's moons. Orbiting the planet at km, it is by far the most distant of Saturn's large moons, and also has the largest orbital inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Earth ...
, at 15.47°. Iapetus has long been known for its unusual two-toned surface; its leading hemisphere is pitch-black and its trailing hemisphere is almost as bright as fresh snow. ''Cassini'' images showed that the dark material is confined to a large near-equatorial area on the leading hemisphere called Cassini Regio
Cassini Regio (adjective ''Cassinian'' ) is the enigmatic dark area that covers the leading half of Saturn's moon Iapetus. It is named after Giovanni Cassini, the discoverer of Iapetus; ' Regio' is a term used in planetary geology for a large a ...
, which extends approximately from 40°N to 40°S. The pole regions of Iapetus are as bright as its trailing hemisphere. ''Cassini'' also discovered a 20 km tall equatorial ridge, which spans nearly the moon's entire equator. Otherwise both dark and bright surfaces of Iapetus are old and heavily cratered. The images revealed at least four large impact basins with diameters from 380 to 550 km and numerous smaller impact craters. No evidence of any endogenic activity has been discovered. A clue to the origin of the dark material covering part of Iapetus's starkly dichromatic surface may have been found in 2009, when NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope discovered a vast, nearly invisible disk around Saturn, just inside the orbit of the moon Phoebe – the Phoebe ring
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entire ...
. Scientists believe that the disk originates from dust and ice particles kicked up by impacts on Phoebe. Because the disk particles, like Phoebe itself, orbit in the opposite direction to Iapetus, Iapetus collides with them as they drift in the direction of Saturn, darkening its leading hemisphere slightly. Once a difference in albedo, and hence in average temperature, was established between different regions of Iapetus, a thermal runaway
Thermal runaway describes a process that is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. Thermal runaway occurs in situations where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way t ...
process of water ice sublimation from warmer regions and deposition of water vapor onto colder regions ensued. Iapetus's present two-toned appearance results from the contrast between the bright, primarily ice-coated areas and regions of dark lag, the residue left behind after the loss of surface ice.
Irregular

Irregular moon
In astronomy, an irregular moon, irregular satellite or irregular natural satellite is a natural satellite following a distant, inclined, and often eccentric and retrograde orbit. They have been captured by their parent planet, unlike regular s ...
s are small satellites with large-radii, inclined, and frequently retrograde orbits, believed to have been acquired by the parent planet through a capture process. They often occur as collisional families or groups. The precise size as well as albedo of the irregular moons are not known for sure because the moons are very small to be resolved by a telescope, although the latter is usually assumed to be quite low—around 6% (albedo of Phoebe) or less. The irregulars generally have featureless visible and near infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from arou ...
spectra dominated by water absorption bands. They are neutral or moderately red in color—similar to C-type, P-type, or D-type asteroid
D-type asteroids have a very low albedo and a featureless reddish spectrum. It has been suggested that they have a composition of organic-rich silicates, carbon and anhydrous silicates, possibly with water ice in their interiors. D-type asteroids ...
s, though they are much less red than Kuiper belt objects.
Inuit
The Inuit group includes eight prograde outer moons that are similar enough in their distances from the planet (186–297 radii of Saturn), their orbital inclinations (45–50°) and their colors that they can be considered a group. The moons are Ijiraq,Kiviuq
Kiviuq (also spelled "Qiviuq", "Kiviok" and other variants) is a legendary hero of the epic stories of the Inuit of the Arctic regions of northern Canada, Alaska and Greenland.
Kiviuq is an eternal Inuit wanderer. Spirits, giants, cannibals, bea ...
, Paaliaq
Paaliaq is a prograde irregular satellite of Saturn. It was discovered by J. J. Kavelaars, Brett J. Gladman, Jean-Marc Petit, Hans Scholl, Matthew J. Holman, Brian G. Marsden, Philip D. Nicholson and Joseph A. Burns in early October 2000, and gi ...
, Siarnaq, and Tarqeq, along with three unnamed moons Saturn LX, S/2004 S 31, and S/2019 S 1. The largest among them is Siarnaq with an estimated size of about 40 km.
Gallic
The Gallic group are four prograde outer moons that are similar enough in their distance from the planet (207–302 radii of Saturn), their orbital inclination (35–40°) and their color that they can be considered a group. They are Albiorix, Bebhionn,Erriapus
Erriapus , or Saturn XXVIII (28), is a prograde irregular satellite of Saturn. It was discovered by Brett Gladman, John J. Kavelaars and colleagues in 2000, and given the temporary designation S/2000 S 10. It was named Erriapo in ...
, and Tarvos. The largest among these moons is Albiorix with an estimated size of about 32 km. There is an additional satellite S/2004 S 24
S/2004 S 24 is a natural satellite of Saturn, and the outermost known prograde satellite. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, and Jan Kleyna on October 7, 2019 from observations taken between December 12, 2004 and ...
that could belong to this group, but more observations are needed to confirm or disprove its categorization. S/2004 S 24 has the most distant prograde orbit of Saturn's known satellites.
Norse
The Norse (or Phoebe) group consists of 46 retrograde outer moons. They are Aegir, Angrboda, Alvaldi, Beli, Bergelmir,Bestla
Bestla (Old Norse: ) is a jötunn in Norse mythology, and the mother of the gods Odin, Vili and Vé (by way of Borr). She is also the sister of an unnamed man who assisted Odin, and the daughter (or granddaughter depending on the source) of th ...
, Eggther, Farbauti, Fenrir
Fenrir (Old Norse: ; "fen-dweller")Orchard (1997:42). or Fenrisúlfr (O.N.: ; "Fenrir's wolf", often translated "Fenris-wolf"),Simek (2007:81). also referred to as Hróðvitnir (O.N.: ; "fame-wolf")Simek (2007:160). and Vánagandr (O.N.: ; " ...
, Fornjot, Geirrod, Gerd Gerd or GERD may refer to:
* Gerd (given name), a list of people with the given name or nickname
* Gerd (moon), a moon of Saturn
* Gerd Island, South Orkney Islands, Antarctica
* Gastroesophageal reflux disease, a chronic symptom of mucosal damage ...
, Greip, Gridr, Gunnlod, Hati, Hyrrokkin
Hyrrokkin (Old Norse: ) is a female jötunn in Norse mythology. According to 13th-century poet Snorri Sturluson, she launched the largest of all ships at Baldr's funeral after the Æsir gods were unable to budge the vessel.
Hyrrokkin was a re ...
, Jarnsaxa, Kari Kari or KARI may refer to:
Places
*Kari, Jhunjhunu, a village in Rajasthan, India
* , a village in Mouhoun Province, Burkina Faso
*Kari, Tikamgarh, a town in Madhya Pradesh, India
* Kari, Iran, a village in Bushehr Province, Iran
* Kari-ye Bozorg ( ...
, Loge, Mundilfari, Narvi, Phoebe, Skathi, Skoll, Skrymir, Surtur, Suttungr, Thiazzi, Thrymr, Ymir
In Norse mythology, Ymir (, ), also called Aurgelmir, Brimir, or Bláinn, is the ancestor of all jötnar. Ymir is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional material, in the ''Prose Edda'', writ ...
, and fifteen unnamed satellites. After Phoebe, Ymir is the largest of the known retrograde irregular moons, with an estimated diameter of only 18 km. The Norse group may itself consist of several smaller subgroups.
* Phoebe, at in diameter, is by far the largest of Saturn's irregular satellites. It has a retrograde orbit and rotates on its axis every 9.3 hours. Phoebe was the first moon of Saturn to be studied in detail by ''Cassini'', in ; during this encounter ''Cassini'' was able to map nearly 90% of the moon's surface. Phoebe has a nearly spherical shape and a relatively high density of about 1.6 g/cm3. ''Cassini'' images revealed a dark surface scarred by numerous impacts—there are about 130 craters with diameters exceeding 10 km. Spectroscopic measurement showed that the surface is made of water ice, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
, phyllosilicate
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually consid ...
s, organics and possibly iron bearing minerals. Phoebe is believed to be a captured centaur that originated in the Kuiper belt. It also serves as a source of material for the largest known ring of Saturn, which darkens the leading hemisphere of Iapetus (see above).
List

Confirmed
The Saturnian moons are listed here byorbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
(or semi-major axis), from shortest to longest. Moons massive enough for their surfaces to have collapsed into a spheroid
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters. A spheroid has ...
are highlighted in bold and marked with a blue background, while the irregular moons are listed in red, orange and gray background. The orbits and mean distances of the irregular moons are strongly variable over short timescales due to frequent planetary and solar perturbations, therefore the listed orbital elements of all irregular moons are averaged over a 300-year numerical integration
In analysis, numerical integration comprises a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral, and by extension, the term is also sometimes used to describe the numerical solution of differential equations ...
. Their orbital elements are all based on the epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
of 1 January 2000. Note: Orbital elements of regular satellites and Phoebe are with respect to the Laplace plane The Laplace plane or Laplacian plane of a planetary satellite, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (1749–1827), is a mean or reference plane about whose axis the instantaneous orbital plane of that satellite precesses.
Laplace's ...
, while orbital elements of irregular satellites are with respect to the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
.
, , , , , , , , , , outer B Ring , , 2009 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , ( , , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , , 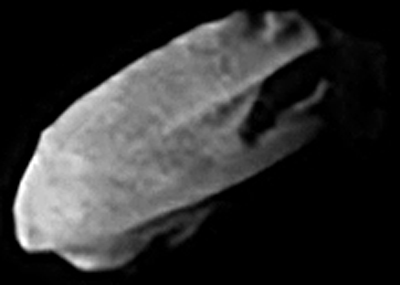 , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , ,  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''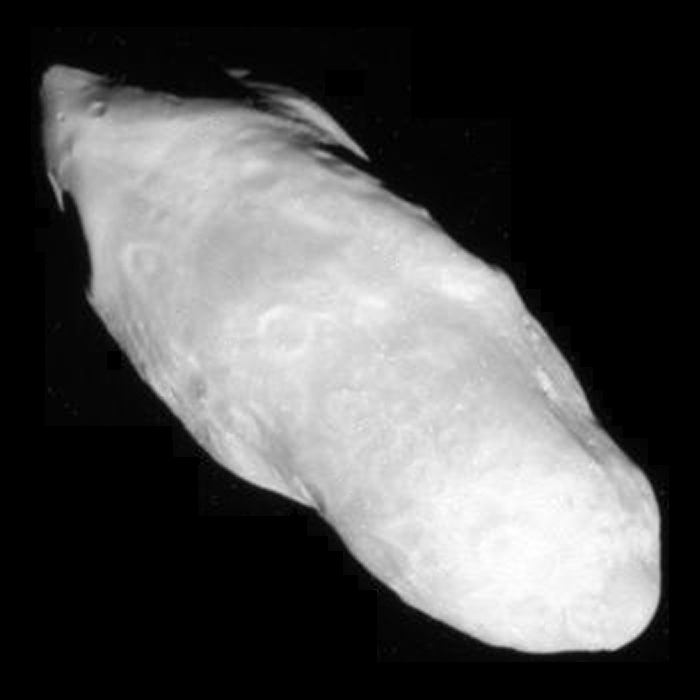 , , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''
, , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , '' , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , , Janus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , , Janus , , , , style="background:black;", 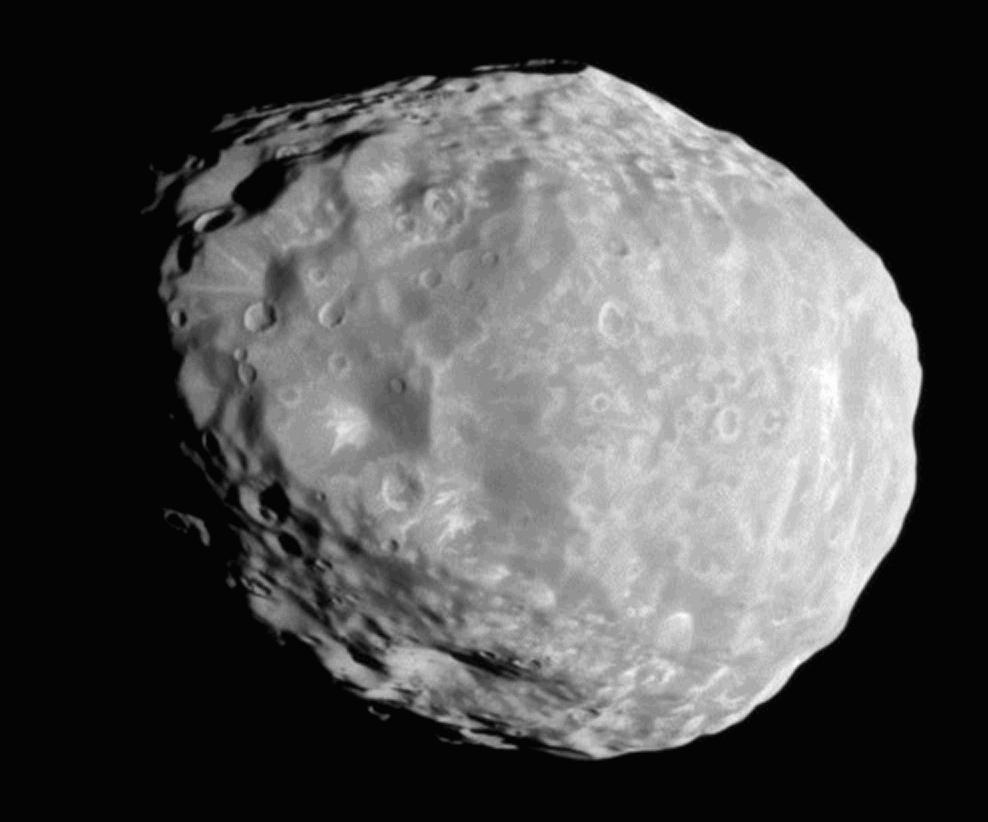 , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , † Mimas , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , † Mimas , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , † , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",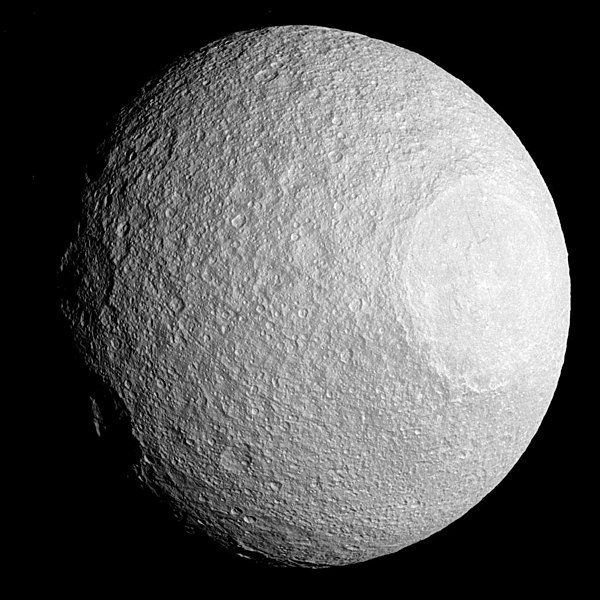  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , 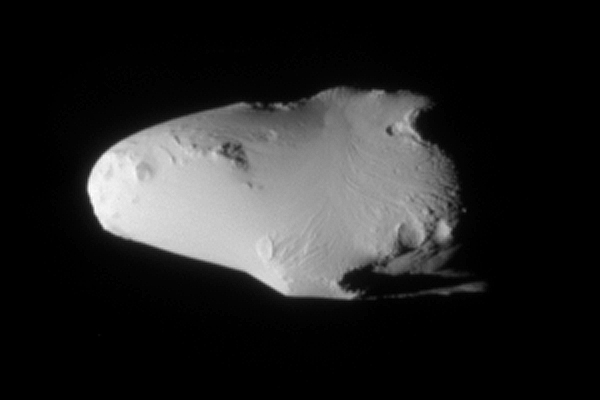 , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , † Dione , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , † Dione , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠ Titan , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠ Titan , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , , Huygens
, -
, 23, , , , Hyperion , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , , Huygens
, -
, 23, , , , Hyperion , , , , style="background:black;",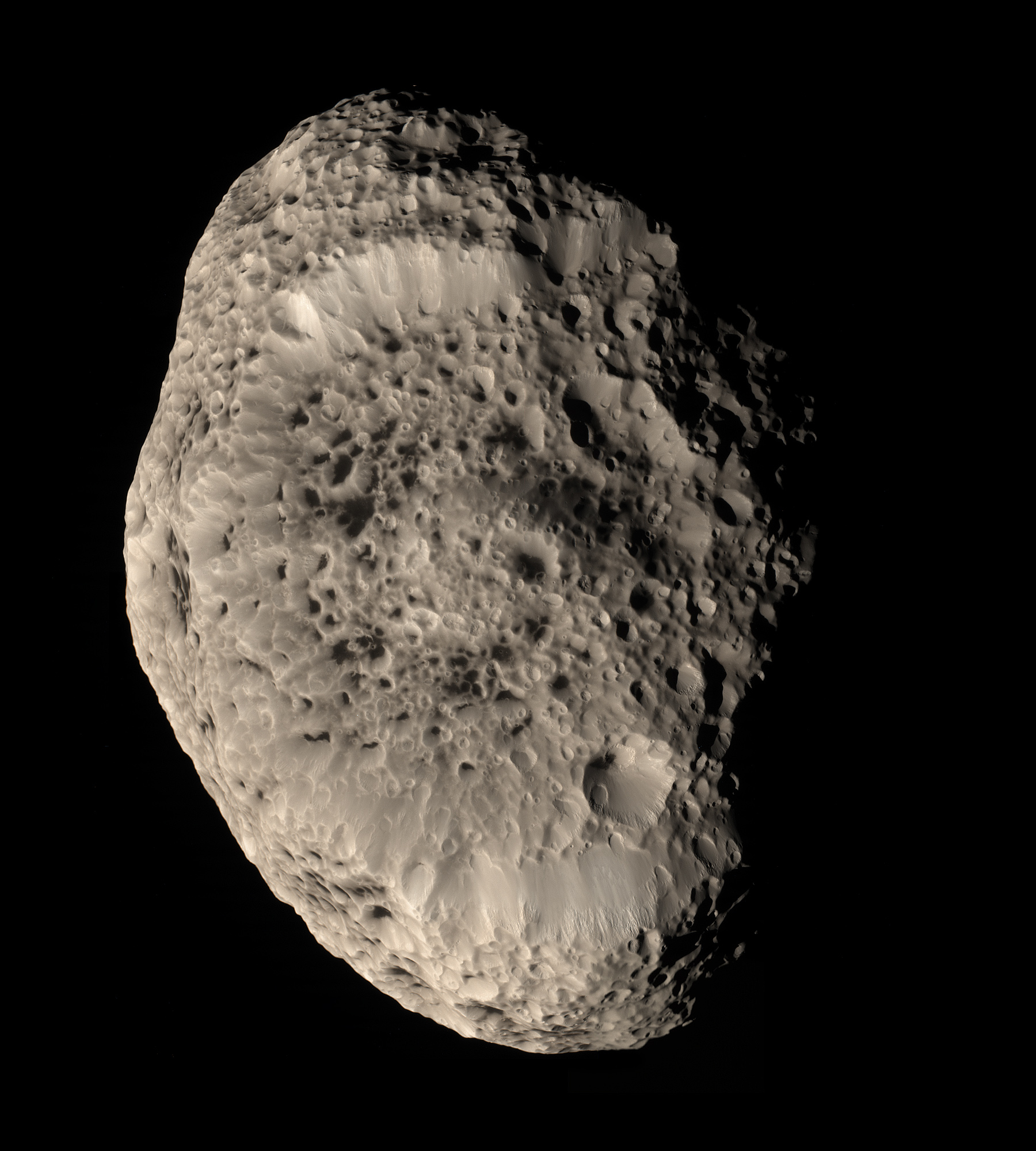  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , ,  , , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , , Inuit group , , 2019 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 26, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , , Inuit group , , 2019 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 26, , , , ‡ , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣ Phoebe , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣ Phoebe , , , , style="background:black;",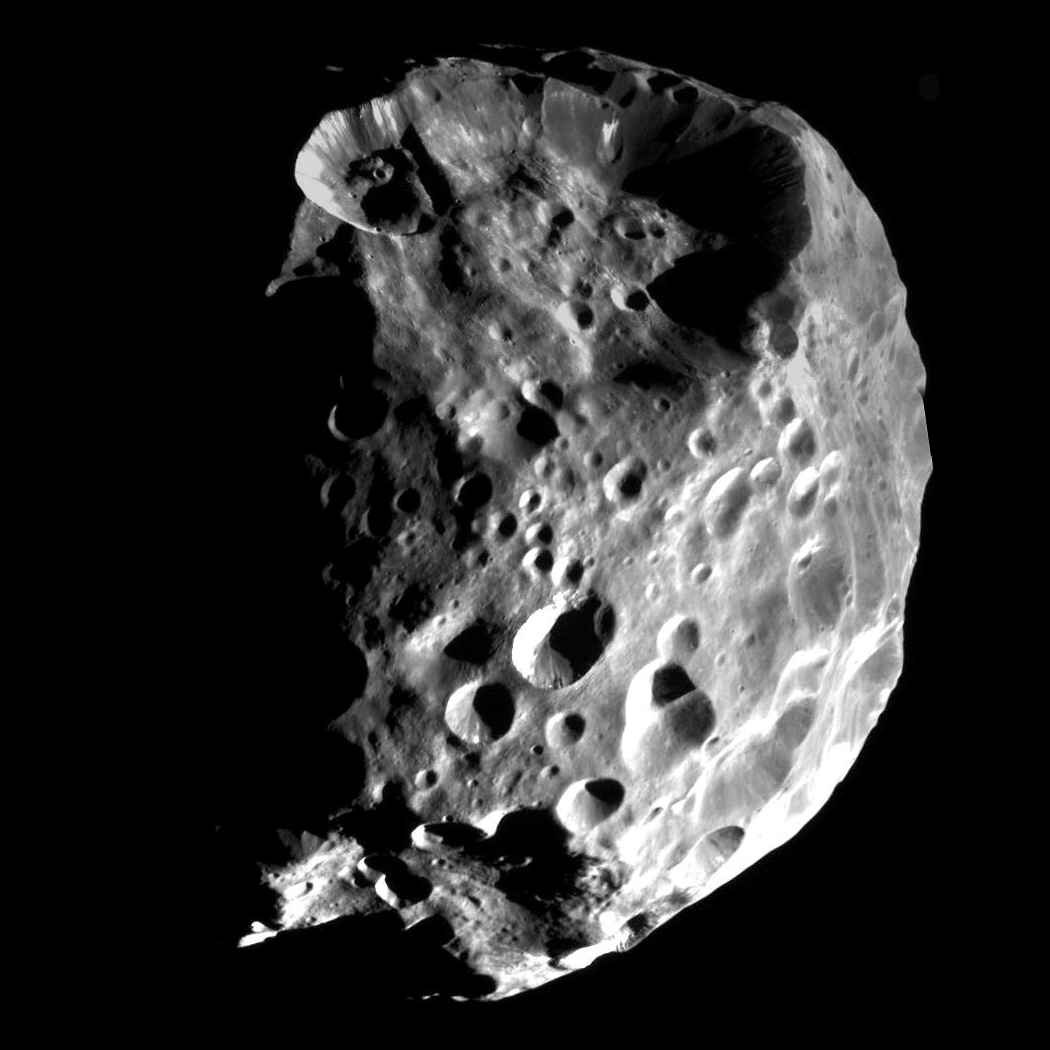  , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , ,  , , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , ,  , , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 31 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.3 , , 0.2020 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 37, , , , ♦
, , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 31 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.3 , , 0.2020 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 37, , , , ♦ , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡ Tarqeq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡ Tarqeq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡ Siarnaq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡ Siarnaq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 13 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.9 , , 0.2660 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 45, , , , ♣ Mundilfari , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 13 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.9 , , 0.2660 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 45, , , , ♣ Mundilfari , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 1 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.2 , , 0.1050 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 47, , , , ♣ Gridr , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.7 , , 0.1820 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 48, , , , ♣ Bergelmir , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 1 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.2 , , 0.1050 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 47, , , , ♣ Gridr , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.7 , , 0.1820 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 48, , , , ♣ Bergelmir , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 17 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.9 , , 0.1790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 52, , , , ♣ Suttungr , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 17 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.9 , , 0.1790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 52, , , , ♣ Suttungr , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.1620 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 54, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 12 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.0 , , 0.3250 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 55, , , , ♣ Eggther , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.3 , , 0.1570 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 56, , , , ♣ Hati , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.1620 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 54, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 12 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.0 , , 0.3250 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 55, , , , ♣ Eggther , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.3 , , 0.1570 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 56, , , , ♣ Hati , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 7 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.3 , , 0.4620 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 61, , , , ♣ Angrboda , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.4 , , 0.2160 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 62, , , , ♣ Beli , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.7 , , 0.0870 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 63, , , , ♣ Aegir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.7 , , 0.2520 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 64, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 7 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.3 , , 0.4620 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 61, , , , ♣ Angrboda , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.4 , , 0.2160 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 62, , , , ♣ Beli , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.7 , , 0.0870 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 63, , , , ♣ Aegir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.7 , , 0.2520 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 64, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣ , , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦
, , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦ , , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
moonlet
A moonlet, minor moon, minor natural satellite, or minor satellite is a particularly small natural satellite orbiting a planet, dwarf planet, or other minor planet.
Up until 1995, moonlets were only hypothetical components of Saturn's F-ring ...
s) , , —, , style="background:white;",  , , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , } , , , , , , , , , , Three 1000 km bands within A Ring , , 2006 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Pan , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.000 , , 0.0000 , , in Encke Division , , 1990 , , Showalter
The Showalter/Schowalter family originates from the Swiss village Strengelbach. The first known member, Hans Schonwalder, was mentioned in a 1566 record tax record. Later, the family converted to Anabaptism. Because of religious persecution and pov ...
, -
, , , , , Daphnis
In Greek mythology, Daphnis (; grc, Δάφνις, from , ''daphne'', "Bay Laurel") was a Sicilian shepherd who was said to be the inventor of pastoral poetry.
Family
According to tradition, he was the son of Hermes and a nymph, despite which ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.004 , , 0.0000 , , in Keeler Gap , , 2005 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, , , , , Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.003 , , 0.0012 , , outer A Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
''
, -
, , , , , Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning " forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titan god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technology, kn ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''
, , , , , , , ,
, , , , 0.008 , , 0.0022 , , inner F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
''
, -
, , , , , Pandora , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.050 , , 0.0042 , , outer F Ring shepherd , , 1980 , , ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
''
, -
, , , , , Epimetheus
In Greek mythology, Epimetheus (; grc-gre, Ἐπιμηθεύς, , afterthought) was the brother of Prometheus (traditionally interpreted as "foresight", literally "fore-thinker"), a pair of Titans who "acted as representatives of mankind". They ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , , Janus , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.335 , , 0.0098 , , co-orbital with Janus , , 1977 , , Fountain & Larson
, -
, , , , , Janus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.165 , , 0.0068 , , co-orbital with Epimetheus , , 1966 , , Dollfus
, -
, , , , , Aegaeon , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , † Mimas , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.001 , , 0.0004 , , G Ring moonlet , , 2008 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 10, , , , † Mimas , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.566 , , , 0.0202 , , , , 1789 , , Herschel
, -
, 11, , , , Methone , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.007 , , 0.0001 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 12, , , , Anthe , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.100 , , 0.0011 , , Alkyonides , , 2007 , , '' Cassini''
, -
, 13, , , , Pallene , , , , style="background:white;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , †
, , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.181 , , 0.0040 , , Alkyonides , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 14, , , , †Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn (19th largest in the Solar System). It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Enceladus is mostly covered by fresh, clean ice, making it one of the most refle ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.010 , , 0.0047 , , Generates the E ring , , 1789 , , Herschel
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 15, , , , † Tethys , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.168 , , 0.0001 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Telesto , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.158 , , 0.0010 , , leading Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Smith
Smith may refer to:
People
* Metalsmith, or simply smith, a craftsman fashioning tools or works of art out of various metals
* Smith (given name)
* Smith (surname), a family name originating in England, Scotland and Ireland
** List of people wi ...
et al.
, -
, , , , , Calypso , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , † Dione , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 1.473 , , 0.0010 , , trailing Tethys trojan () , , 1980 , , Pascu et al.
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 18, , , , † Dione , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.002 , , 0.0022 , , , , 1684 , , Cassini
, -
, , , , , Helene , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.199 , , 0.0022 , , leading Dione trojan () , , 1980 , , Laques & Lecacheux
, -
, , , , , Polydeuces , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.177 , , 0.0192 , , trailing Dione trojan () , , 2004 , , '' Cassini''
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 21, , , , † Rhea , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠ Titan , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.327 , , 0.0013 , , , , 1672 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#ccf;"
, 22, , , , ♠ Titan , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , , Huygens
, -
, 23, , , , Hyperion , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.349 , , 0.0288 , , , , 1655 , , Huygens
, -
, 23, , , , Hyperion , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 0.568 , , 0.1230 , , in 4:3 resonance with Titan , , 1848 , , Bond
Bond or bonds may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bond (finance), a type of debt security
* Bail bond, a commercial third-party guarantor of surety bonds in the United States
* Chemical bond, the attraction of atoms, ions or molecules to form chemica ...
& Lassell
, - style="background:#eef;"
, 24, , , , † Iapetus , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , , Inuit group , , 2019 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 26, , , , ‡
, , , , , , , , , , , , 15.47 , , 0.0286 , , , , 1671 , , Cassini
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 25, , , , ‡ S/2019 S 1 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.7 , , 0.5410 , , Inuit group , , 2019 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 26, , , , ‡Kiviuq
Kiviuq (also spelled "Qiviuq", "Kiviok" and other variants) is a legendary hero of the epic stories of the Inuit of the Arctic regions of northern Canada, Alaska and Greenland.
Kiviuq is an eternal Inuit wanderer. Spirits, giants, cannibals, bea ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 48.6 , , 0.2120 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 27, , , , ‡ Ijiraq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣ Phoebe , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 47.5 , , 0.2720 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 28, , , , ♣ Phoebe , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.2 , , 0.1640 , , Norse group
The Norse group is a large group of retrograde irregular satellites of Saturn. Their semi-major axes range between 12 and 24 Gm, their inclinations between 136° and 175° and their eccentricities between 0.13 and 0.77. Unlike for the Inuit ...
, , 1899 , , Pickering
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 29, , , , ‡Paaliaq
Paaliaq is a prograde irregular satellite of Saturn. It was discovered by J. J. Kavelaars, Brett J. Gladman, Jean-Marc Petit, Hans Scholl, Matthew J. Holman, Brian G. Marsden, Philip D. Nicholson and Joseph A. Burns in early October 2000, and gi ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 44.8 , , 0.3410 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 30, , , , ♣ Skathi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 152.6 , , 0.2720 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 31, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 37 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.3 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 32, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 2 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.2320 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Albiorix , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , ,
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.1 , , 0.4800 , , Gallic group
The Gallic group is a dynamical grouping of the prograde irregular satellites of Saturn following similar orbits. Their semi-major axes range between 16 and 19 Gm, their inclinations between 35° and 40°, and their eccentricities around 0.53. ...
, , 2000 , , Holman Holman may refer to:
People
* Holman (surname), including people with the name
* Holman (given name), a list of people with the name
Places United States
* Holman, Missouri, a former town
* Holman, Texas, a settlement
* Holman, Washington, a s ...
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 33, , , , ♦ Bebhionn , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 31 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.3 , , 0.2020 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 37, , , , ♦
, , , , , , , , , , , , 37.4 , , 0.4820 , , Gallic group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 35, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 29 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 38.6 , , 0.4850 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 36, , , , ‡ S/2004 S 31 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 48.3 , , 0.2020 , , Inuit group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 37, , , , ♦Erriapus
Erriapus , or Saturn XXVIII (28), is a prograde irregular satellite of Saturn. It was discovered by Brett Gladman, John J. Kavelaars and colleagues in 2000, and given the temporary designation S/2000 S 10. It was named Erriapo in ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡ Tarqeq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 34.5 , , 0.4720 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 38, , , , ♣ Skoll , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 161.0 , , 0.4640 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 39, , , , ‡ Tarqeq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡ Siarnaq , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 46.3 , , 0.1680 , , Inuit group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#F4C2C2;"
, 40, , , , ‡ Siarnaq , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 45.8 , , 0.2800 , , Inuit group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#FDD5B1;"
, 41, , , , ♦ Tarvos , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 33.7 , , 0.5380 , , Gallic group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 42, , , , ♣Hyrrokkin
Hyrrokkin (Old Norse: ) is a female jötunn in Norse mythology. According to 13th-century poet Snorri Sturluson, she launched the largest of all ships at Baldr's funeral after the Æsir gods were unable to budge the vessel.
Hyrrokkin was a re ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 151.5 , , 0.3360 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 43, , , , ♣ Greip , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 13 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.9 , , 0.2660 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 45, , , , ♣ Mundilfari , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 174.8 , , 0.3150 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 44, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 13 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.9 , , 0.2660 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 45, , , , ♣ Mundilfari , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 1 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.2 , , 0.1050 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 47, , , , ♣ Gridr , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.7 , , 0.1820 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 48, , , , ♣ Bergelmir , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.4 , , 0.2100 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 46, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 1 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.2 , , 0.1050 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 47, , , , ♣ Gridr , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.7 , , 0.1820 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 48, , , , ♣ Bergelmir , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 158.6 , , 0.1420 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 49, , , , ♣ Narvi , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 17 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.9 , , 0.1790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 52, , , , ♣ Suttungr , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.7 , , 0.4300 , , Norse group , , 2003 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 50, , , , ♣ Jarnsaxa , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.6 , , 0.2180 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 51, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 17 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.9 , , 0.1790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 52, , , , ♣ Suttungr , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.1620 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 54, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 12 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.0 , , 0.3250 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 55, , , , ♣ Eggther , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.3 , , 0.1570 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 56, , , , ♣ Hati , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 175.8 , , 0.1140 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 53, , , , ♣ S/2007 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 175.6 , , 0.1620 , , Norse group , , 2007 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 54, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 12 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.0 , , 0.3250 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 55, , , , ♣ Eggther , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.3 , , 0.1570 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 56, , , , ♣ Hati , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 165.8 , , 0.3710 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 57, , , , ♣Bestla
Bestla (Old Norse: ) is a jötunn in Norse mythology, and the mother of the gods Odin, Vili and Vé (by way of Borr). She is also the sister of an unnamed man who assisted Odin, and the daughter (or granddaughter depending on the source) of th ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",
, , , , , , , , , , , , 145.2 , , 0.5200 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 58, , , , ♣ Farbauti , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.5 , , 0.2410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 59, , , , ♣ Thrymr , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 7 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.3 , , 0.4620 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 61, , , , ♣ Angrboda , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.4 , , 0.2160 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 62, , , , ♣ Beli , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.7 , , 0.0870 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 63, , , , ♣ Aegir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.7 , , 0.2520 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 64, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 177.7 , , 0.4660 , , Norse group, , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 60, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 7 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 163.3 , , 0.4620 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 61, , , , ♣ Angrboda , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 177.4 , , 0.2160 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 62, , , , ♣ Beli , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.7 , , 0.0870 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 63, , , , ♣ Aegir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 166.7 , , 0.2520 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 64, , , , ♣Gerd Gerd or GERD may refer to:
* Gerd (given name), a list of people with the given name or nickname
* Gerd (moon), a moon of Saturn
* Gerd Island, South Orkney Islands, Antarctica
* Gastroesophageal reflux disease, a chronic symptom of mucosal damage ...
, , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 174.3 , , 0.5190 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 65, , , , ♣ Gunnlod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 158.9 , , 0.2540 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 66, , , , ♣ Skrymir , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 176.6 , , 0.4370 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 67, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 28 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 169.4 , , 0.1600 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 68, , , , ♣ Alvaldi , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 176.8 , , 0.2370 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 69, , , , ♣Kari Kari or KARI may refer to:
Places
*Kari, Jhunjhunu, a village in Rajasthan, India
* , a village in Mouhoun Province, Burkina Faso
*Kari, Tikamgarh, a town in Madhya Pradesh, India
* Kari, Iran, a village in Bushehr Province, Iran
* Kari-ye Bozorg ( ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 156.1 , , 0.4760 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 70, , , , ♣ Geirrod , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.3 , , 0.5410 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 71, , , , ♣ S/2006 S 3 , , —, , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 157.3 , , 0.4430 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 72, , , , ♣Fenrir
Fenrir (Old Norse: ; "fen-dweller")Orchard (1997:42). or Fenrisúlfr (O.N.: ; "Fenrir's wolf", often translated "Fenris-wolf"),Simek (2007:81). also referred to as Hróðvitnir (O.N.: ; "fame-wolf")Simek (2007:160). and Vánagandr (O.N.: ; " ...
, , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 165.0 , , 0.1350 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 73, , , , ♣ Surtur , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 169.7 , , 0.4460 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 74, , , , ♣ Loge , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣
, , , , , , , , , , , , 167.7 , , 0.1860 , , Norse group , , 2006 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 75, , , , ♣Ymir
In Norse mythology, Ymir (, ), also called Aurgelmir, Brimir, or Bláinn, is the ancestor of all jötnar. Ymir is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional material, in the ''Prose Edda'', writ ...
, , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦
, , , , , , , , , , , , 173.5 , , 0.3340 , , Norse group , , 2000 , , Gladman et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 76, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 21 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 155.0 , , 0.4090 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 77, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 39 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 167.1 , , 0.1020 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#fdd5b1;"
, 78, , , , ♦S/2004 S 24
S/2004 S 24 is a natural satellite of Saturn, and the outermost known prograde satellite. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, and Jan Kleyna on October 7, 2019 from observations taken between December 12, 2004 and ...
, , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 36.5 , , 0.0720 , , Gallic group? , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 79, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 36 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 152.5 , , 0.6170 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 80, , , , ♣ Thiazzi , , , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 159.1 , , 0.5140 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 81, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 34 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 168.3 , , 0.2790 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 82, , , , ♣ Fornjot , , , , style="background:black;",  , , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, , , , , , , , , , , , 170.4 , , 0.2080 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
, - style="background:#d3d3d3;"
, 83, , , , ♣ S/2004 S 26 , , — , , style="background:black;", , , , , , , , , , , , , 172.9 , , 0.1480 , , Norse group , , 2004 , , Sheppard et al.
Unconfirmed
The following objects (observed by '' Cassini'') have not been confirmed as solid bodies. It is not yet clear if these are real satellites or merely persistent clumps within the F Ring.Spurious
Two moons were claimed to be discovered by different astronomers but never seen again. Both moons were said to orbit between Titan and Hyperion. *Chiron
In Greek mythology, Chiron ( ; also Cheiron or Kheiron; ) was held to be the superlative centaur amongst his brethren since he was called the "wisest and justest of all the centaurs".
Biography
Chiron was notable throughout Greek mythology ...
which was supposedly sighted by Hermann Goldschmidt
Hermann Mayer Salomon Goldschmidt (June 17, 1802 – August 30 or September 10 1866) was a German-French astronomer and painter who spent much of his life in France. He started out as a painter, but after attending a lecture by the famous Fren ...
in 1861, but never observed by anyone else.
*Themis
In Greek mythology and religion, Themis (; grc, Θέμις, Themis, justice, law, custom) is one of the twelve Titan children of Gaia and Uranus, and the second wife of Zeus. She is the goddess and personification of justice, divine order, fai ...
was allegedly discovered in 1905 by astronomer William Pickering, but never seen again. Nevertheless, it was included in numerous almanac
An almanac (also spelled ''almanack'' and ''almanach'') is an annual publication listing a set of current information about one or multiple subjects. It includes information like weather forecasts, farmers' planting dates, tide tables, and othe ...
s and astronomy books until the 1960s.
Hypothetical
In 2022, scientists of theMassachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
proposed the hypothetical former moon Chrysalis, using data from the Cassini–Huygens mission. Chrysalis would have orbited between Titan and Iapetus, but its orbit would have gradually become more eccentric until it was torn apart by Saturn. 99% of its mass would have been absorbed by Saturn, while the remaining 1% would have formed Saturn's rings.
Temporary
Much like Jupiter, asteroids and comets will infrequently make close approaches to Saturn, even more infrequently becoming captured into orbit of the planet. The comet P/2020 F1 (Leonard) is calculated to have made a close approach of km ( mi to Saturn on 8 May 1936, closer than the orbit of Titan to the planet, with an orbital eccentricity of only . The comet may have been orbiting Saturn prior to this as a temporary satellite, but difficulty modelling the non-gravitational forces makes whether or not it was indeed a temporary satellite uncertain. Other comets and asteroids may have temporarily orbited Saturn at some point, but none are presently known to have.Formation
It is thought that the Saturnian system of Titan, mid-sized moons, and rings developed from a set-up closer to the Galilean moons of Jupiter, though the details are unclear. It has been proposed either that a second Titan-sized moon broke up, producing the rings and inner mid-sized moons, or that two large moons fused to form Titan, with the collision scattering icy debris that formed the mid-sized moons. On June 23, 2014, NASA claimed to have strong evidence thatnitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
in the atmosphere of Titan
The atmosphere of Titan is the dense layer of gases surrounding Titan, the largest moon of Saturn. It is the only thick atmosphere of a natural satellite in the Solar System. Titan's lower atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (94.2%), ...
came from materials in the Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
, associated with comets
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ar ...
, and not from the materials that formed Saturn in earlier times. Studies based on Enceladus's tidal-based geologic activity and the lack of evidence of extensive past resonances in Tethys, Dione, and Rhea's orbits suggest that the moons up to and including Rhea may be only 100 million years old.
See also
*List of natural satellites
The Solar System's planets, and its most likely dwarf planets, are known to be orbited by at least 221 natural satellites, or moons. At least 20 of them are large enough to be gravitationally rounded; of these, all are covered by a crust of ...
Notes
References
External links
*Scott S. Sheppard
Scott Sander Sheppard (born 1977) is an American astronomer and a discoverer of numerous moons, comets and minor planets in the outer Solar System.
He is an astronomer in the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism at the Carnegie Institution for Scie ...
Saturn Moons
* * * *
at ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
''
* Planetary Society
The Planetary Society is an American internationally-active non-governmental nonprofit organization. It is involved in research, public outreach, and political space advocacy for engineering projects related to astronomy, planetary science, a ...
br>blog post(2017-05-17) by Emily Lakdawalla with images giving comparative sizes of the moons * Tilmann Denk
Outer Moons of Saturn
{{DEFAULTSORT:Moons Of Saturn Lists of moons