San Francisco (;
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
for "
Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of
Northern California. The city proper is the
fourth most populous in California and
17th most populous in the United States, with 815,201 residents as of 2021. It covers a land area of ,
at the end of the
San Francisco Peninsula
The San Francisco Peninsula is a peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area that separates San Francisco Bay from the Pacific Ocean. On its northern tip is the City and County of San Francisco. Its southern base is Mountain View, south of Palo A ...
, making it the second most densely populated large U.S. city after
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, and the
fifth most densely populated U.S. county, behind only four of the five
New York City boroughs
New York City is composed of five boroughs: The Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, Queens, and Staten Island. Each borough is coextensive with a respective county of New York State, making New York City the largest U.S. municipality situated in mul ...
. Among the 91 U.S. cities proper with over 250,000 residents, San Francisco was ranked first by per capita income (at $160,749) and sixth by aggregate income as of 2021.
Colloquial nicknames for San Francisco include ''SF'', ''San Fran'', ''The '', ''Frisco'', and ''Baghdad by the Bay''.
San Francisco and the surrounding
San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
are a global center of economic activity and the arts and sciences,
spurred by leading universities,
high-tech, healthcare,
FIRE
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition ...
, and professional services sectors. As of 2020, the metropolitan area, with 6.7 million residents, ranked 5th by GDP ($874 billion) and 2nd by GDP per capita ($131,082) across the
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
countries, ahead of
global cities like
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
,
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, and
Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
. San Francisco anchors the
13th most populous metropolitan statistical area in the United States with 4.6 million residents, and the fourth-largest by aggregate income and economic output, with a GDP of $669 billion in 2021.
The wider
San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Gover ...
is the fifth most populous, with 9.5 million residents, and the third-largest by economic output, with a GDP of $1.25 trillion in 2021. In the same year, San Francisco proper had a GDP of $236.4 billion, and a GDP per capita of $289,990.
San Francisco was ranked seventh in the world and third in the United States on the Global Financial Centres Index as of March 2022.
As of June 2022, the Bay Area was home to four of the world's fifteen largest companies by market capitalization, and the city proper is headquarters to companies such as
Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo & Company is an American multinational financial services company with corporate headquarters in San Francisco, California; operational headquarters in Manhattan; and managerial offices throughout the United States and intern ...
,
Salesforce
Salesforce, Inc. is an American cloud-based software company headquartered in San Francisco, California. It provides customer relationship management (CRM) software and applications focused on sales, customer service, marketing automation, a ...
,
Uber
Uber Technologies, Inc. (Uber), based in San Francisco, provides mobility as a service, ride-hailing (allowing users to book a car and driver to transport them in a way similar to a taxi), food delivery (Uber Eats and Postmates), packa ...
,
First Republic Bank
First Republic Bank is an American full-service bank and wealth management company offering personal banking, business banking, trust, and wealth management services, catering to low-risk, high net-worth clientele, and focusing on providing pe ...
,
Airbnb
Airbnb, Inc. ( ), based in San Francisco, California, operates an online marketplace focused on short-term homestays and experiences. The company acts as a broker and charges a commission from each booking. The company was founded in 2008 b ...
,
Twitter
Twitter is an online social media and social networking service owned and operated by American company Twitter, Inc., on which users post and interact with 280-character-long messages known as "tweets". Registered users can post, like, and ...
,
Block
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
,
Levi's,
Gap,
Dropbox
Dropbox is a file hosting service operated by the American company Dropbox, Inc., headquartered in San Francisco, California, U.S. that offers cloud storage, file synchronization, personal cloud, and client software. Dropbox was founded in 2007 ...
,
PG&E
The Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) is an American investor-owned utility (IOU). The company is headquartered in the Pacific Gas & Electric Building, in San Francisco, California. PG&E provides natural gas and electricity to 5.2 millio ...
,
Lyft
Lyft, Inc. offers mobility as a service, ride-hailing, vehicles for hire, motorized scooters, a bicycle-sharing system, rental cars, and food delivery in the United States and select cities in Canada. Lyft sets fares, which vary using a dyn ...
, and
Cruise, although the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
has accelerated the exodus of business from downtown San Francisco.
University of California, San Francisco
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is a public land-grant research university in San Francisco, California. It is part of the University of California system and is dedicated entirely to health science and life science. It con ...
(UCSF), the University of San Francisco
The University of San Francisco (USF) is a private Jesuit university in San Francisco, California. The university's main campus is located on a setting between the Golden Gate Bridge and Golden Gate Park. The main campus is nicknamed "The Hil ...
(USF), San Francisco State University
San Francisco State University (commonly referred to as San Francisco State, SF State and SFSU) is a public research university in San Francisco. As part of the 23-campus California State University system, the university offers 118 different ...
(SFSU), the de Young Museum
The de Young Museum, formally the M. H. de Young Memorial Museum, is a fine arts museum located in San Francisco, California. Located in Golden Gate Park, it is a component of the Fine Arts Museums of San Francisco, along with the California Pala ...
, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
The San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA) is a modern and contemporary art museum located in San Francisco, California. A nonprofit organization, SFMOMA holds an internationally recognized collection of modern and contemporary art, and was ...
, the San Francisco Symphony, the San Francisco Ballet
San Francisco Ballet is the oldest ballet company in the United States, founded in 1933 as the San Francisco Opera Ballet under the leadership of ballet master Adolph Bolm. The company is currently based in the War Memorial Opera House, San Fra ...
, the San Francisco Opera
San Francisco Opera (SFO) is an American opera company founded in 1923 by Gaetano Merola (1881–1953) based in San Francisco, California.
History
Gaetano Merola (1923–1953)
Merola's road to prominence in the Bay Area began in 1906 when h ...
, the SFJAZZ Center, the California Academy of Sciences
The California Academy of Sciences is a research institute and natural history museum in San Francisco, California, that is among the largest museums of natural history in the world, housing over 46 million specimens. The Academy began in 1853 ...
, the San Francisco Giants
The San Francisco Giants are an American professional baseball team based in San Francisco, California. The Giants compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) West division. Founded in 1883 as the New Yor ...
, and the Golden State Warriors
The Golden State Warriors are an American professional basketball team based in San Francisco. The Warriors compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA), as a member of the league's Western Conference Pacific Division. Founded in 194 ...
. A popular tourist destination, San Francisco is known for its steep rolling hills
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit.
Terminology
The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as ...
and eclectic mix of architecture across varied neighborhoods, as well as its cool summers, fog, and landmarks, including the Golden Gate Bridge
The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Golden Gate, the strait connecting San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean. The structure links the U.S. city of San Francisco, California—the northern tip of the San Francisco Pen ...
, cable cars, Alcatraz
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pris ...
, and Chinatown and Mission
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
districts.
San Francisco was founded on June 29, 1776, when colonists from Spain established the Presidio of San Francisco
The Presidio of San Francisco (originally, El Presidio Real de San Francisco or The Royal Fortress of Saint Francis) is a park and former U.S. Army post on the northern tip of the San Francisco Peninsula in San Francisco, California, and is part o ...
at the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
and Mission San Francisco de Asís
Mission San Francisco de Asís ( es, Misión San Francisco de Asís), commonly known as Mission Dolores (as it was founded near the Dolores creek), is a Spanish Californian mission and the oldest surviving structure in San Francisco. Located i ...
a few miles away, both named for Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christianit ...
.California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California fro ...
of 1849 brought rapid growth, transforming an unimportant hamlet into a busy port making it the largest city on the West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
at the time; between 1870 and 1900, approximately one quarter of California's population resided in the city proper.consolidated city-county
In United States local government, a consolidated city-county is formed when one or more cities and their surrounding county ( parish in Louisiana, borough in Alaska) merge into one unified jurisdiction. As such it has the governmental powers o ...
.World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, it was a major port of embarkation for naval service members shipping out to the Pacific Theater.United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
in 1945. After the war, the confluence of returning servicemen, significant immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
, liberalizing attitudes, the rise of the " beatnik" and " hippie" countercultures, the sexual revolution
The sexual revolution, also known as the sexual liberation, was a social movement that challenged traditional codes of behavior related to sexuality and interpersonal relationships throughout the United States and the developed world from the 1 ...
, the peace movement
A peace movement is a social movement which seeks to achieve ideals, such as the ending of a particular war (or wars) or minimizing inter-human violence in a particular place or situation. They are often linked to the goal of achieving world peac ...
growing from opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War
Opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War (before) or anti-Vietnam War movement (present) began with demonstrations in 1965 against the escalating role of the United States in the Vietnam War and grew into a broad social move ...
, and other factors led to the Summer of Love and the gay rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, , 3 ...
movement, cementing San Francisco as a center of liberal activism in the United States. More recently, statewide droughts in California
The historical and ongoing droughts in California result from various complex meteorological phenomena, some of which are not fully understood by scientists.
Drought is generally defined as “a deficiency of precipitation over an extended peri ...
have strained the city's water security
Water security is the focused goal of water policy and water management. A society with a high level of water security makes the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems and limits the risk of destructive impacts associated with water. T ...
.
History
3000 BC–1845 AD: Early history and rule by Spain and Mexico
The earliest archaeological evidence of human habitation
Habitability refers to the adequacy of an environment for human living. Where housing is concerned, there are generally local ordinances which define habitability. If a residence complies with those laws it is said to be habitable. In extreme e ...
of the territory of the city of San Francisco dates to 3000 BC. The Yelamu group of the Ohlone people resided in a few small villages when an overland Spanish exploration party (led by Don Gaspar de Portolá
Gaspar de Portolá y Rovira (January 1, 1716 – October 10, 1786) was a Spanish military officer, best known for leading the Portolá expedition into California and for serving as the first List of governors of California before 1850, Governor ...
) arrived on November 2, 1769, the first documented European visit to San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
. The first European maritime presence occurred on August 5, 1775, when the Spanish ''San Carlos'' commanded by Juan Manuel de Ayala became the first ship to anchor in the bay. Soon after, on March 28, 1776, the Spanish explorer
The first European maritime presence occurred on August 5, 1775, when the Spanish ''San Carlos'' commanded by Juan Manuel de Ayala became the first ship to anchor in the bay. Soon after, on March 28, 1776, the Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza
Juan Bautista de Anza Bezerra Nieto (July 6 or 7, 1736 – December 19, 1788) was an expeditionary leader, military officer, and politician primarily in California and New Mexico under the Spanish Empire. He is credited as one of the founding fa ...
established the Presidio of San Francisco
The Presidio of San Francisco (originally, El Presidio Real de San Francisco or The Royal Fortress of Saint Francis) is a park and former U.S. Army post on the northern tip of the San Francisco Peninsula in San Francisco, California, and is part o ...
. On October 9, Mission San Francisco de Asís
Mission San Francisco de Asís ( es, Misión San Francisco de Asís), commonly known as Mission Dolores (as it was founded near the Dolores creek), is a Spanish Californian mission and the oldest surviving structure in San Francisco. Located i ...
(Mission Dolores) was founded by Padre Francisco Palóu
Francesc Palou (in Catalan) or Francisco Palóu (1723–1789) was a Spanish Franciscan missionary, administrator and historian on the Baja California Peninsula and in Alta California. Palóu made significant contributions to the Alta California ...
.Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
was created, which included San Francisco.
In 1821, the Presidio and the Mission were ceded to Mexico by Spain. The extensive California mission system gradually lost its influence during the period of Mexican rule. Agricultural land became largely privatized as ranchos, as was occurring in other parts of California. Coastal trade increased, including a half-dozen barques
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing vessel with three or more masts having the fore- and mainmasts rigged square and only the mizzen (the aftmost mast) rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, b ...
from various Atlantic ports which regularly sailed in California waters.["From 1820 to the Gold Rush"](_blank)
at San Francisco Museum.org, accessed 2022.06.03.
Yerba Buena
Yerba buena or hierba buena is the Spanish name for a number of aromatic plants, most of which belong to the mint family. ''Yerba buena'' translates as "good herb". The specific plant species regarded as ''yerba buena'' varies from region to regi ...
(after a native herb), a trading post with settlements between the Presidio and Mission grew up around the ''Plaza de Yerba Buena''. The plaza was later renamed Portsmouth Square
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most densel ...
(now located in the city's Chinatown and Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
). The Presidio was commanded in 1833 by Captain Mariano G. Vallejo.Francisco de Haro
Francisco de Haro (1792 – November 28, 1849) was a Californio politician, soldier, and ranchero, who served as the 1st and 5th Alcalde of San Francisco (initially known as Yerba Buena). He notably commissioned the first land survey of Sa ...
became the first Alcalde of Yerba Buena. De Haro was a native of Mexico, from the west coast city of Compostela, Nayarit
Compostela is the name of both a municipality and of a town in it that serves as the seat; both are in the Mexican state of Nayarit. The municipality had 62,925 (2005 census) in a total area of 1,848 km² (713.5 sq mi). The town and its mun ...
. A land survey of Yerba Buena was made by the Swiss immigrant Jean Jacques Vioget Jean Jacques Vioget (1794–1855), originally from Switzerland, was a surveyor and sea captain, who came to California in 1837. He made the first survey and map of Yerba Buena (which later was re-named San Francisco) in 1839. He worked for John S ...
as prelude to the city plan. The second Alcalde José Joaquín Estudillo
José Joaquín Estudillo (May 7, 1800 – June 7, 1852) was a Californio statesman and ranchero who served as the 2nd Alcalde of San Francisco (then known as Yerba Buena). A member of the prominent Estudillo family of California, he is also co ...
was a Californio from a prominent Monterey
Monterey (; es, Monterrey; Ohlone: ) is a city located in Monterey County on the southern edge of Monterey Bay on the U.S. state of California's Central Coast. Founded on June 3, 1770, it functioned as the capital of Alta California under bot ...
family. In 1835, while in office, he approved the first land grant in Yerba Buena: to William Richardson, a naturalized Mexican citizen of English birth. Richardson had arrived in San Francisco aboard a whaling ship
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Jap ...
in 1822. In 1825, he married Maria Antonia Martinez, eldest daughter of the Californio Ygnacio Martínez.
1846–1905: Population growth and American acquisition
 Yerba Buena began to attract American and European settlers; an 1842 census listed 21 residents (11%) born in the United States or Europe, as well as one Filipino merchant. Commodore
Yerba Buena began to attract American and European settlers; an 1842 census listed 21 residents (11%) born in the United States or Europe, as well as one Filipino merchant. Commodore John D. Sloat
John Drake Sloat (July 26, 1781 – November 28, 1867) was a commodore in the United States Navy who, in 1846, claimed California for the United States.
Life
He was born at the family home of Sloat House in Sloatsburg, New York, of Dutch ancestr ...
claimed California for the United States on July 7, 1846, during the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, and Captain John B. Montgomery arrived to claim Yerba Buena two days later. Yerba Buena was renamed San Francisco on January 30 of the next year, and Mexico officially ceded the territory to the United States at the end of the war in 1848. Despite its attractive location as a port and naval base, San Francisco was still a small settlement with inhospitable geography. Its 1847 population was said to be 459.California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California fro ...
brought a flood of treasure seekers (known as "forty-niners", as in "1849"). With their sourdough bread in tow, prospectors accumulated in San Francisco over rival Benicia, raising the population from 1,000 in 1848 to 25,000 by December 1849.saloons
Saloon may refer to:
Buildings and businesses
* One of the bars in a traditional British pub
* An alternative name for a bar (establishment)
* Western saloon, a historical style of American bar
* The Saloon, a bar and music venue in San Francisc ...
, and hotels; many were left to rot, and some were sunk to establish title to the underwater lot. By 1851, the harbor was extended out into the bay by wharves while buildings were erected on piles among the ships. By 1870, Yerba Buena Cove
Yerba Buena Cove was a cove on San Francisco Bay where the Mexican pueblo of Yerba Buena was located. It lay between Clarks Point to the north (southeast of Telegraph Hill, near the corner of Broadway and Battery Streets) and Rincon Point to t ...
had been filled to create new land. Buried ships are occasionally exposed when foundations are dug for new buildings.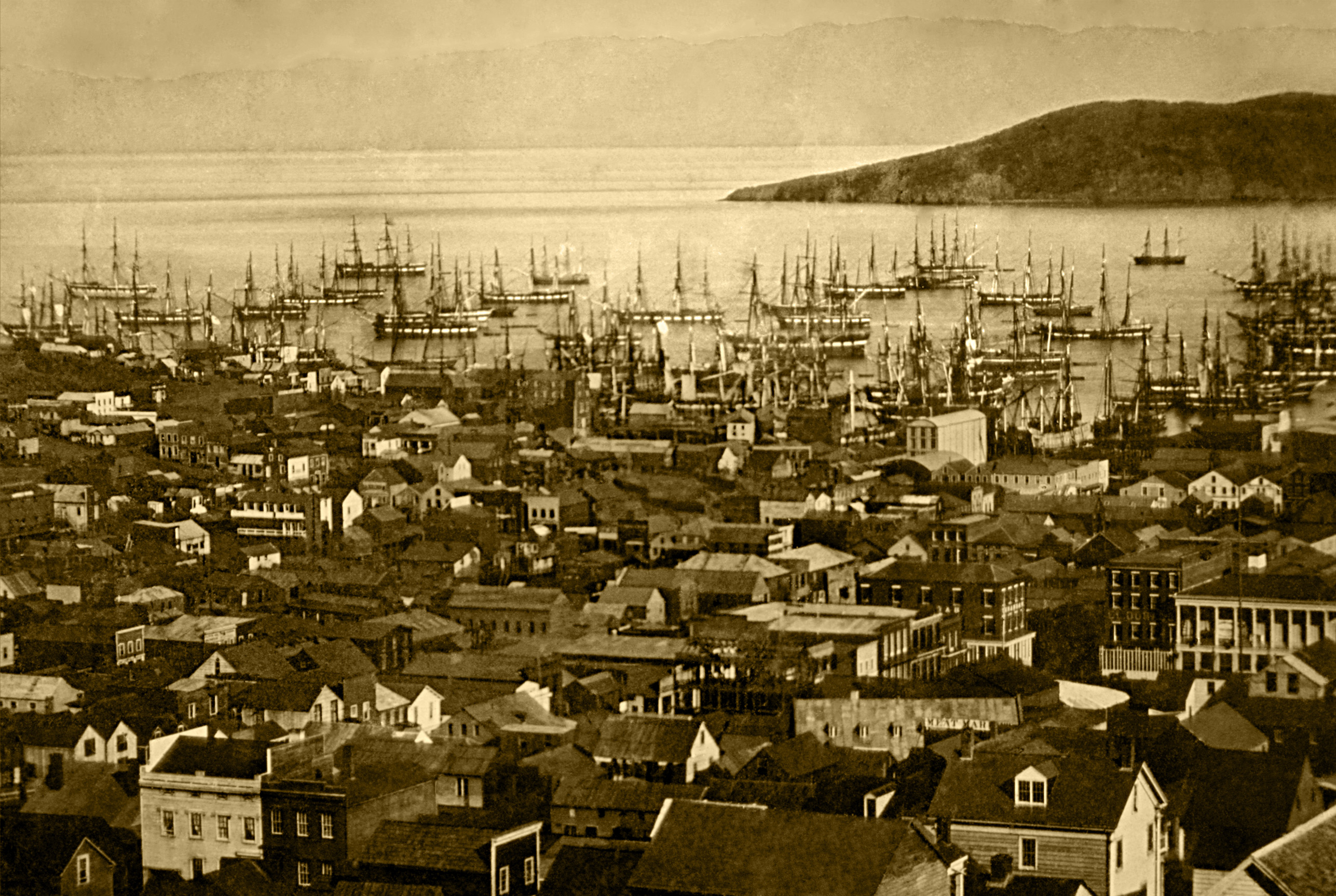 California was quickly granted statehood in 1850, and the U.S. military built Fort Point at the
California was quickly granted statehood in 1850, and the U.S. military built Fort Point at the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
and a fort on Alcatraz Island
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pri ...
to secure the San Francisco Bay. San Francisco County was one of the state's 18 original counties established at California statehood in 1850. Until 1856, San Francisco's city limits extended west to Divisadero Street and Castro Street, and south to 20th Street. In 1856, the California state government divided the county. A straight line was then drawn across the tip of the San Francisco Peninsula just north of San Bruno Mountain. Everything south of the line became the new San Mateo County while everything north of the line became the new consolidated City and County of San Francisco.
 Entrepreneurs sought to capitalize on the wealth generated by the Gold Rush. Silver discoveries, including the
Entrepreneurs sought to capitalize on the wealth generated by the Gold Rush. Silver discoveries, including the Comstock Lode
The Comstock Lode is a lode of silver ore located under the eastern slope of Mount Davidson, a peak in the Virginia Range in Virginia City, Nevada (then western Utah Territory), which was the first major discovery of silver ore in the Unit ...
in Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
in 1859, further drove rapid population growth. With hordes of fortune seekers streaming through the city, lawlessness was common, and the Barbary Coast section of town gained notoriety as a haven for criminals, prostitution, bootlegging, and gambling. Early winners were the banking industry, with the founding of Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo & Company is an American multinational financial services company with corporate headquarters in San Francisco, California; operational headquarters in Manhattan; and managerial offices throughout the United States and intern ...
in 1852 and the Bank of California
The Bank of California was opened in San Francisco, California, on July 4, 1864, by William Chapman Ralston and Darius Ogden Mills. It was the first commercial bank in the Western United States, the second-richest bank in the nation, and considered ...
in 1864. Development of the Port of San Francisco
The Port of San Francisco is a semi-independent organization that oversees the port facilities at San Francisco, California, United States. It is run by a five-member commission, appointed by the Mayor and approved by the Board of Supervisors. Th ...
and the establishment in 1869 of overland access to the eastern U.S. rail system via the newly completed Pacific Railroad
The Pacific Railroad (not to be confused with Union Pacific Railroad) was a railroad based in Missouri. It was a predecessor of both the Missouri Pacific Railroad and St. Louis-San Francisco Railway.
The Pacific was chartered by Missouri in 1849 ...
(the construction of which the city only reluctantly helped support) helped make the Bay Area a center for trade. Catering to the needs and tastes of the growing population, Levi Strauss
Levi Strauss (; born Löb Strauß ; February 26, 1829 – September 26, 1902) was a German-born American businessman who founded the first company to manufacture blue jeans. His firm of Levi Strauss & Co. (Levi's) began in 1853 in San Francisc ...
opened a dry goods
Dry goods is a historic term describing the type of product line a store carries, which differs by region. The term comes from the textile trade, and the shops appear to have spread with the mercantile trade across the British Empire (and forme ...
business and Domingo Ghirardelli began manufacturing chocolate. Chinese immigrants made the city a polyglot culture, drawn to "Old Gold Mountain", creating the city's Chinatown quarter. By 1880, Chinese made up 9.3% of the population. The first cable cars carried San Franciscans up Clay Street in 1873. The city's sea of Victorian house
In Great Britain and former British colonies, a Victorian house generally means any house built during the reign of Queen Victoria. During the Industrial Revolution, successive housing booms resulted in the building of many millions of Victorian ...
s began to take shape, and civic leaders campaigned for a spacious public park, resulting in plans for Golden Gate Park
Golden Gate Park, located in San Francisco, California, United States, is a large urban park consisting of of public grounds. It is administered by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department, which began in 1871 to oversee the development ...
. San Franciscans built schools, churches, theaters, and all the hallmarks of civic life. The Presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th and 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Spanish Philippines in particular, were cen ...
developed into the most important American military installation on the Pacific coast. By 1890, San Francisco's population approached 300,000, making it the eighth-largest city in the United States at the time. Around 1901, San Francisco was a major city known for its flamboyant style, stately hotels, ostentatious mansions on Nob Hill
Nob Hill is a neighborhood of San Francisco, California, United States that is known for its numerous luxury hotels and historic mansions. Nob Hill has historically served as a center of San Francisco's upper class. Nob Hill is among the highes ...
, and a thriving arts scene. The first North American plague epidemic was the San Francisco plague of 1900–1904
The San Francisco plague of 1900–1904 was an epidemic of bubonic plague centered on San Francisco's Chinatown. It was the first plague epidemic in the continental United States. The epidemic was recognized by medical authorities in March 1900, ...
.
1906–1940: San Francisco earthquake and reconstruction
At 5:12 am on April 18, 1906, a major earthquake struck San Francisco and northern California. As buildings collapsed from the shaking, ruptured gas lines ignited fires that spread across the city and burned out of control for several days. With water main
A water distribution system is a part of water supply network with components that carry potable water from a centralized treatment plant or wells to consumers to satisfy residential, commercial, industrial and fire fighting requirements.
Definit ...
s out of service, the Presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th and 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Spanish Philippines in particular, were cen ...
Artillery Corps attempted to contain the inferno
Inferno may refer to:
* Hell, an afterlife place of suffering
* Conflagration, a large uncontrolled fire
Film
* ''L'Inferno'', a 1911 Italian film
* Inferno (1953 film), ''Inferno'' (1953 film), a film noir by Roy Ward Baker
* Inferno (1973 fi ...
by dynamiting blocks of buildings to create firebreaks.East Bay
The East Bay is the eastern region of the San Francisco Bay Area and includes cities along the eastern shores of the San Francisco Bay and San Pablo Bay. The region has grown to include inland communities in Alameda and Contra Costa counties ...
.
Rebuilding was rapid and performed on a grand scale. Rejecting calls to completely remake the street grid, San Franciscans opted for speed.Amadeo Giannini
Amadeo Pietro Giannini (), also known as Amadeo Peter Giannini or A. P. Giannini (May 6, 1870 – June 3, 1949) was an American banker who founded the Bank of Italy, which became Bank of America. Giannini is credited as the inventor of many modern ...
's Bank of Italy
The Bank of Italy ( Italian: ''Banca d'Italia'', informally referred to as ''Bankitalia''), (), is the central bank of Italy and part of the European System of Central Banks. It is located in Palazzo Koch, via Nazionale, Rome. The bank's cur ...
, later to become Bank of America
The Bank of America Corporation (often abbreviated BofA or BoA) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered at the Bank of America Corporate Center in Charlotte, North Carolina. The bank ...
, provided loans for many of those whose livelihoods had been devastated. The influential San Francisco Planning and Urban Research Association
SPUR is a nonprofit public policy organization focused on regional planning, housing, transportation, sustainability and resilience, economic justice, good government, and food and agriculture in the San Francisco Bay Area. Its full name is the S ...
or SPUR was founded in 1910 to address the quality of housing after the earthquake. The earthquake hastened development of western neighborhoods that survived the fire, including Pacific Heights
Pacific Heights is a neighborhood in San Francisco, California. It has panoramic views of the Golden Gate Bridge, San Francisco Bay, the Palace of Fine Arts, Alcatraz, and the Presidio.
The Pacific Heights Residents Association defines the neig ...
, where many of the city's wealthy rebuilt their homes. In turn, the destroyed mansions of Nob Hill became grand hotels. City Hall rose again in splendid Beaux Arts style, and the city celebrated its rebirth at the Panama–Pacific International Exposition
The Panama–Pacific International Exposition was a world's fair held in San Francisco, California, United States, from February 20 to December 4, 1915. Its stated purpose was to celebrate the completion of the Panama Canal, but it was widely s ...
in 1915.
 During this period, San Francisco built some of its most important infrastructure. Civil Engineer
During this period, San Francisco built some of its most important infrastructure. Civil Engineer Michael O'Shaughnessy
Michael Maurice O'Shaughnessy (28 May 1864 – 12 October 1934) was an Irish civil engineer who became city engineer for the city of San Francisco during the early twentieth century and developed both the San Francisco Municipal Railway (Muni) a ...
was hired by San Francisco Mayor James Rolph
James "Sunny Jim" Rolph Jr. (August 23, 1869 – June 2, 1934) was an American politician. A member of the Republican Party, he was elected to a single term as the 27th governor of California from January 6, 1931, until his death on June 2 ...
as chief engineer for the city in September 1912 to supervise the construction of the Twin Peaks Reservoir, the Stockton Street Tunnel, the Twin Peaks Tunnel
The Twin Peaks Tunnel is a light rail/streetcar tunnel in San Francisco, California. The tunnel runs under Twin Peaks and is used by the K Ingleside/T Third Street, M Ocean View and S Shuttle lines of the Muni Metro system.
The eastern entra ...
, the San Francisco Municipal Railway
The San Francisco Municipal Railway (SF Muni or Muni), is the public transit system for the City and County of San Francisco. It operates a system of bus routes (including trolleybuses), the Muni Metro light rail system, three historic cabl ...
, the Auxiliary Water Supply System, and new sewers. San Francisco's streetcar system, of which the J, K, L, M, and N lines survive today, was pushed to completion by O'Shaughnessy between 1915 and 1927. It was the O'Shaughnessy Dam, Hetch Hetchy Reservoir
Hetch Hetchy is a valley, a reservoir, and a water system in California in the United States. The glacial Hetch Hetchy Valley lies in the northwestern part of Yosemite National Park and is drained by the Tuolumne River. For thousands of years bef ...
, and Hetch Hetchy Aqueduct
Hetch Hetchy is a valley, a reservoir, and a water system in California in the United States. The glacial Hetch Hetchy Valley lies in the northwestern part of Yosemite National Park and is drained by the Tuolumne River. For thousands of years bef ...
that would have the largest effect on San Francisco. An abundant water supply enabled San Francisco to develop into the city it has become today.
 In ensuing years, the city solidified its standing as a financial capital; in the wake of the 1929 stock market crash, not a single San Francisco-based bank failed. Indeed, it was at the height of the
In ensuing years, the city solidified its standing as a financial capital; in the wake of the 1929 stock market crash, not a single San Francisco-based bank failed. Indeed, it was at the height of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
that San Francisco undertook two great civil engineering projects, simultaneously constructing the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge
The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge, known locally as the Bay Bridge, is a complex of bridges spanning San Francisco Bay in California. As part of Interstate 80 and the direct road between San Francisco and Oakland, it carries about 260,000 ...
and the Golden Gate Bridge
The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Golden Gate, the strait connecting San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean. The structure links the U.S. city of San Francisco, California—the northern tip of the San Francisco Pen ...
, completing them in 1936 and 1937, respectively. It was in this period that the island of Alcatraz
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pris ...
, a former military stockade, began its service as a federal maximum security prison, housing notorious inmates such as Al Capone
Alphonse Gabriel Capone (; January 17, 1899 – January 25, 1947), sometimes known by the nickname "Scarface", was an American gangster and businessman who attained notoriety during the Prohibition era as the co-founder and boss of the ...
, and Robert Franklin Stroud
Robert Franklin Stroud (January 28, 1890 – November 21, 1963), known as the "Birdman of Alcatraz", was a convicted murderer, American federal prisoner and author who has been cited as one of the most notorious criminals in the United S ...
, the Birdman of Alcatraz. San Francisco later celebrated its regained grandeur with a World's fair
A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition or an expo, is a large international exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specif ...
, the Golden Gate International Exposition
The Golden Gate International Exposition (GGIE) (1939 and 1940), held at San Francisco's Treasure Island, was a World's Fair celebrating, among other things, the city's two newly built bridges. The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge opened in 1936 ...
in 1939–40, creating Treasure Island
''Treasure Island'' (originally titled ''The Sea Cook: A Story for Boys''Hammond, J. R. 1984. "Treasure Island." In ''A Robert Louis Stevenson Companion'', Palgrave Macmillan Literary Companions. London: Palgrave Macmillan. .) is an adventure no ...
in the middle of the bay to house it.
1941–present: World War II and urbanization
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the Hunters Point Naval Shipyard
The Hunters Point Naval Shipyard was a United States Navy shipyard in San Francisco, California, located on of waterfront at Hunters Point in the southeast corner of the city.
Originally, Hunters Point was a commercial shipyard established ...
became a hub of activity, and Fort Mason
Fort Mason, in San Francisco, California originated as a coastal defense site during the American Civil War. The nucleus of the property was owned by John C. Frémont and disputes over compensation by the United States continued into 1968. In 188 ...
became the primary port of embarkation for service members shipping out to the Pacific Theater of Operations.United Nations Charter
The Charter of the United Nations (UN) is the foundational treaty of the UN, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the ...
creating the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
was drafted and signed in San Francisco in 1945 and, in 1951, the Treaty of San Francisco
The , also called the , re-established peaceful relations between Japan and the Allied Powers on behalf of the United Nations by ending the legal state of war and providing for redress for hostile actions up to and including World War II. It w ...
re-established peaceful relations between Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
and the Allied Powers.
Urban planning projects in the 1950s and 1960s involved widespread destruction and redevelopment of west-side neighborhoods and the construction of new freeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
s, of which only a series of short segments were built before being halted by citizen-led opposition. The onset of containerization
Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers (also called shipping containers and ISO containers). Containerization is also referred as "Container Stuffing" or "Container Loading", which is the pro ...
made San Francisco's small piers obsolete, and cargo activity moved to the larger Port of Oakland
The Port of Oakland is a major container ship facility located in Oakland, California, in the San Francisco Bay. It was the first major port on the Pacific Coast of the United States to build terminals for container ships. As of 2011 it was the f ...
. The city began to lose industrial jobs and turned to tourism as the most important segment of its economy. The suburbs experienced rapid growth, and San Francisco underwent significant demographic change, as large segments of the white population left the city, supplanted by an increasing wave of immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
from Asia and Latin America. From 1950 to 1980, the city lost over 10 percent of its population.
 Over this period, San Francisco became a magnet for America's
Over this period, San Francisco became a magnet for America's counterculture
A counterculture is a culture whose values and norms of behavior differ substantially from those of mainstream society, sometimes diametrically opposed to mainstream cultural mores.Eric Donald Hirsch. ''The Dictionary of Cultural Literacy''. Hou ...
. Beat Generation writers fueled the San Francisco Renaissance
The term San Francisco Renaissance is used as a global designation for a range of poetic activity centered on San Francisco, which brought it to prominence as a hub of the American poetry avant-garde in the 1950s. However, others (e.g., Alan Watt ...
and centered on the North Beach neighborhood in the 1950s. Hippies flocked to Haight-Ashbury
Haight-Ashbury () is a district of San Francisco, California, named for the intersection of Haight and Ashbury streets. It is also called The Haight and The Upper Haight. The neighborhood is known as one of the main centers of the counterculture ...
in the 1960s, reaching a peak with the 1967 Summer of Love. In 1974, the Zebra murders
The "Zebra" murders were a string of racially motivated murders and related attacks committed by a group of four black serial killers in San Francisco, California, United States, from October 1973 to April 1974; they killed at least 15 people a ...
left at least 16 people dead. In the 1970s, the city became a center of the gay rights movement
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) movements are social movements that advocate for LGBT people in society. Some focus on equal rights, such as the ongoing movement for same-sex marriage, while others focus on liberation, as in the ...
, with the emergence of The Castro
The Castro District, commonly referred to as the Castro, is a neighborhood in Eureka Valley in San Francisco. The Castro was one of the first gay neighborhoods in the United States. Having transformed from a working-class neighborhood through ...
as an urban gay village
A gay village is a geographical area with generally recognized boundaries that is inhabited or frequented by many lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBT) people. Gay villages often contain a number of gay-oriented establis ...
, the election of Harvey Milk
Harvey Bernard Milk (May 22, 1930 – November 27, 1978) was an American politician and the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, as a member of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors. Milk was born and raised in ...
to the San Francisco Board of Supervisors, Board of Supervisors, and his Moscone–Milk assassinations, assassination, along with that of Mayor George Moscone, in 1978.
Bank of America completed 555 California Street in 1969 and the Transamerica Pyramid was completed in 1972, igniting a wave of "Manhattanization" that lasted until the late 1980s, a period of extensive high-rise development downtown.
Geography
 San Francisco is located on the West Coast of the United States at the north end of the
San Francisco is located on the West Coast of the United States at the north end of the San Francisco Peninsula
The San Francisco Peninsula is a peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area that separates San Francisco Bay from the Pacific Ocean. On its northern tip is the City and County of San Francisco. Its southern base is Mountain View, south of Palo A ...
and includes significant stretches of the Pacific Ocean and San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
within its boundaries. Several picturesque islands of San Francisco Bay, islands—Alcatraz
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pris ...
, Treasure Island
''Treasure Island'' (originally titled ''The Sea Cook: A Story for Boys''Hammond, J. R. 1984. "Treasure Island." In ''A Robert Louis Stevenson Companion'', Palgrave Macmillan Literary Companions. London: Palgrave Macmillan. .) is an adventure no ...
and the adjacent Yerba Buena Island, and small portions of Alameda (island), Alameda Island, Red Rock Island, and Angel Island, California, Angel Island—are part of the city. Also included are the uninhabited Farallon Islands, offshore in the Pacific Ocean. The mainland within the city limits roughly forms a "seven-by-seven-mile square", a common local colloquialism referring to the city's shape, though its total area, including water, is nearly .
There are more than 50 hills within the city limits.Nob Hill
Nob Hill is a neighborhood of San Francisco, California, United States that is known for its numerous luxury hotels and historic mansions. Nob Hill has historically served as a center of San Francisco's upper class. Nob Hill is among the highes ...
, Potrero Hill, San Francisco, Potrero Hill, and Russian Hill, San Francisco, Russian Hill.
Near the geographic center of the city, southwest of the downtown area, are a series of less densely populated hills. Twin Peaks (San Francisco), Twin Peaks, a pair of hills forming one of the city's highest points, forms an overlook spot. San Francisco's tallest hill, Mount Davidson (California), Mount Davidson, is high and is capped with a tall cross built in 1934. Dominating this area is Sutro Tower, a large red and white radio and television transmission tower reaching 1,811 ft (552 m) above sea level.
The nearby San Andreas Fault, San Andreas and Hayward Faults are responsible for much earthquake activity, although neither physically passes through the city itself. The San Andreas Fault caused the earthquakes in 1906 and 1989. Minor earthquakes occur on a regular basis. The threat of major earthquakes plays a large role in the city's infrastructure development. The city constructed an San Francisco Fire Department Auxiliary Water Supply System, auxiliary water supply system and has repeatedly upgraded its building codes, requiring retrofits for older buildings and higher engineering standards for new construction. However, there are still thousands of smaller buildings that remain vulnerable to quake damage. USGS has released the California earthquake forecast which models earthquake occurrence in California.
San Francisco's shoreline has grown beyond its natural limits. Entire neighborhoods such as the Marina District, San Francisco, Marina, Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay, and Hunters Point, San Francisco, Hunters Point, as well as large sections of the The Embarcadero (San Francisco), Embarcadero, sit on areas of Land reclamation, landfill. Treasure Island was constructed from material dredged from the bay as well as material resulting from the excavation of the Yerba Buena Tunnel through Yerba Buena Island during the construction of the Bay Bridge. Such land tends to be unstable during earthquakes. The resulting soil liquefaction causes extensive damage to property built upon it, as was evidenced in the Marina district during the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake. Most of the city's natural watercourses, such as Islais Creek and Mission Creek, have been culverted and built over, although the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission, Public Utilities Commission is studying proposals to daylight or restore some creeks.
Cityscape

Neighborhoods
 The historic center of San Francisco is the northeast quadrant of the city anchored by Market Street (San Francisco), Market Street and the waterfront. It is here that the
The historic center of San Francisco is the northeast quadrant of the city anchored by Market Street (San Francisco), Market Street and the waterfront. It is here that the Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
is centered, with Union Square (San Francisco), Union Square, the principal shopping and hotel district, and the Tenderloin, San Francisco, Tenderloin nearby. Cable car (railway), Cable cars carry riders up steep inclines to the summit of Nob Hill, once the home of the city's business tycoons, and down to the waterfront tourist attractions of Fisherman's Wharf, San Francisco, Fisherman's Wharf, and Pier 39, where many restaurants feature Dungeness crab from a still-active fishing industry. Also in this quadrant are Russian Hill, San Francisco, Russian Hill, a residential neighborhood with the famously crooked Lombard Street (San Francisco), Lombard Street; North Beach, the city's Little Italy and the former center of the Beat Generation; and Telegraph Hill, San Francisco, Telegraph Hill, which features Coit Tower. Abutting Russian Hill and North Beach is San Francisco's Chinatown, the oldest Chinatown in North America.[Bacon, Daniel: Walking the Barbary Coast Trail 2nd ed., pp. 52–53, Quicksilver Press, 1997] The South of Market, San Francisco, South of Market, which was once San Francisco's industrial core, has seen significant redevelopment following the construction of Oracle Park and an infusion of Startup company, startup companies. New skyscrapers, live-work lofts, and condominiums dot the area. Further development is taking place just to the south in Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay area, a former railroad yard, which now has a second campus of the University of California, San Francisco
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is a public land-grant research university in San Francisco, California. It is part of the University of California system and is dedicated entirely to health science and life science. It con ...
and Chase Center, which opened in 2019–20 Golden State Warriors season, 2019 as the new home of the Golden State Warriors
The Golden State Warriors are an American professional basketball team based in San Francisco. The Warriors compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA), as a member of the league's Western Conference Pacific Division. Founded in 194 ...
.
West of downtown, across Van Ness Avenue (San Francisco), Van Ness Avenue, lies the large Western Addition, San Francisco, Western Addition neighborhood, which became established with a large African American population after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The Western Addition is usually divided into smaller neighborhoods including Hayes Valley, San Francisco, Hayes Valley, Fillmore District, San Francisco, the Fillmore, and Japantown, San Francisco, Japantown, which was once the largest Japantown in North America but suffered when its Japanese American residents were Japanese American internment, forcibly removed and interned during World War II. The Western Addition survived the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, 1906 earthquake with its Victorian house, Victorians largely intact, including the famous "Painted Ladies", standing alongside Alamo Square. To the south, near the geographic center of the city is Haight-Ashbury
Haight-Ashbury () is a district of San Francisco, California, named for the intersection of Haight and Ashbury streets. It is also called The Haight and The Upper Haight. The neighborhood is known as one of the main centers of the counterculture ...
, famously associated with 1960s hippie culture. The Haight is now home to some expensive boutiques and a few controversial chain stores, although it still retains some Bohemianism, bohemian character.
North of the Western Addition is Pacific Heights
Pacific Heights is a neighborhood in San Francisco, California. It has panoramic views of the Golden Gate Bridge, San Francisco Bay, the Palace of Fine Arts, Alcatraz, and the Presidio.
The Pacific Heights Residents Association defines the neig ...
, an affluent neighborhood that features the homes built by wealthy San Franciscans in the wake of the 1906 earthquake. Directly north of Pacific Heights facing the waterfront is the Marina District, San Francisco, Marina, a neighborhood popular with young professionals that was largely built on reclaimed land from the Bay.
In the southeast quadrant of the city is the Mission District—populated in the 19th century by Californios and working-class immigrants from Germany, Ireland, Italy, and Scandinavia. In the 1910s, a wave of Central American immigrants settled in the Mission and, in the 1950s, immigrants from Mexican American, Mexico began to predominate. In recent years, gentrification has changed the demographics of parts of the Mission from Latino, to Twentysomething (term), twenty-something professionals. Noe Valley, San Francisco, Noe Valley to the southwest and Bernal Heights, San Francisco, Bernal Heights to the south are both increasingly popular among young families with children. East of the Mission is the Potrero Hill neighborhood, a mostly residential neighborhood that features sweeping views of downtown San Francisco. West of the Mission, the area historically known as Eureka Valley, San Francisco, Eureka Valley, now popularly called The Castro, San Francisco, the Castro, was once a working-class Scandinavian and Irish area. It has become North America's first gay village
A gay village is a geographical area with generally recognized boundaries that is inhabited or frequented by many lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBT) people. Gay villages often contain a number of gay-oriented establis ...
, and is now the center of homosexuality, gay life in the city. Located near the city's southern border, the Excelsior District, San Francisco, Excelsior District is one of the most ethnically diverse neighborhoods in San Francisco. The predominantly African American Bayview–Hunters Point, San Francisco, Bayview-Hunters Point in the far southeast corner of the city is one of the poorest neighborhoods and suffers from a high rate of crime, though the area has been the focus of several revitalizing and controversial urban renewal projects.
 The construction of the
The construction of the Twin Peaks Tunnel
The Twin Peaks Tunnel is a light rail/streetcar tunnel in San Francisco, California. The tunnel runs under Twin Peaks and is used by the K Ingleside/T Third Street, M Ocean View and S Shuttle lines of the Muni Metro system.
The eastern entra ...
in 1918 connected southwest neighborhoods to downtown via streetcar, hastening the development of West Portal, San Francisco, West Portal, and nearby affluent Forest Hill, San Francisco, Forest Hill and St. Francis Wood, San Francisco, St. Francis Wood. Further west, stretching all the way to the Pacific Ocean and north to Golden Gate Park
Golden Gate Park, located in San Francisco, California, United States, is a large urban park consisting of of public grounds. It is administered by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department, which began in 1871 to oversee the development ...
lies the vast Sunset District, San Francisco, Sunset District, a large middle-class area with a predominantly Asian population.
The northwestern quadrant of the city contains the Richmond District, San Francisco, Richmond, a mostly middle-class neighborhood north of Golden Gate Park, home to immigrants from other parts of Asia as well as many Russian people, Russian and Ukrainian people, Ukrainian immigrants. Together, these areas are known as Neighborhoods in San Francisco, The Avenues. These two districts are each sometimes further divided into two regions: the Outer Richmond and Outer Sunset can refer to the more western portions of their respective district and the Inner Richmond and Inner Sunset can refer to the more eastern portions.
Many piers remained derelict for years until the demolition of the Embarcadero Freeway reopened the downtown waterfront, allowing for redevelopment. The centerpiece of the port, the San Francisco Ferry Building, Ferry Building, while still receiving commuter ferry traffic, has been restored and redeveloped as a gourmet marketplace.
Climate
San Francisco has a warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification, Köppen ''Csb'') characteristic of California's coast, with moist, mild winters and dry summers. San Francisco's weather is strongly influenced by the California Current, cool currents of the Pacific Ocean on the west side of the city, and the water of San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
to the north and east. This moderates temperature swings and produces a remarkably mild year-round climate with little seasonal temperature variation.
 Among major U.S. cities, San Francisco has the coolest daily mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures for June, July, and August.
During the summer, rising hot air in California's interior valleys creates a low-pressure area that draws winds from the North Pacific High through the
Among major U.S. cities, San Francisco has the coolest daily mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures for June, July, and August.
During the summer, rising hot air in California's interior valleys creates a low-pressure area that draws winds from the North Pacific High through the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by t ...
, which creates the city's San Francisco fog, characteristic cool winds and fog. The fog is less pronounced in eastern neighborhoods and during the late summer and early fall. As a result, the year's warmest month, on average, is September, and on average, October is warmer than July, especially in daytime.
Temperatures reach or exceed on an average of only 21 and 23 days a year at downtown and San Francisco International Airport (SFO), respectively.
Flora and fauna
Historically, tule elk were present in San Francisco County, based on archeological evidence of elk remains in at least five different Native Americans in the United States, Native American shellmounds: at Hunter's Point, Fort Mason, Stevenson Street, Market Street, and Yerba Buena. Perhaps the first historical observer record was from the De Anza Expedition on March 23, 1776. Herbert Eugene Bolton wrote about the expedition camp at Mountain Lake, near the southern end of today's Presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th and 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Spanish Philippines in particular, were cen ...
: "Round about were grazing deer, and scattered here and there were the antlers of large elk." Also, when Richard Henry Dana Jr. visited San Francisco Bay in 1835, he wrote about vast elk herds near the Golden Gate: on December 27 "...we came to anchor near the mouth of the bay, under a high and beautifully sloping hill, upon which herds of hundreds and hundreds of red deer [note: "red deer" is the European term for "elk"], and the stag, with his high branching antlers, were bounding about...", although it is not clear whether this was the Marin side or the San Francisco side.
Demographics
The 2020 United States census showed San Francisco's population to be 873,965, an increase of 8.5% from the 2010 United States census, 2010 census. With roughly one-quarter the population density of Manhattan, San Francisco is the List of United States cities by population density, second-most densely populated large American city, behind only New York City among cities greater than 200,000 population, and the County statistics of the United States, fifth-most densely populated U.S. county, following only four of the five New York City Boroughs of New York City, boroughs.
San Francisco forms part of the five-county San Francisco–Oakland–Hayward, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, a region of 4.7 million people (Metropolitan statistical area, 13th most populous in the U.S.), and has served as its traditional demographic focal point. It is also part of the greater 14-county San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area, whose population is over 9.6 million, making it the Combined statistical area, fifth-largest in the United States as of 2018.
Race, ethnicity, religion, and languages
San Francisco has a majority minority population, as non-Hispanic whites comprise less than half of the population, 41.9%, down from 92.5% in 1940.New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, and Los Angeles, respectively. According to a 2018 study by the Jewish Community Federation of San Francisco, Jews make up 10% (80,000) of the city's population, making Judaism the second-largest religion in San Francisco after Christianity.
According to a 2018 study by the Jewish Community Federation of San Francisco, Jews make up 10% (80,000) of the city's population, making Judaism the second-largest religion in San Francisco after Christianity.Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, 3% (25,767) Tagalog language, Tagalog, and 2% (14,017) Russian language, Russian. In total, 45% (342,693) of San Francisco's population spoke a language at home other than English.
Ethnic clustering
San Francisco has several prominent Chinese, Mexican, and Filipino neighborhoods including Chinatown and Mission District, San Francisco, the Mission District. Research collected on the immigrant clusters in the city show that more than half of the Asian population in San Francisco is either Chinese-born (40.3%) or Philippine-born (13.1%), and of the Mexican population 21% were Mexican-born, meaning these are people who recently immigrated to the United States.
Education, households, and income
Of all major cities in the United States, San Francisco has the second-highest percentage of residents with a college degree, second only to Seattle. Over 44% of adults have a bachelor's or higher degree.
Homelessness
Homelessness has been a Homelessness in the San Francisco Bay Area, major problem in the city and remains a growing problem in modern times.
8,035 homeless people were counted in San Francisco's 2019 point-in-time street and shelter count. This was an increase of more than 17% over the 2017 count of 6,858 people. 5,180 of the people were living unsheltered on the streets and in parks.
Crime
In 2011, 50 murders were reported, which is 6.1 per 100,000 people. There were about 134 rapes, 3,142 robberies, and about 2,139 assaults. There were about 4,469 burglaries, 25,100 thefts, and 4,210 motor vehicle thefts. The Tenderloin, San Francisco, Tenderloin area has the highest crime rate in San Francisco: 70% of the city's violent crimes, and around one-fourth of the city's murders, occur in this neighborhood. The Tenderloin also sees high rates of drug abuse, gang violence, and prostitution. Another area with high crime rates is the Bayview–Hunters Point, San Francisco, Bayview-Hunters Point area. In the first six months of 2015 there were 25 murders compared to 14 in the first six months of 2014. However, the murder rate is still much lower than in past decades. That rate, though, did rise again by the close of 2016. According to the San Francisco Police Department, there were 59 murders in the city in 2016, an annual total that marked a 13.5% increase in the number of homicides (52) from 2015. The city has also gained a reputation for car break-ins, with over 19,000 car break-ins occurring in 2021.
During the first half of 2018, human feces on San Francisco sidewalks were the second-most-frequent complaint of city residents, with about 65 calls per day. The city has formed a "poop patrol" to attempt to combat the problem.
Gangs
Several street gangs have operated in the city over the decades, including MS-13, the Sureños and Norteños in the Mission District. In 2008, a MS-13 member Murder of the Bologna family, killed three family members as they were arriving home in the city's Excelsior District. His victims had no relationship with him, nor did they have any known gang or street crime involvement.
African-American street gangs familiar in other cities, including the Bloods gang, Bloods, Crips and their sets, have struggled to establish footholds in San Francisco, while police and prosecutors have been accused of liberally labeling young African-American males as gang members. However, gangs founded in San Francisco with majority Black memberships have made their presence in the city. The gang Westmob, associated with Oakdale Mob and Sunnydale housing project gangs from the southeast area of the city, was involved in a gang war with Hunters Point-based Big Block from 1999 to the 2000s. They claim territory from West Point to Middle Point in the Hunters Point, San Francisco, California, Hunters Point projects. In 2004, a Westmob member fatally shot a SFPD officer and wounded his partner; he was sentenced to life without parole in 2007.
Criminal gangs with shotcallers in China, including Triad (organized crime), Triad groups such as the Wo Hop To, have been reported active in San Francisco. In 1977, an ongoing rivalry between two Chinese gangs led to a Golden Dragon massacre, shooting attack at the Golden Dragon restaurant in Chinatown, which left 5 people dead and 11 wounded. None of the victims in this attack were gang members. Five members of the Joe Boys gang were arrested and convicted of the crime. In 1990, a gang-related shooting killed one man and wounded six others outside a nightclub near Chinatown. In 1998, six teenagers were shot and wounded at the Chinese Playground; a 16-year-old boy was subsequently arrested.
Economy
 According to academic Rob Wilson, San Francisco is a global city, a status that pre-dated the city's popularity during the
According to academic Rob Wilson, San Francisco is a global city, a status that pre-dated the city's popularity during the California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California fro ...
.COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
has accelerated the exodus of business from the downtown core of San Francisco.Golden Gate Bridge
The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Golden Gate, the strait connecting San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean. The structure links the U.S. city of San Francisco, California—the northern tip of the San Francisco Pen ...
, and San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County, directly to the south on the San Francisco Peninsula, Peninsula, were the 6th and 9th highest-income counties respectively. The legacy of the California Gold Rush turned San Francisco into the principal banking and finance center of the
The legacy of the California Gold Rush turned San Francisco into the principal banking and finance center of the West Coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
in the early twentieth century.Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
became known as the "Wall Street of the West", home to the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, the Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo & Company is an American multinational financial services company with corporate headquarters in San Francisco, California; operational headquarters in Manhattan; and managerial offices throughout the United States and intern ...
corporate headquarters, and the site of the now-defunct Pacific Exchange, Pacific Coast Stock Exchange.Bank of America
The Bank of America Corporation (often abbreviated BofA or BoA) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered at the Bank of America Corporate Center in Charlotte, North Carolina. The bank ...
, a pioneer in making banking services accessible to the middle class, was founded in San Francisco and in the 1960s, built the landmark modern skyscraper at 555 California Street for its corporate headquarters. Many large financial institutions, multinational banks, and venture capital firms are based in or have regional headquarters in the city. With over 30 international financial institutions, Beginning in the 1990s, San Francisco's economy diversified away from finance and tourism towards the growing fields of high tech, biotechnology, and medical research.
Beginning in the 1990s, San Francisco's economy diversified away from finance and tourism towards the growing fields of high tech, biotechnology, and medical research.University of California, San Francisco
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is a public land-grant research university in San Francisco, California. It is part of the University of California system and is dedicated entirely to health science and life science. It con ...
(UCSF). Mission Bay hosts the UCSF Medical Center, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine, California Institute for Quantitative Biosciences, and Gladstone Institutes, as well as more than 40 private-sector life sciences companies.
The top employer in the city is the city government itself, employing 5.6% (31,000+ people) of the city's workforce, followed by UCSF with over 25,000 employees. Manufacturing in the United States, Like many U.S. cities, San Francisco once had a significant manufacturing sector employing nearly 60,000 workers in 1969, but nearly all production left for cheaper locations by the 1980s.
Manufacturing in the United States, Like many U.S. cities, San Francisco once had a significant manufacturing sector employing nearly 60,000 workers in 1969, but nearly all production left for cheaper locations by the 1980s.[
] , San Francisco has seen a small resurgence in manufacturing, with more than 4,000 manufacturing jobs across 500 companies, doubling since 2011. The city's largest manufacturing employer is Anchor Brewing Company, and the largest by revenue is Timbuk2.
Technology
San Francisco became a hub for technological driven economic growth during the internet boom of the 1990s, and still holds an important position in the world city network today.
Tourism and conventions
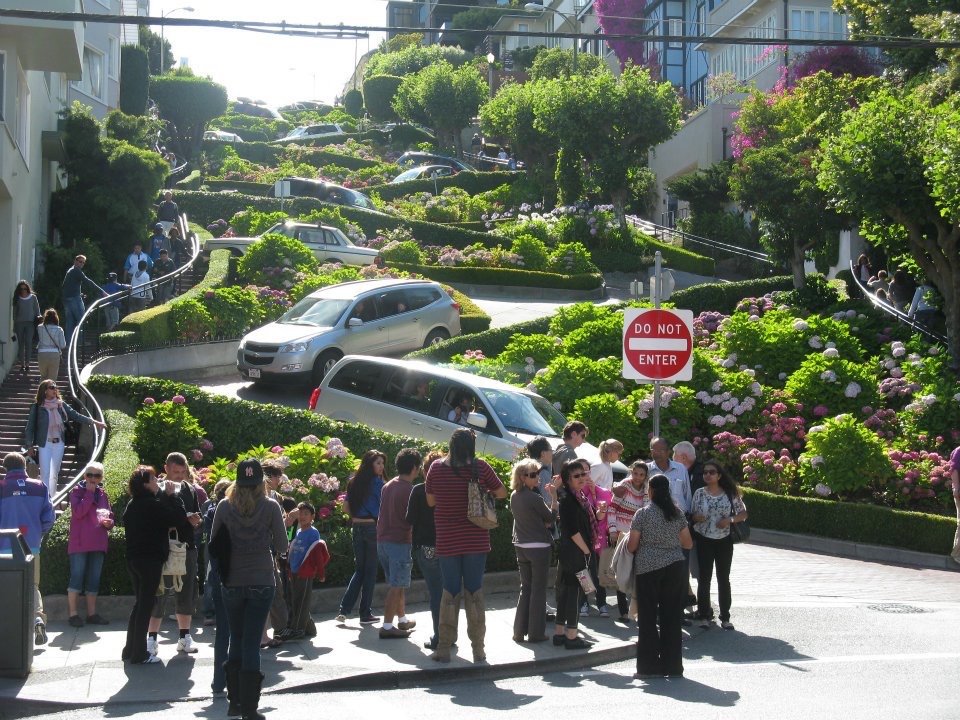

 Tourism is one of the city's largest private-sector industries, accounting for more than one out of seven jobs in the city.
Tourism is one of the city's largest private-sector industries, accounting for more than one out of seven jobs in the city.Golden Gate Bridge
The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Golden Gate, the strait connecting San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean. The structure links the U.S. city of San Francisco, California—the northern tip of the San Francisco Pen ...
and Alamo Square, San Francisco, Alamo Square Park, which is home to the famous "Painted Ladies". Both of these locations were often used as landscape shots for the hit American televisionsitcom ''Full House''. There is also Lombard Street (San Francisco), Lombard Street, known for its "crookedness" and extensive views. Tourists also visit Pier 39, which offers dining, shopping, entertainment, and views of the bay, sunbathing California sea lions, the Aquarium of the Bay, and the famous Alcatraz Island
Alcatraz Island () is a small island in San Francisco Bay, offshore from San Francisco, California, United States. The island was developed in the mid-19th century with facilities for a lighthouse, a military fortification, and a military pri ...
.
San Francisco also offers tourists cultural and unique nightlife in its neighborhoods.
The new Terminal Project at Pier 27 opened September 25, 2014, as a replacement for the old Pier 35. Itineraries from San Francisco usually include round-trip cruises to Alaska and Mexico.
A heightened interest in conventioneering in San Francisco, marked by the establishment of convention centers such as Yerba Buena, acted as a feeder into the local tourist economy and resulted in an increase in the hotel industry: "In 1959, the city had fewer than thirty-three hundred first-class hotel rooms; by 1970, the number was nine thousand; and by 1999, there were more than thirty thousand." The pink capitalism, commodification of the Castro District, San Francisco, Castro District has contributed to San Francisco's tourist economy.
Arts and culture
 Although the
Although the Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
, Union Square, San Francisco, Union Square, and Fisherman's Wharf, San Francisco, Fisherman's Wharf are well known around the world, San Francisco is also characterized by its numerous culturally rich streetscapes featuring mixed-use development, mixed-use neighborhoods anchored around List of streets in San Francisco, central commercial corridors to which residents and visitors alike can walk. Because of these characteristics, San Francisco is ranked the "most walkable" city in the United States by Walkscore.com. Many neighborhoods feature a mix of businesses, restaurants and venues that cater to the daily needs of local residents while also serving many visitors and tourists. Some neighborhoods are dotted with boutiques, cafés and nightlife such as Union Street in Cow Hollow, San Francisco, Cow Hollow, 24th Street in Noe Valley, San Francisco, Noe Valley, Valencia Street in the Mission
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
, Grant Avenue in North Beach, and Irving Street in the Sunset District, San Francisco, Inner Sunset. This approach especially has influenced the continuing South of Market neighborhood redevelopment with businesses and neighborhood services rising alongside high-rise residences. Since the 1990s, the demand for skilled information technology workers from local startups and nearby Silicon Valley has attracted white-collar workers from all over the world and created a high standard of living in San Francisco. Many neighborhoods that were once blue-collar, middle, and lower class have been Gentrification, gentrifying, as many of the city's traditional business and industrial districts have experienced a renaissance driven by the redevelopment of the The Embarcadero (San Francisco), Embarcadero, including the neighborhoods South Beach, San Francisco, South Beach and Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay. The city's property values and household income have risen to among the highest in the nation,
Since the 1990s, the demand for skilled information technology workers from local startups and nearby Silicon Valley has attracted white-collar workers from all over the world and created a high standard of living in San Francisco. Many neighborhoods that were once blue-collar, middle, and lower class have been Gentrification, gentrifying, as many of the city's traditional business and industrial districts have experienced a renaissance driven by the redevelopment of the The Embarcadero (San Francisco), Embarcadero, including the neighborhoods South Beach, San Francisco, South Beach and Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay. The city's property values and household income have risen to among the highest in the nation,Haight-Ashbury
Haight-Ashbury () is a district of San Francisco, California, named for the intersection of Haight and Ashbury streets. It is also called The Haight and The Upper Haight. The neighborhood is known as one of the main centers of the counterculture ...
district during the 1960s, San Francisco became a center of Modern liberalism in the United States, liberal activism and of the counterculture
A counterculture is a culture whose values and norms of behavior differ substantially from those of mainstream society, sometimes diametrically opposed to mainstream cultural mores.Eric Donald Hirsch. ''The Dictionary of Cultural Literacy''. Hou ...
that arose at that time. The Democratic Party (United States), Democrats and to a lesser extent the Green Party (United States), Green Party have dominated Politics of San Francisco, city politics since the late 1970s, after the John Barbagelata, last serious Republican Party (United States), Republican challenger for city office 1975 San Francisco mayoral election, lost the 1975 mayoral election by a narrow margin. San Francisco has not voted more than 20% for a Republican Party (United States), Republican presidential or senatorial candidate since 1988 United States presidential election, 1988. In 2007, the city expanded its Medicaid and other indigent medical programs into the Healthy San Francisco program, which subsidy, subsidizes certain medical services for eligible residents.
Since 1993, the San Francisco Department of Public Health has distributed 400,000 Needle and syringe programmes#San Francisco, free syringes every month aimed at reducing HIV and other health risks for drug users, as well as providing disposal sites and services.
San Francisco also has had a very active environmental community. Starting with the founding of the Sierra Club in 1892 to the establishment of the non-profit Friends of the Urban Forest in 1981, San Francisco has been at the forefront of many global discussions regarding the environment. The 1980 San Francisco Mandatory Recycling and Composting Ordinance, San Francisco Recycling Program was one of the earliest curbside recycling programs. The city's GoSolarSF incentive promotes solar installations and the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission is rolling out the CleanPowerSF program to sell electricity from local renewable sources. SF Greasecycle is a program to recycle used cooking oil for conversion to biodiesel.
The Sunset Reservoir Solar Project, completed in 2010, installed 24,000 solar panels on the roof of the reservoir. The 5-megawatt plant more than tripled the city's 2-megawatt solar generation capacity when it opened in December 2010.
LGBT
 San Francisco has long had an LGBT-friendly LGBT culture in San Francisco, history. It was home to the first lesbian-rights organization in the United States, Daughters of Bilitis; the first openly gay person to run for public office in the United States, José Sarria; the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California,
San Francisco has long had an LGBT-friendly LGBT culture in San Francisco, history. It was home to the first lesbian-rights organization in the United States, Daughters of Bilitis; the first openly gay person to run for public office in the United States, José Sarria; the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, Harvey Milk
Harvey Bernard Milk (May 22, 1930 – November 27, 1978) was an American politician and the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California, as a member of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors. Milk was born and raised in ...
; the first openly lesbian judge appointed in the U.S., Mary C. Morgan; and the first transgender police commissioner, Theresa Sparks. The city's large gay population has created and sustained a politically and culturally active community over many decades, developing a powerful presence in San Francisco's civic life. Survey data released in 2015 by Gallup (company), Gallup places the proportion of LGBT adults in the San Francisco metro area at 6.2%, which is the highest proportion of the 50 most populous metropolitan areas as measured by the polling organization.
One of the most popular destinations for gay tourists internationally, the city hosts San Francisco Pride, one of the largest and oldest pride parades. San Francisco Pride events have been held continuously since 1972. The events are themed and a new theme is created each year. In 2013, over 1.5 million people attended, around 500,000 more than the previous year.
The Folsom Street Fair (FSF) is an annual BDSM and leather subculture street fair that is held in September, capping San Francisco's "Leather Pride Week". It started in 1984 and is California's third-largest single-day, outdoor spectator event and the world's largest leather event and showcase for BDSM products and culture.
The Folsom Street Fair (FSF) is an annual BDSM and leather subculture street fair that is held in September, capping San Francisco's "Leather Pride Week". It started in 1984 and is California's third-largest single-day, outdoor spectator event and the world's largest leather event and showcase for BDSM products and culture.
Performing arts
 San Francisco's San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center, War Memorial and Performing Arts Center hosts some of the most enduring performing-arts companies in the country. The War Memorial Opera House houses the
San Francisco's San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center, War Memorial and Performing Arts Center hosts some of the most enduring performing-arts companies in the country. The War Memorial Opera House houses the San Francisco Opera
San Francisco Opera (SFO) is an American opera company founded in 1923 by Gaetano Merola (1881–1953) based in San Francisco, California.
History
Gaetano Merola (1923–1953)
Merola's road to prominence in the Bay Area began in 1906 when h ...
, the second-largest opera company in North America as well as the San Francisco Ballet
San Francisco Ballet is the oldest ballet company in the United States, founded in 1933 as the San Francisco Opera Ballet under the leadership of ballet master Adolph Bolm. The company is currently based in the War Memorial Opera House, San Fra ...
, while the San Francisco Symphony plays in Louise M. Davies Symphony Hall, Davies Symphony Hall. Opened in 2013, the SFJAZZ Center hosts jazz performances year round.
The Fillmore is a music venue located in the Western Addition, San Francisco, Western Addition. It is the second incarnation of the historic venue that gained fame in the 1960s, housing the stage where now-famous musicians such as the Grateful Dead, Janis Joplin, Led Zeppelin and Jefferson Airplane first performed, fostering the San Francisco Sound.
San Francisco has a large number of List of theatres in San Francisco, theaters and live performance venues. Local theater companies have been noted for risk taking and innovation. The Tony Award-winning non-profit American Conservatory Theater (A.C.T.) is a member of the national League of Resident Theatres. Other local winners of the Regional Theatre Tony Award include the San Francisco Mime Troupe.
San Francisco theaters frequently host pre-Broadway theatre, Broadway engagements and tryout runs, and some original San Francisco productions have later moved to Broadway.
Museums
The San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
The San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA) is a modern and contemporary art museum located in San Francisco, California. A nonprofit organization, SFMOMA holds an internationally recognized collection of modern and contemporary art, and was ...
(SFMOMA) houses 20th century and contemporary works of art. It moved to its current building in the South of Market, San Francisco, South of Market neighborhood in 1995 and attracted more than 600,000 visitors annually. SFMOMA closed for renovation and expansion in 2013. The museum reopened on May 14, 2016, with an addition, designed by Snøhetta (company), Snøhetta, that has doubled the museum's size.
The California Palace of the Legion of Honor, Palace of the Legion of Honor holds primarily European antiquities and works of art at its Lincoln Park (San Francisco), Lincoln Park building modeled after its Palais de la Légion d'Honneur, Parisian namesake. The M. H. de Young Memorial Museum, de Young Museum in Golden Gate Park features American decorative pieces and anthropological holdings from Africa, Oceania and the Americas, while Asian art is housed in the Asian Art Museum of San Francisco, Asian Art Museum. Opposite the de Young stands the California Academy of Sciences
The California Academy of Sciences is a research institute and natural history museum in San Francisco, California, that is among the largest museums of natural history in the world, housing over 46 million specimens. The Academy began in 1853 ...
, a natural history museum that also hosts the Morrison Planetarium and Steinhart Aquarium. Located on Pier 15 on the Embarcadero, the Exploratorium is an interactive science museum. The Contemporary Jewish Museum is a non-collecting institution that hosts a broad array of temporary exhibitions. On Nob Hill, the San Francisco Cable Car Museum, Cable Car Museum is a working museum featuring the cable car powerhouse, which drives the cables.
Sports
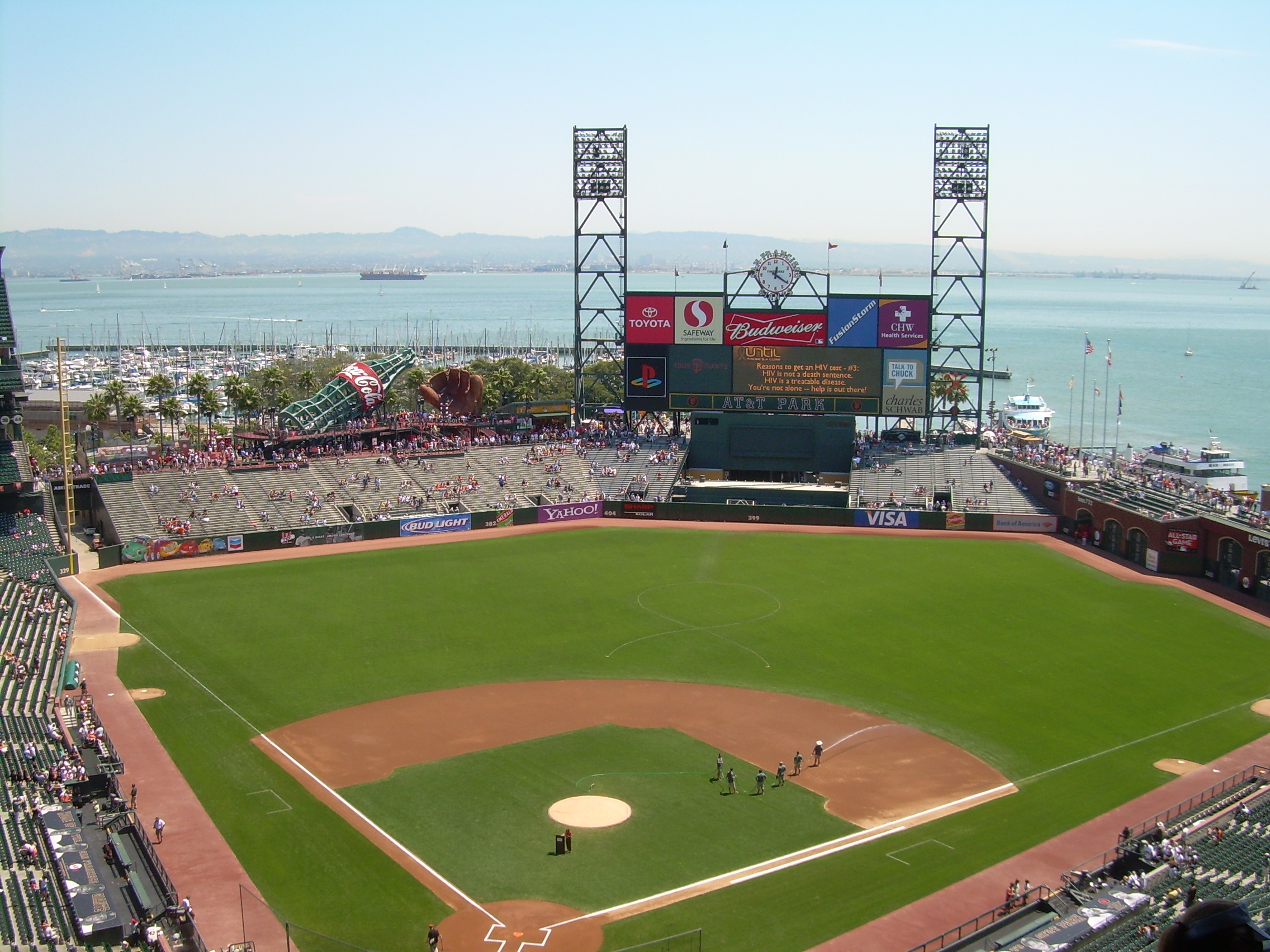
 Major League Baseball's
Major League Baseball's San Francisco Giants
The San Francisco Giants are an American professional baseball team based in San Francisco, California. The Giants compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) West division. Founded in 1883 as the New Yor ...
have played in San Francisco since moving from New York in 1958. The Giants play at Oracle Park, which opened in 2000. The Giants won World Series titles in 2010 World Series, 2010, 2012 World Series, 2012, and in 2014 World Series, 2014. The Giants have boasted such stars as Willie Mays, Willie McCovey and Barry Bonds. In 2012, San Francisco was ranked No. 1 in a study that examined which U.S. metro areas have produced the most Major Leaguers since 1920.
The San Francisco 49ers of the National Football League (NFL) began play in 1946 as an All-America Football Conference (AAFC) league charter member, moved to the NFL in 1950 and into Candlestick Park in 1971. The team began playing its home games at Levi's Stadium in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara in 2014. The 49ers won five Super Bowl titles between 1982 and 1995.
The San Francisco Warriors played in the NBA from 1962 to 1971, before being renamed the Golden State Warriors
The Golden State Warriors are an American professional basketball team based in San Francisco. The Warriors compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA), as a member of the league's Western Conference Pacific Division. Founded in 194 ...
prior to the 1971–1972 season in an attempt to present the team as a representation of the whole state of California, which had already adopted "The Golden State" nickname. The Warriors' arena, Chase Center, is located in San Francisco. They have won seven championships, and made five consecutive NBA Finals from 2015 to 2019, winning three of them. They won again in 2022, the franchise's first championship while residing in San Francisco proper.
At the collegiate level, the San Francisco Dons compete in NCAA Division I. Bill Russell led the Dons basketball team to NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, NCAA championships in 1955 and 1956. There is also the San Francisco State Gators, who compete in NCAA Division II. Oracle Park hosted the annual Fight Hunger Bowl college football game from 2002 through 2013 before it moved to Santa Clara.
There are a handful of lower-league soccer clubs in San Francisco playing mostly from April – June.
The Bay to Breakers footrace, held annually since 1912, is best known for colorful costumes and a celebratory community spirit. The San Francisco Marathon attracts more than 21,000 participants. The Escape from Alcatraz (triathlon), Escape from Alcatraz triathlon has, since 1980, attracted 2,000 top professional and amateur triathletes for its annual race. The Olympic Club, founded in 1860, is the oldest Sports club, athletic club in the United States. Its private golf course has hosted the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open on five occasions. San Francisco hosted the 2013 America's Cup yacht racing competition.
With an ideal climate for outdoor activities, San Francisco has ample resources and opportunities for amateur and participatory sports and recreation. There are more than of segregated cycle facilities, bicycle paths, lanes and bike routes in the city.
San Francisco residents have often ranked among the fittest in the country.Golden Gate Park
Golden Gate Park, located in San Francisco, California, United States, is a large urban park consisting of of public grounds. It is administered by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department, which began in 1871 to oversee the development ...
has miles of paved and unpaved running trails as well as a golf course and disc golf course.
Boating, sailing, windsurfing and kitesurfing are among the popular activities on San Francisco Bay, and the city maintains a yacht harbor in the Marina District, San Francisco, Marina District.
San Francisco also has had Esports teams, such as the Overwatch League's San Francisco Shock. Established in 2017, they won two back-to-back championship titles in 2019 and 2020.
Parks and recreation
 Several of San Francisco's parks and nearly all of its beaches form part of the regional Golden Gate National Recreation Area, one of the most visited units of the National Park Service, National Park system in the United States with over 13 million visitors a year. Among the GGNRA's attractions within the city are Ocean Beach, San Francisco, Ocean Beach, which runs along the Pacific Ocean shoreline and is frequented by a vibrant surfing community, and Baker Beach, which is located in a cove west of the Golden Gate and part of the
Several of San Francisco's parks and nearly all of its beaches form part of the regional Golden Gate National Recreation Area, one of the most visited units of the National Park Service, National Park system in the United States with over 13 million visitors a year. Among the GGNRA's attractions within the city are Ocean Beach, San Francisco, Ocean Beach, which runs along the Pacific Ocean shoreline and is frequented by a vibrant surfing community, and Baker Beach, which is located in a cove west of the Golden Gate and part of the Presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th and 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Spanish Philippines in particular, were cen ...
, a former military base. Also within the Presidio is Crissy Field, a former airfield that was restored to its natural salt marsh ecosystem. The GGNRA also administers Fort Funston, Lands End, San Francisco, Lands End, Fort Mason
Fort Mason, in San Francisco, California originated as a coastal defense site during the American Civil War. The nucleus of the property was owned by John C. Frémont and disputes over compensation by the United States continued into 1968. In 188 ...
, and Alcatraz. The National Park Service separately administers the San Francisco Maritime National Historical Park – a fleet of historic ships and waterfront property around Aquatic Park Historic District, Aquatic Park.
 There are more than List of parks in San Francisco, 220 parks maintained by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department. The largest and best-known city park is
There are more than List of parks in San Francisco, 220 parks maintained by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department. The largest and best-known city park is Golden Gate Park
Golden Gate Park, located in San Francisco, California, United States, is a large urban park consisting of of public grounds. It is administered by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department, which began in 1871 to oversee the development ...
, which stretches from the center of the city west to the Pacific Ocean. Once covered in native grasses and sand dunes, the park was conceived in the 1860s and was created by the extensive planting of thousands of non-native trees and plants. The large park is rich with cultural and natural attractions such as the Conservatory of Flowers, Japanese Tea Garden (San Francisco), Japanese Tea Garden and San Francisco Botanical Garden. Lake Merced is a fresh-water lake surrounded by parkland and near the San Francisco Zoo, a city-owned park that houses more than 250 animal species, many of which are endangered. The only List of California state parks, park managed by the California Department of Parks and Recreation, California State Park system located principally in San Francisco, Candlestick Point State Recreation Area, Candlestick Point was the state's first urban recreation area.
San Francisco is the first city in the U.S. to have a park within a 10-Minute Walk of every resident. It also ranks fifth in the U.S. for park access and quality in the 2018 ParkScore ranking of the top 100 park systems across the United States, according to the nonprofit Trust for Public Land.
Government
San Francisco—officially known as the City and County of San Francisco—is
consolidated city-county
a status it has held since the 1856 secession of what is now San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County. The members of the Board of Supervisors are elected as representatives of specific districts within the city.
The members of the Board of Supervisors are elected as representatives of specific districts within the city.Presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th and 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Spanish Philippines in particular, were cen ...
, Treasure Island
''Treasure Island'' (originally titled ''The Sea Cook: A Story for Boys''Hammond, J. R. 1984. "Treasure Island." In ''A Robert Louis Stevenson Companion'', Palgrave Macmillan Literary Companions. London: Palgrave Macmillan. .) is an adventure no ...
, and San Francisco Naval Shipyard, Hunters Point—a legacy still reflected in the annual celebration of Fleet Week. The State of California uses San Francisco as the home of the Supreme Court of California, state supreme court and other state agencies. Foreign governments maintain more than seventy consulates in San Francisco.
The municipal budget for fiscal year 2015–16 was $8.99 billion, and is one of the largest city budgets in the United States.
Education
Colleges and universities

 The
The University of California, San Francisco
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is a public land-grant research university in San Francisco, California. It is part of the University of California system and is dedicated entirely to health science and life science. It con ...
is the sole campus of the University of California, University of California system entirely dedicated to graduate education in health and biomedical sciences. It is ranked among the top five medical schools in the United States and operates the UCSF Medical Center, which ranks as the number one hospital in California and the number 5 in the country. UCSF is a major local employer, second in size only to the city and county government. A Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay campus was opened in 2003, complementing its original facility in List of hills in San Francisco, Parnassus Heights. It contains research space and facilities to foster biotechnology and life sciences entrepreneurship and will double the size of UCSF's research enterprise. All in all, UCSF operates more than 20 facilities across San Francisco. The University of California, Hastings College of the Law, founded in Civic Center, San Francisco, Civic Center in 1878, is the oldest law school in California and claims more judges on the state bench than any other institution.
San Francisco's two University of California institutions have recently formed an official affiliation in the UCSF/UC Hastings Consortium on Law, Science & Health Policy.
San Francisco State University
San Francisco State University (commonly referred to as San Francisco State, SF State and SFSU) is a public research university in San Francisco. As part of the 23-campus California State University system, the university offers 118 different ...
is part of the California State University system and is located near Lake Merced.[ The City College of San Francisco, with its main facility in the Ingleside district, is one of the largest two-year community colleges in the country. It has an enrollment of about 100,000 students and offers an extensive continuing education program.
Founded in 1855, the ]University of San Francisco
The University of San Francisco (USF) is a private Jesuit university in San Francisco, California. The university's main campus is located on a setting between the Golden Gate Bridge and Golden Gate Park. The main campus is nicknamed "The Hil ...
, a private Society of Jesus, Jesuit university located on Lone Mountain (California), Lone Mountain, is the oldest institution of higher education in San Francisco and one of the oldest universities established west of the Mississippi River. Golden Gate University is a private, nonsectarian, coeducational university formed in 1901 and located in the Financial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
.
With an enrollment of 13,000 students, the Academy of Art University is the largest institute of art and design in the nation. Founded in 1871, the San Francisco Art Institute is the oldest art school west of the Mississippi. The California College of the Arts, located north of Potrero Hill, San Francisco, Potrero Hill, has programs in architecture, fine arts, design, and writing. The San Francisco Conservatory of Music, the only independent music school on the West Coast, grants degrees in orchestral instruments, chamber music, composition, and conducting. The California Culinary Academy, associated with the Le Cordon Bleu program, offers programs in the culinary arts, baking and pastry arts, and hospitality and restaurant management.
California Institute of Integral Studies, founded in 1968, offers a variety of graduate programs in its Schools of Professional Psychology & Health, and Consciousness and Transformation.
Primary and secondary schools
Public school (government funded), Public schools are run by the San Francisco Unified School District, which covers the entire city and county, as well as the California State Board of Education for some charter schools. Lowell High School (San Francisco), Lowell High School, the oldest public high school in the U.S. west of the Mississippi River, Mississippi, and the smaller School of the Arts High School (San Francisco), School of the Arts High School are two of San Francisco's magnet schools at the secondary level. Public school students attend schools based on an assignment system rather than neighborhood proximity.
Just under 30% of the city's school-age population attends one of San Francisco's more than 100 private school, private or parochial schools, compared to a 10% rate nationwide.
Early education
San Francisco has nearly 300 preschool programs primarily operated by Head Start (program), Head Start, San Francisco Unified School District, private for-profit, private non-profit and Child care#Licensed home day care or family child care, family child care providers. All 4-year-old children living in San Francisco are offered Universal preschool, universal access to preschool through the Preschool for All program.
Media
 The major daily newspaper in San Francisco is the ''San Francisco Chronicle'', which is currently Northern California's most widely circulated newspaper. The Chronicle is most famous for a former columnist, the late Herb Caen, whose daily musings attracted critical acclaim and represented the "voice of San Francisco". ''The San Francisco Examiner'', once the cornerstone of William Randolph Hearst's media empire and the home of Ambrose Bierce, declined in circulation over the years and now takes the form of a free daily tabloid, under new ownership. ''Sing Tao Daily'' claims to be the largest of several Chinese language dailies that serve the Bay Area. ''SF Weekly, SF Weekly'' is the city's alternative weekly newspaper. ''San Francisco (magazine), San Francisco'' and ''7x7 (magazine), 7x7'' are major glossy magazines about San Francisco. The national newsmagazine ''Mother Jones (magazine), Mother Jones'' is also based in San Francisco. San Francisco is home to online-only media publications such as SFist, and ''AsianWeek'', which was the first and the largest English language publication focusing on Asian Americans.
The San Francisco Bay Area is the sixth-largest designated market area, television market and the fourth-largest designated market area, radio market in the U.S. The city's oldest radio station, KCBS (AM), KCBS, began as an experimental station in San Jose in 1909, before the beginning of commercial broadcasting. KALW was the city's first FM radio station when it signed on the air in 1941. The city's first television station was KPIX, which began broadcasting in 1948.
All major U.S. television networks have List of television stations in the San Francisco Bay Area, affiliates serving the region, with most of them based in the city. CNN, MSNBC, BBC, RT (TV network), Russia Today, and CCTV America also have regional news bureaus in San Francisco. Bloomberg West was launched in 2011 from a studio on the Embarcadero and CNBC broadcasts from One Market Plaza since 2015. ESPN uses the local ABC studio for their broadcasting. The regional sports network, Comcast SportsNet Bay Area and its sister station Comcast SportsNet California, are both located in San Francisco. The Pac-12 Network is also based in San Francisco.
Public broadcasting outlets include both a KQED-TV, television station and a KQED-FM, radio station, both broadcasting under the call letters KQED from a facility near the Potrero Hill, San Francisco, Potrero Hill neighborhood. KQED-FM is the most-listened-to National Public Radio affiliate in the country. Another local broadcaster, KPOO, is an independent, African-American owned and operated noncommercial radio station established in 1971. CNET Networks, CNET, founded 1994, and Salon.com, 1995, are based in San Francisco.
San Francisco-based inventors made important contributions to modern media. During the 1870s, Eadweard Muybridge began recording motion photographically and invented a zoopraxiscope with which to view his recordings. These were the first motion pictures. Then in 1927, Philo Farnsworth's image dissector camera tube transmitted its first image. This was a refinement of the first television system which was invented by John Logie Baird in 1926.
The major daily newspaper in San Francisco is the ''San Francisco Chronicle'', which is currently Northern California's most widely circulated newspaper. The Chronicle is most famous for a former columnist, the late Herb Caen, whose daily musings attracted critical acclaim and represented the "voice of San Francisco". ''The San Francisco Examiner'', once the cornerstone of William Randolph Hearst's media empire and the home of Ambrose Bierce, declined in circulation over the years and now takes the form of a free daily tabloid, under new ownership. ''Sing Tao Daily'' claims to be the largest of several Chinese language dailies that serve the Bay Area. ''SF Weekly, SF Weekly'' is the city's alternative weekly newspaper. ''San Francisco (magazine), San Francisco'' and ''7x7 (magazine), 7x7'' are major glossy magazines about San Francisco. The national newsmagazine ''Mother Jones (magazine), Mother Jones'' is also based in San Francisco. San Francisco is home to online-only media publications such as SFist, and ''AsianWeek'', which was the first and the largest English language publication focusing on Asian Americans.
The San Francisco Bay Area is the sixth-largest designated market area, television market and the fourth-largest designated market area, radio market in the U.S. The city's oldest radio station, KCBS (AM), KCBS, began as an experimental station in San Jose in 1909, before the beginning of commercial broadcasting. KALW was the city's first FM radio station when it signed on the air in 1941. The city's first television station was KPIX, which began broadcasting in 1948.
All major U.S. television networks have List of television stations in the San Francisco Bay Area, affiliates serving the region, with most of them based in the city. CNN, MSNBC, BBC, RT (TV network), Russia Today, and CCTV America also have regional news bureaus in San Francisco. Bloomberg West was launched in 2011 from a studio on the Embarcadero and CNBC broadcasts from One Market Plaza since 2015. ESPN uses the local ABC studio for their broadcasting. The regional sports network, Comcast SportsNet Bay Area and its sister station Comcast SportsNet California, are both located in San Francisco. The Pac-12 Network is also based in San Francisco.
Public broadcasting outlets include both a KQED-TV, television station and a KQED-FM, radio station, both broadcasting under the call letters KQED from a facility near the Potrero Hill, San Francisco, Potrero Hill neighborhood. KQED-FM is the most-listened-to National Public Radio affiliate in the country. Another local broadcaster, KPOO, is an independent, African-American owned and operated noncommercial radio station established in 1971. CNET Networks, CNET, founded 1994, and Salon.com, 1995, are based in San Francisco.
San Francisco-based inventors made important contributions to modern media. During the 1870s, Eadweard Muybridge began recording motion photographically and invented a zoopraxiscope with which to view his recordings. These were the first motion pictures. Then in 1927, Philo Farnsworth's image dissector camera tube transmitted its first image. This was a refinement of the first television system which was invented by John Logie Baird in 1926.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Public transportation
 Transit is the most used form of transportation every day in San Francisco. Every weekday, more than 560,000 people travel on Muni's 69 bus routes and more than 140,000 customers ride the Muni Metro light rail system.
Transit is the most used form of transportation every day in San Francisco. Every weekday, more than 560,000 people travel on Muni's 69 bus routes and more than 140,000 customers ride the Muni Metro light rail system.San Francisco Municipal Railway
The San Francisco Municipal Railway (SF Muni or Muni), is the public transit system for the City and County of San Francisco. It operates a system of bus routes (including trolleybuses), the Muni Metro light rail system, three historic cabl ...
, primarily known as Muni, is the primary public transit system of San Francisco. Muni is the seventh-largest transit system in the United States, with 210,848,310 rides in 2006. The system operates a combined light rail and subway system, the Muni Metro, as well as large bus and Trolleybuses in San Francisco, trolley coach networks.East Bay
The East Bay is the eastern region of the San Francisco Bay Area and includes cities along the eastern shores of the San Francisco Bay and San Pablo Bay. The region has grown to include inland communities in Alameda and Contra Costa counties ...
and San Jose through the underwater Transbay Tube. The line runs under Market Street to Civic Center, San Francisco, Civic Center where it turns south to the Mission District, the southern part of the city, and through northern San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County, to the San Francisco International Airport, and Millbrae, California, Millbrae.San Francisco Peninsula
The San Francisco Peninsula is a peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area that separates San Francisco Bay from the Pacific Ocean. On its northern tip is the City and County of San Francisco. Its southern base is Mountain View, south of Palo A ...
to San Jose, California, San Jose. San Francisco Bay Ferry operates from the San Francisco Ferry Building, Ferry Building and Pier 39 to points in Oakland, California, Oakland, Alameda, California, Alameda, Bay Farm Island, Alameda, California, Bay Farm Island, South San Francisco, California, South San Francisco, and north to Vallejo, California, Vallejo in Solano County, California, Solano County. The Golden Gate Ferry is the other ferry operator with service between San Francisco and Marin County. SolTrans runs supplemental bus service between the Ferry Building and Vallejo.
San Francisco was an early adopter of carsharing in America. The non-profit City CarShare opened in 2001. Zipcar closely followed.
To accommodate the large amount of San Francisco citizens who commute to the Silicon Valley daily, employers like Genentech, Google, and Apple Inc., Apple have begun to provide private bus transportation for their employees, from San Francisco locations. These buses have quickly become a heated topic of debate within the city, as San Francisco tech bus protests, protesters claim they block bus lanes and delay public buses.
San Francisco Bay Ferry operates from the San Francisco Ferry Building, Ferry Building and Pier 39 to points in Oakland, California, Oakland, Alameda, California, Alameda, Bay Farm Island, Alameda, California, Bay Farm Island, South San Francisco, California, South San Francisco, and north to Vallejo, California, Vallejo in Solano County, California, Solano County. The Golden Gate Ferry is the other ferry operator with service between San Francisco and Marin County. SolTrans runs supplemental bus service between the Ferry Building and Vallejo.
San Francisco was an early adopter of carsharing in America. The non-profit City CarShare opened in 2001. Zipcar closely followed.
To accommodate the large amount of San Francisco citizens who commute to the Silicon Valley daily, employers like Genentech, Google, and Apple Inc., Apple have begun to provide private bus transportation for their employees, from San Francisco locations. These buses have quickly become a heated topic of debate within the city, as San Francisco tech bus protests, protesters claim they block bus lanes and delay public buses.
Freeways and roads
In 2014, only 41.3% of residents commuted by driving alone or carpooling in private vehicles in San Francisco, a decline from 48.6% in 2000.Golden Gate Bridge
The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Golden Gate, the strait connecting San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean. The structure links the U.S. city of San Francisco, California—the northern tip of the San Francisco Pen ...
, the only direct automobile link to Marin County and the North Bay.
As part of the retrofitting of the Golden Gate Bridge and installation of a suicide barrier, starting in 2019 the railings on the west side of the pedestrian walkway were replaced with thinner, more flexible slat (aircraft), slats in order to improve the bridge's aerodynamic tolerance of high wind to . Starting in June 2020, reports were received of a loud hum produced by the new railing slats, heard across the city when a strong west wind was blowing.
= Vision Zero
=
In 2014, San Francisco committed to Vision Zero, with the goal of ending all traffic fatalities caused by motor vehicles within the city by 2024. San Francisco's Vision Zero plan calls for investing in engineering, enforcement, and education, and focusing on dangerous intersections. In 2013, 25 people were killed by car and truck drivers while walking and biking in the city and 9 car drivers and passengers were killed in collisions. In 2019, 42 people were killed in traffic collisions in San Francisco.
Airports
 Though located south of downtown in Unincorporated area, unincorporated San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County, San Francisco International Airport (SFO) is under the jurisdiction of the City and County of San Francisco. SFO is a hub for United Airlines
Though located south of downtown in Unincorporated area, unincorporated San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County, San Francisco International Airport (SFO) is under the jurisdiction of the City and County of San Francisco. SFO is a hub for United AirlinesSan Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
, it is greater driving distance from San Francisco.
Cycling and walking
 Cycling is a popular mode of transportation in San Francisco, with 75,000 residents commuting by bicycle each day.
Cycling is a popular mode of transportation in San Francisco, with 75,000 residents commuting by bicycle each day.
Public safety
The San Francisco Police Department was founded in 1849. The portions of the Golden Gate National Recreation Area located within the city, including the Presidio
A presidio ( en, jail, fortification) was a fortified base established by the Spanish Empire around between 16th and 18th centuries in areas in condition of their control or influence. The presidios of Spanish Philippines in particular, were cen ...
and Ocean Beach, San Francisco, Ocean Beach, are patrolled by the United States Park Police.
The San Francisco Fire Department provides both fire suppression and emergency medical services to the city.
Nicknames
Bay Area residents generally refer to San Francisco as "the City".
Sister cities
San Francisco participates in the Sister Cities International, Sister Cities program. A total of 41 consulates general and 23 honorary consulates have offices in the San Francisco Bay Area.
Notable residents
See also
* San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area Go ...
* List of cities and towns in California
* List of counties in California
* List of people from San Francisco
* Northern California Megaregion
* Ships lost in San Francisco
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Heller, Nathan
''Bay Watched – How San Francisco's New Entrepreneurial Culture is Changing the Country'' (article)
(October 2013). ''The New Yorker''
*
*
*
*
* Solnit, Rebecca. ''Infinite City: A San Francisco Atlas'' (University of California Press, 2010). 144 pp.
online review
*
*
* Winfield, P.H., ''The Charter of San Francisco'' (The fortnightly review Vol. 157–58:2 (1945), p. 69–75)
External links
*
Virtual Museum of the City of San Francisco
{{Authority control
San Francisco,
1776 establishments in Alta California
1850 establishments in California
California counties
Cities in the San Francisco Bay Area
Consolidated city-counties
Counties in the San Francisco Bay Area
County seats in California
Hudson's Bay Company trading posts
Incorporated cities and towns in California
Populated coastal places in California
Populated places established in 1776
Port cities in California
Spanish mission settlements in North America
Majority-minority counties in California
 The first European maritime presence occurred on August 5, 1775, when the Spanish ''San Carlos'' commanded by Juan Manuel de Ayala became the first ship to anchor in the bay. Soon after, on March 28, 1776, the Spanish explorer
The first European maritime presence occurred on August 5, 1775, when the Spanish ''San Carlos'' commanded by Juan Manuel de Ayala became the first ship to anchor in the bay. Soon after, on March 28, 1776, the Spanish explorer  Yerba Buena began to attract American and European settlers; an 1842 census listed 21 residents (11%) born in the United States or Europe, as well as one Filipino merchant. Commodore
Yerba Buena began to attract American and European settlers; an 1842 census listed 21 residents (11%) born in the United States or Europe, as well as one Filipino merchant. Commodore  California was quickly granted statehood in 1850, and the U.S. military built Fort Point at the
California was quickly granted statehood in 1850, and the U.S. military built Fort Point at the  Entrepreneurs sought to capitalize on the wealth generated by the Gold Rush. Silver discoveries, including the
Entrepreneurs sought to capitalize on the wealth generated by the Gold Rush. Silver discoveries, including the  During this period, San Francisco built some of its most important infrastructure. Civil Engineer
During this period, San Francisco built some of its most important infrastructure. Civil Engineer  In ensuing years, the city solidified its standing as a financial capital; in the wake of the 1929 stock market crash, not a single San Francisco-based bank failed. Indeed, it was at the height of the
In ensuing years, the city solidified its standing as a financial capital; in the wake of the 1929 stock market crash, not a single San Francisco-based bank failed. Indeed, it was at the height of the  Over this period, San Francisco became a magnet for America's
Over this period, San Francisco became a magnet for America's  San Francisco is located on the West Coast of the United States at the north end of the
San Francisco is located on the West Coast of the United States at the north end of the 
 The historic center of San Francisco is the northeast quadrant of the city anchored by Market Street (San Francisco), Market Street and the waterfront. It is here that the
The historic center of San Francisco is the northeast quadrant of the city anchored by Market Street (San Francisco), Market Street and the waterfront. It is here that the  Among major U.S. cities, San Francisco has the coolest daily mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures for June, July, and August.
During the summer, rising hot air in California's interior valleys creates a low-pressure area that draws winds from the North Pacific High through the
Among major U.S. cities, San Francisco has the coolest daily mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures for June, July, and August.
During the summer, rising hot air in California's interior valleys creates a low-pressure area that draws winds from the North Pacific High through the  According to a 2018 study by the Jewish Community Federation of San Francisco, Jews make up 10% (80,000) of the city's population, making Judaism the second-largest religion in San Francisco after Christianity. A prior 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, the largest religious groupings in San Francisco's San Francisco–Oakland–Hayward, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, metropolitan area are Christianity, Christians (48%), followed by those of Irreligion, no religion (35%), Hinduism, Hindus (5%), Judaism, Jews (3%), Buddhism, Buddhists (2%), Islam, Muslims (1%) and a variety of other religions have smaller followings. According to the same study by the Pew Research Center, about 20% of residents in the area are Protestantism, Protestant, and 25% professing Catholic Church, Roman Catholic beliefs. Meanwhile, 10% of the residents in metropolitan San Francisco identify as agnostics, while 5% identify as Atheism, atheists.
, 55% (411,728) of San Francisco residents spoke only English language, English at home, while 19% (140,302) spoke a variety of Chinese (mostly Taishanese and Cantonese), 12% (88,147)
According to a 2018 study by the Jewish Community Federation of San Francisco, Jews make up 10% (80,000) of the city's population, making Judaism the second-largest religion in San Francisco after Christianity. A prior 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, the largest religious groupings in San Francisco's San Francisco–Oakland–Hayward, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, metropolitan area are Christianity, Christians (48%), followed by those of Irreligion, no religion (35%), Hinduism, Hindus (5%), Judaism, Jews (3%), Buddhism, Buddhists (2%), Islam, Muslims (1%) and a variety of other religions have smaller followings. According to the same study by the Pew Research Center, about 20% of residents in the area are Protestantism, Protestant, and 25% professing Catholic Church, Roman Catholic beliefs. Meanwhile, 10% of the residents in metropolitan San Francisco identify as agnostics, while 5% identify as Atheism, atheists.
, 55% (411,728) of San Francisco residents spoke only English language, English at home, while 19% (140,302) spoke a variety of Chinese (mostly Taishanese and Cantonese), 12% (88,147)  According to academic Rob Wilson, San Francisco is a global city, a status that pre-dated the city's popularity during the
According to academic Rob Wilson, San Francisco is a global city, a status that pre-dated the city's popularity during the  The legacy of the California Gold Rush turned San Francisco into the principal banking and finance center of the
The legacy of the California Gold Rush turned San Francisco into the principal banking and finance center of the  Beginning in the 1990s, San Francisco's economy diversified away from finance and tourism towards the growing fields of high tech, biotechnology, and medical research. Technology jobs accounted for just 1 percent of San Francisco's economy in 1990, growing to 4 percent in 2010 and an estimated 8 percent by the end of 2013. San Francisco became a center of Internet Startup company, start-up companies during the dot-com bubble of the 1990s and the subsequent social media boom of the late 2000s (decade). Since 2010, San Francisco proper has attracted an increasing share of venture capital investments as compared to nearby Silicon Valley, attracting 423 financings worth US$4.58 billion in 2013. In 2004, the city approved a payroll tax exemption for biotechnology companies to foster growth in the Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay neighborhood, site of a second campus and hospital of the
Beginning in the 1990s, San Francisco's economy diversified away from finance and tourism towards the growing fields of high tech, biotechnology, and medical research. Technology jobs accounted for just 1 percent of San Francisco's economy in 1990, growing to 4 percent in 2010 and an estimated 8 percent by the end of 2013. San Francisco became a center of Internet Startup company, start-up companies during the dot-com bubble of the 1990s and the subsequent social media boom of the late 2000s (decade). Since 2010, San Francisco proper has attracted an increasing share of venture capital investments as compared to nearby Silicon Valley, attracting 423 financings worth US$4.58 billion in 2013. In 2004, the city approved a payroll tax exemption for biotechnology companies to foster growth in the Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay neighborhood, site of a second campus and hospital of the  Manufacturing in the United States, Like many U.S. cities, San Francisco once had a significant manufacturing sector employing nearly 60,000 workers in 1969, but nearly all production left for cheaper locations by the 1980s.
, San Francisco has seen a small resurgence in manufacturing, with more than 4,000 manufacturing jobs across 500 companies, doubling since 2011. The city's largest manufacturing employer is Anchor Brewing Company, and the largest by revenue is Timbuk2.
As of the first quarter of 2022, the median value of homes in San Francisco County was $1,297,030. It ranked third in the US for counties with highest median home value, behind Nantucket and San Mateo County, California, San Mateo.
Manufacturing in the United States, Like many U.S. cities, San Francisco once had a significant manufacturing sector employing nearly 60,000 workers in 1969, but nearly all production left for cheaper locations by the 1980s.
, San Francisco has seen a small resurgence in manufacturing, with more than 4,000 manufacturing jobs across 500 companies, doubling since 2011. The city's largest manufacturing employer is Anchor Brewing Company, and the largest by revenue is Timbuk2.
As of the first quarter of 2022, the median value of homes in San Francisco County was $1,297,030. It ranked third in the US for counties with highest median home value, behind Nantucket and San Mateo County, California, San Mateo.

 Tourism is one of the city's largest private-sector industries, accounting for more than one out of seven jobs in the city. The city's San Francisco in popular culture, frequent portrayal in music, film, and popular culture has made the city and its landmarks recognizable worldwide. In 2016, it attracted the fifth-highest number of foreign tourists of any city in the United States. More than 25 million visitors arrived in San Francisco in 2016, adding US$9.96 billion to the economy.
With a large hotel infrastructure and a world-class convention facility in the Moscone Center, San Francisco is a popular destination for annual conventions and conferences.
Some of the most popular tourist attractions in San Francisco noted by the Travel Channel include the
Tourism is one of the city's largest private-sector industries, accounting for more than one out of seven jobs in the city. The city's San Francisco in popular culture, frequent portrayal in music, film, and popular culture has made the city and its landmarks recognizable worldwide. In 2016, it attracted the fifth-highest number of foreign tourists of any city in the United States. More than 25 million visitors arrived in San Francisco in 2016, adding US$9.96 billion to the economy.
With a large hotel infrastructure and a world-class convention facility in the Moscone Center, San Francisco is a popular destination for annual conventions and conferences.
Some of the most popular tourist attractions in San Francisco noted by the Travel Channel include the  Although the
Although the  Since the 1990s, the demand for skilled information technology workers from local startups and nearby Silicon Valley has attracted white-collar workers from all over the world and created a high standard of living in San Francisco. Many neighborhoods that were once blue-collar, middle, and lower class have been Gentrification, gentrifying, as many of the city's traditional business and industrial districts have experienced a renaissance driven by the redevelopment of the The Embarcadero (San Francisco), Embarcadero, including the neighborhoods South Beach, San Francisco, South Beach and Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay. The city's property values and household income have risen to among the highest in the nation, creating a large and upscale restaurant, retail, and entertainment scene. According to a 2014 quality of life survey of global cities, San Francisco has the Most livable cities, highest quality of living of any U.S. city. However, due to the exceptionally high cost of living, many of the city's middle and lower-class families have been leaving the city for the outer suburbs of the Bay Area, or for California's Central Valley (California), Central Valley. By June 2, 2015, the median rent was reported to be as high as $4,225. The high cost of living is due in part to restrictive planning laws which limit new residential construction.
The international character that San Francisco has enjoyed since its founding is continued today by large numbers of immigrants from Asia and Latin America. With 39% of its residents born overseas, San Francisco has numerous neighborhoods filled with businesses and civic institutions catering to new arrivals. In particular, the arrival of many ethnic Chinese, which began to accelerate in the 1970s, has complemented the long-established community historically based in Chinatown throughout the city and has transformed the annual San Francisco Chinese New Year Festival and Parade, Chinese New Year Parade into the largest event of its kind in its hemisphere.
With the arrival of the Beat Generation, "beat" writers and artists of the 1950s and societal changes culminating in the Summer of Love in the
Since the 1990s, the demand for skilled information technology workers from local startups and nearby Silicon Valley has attracted white-collar workers from all over the world and created a high standard of living in San Francisco. Many neighborhoods that were once blue-collar, middle, and lower class have been Gentrification, gentrifying, as many of the city's traditional business and industrial districts have experienced a renaissance driven by the redevelopment of the The Embarcadero (San Francisco), Embarcadero, including the neighborhoods South Beach, San Francisco, South Beach and Mission Bay, San Francisco, Mission Bay. The city's property values and household income have risen to among the highest in the nation, creating a large and upscale restaurant, retail, and entertainment scene. According to a 2014 quality of life survey of global cities, San Francisco has the Most livable cities, highest quality of living of any U.S. city. However, due to the exceptionally high cost of living, many of the city's middle and lower-class families have been leaving the city for the outer suburbs of the Bay Area, or for California's Central Valley (California), Central Valley. By June 2, 2015, the median rent was reported to be as high as $4,225. The high cost of living is due in part to restrictive planning laws which limit new residential construction.
The international character that San Francisco has enjoyed since its founding is continued today by large numbers of immigrants from Asia and Latin America. With 39% of its residents born overseas, San Francisco has numerous neighborhoods filled with businesses and civic institutions catering to new arrivals. In particular, the arrival of many ethnic Chinese, which began to accelerate in the 1970s, has complemented the long-established community historically based in Chinatown throughout the city and has transformed the annual San Francisco Chinese New Year Festival and Parade, Chinese New Year Parade into the largest event of its kind in its hemisphere.
With the arrival of the Beat Generation, "beat" writers and artists of the 1950s and societal changes culminating in the Summer of Love in the  San Francisco has long had an LGBT-friendly LGBT culture in San Francisco, history. It was home to the first lesbian-rights organization in the United States, Daughters of Bilitis; the first openly gay person to run for public office in the United States, José Sarria; the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California,
San Francisco has long had an LGBT-friendly LGBT culture in San Francisco, history. It was home to the first lesbian-rights organization in the United States, Daughters of Bilitis; the first openly gay person to run for public office in the United States, José Sarria; the first openly gay man to be elected to public office in California,  San Francisco's San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center, War Memorial and Performing Arts Center hosts some of the most enduring performing-arts companies in the country. The War Memorial Opera House houses the
San Francisco's San Francisco War Memorial and Performing Arts Center, War Memorial and Performing Arts Center hosts some of the most enduring performing-arts companies in the country. The War Memorial Opera House houses the 
 Major League Baseball's
Major League Baseball's  Several of San Francisco's parks and nearly all of its beaches form part of the regional Golden Gate National Recreation Area, one of the most visited units of the National Park Service, National Park system in the United States with over 13 million visitors a year. Among the GGNRA's attractions within the city are Ocean Beach, San Francisco, Ocean Beach, which runs along the Pacific Ocean shoreline and is frequented by a vibrant surfing community, and Baker Beach, which is located in a cove west of the Golden Gate and part of the
Several of San Francisco's parks and nearly all of its beaches form part of the regional Golden Gate National Recreation Area, one of the most visited units of the National Park Service, National Park system in the United States with over 13 million visitors a year. Among the GGNRA's attractions within the city are Ocean Beach, San Francisco, Ocean Beach, which runs along the Pacific Ocean shoreline and is frequented by a vibrant surfing community, and Baker Beach, which is located in a cove west of the Golden Gate and part of the  There are more than List of parks in San Francisco, 220 parks maintained by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department. The largest and best-known city park is
There are more than List of parks in San Francisco, 220 parks maintained by the San Francisco Recreation & Parks Department. The largest and best-known city park is  The members of the Board of Supervisors are elected as representatives of specific districts within the city. Upon the death or resignation of the mayor, the President of the Board of Supervisors becomes acting mayor until the full Board elects an interim replacement for the remainder of the term. In 1978, Dianne Feinstein assumed the office following the assassination of George Moscone and was later selected by the board to finish the term. In 2011, Ed Lee (politician), Ed Lee was selected by the board to finish the term of Gavin Newsom, who resigned to take office as Lieutenant Governor of California. Lee (who won two elections to remain mayor) was temporarily replaced by San Francisco Board of Supervisors President London Breed after he died on December 12, 2017. Supervisor Mark Farrell (politician), Mark Farrell was appointed by the Board of Supervisors to finish Lee's term on January 23, 2018.
Because of its unique city-county status, the local government is able to exercise jurisdiction over certain property outside city limits. San Francisco International Airport, though located in San Mateo County, is owned and operated by the City and County of San Francisco. San Francisco's largest jail complex (County Jail No. 5) is located in San Mateo County, in an unincorporated area adjacent to San Bruno, California, San Bruno. San Francisco was also granted a perpetual leasehold over the Hetch Hetchy Valley and drainage basin, watershed in Yosemite National Park by the Raker Act in 1913.
San Francisco serves as the regional hub for many arms of the federal bureaucracy, including the Ninth Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals, U.S. Court of Appeals, the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, Federal Reserve Bank, and the United States Mint, U.S. Mint. Until Base Realignment and Closure, decommissioning in the early 1990s, the city had major military installations at the
The members of the Board of Supervisors are elected as representatives of specific districts within the city. Upon the death or resignation of the mayor, the President of the Board of Supervisors becomes acting mayor until the full Board elects an interim replacement for the remainder of the term. In 1978, Dianne Feinstein assumed the office following the assassination of George Moscone and was later selected by the board to finish the term. In 2011, Ed Lee (politician), Ed Lee was selected by the board to finish the term of Gavin Newsom, who resigned to take office as Lieutenant Governor of California. Lee (who won two elections to remain mayor) was temporarily replaced by San Francisco Board of Supervisors President London Breed after he died on December 12, 2017. Supervisor Mark Farrell (politician), Mark Farrell was appointed by the Board of Supervisors to finish Lee's term on January 23, 2018.
Because of its unique city-county status, the local government is able to exercise jurisdiction over certain property outside city limits. San Francisco International Airport, though located in San Mateo County, is owned and operated by the City and County of San Francisco. San Francisco's largest jail complex (County Jail No. 5) is located in San Mateo County, in an unincorporated area adjacent to San Bruno, California, San Bruno. San Francisco was also granted a perpetual leasehold over the Hetch Hetchy Valley and drainage basin, watershed in Yosemite National Park by the Raker Act in 1913.
San Francisco serves as the regional hub for many arms of the federal bureaucracy, including the Ninth Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals, U.S. Court of Appeals, the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, Federal Reserve Bank, and the United States Mint, U.S. Mint. Until Base Realignment and Closure, decommissioning in the early 1990s, the city had major military installations at the  The
The  The major daily newspaper in San Francisco is the ''San Francisco Chronicle'', which is currently Northern California's most widely circulated newspaper. The Chronicle is most famous for a former columnist, the late Herb Caen, whose daily musings attracted critical acclaim and represented the "voice of San Francisco". ''The San Francisco Examiner'', once the cornerstone of William Randolph Hearst's media empire and the home of Ambrose Bierce, declined in circulation over the years and now takes the form of a free daily tabloid, under new ownership. ''Sing Tao Daily'' claims to be the largest of several Chinese language dailies that serve the Bay Area. ''SF Weekly, SF Weekly'' is the city's alternative weekly newspaper. ''San Francisco (magazine), San Francisco'' and ''7x7 (magazine), 7x7'' are major glossy magazines about San Francisco. The national newsmagazine ''Mother Jones (magazine), Mother Jones'' is also based in San Francisco. San Francisco is home to online-only media publications such as SFist, and ''AsianWeek'', which was the first and the largest English language publication focusing on Asian Americans.
The San Francisco Bay Area is the sixth-largest designated market area, television market and the fourth-largest designated market area, radio market in the U.S. The city's oldest radio station, KCBS (AM), KCBS, began as an experimental station in San Jose in 1909, before the beginning of commercial broadcasting. KALW was the city's first FM radio station when it signed on the air in 1941. The city's first television station was KPIX, which began broadcasting in 1948.
All major U.S. television networks have List of television stations in the San Francisco Bay Area, affiliates serving the region, with most of them based in the city. CNN, MSNBC, BBC, RT (TV network), Russia Today, and CCTV America also have regional news bureaus in San Francisco. Bloomberg West was launched in 2011 from a studio on the Embarcadero and CNBC broadcasts from One Market Plaza since 2015. ESPN uses the local ABC studio for their broadcasting. The regional sports network, Comcast SportsNet Bay Area and its sister station Comcast SportsNet California, are both located in San Francisco. The Pac-12 Network is also based in San Francisco.
Public broadcasting outlets include both a KQED-TV, television station and a KQED-FM, radio station, both broadcasting under the call letters KQED from a facility near the Potrero Hill, San Francisco, Potrero Hill neighborhood. KQED-FM is the most-listened-to National Public Radio affiliate in the country. Another local broadcaster, KPOO, is an independent, African-American owned and operated noncommercial radio station established in 1971. CNET Networks, CNET, founded 1994, and Salon.com, 1995, are based in San Francisco.
San Francisco-based inventors made important contributions to modern media. During the 1870s, Eadweard Muybridge began recording motion photographically and invented a zoopraxiscope with which to view his recordings. These were the first motion pictures. Then in 1927, Philo Farnsworth's image dissector camera tube transmitted its first image. This was a refinement of the first television system which was invented by John Logie Baird in 1926.
The major daily newspaper in San Francisco is the ''San Francisco Chronicle'', which is currently Northern California's most widely circulated newspaper. The Chronicle is most famous for a former columnist, the late Herb Caen, whose daily musings attracted critical acclaim and represented the "voice of San Francisco". ''The San Francisco Examiner'', once the cornerstone of William Randolph Hearst's media empire and the home of Ambrose Bierce, declined in circulation over the years and now takes the form of a free daily tabloid, under new ownership. ''Sing Tao Daily'' claims to be the largest of several Chinese language dailies that serve the Bay Area. ''SF Weekly, SF Weekly'' is the city's alternative weekly newspaper. ''San Francisco (magazine), San Francisco'' and ''7x7 (magazine), 7x7'' are major glossy magazines about San Francisco. The national newsmagazine ''Mother Jones (magazine), Mother Jones'' is also based in San Francisco. San Francisco is home to online-only media publications such as SFist, and ''AsianWeek'', which was the first and the largest English language publication focusing on Asian Americans.
The San Francisco Bay Area is the sixth-largest designated market area, television market and the fourth-largest designated market area, radio market in the U.S. The city's oldest radio station, KCBS (AM), KCBS, began as an experimental station in San Jose in 1909, before the beginning of commercial broadcasting. KALW was the city's first FM radio station when it signed on the air in 1941. The city's first television station was KPIX, which began broadcasting in 1948.
All major U.S. television networks have List of television stations in the San Francisco Bay Area, affiliates serving the region, with most of them based in the city. CNN, MSNBC, BBC, RT (TV network), Russia Today, and CCTV America also have regional news bureaus in San Francisco. Bloomberg West was launched in 2011 from a studio on the Embarcadero and CNBC broadcasts from One Market Plaza since 2015. ESPN uses the local ABC studio for their broadcasting. The regional sports network, Comcast SportsNet Bay Area and its sister station Comcast SportsNet California, are both located in San Francisco. The Pac-12 Network is also based in San Francisco.
Public broadcasting outlets include both a KQED-TV, television station and a KQED-FM, radio station, both broadcasting under the call letters KQED from a facility near the Potrero Hill, San Francisco, Potrero Hill neighborhood. KQED-FM is the most-listened-to National Public Radio affiliate in the country. Another local broadcaster, KPOO, is an independent, African-American owned and operated noncommercial radio station established in 1971. CNET Networks, CNET, founded 1994, and Salon.com, 1995, are based in San Francisco.
San Francisco-based inventors made important contributions to modern media. During the 1870s, Eadweard Muybridge began recording motion photographically and invented a zoopraxiscope with which to view his recordings. These were the first motion pictures. Then in 1927, Philo Farnsworth's image dissector camera tube transmitted its first image. This was a refinement of the first television system which was invented by John Logie Baird in 1926.
 Transit is the most used form of transportation every day in San Francisco. Every weekday, more than 560,000 people travel on Muni's 69 bus routes and more than 140,000 customers ride the Muni Metro light rail system. 32% of San Francisco residents use public transportation for their daily commute to work, ranking it first on the West Coast and third overall in the United States. The
Transit is the most used form of transportation every day in San Francisco. Every weekday, more than 560,000 people travel on Muni's 69 bus routes and more than 140,000 customers ride the Muni Metro light rail system. 32% of San Francisco residents use public transportation for their daily commute to work, ranking it first on the West Coast and third overall in the United States. The 
 Cycling is a popular mode of transportation in San Francisco, with 75,000 residents commuting by bicycle each day. In recent years, the city has installed better cycling infrastructure such as protected bike lanes and parking racks. Bay Wheels, previously named Bay Area Bike Share at inception, launched in August 2013 with 700 bikes in downtown San Francisco, selected cities in the East Bay, and San Jose. The San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency and Bay Area Air Quality Management District are responsible for the operation with management provided by Motivate (company), Motivate. A major expansion started in 2017, along with a rebranding as Ford GoBike; the company received its current name in 2019.
Pedestrian traffic is also widespread. In 2015, Walk Score ranked San Francisco the second-most walkable city in the United States.
San Francisco has significantly higher rates of pedestrian and bicyclist traffic deaths than the United States on average. In 2013, 21 pedestrians were killed in vehicle collisions, the highest since 2001, which is 2.5 deaths per 100,000 population – 70% higher than the national average of 1.5.
Cycling in San Francisco, Cycling is becoming increasingly popular in the city. Annual bicycle counts conducted by the San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency, Municipal Transportation Agency (MTA) in 2010 showed the number of cyclists at 33 locations had increased 58% from the 2006 baseline counts. In 2008, the MTA estimated that about 128,000 trips were made by bicycle each day in the city, or 6% of total trips. As of 2019, 2.6% of the city's streets have protected bike lanes, with 28 miles of protected bike lanes in the city. Since 2006, San Francisco has received a Bicycle Friendly Community status of "Gold" from the League of American Bicyclists. In 2022 a measure on the ballot passed to protect JFK drive in Golden Gate Park as a pedestrian and biking space with 59% of voters in favor.
Cycling is a popular mode of transportation in San Francisco, with 75,000 residents commuting by bicycle each day. In recent years, the city has installed better cycling infrastructure such as protected bike lanes and parking racks. Bay Wheels, previously named Bay Area Bike Share at inception, launched in August 2013 with 700 bikes in downtown San Francisco, selected cities in the East Bay, and San Jose. The San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency and Bay Area Air Quality Management District are responsible for the operation with management provided by Motivate (company), Motivate. A major expansion started in 2017, along with a rebranding as Ford GoBike; the company received its current name in 2019.
Pedestrian traffic is also widespread. In 2015, Walk Score ranked San Francisco the second-most walkable city in the United States.
San Francisco has significantly higher rates of pedestrian and bicyclist traffic deaths than the United States on average. In 2013, 21 pedestrians were killed in vehicle collisions, the highest since 2001, which is 2.5 deaths per 100,000 population – 70% higher than the national average of 1.5.
Cycling in San Francisco, Cycling is becoming increasingly popular in the city. Annual bicycle counts conducted by the San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency, Municipal Transportation Agency (MTA) in 2010 showed the number of cyclists at 33 locations had increased 58% from the 2006 baseline counts. In 2008, the MTA estimated that about 128,000 trips were made by bicycle each day in the city, or 6% of total trips. As of 2019, 2.6% of the city's streets have protected bike lanes, with 28 miles of protected bike lanes in the city. Since 2006, San Francisco has received a Bicycle Friendly Community status of "Gold" from the League of American Bicyclists. In 2022 a measure on the ballot passed to protect JFK drive in Golden Gate Park as a pedestrian and biking space with 59% of voters in favor.