Roman siege engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Roman
 To facilitate this organization and the army's self-sufficiency, an engineering corps was developed. An officer of engineers, or ''praefectus fabrum'', is referenced in armies of the late republic, but this post is not verifiable in all accounts and may have simply been a military advisor on the personal staff of a commanding officer. There were legion architects (whose rank is yet unknown) who were responsible for the construction of war machines who would also assure that all artillery constructions in the field were level. Ensuring that constructions were level was the job of the ''libratores'', who would also launch missiles and other projectiles (on occasion) during battle (Le Bohec 1994: 52). The engineering corps was in charge of massive production, frequently prefabricating
To facilitate this organization and the army's self-sufficiency, an engineering corps was developed. An officer of engineers, or ''praefectus fabrum'', is referenced in armies of the late republic, but this post is not verifiable in all accounts and may have simply been a military advisor on the personal staff of a commanding officer. There were legion architects (whose rank is yet unknown) who were responsible for the construction of war machines who would also assure that all artillery constructions in the field were level. Ensuring that constructions were level was the job of the ''libratores'', who would also launch missiles and other projectiles (on occasion) during battle (Le Bohec 1994: 52). The engineering corps was in charge of massive production, frequently prefabricating
 Roman artillery was very efficient at that time, and during a siege the Romans would attack the weakest area of their enemy's defenses and attempt to breach the walls at that point. To support this effort, artillery fire would commence, with three main objectives:Le Bohec 1994: 138 to cause damage to defenses, casualties among the opposing army, and loss of enemy morale. It would also provide cover fire for troops building siege ramps or those in siege towers. There were machines called '' tormenta '', which would launch (sometimes incendiary) projectiles such as javelins, arrows, rocks, or beams. These devices were on wheeled platforms to follow the line's advance. All were "predicated on a principle of physics: a lever was inserted into a skein of twisted horsehair to increase torsion, and when the arm was released, a considerable amount of energy was thus freed". It was later stated that sinew, instead of twisted hair, provided a better “spring.” These weapons were high-maintenance devices and vulnerable to having their leather, sinew, or hemp skeins affected by wet or even damp, which would cause them to slacken and lose tension, rendering the engine useless.Catapulta at LegionXXIV
Roman artillery was very efficient at that time, and during a siege the Romans would attack the weakest area of their enemy's defenses and attempt to breach the walls at that point. To support this effort, artillery fire would commence, with three main objectives:Le Bohec 1994: 138 to cause damage to defenses, casualties among the opposing army, and loss of enemy morale. It would also provide cover fire for troops building siege ramps or those in siege towers. There were machines called '' tormenta '', which would launch (sometimes incendiary) projectiles such as javelins, arrows, rocks, or beams. These devices were on wheeled platforms to follow the line's advance. All were "predicated on a principle of physics: a lever was inserted into a skein of twisted horsehair to increase torsion, and when the arm was released, a considerable amount of energy was thus freed". It was later stated that sinew, instead of twisted hair, provided a better “spring.” These weapons were high-maintenance devices and vulnerable to having their leather, sinew, or hemp skeins affected by wet or even damp, which would cause them to slacken and lose tension, rendering the engine useless.Catapulta at LegionXXIV
/ref> It is somewhat difficult to clearly define and describe Roman artillery, as names are easily confused and historians still do not agree on all definitions. Perhaps best known are the ''

 After the absorption of the ancient Greek city states into the
After the absorption of the ancient Greek city states into the
 The early Roman ''ballistae ''were made of wood, and held together with iron plates around the frames and iron nails in the stand. The main stand had a slider on the top, into which were loaded the bolts or stone 'shot'. Attached to this, at the back, was a pair of
The early Roman ''ballistae ''were made of wood, and held together with iron plates around the frames and iron nails in the stand. The main stand had a slider on the top, into which were loaded the bolts or stone 'shot'. Attached to this, at the back, was a pair of
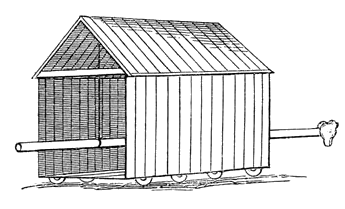
 Roman battering rams, or ''aries'', were an effective weapon for breaking down an enemy's walls, as well as their morale. Under
Roman battering rams, or ''aries'', were an effective weapon for breaking down an enemy's walls, as well as their morale. Under
 According to
According to
siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while oth ...
s were, for the most part, adapted from Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
siege technology. Relatively small efforts were made to develop the technology; however, the Romans brought an unrelentingly aggressive style to siege warfare
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterize ...
Goldsworthy 2000: 144 that brought them repeated success. Up to the first century BC, the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
utilized siege weapons only as required and relied for the most part on ladders, towers and rams to assault a fortified town. ''Ballistae'' were also employed, but held no permanent place within a legion's roster, until later in the republic, and were used sparingly.
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
took great interest in the integration of advanced siege engines, organizing their use for optimal battlefield efficiency.Keppie 1984: 99
Army engineering corps
 To facilitate this organization and the army's self-sufficiency, an engineering corps was developed. An officer of engineers, or ''praefectus fabrum'', is referenced in armies of the late republic, but this post is not verifiable in all accounts and may have simply been a military advisor on the personal staff of a commanding officer. There were legion architects (whose rank is yet unknown) who were responsible for the construction of war machines who would also assure that all artillery constructions in the field were level. Ensuring that constructions were level was the job of the ''libratores'', who would also launch missiles and other projectiles (on occasion) during battle (Le Bohec 1994: 52). The engineering corps was in charge of massive production, frequently prefabricating
To facilitate this organization and the army's self-sufficiency, an engineering corps was developed. An officer of engineers, or ''praefectus fabrum'', is referenced in armies of the late republic, but this post is not verifiable in all accounts and may have simply been a military advisor on the personal staff of a commanding officer. There were legion architects (whose rank is yet unknown) who were responsible for the construction of war machines who would also assure that all artillery constructions in the field were level. Ensuring that constructions were level was the job of the ''libratores'', who would also launch missiles and other projectiles (on occasion) during battle (Le Bohec 1994: 52). The engineering corps was in charge of massive production, frequently prefabricating artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
and siege equipment to facilitate its transportation.
Artillery
 Roman artillery was very efficient at that time, and during a siege the Romans would attack the weakest area of their enemy's defenses and attempt to breach the walls at that point. To support this effort, artillery fire would commence, with three main objectives:Le Bohec 1994: 138 to cause damage to defenses, casualties among the opposing army, and loss of enemy morale. It would also provide cover fire for troops building siege ramps or those in siege towers. There were machines called '' tormenta '', which would launch (sometimes incendiary) projectiles such as javelins, arrows, rocks, or beams. These devices were on wheeled platforms to follow the line's advance. All were "predicated on a principle of physics: a lever was inserted into a skein of twisted horsehair to increase torsion, and when the arm was released, a considerable amount of energy was thus freed". It was later stated that sinew, instead of twisted hair, provided a better “spring.” These weapons were high-maintenance devices and vulnerable to having their leather, sinew, or hemp skeins affected by wet or even damp, which would cause them to slacken and lose tension, rendering the engine useless.Catapulta at LegionXXIV
Roman artillery was very efficient at that time, and during a siege the Romans would attack the weakest area of their enemy's defenses and attempt to breach the walls at that point. To support this effort, artillery fire would commence, with three main objectives:Le Bohec 1994: 138 to cause damage to defenses, casualties among the opposing army, and loss of enemy morale. It would also provide cover fire for troops building siege ramps or those in siege towers. There were machines called '' tormenta '', which would launch (sometimes incendiary) projectiles such as javelins, arrows, rocks, or beams. These devices were on wheeled platforms to follow the line's advance. All were "predicated on a principle of physics: a lever was inserted into a skein of twisted horsehair to increase torsion, and when the arm was released, a considerable amount of energy was thus freed". It was later stated that sinew, instead of twisted hair, provided a better “spring.” These weapons were high-maintenance devices and vulnerable to having their leather, sinew, or hemp skeins affected by wet or even damp, which would cause them to slacken and lose tension, rendering the engine useless.Catapulta at LegionXXIV/ref> It is somewhat difficult to clearly define and describe Roman artillery, as names are easily confused and historians still do not agree on all definitions. Perhaps best known are the ''
ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant ...
'', the ''onager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
'', and the '' scorpio''.
''Ballista''

 After the absorption of the ancient Greek city states into the
After the absorption of the ancient Greek city states into the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
in 146 BC, some advanced Greek technologies began to spread across many areas of Roman influence. This included the hugely advantageous military advances the Greeks had made (most notably by Dionysus of Syracuse), as well as all the scientific, mathematical, political and artistic developments.
The Romans 'inherited' the torsion powered ''ballistae'' which had by now spread to several cities around the Mediterranean, all of which became Roman spoils of war in time, including one from Pergamum
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
, which was depicted among a pile of 'trophy' weapons in relief on a balustrade.
The torsion ''ballista'', developed by Alexander, was a far more complicated weapon than its predecessor, and the Romans developed it even further.
Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled '' De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attribut ...
, in his '' De Architectura'' book X, describes the construction and tuning of ''ballistae''.
Every century (group of 60-100 men) in the Roman army had a ''ballista'' by the 1st century AD. It was the command of the chief of the ''ballistae'', under whom were the artillery experts, or ''doctores ballistarum'' and finally, the artillerymen, or ''ballistarii''. ''Ballistae'' were heavy missile weapons, hurling large rocks great distances to damage rampart walls. They resembled large crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an elastic launching device consisting of a bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock of a long fire ...
s, rather than catapults
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of store ...
. They were powered by two horizontal like arms, which were inserted into two vertical and tightly wound "skein" springs contained in a rectangular frame structure making up the head or principal part of the weapon. The arms were drawn rearward with a winch lever to further twist the skeins and thus gain the torsion power to cast a projectile. It has been said that the whirring sound of a ''ballista''-fired stone struck fear and dread into the hearts of those inside the walls of besieged cities. The stones chosen to be used in the ''ballista'' had to be a particular sort. According to Vegetius
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also r ...
, river stones were best, since they are round, smooth, and dense. ''Ballista'' stones found at the site of Masada
Masada ( he, מְצָדָה ', "fortress") is an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel situated on top of an isolated rock plateau, akin to a mesa. It is located on the eastern edge of the Judaean Desert, overlooking the D ...
were chiseled to make them as round as possible.
Early Roman ''ballistae''
winch
A winch is a mechanical device that is used to pull in (wind up) or let out (wind out) or otherwise adjust the tension of a rope or wire rope (also called "cable" or "wire cable").
In its simplest form, it consists of a spool (or drum) attach ...
es and a claw, used to ratchet the bowstring back to the armed firing position. A slider passed through the field frames of the weapon, in which were located the torsion springs (rope made of animal sinew), which were twisted around the bow arms, which in turn were attached to the bowstring.
Drawing the bowstring back with the winches twisted the already taut springs, storing the energy to fire the projectiles.
The ''ballista'' was a highly accurate weapon (there are many accounts right from its early history of single soldiers being picked off by the operators), but some design aspects meant it could compromise its accuracy for range. The lightweight bolts could not gain the high momentum of the stones over the same distance as those thrown by the later onager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
s, trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weight ...
s, or mangonel
The mangonel, also called the traction trebuchet, was a type of trebuchet used in Ancient China starting from the Warring States period, and later across Eurasia by the 6th century AD. Unlike the later counterweight trebuchet, the mangonel o ...
s; these could be as heavy as 90–135 kg (200-300 pounds).
The Romans continued the development of the ''ballista'', and it became a highly prized and valued weapon in the army of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
.
It was used, just before the start of the empire, by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
during his conquest of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
and on both of his expeditions to Britain. Both attempted invasions of Britain and the siege of Alesia are recorded in his own ''commentarii Commentarii (Latin, Greek: ''hupomnemata'') are notes to assist the memory, or memoranda. This original idea of the word gave rise to a variety of meanings: notes and abstracts of speeches for the assistance of orators; family memorials, the orig ...
'' (journal), ''The Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
''(''De Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; en, Commentaries on the Gallic War, italic=yes), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' ( en, Gallic War, italic=yes), is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it Ca ...
'').
First invasion of Britain
The first invasion of Britain took place in 55 BC, after a rapid and successful initial conquest of Gaul, in part as an exploratory expedition, and more practically to try to put an end to the re-enforcements sent by the nativeBritons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
to fight the Romans in Gaul.
A total of eighty transports, carrying two legions, attempted to land on the British shore, only to be driven back by the many British warriors assembled along the shoreline. The ships had to unload their troops on the beach, as it was the only one suitable for many kilometers, yet the massed ranks of British charioteers and javeliners were making it impossible.
Seeing this, Caesar ordered the warships – which were swifter and easier to handle than the transports, and likely to impress the natives more by their unfamiliar appearance – to be removed a short distance from the others, and then be rowed hard and run ashore on the enemy’s right flank, from which position the slings, bows and artillery could be used by men on deck to drive them back. This manoeuvre was highly successful.
Scared by the strange shape of the warships, the motion of the oars, and the unfamiliar machines, the natives halted and then retreated a little. (Caesar, ''The Conquest of Gaul'', p. 99)
Siege of Alesia
In Gaul, the stronghold of Alesia was under a Roman siege in 52 BC, and surrounded by Roman fortifications. As was standard siege technique at the time, ''ballistae'' were placed up in the towers with other soldiers armed with either bows or slings.Onager
The ''onager'' was a post-classical Roman siege engine, which derived its name from the kicking action of the machine, similar to that of anonager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
(wild ass). It is a type of catapult that uses torsional
In the field of solid mechanics, torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied torque. Torsion is expressed in either the pascal (Pa), an SI unit for newtons per square metre, or in pounds per square inch (psi) while torque is expressed ...
pressure, generally from twisted rope, to store energy for the shot.
The onager consisted of a frame placed on the ground to whose front end a vertical frame of solid timber was rigidly fixed; through the vertical frame ran an axle, which had a single stout spoke. On the extremity of the spoke was a sling used to launch a projectile.
In action the spoke was forced down, against the tension of twisted rope
A rope is a group of yarns, plies, fibres, or strands that are twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have tensile strength and so can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger than similar ...
s or other spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season)
Spring, also known as springtime, is one of the four temperate seasons, succeeding winter and preceding summer. There are various technical definitions of spring, but local usage of ...
s, by a windlass, and then suddenly released. The spoke thus kicked the crosspiece of the vertical frame, and the projectile at its extreme end was shot forward.
The onagers of the Roman Empire were mainly used for besieging forts or settlements. They would often be loaded with large stones or rocks that could be covered with a flammable substance and set alight.
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
(recorded from around 1200 A.D.) a less powerful version of the onager was used that employed a fixed bowl rather than a sling, so that many small projectiles could be thrown, as opposed to a single large one. This engine was sometimes called the ''mangonel
The mangonel, also called the traction trebuchet, was a type of trebuchet used in Ancient China starting from the Warring States period, and later across Eurasia by the 6th century AD. Unlike the later counterweight trebuchet, the mangonel o ...
'', although the same name may have been used for a variety of siege engines.
Scorpio
The ''scorpio'' was acrossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an elastic launching device consisting of a bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock of a long fire ...
-like device that shot smaller arrows with deadly accuracy used both in the field and in sieges. They were so-named for their deadly, armor-piercing sting and could be operated by just one or two men. Scorpios were meant to kill and injure enemy troops, rather than break down enemy fortifications. Thanks to their smaller size, they could be mounted on or in siege towers
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
. During the Siege of Amida, a scorpio-fired arrow killed the son of Grumbates
Grumbates or Krumbates was a king of the Chionitae, probably of the Kidarites tribe, an ancient nomadic tribe of Transoxiana.
Etymology
The exact origin of his name is not fully known. Hyun Jin Kim etymologized his name as ''*Qurum-pat'', "rul ...
, king of the Chionitae, when he was approaching the city to surrender.
There has been some research done into the existence of the self-loading, serial-fire ''scorpio'' or polybolos
The polybolos (the name means "multi-thrower" in Greek) was an ancient Greek repeating ballista, reputedly invented by Dionysius of Alexandria (a 3rd-century BC Greek engineer at the Rhodes arsenal,) and used in antiquity. The polybolos w ...
. Legionaries
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius'', plural ''legionarii'') was a professional heavy infantryman of the Roman army after the Marian reforms. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the late Republi ...
on either side would continuously keep turning cranks which turned a chain, which operated the various mechanisms to load and fire the catapult. All that was needed was for another soldier to keep feeding in more arrows.
Breaking the walls
Battering ram

 Roman battering rams, or ''aries'', were an effective weapon for breaking down an enemy's walls, as well as their morale. Under
Roman battering rams, or ''aries'', were an effective weapon for breaking down an enemy's walls, as well as their morale. Under Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Ju ...
, any defenders who failed to surrender before the first ram touched their wall were denied any rights. The moment they heard the ram hit the wall, those inside the city knew that the siege proper had begun and there was no turning back.
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
describes the battering ram used at Jotapata thus:
It is an immense beam, similar to a ship’s mast, with one end covered with iron shaped into a ram’s head; hence its name. It is suspended from another beam like a balance arm by cables around its middle, and this in turn is supported at both ends by posts fixed in the ground. It is drawn back by a huge number of men who then push it forward in unison with all their might so that it hits the wall with its iron head. There is no tower strong enough nor any wall thick enough to withstand repeated blows of this kind, and many cannot resist the first shock.
Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled '' De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attribut ...
in '' De Architectura ''Book X describes the construction and use of battering rams.
For protection, a battering ram was suspended in a mobile shelter called a tortoise, or ''testudo''. According to Vegetius
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also r ...
, it was given this name because the ram would swing out of the shelter much like a tortoise's head comes out of its shell. Such shelters would provide the men within protection against missiles and incendiary devices. They were constructed from a framework of strong timbers with planks and wicker hurdles on the sides. The entire shelter would then be covered with a fireproof material such as uncured hides. According to Apollodorus of Damascus
Apollodorus of Damascus ( grc, Ἀπολλόδωρος ὁ Δαμασκηνός) was a Nabataean architect and engineer from Damascus, Roman Syria, who flourished during the 2nd century AD. As an engineer he authored several technical treatises, ...
, the shelter should be fixed to the ground while the ram was being used to both prevent skidding and strain on the axles from the weight of the moving apparatus. This would also increase the strength of the impact on the walls.
Siege tower
 According to
According to Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
, the Roman siege towers at Jotapata were 50 feet high and iron-plated to protect them from fire; those at Masada
Masada ( he, מְצָדָה ', "fortress") is an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel situated on top of an isolated rock plateau, akin to a mesa. It is located on the eastern edge of the Judaean Desert, overlooking the D ...
were reported to be 75 feet high. It was possible to have many different devices on siege towers, such as artillery, draw bridges and rams. Those at the top of the tower were to keep defenders off the walls while those below them attempted to breach the wall using ramps. In the battle of Jerusalem in 70 AD the Romans began assault on the third defensive wall within Jerusalem, the tower stood 75 ft tall and was compromised when the Jewish resistance tunneled underneath the tower leading it to collapse. Following a basic design, details of tower construction varied from siege to siege and there is no known treatise which specifies at which level siege equipment should be placed. Vegetius
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also r ...
noted that, “besiegers sometimes built a tower with another turret inside it that could suddenly be raised by ropes and pulleys to over-top the wall”.
Mine
Mines could be dug under city walls as a means of entering a city secretly and capturing it but were more frequently constructed to weaken city walls. Once dug,sappers
A sapper, also called a pioneer or combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparing fie ...
would underpin the walls with wood and cause the walls to collapse by firing the supports with resin, sulfur and other incendiary materials.Gilliver 1999: 140
Corvus
In chapter 1.22 "The Victory of Mylae" of his ''History,'' Polybius writes:Now their ships were badly fitted out and not easy to manage, and so some one suggested to them as likely to serve their turn in a fight the construction of what were afterwards called "crows".Histories. Polybius. Evelyn S. Shuckburgh. translator. London, New York. Macmillan. 1889. Reprint Bloomington 1962.http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Plb.+1.22&fromdoc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0234Corvus means "crow" or "raven" in
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and was the name given to a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
boarding device first documented during the First Punic War against Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
. Polybius goes on to describe this siege engine as a bridge used to span the distance between two ships in battle. The device was a plank, 4 ft wide and 36 ft long, affixed to the Roman vessel around a pole. This construction allowed the bridge to be swung port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
to starboard and therefore used on either side of the ship. A pulley at the top of the pole allowed the planks to be raised and lowered on command. At the end of the bridge there was a heavy metal spike that when dropped on the deck of an enemy ship would, with the aid of gravity, become imbedded in the deck. By connecting the two ships in such a way, Roman soldiers
This is a list of Roman army units and bureaucrats.
*'' Accensus'' – Light infantry men in the armies of the early Roman Republic, made up of the poorest men of the army.
*'' Actuarius'' – A military who served food.
*''Adiutor'' – A camp o ...
could gain access to the deck of the enemy ship and engage in hand-to-hand combat instead of depending on ship-to-ship combat. Polybius also includes an insight on how these siege engines would have practically functioned in battle: And as soon as the "crows" were fixed in the planks of the decks and grappled the ships together, if the ships were alongside of each other, the men leaped on board anywhere along the side, but if they were prow to prow, they used the "crow" itself for boarding, and advanced over it two abreast. The first two protected their front by holding up before them their shields, while those who came after them secured their sides by placing the rims of their shields upon the top of the railing. Such were the preparations which they made; and having completed them they watched an opportunity of engaging at sea.Based on this historical description the Corvus used some mechanisms seen in the more complex
siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s or the sheds constructed around battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried b ...
s. They protected, to an extent, the Roman soldiers
This is a list of Roman army units and bureaucrats.
*'' Accensus'' – Light infantry men in the armies of the early Roman Republic, made up of the poorest men of the army.
*'' Actuarius'' – A military who served food.
*''Adiutor'' – A camp o ...
as they gained entry to the enemy's space where they could engage in combat.
See also
* * *Notes
References
* * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Roman Siege Engines