Robotics in Italy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Robotics in Italy is a high technology area where Italy hosts numerous research centers.
The first project documented of a

This program is part of an important agreement with INAIL to provide potential applications in the Italian national health system in the short term.
History
The origins of this technology in Italy, but also in the world, which requires knowledge of many sciences to be applied, beginning in theItalian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( it, Rinascimento ) was a period in Italian history covering the 15th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Europe and marked the trans ...
with the studies of Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
.The first project documented of a
robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may ...
, in particular of an android, is signed by Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
in the 1495.


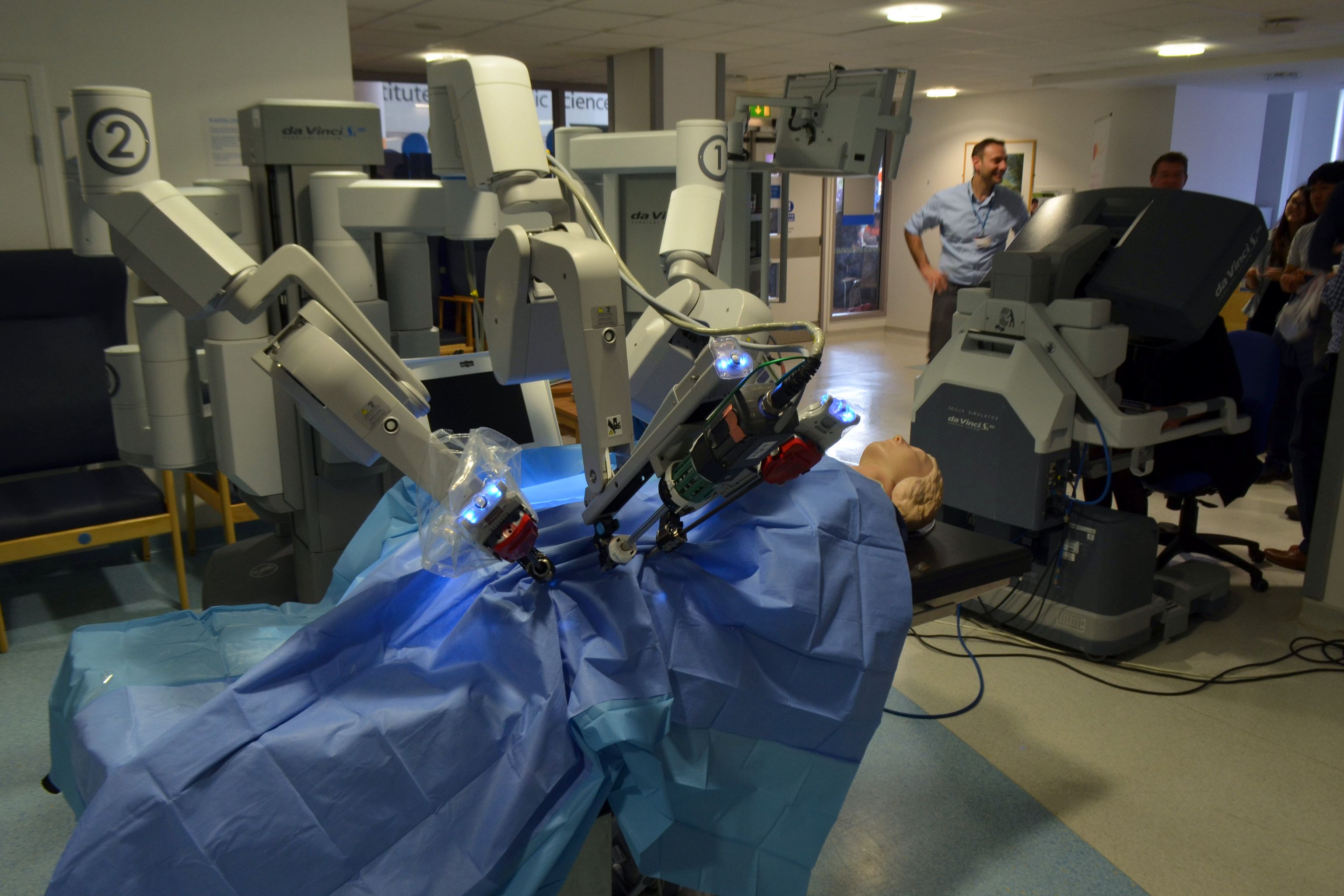
Robotic Surgery
Almost all theItalian regions
The regions of Italy ( it, regioni d'Italia) are the first-level administrative divisions of the Italian Republic, constituting its second NUTS administrative level. There are twenty regions, five of which have higher autonomy than the rest. U ...
are equipped with robots in the operating room and about 18 thousand robotic surgery operations were carried out in 2017.
"The da Vinci robotic surgery - explains Walter Artibani, Director of the UO of Urology
Urology (from Greek οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and '' -logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary-tract system and the reproductive org ...
of the Integrated AOU of Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
and Secretary General of the Italian Society of Urology - is emblematic of minimally invasive surgery.
The robot allows a precision not comparable with other techniques and allows to overcome the limits linked to the difficulty of treating pathologies in difficult-to-reach anatomical sites with laparoscopy Italian urology is an excellence in the field of robotics.
In urology the reasons for success are many and simple: the precision of the robot allows greater ease of access to more complex anatomies, a demolithic and reconstructive precision, less blood loss, a reduction in post-operative hospitalization and a reduction in side effects. (erectile dysfunction and incontinence). Added to this are characteristics such as immersive three-dimensional vision able to multiply up to 10 times the normal vision of the human eye.
Robotic Doctor
Robotic Exoskeleton
TheItalian Institute of Technology
The Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) (in English: Italian Institute of Technology) is a scientific research centre based in Genoa (Italy, EU).
Its main goal is the advancement of science, in Italy and worldwide, through projects and discoveri ...
of Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
started in December 2013 a research program called Robot Rehab that focuses on robotic rehabilitation
Rehabilitation robotics is a field of research dedicated to understanding and augmenting rehabilitation through the application of robotic devices. Rehabilitation robotics includes development of robotic devices tailored for assisting different se ...
by developing exoskeletons
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
for the disabled, prosthetic devices and new rehabilitation instruments.This program is part of an important agreement with INAIL to provide potential applications in the Italian national health system in the short term.
Robotic Exoskeleton Suit
* XoSoftRobotic Plant
The Plantoid is a machine or a synthetic organism designed to behave, act and grow like a plant. The concept was published for the first time in 2010. A prototype for the European Space Agency is now under development. One of the first prototypes was realized by the Micro-Biorobotics Center of theItalian Institute of Technology
The Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) (in English: Italian Institute of Technology) is a scientific research centre based in Genoa (Italy, EU).
Its main goal is the advancement of science, in Italy and worldwide, through projects and discoveri ...
in Pontedera
Pontedera (; la, Pons Herae) is an italian comune with a population of 29.270 inhabitants, located in the province of Pisa, Tuscany, central Italy.
The town is located 20 km (12 miles) from Pisa and 50 km (31 miles) from Florence.
It house ...
in 2015.
Robotic Runner
The Robot R1, the humanoid robot built byItalian Institute of Technology
The Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) (in English: Italian Institute of Technology) is a scientific research centre based in Genoa (Italy, EU).
Its main goal is the advancement of science, in Italy and worldwide, through projects and discoveri ...
in Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
.
Sunday, October 14, 2018 at 10, at the start of the "StraGenova del cuore", the non-competitive race dedicated to the memory of the 43 victims of the collapse of Ponte Morandi
(English: Morandi Bridge), officially (English: Polcevera Viaduct), was a road viaduct in Genoa, Liguria, Italy, constructed between 1963 and 1967 along the A10 motorway over the Polcevera River, from which it derived its official name. It ...
, there will also be R1, the humanoid robot built by Italian Institute of Technology
The Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) (in English: Italian Institute of Technology) is a scientific research centre based in Genoa (Italy, EU).
Its main goal is the advancement of science, in Italy and worldwide, through projects and discoveri ...
, in the special role of mascot which will have the task of symbolically giving the start to the race.
Cyborg in Italy
The first experiment in the world, took place in Italy, in 2014 to have installed the bionic hand that perceives the touch was a Danish 36-year-old Dennis Aabo Sørensen. The bionic hand called LifeHand2 works with a sensitivity similar to the natural one: it is the first time that an artificial limb allows the wearer to perceive and recognize the objects he touches. The result, published in the journal Science Traslational Medicine, is an Italian research project and has origin from a vast international collaboration, coordinated by Silvestro Micera, of the Polytechnic of Lausanne. The project was developed largely in Italy, by the BioRobotics Institute of the Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies in Pisa, in collaboration with the GermanUniversity of Fribourg
The University of Fribourg (french: Université de Fribourg; german: Universität Freiburg) is a public university located in Fribourg, Switzerland.
The roots of the university can be traced back to 1580, when the notable Jesuit Peter Canisi ...
.
A woman is the first Italian cyborg
A cyborg ()—a portmanteau of ''cybernetic'' and ''organism''—is a being with both organic and biomechatronic body parts. The term was coined in 1960 by Manfred Clynes and Nathan S. Kline.
woman who has been implanted the bionic hand that perceives the contact with objects, made by the group of Silvestro Micera, the Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna and the Polytechnic of Lausanne. The intervention was performed in June 2016 at the Policlinico Gemelli in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
by the group of neurologist Paolo Maria Rossini.
In the experiment, which lasted six months, the bionic hand was implanted to Mrs. Almerina Mascarello, who lives in Veneto
it, Veneto (man) it, Veneta (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 = ...
and who had lost her left hand in an accident.
Italian robotics companies
Industrial robotics
*Comau
Comau (''COnsorzio MAcchine Utensili'') is an Italian multinational company in the automation field based in Turin, Italy, and part of the automaker Stellantis. The company is present in 13 countries and employs 4,000 people and provides service ...
* Aitonomi
See also
* Android *Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
* Cyborg
A cyborg ()—a portmanteau of ''cybernetic'' and ''organism''—is a being with both organic and biomechatronic body parts. The term was coined in 1960 by Manfred Clynes and Nathan S. Kline.
* LifeHand
* iCub
iCub is a 1 metre tall open source robotics humanoid robot testbed for research into human cognition and artificial intelligence.
It was designed by the RobotCub Consortium of several European universities and built by Italian Institute of ...
* WALK-MAN
* HyQReal
* CENTAURO
The Centauro is a family of Italian military vehicles originating from a wheeled tank destroyer for light to medium territorial defense and tactical reconnaissance. It was developed by a consortium of manufacturers, the Società Consortile Ive ...
* Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia
* DARPA Robotics Challenge
The DARPA Robotics Challenge (DRC) was a prize competition funded by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. Held from 2012 to 2015, it aimed to develop semi-autonomous ground robots that could do "complex tasks in dangerous, degraded, ...
* Three Laws of Robotics
The Three Laws of Robotics (often shortened to The Three Laws or known as Asimov's Laws) are a set of rules devised by science fiction author Isaac Asimov. The rules were introduced in his 1942 short story " Runaround" (included in the 1950 colle ...
* Festival internazionale della Robotica
* Industry 4.0
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, 4IR, or Industry 4.0, conceptualizes rapid change to technology, industries, and societal patterns and processes in the 21st century due to increasing interconnectivity and smart automation. The term has bee ...
References
External links
Humanoid robots {{Robotics-stub