Rare earth elements on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the
 As seen in the chart to the right, rare-earth elements are found on earth at similar concentrations to many common transition metals. The most abundant rare-earth element is
As seen in the chart to the right, rare-earth elements are found on earth at similar concentrations to many common transition metals. The most abundant rare-earth element is
"Rare earth elements plentiful in ocean sediments"
'' ScienceNews'', 3 July 2011. Via Kurt Brouwer'
Fundmastery Blog
''MarketWatch'', 2011-07-05. Retrieved 2011-07-05.
 Until 1948, most of the world's rare earths were sourced from placer sand deposits in
Until 1948, most of the world's rare earths were sourced from placer sand deposits in
Reuters. August 31, 2009. Retrieved Aug 31, 2009. In 2013, it was stated that the demand for REEs would increase due to the dependence of the EU on these elements, the fact that rare earth elements cannot be substituted by other elements and that REEs have a low recycling rate. Furthermore, due to the increased demand and low supply, future prices are expected to increase and there is a chance that countries other than China will open REE mines. REE is increasing in demand due to the fact that they are essential for new and innovative technology that is being created. These new products that need REEs to be produced are high technology equipment such as smart phones, digital cameras, computer parts, semiconductors, etc. In addition, these elements are more prevalent in the following industries: renewable energy technology, military equipment, glass making, and metallurgy.
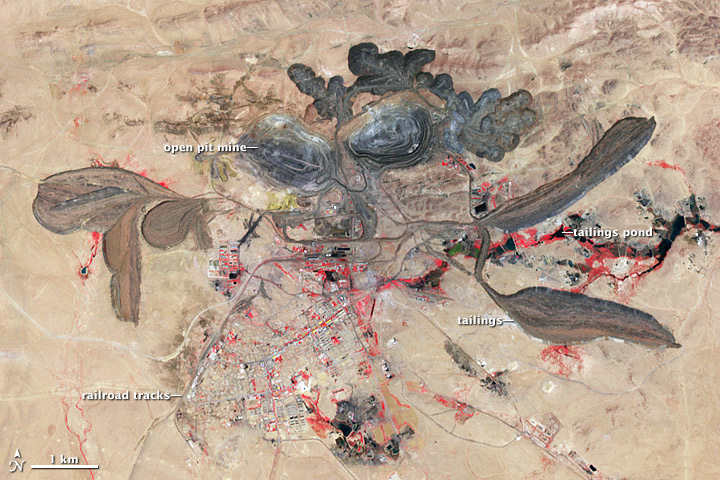 Mining, refining, and recycling of rare earths have serious environmental consequences if not properly managed. Low-level radioactive
Mining, refining, and recycling of rare earths have serious environmental consequences if not properly managed. Low-level radioactive
"Malaysia Rare Earths in Largest Would-Be Refinery Incite Protest"
'' Bloomberg Markets Magazine'', May 31, 2011 5:00 PM ET. Construction of the facility has been halted until an independent
 China has officially cited
China has officially cited
lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yttr ...
s (yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with the symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a "rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in com ...
and scandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the Lanthanides. It was discovered in ...
are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals are generally defined as ...
. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes.
Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 Apr ...
deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles ...
.
These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously.
These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, such as in lanthanide-dependent methanol dehydrogenases in bacteria. The water-soluble compounds are mildly to moderately toxic, but the insoluble ones are not.
Despite their name, rare-earth elements are relatively plentiful in Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
, with cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 o ...
being the 25th most abundant element at 68 parts per million, more abundant than copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
. All isotopes of promethium
Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is extremely rare, with only about 500–600 grams naturally occurring in Earth's crust at any given time. Promethium is one of onl ...
are radioactive, and it does not occur naturally in the earth's crust, except for a trace amount generated by spontaneous fission
Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of radioactive decay that is found only in very heavy chemical elements. The nuclear binding energy of the elements reaches its maximum at an atomic mass number of about 56 (e.g., iron-56); spontaneous breakdo ...
of Uranium-238
Uranium-238 (238U or U-238) is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it ...
. They are often found in minerals with thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high me ...
, and less commonly uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
.
Because of their geochemical properties, rare-earth elements are typically dispersed and not often found concentrated in rare-earth minerals. Consequently, economically exploitable ore deposits
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 April ...
are sparse (i.e. "rare"). The first rare-earth mineral discovered (1787) was gadolinite, a black mineral composed of cerium, yttrium, iron, silicon, and other elements. This mineral was extracted from a mine in the village of Ytterby
Ytterby () is a village on the Swedish island of Resarö, in Vaxholm Municipality in the Stockholm archipelago. Today the residential area is dominated by suburban homes.
The name of the village translates to "outer village". Ytterby is per ...
in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
; four of the rare-earth elements bear names derived from this single location.
List
A table listing the 17 rare-earth elements, theiratomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
and symbol, the etymology of their names, and their main uses (see also Applications of lanthanides) is provided here. Some of the rare-earth elements are named after the scientists who discovered them, or elucidated their elemental properties, and some after the geographical locations where discovered.
A mnemonic for the names of the sixth-row elements in order is "Lately college parties never produce sexy European girls that drink heavily even though you look".
Discovery and early history
Rare earths were mainly discovered as components of minerals. Ytterbium was found in the "ytterbite" (renamed to gadolinite in 1800). It was discovered by LieutenantCarl Axel Arrhenius
Carl Axel Arrhenius (29 March 1757 – 20 November 1824) was an officer in the Swedish army as well as an amateur geologist and chemist. He is best known for his discovery of the mineral ytterbite (later called gadolinite) in 1787.
The disc ...
in 1787 at a quarry in the village of Ytterby
Ytterby () is a village on the Swedish island of Resarö, in Vaxholm Municipality in the Stockholm archipelago. Today the residential area is dominated by suburban homes.
The name of the village translates to "outer village". Ytterby is per ...
, Sweden. Arrhenius's "ytterbite" reached Johan Gadolin
Johan Gadolin (5 June 176015 August 1852) was a Finnish chemist, physicist and mineralogist. Gadolin discovered a " new earth" containing the first rare-earth compound yttrium, which was later determined to be a chemical element. He is also ...
, a Royal Academy of Turku
The Royal Academy of Turku or the Royal Academy of Åbo ( sv, Kungliga Akademin i Åbo or ; la, Regia Academia Aboensis; fi, Turun akatemia) was the first university in Finland, and the only Finnish university that was founded when the country ...
professor, and his analysis yielded an unknown oxide ("earth"), which he called yttria
Yttrium oxide, also known as yttria, is Y2 O3. It is an air-stable, white solid substance.
The thermal conductivity of yttrium oxide is 27 W/(m·K).
Uses Phosphors
Yttria is widely used to make Eu:YVO4 and Eu:Y2O3 phosphors that give the red ...
. Anders Gustav Ekeberg
Anders Gustaf Ekeberg ( Stockholm, Sweden, 16 January 1767 – Uppsala, Sweden, 11 February 1813) was a Swedish analytical chemist who discovered tantalum in 1802. - subscription required
He was notably deaf.
Education
Anders Gustav Ekeberg ...
isolated beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form mi ...
from the gadolinite but failed to recognize other elements in the ore. After this discovery in 1794, a mineral from Bastnäs near Riddarhyttan
Riddarhyttan is a locality in Skinnskatteberg Municipality, Västmanland County, Sweden, with 431 inhabitants in 2010. It has an old iron mining tradition, which can be followed back to the last centuries before Christ. The last mine was closed ...
, Sweden, which was believed to be an iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
–tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolat ...
mineral, was re-examined by Jöns Jacob Berzelius
Baron Jöns Jacob Berzelius (; by himself and his contemporaries named only Jacob Berzelius, 20 August 1779 – 7 August 1848) was a Swedish chemist. Berzelius is considered, along with Robert Boyle, John Dalton, and Antoine Lavoisier, to be on ...
and Wilhelm Hisinger
Wilhelm Hisinger (23 December 1766 – 28 June 1852) was a Swedish physicist and chemist who in 1807, working in coordination with Jöns Jakob Berzelius, noted that in electrolysis any given substance always went to the same pole, and that substan ...
. In 1803 they obtained a white oxide and called it ceria
Cerium(IV) oxide, also known as ceric oxide, ceric dioxide, ceria, cerium oxide or cerium dioxide, is an oxide of the rare-earth metal cerium. It is a pale yellow-white powder with the chemical formula CeO2. It is an important commercial produ ...
. Martin Heinrich Klaproth
Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1 December 1743 – 1 January 1817) was a German chemist. He trained and worked for much of his life as an apothecary, moving in later life to the university. His shop became the second-largest apothecary in Berlin, and ...
independently discovered the same oxide and called it ''ochroia''. It took another 30 years for researchers to determine that other elements were contained in the two ores ceria and yttria (the similarity of the rare-earth metals' chemical properties made their separation difficult).
In 1839 Carl Gustav Mosander
Carl Gustaf Mosander (10 September 1797 – 15 October 1858) was a Swedish chemist. He discovered the rare earth elements lanthanum, erbium and terbium.
Early life and education
Born in Kalmar, Mosander attended school there until he moved t ...
, an assistant of Berzelius, separated ceria by heating the nitrate and dissolving the product in nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
. He called the oxide of the soluble salt ''lanthana''. It took him three more years to separate the lanthana further into ''didymia'' and pure lanthana. Didymia, although not further separable by Mosander's techniques, was in fact still a mixture of oxides.
In 1842 Mosander also separated the yttria into three oxides: pure yttria, terbia and erbia (all the names are derived from the town name "Ytterby"). The earth giving pink salts he called ''terbium''; the one that yielded yellow peroxide he called ''erbium''.
So in 1842 the number of known rare-earth elements had reached six: yttrium, cerium, lanthanum, didymium, erbium and terbium.
Nils Johan Berlin
Nils Johan Berlin (Nils Johannes Berlin) (18 February 1812 – 27 December 1891) was a Swedish chemist and physician, who held various professorships at the University of Lund from 1843 to 1864. Berlin was the first chemist who took the initiativ ...
and Marc Delafontaine
Marc Delafontaine (March 31, 1837/1838, Céligny, Switzerland–1911) was a Swiss chemist and spectroscopist who was involved in discovering and investigating some of the rare earth elements.
Career
Delafontaine studied with Jean Charles Galis ...
tried also to separate the crude yttria and found the same substances that Mosander obtained, but Berlin named (1860) the substance giving pink salts ''erbium'', and Delafontaine named the substance with the yellow peroxide ''terbium''. This confusion led to several false claims of new elements, such as the ''mosandrium'' of J. Lawrence Smith, or the ''philippium'' and ''decipium
Decipium was the proposed name for a new chemical element isolated by Marc Delafontaine from the mineral samarskite. He published his discovery in 1878 and later published a follow-up paper in 1881.
Decipium was considered to be in the cerium gro ...
'' of Delafontaine. Due to the difficulty in separating the metals (and determining the separation is complete), the total number of false discoveries was dozens, with some putting the total number of discoveries at over a hundred.
Spectroscopic identification
There were no further discoveries for 30 years, and the elementdidymium
Didymium ( el, , twin) is a mixture of the elements praseodymium and neodymium. It is used in safety glasses for glassblowing and blacksmithing, especially with a gas ( propane)-powered forge, where it provides a filter that selectively block ...
was listed in the periodic table of elements with a molecular mass of 138. In 1879 Delafontaine used the new physical process of optical flame spectroscopy and found several new spectral lines in didymia. Also in 1879, the new element ''samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samar ...
'' was isolated by Paul Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran
Paul may refer to:
*Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
*Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chris ...
from the mineral samarskite
Samarskite is a radioactive rare earth mineral series which includes samarskite-(Y), with the chemical formula and samarskite-(Yb), with the chemical formula . The formula for samarskite-(Y) is also given as .
Samarskite crystallizes in the orth ...
.
The samaria earth was further separated by Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1886, and a similar result was obtained by Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac
Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac (24 April 1817 – 15 April 1894) was a Swiss chemist whose work with atomic weights suggested the possibility of isotopes and the packing fraction of nuclei. His study of the rare earth elements led to h ...
by direct isolation from samarskite. They named the element ''gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
'' after Johan Gadolin
Johan Gadolin (5 June 176015 August 1852) was a Finnish chemist, physicist and mineralogist. Gadolin discovered a " new earth" containing the first rare-earth compound yttrium, which was later determined to be a chemical element. He is also ...
, and its oxide was named " gadolinia".
Further spectroscopic analysis between 1886 and 1901 of samaria, yttria, and samarskite by William Crookes
Sir William Crookes (; 17 June 1832 – 4 April 1919) was a British chemist and physicist who attended the Royal College of Chemistry, now part of Imperial College London, and worked on spectroscopy. He was a pioneer of vacuum tubes, inventing t ...
, Lecoq de Boisbaudran and Eugène-Anatole Demarçay
Eugène-Anatole Demarçay (1 January 1852 – 5 March 1903) was a French chemist who designed an apparatus to produce a spark using an induction coil and used it to generate the spectra of Rare-earth element, rare earth elements which he examin ...
yielded several new spectroscopic lines
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to iden ...
that indicated the existence of an unknown element. The fractional crystallization of the oxides then yielded ''europium
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lanth ...
'' in 1901.
In 1839 the third source for rare earths became available. This is a mineral similar to gadolinite, ''uranotantalum'' (now called "samarskite"). This mineral from Miass
Miass ( rus, Миа́сс, p=mʲɪˈas) is a city in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located west of Chelyabinsk, on the eastern slope of the Southern Ural Mountains, on the bank of the river Miass. Population:
Name
The name Miass is taken from ...
in the southern Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
was documented by Gustav Rose
Prof Gustavus ("Gustav") Rose FRSFor HFRSE (18 March 1798 – 15 July 1873) was a German mineralogist who was a native of Berlin. He was President of the German Geological Society from 1863 to 1873.
Life
He was born in Berlin the son of pharmaco ...
. The Russian chemist R. Harmann proposed that a new element he called "ilmenium Ilmenium was the proposed name for a new element found by the chemist R. Hermann in 1847. During the analysis of the mineral samarskite, he concluded that it does contain an element similar to niobium and tantalum. The similar reactivity of niobium ...
" should be present in this mineral, but later, Christian Wilhelm Blomstrand
Christian Wilhelm Blomstrand (20 October 1826 – 5 November 1897) was a Swedish mineralogist and chemist. He was a professor at the University of Lund from 1862-1895, where he isolated the element niobium in 1864. He developed an early version of ...
, Galissard de Marignac, and Heinrich Rose
Heinrich Rose (6 August 1795 – 27 January 1864) was a German mineralogist and analytical chemist. He was the brother of the mineralogist Gustav Rose and a son of Valentin Rose.
Rose's early works on phosphorescence were noted in the Quarter ...
found only tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is ...
and niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
(columbium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
) in it.
The exact number of rare-earth elements that existed was highly unclear, and a maximum number of 25 was estimated. The use of X-ray spectra
X-ray spectroscopy is a general term for several spectroscopic techniques for characterization of materials by using x-ray radiation.
Characteristic X-ray spectroscopy
When an electron from the inner shell of an atom is excited by the energy o ...
(obtained by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
) by Henry Gwyn Jeffreys Moseley made it possible to assign atomic numbers to the elements. Moseley found that the exact number of lanthanides had to be 15, and that element 61 had yet to be discovered.
Using these facts about atomic numbers from X-ray crystallography, Moseley also showed that hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
(element 72) would not be a rare-earth element. Moseley was killed in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in 1915, years before hafnium was discovered. Hence, the claim of Georges Urbain Georges Urbain (12 April 1872 – 5 November 1938) was a French chemist, a professor of the Sorbonne, a member of the Institut de France, and director of the Institute of Chemistry in Paris. Much of his work focused on the rare earths, isolating a ...
that he had discovered element 72 was untrue. Hafnium is an element that lies in the periodic table immediately below zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'', ...
, and hafnium and zirconium are very similar in their chemical and physical properties.
During the 1940s, Frank Spedding
Frank Harold Spedding (22 October 1902 – 15 December 1984) was a Canadian American chemist. He was a renowned expert on rare earth elements, and on extraction of metals from minerals. The uranium extraction process helped make it possible for ...
and others in the United States (during the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
) developed chemical ion-exchange procedures for separating and purifying the rare-earth elements. This method was first applied to the actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The inform ...
s for separating plutonium-239
Plutonium-239 (239Pu or Pu-239) is an isotope of plutonium. Plutonium-239 is the primary fissile isotope used for the production of nuclear weapons, although uranium-235 is also used for that purpose. Plutonium-239 is also one of the three main ...
and neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactivity, radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after ...
from uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
, thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high me ...
, actinium
Actinium is a chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89. It was first isolated by Friedrich Oskar Giesel in 1902, who gave it the name ''emanium''; the element got its name by being wrongly identified with a substance An ...
, and the other actinides in the materials produced in nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nu ...
s. Plutonium-239 was very desirable because it is a fissile material
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction. By definition, fissile material can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of thermal energy. The predominant neutron energy may be ty ...
.
The principal sources of rare-earth elements are the minerals bastnäsite
The mineral bastnäsite (or bastnaesite) is one of a family of three carbonate-fluoride minerals, which includes bastnäsite-( Ce) with a formula of (Ce, La)CO3F, bastnäsite-( La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F, and bastnäsite-( Y) with a formul ...
, monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium- ...
, and loparite
Loparite-(Ce) is a granular, brittle oxide mineral of the perovskite class. It is black to dark grey and may appear grey to white in reflected light on polished thin section with reddish brown internal reflections.Loparite-(Ce) oWebmineral/ref> It ...
and the lateritic
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by ...
ion-adsorption clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
s. Despite their high relative abundance, rare-earth minerals are more difficult to mine and extract than equivalent sources of transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
s (due in part to their similar chemical properties), making the rare-earth elements relatively expensive. Their industrial use was very limited until efficient separation techniques were developed, such as ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one kind of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid with the reaction being used especially for softening or making water demineralised, ...
, fractional crystallization and liquid–liquid extraction
Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE), also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes, based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water (polar) and an orga ...
during the late 1950s and early 1960s.
Some ilmenite concentrates contain small amounts of scandium and other rare-earth elements, which could be analysed by XRF.
Early classification
Before the time that ion-exchange methods andelution
In analytical and organic chemistry, elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent; as in washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove captured ions.
In a liquid chromatography experiment, for exam ...
were available, the separation of the rare earths was primarily achieved by repeated precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
or crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposi ...
. In those days, the first separation was into two main groups, the cerium earths (scandium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, and samarium) and the yttrium earths (yttrium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium). Europium, gadolinium, and terbium were either considered as a separate group of rare-earth elements (the terbium group), or europium was included in the cerium group, and gadolinium and terbium were included in the yttrium group. The reason for this division arose from the difference in solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
of rare-earth double sulfates with sodium and potassium. The sodium double sulfates of the cerium group are poorly soluble, those of the terbium group slightly, and those of the yttrium group are very soluble. Sometimes, the yttrium group was further split into the erbium group (dysprosium, holmium, erbium, and thulium) and the ytterbium group (ytterbium and lutetium), but today the main grouping is between the cerium and the yttrium groups. Today, the rare-earth elements are classified as light or heavy rare-earth elements, rather than in cerium and yttrium groups.
Light versus heavy classification
The classification of rare-earth elements is inconsistent between authors. The most common distinction between rare-earth elements is made byatomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
s; those with low atomic numbers are referred to as light rare-earth elements (LREE), those with high atomic numbers are the heavy rare-earth elements (HREE), and those that fall in between are typically referred to as the middle rare-earth elements (MREE). Commonly, rare-earth elements with atomic numbers 57 to 61 (lanthanum to promethium) are classified as light and those with atomic numbers 62 and greater are classified as heavy-rare earth elements. Increasing atomic numbers between light and heavy rare-earth elements and decreasing atomic radii throughout the series causes chemical variations. Europium is exempt of this classification as it has two valence states: Eu and Eu. Yttrium is grouped as heavy rare-earth element due to chemical similarities. The break between the two groups is sometimes put elsewhere, such as between elements 63 (europium) and 64 (gadolinium). The actual metallic densities of these two groups overlap, with the "light" group having densities from 6.145 (lanthanum) to 7.26 (promethium) or 7.52 (samarium) g/cc, and the "heavy" group from 6.965 (ytterbium) to 9.32 (thulium), as well as including yttrium at 4.47. Europium has a density of 5.24.
Origin
Rare-earth elements, exceptscandium
Scandium is a chemical element with the symbol Sc and atomic number 21. It is a silvery-white metallic d-block element. Historically, it has been classified as a rare-earth element, together with yttrium and the Lanthanides. It was discovered in ...
, are heavier than iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
and thus are produced by supernova nucleosynthesis
Supernova nucleosynthesis is the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements in supernova explosions.
In sufficiently massive stars, the nucleosynthesis by fusion of lighter elements into heavier ones occurs during sequential hydrostatic burning processe ...
or by the s-process
The slow neutron-capture process, or ''s''-process, is a series of reactions in nuclear astrophysics that occur in stars, particularly asymptotic giant branch stars. The ''s''-process is responsible for the creation (nucleosynthesis) of approximat ...
in asymptotic giant branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ...
stars. In nature, spontaneous fission
Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of radioactive decay that is found only in very heavy chemical elements. The nuclear binding energy of the elements reaches its maximum at an atomic mass number of about 56 (e.g., iron-56); spontaneous breakdo ...
of uranium-238
Uranium-238 (238U or U-238) is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it ...
produces trace amounts of radioactive promethium
Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is extremely rare, with only about 500–600 grams naturally occurring in Earth's crust at any given time. Promethium is one of onl ...
, but most promethium is synthetically produced in nuclear reactors.
Due to their chemical similarity, the concentrations of rare earths in rocks are only slowly changed by geochemical processes, making their proportions useful for geochronology
Geochronology is the science of determining the age of rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, whereas relative geochronology is ...
and dating fossils.
Geological distribution
cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 o ...
, which is actually the 25th most abundant element in Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
, having 68 parts per million (about as common as copper). The exception is the highly unstable and radioactive promethium
Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is extremely rare, with only about 500–600 grams naturally occurring in Earth's crust at any given time. Promethium is one of onl ...
"rare earth" is quite scarce. The longest-lived isotope of promethium has a half-life of 17.7 years, so the element exists in nature in only negligible amounts (approximately 572 g in the entire Earth's crust). Promethium is one of the two elements that do not have stable (non-radioactive) isotopes and are followed by (i.e. with higher atomic number) stable elements (the other being technetium
Technetium is a chemical element with the symbol Tc and atomic number 43. It is the lightest element whose isotopes are all radioactive. All available technetium is produced as a synthetic element. Naturally occurring technetium is a spontaneous ...
).
The rare-earth elements are often found together. During the sequential accretion of the Earth, the dense rare-earth elements were incorporated into the deeper portions of the planet. Early differentiation of molten material largely incorporated the rare-earths into mantle rocks. The high field strength and large ionic radii
Ionic radius, ''r''ion, is the radius of a monatomic ion in an ionic crystal structure. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries, they are treated as if they were hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cation ...
of rare-earths make them incompatible with the crystal lattices of most rock-forming minerals, so REE will undergo strong partitioning into a melt phase if one is present. REE are chemically very similar and have always been difficult to separate, but a gradual decrease in ionic radius from light REE (LREE) to heavy REE (HREE), called lanthanide contraction
The lanthanide contraction is the greater-than-expected decrease in atomic radii/ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series from atomic number 57, lanthanum, to 71, lutetium, which results in smaller than otherwise expected atomic radii ...
, can produce a broad separation between light and heavy REE. The larger ionic radii of LREE make them generally more incompatible than HREE in rock-forming minerals, and will partition more strongly into a melt phase, while HREE may prefer to remain in the crystalline residue, particularly if it contains HREE-compatible minerals like garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
. The result is that all magma formed from partial melting will always have greater concentrations of LREE than HREE, and individual minerals may be dominated by either HREE or LREE, depending on which range of ionic radii best fits the crystal lattice.
Among the anhydrous rare-earth phosphates, it is the tetragonal mineral xenotime
Xenotime is a rare-earth phosphate mineral, the major component of which is yttrium orthophosphate ( Y P O4). It forms a solid solution series with chernovite-(Y) ( Y As O4) and therefore may contain trace impurities of arsenic, as well as sili ...
that incorporates yttrium and the HREE, whereas the monoclinic monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium- ...
phase incorporates cerium and the LREE preferentially. The smaller size of the HREE allows greater solid solubility in the rock-forming minerals that make up Earth's mantle, and thus yttrium and the HREE show less enrichment in Earth's crust relative to chondritic
A chondrite is a stony (non-metallic) meteorite that has not been modified, by either melting or differentiation of the parent body. They are formed when various types of dust and small grains in the early Solar System accreted to form pri ...
abundance than does cerium and the LREE. This has economic consequences: large ore bodies of LREE are known around the world and are being exploited. Ore bodies for HREE are more rare, smaller, and less concentrated. Most of the current supply of HREE originates in the "ion-absorption clay" ores of Southern China. Some versions provide concentrates containing about 65% yttrium oxide, with the HREE being present in ratios reflecting the Oddo–Harkins rule The Oddo–Harkins rule holds that an element with an even atomic number (such as carbon, element 6) is more abundant than both elements with the adjacently larger and smaller odd atomic numbers (such as boron, element 5, and nitrogen, element 7, ...
: even-numbered REE at abundances of about 5% each, and odd-numbered REE at abundances of about 1% each. Similar compositions are found in xenotime or gadolinite.
Well-known minerals containing yttrium, and other HREE, include gadolinite, xenotime, samarskite
Samarskite is a radioactive rare earth mineral series which includes samarskite-(Y), with the chemical formula and samarskite-(Yb), with the chemical formula . The formula for samarskite-(Y) is also given as .
Samarskite crystallizes in the orth ...
, euxenite
Euxenite, or euxenite-(Y) (the official mineralogical name), is a brownish black mineral with a metallic luster.
Chemistry
It contains calcium, niobium, tantalum, cerium, titanium, yttrium, and typically uranium and thorium, with some other meta ...
, fergusonite
Fergusonite is a mineral comprising a complex oxide of various rare-earth elements. The general chemical formula of fergusonite is (Y,REE)NbO4, where REE = rare-earth elements in solid solution with Y. Yttrium is usually dominant (the mineral in ...
, yttrotantalite, yttrotungstite, yttrofluorite (a variety of fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs sca ...
), thalenite, yttrialite
Yttrialite or Yttrialite-(Y) is a rare yttrium thorium sorosilicate mineral with formula: ( Y, Th)2 Si2 O7. It forms green to orange yellow masses with conchoidal fracture. It crystallizes in the monoclinic-prismatic crystal system. It has a Mohs h ...
. Small amounts occur in zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the r ...
, which derives its typical yellow fluorescence from some of the accompanying HREE. The zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name ''zirconium'' is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. The word is related to Persian '' zargun'' (zircon; ''zar-gun'', ...
mineral eudialyte
Eudialyte, whose name derives from the Greek phrase , , meaning "well decomposable", is a somewhat rare, nine member ring cyclosilicate mineral, which forms in alkaline igneous rocks, such as nepheline syenites. Its name alludes to its ready ...
, such as is found in southern Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
, contains small but potentially useful amounts of yttrium. Of the above yttrium minerals, most played a part in providing research quantities of lanthanides during the discovery days. Xenotime
Xenotime is a rare-earth phosphate mineral, the major component of which is yttrium orthophosphate ( Y P O4). It forms a solid solution series with chernovite-(Y) ( Y As O4) and therefore may contain trace impurities of arsenic, as well as sili ...
is occasionally recovered as a byproduct of heavy-sand processing, but is not as abundant as the similarly recovered monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium- ...
(which typically contains a few percent of yttrium). Uranium ores from Ontario have occasionally yielded yttrium as a byproduct.
Well-known minerals containing cerium, and other LREE, include bastnäsite
The mineral bastnäsite (or bastnaesite) is one of a family of three carbonate-fluoride minerals, which includes bastnäsite-( Ce) with a formula of (Ce, La)CO3F, bastnäsite-( La) with a formula of (La, Ce)CO3F, and bastnäsite-( Y) with a formul ...
, monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium- ...
, allanite
Allanite (also called orthite) is a sorosilicate group of minerals within the broader epidote group that contain a significant amount of rare-earth elements. The mineral occurs mainly in metamorphosed clay-rich sediments and felsic igneous rock ...
, loparite
Loparite-(Ce) is a granular, brittle oxide mineral of the perovskite class. It is black to dark grey and may appear grey to white in reflected light on polished thin section with reddish brown internal reflections.Loparite-(Ce) oWebmineral/ref> It ...
, ancylite
Ancylite is a group of hydrous strontium carbonate minerals containing cerium, lanthanum and minor amounts of other rare-earth elements. The chemical formula is with ancylite-Ce enriched in cerium and ancylite-La in lanthanum.http://webmineral.c ...
, parisite
Parisite is a rare mineral consisting of cerium, lanthanum and calcium fluoro-carbonate, . Parisite is mostly parisite-(Ce), but when neodymium is present in the structure the mineral becomes parisite-(Nd).
It is found only as crystals, which bel ...
, lanthanite
Lanthanites are a group of isostructural rare earth element (REE) carbonate minerals. This group comprises the minerals lanthanite-(La), lanthanite-(Ce), and lanthanite-(Nd). This mineral group has the general chemical formula of (''REE'')2(CO3)3� ...
, chevkinite, cerite
Cerite is a complex silicate mineral group containing cerium, formula .http://rruff.geo.arizona.edu/doclib/hom/ceritece.pdf Handbook of Mineralogy The cerium and lanthanum content varies with the Ce rich species (cerite-(Ce)) and the La rich speci ...
, stillwellite
Stillwellite-(Ce) is a rare-earth boro-silicate mineral with chemical formula .
Location
It occurs as a metasomatic replacement of metamorphosed limestones in the Mary Kathleen mine, Australia and in alkalic pegmatites associated with syenite ...
, britholite, fluocerite
Fluocerite, also known as tysonite, is a mineral consisting of cerium and lanthanum fluorides, with the chemical formula . The end members are classified as two different mineral types depending on the cation, fluocerite-(Ce) and fluocerite-(La) ...
, and cerianite. Monazite (marine sands from Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, or Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
; rock from South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
), bastnäsite (from Mountain Pass rare earth mine
The Mountain Pass Mine, owned by MP Materials, is an open-pit mine of rare-earth elements on the south flank of the Clark Mountain Range in California, southwest of Las Vegas, Nevada. In 2020 the mine supplied 15.8% of the world's rare-earth p ...
, or several localities in China), and loparite
Loparite-(Ce) is a granular, brittle oxide mineral of the perovskite class. It is black to dark grey and may appear grey to white in reflected light on polished thin section with reddish brown internal reflections.Loparite-(Ce) oWebmineral/ref> It ...
(Kola Peninsula
sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк
, image_name= Kola peninsula.png
, image_caption= Kola Peninsula as a part of Murmansk Oblast
, image_size= 300px
, image_alt=
, map_image= Murmansk in Russia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Murmansk Oblas ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
) have been the principal ores of cerium and the light lanthanides.
Enriched deposits of rare-earth elements at the surface of the Earth, carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive rock, intrusive or extrusive rock, extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geoche ...
s and pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic com ...
s, are related to alkaline plutonism
Plutonism is the geologic theory that the igneous rocks forming the Earth originated from intrusive magmatic activity, with a continuing gradual process of weathering and erosion wearing away rocks, which were then deposited on the sea bed, re- ...
, an uncommon kind of magmatism that occurs in tectonic settings where there is rifting or that are near subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
zones. In a rift setting, the alkaline magma is produced by very small degrees of partial melting (<1%) of garnet peridotite in the upper mantle
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle at . Temperatures range from appr ...
(200 to 600 km depth). This melt becomes enriched in incompatible elements, like the rare-earth elements, by leaching them out of the crystalline residue. The resultant magma rises as a diapir
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–T ...
, or diatreme
A diatreme, sometimes known as a maar-diatreme volcano, is a volcanic pipe formed by a gaseous explosion. When magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the ...
, along pre-existing fractures, and can be emplaced deep in the crust
''The Crust'' is a British television series about a pizza parlour which was originally shown by CBBC. It was produced by Darrall Macqueen
Darrall Macqueen is an independent children's television production company based in London, United ...
, or erupted at the surface. Typical REE enriched deposits types forming in rift settings are carbonatites, and A- and M-Type granitoids. Near subduction zones, partial melting of the subducting plate within the asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between ~ below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere is not ...
(80 to 200 km depth) produces a volatile-rich magma (high concentrations of and water), with high concentrations of alkaline elements, and high element mobility that the rare-earths are strongly partitioned into. This melt may also rise along pre-existing fractures, and be emplaced in the crust above the subducting slab or erupted at the surface. REE enriched deposits forming from these melts are typically S-Type granitoids.
Alkaline magmas enriched with rare-earth elements include carbonatites, peralkaline granites (pegmatites), and nepheline syenite
Nepheline syenite is a holocrystalline plutonic rock that consists largely of nepheline and alkali feldspar. The rocks are mostly pale colored, grey or pink, and in general appearance they are not unlike granites, but dark green varieties are al ...
. Carbonatite
Carbonatite () is a type of intrusive rock, intrusive or extrusive rock, extrusive igneous rock defined by mineralogic composition consisting of greater than 50% carbonate minerals. Carbonatites may be confused with marble and may require geoche ...
s crystallize from -rich fluids, which can be produced by partial melting of hydrous-carbonated lherzolite
Lherzolite is a type of ultramafic igneous rock. It is a coarse-grained rock consisting of 40 to 90% olivine along with significant orthopyroxene and lesser amounts of calcic chromium-rich clinopyroxene. Minor minerals include chromium and alu ...
to produce a CO-rich primary magma, by fractional crystallization of an alkaline primary magma, or by separation of a -rich immiscible liquid from. These liquids are most commonly forming in association with very deep Precambrian Craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s, like the ones found in Africa and the Canadian Shield. Ferrocarbonatites are the most common type of carbonatite to be enriched in REE, and are often emplaced as late-stage, breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of di ...
ted pipes at the core of igneous complexes; they consist of fine-grained calcite and hematite, sometimes with significant concentrations of ankerite and minor concentrations of siderite. Large carbonatite deposits enriched in rare-earth elements include Mount Weld in Australia, Thor Lake in Canada, Zandkopsdrift in South Africa, and Mountain Pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since many of the world's mountain ranges have presented formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human a ...
in the USA. Peralkaline granites (A-Type granitoids) have very high concentrations of alkaline elements and very low concentrations of phosphorus; they are deposited at moderate depths in extensional zones, often as igneous ring complexes, or as pipes, massive bodies, and lenses. These fluids have very low viscosities and high element mobility, which allows for crystallization of large grains, despite a relatively short crystallization time upon emplacement; their large grain size is why these deposits are commonly referred to as pegmatites. Economically viable pegmatites are divided into Lithium-Cesium-Tantalum (LCT) and Niobium-Yttrium-Fluorine (NYF) types; NYF types are enriched in rare-earth minerals. Examples of rare-earth pegmatite deposits include Strange Lake in Canada, and Khaladean-Buregtey in Mongolia. Nepheline syenite (M-Type granitoids) deposits are 90% feldspar and feldspathoid minerals, and are deposited in small, circular massifs. They contain high concentrations of rare-earth-bearing accessory minerals. For the most part these deposits are small but important examples include Illimaussaq-Kvanefeld in Greenland, and Lovozera in Russia.
Rare-earth elements can also be enriched in deposits by secondary alteration either by interactions with hydrothermal fluids or meteoric water or by erosion and transport of resistate REE-bearing minerals. Argillization of primary minerals enriches insoluble elements by leaching out silica and other soluble elements, recrystallizing feldspar into clay minerals such kaolinite, halloysite and montmorillonite. In tropical regions where precipitation is high, weathering forms a thick argillized regolith, this process is called supergene enrichment and produces laterite
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by ...
deposits; heavy rare-earth elements are incorporated into the residual clay by absorption. This kind of deposit is only mined for REE in Southern China, where the majority of global heavy rare-earth element production occurs. REE-laterites do form elsewhere, including over the carbonatite at Mount Weld in Australia. REE may also by extracted from placer deposits if the sedimentary parent lithology contained REE-bearing, heavy resistate minerals.
In 2011, Yasuhiro Kato, a geologist at the University of Tokyo
, abbreviated as or UTokyo, is a public research university located in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Established in 1877, the university was the first Imperial University and is currently a Top Type university of the Top Global University Project by ...
who led a study of Pacific Ocean seabed mud, published results indicating the mud could hold rich concentrations of rare-earth minerals. The deposits, studied at 78 sites, came from " t plumes from hydrothermal vents pull ngthese materials out of seawater and deposit ngthem on the seafloor, bit by bit, over tens of millions of years. One square patch of metal-rich mud 2.3 kilometers wide might contain enough rare earths to meet most of the global demand for a year, Japanese geologists report in ''Nature Geoscience
''Nature Geoscience'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Nature Publishing Group. The Chief Editor is Tamara Goldin, who took over from Heike Langenberg in February 2020. It was established in January 2008.
Scope
The ...
''." "I believe that rare arth resources undersea are much more promising than on-land resources," said Kato. " ncentrations of rare earths were comparable to those found in clays mined in China. Some deposits contained twice as much heavy rare earths such as dysprosium, a component of magnets in hybrid car motors."Powell, Devin"Rare earth elements plentiful in ocean sediments"
'' ScienceNews'', 3 July 2011. Via Kurt Brouwer'
Fundmastery Blog
''MarketWatch'', 2011-07-05. Retrieved 2011-07-05.
Notes on rare-earth elements geochemistry
The REE geochemical classification is usually done on the basis of theiratomic weight
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a giv ...
. One of the most common classifications divides REE into 3 groups: light rare earths (LREE - from 57La to 64Nd), intermediate (MREE - from 62Sm to 67Ho) and heavy (HREE - from 68Er to 71Lu). REE usually appear as trivalent ions, except for Ce and Eu which can take the form of Ce4+ and Eu2+ depending on the redox conditions of the system.
Unlike Y, the lanthanides are characterized by the progressive filling of the 4''f'' orbital. The latter is not the outermost orbital and therefore the electrons contained in it are not part of the valence electrons
In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron in the outer shell associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms ...
, which are instead represented by the 2 electrons in the 6''s'' orbital and by the single electron in the 5''d'' orbital. This electron behaviour is highlighted by the radial distribution function
In statistical mechanics, the radial distribution function, (or pair correlation function) g(r) in a system of particles (atoms, molecules, colloids, etc.), describes how density varies as a function of distance from a reference particle.
If ...
of the electrons around the nucleus of the lanthanides for the various external orbitals, from which it can be deduced that the function relative to the 4''f'' orbital is closer to the nucleus of the element than those of the 6''s'' and 5''d'' orbitals. This does not apply to the Y since it does not have electrons in the 4''f'' orbitals. Therefore, the external electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom ...
is the same for all lanthanides, being efn6s25d1 in the neutral form and efn6s05d0 in the ionic form. Consequentially, REE are characterized by a substantial identity in their chemical reactivity, which results in a serial behaviour during geochemical processes rather than being characteristic of a single element of the series.
A distinguishing factor in the geochemical behaviour of the REE is linked to the so-called "lanthanide contraction
The lanthanide contraction is the greater-than-expected decrease in atomic radii/ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series from atomic number 57, lanthanum, to 71, lutetium, which results in smaller than otherwise expected atomic radii ...
" which represents a higher-than-expected decrease in the atomic/ionic radius of the elements along the series. This is determined by the variation of the shielding effect
In chemistry, the shielding effect sometimes referred to as atomic shielding or electron shielding describes the attraction between an electron and the nucleus in any atom with more than one electron. The shielding effect can be defined as a re ...
towards the nuclear charge due to the progressive filling of the 4''f'' orbital which acts against the electrons of the 6''s'' and 5''d'' orbitals.The lanthanide contraction has a direct effect on the geochemistry of the lanthanides, which show a different behaviour depending on the systems and processes in which they are involved. The effect of the lanthanide contraction can be observed in the REE behaviour both in a CHARAC-type geochemical system (CHArge-and-RAdius-Controlled) where elements with similar charge and radius should show coherent geochemical behaviour, and in non-CHARAC systems, such as aqueous solutions, where the electron structure is also an important parameter to consider as the lanthanide contraction affects the ionic potential
Ionic potential is the ratio of the electrical charge (''z'') to the radius (''r'') of an ion.
\text = \frac = \frac
As such, this ratio is a measure of the charge density at the surface of the ion; usually the denser the charge, the stronger ...
. A direct consequence is that, during the formation of coordination bonds, the REE behaviour gradually changes along the series. Furthermore, the lanthanide contraction causes the ionic radius of Ho3+ (0.901 Å) to be almost identical to that of Y3+ (0.9 Å), justifying the inclusion of the latter among the REE.
Geochemistry applications
The application of rare-earth elements to geology is important to understanding the petrological processes ofigneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
, sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic matter, organic particles at Earth#Surface, Earth's surface, followed by cementation (geology), cementation. Sedimentati ...
and metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causin ...
rock formation. In geochemistry
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the e ...
, rare-earth elements can be used to infer the petrological mechanisms that have affected a rock due to the subtle atomic size
The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the Atomic nucleus, nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physica ...
differences between the elements, which causes preferential fractionation
Fractionation is a separation process in which a certain quantity of a mixture (of gases, solids, liquids, enzymes, or isotopes, or a suspension) is divided during a phase transition, into a number of smaller quantities (fractions) in which the ...
of some rare earths relative to others depending on the processes at work.
The geochemical study of the REE is not carried out on absolute concentrations – as it is usually done with other chemical elements – but on normalized concentrations in order to observe their serial behaviour. In geochemistry, rare-earth elements are typically presented in normalized "spider" diagrams, in which concentration of rare-earth elements are normalized to a reference standard and are then expressed as the logarithm to the base 10 of the value.
Commonly, the rare-earth elements are normalized to chondritic meteorites, as these are believed to be the closest representation of unfractionated solar system material. However, other normalizing standards can be applied depending on the purpose of the study. Normalization to a standard reference value, especially of a material believed to be unfractionated, allows the observed abundances to be compared to initial abundances of the element. Normalization also removes the pronounced 'zig-zag' pattern caused by the differences in abundance between even and odd atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
s. Normalization is carried out by dividing the analytical concentrations of each element of the series by the concentration of the same element in a given standard, according to the equation:
where ''n'' indicates the normalized concentration, the analytical concentration of element measured in the sample, and the concentration of the same element in the reference material.
It is possible to observe the serial trend of the REE by reporting their normalized concentrations against the atomic number. The trends that are observed in "spider" diagrams are typically referred to as "patterns", which may be diagnostic of petrological processes that have affected the material of interest.
According to the general shape of the patterns or thanks to the presence (or absence) of so-called "anomalies", information regarding the system under examination and the occurring geochemical processes can be obtained. The anomalies represent enrichment (positive anomalies) or depletion (negative anomalies) of specific elements along the series and are graphically recognizable as positive or negative “peaks” along the REE patterns. The anomalies can be numerically quantified as the ratio between the normalized concentration of the element showing the anomaly and the predictable one based on the average of the normalized concentrations of the two elements in the previous and next position in the series, according to the equation:
where is the normalized concentration of the element whose anomaly has to be calculated, and the normalized concentrations of the respectively previous and next elements along the series.
The rare-earth elements patterns observed in igneous rocks are primarily a function of the chemistry of the source where the rock came from, as well as the fractionation history the rock has undergone. Fractionation is in turn a function of the partition coefficient
In the physical sciences, a partition coefficient (''P'') or distribution coefficient (''D'') is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. This ratio is therefore a comparison of the solub ...
s of each element. Partition coefficients are responsible for the fractionation of a trace elements (including rare-earth elements) into the liquid phase (the melt/magma) into the solid phase (the mineral). If an element preferentially remains in the solid phase it is termed ‘compatible’, and it preferentially partitions into the melt phase it is described as ‘incompatible’. Each element has a different partition coefficient, and therefore fractionates into solid and liquid phases distinctly. These concepts are also applicable to metamorphic and sedimentary petrology.
In igneous rocks, particularly in felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, whi ...
melts, the following observations apply: anomalies in europium are dominated by the crystallization of feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldsp ...
s. Hornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rocks ...
, controls the enrichment of MREE compared to LREE and HREE. Depletion of LREE relative to HREE may be due to the crystallization of olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickl ...
, orthopyroxene, and clinopyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
. On the other hand, depletion of HREE relative to LREE may be due to the presence of garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
, as garnet preferentially incorporates HREE into its crystal structure. The presence of zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the r ...
may also cause a similar effect.
In sedimentary rocks, rare-earth elements in clastic sediments are a representation provenance. The rare-earth element concentrations are not typically affected by sea and river waters, as rare-earth elements are insoluble and thus have very low concentrations in these fluids. As a result, when a sediment is transported, rare-earth element concentrations are unaffected by the fluid and instead the rock retains the rare-earth element concentration from its source.
Sea and river waters typically have low rare-earth element concentrations. However, aqueous geochemistry is still very important. In oceans, rare-earth elements reflect input from rivers, hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s, and aeolian sources; this is important in the investigation of ocean mixing and circulation.
Rare-earth elements are also useful for dating rocks, as some radioactive isotopes
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
display long half-lives. Of particular interest are the La-Ce, Sm-Nd, and Lu-Hf systems.
Production
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. Through the 1950s, South Africa was the world's rare-earth source, from a monazite-rich reef at the Steenkampskraal mine in Western Cape
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , and the third most populous, with an estimated 7 million inhabitants in 2020 ...
province. Through the 1960s until the 1980s, the Mountain Pass rare earth mine
The Mountain Pass Mine, owned by MP Materials, is an open-pit mine of rare-earth elements on the south flank of the Clark Mountain Range in California, southwest of Las Vegas, Nevada. In 2020 the mine supplied 15.8% of the world's rare-earth p ...
in California made the United States the leading producer. Today, the Indian and South African deposits still produce some rare-earth concentrates, but they are dwarfed by the scale of Chinese production. In 2017, China produced 81% of the world's rare-earth supply, mostly in Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, China's Rare Earth Dominance, Wikinvest. Retrieved on 11 Aug 2010. although it had only 36.7% of reserves. Australia was the second and only other major producer with 15% of world production. All of the world's heavy rare earths (such as dysprosium) come from Chinese rare-earth sources such as the polymetal
In chemistry or mining, polymetal or polymetallic is a substance composed of a combination of different metals. When the substance contains only two metals the term ''bimetal'' (''bimetallic'') is sometimes preferred. A (or ') is an ore that is ...
lic Bayan Obo
Bayan'obo Mining District, ( Mongolian: ''Bayan Oboɣ-a Aɣurqai-yin toɣoriɣ'', Баян-Овоо Уурхайн тойрог ( mn, italic=yes, "rich" + ovoo); ), or Baiyun-Obo or Baiyun'ebo, is a mining town in the west of Inner Mongolia, ...
deposit. The Browns Range mine, located 160 km south east of Halls Creek
Halls is a plural of the word hall.
Halls may also refer to:
People
* Walter Halls (1871–1953), British trade unionist and politician
* Ethel May Halls (1882–1967), American actress
* Julian Halls (born 1967), British field hockey player
* ...
in northern Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
, is currently under development and is positioned to become the first significant dysprosium producer outside of China.
Increased demand has strained supply, and there is growing concern that the world may soon face a shortage of the rare earths. In several years from 2009 worldwide demand for rare-earth elements is expected to exceed supply by 40,000 tonnes annually unless major new sources are developed."As hybrid cars gobble rare metals, shortage looms"Reuters. August 31, 2009. Retrieved Aug 31, 2009. In 2013, it was stated that the demand for REEs would increase due to the dependence of the EU on these elements, the fact that rare earth elements cannot be substituted by other elements and that REEs have a low recycling rate. Furthermore, due to the increased demand and low supply, future prices are expected to increase and there is a chance that countries other than China will open REE mines. REE is increasing in demand due to the fact that they are essential for new and innovative technology that is being created. These new products that need REEs to be produced are high technology equipment such as smart phones, digital cameras, computer parts, semiconductors, etc. In addition, these elements are more prevalent in the following industries: renewable energy technology, military equipment, glass making, and metallurgy.
China
These concerns have intensified due to the actions of China, the predominant supplier. Specifically, China has announced regulations on exports and a crackdown on smuggling. On September 1, 2009, China announced plans to reduce its export quota to 35,000 tons per year in 2010–2015 to conserve scarce resources and protect the environment. On October 19, 2010, ''China Daily
''China Daily'' () is an English-language daily newspaper owned by the Central Propaganda Department of the Chinese Communist Party.
Overview
''China Daily'' has the widest print circulation of any English-language newspaper in China. T ...
'', citing an unnamed Ministry of Commerce official, reported that China will "further reduce quotas for rare-earth exports by 30 percent at most next year to protect the precious metals from over-exploitation." The government in Beijing further increased its control by forcing smaller, independent miners to merge into state-owned corporations or face closure. At the end of 2010, China announced that the first round of export quotas in 2011 for rare earths would be 14,446 tons, which was a 35% decrease from the previous first round of quotas in 2010. China announced further export quotas on 14 July 2011 for the second half of the year with total allocation at 30,184 tons with total production capped at 93,800 tonnes. In September 2011, China announced the halt in production of three of its eight major rare-earth mines, responsible for almost 40% of China's total rare-earth production. In March 2012, the US, EU, and Japan confronted China at WTO about these export and production restrictions. China responded with claims that the restrictions had environmental protection in mind. In August 2012, China announced a further 20% reduction in production.
The United States, Japan, and the European Union filed a joint lawsuit with the World Trade Organization in 2012 against China, arguing that China should not be able to deny such important exports.
In response to the opening of new mines in other countries (Lynas
Lynas Rare Earths, Ltd. is an Australian rare-earths mining company, listed on the Australian Securities Exchange as a S&P/ASX 200 company. It has two major operations: a mining and concentration plant at Mount Weld, Western Australia, ...
in Australia and Molycorp
Molycorp Inc. was an American mining corporation headquartered in Greenwood Village, Colorado. The corporation, which was formerly traded on the New York Stock Exchange, owned the Mountain Pass rare earth mine in California. It filed for bankrup ...
in the United States), prices of rare earths dropped.
The price of dysprosium oxide was 994 USD
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
/kg in 2011, but dropped to US$265/kg by 2014.
On August 29, 2014, the WTO ruled that China had broken free-trade agreements, and the WTO said in the summary of key findings that "the overall effect of the foreign and domestic restrictions is to encourage domestic extraction and secure preferential use of those materials by Chinese manufacturers." China declared that it would implement the ruling on September 26, 2014, but would need some time to do so. By January 5, 2015, China had lifted all quotas from the export of rare earths, but export licences will still be required.
In 2019, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
supplied between 85% and 95% of the global demand for the 17 rare earth powders, half of them sourced from Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
. After the 2021 military coup in that country, future supplies of critical ores were possibly constrained. Additionally, it was speculated that the PRC could again reduce rare earth exports to counter-act economic sanction
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstances—they ma ...
s imposed by the US and EU countries. Rare earth metals serve as crucial materials for EV-manufacturing and high-tech military applications.
Outside China
As a result of the increased demand and tightening restrictions on exports of the metals from China, some countries are stockpiling rare-earth resources. Searches for alternative sources inAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
, Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
, and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
are ongoing. Mines in these countries were closed when China undercut world prices in the 1990s, and it will take a few years to restart production as there are many barriers to entry
In theories of competition in economics, a barrier to entry, or an economic barrier to entry, is a fixed cost that must be incurred by a new entrant, regardless of production or sales activities, into a market that incumbents do not have or have ...
. Significant sites under development outside China include Steenkampskraal in South Africa, the world's highest grade rare earths and thorium mine, closed in 1963, but has been gearing to go back into production. Over 80% of the infrastructure is already complete. Other mines include the Nolans Project in Central Australia, the Bokan Mountain Bokan may refer to:
Places
* Boken, Rawalpindi, a village in Punjab, Pakistan
*Bukan, a city in Iran
People
*Beau Bokan (born 1981), American musician and singer
*Dragoslav Bokan (born 1961), Serbian film director and writer
* Neda Bokan (born 194 ...
project in Alaska, the remote Hoidas Lake
Hoidas Lake is a remote northern Canadian lake which lies approximately 50 kilometers north of Uranium City, Saskatchewan. Named in honor of Irvin Frank Hoidas, a Royal Canadian Air Force pilot officer killed in action during the Second World War ...
project in northern Canada, and the Mount Weld
Mount Weld mine is a rare earth mine in Western Australia, located about south of Laverton and east of Leonora. It ranks as one of the richest major rare-earth deposits in the world.
Rare earths are contained in secondary phosphates and a ...
project in Australia. The Hoidas Lake
Hoidas Lake is a remote northern Canadian lake which lies approximately 50 kilometers north of Uranium City, Saskatchewan. Named in honor of Irvin Frank Hoidas, a Royal Canadian Air Force pilot officer killed in action during the Second World War ...
project has the potential to supply about 10% of the $1 billion of REE consumption that occurs in North America every year. Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
signed an agreement in October 2010 to supply Japan with rare earths from its northwestern Lai Châu Province
Lai or LAI may refer to:
Abbreviations
* Austrian Latin America Institute (Österreichisches Lateinamerika-Institut)
* ''Latin American Idol'', TV series
* La Trobe Institute, Melbourne, Australia
* Leaf area index, leaf area of a crop or ve ...
, however the deal was never realized due to disagreements.
The largest rare earth deposit in the U.S. is at Mountain Pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since many of the world's mountain ranges have presented formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human a ...
, California, sixty miles south of Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
. Originally opened by Molycorp
Molycorp Inc. was an American mining corporation headquartered in Greenwood Village, Colorado. The corporation, which was formerly traded on the New York Stock Exchange, owned the Mountain Pass rare earth mine in California. It filed for bankrup ...
, the deposit has been mined, off and on, since 1951. A second large deposit of REEs at Elk Creek in southeast Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwe ...
is under consideration by NioCorp Development Ltd who hopes to open a niobium, scandium, and titanium mine there. That mine may be able to produce as much as 7200 tonnes of ferro niobium and 95 tonnes of scandium trioxide annually, although, as of 2022, financing is still in the works.
In the UK, Pensana have begun construction of their US$195 million rare earth processing plant which secured funding from the UK government's Automotive Transformation Fund. The plant will process ore from the Longonjo mine in Angola and other sources as they become available. The company are targeting production in late 2023, before ramping up to full capacity in 2024. Pensana aim to produce 12,500 metric tons of separated rare earths, including 4,500 tons of magnet metal rare earths.
Also under consideration for mining are sites such as Thor Lake
Thor Lake is a deposit of rare metals located in the Blachford Lake intrusive complex. It is situated 5 km north of the Hearne Channel of Great Slave Lake, Northwest Territories, Canada, approximately 100 kilometers east-southeast of the cap ...
in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
, and various locations in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
.
Additionally, in 2010, a large deposit of rare-earth minerals was discovered in Kvanefjeld in southern Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
. Pre-feasibility drilling at this site has confirmed significant quantities of black lujavrite, which contains about 1% rare-earth oxides (REO). The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
has urged Greenland to restrict Chinese development of rare-earth projects there, but as of early 2013, the government of Greenland
Naalakkersuisut ( en, Cabinet of Greenland, da, Grønlands Regering), is the chief executive body and the government of Greenland since the island became self-governing in 1979. An "autonomous territory" ( da, land) of the Kingdom of Denmark, ta ...
has said that it has no plans to impose such restrictions. Many Danish politicians have expressed concerns that other nations, including China, could gain influence in thinly populated Greenland, given the number of foreign workers and investment that could come from Chinese companies in the near future because of the law passed December 2012.
In central Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, Ciudad Real Province, the proposed rare-earth mining project 'Matamulas' may provide, according to its developers, up to 2,100 Tn/year (33% of the annual UE demand). However, this project has been suspended by regional authorities due to social and environmental concerns.
Adding to potential mine sites, ASX
Australian Securities Exchange Ltd or ASX, is an Australian public company that operates Australia's primary securities exchange, the Australian Securities Exchange (sometimes referred to outside of Australia as, or confused within Australia as ...
listed Peak Resources announced in February 2012, that their Tanzanian-based Ngualla
Mount Ngualla, often referred to simply as Ngualla, is a collapsed volcano located in the remote south west of Tanzania. It is approximately 200 km north of the Mbeya township.
Formation
Ngualla is a Proterozoic carbonatite estimated to be ab ...
project contained not only the 6th largest deposit by tonnage outside of China, but also the highest grade of rare-earth elements of the 6.
North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
has been reported to have exported rare-earth ore to China, about US$1.88 million worth during May and June 2014.
In May 2012, researchers from two universities in Japan announced that they had discovered rare earths in Ehime Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Shikoku. Ehime Prefecture has a population of 1,342,011 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 5,676 km2 (2,191 sq mi). Ehime Prefecture borders Kagawa Prefecture to the northeast, Toku ...
, Japan.
Malaysian refining plans
In early 2011, Australian mining companyLynas
Lynas Rare Earths, Ltd. is an Australian rare-earths mining company, listed on the Australian Securities Exchange as a S&P/ASX 200 company. It has two major operations: a mining and concentration plant at Mount Weld, Western Australia, ...
was reported to be "hurrying to finish" a US$230 million rare-earth refinery on the eastern coast of Peninsular Malaysia's industrial port of Kuantan
Kuantan ( Jawi: ) is a city and the state capital of Pahang, Malaysia. It is located near the mouth of the Kuantan River. Kuantan is the 18th largest city in Malaysia based on 2010 population, and the largest city in the East Coast of Penin ...
. The plant would refine ore — lanthanides concentrate from the Mount Weld
Mount Weld mine is a rare earth mine in Western Australia, located about south of Laverton and east of Leonora. It ranks as one of the richest major rare-earth deposits in the world.
Rare earths are contained in secondary phosphates and a ...
mine in Australia. The ore would be trucked to Fremantle
Fremantle () () is a port city in Western Australia, located at the mouth of the Swan River in the metropolitan area of Perth, the state capital. Fremantle Harbour serves as the port of Perth. The Western Australian vernacular diminutive for ...
and transported by container ship
A container ship (also called boxship or spelled containership) is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermodal ...
to Kuantan. Within two years, Lynas was said to expect the refinery to be able to meet nearly a third of the world's demand for rare-earth materials, not counting China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. The Kuantan development brought renewed attention to the Malaysian town of Bukit Merah in Perak
Perak () is a state of Malaysia on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula. Perak has land borders with the Malaysian states of Kedah to the north, Penang to the northwest, Kelantan and Pahang to the east, and Selangor to the south. Thailand's ...
, where a rare-earth mine operated by a Mitsubishi Chemical subsidiary, Asian Rare Earth, closed in 1994 and left continuing environmental and health concerns. In mid-2011, after protests, Malaysian government restrictions on the Lynas plant were announced. At that time, citing subscription-only ''Dow Jones Newswire
Dow Jones & Company, Inc. is an American publishing firm owned by News Corp and led by CEO Almar Latour.
The company publishes ''The Wall Street Journal'', '' Barron's'', ''MarketWatch'', ''Mansion Global'', ''Financial News'' and ''Private E ...
'' reports, a '' Barrons'' report said the Lynas investment was $730 million, and the projected share of the global market it would fill put at "about a sixth." An independent review initiated by the Malaysian Government, and conducted by the International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
(IAEA) in 2011 to address concerns of radioactive hazards, found no non-compliance with international radiation safety standards.
However, the Malaysian authorities confirmed that as of October 2011, Lynas was not given any permit to import any rare-earth ore into Malaysia. On February 2, 2012, the Malaysian AELB (Atomic Energy Licensing Board) recommended that Lynas be issued a temporary operating license subject to meeting a number of conditions. On 2 September 2014, Lynas was issued a 2-year full operating stage license by the AELB.
Other sources
Mine tailings
Significant quantities of rare-earth oxides are found in tailings accumulated from 50 years ofuranium ore
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within the Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the more common elements in the Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It ...
, shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
and loparite
Loparite-(Ce) is a granular, brittle oxide mineral of the perovskite class. It is black to dark grey and may appear grey to white in reflected light on polished thin section with reddish brown internal reflections.Loparite-(Ce) oWebmineral/ref> It ...
mining at Sillamäe
Sillamäe (Estonian for 'Bridge Hill'; also known by the Germanised names of ''Sillamäggi'' or ''Sillamägi'') is a town in Ida-Viru County in the northern part of Estonia, on the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland. It has a population of ...
, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
. Due to the rising prices of rare earths, extraction of these oxides has become economically viable. The country currently exports around 3,000 tonnes per year, representing around 2% of world production. Similar resources are suspected in the western United States, where gold rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Z ...
-era mines are believed to have discarded large amounts of rare earths, because they had no value at the time.
Ocean mining
In January 2013 a Japanese deep-sea research vessel obtained seven deep-sea mud core samples from the Pacific Ocean seafloor at 5,600 to 5,800 meters depth, approximately south of the island ofMinami-Tori-Shima
, also known as Marcus Island, is an isolated Japanese coral atoll in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, located some southeast of Tokyo and east of the closest Japanese island, South Iwo Jima of the Ogasawara Islands, and nearly on a straight li ...
. The research team found a mud layer 2 to 4 meters beneath the seabed with concentrations of up to 0.66% rare-earth oxides. A potential deposit might compare in grade with the ion-absorption-type deposits in southern China that provide the bulk of Chinese REO mine production, which grade in the range of 0.05% to 0.5% REO.
Waste
Another recently developed source of rare earths iselectronic waste
Electronic waste or e-waste describes discarded electrical or electronic devices. Used electronics which are destined for refurbishment, reuse, resale, salvage recycling through material recovery, or disposal are also considered e-waste. Informa ...
and other waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste prod ...
s that have significant rare-earth components. Advances in recycling technology have made extraction of rare earths from these materials less expensive. Recycling plants operate in Japan, where an estimated 300,000 tons of rare earths are found in unused electronics. In France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, the Rhodia group is setting up two factories, in La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. With ...
and Saint-Fons
Saint-Fons (; frp, Cent-Fonts) is a commune in the Metropolis of Lyon in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in eastern France. It was created in 1888 from part of the commune of Vénissieux.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Metropolis of Lyon ...
, that will produce 200 tons of rare earths a year from used fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet lig ...
s, magnets and batteries. Coal and coal by-products are a potential source of critical elements including rare earth elements (REE) with estimated amounts in the range of 50 million metric tons.
Methods
One study mixedfly ash
Fly ash, flue ash, coal ash, or pulverised fuel ash (in the UK) plurale tantum: coal combustion residuals (CCRs)is a coal combustion product that is composed of the particulates (fine particles of burned fuel) that are driven out of coal-fired ...
with carbon black and then sent a 1-second current pulse through the mixture, heating it to . The fly ash contains microscopic bits of glass that encapsulate the metals. The heats shatters the glass, exposing the rare earths. Flash heating also converts phosphates
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
into oxides, which are more soluble and extractable. Using hydrochloric acid at concentrations less than 1% of conventional methods, the process extracted twice as much material.
Properties
According to chemistry professor Andrea Sella, rare-earth elements differ from other elements, in that when looked at analytically, they are virtually inseparable, having almost the same chemical properties. However, in terms of their electronic and magnetic properties, each one occupies a unique technological niche that nothing else can.Professor of Chemistry atUniversity College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
, Andrea Sella, , Interview on TRT World
TRT World is a Turkish public broadcaster international news channel which broadcasts in English 24 hours a day, operated by the TRT and based in Taksim Square, Istıklal Avenue, Beyoğlu, Istanbul. It provides worldwide news and current affai ...
/ Oct 2016, minutes 4:40 - ff. For example, "the rare-earth elements praseodymium
Praseodymium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pr and the atomic number 59. It is the third member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile ...
(Pr) and neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes i ...
(Nd) can both be embedded inside glass and they completely cut out the glare from the flame when one is doing glass-blowing
Glassblowing is a glassforming technique that involves inflating molten glass into a bubble (or parison) with the aid of a blowpipe (or blow tube). A person who blows glass is called a ''glassblower'', ''glassmith'', or ''gaffer''. A '' lampworke ...
."
Uses
The uses, applications, and demand for rare-earth elements has expanded over the years. Globally, most REEs are used forcatalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s and magnets. In USA, more than half of REEs are used for catalysts, and ceramics, glass and polishing are also main uses.
Other important uses of rare-earth elements are applicable to the production of high-performance magnets, alloys, glasses, and electronics. Ce and La are important as catalysts, and are used for petroleum refining
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefi ...
and as diesel additives. Nd is important in magnet production in traditional and low-carbon technologies. Rare-earth elements in this category are used in the electric motors of hybrid
Hybrid may refer to:
Science
* Hybrid (biology), an offspring resulting from cross-breeding
** Hybrid grape, grape varieties produced by cross-breeding two ''Vitis'' species
** Hybridity, the property of a hybrid plant which is a union of two dif ...
and electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes cha ...
s, generators in wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. ...
s, hard disc drives, portable electronics, microphones, speakers.
Ce, La and Nd are important in alloy making, and in the production of fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requ ...
s and nickel-metal hydride batteries. Ce, Ga and Nd are important in electronics and are used in the production of LCD and plasma screens, fiber optics, lasers, as well as in medical imaging. Additional uses for rare-earth elements are as tracers in medical applications, fertilizers, and in water treatment.
REEs have been used in agriculture to increase plant growth, productivity, and stress resistance seemingly without negative effects for human and animal consumption. REEs are used in agriculture through REE-enriched fertilizers which is a widely used practice in China. In addition, REEs are feed additives for livestock which has resulted in increased production such as larger animals and a higher production of eggs and dairy products. However, this practice has resulted in REE bio-accumulation within livestock and has impacted vegetation and algae growth in these agricultural areas. Additionally while no ill effects have been observed at current low concentrations the effects over the long term and with accumulation over time are unknown prompting some calls for more research into their possible effects.
Given the limited supply, industries directly compete with each other for resources, e.g. the electronics sector is in direct competition with renewable energy use in windfarms, solar panels and batteries.
Environmental considerations
REEs are naturally found in very low concentration in the environment. Mines are often in countries where environmental and social standards are very low, leading to human rights violations, deforestation and contamination of land and water. Near mining and industrial sites, the concentrations of REEs can rise to many times the normal background levels. Once in the environment, REEs can leach into the soil where their transport is determined by numerous factors such as erosion, weathering, pH, precipitation, ground water, etc. Acting much like metals, they can speciate depending on the soil condition being either motile or adsorbed to soil particles. Depending on their bio-availability, REEs can be absorbed into plants and later consumed by humans and animals. The mining of REEs, use of REE-enriched fertilizers, and the production of phosphorus fertilizers all contribute to REE contamination. Furthermore, strong acids are used during the extraction process of REEs, which can then leach out in to the environment and be transported through water bodies and result in the acidification of aquatic environments. Another additive of REE mining that contributes to REE environmental contamination iscerium oxide Cerium oxide may refer to:
*Cerium(III) oxide, Ce2O3, also known as dicerium trioxide
* Cerium(III, IV) oxide, Ce3O4 (dark blue)
*Cerium(IV) oxide
Cerium(IV) oxide, also known as ceric oxide, ceric dioxide, ceria, cerium oxide or cerium dioxide, ...
(), which is produced during the combustion of diesel and released as exhaust, contributing heavily to soil and water contamination.
 Mining, refining, and recycling of rare earths have serious environmental consequences if not properly managed. Low-level radioactive
Mining, refining, and recycling of rare earths have serious environmental consequences if not properly managed. Low-level radioactive tailings
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overlie ...
resulting from the occurrence of thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high me ...
and uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
in rare-earth element ores present a potential hazard and improper handling of these substances can result in extensive environmental damage. In May 2010, China announced a major, five-month crackdown on illegal mining in order to protect the environment and its resources. This campaign is expected to be concentrated in the South, where mines – commonly small, rural, and illegal operations – are particularly prone to releasing toxic waste into the general water supply. However, even the major operation in Baotou
Baotou (; mn, Buɣutu qota, Бугат хот) is the largest city by urban population in Inner Mongolia, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, as of the 2020 census, its built-up (''or metro'') area made up of its 5 urban districts is h ...
, in Inner Mongolia, where much of the world's rare-earth supply is refined, has caused major environmental damage. China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology estimated that cleanup costs in Jiangxi province at $5.5 billion.
It is, however, possible to filter out and recover any rare earth elements that flow out with the wastewater from mining facilities. However, such filtering and recovery equipment may not always be present on the outlets carrying the wastewater.
Recycling and reusing REEs
Literature published in 2004 suggests that, along with previously established pollution mitigation, a more circular supply chain would help mitigate some of the pollution at the extraction point. This means recycling and reusing REEs that are already in use or reaching the end of their life cycle. A study published in 2014 suggests a method to recycle REEs from waste nickel-metal hydride batteries, demonstrating a recovery rate of 95.16%. Rare-earth elements could also be recovered from industrial wastes with practical potential to reduce environmental and health impacts from mining, waste-generation and imports if known and experimental processes are scaled up. A study suggests that "fulfillment of the circular economy approach could reduce up to 200 times the impact in the climate change category and up to 70 times the cost due to the REE mining." In most of the reported studies reviewed by ascientific review
A review article is an article that summarizes the current state of understanding on a topic within a certain discipline. A review article is generally considered a secondary source since it may analyze and discuss the method and conclusions i ...
, "secondary waste is subjected to chemical and or bioleaching followed by solvent extraction processes for clean separation of REEs."
Impact of REE contamination
On vegetation
The mining of REEs has caused thecontamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
W ...
of soil and water around production areas, which has impacted vegetation in these areas by decreasing chlorophyll production which affects photosynthesis and inhibits the growth of the plants. However, the impact of REE contamination on vegetation is dependent on the plants present in the contaminated environment: some plants retain and absorb REEs and some don't. Also, the ability for the vegetation to intake the REE is dependent on the type of REE present in the soil, hence there are a multitude of factors that influence this process. Agricultural plants are the main type of vegetation affected by REE contamination in the environment, the two plants with a higher chance of absorbing and storing REEs being apples and beets. Furthermore, there is a possibility that REEs can leach out into aquatic environments and be absorbed by aquatic vegetation, which can then bio-accumulate and potentially enter the human food-chain if livestock or humans choose to eat the vegetation. An example of this situation was the case of the water hyacinth
''Pontederia crassipes'' (formerly ''Eichhornia crassipes''), commonly known as common water hyacinth is an aquatic plant native to South America, naturalized throughout the world, and often invasive outside its native range.cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 o ...
and resulted in the water hyacinth becoming three times more concentrated in cerium than its surrounding water.
On human health
REEs are a large group with many different properties and levels in the environment. Because of this, and limited research, it has been difficult to determine safe levels of exposure for humans. A number of studies have focused on risk assessment based on routes of exposure and divergence from background levels related to nearby agriculture, mining, and industry. It has been demonstrated that numerous REEs have toxic properties and are present in the environment or in work places. Exposure to these can lead to a wide range of negative health outcomes such as cancer, respiratory issues, dental loss, and even death. However REEs are numerous and present in many different forms and at different levels of toxicity, making it difficult to give blanket warnings oncancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
risk and toxicity as some of these are harmless while others pose a risk.
What toxicity is shown appears to be at very high levels of exposure through ingestion of contaminated food and water, through inhalation of dust/smoke particles either as an occupational hazard or due to proximity to contaminated sites such as mines and cities. Therefore, the main issues that these residents would face is bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost or eliminated ...
of REEs and the impact on their respiratory system but overall, there can be other possible short term and long-term health effects. It was found that people living near mines in China had many times the levels of REEs in their blood, urine, bone and hair compared to controls far from mining sites. This higher level was related to the high levels of REEs present in the vegetables they cultivated, the soil, and the water from the wells, indicating that the high levels were caused by the nearby mine. While REE levels varied between men and women, the group most at risk were children because REEs can impact the neurological development of children, affecting their IQ and potentially causing memory loss.
The rare earth mining and smelting process can release airborne fluoride which will associate with total suspended particles (TSP) to form aerosols that can enter human respiratory systems and cause damage and respiratory diseases. Research from Baotou, China shows that the fluoride concentration in air near REE mines is higher than the limit value from WHO, which can affect the surrounding environment and become a risk to those that live or work nearby.
Residents blamed a rare-earth refinery at Bukit Merah for birth defects
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
and eight leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ' ...
cases within five years in a community of 11,000 — after many years with no leukemia cases. Seven of the leukemia victims died. Osamu Shimizu, a director of Asian Rare Earth, said "the company might have sold a few bags of calcium phosphate fertilizer on a trial basis as it sought to market byproducts; calcium phosphate is not radioactive or dangerous" in reply to a former resident of Bukit Merah who said that "The cows that ate the grass rown with the fertilizerall died." Malaysia's Supreme Court ruled on 23 December 1993 that there was no evidence that the local chemical joint venture Asian Rare Earth was contaminating the local environment.
On animal health
Experiments exposing rats to various cerium compounds have found accumulation primarily in the lungs and liver. This resulted in various negative health outcomes associated with those organs. REEs have been added to feed in livestock to increase their body mass and increase milk production. They are most commonly used to increase the body mass of pigs, and it was discovered that REEs increase the digestibility and nutrient use of pigs' digestive systems. Studies point to a dose response when considering toxicity versus positive effects. While small doses from the environment or with proper administration seem to have no ill effects, larger doses have been shown to have negative effects specifically in the organs where they accumulate. The process of mining REEs in China has resulted in soil and water contamination in certain areas, which when transported into aquatic bodies could potentially bio-accumulate within aquatic biota. Furthermore, in some cases animals that live in the REE-contaminated areas have been diagnosed with organ or system problems. REEs have been used in freshwater fish farming because it protects the fish from possible diseases. One main reason why they have been avidly used in animal livestock feeding is that they have had better results than inorganic livestock feed enhancers.Remediation after pollution
After the1982 Bukit Merah radioactive pollution
The 1982 Bukit Merah radioactive pollution is a radioactive waste pollution incident in Bukit Merah of Kinta District in Central Perak, Malaysia. The outcome of the pollution case took several years to complete with no acknowledgement of resp ...
, the mine in Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
has been the focus of a US$100 million cleanup that is proceeding in 2011. After having accomplished the hilltop entombment of 11,000 truckloads of radioactively contaminated material, the project is expected to entail in summer, 2011, the removal of "more than 80,000 steel barrels of radioactive waste to the hilltop repository."
In May 2011, after the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and ...
, widespread protests took place in Kuantan over the Lynas refinery and radioactive waste from it. The ore to be processed has very low levels of thorium, and Lynas founder and chief executive Nicholas Curtis said "There is absolutely no risk to public health." T. Jayabalan, a doctor who says he has been monitoring and treating patients affected by the Mitsubishi plant, "is wary of Lynas's assurances. The argument that low levels of thorium in the ore make it safer doesn't make sense, he says, because radiation exposure is cumulative."Lee, Yoolim"Malaysia Rare Earths in Largest Would-Be Refinery Incite Protest"
'' Bloomberg Markets Magazine'', May 31, 2011 5:00 PM ET. Construction of the facility has been halted until an independent
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
IAEA
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
panel investigation is completed, which is expected by the end of June 2011. New restrictions were announced by the Malaysian government in late June.
IAEA
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
panel investigation is completed and no construction has been halted. Lynas is on budget and on schedule to start producing 2011. The IAEA report has concluded in a report issued on Thursday June 2011 said it did not find any instance of "any non-compliance with international radiation safety standards" in the project.
If the proper safety standards are followed, REE mining is relatively low impact. Molycorp (before going bankrupt) often exceeded environmental regulations to improve public image.
In Greenland there is a significant dispute on whether to start a new rare earth mine in Kvanefjeld due to environmental concerns.
Geo-political considerations
resource depletion
Resource depletion is the consumption of a resource faster than it can be replenished. Natural resources are commonly divided between renewable resources and non-renewable resources (see also mineral resource classification). Use of either ...
and environmental concerns as the reasons for a nationwide crackdown on its rare-earth mineral production sector. However, non-environmental motives have also been imputed to China's rare-earth policy. According to ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econo ...
'', "Slashing their exports of rare-earth metals… is all about moving Chinese manufacturers up the supply chain, so they can sell valuable finished goods to the world rather than lowly raw materials." Furthermore, China currently has an effective monopoly on the world's REE Value Chain. (all the refineries and processing plants that transform the raw ore into valuable elements). In the words of Deng Xiaoping, a Chinese politician from the late 1970s to the late 1980s, "The Middle East has oil; we have rare earths ... it is of extremely important strategic significance; we must be sure to handle the rare earth issue properly and make the fullest use of our country's advantage in rare earth resources."
One possible example of market control is the division of General Motors that deals with miniaturized magnet research, which shut down its US office and moved its entire staff to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
in 2006 (China's export quota only applies to the metal but not products made from these metals such as magnets).
It was reported, but officially denied, that China instituted an export ban on shipments of rare-earth oxides (but not alloys) to Japan on 22 September 2010, in response to the detainment of a Chinese fishing boat captain by the Japanese Coast Guard
The is the coast guard of Japan.
The Japan Coast Guard consists of about 13,700 personnel and is responsible for the protection of the coastline of Japan under the oversight of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. ...
. On September 2, 2010, a few days before the fishing boat incident, ''The Economist'' reported that "China...in July announced the latest in a series of annual export reductions, this time by 40% to precisely 30,258 tonnes."
The United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
in its 2010 Critical Materials Strategy report identified dysprosium
Dysprosium is the chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare-earth element in the lanthanide series with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though, like other lanthanides, it ...
as the element that was most critical in terms of import reliance.
A 2011 report "China's Rare-Earth Industry", issued by the US Geological Survey and US Department of the Interior, outlines industry trends within China and examines national policies that may guide the future of the country's production. The report notes that China's lead in the production of rare-earth minerals has accelerated over the past two decades. In 1990, China accounted for only 27% of such minerals. In 2009, world production was 132,000 metric tons; China produced 129,000 of those tons. According to the report, recent patterns suggest that China will slow the export of such materials to the world: "Owing to the increase in domestic demand, the Government has gradually reduced the export quota during the past several years." In 2006, China allowed 47 domestic rare-earth producers and traders and 12 Sino-foreign rare-earth producers to export. Controls have since tightened annually; by 2011, only 22 domestic rare-earth producers and traders and 9 Sino-foreign rare-earth producers were authorized. The government's future policies will likely keep in place strict controls: "According to China's draft rare-earth development plan, annual rare-earth production may be limited to between 130,000 and 140,000 etric tonsduring the period from 2009 to 2015. The export quota for rare-earth products may be about 35,000 etric tonsand the Government may allow 20 domestic rare-earth producers and traders to export rare earths."
The United States Geological Survey is actively surveying southern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
for rare-earth deposits under the protection of United States military forces. Since 2009 the USGS has conducted remote sensing surveys as well as fieldwork to verify Soviet claims that volcanic rocks containing rare-earth metals exist in Helmand Province
Helmand (Pashto/Dari: ; ), also known as Hillmand, in ancient times, as Hermand and Hethumand, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan
Afghanistan is divided into 34 provinces (, '' wilåyat''). The provinces of Afghanistan are the primar ...
near the village of Khanashin
Khanashin, or Khan Neshin, (other names: Khān Neshīn, Khannesin, Khan Nashin, Khān Nashīn, Khan Nashim, Khānnešīn) is a village located in the Reg District of Helmand Province, Afghanistan at at 642 altitude. It is close to the Helmand Ri ...
. The USGS study team has located a sizable area of rocks in the center of an extinct volcano containing light rare-earth elements including cerium and neodymium. It has mapped 1.3 million metric tons of desirable rock, or about ten years of supply at current demand levels. The Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek πέντε ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and γωνία ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simpl ...
has estimated its value at about $7.4 billion.
It has been argued that the geopolitical importance of rare earths has been exaggerated in the literature on the geopolitics of renewable energy, underestimating the power of economic incentives for expanded production. This especially concerns neodymium. Due to its role in permanent magnets used for wind turbines, it has been argued that neodymium will be one of the main objects of geopolitical competition in a world running on renewable energy. But this perspective has been criticised for failing to recognise that most wind turbines have gears and do not use permanent magnets.
Prices
The Institute of Rare Earths Elements and Strategic Metals is an informal network in the international ''raw metall market''. The main interest of the institut's customers is the database, which is available on a subscription base with daily updatet prices: In addition with the eponymous ''rare-earth elements'', 900 pure metalls and 4,500 other metall products are listed there. The company's headquartesr are located inLucerne
Lucerne ( , ; High Alemannic German, High Alemannic: ''Lozärn'') or Luzern ()Other languages: gsw, Lozärn, label=Lucerne German; it, Lucerna ; rm, Lucerna . is a city in central Switzerland, in the Languages of Switzerland, German-speaking po ...
, Switzerland.
See also
* Rare-earth mineral * Rare-earth magnet *List of elements facing shortage
Since 2011, the European Commission assesses a 3-year list of Critical Raw Materials (CRMs) for the EU economy within its Raw Materials Initiative. To date, 14 CRMs were identified in 2011, 20 in 2014, 27 in 2017 and 30 in 2020. These materials ar ...
*Material passport
A material passport is a document consisting of all the materials that are included in a product or construction. It consists of a set of data describing defined characteristics of materials in products, which give them value for recovery, recycl ...
: lists used materials in products
*Digital Product Passport Produce traceability makes it possible to track produce from its point of origin to a retail location where it is purchased by consumers.
Produce traceability is an important link in protecting public health since it allows health agencies to more ...
: renewed in function of the Circular Economy Action Plan
The European Green Deal, approved 2020, is a set of policy initiatives by the European Commission with the overarching aim of making the European Union (EU) climate neutral in 2050. An impact assessed plan will also be presented to increase the ...
*Pensana Salt End
Pensana Saltend is a future processing facility for rare earth metals at Salt End, near Hull in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. When operating at capability, the plant aims to produce 5% of world demand for neodymium and praseodymium ox ...
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Sets of chemical elements Metallic elements