Northern Friesland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
North Frisia (; ; ) is the northernmost portion of
 The
The
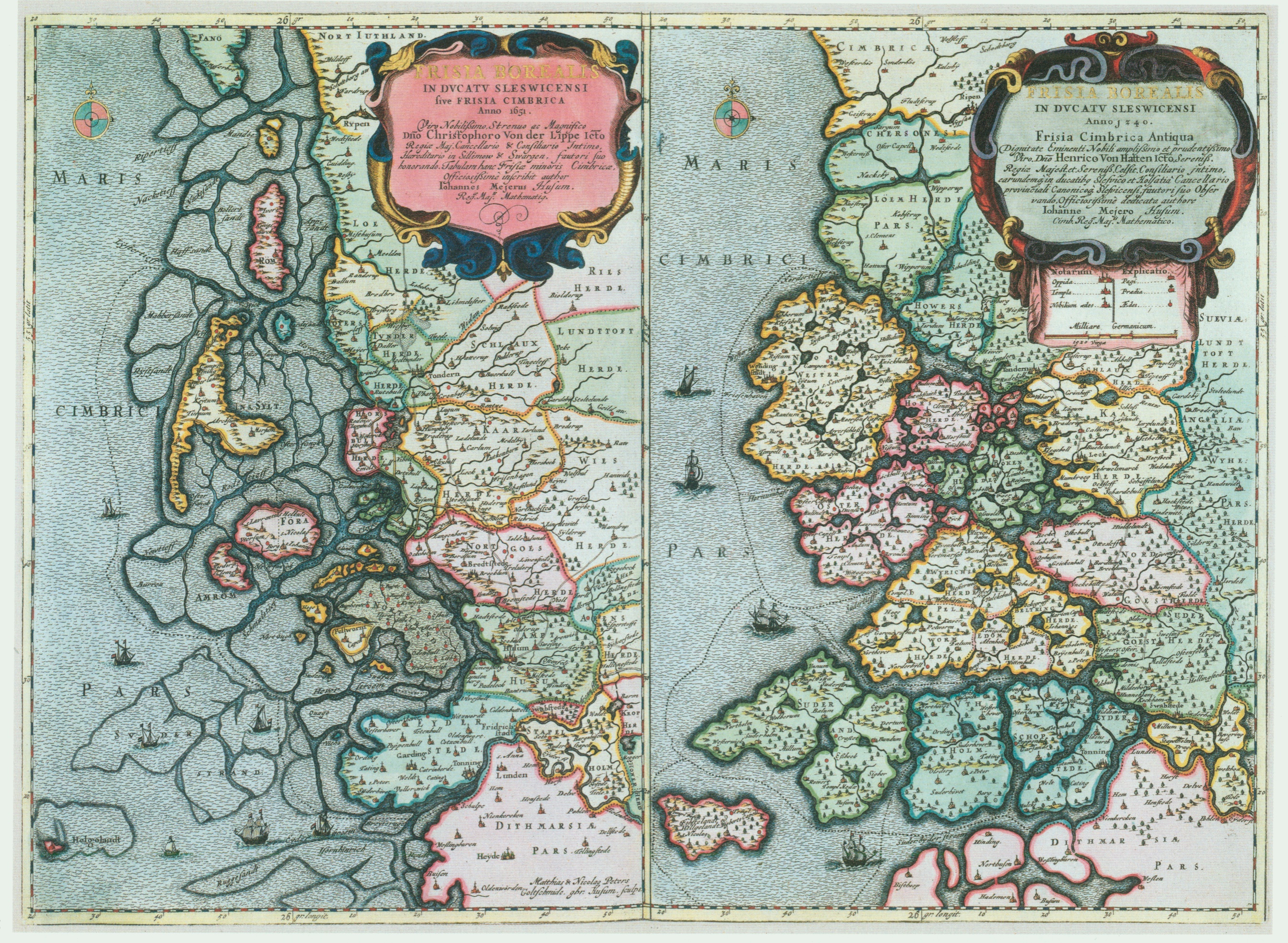 Several floods such as the ''
Several floods such as the '' Until 1864, North Frisia was a part of the Danish Duchy of
Until 1864, North Frisia was a part of the Danish Duchy of
 North Frisia is now part of the German state of
North Frisia is now part of the German state of
Nordfriisk Instituut
homepage of the North Frisian Institute. Information available in English. {{Authority control Regions of Schleswig-Holstein
Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Ger ...
, located in Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sch ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
between the rivers Eider
Eiders () are large seaducks in the genus ''Somateria''. The three extant species all breed in the cooler latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.
The down feathers of eider ducks, and some other ducks and geese, are used to fill pillows and quilt ...
and Wiedau
Wiedau is a river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a left-hand tributary of the Wümme.
The Wiedau begins near Bellen (a district of Brockel) in the vicinity of Hemslingen in the district of at the confluence of the Hahnenbach and the Mehlandsb ...
. It also includes the North Frisian Islands
The North Frisian Islands (''Öömrang'' and ''Fering'' frr, Nuurdfresk Eilunen, ''Söl'ring'' frr, Nuurđfriisk Ailönen, link=no, da, Nordfrisiske Øer, german: Nordfriesische Inseln) are the Frisian Islands off the coast of North Frisia.
The ...
and Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions ...
. The region is traditionally inhabited by the North Frisians
North Frisians (german: Nordfriesen; da, Nordfrisere; frr, Nuurdfresen) are the inhabitants of the district of Nordfriesland in the north German state of Schleswig-Holstein. Used in a narrower sense, the term also refers to an ethnic sub-group o ...
.
History
Ancient settlements
 The
The geest
Geest is a type of landform, slightly raised above the surrounding countryside, that occurs on the plains of Northern Germany, the Northern Netherlands and Denmark. It is a landscape of sandy and gravelly soils formed as a glacial outwash plai ...
land islands along the North Frisian coastline were already densely settled in the time of the early Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
while the marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
es further inland were not suited for settling. Only a few ancient marshland settlements have been found during archaeological excavations, namely in the modern area of southern Sylt
Sylt (; da, Sild; Sylt North Frisian, Söl'ring North Frisian: ) is an island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, and well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian ...
, the Wiedingharde
Wiedingharde ( Wiedingharde North Frisian: ''Wiringhiird'') was an ''amt'' (collective municipality) in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It was situated on the North Sea coast and on the border with Denmark. Its seat ...
and along the southern Eiderstedt
Eiderstedt (german: Eiderstedt, ; da, Ejdersted; North Frisian: ''Ääderstää'') is a peninsula in the district of Nordfriesland in the German federal state of Schleswig-Holstein.
Overview
It is approximately 30 km in length and 15&nbs ...
peninsula. With the beginning of the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
, the number of settlements in North Frisia became ever lesser and many were totally abandoned. A new increase in population in the 8th century has been attributed to immigration but it is thought that the area had not been completely depopulated before.Kühn, Hans Joachim, "Archäologische Zeugnisse der Friesen in Nordfriesland" rchaeological Evidence Pertaining to the Frisians in North Frisia In Munske (2001), ''Handbuch des Friesischen'', pp. 499–503
Medieval North Frisia
TheFrisians
The Frisians are a Germanic ethnic group native to the coastal regions of the Netherlands and northwestern Germany. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, ...
migrated to North Frisia from the South in two waves. During the 8th century A.D. they mostly settled on the islands Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions ...
, Sylt, Föhr
Föhr ( ''Fering'' North Frisian: ''Feer''; da, Før) is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German coast of the North Sea. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Föhr is the second-largest No ...
, Amrum
Amrum (; Öömrang, ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the Germany, German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-H ...
and presumably also in parts of the Eiderstedt
Eiderstedt (german: Eiderstedt, ; da, Ejdersted; North Frisian: ''Ääderstää'') is a peninsula in the district of Nordfriesland in the German federal state of Schleswig-Holstein.
Overview
It is approximately 30 km in length and 15&nbs ...
peninsula. The coastal marshlands of the mainland were settled in a second wave and after a series of storm surges the Frisians also used to settle on the higher inland geest
Geest is a type of landform, slightly raised above the surrounding countryside, that occurs on the plains of Northern Germany, the Northern Netherlands and Denmark. It is a landscape of sandy and gravelly soils formed as a glacial outwash plai ...
, where Danes (Jutes) already lived. While the marshland and its bogs had to be drained, the higher geestland cores of the islands were in turn mostly barren and needed fertilisation
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
before a proper agriculture could be established.
During the Middle Ages, trade flourished between North Frisia and East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
, England. In particular, pottery was imported from the town of Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line r ...
and it has been suggested that relations between Frisians and East Anglians must have lasted for several centuries. In 1252, a united army of North Frisians from all territories between the Eiderstedt
Eiderstedt (german: Eiderstedt, ; da, Ejdersted; North Frisian: ''Ääderstää'') is a peninsula in the district of Nordfriesland in the German federal state of Schleswig-Holstein.
Overview
It is approximately 30 km in length and 15&nbs ...
peninsula and the northern islands succeeded in defeating a Danish army led by king Abel. Salt making became a considerable trade in the 14th and 15th century when the North Frisians used saline peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
as a resource. The salt trade coincided with an increase in international herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
fishery off Heligoland. Treaties of 14th century farmers from Edoms Hundred
Edoms Hundred (german: Edomsharde, da, Edoms Herred) was a mediaeval hundred located in the southern part of North Frisia in the Danish region of Southern Schleswig, part of the Frisian Uthlande. It encompassed the eastern part of the island of S ...
with Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
based merchants and even the Counts of Flanders respectively have been preserved.
The Frisian Uthlande
Uthlande, Utlande (Low German or Old Danish: ''The outer lands'', in Danish also: ''Friselagen'') is a term for the islands, halligen and marshes off the mainland of North Frisia in the Southwest Jutland, modern Nordfriesland district, Germany.
...
region used to have its own jurisdiction, it was laid down for the first time in the so-called ''Siebenhardenbeliebung'' (the compact of the seven hundreds) in 1424. North Frisia as a region was first recorded in 1424 although Saxo Grammaticus
Saxo Grammaticus (c. 1150 – c. 1220), also known as Saxo cognomine Longus, was a Danish historian, theologian and author. He is thought to have been a clerk or secretary to Absalon, Archbishop of Lund, the main advisor to Valdemar I of Denmark. ...
had written about ''Frisia minor'' esser Frisia Esser is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Esser (musician), English musician born Ben Esser
*Bernard Esser (1840-1901), American farmer
* Clarence Esser (1921–2009), American football player
* Dave Esser (born 1957), English ...
a region in Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
, already in 1180.
Modern era
Grote Mandrenke
Saint Marcellus's flood or (Low Saxon: ; da, Den Store Manddrukning, 'Great Drowning of Men') was an intense extratropical cyclone, coinciding with a new moon, which swept across the British Isles, the Netherlands, northern Germany, and Denmark ...
'' in 1362 and the Burchardi Flood of 1634 damaged great parts of the North Frisian coastal area. In these floods entire islands were destroyed and a great part of North Frisian language was torn apart in linguistical and political terms. Additional hardship was brought about by a number of wars, such as the Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an es ...
that reached North Frisia in 1627, the Second Northern War
The Second Northern War (1655–60), (also First or Little Northern War) was fought between Sweden and its adversaries the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1655–60), the Tsardom of Russia (Russo-Swedish War (1656–1658), 1656–58), Brande ...
between Sweden and Denmark 1657–1660, and the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedi ...
from 1700–1721 where Tönning
Tönning (German; Low German ''Tünn'', ''Tönn'' or ''Tönnen''; Danish: ''Tønning''; North Frisian: ''Taning'') is a town in the district of Nordfriesland in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein.
History
Tönning was destroyed in the Bu ...
was besieged and partially destroyed in 1713.
With the onset of whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industry ...
in the 17th and 18th century, the people from the North Frisian Islands
The North Frisian Islands (''Öömrang'' and ''Fering'' frr, Nuurdfresk Eilunen, ''Söl'ring'' frr, Nuurđfriisk Ailönen, link=no, da, Nordfrisiske Øer, german: Nordfriesische Inseln) are the Frisian Islands off the coast of North Frisia.
The ...
soon developed a reputation of being very skilled mariners, and most Dutch and English whaling ships bound for Greenland and Svalbard would have a crew of North Frisian islanders. Around the year 1700, Föhr
Föhr ( ''Fering'' North Frisian: ''Feer''; da, Før) is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German coast of the North Sea. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Föhr is the second-largest No ...
had a total population of roughly 6,000 people, 1,600 of whom were whalers. At the height of Dutch whaling in the year 1762, 1,186 seamen from Föhr were serving on Dutch whaling vessels alone and 25% of all shipmasters on Dutch whaling vessels were people from Föhr. Another example is the London-based South Sea Company
The South Sea Company (officially The Governor and Company of the merchants of Great Britain, trading to the South Seas and other parts of America, and for the encouragement of the Fishery) was a British joint-stock company founded in Ja ...
whose commanding officers and harpooners were exclusively from Föhr
Föhr ( ''Fering'' North Frisian: ''Feer''; da, Før) is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German coast of the North Sea. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Föhr is the second-largest No ...
. In the early 18th century, Sylt
Sylt (; da, Sild; Sylt North Frisian, Söl'ring North Frisian: ) is an island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, and well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian ...
island was home to 20 captains who took part in the Greenland whaling.
 Until 1864, North Frisia was a part of the Danish Duchy of
Until 1864, North Frisia was a part of the Danish Duchy of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km ...
(South Jutland) but was transferred to Prussia after the Second Schleswig War
The Second Schleswig War ( da, Krigen i 1864; german: Deutsch-Dänischer Krieg) also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War was the second military conflict over the Schleswig-Holstein Question of the nineteenth century. T ...
. During this time of German-Danish conflicts, a North Frisian identity was propagated by people such as Christian Feddersen (1786-1874) who simultaneously denounced nationalist tendencies. The North Frisian coat of arms has been attributed to him. While not designed according to heraldic rules, the shield contains a Frisian eagle
A Frisian eagle is a specific kind of eagle in Dutch heraldry, consisting of half of a black double-headed eagle on the ''dexter'' side of a shield parted per pale.
It originated as a mark of favour granted to certain Frisian noblemen by the Hol ...
on the right side and on the left there is a golden crown in blue above a black kettle in a red field. The eagle has been interpreted as a symbol of the Frisian freedom granted by the Holy Roman emperor, the crown represents the Danish kings who ruled the area until the mid 19th century. The kettle or pot has been seen as a symbol of the Frisian brotherhood advocated by Feddersen. Also the motto which may be represented in the various dialects of the North Frisian language
North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are thems ...
and always translates to "Rather dead than slave" is seen as originating from Feddersen's views. After the Second Schleswig War, when anti-Danish tendencies came up, this motto and also the eagle were re-attributed to a German identity and chronicler C. P. Hansen from Sylt invented the legend that the pot was reminiscent of Frisian women who contributed in a battle against the Danes.
North Frisia today
 North Frisia is now part of the German state of
North Frisia is now part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sch ...
with all of it except for Heligoland contained within the district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
of Nordfriesland
Nordfriesland (; da, Nordfrisland; frr, Nordfraschlönj ), also known as North Frisia, is the northernmost district of Germany, part of the state of Schleswig-Holstein. It includes almost all of traditional North Frisia (with the exception o ...
. The district extends beyond the traditional area of North Frisia to the south and east.
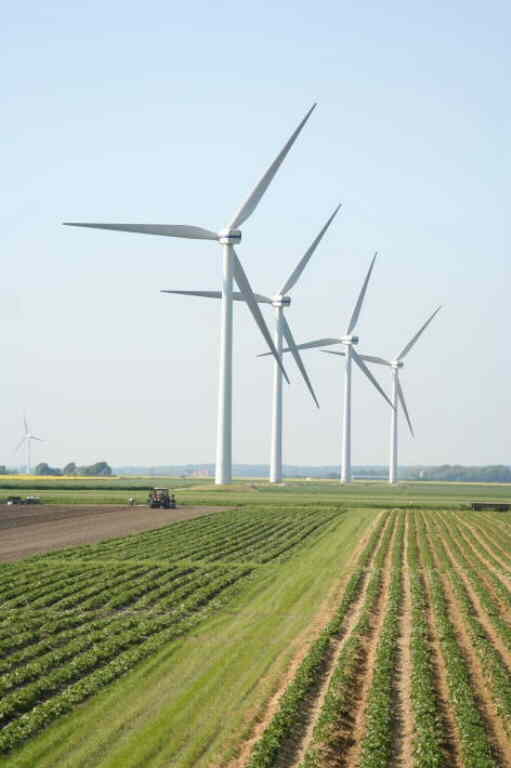
Today there are more than 60 wind farm
A wind farm or wind park, also called a wind power station or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used Wind power, to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundre ...
s with a capacity of about 700 MW in North Frisia, and 90 percent are community-owned. North Frisia is seen to be a model location for community wind energy, leading the way for other regions, especially in southern Germany.
North Frisia is home to two card games of historical and cultural interest, both descended from Karnöffel
Karnöffel is a trick-taking card game which probably came from the upper-German language area in Europe in the first quarter of the 15th century. It first appeared listed in a municipal ordinance of Nördlingen, Bavaria, in 1426 among the games ...
, the oldest card game in Europe with a continuous tradition of play. Bruus is played in the hinterland of Husum
Husum (, frr, Hüsem) is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) Nordfriesland in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town was the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Storm, who coined the epithet "the grey town by the sea". It is also the home of ...
in the villages of Schwesing
Schwesing ( da, Svesing, North Frisian: ''Swiasing'') is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
History
From September 25, 1944 until December 11, 1944 a concentration camp was established near Glasau. ...
, Oster-Ohrstedt
Oster-Ohrstedt ( da, Øster Ørsted, North Frisian: ''Aaster Uurst'') is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central E ...
and Treia
Treia is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Macerata in the central Marche (Italy). It is north of Pollenza, west of Macerata, and north-northeast of Tolentino.
Geography
The site of the abandoned Roman municipium of Trea is situated ...
where regular tournaments are held. Meanwhile Knüffeln
Knüffeln is a very old trick-taking card game for four players, playing in pairs, that is still played in North Germany. Once considered the national game of Frisia, Knüffeln is a descendant of Karnöffel, the oldest identifiable European card ...
is played in the region north of the River Arlau towards the Danish border. Regular courses are held and the game has experienced something of a revival.
Languages and names
In addition tostandard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
, North Frisia has speakers of Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle L ...
, the various dialects of the North Frisian language
North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are thems ...
, and Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
, including South Jutlandic
South Jutlandic or South Jutish (South Jutish: ; da, Sønderjysk; german: Südjütisch or Plattdänisch) is a dialect of the Danish language. South Jutlandic is spoken in Southern Jutland (''Sønderjylland''; also called Schleswig or Slesvig) o ...
. Today some 10,000 people still speak a dialect of North Frisian.
North Frisia is called ''Nordfriesland'' in German and ''Noordfreesland'' in Low German. In the various North Frisian dialects, it is called ''Nordfraschlönj'' in ''Mooring'', ''Noordfreeskluin'' in Wiedingharde Frisian
Wiedingharde Frisian (North Frisian: ''Wiringhiirder freesk'', Danish: ''Vidingherredfrisisk'') is a dialect of the North Frisian language spoken in the German ''amt'' of Wiedingharde south of the border to Denmark in North Frisia (''historic s ...
, ''Nuurdfriislön’'' in Söl'ring
Sylt Frisian, or ''Söl'ring'', is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the island of Sylt in the German region of North Frisia. ''Söl'ring'' refers to the ''Söl'ring'' Frisian word for Sylt, ''Söl''. Together with the Ferin ...
, ''Nuurdfresklun'', ''Nuardfresklun'' or ''nordfriislun'' in '' Fering'', and ''Nöördfreesklöön'' in Halligen Frisian
Halligen Frisian ( frr, Halifreesk) is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the Halligen islands, primarily Langeneß and Hooge, in the German region of North Frisia. The dialect has survived despite the islands' being home to le ...
. The region is called ''Nordfrisland'' in Danish.
Notable North Frisians
*Matthias Petersen
Matthias Petersen (born Matz Peters; 24 December 1632, in Oldsum – 16 September 1706) was a sea captain and whaler from Oldsum on the North Frisian island of Föhr. He became known for catching 373 whales throughout his career.
Life
He was born ...
, born 1632 on the North Frisian island of Föhr was a sea captain. He became known for catching 373 whales throughout his career.
* Oluf Braren
Oluf Braren (25 February 1787 – 22 March 1839) was a painter of naïve art from the north Frisian island of Föhr. Some of his works show a strong affinity to his Frisian homeland.
His paintings include portraits and depictions of public life as ...
, born 1787 in Oldsum
Oldsum (Fering: ''Olersem'') is a municipality on the island of Föhr, in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
Geography
The municipality of Oldsum consists of the three hamlets of Oldsum, Klintum (Fering: ''Klantem'') ...
on Föhr island, was a painter of naive art
Naivety (also spelled naïvety), naiveness, or naïveté is the state of being naive. It refers to an apparent or actual lack of experience and sophistication, often describing a neglect of pragmatism in favor of moral idealism. A ''naïve'' may b ...
.
* Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th cent ...
, born in Garding, Eiderstedt, is considered one of the most important 19th century German historians.
* Painter Emil Nolde
Emil Nolde (born Hans Emil Hansen; 7 August 1867 – 13 April 1956) was a German-Danish painter and printmaker. He was one of the first Expressionists, a member of Die Brücke, and was one of the first oil painting and watercolor painters of the ...
(born Emil Hansen) from Nolde, now part of Denmark, called his father a North Frisian. For most of his life, Nolde lived in Seebüll near the Vidå river.
* Frederik Paulsen Sr Dr Frederik Paulsen Sr (born Friedrich Paulsen; 31 July 1909, in Dagebüll – 1997 in Alkersum) was a medical doctor and the founder of Ferring Pharmaceuticals.
Friedrich Paulsen was born in the tiny port hamlet of Dagebüll on the North Frisian ...
, founder of Ferring Pharmaceuticals and the Ferring Foundation.
* Friede Springer
Friede Springer (born Friede Riewerts on 15 August 1942 in Oldsum on the island of Föhr) is a German publisher and widow of Axel Springer. She is the main owner of the Axel Springer SE media conglomerate, and thus of Europe's largest newspaper ''B ...
(born 1942 in Oldsum) is a publisher and widow of Axel Springer.
* Theodor Storm
Hans Theodor Woldsen Storm (; 14 September 18174 July 1888), commonly known as Theodor Storm, was a German writer. He is considered to be one of the most important figures of German realism.
Life
Storm was born in the small town of Husum, on th ...
is probably the most notable author from North Frisia. He was born in Husum
Husum (, frr, Hüsem) is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) Nordfriesland in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town was the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Storm, who coined the epithet "the grey town by the sea". It is also the home of ...
.
* Ferdinand Tönnies
Ferdinand Tönnies (; 26 July 1855 – 9 April 1936) was a German sociologist, economist, and philosopher. He was a significant contributor to sociological theory and field studies, best known for distinguishing between two types of social gro ...
(born in Oldenswort
Oldenswort ( da, Oldensvort) is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, next to the river Eider.
Personalities
The earliest atheist known by name in modern Europe, Matthias Knutzen, was born here sometime ...
) was a major contributor to early sociology
Sociology is a social science that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of Interpersonal ties, social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. It uses various methods of Empirical ...
.
* Oskar Vogt
Oskar Vogt (6 April 1870, in Husum – 30 July 1959, in Freiburg im Breisgau) was a German physician and neurologist. He and his wife Cécile Vogt-Mugnier are known for their extensive cytoarchetectonic studies on the brain.
Personal life
He wa ...
(born in Husum
Husum (, frr, Hüsem) is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) Nordfriesland in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town was the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Storm, who coined the epithet "the grey town by the sea". It is also the home of ...
) was a pioneer of modern neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, development ...
.
References
;Works cited * *External links
Nordfriisk Instituut
homepage of the North Frisian Institute. Information available in English. {{Authority control Regions of Schleswig-Holstein