Military history of Latvia during World War II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
After the occupation of Latvia by the USSR in June 1940, much of the previous Latvian army was disbanded and many of its soldiers and officers were arrested and imprisoned or executed. The following year Nazi Germany occupied Latvia during the offensive of 

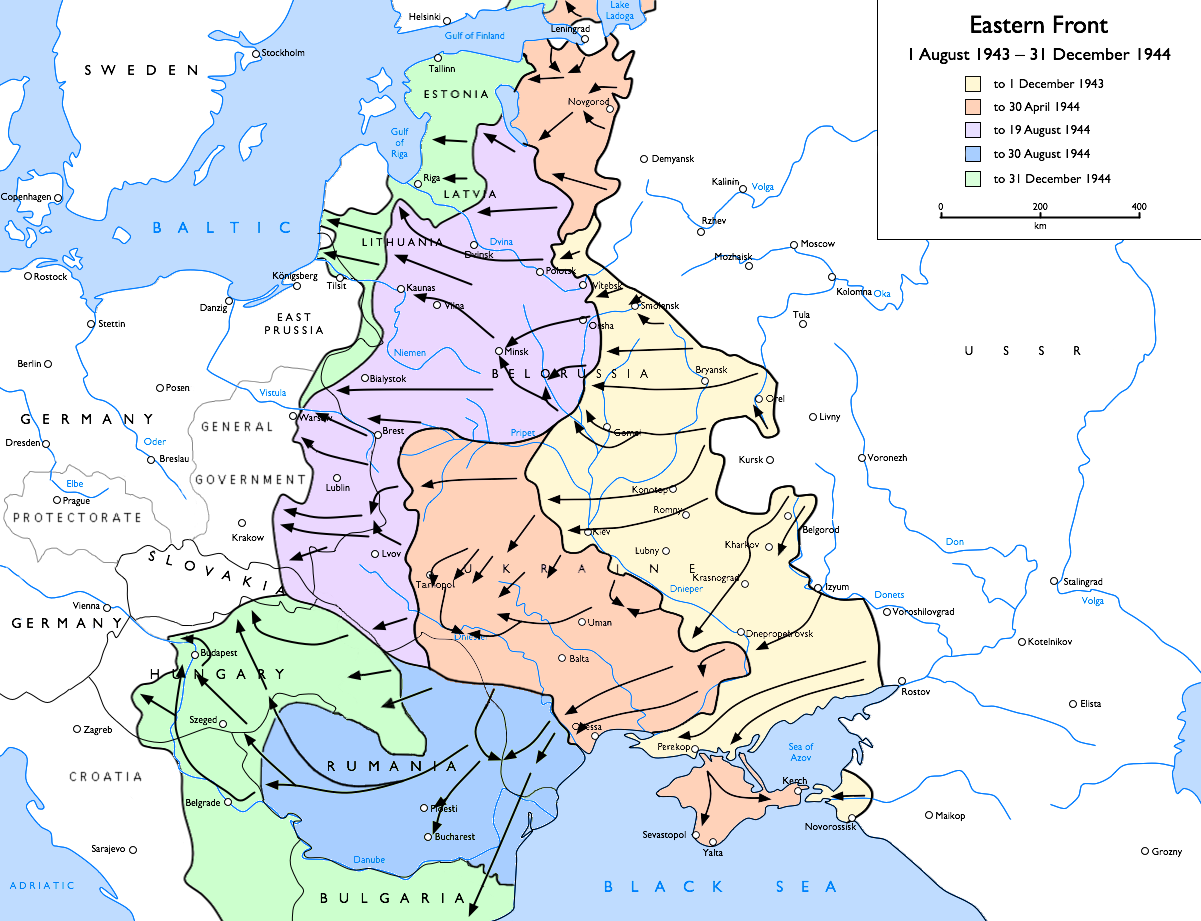 While the
While the
 A massive Soviet assault sliced through the German lines and Army Group North was completely isolated from its neighbour. Strachwitz was trapped outside the pocket, and ''Panzerverband von Strachwitz'' was reformed, this time from elements of the 101st Panzer Brigade of panzer-ace Oberst
A massive Soviet assault sliced through the German lines and Army Group North was completely isolated from its neighbour. Strachwitz was trapped outside the pocket, and ''Panzerverband von Strachwitz'' was reformed, this time from elements of the 101st Panzer Brigade of panzer-ace Oberst  On January 15, 1945,
On January 15, 1945,
Army Group North
Army Group North (german: Heeresgruppe Nord) was a German strategic formation, commanding a grouping of field armies during World War II. The German Army Group was subordinated to the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' (OKH), the German army high comma ...
. The German Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the im ...
were aided by a group known as Arajs Kommando
The Arajs ''Kommando'' (also: ''Sonderkommando Arajs''; ), led by SS commander and Nazi collaborator Viktors Arājs, was a unit of Latvian Auxiliary Police (german: Lettische Hilfspolizei) subordinated to the German ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD). It ...
in the killing of Latvian Jews as part of the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. Latvian soldiers fought on both sides of the conflict against their will, and in 1943 180,000 Latvian men were drafted into the Latvian Legion
The Latvian Legion ( lv, Latviešu leģions) was a formation of the German Waffen-SS during World War II. Created in 1943, it consisted primarily of ethnic Latvian personnel.Gerhard P. Bassler, ''Alfred Valdmanis and the politics of survival'', 20 ...
of the Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
and other German auxiliary forces.
In the Baltic Offensive of autumn 1944 the Soviet Union recaptured much of its Baltic coastline, leaving 200,000 troops of Army Group North cut off in the Courland Pocket
The Courland Pocket (Blockade of the Courland army group), (german: Kurland-Kessel)/german: Kurland-Brückenkopf (Courland Bridgehead), lv, Kurzemes katls (Courland Cauldron) or ''Kurzemes cietoksnis'' (Courland Fortress)., group=lower-alpha ...
. Formed into Army Group Courland
Army Group Courland (german: Heeresgruppe Kurland) was a German Army Group on the Eastern Front which was created from remnants of the Army Group North, isolated in the Courland Peninsula by the advancing Soviet Army forces during the 1944 Balt ...
, this force held out until the end of the war in May 1945, when it surrendered to the Soviet forces and the troops were sent to prison camps.
Coup
Kārlis Ulmanis
Kārlis Augusts Vilhelms Ulmanis (; 4 September 1877 – 20 September 1942) was a Latvian politician. He was one of the most prominent Latvian politicians of pre-World War II Latvia during the Interwar period of independence from November 1918 to ...
staged a bloodless coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
on May 15, 1934, establishing a nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
dictatorship
A dictatorship is a form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, which holds governmental powers with few to no limitations on them. The leader of a dictatorship is called a dictator. Politics in a dictatorship are ...
that lasted until 1940. Most of the Baltic German
Baltic Germans (german: Deutsch-Balten or , later ) were ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their coerced resettlement in 1939, Baltic Germans have markedly declined ...
s left Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
by agreement between Ulmanis' government and Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
after the conclusion of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
, long_name = Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
, image = Bundesarchiv Bild 183-H27337, Moskau, Stalin und Ribbentrop im Kreml.jpg
, image_width = 200
, caption = Stalin and Ribbentrop shaking ...
. On October 5, 1939, Latvia was forced to accept a "mutual assistance" pact with the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, granting the Soviets the right to station 25,000 troops on Latvian territory. On June 16, 1940, Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov. ; (;. 9 March Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">O._S._25_February.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O. S. 25 February">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dat ...
presented the Latvian representative in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
with an ultimatum accusing Latvia of violations of that pact.
Soviet annexation
On June 17 theRed Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
occupied the country. Rigged elections for a "People's Saeima
People's, branded as ''People's Viennaline'' until May 2018, and legally ''Altenrhein Luftfahrt GmbH'', is an Austrian airline headquartered in Vienna. It operates scheduled and charter passenger flights mainly from its base at St. Gallen-Altenr ...
" were held, and a puppet government
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sovere ...
headed by Augusts Kirhenšteins
Augusts Kirhenšteins, formerly spelt Kirchenšteins (18 September 1872 in Mazsalaca – 3 November 1963 in Riga), was a Latvian and Soviet microbiologist, politician and educator. He was the ''de facto'' prime minister of Latvia from 20 June 1 ...
led Latvia into the USSR. The annexation was formalized on August 5, 1940. The ensuing months would become known in Latvia as ''Baigais Gads
The Soviet occupation of Latvia in 1940 refers to the military occupation of the Republic of Latvia by the Soviet Union under the provisions of the 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact with Nazi Germany and its Secret Additional Protocol signed in A ...
'', the Year of Horror. Mass arrests, disappearances, and deportations culminated on the night of June 14, 1941. Prior to the German invasion, in less than a year, at least 27,586 persons were arrested; most were deported, and about 945 persons were shot.
After the occupation of Latvia in June 1940 the annihilation of the Latvian army began. The army was renamed People’s Army, and in September–November 1940, the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
’s 24th Territorial Rifle Corps. In September the corps contained 24,416 men but in autumn more than 800 officers and about 10,000 instructors and soldiers were discharged. The arresting of soldiers continued in the following months. In June 1940, the entire Territorial Corps was sent to Litene
Litene (german: Lettin) is the center of Litene Parish, in Gulbene Municipality, in north-eastern Latvia. Other names: Lytene, Myza Lytene.No NKVD līdz KGB. Politiskās prāvas Latvijā 1940–1986: Noziegumos pret padomju valsti apsūdzēto L ...
camp. Before leaving the camp, Latvians drafted in 1939 were demobilised, and replaced by about 4,000 Russian soldiers from area around Moscow. On June 10, the corps senior officers were sent to Russia where they were arrested and most of them shot. On June 14 at least 430 officers were arrested and sent to Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ...
camps. After the German attack on the Soviet Union, from June 29 to July 1 more than 2,080 Latvian soldiers were demobilised, fearing that they might turn their weapons against the Russian commissars and officers. Simultaneously, many soldiers and officers deserted and when the corps crossed the Latvian border only about 3,000 Latvian soldiers remained.
German occupation

Army Group North
Army Group North (german: Heeresgruppe Nord) was a German strategic formation, commanding a grouping of field armies during World War II. The German Army Group was subordinated to the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' (OKH), the German army high comma ...
's objective
Objective may refer to:
* Objective (optics), an element in a camera or microscope
* ''The Objective'', a 2008 science fiction horror film
* Objective pronoun, a personal pronoun that is used as a grammatical object
* Objective Productions, a Brit ...
was Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
via the Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
. Comprising the 16th and 18th Armies and 4th Panzer Group, this formation drove through Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
and the cities of Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
of Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
and Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ol ...
. While under German occupation, Latvia was administered as part of Reichskommissariat Ostland
The Reichskommissariat Ostland (RKO) was established by Nazi Germany in 1941 during World War II. It became the civilian occupation regime in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and the western part of Byelorussian SSR. German planning documents initia ...
. In 1941 empowered by the Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the im ...
and Nazi war criminal Franz Walter Stahlecker
Franz Walter Stahlecker (10 October 1900 – 23 March 1942) was commander of the SS security forces (''Sicherheitspolizei'' (SiPo) and the ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD) for the ''Reichskommissariat Ostland'' in 1941–42. Stahlecker commanded ''Eins ...
the far-right-wing extremist group of 500 Arajs Kommando
The Arajs ''Kommando'' (also: ''Sonderkommando Arajs''; ), led by SS commander and Nazi collaborator Viktors Arājs, was a unit of Latvian Auxiliary Police (german: Lettische Hilfspolizei) subordinated to the German ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD). It ...
led by Viktors Arājs
Viktors Arājs (13 January 1910 – 13 January 1988) was a Latvian/Baltic German collaborator and Nazi SS SD officer who took part in the Holocaust during the German occupation of Latvia and Belarus as the leader of the Arajs Kommando. The Ara ...
participated in the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. 80,000 to 100,000 Latvian citizens were killed during the Nazi occupation, including ca. 70,000 Latvian Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
; about 20,000 Jews brought from Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
were also murdered in Latvia. Nearly three years later in 1943, forced conscription of 180,000 Latvian men into the German auxiliary forces was ordered by Hitler. Latvian soldiers fought on both sides of the conflict against their will, including in the Latvian Legion
The Latvian Legion ( lv, Latviešu leģions) was a formation of the German Waffen-SS during World War II. Created in 1943, it consisted primarily of ethnic Latvian personnel.Gerhard P. Bassler, ''Alfred Valdmanis and the politics of survival'', 20 ...
of the Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
, most of them conscripted by the occupying authorities.
 While the
While the Army Group North
Army Group North (german: Heeresgruppe Nord) was a German strategic formation, commanding a grouping of field armies during World War II. The German Army Group was subordinated to the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' (OKH), the German army high comma ...
held back the Soviet Estonian Operation, the Soviet Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration (; russian: Операция Багратио́н, Operatsiya Bagration) was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (russian: Белорусская наступательная оп� ...
achieved unbelievable success. Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre (german: Heeresgruppe Mitte) was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created on 22 June 1941, as one of three German Army fo ...
was in tatters, and the northern edge of the Soviet assault threatened to trap Army Group North
Army Group North (german: Heeresgruppe Nord) was a German strategic formation, commanding a grouping of field armies during World War II. The German Army Group was subordinated to the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' (OKH), the German army high comma ...
in a pocket in Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. ...
. Panzer
This article deals with the tanks (german: panzer) serving in the German Army (''Deutsches Heer'') throughout history, such as the World War I tanks of the Imperial German Army, the interwar and World War II tanks of the Nazi German Wehrmacht, ...
s of Hyazinth Graf Strachwitz von Gross-Zauche und Camminetz
Hyazinth Graf Strachwitz (also known as Hyazinth Graf Strachwitz von Groß-Zauche und Camminetz) (30 July 1893 – 25 April 1968) was a German officer of aristocratic descent in the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of the Kn ...
had been sent back to the capital of Ostland, Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
and in ferocious defensive battles had halted the Soviet advance in late April, 1944. Strachwitz had been needed elsewhere, and was soon back to acting as the Army Group's fire brigade. Strachwitz's Panzerverband was broken up in late July. By early August, the Soviets were again ready to attempt to cut off Army Group North from Army Group Centre.
Battle of the Baltic
 A massive Soviet assault sliced through the German lines and Army Group North was completely isolated from its neighbour. Strachwitz was trapped outside the pocket, and ''Panzerverband von Strachwitz'' was reformed, this time from elements of the 101st Panzer Brigade of panzer-ace Oberst
A massive Soviet assault sliced through the German lines and Army Group North was completely isolated from its neighbour. Strachwitz was trapped outside the pocket, and ''Panzerverband von Strachwitz'' was reformed, this time from elements of the 101st Panzer Brigade of panzer-ace Oberst Meinrad von Lauchert
__NOTOC__
Meinrad von Lauchert (29 August 1905 – 4 December 1987) was a German general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves.
On the eve of the Battle o ...
and the newly formed SS Panzer Brigade Gross
SS Panzer Brigade ''Gross'' was a unit of the Waffen-SS of Nazi Germany during World War II, under the command of Obersturmbannführer Martin Gross. The brigade was formed from the SS Panzer Training and Replacement Regiment based in Dundaga, Lat ...
under SS-Sturmbannführer Gross. Inside the trapped pocket, the remaining panzers and StuG IIIs of the ''Hermann von Salza'' and the last of Jähde's Tigers were formed into another Kampfgruppe to attack from the inside of the trap. On 19 August 1944, the assault, which had been dubbed Unternehmen Doppelkopf (Operation Doppelkopf
Operation Doppelkopf (german: Unternehmen Doppelkopf) and the following Operation Cäsar were German counter-offensives on the Eastern Front in the late summer of 1944 in the aftermath of the major Soviet advance in Operation Bagration with the ...
) got underway. It was preceded by a bombardment by the Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles.
The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hu ...
Prinz Eugen's 380mm guns, which destroyed forty-eight T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank introduced in 1940. When introduced its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was less powerful than its contemporaries while its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against Anti-tank warfare, anti-tan ...
s assembling in the square at Tukums
Tukums (; german: Tuckum; liv, Tukāmō) is a town in the Zemgale region of Latvia.
History
The historical center of Tukums developed between trade routes leading from the mouth of the Daugava River to Prussia. The oldest part is today's Ta ...
. Contact was restored between the army groups. The 101.Panzerbrigade was now assigned to the army detachment "Narwa at the Emajõgi River Front in Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
, bolstering the defenders' armour strength. Disaster had been averted, but the warning was clear. Army Group North was extremely vulnerable to being cut off. In 1944, the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
lifted the siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
and re-conquered the Baltic area along with much of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
. However, some 200,000 German troops held out in Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. ...
. They were besieged with their backs to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. They were senselessly stuck there; the Red Army naturally did not pay much attention while concentrating its men and weapons on the attacks on East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, and ultimately Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
. Colonel-General
Colonel general is a three- or four-star military rank used in some armies. It is particularly associated with Germany, where historically general officer ranks were one grade lower than in the Commonwealth and the United States, and was a ra ...
Heinz Guderian
Heinz Wilhelm Guderian (; 17 June 1888 – 14 May 1954) was a German general during World War II who, after the war, became a successful memoirist. An early pioneer and advocate of the " blitzkrieg" approach, he played a central role in t ...
, the Chief of the German General Staff
The German General Staff, originally the Prussian General Staff and officially the Great General Staff (german: Großer Generalstab), was a full-time body at the head of the Prussian Army and later, the German Army, responsible for the continuou ...
, insisted to Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
that the troops in Courland should be evacuated by sea and used for the defense of the Reich
''Reich'' (; ) is a German language, German noun whose meaning is analogous to the meaning of the English word "realm"; this is not to be confused with the German adjective "reich" which means "rich". The terms ' (literally the "realm of an emp ...
. However, Hitler refused and ordered the German forces in Courland to hold out. He believed them necessary to protect German submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
bases along the Baltic coast.
 On January 15, 1945,
On January 15, 1945, Army Group Courland
Army Group Courland (german: Heeresgruppe Kurland) was a German Army Group on the Eastern Front which was created from remnants of the Army Group North, isolated in the Courland Peninsula by the advancing Soviet Army forces during the 1944 Balt ...
(''Heeresgruppe Kurland'') was formed under Colonel-General
Colonel general is a three- or four-star military rank used in some armies. It is particularly associated with Germany, where historically general officer ranks were one grade lower than in the Commonwealth and the United States, and was a ra ...
Dr. Lothar Rendulic
Lothar Rendulic ( hr, Rendulić; 23 October 1887 – 17 January 1971)Rudolf Neck, Adam Wandruszka, Isabella Ackerl (ed.) (1980): ''Protokolle des Ministerrates der Ersten Republik, 1918–1938, Abteilung VIII, 20. Mai 1932 bis 25. Juli 1934''. ...
. Until the end of the war, Army Group Courland (including divisions such as the Latvian Freiwiliger SS Legion) successfully defended the Courland Peninsula
The Courland Peninsula (, German: ''Kurland'') is a historical and cultural region in western Latvia in the north-western part of Courland. Fourteen coastal villages on the peninsula make of the Livonian core area.
It is bordered by the Baltic S ...
. It held out until May 8, 1945, when it surrendered under Colonel-General
Colonel general is a three- or four-star military rank used in some armies. It is particularly associated with Germany, where historically general officer ranks were one grade lower than in the Commonwealth and the United States, and was a ra ...
Carl Hilpert
__NOTOC__
Carl Hilpert (12 September 1888 – 1 February 1947) was a German general during World War II.
Biography
When World War II broke out in September 1939, Hilpert became chief of the staff of ''Armeeabteilung A'' on 9 September 1939 unde ...
, the army group's last commander. He surrendered to Marshal Leonid Govorov
Leonid Aleksandrovich Govorov (russian: Леони́д Алекса́ндрович Го́воров; – 19 March 1955) was a Soviet military commander. Trained as an artillery officer, he joined the Red Army in 1920. He graduated from several ...
, the commander of opposing Soviet forces on the Courland perimeter. At this time the group still consisted of some 31 divisions of varying strength. After May 9, 1945 approximately 203,000 troops of Army Group Courland began moving to Soviet prison camps in the East. Many soldiers evaded capture and joined the Forest Brothers
The Guerrilla war in the Baltic states was an armed struggle which was waged by the Latvian, Lithuanian, and Estonian partisans, called the Forest Brothers (also: the "Brothers of the Wood" and the "Forest Friars"; et, metsavennad, lv, mež ...
resistance that waged unsuccessful guerilla warfare for several years.
Timeline
1939
* August 23, 1939Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
, long_name = Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
, image = Bundesarchiv Bild 183-H27337, Moskau, Stalin und Ribbentrop im Kreml.jpg
, image_width = 200
, caption = Stalin and Ribbentrop shaking ...
signed. Pact gave Soviet Union free hand in Estonia, Latvia and Finland.
* October 2, 1939 Soviet Union demands mutual assistance pact with Latvia.
* October 5, 1939 Latvia gives in to Soviet bases demands and Soviet–Latvian Mutual Assistance Treaty
The Soviet–Latvian Mutual Assistance Treaty (russian: Пакт о взаимопомощи между СССР и Латвийской Республикой, lv, Savstarpējās palīdzības pakts starp Latviju un PSRS) was a bilateral treaty ...
signed.
1940
* June 15, 1940 at dawn Soviet troops storm and capture Latvian border posts Masļenki and Šmaiļi. * June 16, 1940 Similar ultimatums were given to Estonia and Latvia. * June 17, 1940 Estonia and Latvia gave in to the Soviet demands and are occupied. * June 20, 1940 New Latvian government of Moscow-approved ministers is formed. * July 14-July 15, 1940 Elections in Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, where non-communist candidates were disqualified, harassed and beaten. * July 21, 1940 New LatvianSaeima
The Saeima () is the parliament of the Latvia, Republic of Latvia. It is a unicameral parliament consisting of 100 members who are elected by proportional representation, with seats allocated to political parties which gain at least 5% of the po ...
accepts wide nationalisation and Sovietization
Sovietization (russian: Советизация) is the adoption of a political system based on the model of soviets (workers' councils) or the adoption of a way of life, mentality, and culture modelled after the Soviet Union. This often included ...
decrees.
* July 22, 1940 The president of Latvia, Kārlis Ulmanis
Kārlis Augusts Vilhelms Ulmanis (; 4 September 1877 – 20 September 1942) was a Latvian politician. He was one of the most prominent Latvian politicians of pre-World War II Latvia during the Interwar period of independence from November 1918 to ...
, is arrested and deported to Russia, never returning. He died in a prison in Krasnovodsk on September 20, 1942.
* August 5, 1940 Soviet Union annexes Latvia.
1941
June 14, 1941 The Soviet Union deports 15,424 Latvians including over 3,000 children by train to Siberia.1942
1943
1944
1945
See also
*Latvian SSR
The Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic (Latvian SSR), also known as Soviet Latvia or simply Latvia, was a federated republic within the Soviet Union, and formally one of its 16 (later 15) constituent republics. The Latvian Soviet Socialist Rep ...
* Latvian fleet that fought for the Allies in World War II
The part of the Latvian fleet that fought for the Allies in World War II under the flag of Latvia consisted of eight freighters: ''Abagra'', ''Ciltvaira'', ''Regent'', ''Everasma'', '' Everalda'', ''Everelza'', ''Ķegums'', and ''Everagra''. Only ...
References
{{Soviet Union topics Latvian Soviet Socialist RepublicLatvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
1940s in Latvia
Jewish Latvian history
Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...