Lotus 25 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lotus 25 was a racing car designed by

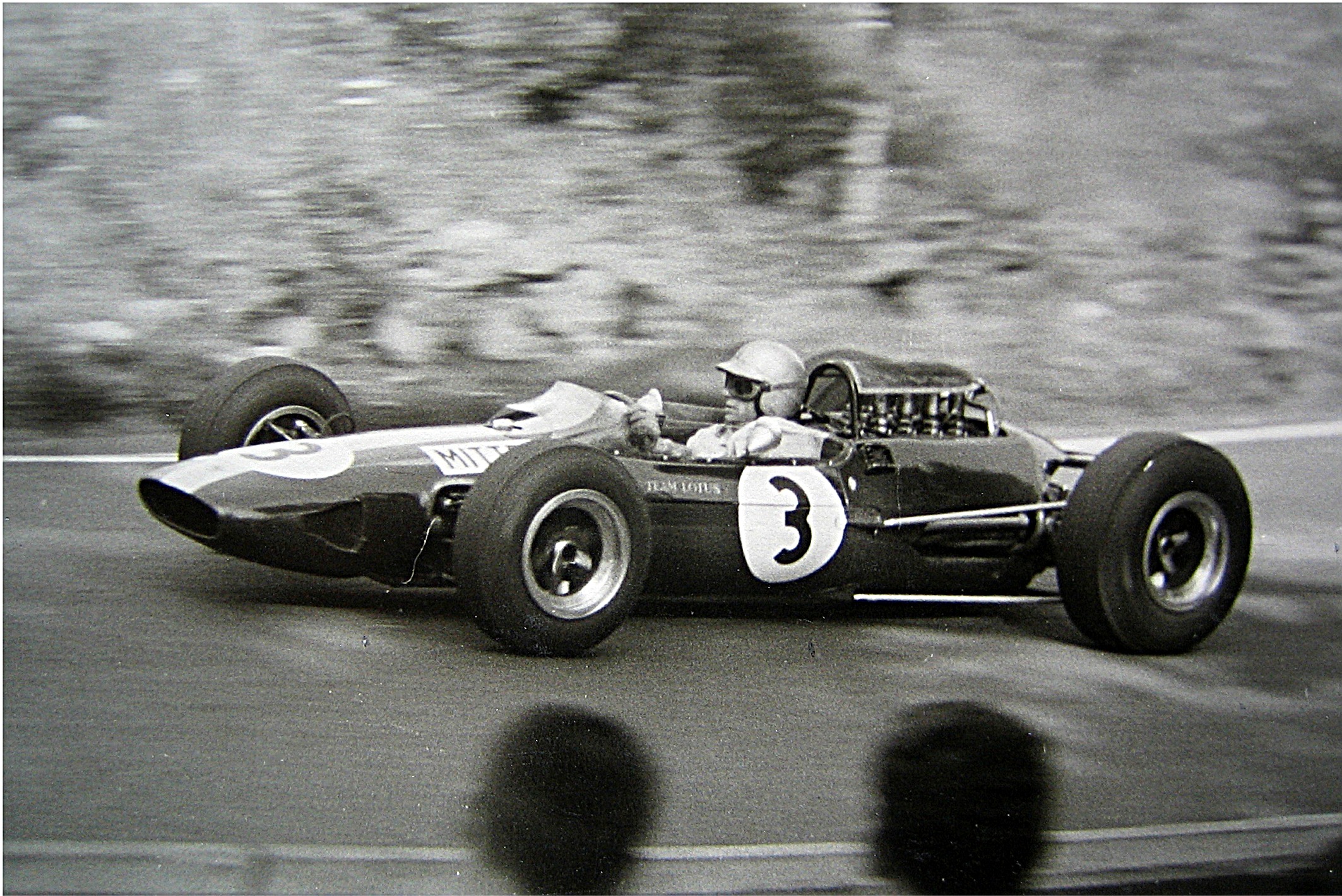
 An early brainchild of Chapman's fertile mind, the original sketches for the car were made on napkins while Chapman discussed his idea while dining out with
An early brainchild of Chapman's fertile mind, the original sketches for the car were made on napkins while Chapman discussed his idea while dining out with
Colin Chapman
Anthony Colin Bruce Chapman (19 May 1928 – 16 December 1982) was an English design engineer, inventor, and builder in the automotive industry, and founder of Lotus Cars.
In 1952 he founded the sports car company Lotus Cars. Chapman ...
for the 1962 Formula One season
The 1962 Formula One season was the 16th season of FIA Formula One motor racing. It featured the 1962 World Championship of Drivers and the 1962 International Cup for F1 ManufacturersFIA Yearbook 1974, Grey Section, pages 118–121 which were cont ...
. It was a revolutionary design, the first fully stressed monocoque
Monocoque ( ), also called structural skin, is a structural system in which loads are supported by an object's external skin, in a manner similar to an egg shell. The word ''monocoque'' is a French term for "single shell".
First used for boats, ...
chassis to appear in Formula One. In the hands of Jim Clark
James Clark Jr. OBE (4 March 1936 – 7 April 1968) was a British Formula One racing driver from Scotland, who won two World Championships, in 1963 and 1965. A versatile driver, he competed in sports cars, touring cars and in the Indianapol ...
it took 14 World Championship Grand Prix wins and propelled him to his 1963 World Championship title. Its last World Championship win was at the 1965 French Grand Prix.
It was the first Formula One
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, ...
car to use Esso
Esso () is a trading name for ExxonMobil. Originally, the name was primarily used by its predecessor Standard Oil of New Jersey after the breakup of the original Standard Oil company in 1911. The company adopted the name "Esso" (the phonetic p ...
fuel.
History


 An early brainchild of Chapman's fertile mind, the original sketches for the car were made on napkins while Chapman discussed his idea while dining out with
An early brainchild of Chapman's fertile mind, the original sketches for the car were made on napkins while Chapman discussed his idea while dining out with Frank Costin
Francis Albert Costin (8 June 1920 – 5 February 1995) was a British automotive engineer who advanced monocoque chassis design and was instrumental in adapting aircraft aerodynamic knowledge for automobile use.
Career
Costin was an engineer ...
(designer of Vanwall
Vanwall was a motor racing team and racing car constructor that was active in Formula One during the 1950s. Founded by Tony Vandervell, the Vanwall name was derived by combining the name of the team owner with that of his Thinwall bearings ...
, Lotus Mk.8, 9, 10, 11 and Lotus 16
The Lotus 16 was the second single-seat racing car designed by Colin Chapman, and was built by his Lotus Cars manufacturing company for the Team Lotus racing squad. The Lotus 16 was constructed to compete in both the Formula One and Formula Tw ...
bodies, later of Marcos Marcos may refer to:
People with the given name ''Marcos''
*Marcos (given name)
Sports
;Surnamed
* Dayton Marcos, Negro league baseball team from Dayton, Ohio (early twentieth-century)
* Dimitris Markos, Greek footballer
* Nélson Marcos, Portug ...
fame). The unveiling of the 25 at Zandvoort
Zandvoort () is a municipality in the province of North Holland, Netherlands. It is one of the major beach resorts of the Netherlands; it has a long sandy beach. It is bordered by coastal dunes of Zuid-Kennemerland National Park and the Amsterdam ...
in 1962 was a shock for the competition, and particularly for teams like Brabham
Brabham () is the common name for Motor Racing Developments Ltd., a British racing car manufacturer and Formula One racing team. Founded in 1960 by Australian driver Jack Brabham and British-Australian designer Ron Tauranac, the team won four ...
and UDT/Laystall who had recently purchased 24s from Lotus, with the understanding that they would be "mechanically identical" to the works cars - Chapman reserved the right to alter the bodywork of the cars.
The monocoque made the car more rigid and structurally stronger than typical F1 cars of the period. The 25 was three times stiffer than the interim 24, while the chassis weighed only half as much. The car also was extremely low and narrow, with a frontal area of 8.0 ft², 0.74m² as compared to the normal 9.5 ft², 0.88 m²Setright, p.1230. It was also envisaged to have a column gear lever, to keep the cockpit width to a minimum, although this was only experimental and discarded. To assist the low profile and low frontal area, the driver reclined sharply behind the wheel (an idea seen in the 18, and pioneered over a decade previously by Gustav Baumm
Gustav, Gustaf or Gustave may refer to:
*Gustav (name), a male given name of Old Swedish origin
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''Primeval'' (film), a 2007 American horror film
* ''Gustav'' (film series), a Hungarian series of animated short cart ...
at NSU), leading to the nickname 'The Bathtub', while front coil/damper units were moved inboard (as in the 1948 Maserati
Maserati S.p.A. () is an Italian luxury vehicle manufacturer. Established on 1 December 1914, in Bologna, Italy, the company's headquarters are now in Modena, and its emblem is a trident. The company has been owned by Stellantis since 2021. Ma ...
). The 25 was powered by the Mk.II 1496cc through to the Mk.5 1499cc versions of the Coventry Climax FWMV
Coventry Climax was a British forklift truck, fire pump, racing, and other specialty engine manufacturer.
History
Pre WW1
The company was started in 1903 as Lee Stroyer, but two years later, following the departure of Stroyer, it was reloca ...
V8 in crossplane and flatplane formats. Later, Reg Parnell Racing
Reg Parnell Racing was a privateer Formula One team during the 1950s and 1960s. The team was founded by ex-Formula One driver Reg Parnell after he retired from racing. It raced as Yeoman Credit Racing in 1961 and as the Bowmaker Racing Team in ...
in 1964 fitted BRM P56s of similar specification to their second-hand 25s.
Some privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s who had been buying Lotus chassis were disgruntled by the fact Chapman refused to provide them 25s. These teams, including Rob Walker Racing, were given Lotus 24
The Lotus 24 was a Formula One racing car''Automobile Year'', No. 10, 1962-1963, Page 198. designed by Team Lotus for the 1962 Formula One season. Despite some early success in non-Championship Grands Prix, it was eclipsed by the technically s ...
s, while the works team had exclusive use of the 25 for Jim Clark
James Clark Jr. OBE (4 March 1936 – 7 April 1968) was a British Formula One racing driver from Scotland, who won two World Championships, in 1963 and 1965. A versatile driver, he competed in sports cars, touring cars and in the Indianapol ...
and Trevor Taylor. When it first appeared at the Dutch Grand Prix
The Dutch Grand Prix ( nl, Grote Prijs van Nederland) is a Formula One motor racing event held at Circuit Zandvoort, North Holland, the Netherlands, from 1950 to 1985 and from 2021 onwards. It was a part of the World Championship from 1952, ...
, the futuristic 25 was inspected by John Cooper, who asked Chapman where he had put the frame tubes in the car.
Seven cars were built in total, numbered R1 to R7. Four cars - R1, R2, R3 and R5 - were written off (three of them by Trevor Taylor) in accidents between 1962 and 1966. The most successful was R4, which Clark drove to all seven of his World Championship wins in 1963. This car was later crashed by Richard Attwood
Richard James David "Dickie" Attwood (born 4 April 1940, Wolverhampton, Staffordshire) is a British motor racing driver, from England. During his career he raced for the BRM, Lotus and Cooper Formula One teams. He competed in 17 World Championsh ...
then rebuilt as a Lotus 33
The Lotus 33 was a Formula One car designed by Colin Chapman and Len Terry and built by Team Lotus. A development of the successful Lotus 25, in the hands of Jim Clark it won five World Championship Grands Prix in 1965, taking Clark to his ...
using a spare monocoque of that type and unofficially known as R13.
Racing history
The car gave Clark his first World Championship Grand Prix victory, atSpa
A spa is a location where mineral-rich spring water (and sometimes seawater) is used to give medicinal baths. Spa towns or spa resorts (including hot springs resorts) typically offer various health treatments, which are also known as balneoth ...
in 1962. He took another win in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
and again in the USA
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, which put him in contention for the title, but while leading the final race in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
a much publicised engine seizure cost him the title to Graham Hill
Norman Graham Hill (15 February 1929 – 29 November 1975) was a British racing driver and team owner, who was the Formula One World Champion twice, winning in and as well as being runner up on three occasions (1963, 1964 and 1965). Despite ...
.
Clark gained his revenge the following year, taking his first World Championship in the 25, by winning 7 races, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
, Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
, and Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. Lotus also won its first constructors' championship. Following the United States GP, a 25 was taken to the Indianapolis Motor Speedway
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is an automobile racing circuit located in Speedway, Indiana, an enclave suburb of Indianapolis, Indiana. It is the home of the Indianapolis 500 and the Verizon 200, and and formerly the home of the United State ...
for evaluation, where they also trialled Lucas
Lucas or LUCAS may refer to:
People
* Lucas (surname)
* Lucas (given name)
Arts and entertainment
* Luca Family Singers, also known as "lucas ligner en torsk"
* ''Lucas'' (album) (2007), an album by Skeletons and the Kings of All Cities
* ''L ...
electronic ignition
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, Rocket engine#Ignition, rocket engines, etc. The widest ...
for Ford. The results were encouraging enough for Colin Chapman to mount his ultimately successful challenge on the Indianapolis 500
The Indianapolis 500, formally known as the Indianapolis 500-Mile Race, and commonly called the Indy 500, is an annual automobile race held at Indianapolis Motor Speedway (IMS) in Speedway, Indiana, United States, an enclave suburb of Indi ...
.
The 25 was again used during the 1964 season, winning a further three races in Clark's hands. At the final race in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, just as in 1962, the Climax engine developed an oil leak and with literally a lap to run Clark coasted to a halt in sight of world championship victory, this time conceding to John Surtees
John Surtees, (11 February 1934 – 10 March 2017) was a British Grand Prix motorcycle road racer and Formula One driver. On his way to become a seven-time Grand Prix motorcycle World Champion, he won his first title in 1956, and followed with ...
. Despite the introduction of the Lotus 33
The Lotus 33 was a Formula One car designed by Colin Chapman and Len Terry and built by Team Lotus. A development of the successful Lotus 25, in the hands of Jim Clark it won five World Championship Grands Prix in 1965, taking Clark to his ...
in 1964, the 25 was still used until well into the 1965 season, Clark taking the car's final win at the 1965 French Grand Prix.
In 1964, Reg Parnell Racing
Reg Parnell Racing was a privateer Formula One team during the 1950s and 1960s. The team was founded by ex-Formula One driver Reg Parnell after he retired from racing. It raced as Yeoman Credit Racing in 1961 and as the Bowmaker Racing Team in ...
began racing the 25, using the BRM
British Racing Motors (BRM) was a British Formula One motor racing team. Founded in 1945 and based in the market town of Bourne in Lincolnshire, it participated from 1951 to 1977, competing in 197 grands prix and winning seventeen. BRM wo ...
P56 V8 engine, with limited success. Chris Irwin
Chris Irwin (born 27 June 1942 in Wandsworth, London) is a British former racing driver. He participated in 10 Formula One World Championship Grands Prix, debuting on 16 July 1966. He scored two championship points.
Irwin's career was ended p ...
placed Reg Parnell Racing
Reg Parnell Racing was a privateer Formula One team during the 1950s and 1960s. The team was founded by ex-Formula One driver Reg Parnell after he retired from racing. It raced as Yeoman Credit Racing in 1961 and as the Bowmaker Racing Team in ...
's 25/33 hybrid 7th in its final World Championship race at the 1967 Dutch Grand Prix
The 1967 Dutch Grand Prix was a Formula One motor race held at Zandvoort on June 4, 1967. It was race 3 of 11 in both the 1967 World Championship of Drivers and the 1967 International Cup for Formula One Manufacturers.
The race saw the debut of t ...
, scene of the model's debut five years earlier.
World Championship results
(key
Key or The Key may refer to:
Common meanings
* Key (cryptography), a piece of information that controls the operation of a cryptography algorithm
* Key (lock), device used to control access to places or facilities restricted by a lock
* Key (map ...
) (results in bold indicate pole position; results in ''italics'' indicate fastest lap)
: Points were awarded on a 9-6-4-3-2-1 basis to the first six finishers at each round, but only the best placed car for each make was eligible to score points. In 1962 and 1966 only the best five results from the season were retained, and only the best six results for 1963, 1964 and 1965. In 1967 the best five results from the first six rounds and the best four results from the last five rounds were retained.
: Jack Brabham raced the spare works Lotus after engine failure forced him to retire his own car.
: Plans for Arundell to race the spare car were abandoned.
: Clark swapped cars with Spence's Lotus 33
The Lotus 33 was a Formula One car designed by Colin Chapman and Len Terry and built by Team Lotus. A development of the successful Lotus 25, in the hands of Jim Clark it won five World Championship Grands Prix in 1965, taking Clark to his ...
during the race following mechanical problems.
: Revson tried out Hailwood's car in practice while the latter was away qualifying for the TT.
: Total points scored by all Lotus-Climax cars, including 45 points scored by drivers of Lotus 33
The Lotus 33 was a Formula One car designed by Colin Chapman and Len Terry and built by Team Lotus. A development of the successful Lotus 25, in the hands of Jim Clark it won five World Championship Grands Prix in 1965, taking Clark to his ...
variants.
: Total points scored by all Lotus-Climax cars, including 8 points scored by drivers of Lotus 33
The Lotus 33 was a Formula One car designed by Colin Chapman and Len Terry and built by Team Lotus. A development of the successful Lotus 25, in the hands of Jim Clark it won five World Championship Grands Prix in 1965, taking Clark to his ...
variants.
References
Notes
Bibliography
*External links
{{F1 cars 1967 25 Formula One championship-winning cars