Lophophora williamsii on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless
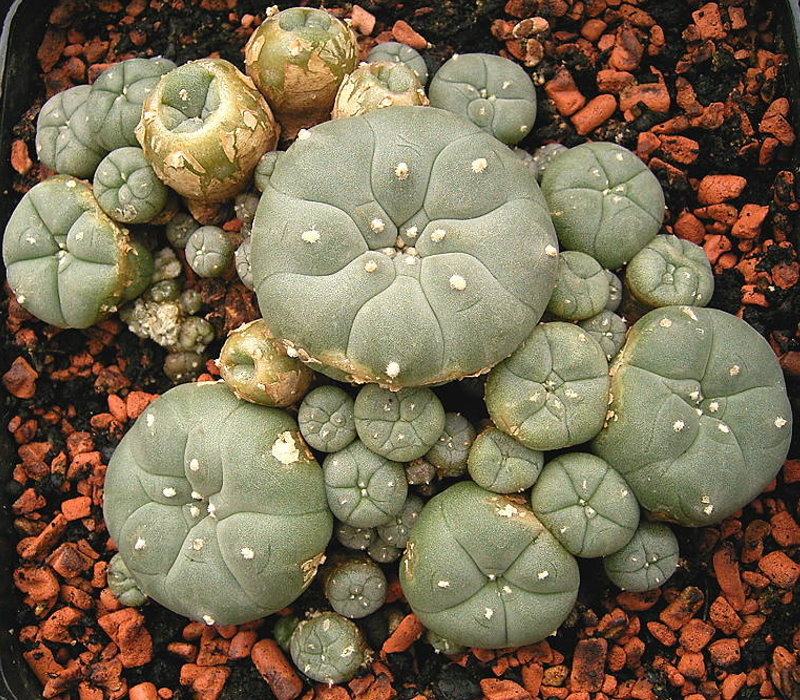

 The various species of the genus ''
The various species of the genus '' The cactus produces flowers sporadically; these are followed by small edible pink fruit. The club-shaped to elongated, fleshy fruits are bare and more or less rosy colored. At maturity, they are brownish-white and dry. The fruits do not burst open on their own and they are between long. They contain black, pear-shaped seeds that are 1 to 1.5 mm long and 1 mm wide. The seeds require hot and humid conditions to germinate. Peyote contains a large spectrum of
The cactus produces flowers sporadically; these are followed by small edible pink fruit. The club-shaped to elongated, fleshy fruits are bare and more or less rosy colored. At maturity, they are brownish-white and dry. The fruits do not burst open on their own and they are between long. They contain black, pear-shaped seeds that are 1 to 1.5 mm long and 1 mm wide. The seeds require hot and humid conditions to germinate. Peyote contains a large spectrum of
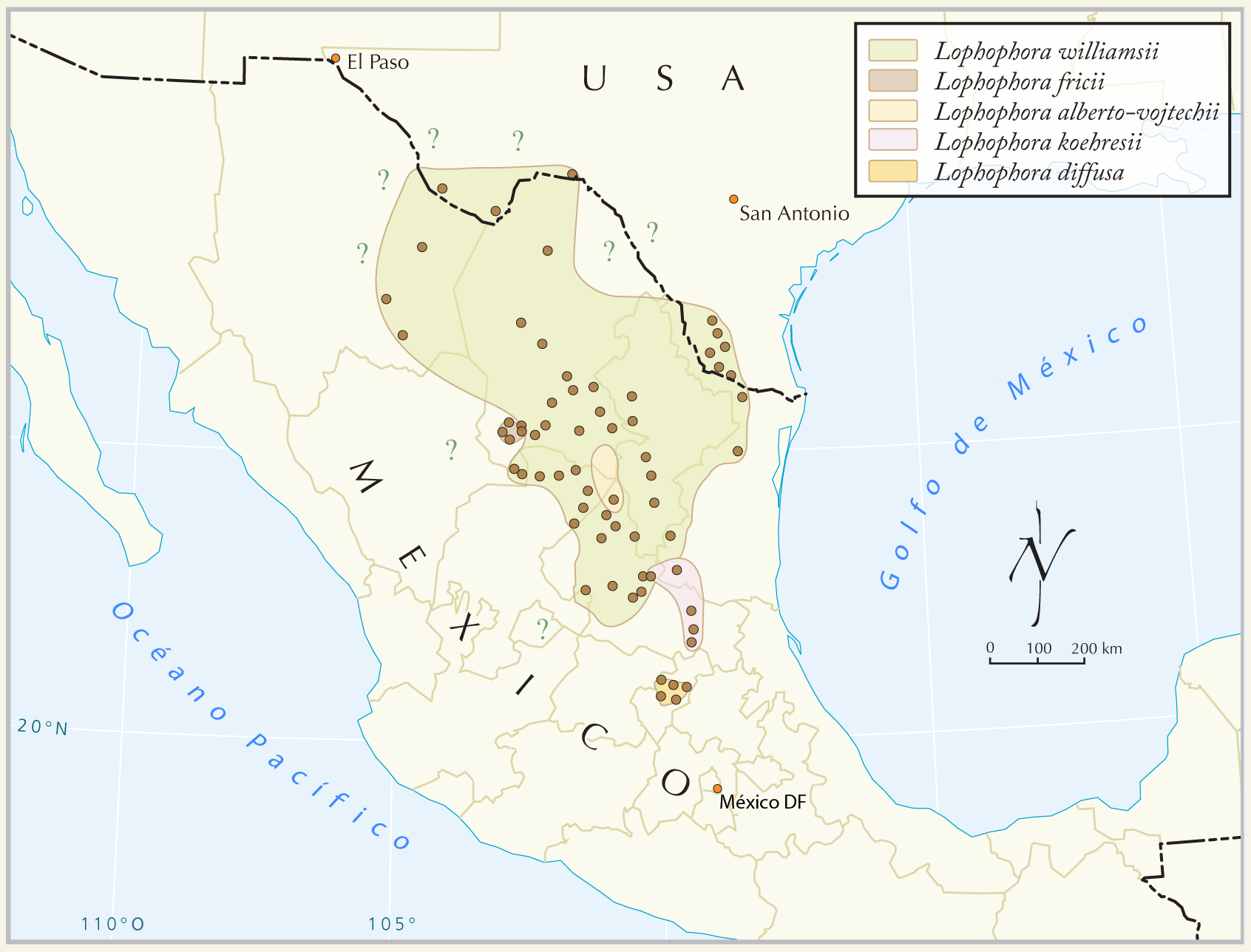 ''L. williamsii'' is native to southern
''L. williamsii'' is native to southern
 When used for its
When used for its  Peyote also contains the alkaloid called
Peyote also contains the alkaloid called
 From earliest recorded time, peyote has been used by indigenous peoples, such as the
From earliest recorded time, peyote has been used by indigenous peoples, such as the

File:Arte Huichol A.JPG
File:MaskNecklacesTep.JPG
File:Huichol-Fadenbild.jpg
File:Huichol Trabajando.JPG
A Note on the Safety of Peyote when Used Religiously
Council on Spiritual Practices, 1996. * Labate, Beatriz; Cavnar, Clancy: ''Peyote: History, Tradition, Politics, and Conservation.'' Praeger, 2016. * Rätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants, Enthnopharmacology and Its Applications'' 1998/2005, Rochester, Vermont, Park Street Press, * Pollan, Michael 2021 This Is Your Mind on Plants © 2021 Penguin Books
USDA: NRCS Plants Profile ''Lophophora williamsii''
{{Authority control Lophophora Entheogens Herbal and fungal hallucinogens Flora of the Chihuahuan Desert Flora of Texas Flora of New Mexico Flora of Northeastern Mexico Flora of the Rio Grande valleys Flora of Zacatecas Native American Church Native American religion Huichol Plants used in traditional Native American medicine Psychedelic phenethylamine carriers Religion and politics Cacti of the United States Cacti of Mexico Psychoactive cacti
cactus
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek ...
which contains psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline
Mescaline or mescalin (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin.
Biological sou ...
. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller ...
(), meaning "caterpillar cocoon", from a root , "to glisten". p. 246. See peyotl
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains Psychoactive cactus, psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar Pupa#Cocoo ...
in Wiktionary. Peyote is native to Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
and southwestern Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. It is found primarily in the Sierra Madre Occidental
The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American C ...
, the Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert ( es, Desierto de Chihuahua, ) is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lower P ...
and in the states of Nayarit
Nayarit (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Nayarit), is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its ...
, Coahuila
Coahuila (), formally Coahuila de Zaragoza (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza), is one of the 32 states of Mexico.
Coahuila borders the Mexican states of N ...
, Nuevo León
Nuevo León () is a state in the northeast region of Mexico. The state was named after the New Kingdom of León, an administrative territory from the Viceroyalty of New Spain, itself was named after the historic Spanish Kingdom of León. With a ...
, Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas), is a state in the northeast region of Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entiti ...
, and San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí), is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and i ...
among scrub. It flowers from March to May, and sometimes as late as September. The flowers are pink, with thigmotactic
A taxis (; ) is the movement of an organism in response to a stimulus such as light or the presence of food. Taxes are innate behavioural responses. A taxis differs from a tropism (turning response, often growth towards or away from a stimulu ...
anthers (like ''Opuntia
''Opuntia'', commonly called prickly pear or pear cactus, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae. Prickly pears are also known as ''tuna'' (fruit), ''sabra'', ''nopal'' (paddle, plural ''nopales'') from the Nahuatl word f ...
'').
Known for its psychoactive
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
properties when ingested, peyote has at least 5,500 years of entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoac ...
ic and medicinal
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
use by indigenous North Americans.
Description

 The various species of the genus ''
The various species of the genus ''Lophophora
''Lophophora'' () is a genus of spineless, button-like cacti. Its area range covers southern through northeastern and north-central Mexico to Querétaro in central Mexico. The species are extremely slow growing, sometimes taking up to thirty ye ...
'' grow low to the ground and they often form groups with numerous, crowded shoots. The blue-green, yellow-green or sometimes reddish-green shoots are mostly flattened spheres with sunken shoot tips. They can reach heights of and diameters of . There are often significant, vertical ribs consisting of low and rounded or hump-like bumps. From the cusp areole
In botany, areoles are small light- to dark-colored bumps on cacti out of which grow clusters of spines. Areoles are important diagnostic features of cacti, and identify them as a family distinct from other succulent plants. Gordon Rowley - W ...
s arises a tuft of soft, yellowish or whitish woolly hairs. Spines are absent. Flowers are pink or white to slightly yellowish, sometimes reddish. They open during the day, are from long, and reach a diameter from .
phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amin ...
alkaloids. The principal one is mescaline for which the content of ''Lophophora williamsii'' is about 0.4% fresh (undried) and 3–6% dried.
Taxonomy
French botanistCharles Antoine Lemaire
Charles Antoine Lemaire (1 November 1800, in Paris – 22 June 1871, in Paris), was a French botanist and botanical author, noted for his publications on Cactaceae.
Education
Born the son of Antoine Charles Lemaire and Marie Jeanne Davio, he ha ...
described the species as ''Echinocactus williamsii'' in 1845. It was placed in the new genus ''Lophophora'' in 1894 by American botanist John Merle Coulter
John Merle Coulter, Ph. D. (November 20, 1851 – December 23, 1928) was an American botanist and educator. In his career in education administration, Coulter is notable for serving as the president of Indiana University and Lake Forest College a ...
.
Distribution and habitat
 ''L. williamsii'' is native to southern
''L. williamsii'' is native to southern North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, mainly distributed in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. In the United States, it grows in Southern Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. In Mexico, it grows in the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila
Coahuila (), formally Coahuila de Zaragoza (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza), is one of the 32 states of Mexico.
Coahuila borders the Mexican states of N ...
, Nuevo León
Nuevo León () is a state in the northeast region of Mexico. The state was named after the New Kingdom of León, an administrative territory from the Viceroyalty of New Spain, itself was named after the historic Spanish Kingdom of León. With a ...
, and Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas), is a state in the northeast region of Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entiti ...
in the north to San Luis Potosi and Zacatecas
, image_map = Zacatecas in Mexico (location map scheme).svg
, map_caption = State of Zacatecas within Mexico
, coordinates =
, coor_pinpoint =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type ...
. It is primarily found at elevations of and exceptionally up to in the Chihuahuan desert
The Chihuahuan Desert ( es, Desierto de Chihuahua, ) is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lower P ...
, but is also present in the more mild climate of Tamaulipas. Its habitat is primarily in desert scrub, particularly thorn scrub in Tamaulipas. It is common on or near limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
hills.
Cultivation
Peyote is extremely slow growing. Cultivated specimens grow considerably faster, sometimes taking less than three years to go from seedling to mature flowering adult. More rapid growth can be achieved by grafting peyote onto mature San Pedro root stock. The top of the above-ground part of the cactus, the crown, consists of disc-shaped buttons. These are cut above the roots and sometimes dried. When done properly, the top of the root forms a callus and the root does not rot. When poor harvesting techniques are used, however, the entire plant dies. Currently in South Texas, peyote grows naturally but has been over-harvested, to the point that the state has listed it as anendangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
. Cultivation is an important conservation tool for this particular species.
Uses
Psychoactive and medicinal
 When used for its
When used for its psychoactive
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
properties, common doses for pure mescaline range from roughly 200 to 400 mg. This translates to a dose of roughly 10 to 20 g of dried peyote buttons of average potency; however, potency varies considerably between samples, making it difficult to measure doses accurately without first extracting the mescaline. The effects last about 10 to 12 hours. Peyote is reported to trigger rich visual or auditory effects (see synesthesia
Synesthesia (American English) or synaesthesia (British English) is a perceptual phenomenon in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway. People who re ...
) and spiritual or philosophical insights.
In addition to psychoactive use, some Native American tribes use the plant in the belief it may have curative properties. They employ peyote for such varied ailments as toothache, pain in childbirth, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, breast pain, skin diseases, rheumatism
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including art ...
, diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, colds, and blindness. Although uncommon, use of peyote and mescaline has been associated with clinically significant effects requiring treatment.
The US Dispensary lists peyote under the name ''Anhalonium
''Ariocarpus'' is a small genus of succulent, subtropical plants of the family Cactaceae.
The name comes from the ancient Greek "aria" (an oak type) and "carpos" (=fruit) because of the resemblance of the fruit of the two genus in acorn form. A ...
'', and states it can be used in various preparations for neurasthenia
Neurasthenia (from the Ancient Greek νεῦρον ''neuron'' "nerve" and ἀσθενής ''asthenés'' "weak") is a term that was first used at least as early as 1829 for a mechanical weakness of the nerves and became a major diagnosis in North A ...
, hysteria
Hysteria is a term used colloquially to mean ungovernable emotional excess and can refer to a temporary state of mind or emotion. In the nineteenth century, hysteria was considered a diagnosable physical illness in women. It is assumed that ...
, and asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
.
hordenine
Hordenine is an alkaloid of the phenethylamine class that occurs naturally in a variety of plants, taking its name from one of the most common, barley (''Hordeum'' species). Chemically, hordenine is the ''N''-methyl derivative of ''N''-methyltyra ...
(also called peyocactin).
History
In 2005, researchers usedradiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
and alkaloid analysis to study two specimens of peyote buttons found in archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
digs from a site called Shumla Cave No. 5 on the Rio Grande in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. The results dated the specimens to between 3780 and 3660 BCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
. Alkaloid extraction yielded approximately 2% of the alkaloids including mescaline in both samples. This indicates that native North Americans were likely to have used peyote since at least five-and-a-half thousand years ago.
Specimens from a burial cave in west central Coahuila
Coahuila (), formally Coahuila de Zaragoza (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza), is one of the 32 states of Mexico.
Coahuila borders the Mexican states of N ...
, Mexico have been similarly analyzed and dated to 810 to 1070 CE.
 From earliest recorded time, peyote has been used by indigenous peoples, such as the
From earliest recorded time, peyote has been used by indigenous peoples, such as the Huichol
The Huichol or Wixárika are an indigenous people of Mexico and the United States living in the Sierra Madre Occidental range in the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, Zacatecas, and Durango, as well as in the United States in the states of California ...
of northern Mexico and by various Native American tribes, native to or relocated to the Southern Plains states of present-day Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
and Texas. Its usage was also recorded among various Southwestern Athabaskan-language tribal groups. The Tonkawa
The Tonkawa are a Native American tribe indigenous to present-day Oklahoma. Their Tonkawa language, now extinct, is a linguistic isolate.
Today, Tonkawa people are enrolled in the federally recognized Tonkawa Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma.
...
, the Mescalero
Mescalero or Mescalero Apache ( apm, Naa'dahéńdé) is an Apache tribe of Southern Athabaskan–speaking Native Americans. The tribe is federally recognized as the Mescalero Apache Tribe of the Mescalero Apache Reservation, located in south-cen ...
, and Lipan Apache
Lipan Apache are a band of Apache, a Southern Athabaskan Indigenous people, who have lived in the Southwest and Southern Plains for centuries. At the time of European and African contact, they lived in New Mexico, Colorado, Oklahoma, Texas, and ...
were the source or first practitioners of peyote religion
The Native American Church (NAC), also known as Peyotism and Peyote Religion, is a Native American religion that teaches a combination of traditional Native Americans in the United States, Native American beliefs and Christianity, with sacrament ...
in the regions north of present-day Mexico. They were also the principal group to introduce peyote to newly arrived migrants, such as the Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
and Kiowa
Kiowa () people are a Native American tribe and an indigenous people of the Great Plains of the United States. They migrated southward from western Montana into the Rocky Mountains in Colorado in the 17th and 18th centuries,Pritzker 326 and eve ...
from the Northern Plains. The religious, ceremonial, and healing uses of peyote may date back over 2,000 years.
Under the auspices of what came to be known as the Native American Church
The Native American Church (NAC), also known as Peyotism and Peyote Religion, is a Native American religion that teaches a combination of traditional Native American beliefs and Christianity, with sacramental use of the entheogen peyote. The re ...
, in the 19th century, American Indians in more widespread regions to the north began to use peyote in religious practices, as part of a revival of native spirituality. Its members refer to peyote as "the sacred medicine", and use it to combat spiritual, physical, and other social ills. Concerned about the drug's psychoactive effects, between the 1880s and 1930s, U.S. authorities attempted to ban Native American religious rituals involving peyote, including the Ghost Dance
The Ghost Dance ( Caddo: Nanissáanah, also called the Ghost Dance of 1890) was a ceremony incorporated into numerous Native American belief systems. According to the teachings of the Northern Paiute spiritual leader Wovoka (renamed Jack Wilso ...
. Today the Native American Church is one among several religious organizations to use peyote as part of its religious practice. Some users claim the drug connects them to God.
Traditional Navajo belief or ceremonial practice did not mention the use of peyote before its introduction by the neighboring Utes. The Navajo Nation now has the most members of the Native American Church.
John Raleigh Briggs (1851–1907) was the first to draw scientific attention of the Western scientific world to peyote. Louis Lewin
Louis Lewin (9 November 1850 - 1 December 1929) was a German pharmacologist. In 1887 he received his first sample of the Peyote cactus from Dallas, Texas-based physician John Raleigh Briggs (1851-1907), and later published the first methodical ...
described ''Anhalonium lewinii'' in 1888. Arthur Heffter
Arthur Carl Wilhelm Heffter (15 June 1859, in Leipzig – 8 February 1925, in Berlin) was a German pharmacologist and chemist. He was the first chairman of the German Society of Pharmacologists, and was largely responsible for the first ''Handbo ...
conducted self experiments on its effects in 1897. Similarly, Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
ethnographer
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject o ...
Carl Sofus Lumholtz studied and wrote about the use of peyote among the Indians of Mexico. Lumholtz also reported that, lacking other intoxicants, Texas Rangers captured by Union forces during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
soaked peyote buttons in water and became "intoxicated with the liquid".
Adverse reactions
A study published in 2007 found no evidence of long-term cognitive problems related to peyote use inNative American Church
The Native American Church (NAC), also known as Peyotism and Peyote Religion, is a Native American religion that teaches a combination of traditional Native American beliefs and Christianity, with sacramental use of the entheogen peyote. The re ...
ceremonies, but researchers stressed their results may not apply to those who use peyote in other contexts. A four-year large-scale study of Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United ...
who regularly ingested peyote found only one case where peyote was associated with a psychotic break
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior t ...
in an otherwise healthy person; other psychotic episodes were attributed to peyote use in conjunction with pre-existing substance abuse or mental health problems. Later research found that those with pre-existing mental health issues are more likely to have adverse reactions to peyote. Peyote use does not appear to be associated with hallucinogen persisting perception disorder
Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) is a non-psychotic disorder in which a person experiences apparent lasting or persistent visual hallucinations or perceptual distortions after a previous use of drugs, including but not limited t ...
(a.k.a. "flashbacks") after religious use. Peyote also does not seem to be associated with physical dependence
Physical dependence is a physical condition caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug, in which abrupt or gradual drug withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms. Physical dependence can develop from low-dose therapeutic use of certai ...
, but some users may experience psychological dependence
Psychological dependence is a cognitive disorder that involves emotional–motivational withdrawal symptoms—e.g. anxiety and anhedonia—upon cessation of prolonged drug abuse or certain repetitive behaviors. It develops through frequent exp ...
.
Peyote can have strong emetic
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
effects, and one death has been attributed to esophageal bleeding caused by vomiting after peyote ingestion in a Native American patient with a history of alcohol abuse. Peyote is also known to cause potentially serious variations in heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and pupillary dilation
Pupillary response is a physiological response that varies the size of the pupil, via the optic and oculomotor cranial nerve.
A constriction response (miosis), is the narrowing of the pupil, which may be caused by scleral buckles or drugs such a ...
.
Research into the huichol
The Huichol or Wixárika are an indigenous people of Mexico and the United States living in the Sierra Madre Occidental range in the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, Zacatecas, and Durango, as well as in the United States in the states of California ...
natives of central-western Mexico, who have taken peyote regularly for an estimated 1,500 years or more, found no evidence of chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
damage in either men or women.
Cultural significance

Wixarika (Huichol) culture
The Wixarika religion consists of four principaldeities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
: Corn, Kayumarie (Blue Deer), Hikuri (Peyote), and the Eagle, all descended from their Sun God. Schaefer has interpreted this to mean that peyote is the soul of their religious culture and a visionary
A visionary, defined broadly, is one who can envision the future. For some groups, this can involve the supernatural.
The visionary state is achieved via meditation, lucid dreams, daydreams, or art. One example is Hildegard of Bingen, a 12th-c ...
sacrament
A sacrament is a Christianity, Christian Rite (Christianity), rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments ...
that opens a pathway to the other deities.
Legality
United Nations
Canada
Mescaline is listed as a Schedule III controlled substance under the CanadianControlled Drugs and Substances Act
The ''Controlled Drugs and Substances Act'' (french: Loi réglementant certaines drogues et autres substances) (the ''Act'') is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals ...
, but peyote is specifically exempt. Possession and use of peyote plants is legal.
United States
Non-drug uses of peyote in religious ceremonies by the Native American Church and its members is exempt from registration. This law has been codified as astatute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by le ...
in the American Indian Religious Freedom Act
The American Indian Religious Freedom Act, Public Law No. 95–341, 92 Stat. 469 (Aug. 11, 1978) (commonly abbreviated to AIRFA), codified at , is a United States federal law, enacted by joint resolution of the Congress in 1978. Prior to the ac ...
of 1978, and made part of the common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
in '' Peyote Way Church of God, Inc. v. Thornburgh'', (5th Cir. 1991); it is also in administrative law
Administrative law is the division of law that governs the activities of government agency, executive branch agencies of Forms of government, government. Administrative law concerns executive branch rule making (executive branch rules are gener ...
at the which states for "Special Exempt Persons":
Section 1307.31 Native American Church. The listing of peyote as a controlled substance in Schedule I does not apply to the nondrug use of peyote in bona fide religious ceremonies of the Native American Church, and members of the Native American Church so using peyote are exempt from registration. Any person who manufactures peyote for or distributes peyote to the Native American Church, however, is required to obtain registration annually and to comply with all other requirements of law.''U.S. v. Boyll'', 774 F.Supp. 1333 (D.N.M. 1991) addresses this racial issue specifically and concludes:
For the reasons set out in this Memorandum Opinion and Order, the Court holds that, pursuant to 21 C.F.R. § 1307.31 (1990), the classification of peyote as a Schedule I controlled substance, see 21 U.S.C. § 812(c), Schedule I(c)(12), does not apply to the importation, possession or use of peyote for 'bona fide' ceremonial use by members of the Native American Church, regardless of race.Following the passage of the
American Indian Religious Freedom Act
The American Indian Religious Freedom Act, Public Law No. 95–341, 92 Stat. 469 (Aug. 11, 1978) (commonly abbreviated to AIRFA), codified at , is a United States federal law, enacted by joint resolution of the Congress in 1978. Prior to the ac ...
Amendments of 1994, United States federal law
Federal law is the body of law created by the federal government of a country. A federal government is formed when a group of political units, such as states or provinces join in a federation, delegating their individual sovereignty and many po ...
(and many state law State law refers to the law of a federated state, as distinguished from the law of the federation of which it is a part. It is used when the constituent components of a federation are themselves called states. Federations made up of provinces, cant ...
s) protects the harvest
Harvesting is the process of gathering a ripe crop from the fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most labor-i ...
, possession
Possession may refer to:
Law
* Dependent territory, an area of land over which another country exercises sovereignty, but which does not have the full right of participation in that country's governance
* Drug possession, a crime
* Ownership
* ...
, consumption
Consumption may refer to:
*Resource consumption
*Tuberculosis, an infectious disease, historically
* Consumption (ecology), receipt of energy by consuming other organisms
* Consumption (economics), the purchasing of newly produced goods for curren ...
and cultivation of peyote as part of "bona fide
In human interactions, good faith ( la, bona fides) is a sincere intention to be fair, open, and honest, regardless of the outcome of the interaction. Some Latin phrases have lost their literal meaning over centuries, but that is not the case ...
religious ceremonies" (the federal statute is the American Indian Religious Freedom Act, codified at , "Traditional Indian religious use of the peyote sacrament", exempting only use by Native American persons. US v. Boyll expanded permitted use to all persons engaged in traditional Indian religious use, regardless of race. All US states with the exception of Idaho, Utah, and Texas allow usage by non-native, non-enrolled persons in the context of ceremonies of the Native American Church
The Native American Church (NAC), also known as Peyotism and Peyote Religion, is a Native American religion that teaches a combination of traditional Native American beliefs and Christianity, with sacramental use of the entheogen peyote. The re ...
. Some states such as Arizona additionally exempt any general bona fide religious activity or spiritual intent. US jurisdictions enacted these specific statutory exemptions in reaction to the US Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point of ...
's decision in ''Employment Division v. Smith
''Employment Division, Department of Human Resources of Oregon v. Smith'', 494 U.S. 872 (1990), is a United States Supreme Court case that held that the state could deny unemployment benefits to a person fired for violating a state prohibition on t ...
'', , which held that laws prohibiting the use of peyote that do not specifically exempt religious use nevertheless do not violate the Free Exercise Clause
The Free Exercise Clause accompanies the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the United States Constitution. The ''Establishment Clause'' and the ''Free Exercise Clause'' together read:
Free exercise is the liberty of persons to re ...
of the First Amendment
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
. Though use in Native American Church ceremonies or traditional Indian religious use, regardless of race, is legal under US federal law and additional uses are legal under some state laws, peyote is listed by the United States DEA as a Schedule I controlled substance.
The US military prohibits inductees from enlistment for prior drug usage, however past usage of peyote is permissable if found to be used in accordance with Native American cultural practices.https://web.archive.org/web/20040712040446im_/http://usmilitary.about.com/library/pdf/navrecruit.pdf
See also
*Ayahuasca
AyahuascaPronounced as in the UK and in the US. Also occasionally known in English as ''ayaguasca'' (Spanish-derived), ''aioasca'' (Brazilian Portuguese-derived), or as ''yagé'', pronounced or . Etymologically, all forms but ''yagé'' descen ...
* Carlos Castaneda
Carlos Castañeda (December 25, 1925 – April 27, 1998) was an American writer. Starting with '' The Teachings of Don Juan'' in 1968, Castaneda wrote a series of books that purport to describe training in shamanism that he received under the ...
– an author of books involving his experiences with peyote.
* Convention on Psychotropic Substances: Psychedelic plants and fungi
* N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
''N'',''N''-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT or ''N'',''N''-DMT, SPL026) is a substituted tryptamine that occurs in many plants and animals, including human beings, and which is both a derivative and a structural analog of tryptamine. It is used as a ...
* Psychedelic experience
A psychedelic experience (known colloquially as a trip) is a temporary altered state of consciousness induced by the consumption of a psychedelic substance (most commonly LSD, mescaline, psilocybin mushrooms, or DMT). For example, an acid tr ...
* Peyote song
Peyote songs are a form of Native American music, now most often performed as part of the Native American Church. They are typically accompanied by a rattle and water drum, and are used in a ceremonial aspect during the sacramental taking of pe ...
* Reuben Snake
Reuben Alvis Snake, Jr. (1937–1993) was an American Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) activist, educator, spiritual leader, and tribal leader. He served as a leader within the American Indian Movement (AIM) in the 1970s, and in the National Congress of Amer ...
* R. Gordon Wasson
References
Further reading
* Calabrese, Joseph D. "The Therapeutic Use of Peyote in the Native American Church" Chapter 3 in Vol. 1 of ''Psychedelic Medicine: New Evidence for Hallucinogens as Treatments'', Michael J. Winkelman and Thomas B. Roberts (editors) (2007). Westport, CT: Praeger/Greenwood. * Dawson, Alexander S. 2018. ''The Peyote Effect: From the Inquisition to the War on Drugs''. University of California Press, 2018. * Jay, Mike. 2019. ''Mescaline: A Global History of the First Psychedelic''. Yale University Press *Feeney, Kevin. "The Legal Basis for Religious Peyote Use." Chapter 13 in Vol 1 of ''Psychedelic Medicine: New Evidence for Hallucinogens as Treatments'', Michael J. Winkelman and Thomas B. Roberts (editors) (2007). Westport, CT: Praeger/Greenwood. * Baggot, Matthew JA Note on the Safety of Peyote when Used Religiously
Council on Spiritual Practices, 1996. * Labate, Beatriz; Cavnar, Clancy: ''Peyote: History, Tradition, Politics, and Conservation.'' Praeger, 2016. * Rätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants, Enthnopharmacology and Its Applications'' 1998/2005, Rochester, Vermont, Park Street Press, * Pollan, Michael 2021 This Is Your Mind on Plants © 2021 Penguin Books
External links
USDA: NRCS Plants Profile ''Lophophora williamsii''
{{Authority control Lophophora Entheogens Herbal and fungal hallucinogens Flora of the Chihuahuan Desert Flora of Texas Flora of New Mexico Flora of Northeastern Mexico Flora of the Rio Grande valleys Flora of Zacatecas Native American Church Native American religion Huichol Plants used in traditional Native American medicine Psychedelic phenethylamine carriers Religion and politics Cacti of the United States Cacti of Mexico Psychoactive cacti