Kilflynn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kilflynn () is a village and a civil parish in north County Kerry,
 Samuel Lewis wrote it 'Kilflyn' in 1840 and this spelling is extant in places. Locally, and in most documentation, it is spelt Kilflynn.
Samuel Lewis wrote it 'Kilflyn' in 1840 and this spelling is extant in places. Locally, and in most documentation, it is spelt Kilflynn.
 Immediately to the north and west the bedrock is
Immediately to the north and west the bedrock is

 Prior to this the Velabri around Kerry Head and further south the
Prior to this the Velabri around Kerry Head and further south the 
 Kilflynn had been known as Stackstown, and the name remains geographically in Stack's Mountains south-east of Kilflynn. The family landowners, namely James (owner of Garrynagore, Gortclohy and Cloghanaleskirt), John (owner of Aghacoora), Richard (owner of Killaspicktarvin (and more northerly townlands)) and Thomas Stack (owner of Gortaneare, Ballyconnell, Castletown, Crotta, Glanballyma, Knocknahila, Cloonnafinneela, and Cappagh) forfeited their landed possessions because of their support for the Irish Rebellion of 1641 and the subsequent
Kilflynn had been known as Stackstown, and the name remains geographically in Stack's Mountains south-east of Kilflynn. The family landowners, namely James (owner of Garrynagore, Gortclohy and Cloghanaleskirt), John (owner of Aghacoora), Richard (owner of Killaspicktarvin (and more northerly townlands)) and Thomas Stack (owner of Gortaneare, Ballyconnell, Castletown, Crotta, Glanballyma, Knocknahila, Cloonnafinneela, and Cappagh) forfeited their landed possessions because of their support for the Irish Rebellion of 1641 and the subsequent  From 1840 the Poor Law Union plans (as basic administrative division) of
From 1840 the Poor Law Union plans (as basic administrative division) of
 Kilflynn
Kilflynn
Crotta GAA
{{County Kerry Towns and villages in County Kerry
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Ãire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
. It is 11 km north-east of Tralee
Tralee ( ; ga, TrÃĄ LÃ, ; formerly , meaning 'strand of the Lee River') is the county town of County Kerry in the south-west of Ireland. The town is on the northern side of the neck of the Dingle Peninsula, and is the largest town in Count ...
just off the N69 road from Tralee
Tralee ( ; ga, TrÃĄ LÃ, ; formerly , meaning 'strand of the Lee River') is the county town of County Kerry in the south-west of Ireland. The town is on the northern side of the neck of the Dingle Peninsula, and is the largest town in Count ...
to Listowel
Listowel ( ; , IPA: lĘēÉŠsË ËtĖŠË uÉhÉlĘē is a heritage market town in County Kerry, Ireland. It is on the River Feale, from the county town, Tralee. The town of Listowel had a population of 4,820 according to the CSO Census 2016.
Desc ...
.
Etymology
The origin of the place name Cill Flainn is unknown. Two suggestions are commonly circulated. âCillâ inIrish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Ãire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
can mean 'cell' or 'churchyard' so in context might mean 'church of Flainn.' A popularised tale is that it was named after a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
hermit monk, Flainn, said to have lived by the River Shannow (which runs through Kilflynn). Crippled and blind, he was visited by the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ÜĄÜŠÜÜĄ, translit=Mariam; ar, Ų
ØąŲŲ
, translit=Maryam; grc, ÎÎąÏÎŊÎą, translit=MarÃa; la, Maria; cop, âēâēâēĢâēâē, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
, who offered to restore his ailing sight. Flainn declined, asking for the miraculous power to be transferred to others via a local well (now Tobar Flainn, well or spring of Flainn). Some refer to this person as âSt Flainn,â but no such person was canonised. There is possible confusion with St Flannan, originally from Killaloe in County Clare
County Clare ( ga, Contae an ChlÃĄir) is a county in Ireland, in the Southern Region and the province of Munster, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the local authority. The county had a population of 118,81 ...
.
The alternative suggestion is that the name derives from the 'OâFlannan tribe': in August 1931, in the Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy, a paper referencing a 15th-century manuscript (itself said to be a copy of a 12th-century document) listing rents in Clanmaurice presents both 'O Flannayn' and 'Kyllflanyn' as 'Kilflyn' in the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
translation from the original Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, a significant error which may be the root of the suggestion. The cantred
A cantred was a subdivision of a county in the Anglo-Norman Lordship of Ireland between the thirteenth and fifteenth centuries, analogous to the cantref of Wales or the hundred of England. In County Dublin the equivalent unit was termed a serjeant ...
(cf. Welsh cantref or English hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101.
In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to des ...
) or rural deanery
In the Roman Catholic Church and the Anglican Communion as well as some Lutheran denominations, a rural dean is a member of clergy who presides over a "rural deanery" (often referred to as a deanery); "ruridecanal" is the corresponding adjectiv ...
of Othorna & Oflannan (Irish UÃ Thorna & UÃ FlannÃĄin) was an Anglo-Norman Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
* Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
* Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 10 ...
sub-division, in this case generally along the historical boundaries of much older kingdoms and regions which were part of West Munster (Irish Iarmuman or Iar Mbumba), in the realm of the Ciarraighe, and which later became County Kerry some time between 1222 and 1229.
Different anglicised spellings appeared over the years. In William Petty
Sir William Petty FRS (26 May 1623 â 16 December 1687) was an English economist, physician, scientist and philosopher. He first became prominent serving Oliver Cromwell and the Commonwealth in Ireland. He developed efficient methods to s ...
's Down Survey
The Down Survey was a cadastral survey of Ireland, carried out by English scientist, William Petty, in 1655 and 1656.
The survey was apparently called the "Down Survey" by Petty, either because the results were set down in maps or because the s ...
of Ireland (1655-1656) the parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one o ...
appears as 'Kilfloinie Parish'. Charles Smith wrote it as 'Kilflin' in 1756, as did William Wilson 30 years later. In Taylor and Skinnerâs road maps of 1777 it is spelt 'Kilftyn', likely a transcription error. Samuel Lewis wrote it 'Kilflyn' in 1840 and this spelling is extant in places. Locally, and in most documentation, it is spelt Kilflynn.
Samuel Lewis wrote it 'Kilflyn' in 1840 and this spelling is extant in places. Locally, and in most documentation, it is spelt Kilflynn.
Geography
The village lies in the southern part of theListowel
Listowel ( ; , IPA: lĘēÉŠsË ËtĖŠË uÉhÉlĘē is a heritage market town in County Kerry, Ireland. It is on the River Feale, from the county town, Tralee. The town of Listowel had a population of 4,820 according to the CSO Census 2016.
Desc ...
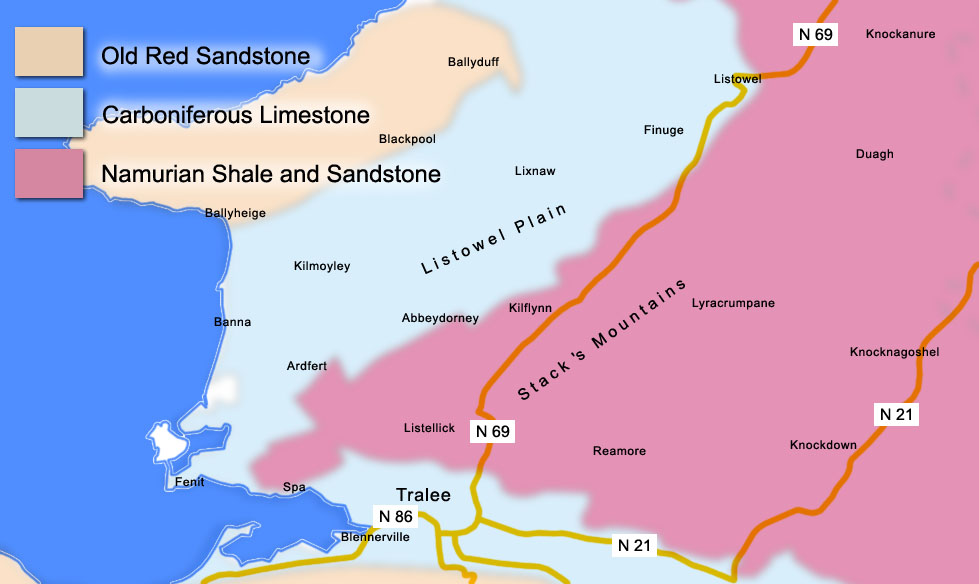
or Kerry plain. The rocks underlying the village area are typically Namurian
The Namurian is a stage in the regional stratigraphy of northwest Europe with an age between roughly 326 and 313 Ma (million years ago). It is a subdivision of the Carboniferous system or period and the regional Silesian series. The Namurian ...
sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
and shale which formed between 326 and 313 million years ago during the Carboniferous period and cover 27% of County Kerry. The centre of Kilflynn is actually on the edge of this area.
 Immediately to the north and west the bedrock is
Immediately to the north and west the bedrock is limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
(later to be sourced from nearby Lixnaw
Lixnaw () is a village in North County Kerry, Ireland. It is located near the River Brick SW of Listowel and NE of Tralee.
History
Lixnaw was once the seat of the Fitzmaurice family, the Earls of Kerry. In 1320 Nicolas, the third baron o ...
and Abbeydorney for use in lime kiln
A lime kiln is a kiln used for the calcination of limestone ( calcium carbonate) to produce the form of lime called quicklime (calcium oxide). The chemical equation for this reaction is
: CaCO3 + heat â CaO + CO2
This reaction can take p ...
s). These rocks, as part of the Western Irish Namurian Basin (or Clare Basin) were formed in a sub-equatorial tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
environment, due to the deposition of fine particles in a delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Î or Îī), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D ( NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also ...
, likely from a river flow to the south-west on a continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas t ...
al mass formed from what are now North America, Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. This area is thus part of the Iapetus Suture
The Iapetus Suture is one of several major Fault (geology), geological faults caused by the collision of several ancient land masses forming a suture (geology), suture. It represents in part the remains of what was once the Iapetus Ocean. Iapet ...
, that is a region where the ancient Iapetus Ocean closed up. The Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
had yet to form.
The area was subject to glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate be ...
during the ice ages
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
. The glacial meltwater evidence coincides with an area to the south and east of Kilflynn and the N26 road, broadly in line with the edge of the hills facing the north-west. The ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at La ...
that covered Ireland split about 19,000 years ago, along a corridor that included the area where Kilflynn lies and going down past Banna Strand (the sea level was lower then) towards the Atlantic. The main ice sheet retreated northwards, separated from the Kerry-Cork ice cap to the south which disappeared approximately 1000 years later.
Kilflynn centre is currently 59m above sea-level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised ...
, but the village elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Ver ...
is between 45 and 70m. Its latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the northâ south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from â90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the eastâ west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
are 52.3505 and -9.6253 respectively (52° 21' 2'' N, 9° 37' 31'' W). As with most of the West of Ireland, the weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmos ...
of the area is strongly affected by the North Atlantic drift
The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.
The NAC originates from where ...
and the prevailing south-westerly winds. Being 10 km inland and well beyond the hills to the south-west, Kilflynn is somewhat sheltered from extremes of wind speed and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
experienced largely in the south and west of County Kerry. The average monthly rainfall (full years from 1981 to 2020) is 98mm, with an average of 20 days per month registering rain (>0.1mm) and 15 wet days per month (>1.0mm), with the wettest months usually between October and January. The average daily maximum temperature is 14 °C and the average daily minimum temperature is 7 °C. Summer and winter temperatures (between 2009 and 2021) are 16 °C and 6 °C respectively. For agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
and horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
, the last spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season)
Spring, also known as springtime, is one of the four temperate seasons, succeeding winter and preceding summer. There are various technical definitions of spring, but local usage of ...
air frost is typically in late March or April, that is to say about five to six weeks later than coastal
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in ...
areas (on exposed land). This is still favourable compared to areas further inland. The agricultural land surrounding the village is regarded as good and mostly unspoilt.
Surface spring water
A spring is a point of exit at which groundwater from an aquifer flows out on top of Earth's crust ( pedosphere) and becomes surface water. It is a component of the hydrosphere. Springs have long been important for humans as a source of fresh ...
was used until the late 1970s for drinking in some surrounding areas. The regional bedrock aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
for the purposes of drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
are regarded as locally important and moderately productive, used where there was no water main
A water distribution system is a part of water supply network with components that carry potable water from a centralized treatment plant or wells to consumers to satisfy residential, commercial, industrial and fire fighting requirements.
Definit ...
connection. In the limestone areas to the north, the aquifers are regionally important. The River Shannow, which runs through Kilflynn, emanates from the hills south-west of the N69 from Tooreen to Stacks Mountain townlands
A townland ( ga, baile fearainn; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a small geographical division of land, historically and currently used in Ireland and in the Western Isles in Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of Gaelic origi ...
and is a tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drai ...
of the River Brick, which in turn joins the River Feale
Beach seine fishing for salmon in River Feale near by town Ballybunion, year 1975.
The River Feale (''An FhÃĐil'' or ''Abhainn na FÃĐile'' in Irish) rises near Rockchapel in the Mullaghareirk Mountains of County Cork in the southwest of Irel ...
, entering the Atlantic south of Ballybunion
Ballybunion or Ballybunnion () is a coastal town and seaside resort in County Kerry, Ireland, on the Wild Atlantic Way, from the town of Listowel.
Tourism
Ballybunion has two main beaches, divided by the Castle Green. The Ladies Beach is to ...
. Up until the 1980s, there were eels
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage ...
and fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
such as brown trout to be found in the river up at least as far as the Waterfall (where the N69 crosses), with birdlife such as various types of finch
The true finches are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Fringillidae. Finches have stout conical bills adapted for eating seeds and nuts and often have colourful plumage. They occupy a great range of habitats where they are usua ...
, dippers
Dippers are members of the genus ''Cinclus'' in the bird family Cinclidae, so-called because of their bobbing or dipping movements. They are unique among passerines for their ability to dive and swim underwater.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Cinclus'' ...
and what are locally called 'cranes' (grey heron
The grey heron (''Ardea cinerea'') is a long-legged wading bird of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more norther ...
s, which were caught and eaten historically). Since then, the river life has been affected by pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
.
Kerry County Council
Kerry County Council ( ga, Comhairle Contae ChiarraÃ) is the authority responsible for local government in County Kerry, Ireland. As a county council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. The council is responsible for housing and ...
, which expects a modest increase in population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
, has made plans for updated local water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
, improvements for pedestrians
A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In modern times, the term usually refers to someone walking on a road or pavement, but this was not the case historically.
The meaning of pedestrian is displayed with ...
and cyclists
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of Bicycle, cycles for transport, recreation, Physical exercise, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", ...
, and supporting repopulation with associated services, also commenting on Kilflynn as a choice for commuters
Commuting is periodically recurring travel between one's place of residence and place of work or study, where the traveler, referred to as a commuter, leaves the boundary of their home community. By extension, it can sometimes be any regu ...
nto Tralee and Listowelwhile impressing the need to retain its peaceful character.
History until 1900
The first known human presence in Ireland after the last ice age has been determined as c.10,500 years B.C. When the originalCelts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
of Ireland actually arrived is unknown, with suggestions having been made of between 100 and 5000 years B.C. from linguistic
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
and other evidence. The late Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Beaker folk introduced their cultural advances possibly from the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, dÃĐi Niddereg LÃĪnnereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
or from Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: PÃĐninsule IbÃĐrique
* mwl, PenÃnsula EibÃĐrica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
; this resulted in key changes and Irish becoming a unique Celtic language
The Celtic languages (usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
. Recent evidence shows a huge number of Irish men have the R1b DNA marker A genetic marker is a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. It can be described as a variation (which may arise due to mutation or alteration in the genomic loci) that can be ...
with similarly high percentages also found in other modern 'celtic' areas on the European Atlantic coast, including the Basque region. The first known farmers in Ireland or Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
landed in Kerry c.4350 B.C. but the incidence of their DNA markers is now very scarce, the R1b marker replacing it c.2500 B.C. This coincides well with the arrival of a dominant Beaker culture, including the introduction of copper mining
Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper consists of a series of physical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, loca ...
and metallurgy in Kerry.
In 2011, archaeologists working on the site of the realignment of the N69 Tralee-Listowel road found evidence for early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
and mediaeval activity in the townlands of Gortclohy and Cloonnafinneela. The Gortclohy dig provided evidence for tool usage from the Beaker period; alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few sp ...
charcoal from the site was carbon-dated
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
to between 2132 and 1920 B.C. This is the most northerly evidence for the Beaker folk in Co.Kerry. The first Cloonnafinneela dig provided evidence of early mediaeval iron-working
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
, with oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
and alder charcoal carbon-dated to between 432 and 595 A.D. and further evidence of pit-kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay int ...
charcoal production 200-300 years later. A second dig at Cloonafinneela gave up evidence of various plants as burnt roofing thatch including rushes, cereals
A cereal is any grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more food ...
, hazel, oak and willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
charcoal, the hazel dated to between 1450 and 1635 A.D.
Kilflynn is in the middle of the area settled in the first century by the Ciarraighe (also Ciarraigh or Ciarraidh], the mediaeval tribe (from which the county name Kerry is derived) and claimed descendants of Ciar the son of the mythological queen Medb of Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms ( Uà Fiachrach, Uà BriÚin, Uà Maine, ConmhaÃcne, and Del ...
and one of her lovers, king Fergus mac RÃģich
Fergus mac RÃģich (literally " manliness, son of great stallion") is a character in the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology. Formerly the king of Ulster, he is tricked out of the kingship and betrayed by Conchobar mac Nessa, becomes the ally and lo ...
of Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''CÚige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, UlstÃĻr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kin ...
.

 Prior to this the Velabri around Kerry Head and further south the
Prior to this the Velabri around Kerry Head and further south the Iverni
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this se ...
people (or Iernoi from the earlier Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
) were noted by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Î ÏÎŋÎŧÎĩΞιáŋÎŋÏ, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
to be concentrated in the south-west area of Ireland, speaking the most primitive Goidelic language
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages ( ga, teangacha Gaelacha; gd, cà nanan Goidhealach; gv, çhengaghyn Gaelgagh) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historically ...
similar to Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switze ...
(as recorded on Ogham
Ogham ( Modern Irish: ; mga, ogum, ogom, later mga, ogam, label=none ) is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the early Irish language (in the "orthodox" inscriptions, 4th to 6th centuries AD), and later the Old Irish langu ...
stones, with examples found close by in Knockbrack and Tralee
Tralee ( ; ga, TrÃĄ LÃ, ; formerly , meaning 'strand of the Lee River') is the county town of County Kerry in the south-west of Ireland. The town is on the northern side of the neck of the Dingle Peninsula, and is the largest town in Count ...
, from the 6th Century). The Ãrainn
The Iverni (, ') were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century ''Geography'' as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis (, ') in their territory, and observes that this se ...
, in Irish tradition, may be the name for the same group of people as there are linguistic links.
Kilflynn was a historical civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authorit ...
in the barony of Clanmaurice
{{Use Irish English, date=May 2021
Clanmaurice (''Clann Mhuiris'') is a barony in County Kerry, Ireland. It contains 16 Parishes and it is roughly 485 km2.
Parishes
*Ardfert
* Ballyheigue
* Duagh
*Dysert (Partly in Trughanacmy)
*Finuge
*Kilcar ...
. This barony developed from the area which had been in the control of native leaders (especially O'Conors) but was taken over by the Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
, Maurice, son of Thomas FitzGerald of Shanid who died in 1213. Thomas FitzGerald himself was son of Maurice FitzGerald, Lord of Llanstephan, who had supported 'Strongbow', Lord Pembroke, in his Cambro-Norman invasion of Ireland in 1169 and who began the Geraldine dynasty in Ireland and their House of Desmond
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
. Later earls
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form '' jarl'', and meant "chieftain", particula ...
of all County Kerry were scions of the FitzMaurice
Fitzmaurice is a Hiberno-Norman, Cambro-Norman, Anglo-Norman surname. It is patronymic as the prefix '' Fitz-'' derives from the Latin'' filius'', meaning "son of".
According to Irish genealogist Edward MacLysaght:
Fitzmaurice is uncommon ...
barons.
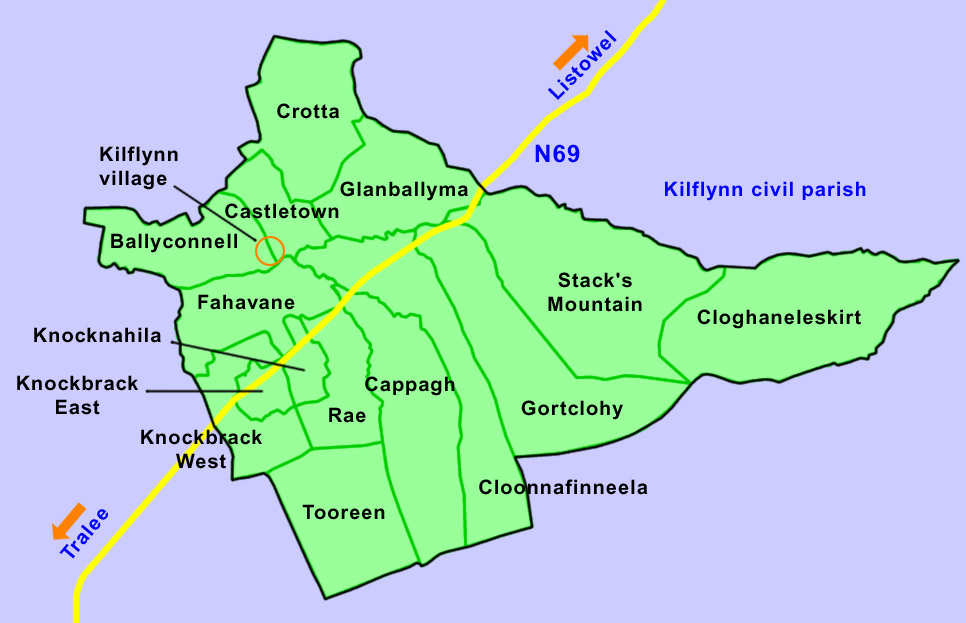
Kilflynn has sixteen constituent townlands: Ballyconnell, Cappagh, Castletown, Cloghaneleskirt, Cloonnafinneela, Crotta
Crotta, ( ga, An Chrotach) is a townland in the Barony of Ormond Lower in County Tipperary, Ireland. It is located between the towns of Borrisokane and Cloughjordan.
The woods at Crotta form a part of Borrisokane Forest which consists of several ...
, Fahavane, Glanballyma, Gortclohy, Kilflynn (village), Knockbrack East, Knockbrack West, Knocknahila, Rea
REA or Rea may refer to:
Places
* Rea, Lombardy, in Italy
* Rea, Missouri, United States
* River Rea, a river in Birmingham, England
* River Rea, Shropshire, a river in Shropshire, England
* Rea, Hungarian name of Reea village in ToteČti Commun ...
, Stackâs Mountain and Tooreen.
The Stack family, also of Norman heritage, had their seat at Crotto (later known as Crotta) just north of Kilflynn and also owned surrounding townlands.

 Kilflynn had been known as Stackstown, and the name remains geographically in Stack's Mountains south-east of Kilflynn. The family landowners, namely James (owner of Garrynagore, Gortclohy and Cloghanaleskirt), John (owner of Aghacoora), Richard (owner of Killaspicktarvin (and more northerly townlands)) and Thomas Stack (owner of Gortaneare, Ballyconnell, Castletown, Crotta, Glanballyma, Knocknahila, Cloonnafinneela, and Cappagh) forfeited their landed possessions because of their support for the Irish Rebellion of 1641 and the subsequent
Kilflynn had been known as Stackstown, and the name remains geographically in Stack's Mountains south-east of Kilflynn. The family landowners, namely James (owner of Garrynagore, Gortclohy and Cloghanaleskirt), John (owner of Aghacoora), Richard (owner of Killaspicktarvin (and more northerly townlands)) and Thomas Stack (owner of Gortaneare, Ballyconnell, Castletown, Crotta, Glanballyma, Knocknahila, Cloonnafinneela, and Cappagh) forfeited their landed possessions because of their support for the Irish Rebellion of 1641 and the subsequent Catholic Confederation
Confederate Ireland, also referred to as the Irish Catholic Confederation, was a period of Irish Catholic self-government between 1642 and 1649, during the Eleven Years' War. Formed by Catholic aristocrats, landed gentry, clergy and military ...
. The reconquest of Ireland between 1649 and 1652 by Cromwellian
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in History of England, English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 ...
forces after the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642â1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
resulted in the Act for the Settlement of Ireland of 1652 which required a survey for the redistribution of land (hence Sir William Petty
Sir William Petty FRS (26 May 1623 â 16 December 1687) was an English economist, physician, scientist and philosopher. He first became prominent serving Oliver Cromwell and the Commonwealth in Ireland. He developed efficient methods to s ...
's survey) often to invading soldiers in lieu of wages. Henry Ponsonby, the younger brother of Sir John Ponsonby (a colonel of horse in the New Model Army), was the recipient of most of the Stacks' (and others') confiscated land - much of which was profitable. This was reconfirmed in 1666, after the Acts of Settlement. Part of the Down's Survey was Pender's Census, taken between 1654 and 1659. The census refers to 'The Barony of Clanmorice', the townland of 'Crottoe' and the 'Tituladoe' as Henry Ponsonby Esq. The population for the whole of Clanmaurice is given as 1126, of whom 86 are English and 1040 Irish. There are 17 with the surname 'Stack' and 17 with 'FitzMorrice and MacMorrice'.
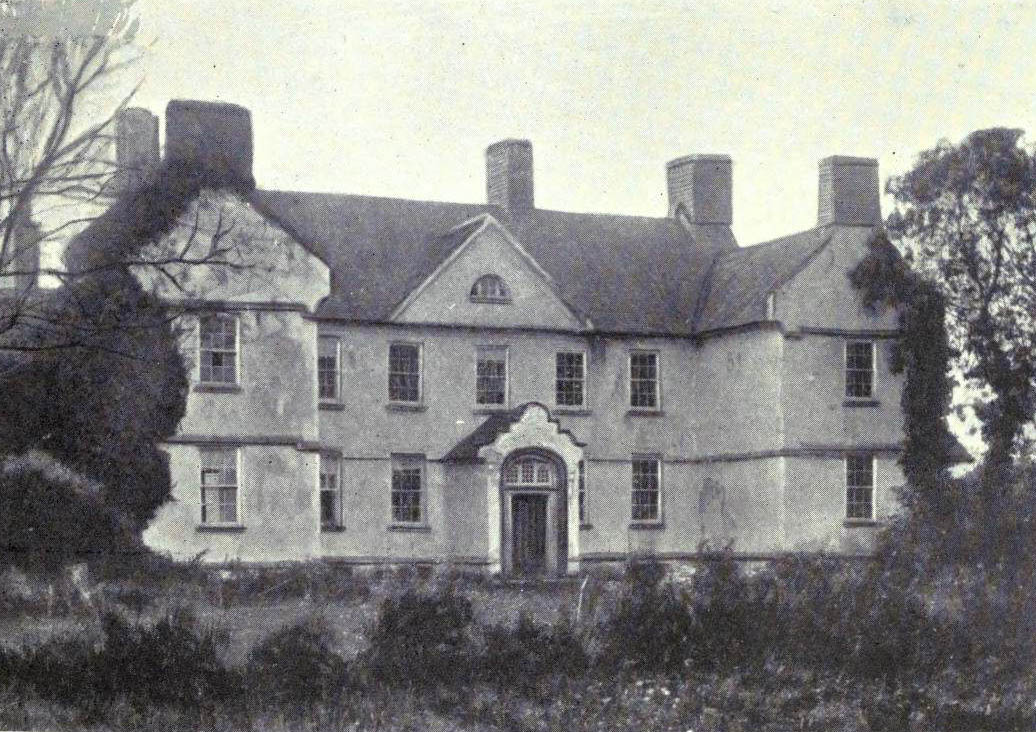
Ponsonby built Crotta House in 1669. The house was sold in 1842 by Thomas Carrique Ponsonby (later resident in Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
, so this possibly marked the end of the Ponsonbys in Kerry) and was being leased by about 1850 by Lieutenant Colonel Henry Horatio Kitchener, father to Horatio Herbert Kitchener
Horatio Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener, (; 24 June 1850 â 5 June 1916) was a senior British Army officer and colonial administrator. Kitchener came to prominence for his imperial campaigns, his scorched earth policy against the Boers, h ...
, the first Earl Kitchener, Earl of Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, اŲØŪØąØ·ŲŲ
, Al-KhuráđÅŦm, din, KaartuÉĖm) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
, Field Marshal of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
and Minister for War for Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
, who spent most of his youth at Crotta. The mostly derelict remains of the house itself collapsed or were demolished in the 20th century.
 From 1840 the Poor Law Union plans (as basic administrative division) of
From 1840 the Poor Law Union plans (as basic administrative division) of Listowel
Listowel ( ; , IPA: lĘēÉŠsË ËtĖŠË uÉhÉlĘē is a heritage market town in County Kerry, Ireland. It is on the River Feale, from the county town, Tralee. The town of Listowel had a population of 4,820 according to the CSO Census 2016.
Desc ...
replaced the Norman Clanmaurice barony and civil parish boundaries (although the latter continued to be used to make comparisons) after the act of 1838.
Kilflynn was on the main road from Tralee
Tralee ( ; ga, TrÃĄ LÃ, ; formerly , meaning 'strand of the Lee River') is the county town of County Kerry in the south-west of Ireland. The town is on the northern side of the neck of the Dingle Peninsula, and is the largest town in Count ...
to County Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
. Farming was the principal industry for centuries and services such as forges for smithing
A metalsmith or simply smith is a craftsperson fashioning useful items (for example, tools, kitchenware, tableware, jewelry, armor and weapons) out of various metals. Smithing is one of the oldest metalworking occupations. Shaping metal with a h ...
, and lime kilns
A lime kiln is a kiln used for the calcination of limestone ( calcium carbonate) to produce the form of lime called quicklime (calcium oxide). The chemical equation for this reaction is
: CaCO3 + heat â CaO + CO2
This reaction can take pl ...
from the late 1600s (to make lime for acidic soils) developed around this. Local forges were still operational in the mid-20th century. The remains of some kilns can still be found dotted about the landscape. There was a population decline, possibly partly associated with the opening of what is now the main Tralee-Listowel road to the south in 1846, and then the North Kerry railway line with stations opening at Abbeydorney and Lixnaw in 1880 (the line ceasing services entirely from 1978). However, there was also from the 1840s onwards the significant effect of the peak years of the Great Famine in which between 20% and 30% of the population of Kerry died or emigrated (see map). In 1841, 1851 and 1861 the population of Kilflynn village was 147, 134 and 119 respectively (in 2011 it was 126). The area covers two election districts
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger State (polity), state (a country, administrative region, ...
(Kilflynn and Kilfeighny) so these figures may not be entirely representative.
History from 1900
Kilflynn people joined theIrish Volunteers
The Irish Volunteers ( ga, Ãglaigh na hÃireann), sometimes called the Irish Volunteer Force or Irish Volunteer Army, was a military organisation established in 1913 by Irish nationalists and republicans. It was ostensibly formed in respon ...
, were involved in the War of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List o ...
and the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
.
The Kilflynn company of the Irish Volunteers was formed in 1913 of about 100 men, drilled by two ex-British soldiers and reservist
A reservist is a person who is a member of a military reserve force. They are otherwise civilians, and in peacetime have careers outside the military. Reservists usually go for training on an annual basis to refresh their skills. This person is ...
s named Collins and Sheehy. On 13 June 1914 a separate corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies great ...
formed in Lixnaw, supported on the day by the Kilflynn and other Volunteers. Later in 1914, the reservists were called up to fight in what became World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and in addition John Redmond
John Edward Redmond (1 September 1856 â 6 March 1918) was an Irish nationalist politician, barrister, and MP in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. He was best known as leader of the moderate Irish Parliamentary Party (IPP) from ...
encouraged the Irish to join the Allied forces, so the company disbanded as a result and didn't reform until 1917 at Lixnaw. Engagements with the Royal Irish Constabulary
The Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC, ga, ConstÃĄblacht RÃoga na hÃireann; simply called the Irish Constabulary 1836â67) was the police force in Ireland from 1822 until 1922, when all of the country was part of the United Kingdom. A separate ...
(R.I.C) and the " Tans" ("Black and Tans
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have ...
", officially the R.I.C. Reserve Force) became vehement from 1919 after Churchill's call to British war veterans
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in a particular occupation or field. A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in a military.
A military veteran that h ...
to assist in Ireland. In March 1921 British forces created a cordon starting from Kilflynn to the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
coast in an attempt to trap and round up IRA
Ira or IRA may refer to:
*Ira (name), a Hebrew, Sanskrit, Russian or Finnish language personal name
*Ira (surname), a rare Estonian and some other language family name
*Iran, UNDP code IRA
Law
*Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, US, on status of ...
members: hundreds of men were imprisoned in Ballyheigue
Ballyheigue ( ), officially Ballyheige ( - meaning ''Settlement of Tadhg'') is a coastal village in County Kerry, Ireland. It is approximately north of Tralee on the R551. It is a scenic locale which forms part of the Wild Atlantic Way and h ...
Castle, including just one IRA man.
After two previous failures, the IRA succeeded in blowing up the bridge over the Shannow where the road to Kilflynn joins the Abbeydorney-Lixnaw road (R557). Units from Kilflynn and Abbeydorney lay in wait for Crown forces
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different ...
and opened fire. There were injuries on both sides and a British officer was killed attempting to cross the river.
 Kilflynn
Kilflynn IRA
Ira or IRA may refer to:
*Ira (name), a Hebrew, Sanskrit, Russian or Finnish language personal name
*Ira (surname), a rare Estonian and some other language family name
*Iran, UNDP code IRA
Law
*Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, US, on status of ...
members in the Civil War (âIrregulars
Irregular military is any non-standard military component that is distinct from a country's national armed forces. Being defined by exclusion, there is significant variance in what comes under the term. It can refer to the type of military orga ...
â) included John McElligott, Danny OâShea, George OâShea, Stephen Fuller and Tim Twomey. The latter three were blown up by Free State soldiers using a landmine
A land mine is an explosive weapon, explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically d ...
at Ballyseedy Cross, near Tralee
Tralee ( ; ga, TrÃĄ LÃ, ; formerly , meaning 'strand of the Lee River') is the county town of County Kerry in the south-west of Ireland. The town is on the northern side of the neck of the Dingle Peninsula, and is the largest town in Count ...
, along with six other Irregulars. Fuller, the only survivor of the explosion, was blown clear and escaped the subsequent coup-de-grÃĒce shooting and bombing. A fabricated explanation of the event, blaming Irregulars for the mine, was given official approval. An investigation by Free State Lieutenant Niall Harrington referred to the report as "totally untrue." The killings came to represent a defining event in modern Irish history.
Fuller later became a Fianna FÃĄil
Fianna FÃĄil (, ; meaning 'Soldiers of Destiny' or 'Warriors of FÃĄl'), officially Fianna FÃĄil â The Republican Party ( ga, audio=ga-Fianna FÃĄil.ogg, Fianna FÃĄil â An PÃĄirtà PoblachtÃĄnach), is a conservative and Christia ...
TD for North Kerry.
Modern-Day Village
In recent decades, especially in the surrounding farmland, migration of youth for better financial prospects has kept a smaller, ageing population present, as is typically reflected elsewhere in rural villages of Ireland. However, a number of new houses have been built and the local school, Scoil Treasa Naofa (St.Teresa's National School) (first sited at Castletown in 1821, just north of the village), has had increased admissions. Kilflynn has two pubs, a fast food restaurant and a beauty parlour. The Catholic Church is St.Maryâs and there is also the 18th century KilflynnChurch of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÃireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the secon ...
which is used as St.Columbaâs Heritage Centre and Museum; these buildings are Recorded Protected Structures. The latter contains the life story of the major local historical figure of note, Horatio Herbert Kitchener
Horatio Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener, (; 24 June 1850 â 5 June 1916) was a senior British Army officer and colonial administrator. Kitchener came to prominence for his imperial campaigns, his scorched earth policy against the Boers, h ...
, Earl of Khartoum, the former British Field Marshal and Secretary of State for War, who was born in Ballylongford and spent most of his youth at nearby Crotta House. A few outbuildings are all that remain of the original estate.
Kilflynn and Abbeydorney are the two villages in which church services are held in the modern Roman Catholic parish of Abbeydorney, whose priest is the Very Reverend Denis OâMahony. The parish is in the deanery of St.Brendan's and is one of 53 in the diocese of Kerry, whose bishop is The Most Reverend Raymond Anthony Browne.
The local parliamentary constituency
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other poli ...
(since 2016) is Kerry
Kerry or Kerri may refer to:
* Kerry (name), a given name and surname of Gaelic origin (including a list of people with the name)
Places
* Kerry, Queensland, Australia
* County Kerry, Ireland
** Kerry Airport, an international airport in Count ...
, returning five Teachtaà DÃĄla (TDs) to the DÃĄil Ãireann. The current TDs are Norma Foley (Fianna FÃĄil
Fianna FÃĄil (, ; meaning 'Soldiers of Destiny' or 'Warriors of FÃĄl'), officially Fianna FÃĄil â The Republican Party ( ga, audio=ga-Fianna FÃĄil.ogg, Fianna FÃĄil â An PÃĄirtà PoblachtÃĄnach), is a conservative and Christia ...
), Pa Daly (Sinn FÃĐin
Sinn FÃĐin ( , ; en, " eOurselves") is an Irish republican and democratic socialist political party active throughout both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.
The original Sinn FÃĐin organisation was founded in 1905 by Arthur G ...
), Brendan Griffin (Fine Gael
Fine Gael (, ; English: "Family (or Tribe) of the Irish") is a liberal-conservative and Christian-democratic political party in Ireland. Fine Gael is currently the third-largest party in the Republic of Ireland in terms of members of DÃĄil à ...
), Danny Healy-Rae (Independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
) and Michael Healy-Rae (Independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
).
See also
* List of towns and villages in IrelandReferences
External links
Crotta GAA
{{County Kerry Towns and villages in County Kerry