Intestinal pseudoobstruction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction (IPO) is a clinical syndrome caused by severe impairment in the ability of the
 The symptoms of IPO are nonspecific. It is not unusual for patients to present repeatedly and to undergo numerous tests. Mechanical causes of intestinal obstruction must be excluded to reach a diagnosis of pseudo-obstruction. Attempts must also be made to determine whether the IPO is the result of a primary or secondary condition. A diagnostic work-up may include:
* Gastric motility studies
* Imaging studies:
**
The symptoms of IPO are nonspecific. It is not unusual for patients to present repeatedly and to undergo numerous tests. Mechanical causes of intestinal obstruction must be excluded to reach a diagnosis of pseudo-obstruction. Attempts must also be made to determine whether the IPO is the result of a primary or secondary condition. A diagnostic work-up may include:
* Gastric motility studies
* Imaging studies:
** 
Gastrointestinal Disorders
has not been studied with regards to CIPO. Any claims to its efficacy for use in CIPO are speculative.
intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
s to push food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
through. It is characterized by the signs and symptoms of intestinal obstruction without any lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
in the intestinal lumen. Clinical features mimic those seen with mechanical intestinal obstructions and can include abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
, abdominal distension, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, foo ...
, dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a disease#Terminology, condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passag ...
and constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel movement ...
depending upon the part of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
involved.
It is a difficult condition to diagnose, requiring exclusion of any other mechanical cause of obstruction. Many patients are diagnosed late in the course of disease after additional symptoms are seen. Mortality is also difficult to accurately determine. One retrospective study estimated mortality to be between 10 and 25% for chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) and to vary greatly depending on the etiology of the condition. When present for less than six months, it is diagnosed as acute IPO or Ogilvie syndrome
Ogilvie syndrome is the acute dilatation of the colon in the absence of any mechanical obstruction in severely ill patients.
Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction is characterized by massive dilatation of the cecum (diameter > 10 cm) and right c ...
. Longer than this is considered chronic. Owing to the difficulty of diagnosis, few studies are available which have attempted to estimate its prevalence.
The condition can begin at any age. Most studies describing CIPO are in pediatric populations. It can be a primary condition ( idiopathic or inherited) or caused by another disease (secondary). It can be a result of myriad of etiologies including infectious, parasitic, autoimmune, genetic, congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
, neurologic
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
, toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
, endocrinological, or anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
.
Treatment targets nutritional support, improving intestinal motility, and minimizing surgical intervention. Bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine can occur in chronic cases – presenting as malabsorption, diarrhea, and nutrient deficiencies – which may require the use of antibiotics.
Presentation
Clinical features of IPO can include abdominal pain, nausea, abdominal distension, vomiting, dysphagia, and constipation. Symptoms depend on the portion of the gastrointestinal tract involved and the duration of symptoms. Symptoms may occur intermittently and over a prolonged period of time. It is not unusual for patients to present several times owing to the nonspecific nature of the symptoms. Conditions and onset will vary if the disease is primary vs secondary and the underlying disease (if a secondary manifestation) and its management. Symptoms indicative of advanced disease and possibleintestinal failure
Short bowel syndrome (SBS, or simply short gut) is a rare malabsorption disorder caused by a lack of functional small intestine. The primary symptom is diarrhea, which can result in dehydration, malnutrition, and weight loss. Other symptoms may in ...
include diarrhea, loss of appetite, sepsis, bloating, fatigue, signs of low volume status, and malabsorption including nutritional deficiencies and foul-smelling stools.
Causes
In primary CIPO (the majority of chronic cases) the condition results from disruption of the intestine's ability to move food. These can be broadly classified asmyopathic
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. This results in muscular weakness. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease (Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meani ...
(affecting the smooth muscle), mesenchymopathic (affecting the interstitial cells of Cajal), or neuropathic (of the nervous system) of the gastrointestinal tract.
In some cases there appears to be a genetic association. One form has been associated with DXYS154.
Secondary chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction can occur as a consequence of a number of other conditions including:
* Hirschsprung's disease
Hirschsprung's disease (HD or HSCR) is a birth defect in which nerves are missing from parts of the intestine. The most prominent symptom is constipation. Other symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and slow growth. Symptoms usu ...
– the absence of colonic nerve cells
* Chagas' disease
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. It is spread mostly by insects in the subfamily ''Triatominae'', known as "kissing bugs". The symptoms change over the cou ...
– a chronic parasitic infection of the colon leading to loss of nerve endings
* Kawasaki disease - a rare presentation for this particular autoimmune disorder of the vasculature
* Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
- related to the neurodegeneration of gastrointestinal tract
* Autoimmune conditions - conditions including systemic lupus erythematosus and scleroderma lead to collagen vascular deposition and gastrointestinal motility disruption
* Mitochondrial disease - IPO is a known presentation for mitochondrial disease
* Endocrine disorder
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Types of disease
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups:
# Endocrin ...
s
* Certain medications.
The term may be used synonymously with enteric neuropathy
Enteric neuropathy is a degenerative neuromuscular condition of the digestive system. In simple terms the gut stops functioning, due to degradation of the nerves and muscles. The condition affects all parts of the digestive tract. There is no kno ...
if a neurological cause is suspected.
Diagnosis
 The symptoms of IPO are nonspecific. It is not unusual for patients to present repeatedly and to undergo numerous tests. Mechanical causes of intestinal obstruction must be excluded to reach a diagnosis of pseudo-obstruction. Attempts must also be made to determine whether the IPO is the result of a primary or secondary condition. A diagnostic work-up may include:
* Gastric motility studies
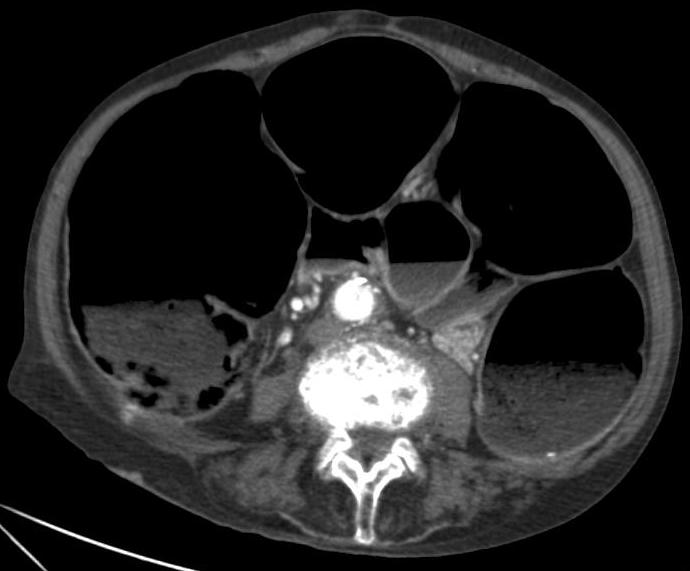
* Imaging studies:
**
The symptoms of IPO are nonspecific. It is not unusual for patients to present repeatedly and to undergo numerous tests. Mechanical causes of intestinal obstruction must be excluded to reach a diagnosis of pseudo-obstruction. Attempts must also be made to determine whether the IPO is the result of a primary or secondary condition. A diagnostic work-up may include:
* Gastric motility studies
* Imaging studies:
** 
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s – may show intestinal air fluid levels (seen with true mechanical intestinal obstruction)
** CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
s
** Barium enema
* Blood tests
* Upper and lower endoscopies
* Manometry – used to measure pressure of esophagus and stomach
Treatment
Treatment for IPO (acute or chronic) is aimed at removing the disease process and/or managing the complications present. Focus is placed on management of pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, nutritional deficiencies, fluid status, infection control, and improving quality of life. When CIPO is secondary to another disease, treatment is addressed towards the underlying condition. Surgery is sometimes required in severe cases of CIPO.Medical treatment
Prucalopride, pyridostigmine, metoclopramide, cisapride,erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used duri ...
and octreotide
Octreotide, sold under the brand name Sandostatin among others, is an octapeptide that mimics natural somatostatin pharmacologically, though it is a more potent inhibitor of growth hormone, glucagon, and insulin than the natural hormone. It was ...
are medications that aim to enhance intestinal motility.
Intestinal stasis, which may lead to bacterial overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), also termed bacterial overgrowth, or small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SBBOS), is a disorder of excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine. Unlike the colon (or large bowel), which is r ...
and subsequently, diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
or malabsorption, is treated with antibiotics.
Nutritional deficiencies are treated by encouraging patients to avoid foods that increase distention and are difficult to digest (e.g. those high in fat and fibre), consuming small frequent meals (5–6 per day), focusing on liquids and soft food. Reducing intake of poorly absorbed sugar alcohols may be of benefit. Referral to an accredited dietitian is recommended. If dietary changes are unsuccessful in meeting nutritional requirements and energy needs, enteral nutrition
Enteral administration is food or drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration (Greek ''para'', "besides" + ''enteros''), which occurs from routes outside the GI tract, ...
is used. Many patients eventually require parenteral nutrition.
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) is a form of long-term nutritional treatment reserved for patients that have severe pseudo-obstruction. TPN dependent patients require frequent checkups to monitor catheter function, check liver enzyme levels, and evaluate for signs of blood infections. TPN format is typically changed depending on loss/gain of weight and bloodwork results, and is specially formulated to meet each individual patient's needs.
Procedures
Intestinal decompression by tube placement in a small stoma can also be used to reduce distension and pressure within the gut. The stoma may be agastrostomy
Gastrostomy is the creation of an artificial external opening into the stomach for nutritional support or gastric decompression.
Typically this would include an incision in the patient's epigastrium as part of a formal operation. It can be perfor ...
, jejunostomy, ileostomy or cecostomy. These may be used for feed (e.g. gastrostomy and jejunostomy) or to flush the intestines.
Colostomy or ileostomy can bypass affected parts if they are distal to (come after) the stoma. For instance, if only the colon is affected, an ileostomy may be helpful. Either of these ostomies are typically placed at or a few centimeters below the patient's navel per doctor recommendation based on the affected area of the intestines as well as concerns for patient comfort and future physical growth for children.
The total removal of the colon, called a colectomy or resection of affected parts of the colon may be needed if part of the gut dies (for instance toxic megacolon
Toxic megacolon is an acute form of colonic distension. It is characterized by a very dilated colon (megacolon), accompanied by abdominal distension (bloating), and sometimes fever, abdominal pain, or shock.
Toxic megacolon is usually a complica ...
), or if there is a localized area of dysmotility.
Gastric and colonic pacemaker
Colon cleansing, also known as colon therapy, or colon hydrotherapy, or a colonic, or colonic irrigation encompasses a number of alternative medical therapies claimed to remove unspecified toxins from the colon and intestinal tract by remov ...
s have been tried. These are strips placed along the colon or stomach which create an electric discharge intended to cause the muscle to contract in a controlled manner.
A potential solution, albeit radical, is intestinal transplantation. This is only appropriate in the case of intestinal failure. These procedures are most frequently described in pediatric cases of CIPO. One operation involving multi-organ transplant of the pancreas, stomach, duodenum, small intestine, and liver, and was performed by Doctor Kareem Abu-Elmagd on Gretchen Miller.
Potential treatments
Further research is necessary into other treatments which may alleviate symptoms. These include stem-cell transplantation andfecal microbiota transplant
Fecal microbiota transplant (FMT), also known as a stool transplant, is the process of transferring fecal bacteria and other microbes from a healthy individual into another individual. FMT is an effective treatment for ''Clostridioides diffici ...
ation. Cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively ...
has not been studied with regards to CIPO. Any claims to its efficacy for use in CIPO are speculative.
Related disorders
*Ogilvie syndrome
Ogilvie syndrome is the acute dilatation of the colon in the absence of any mechanical obstruction in severely ill patients.
Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction is characterized by massive dilatation of the cecum (diameter > 10 cm) and right c ...
: acute pseudoobstruction of the colon in severely ill debilitated patients.
* Hirschsprung's disease
Hirschsprung's disease (HD or HSCR) is a birth defect in which nerves are missing from parts of the intestine. The most prominent symptom is constipation. Other symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and slow growth. Symptoms usu ...
: enlargement of the colon due to lack of development of autonomic ganglia
An autonomic ganglion is a cluster of nerve cell bodies (a ganglion) in the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that s ...
.
* Intestinal neuronal dysplasia
Intestinal neuronal dysplasia (IND) is an inherited disease of the intestine that affects one in 3000 children and adults. The intestine uses peristalsis to push its contents toward the anus; people with IND have a problem with the motor neurons th ...
: a disease of motor neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectl ...
s leading to the bowels.
* Bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or Ileus, functional obstruction of the Gastrointestinal tract#Lower gastrointestinal tract, intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Eith ...
: mechanical or functional obstruction of the bowel, most commonly due to adhesions, hernias or neoplasms.
* Enteric neuropathy
Enteric neuropathy is a degenerative neuromuscular condition of the digestive system. In simple terms the gut stops functioning, due to degradation of the nerves and muscles. The condition affects all parts of the digestive tract. There is no kno ...
: alternative name sometimes used for diagnosis in UK
References
External links
* {{Portal bar, Medicine Diseases of intestines