|
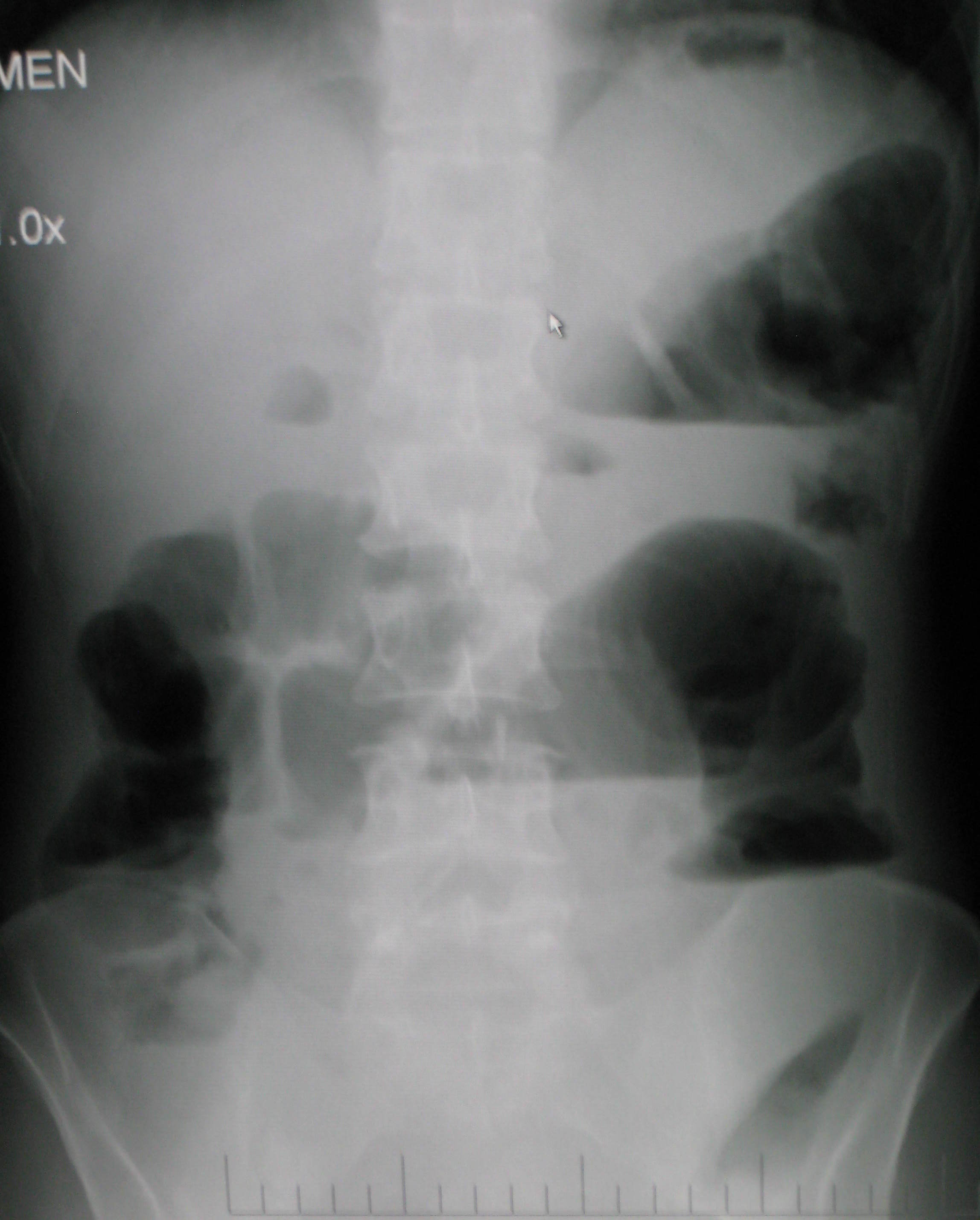
Ogilvie Syndrome
Ogilvie syndrome is the acute dilatation of the colon in the absence of any mechanical obstruction in severely ill patients. Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction is characterized by massive dilatation of the cecum (diameter > 10 cm) and right colon on abdominal X-ray. It is a type of megacolon, sometimes referred to as "acute megacolon," to distinguish it from toxic megacolon. The condition carries the name of the British surgeon Sir William Heneage Ogilvie (1887–1971), who first reported it in 1948. Signs and symptoms Usually the patient has abdominal distention, pain and altered bowel movements. There may also be nausea and vomiting. Cause Ogilvie syndrome may occur after surgery, especially following coronary artery bypass surgery and total joint replacement. Drugs that disturb colonic motility (such as anticholinergics or opioid analgesics) contribute to the development of this condition. Pathophysiology The exact mechanism is not known. The probable explanation is im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or Ileus, functional obstruction of the Gastrointestinal tract#Lower gastrointestinal tract, intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the Small intestine, small bowel or Large intestine, large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, abdominal bloating, bloating and not passing flatulence, gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of acute abdomen, severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital. Causes of bowel obstruction include Adhesion (medicine), adhesions, hernias, volvulus, endometriosis, inflammatory bowel disease, appendicitis, Neoplasm, tumors, diverticulitis, ischemic colitis, ischemic bowel, tuberculosis and intussusception (medical disorder), intussusception. Small bowel obstructions are most often due to adhesions and hernias while large bowel obstructions are most often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteric Nervous System
The enteric nervous system (ENS) or intrinsic nervous system is one of the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract. It is capable of acting independently of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, although it may be influenced by them. The ENS is nicknamed the "second brain". It is derived from neural crest cells. The enteric nervous system is capable of operating independently of the brain and spinal cord, but does rely on innervation from the vagus nerve and prevertebral ganglia in healthy subjects. However, studies have shown that the system is operable with a severed vagus nerve. The neurons of the enteric nervous system control the motor functions of the system, in addition to the secretion of gastrointestinal enzymes. These neurons communicate through many neurotransmitters similar to the CNS, including acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |