Intermittency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
Transition to chaos through intermittency
Dynamical systems

 In
In dynamical system
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a ...
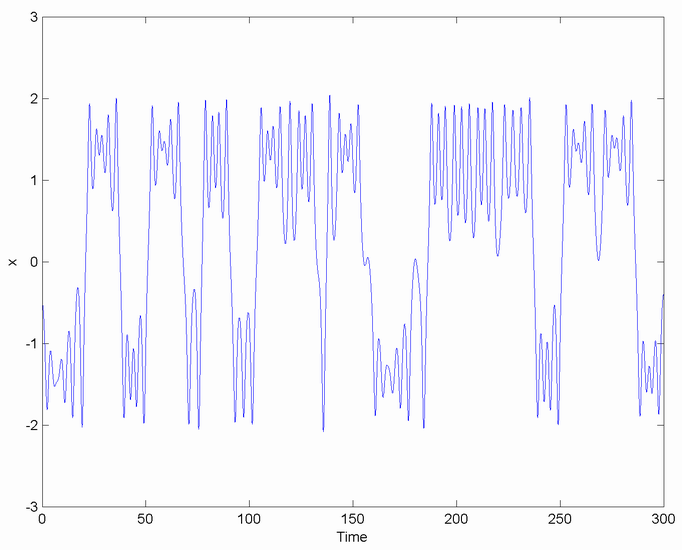
s, intermittency is the irregular alternation of phases of apparently periodic and chaotic
Chaotic was originally a Danish trading card game. It expanded to an online game in America which then became a television program based on the game. The program was able to be seen on 4Kids TV (Fox affiliates, nationwide), Jetix, The CW4Kid ...
dynamics ( Pomeau–Manneville dynamics), or different forms of chaotic dynamics (crisis-induced intermittency).
Pomeau and Manneville described three routes to intermittency where a nearly periodic system shows irregularly spaced bursts of chaos. These (type I, II and III) correspond to the approach to a saddle-node bifurcation, a subcritical Hopf bifurcation
In the mathematical theory of bifurcations, a Hopf bifurcation is a critical point where a system's stability switches and a periodic solution arises. More accurately, it is a local bifurcation in which a fixed point of a dynamical system loses ...
, or an inverse period-doubling bifurcation In dynamical systems theory, a period-doubling bifurcation occurs when a slight change in a system's parameters causes a new periodic trajectory to emerge from an existing periodic trajectory—the new one having double the period of the original. W ...
. In the apparently periodic phases the behaviour is only nearly periodic, slowly drifting away from an unstable periodic orbit In mathematics, in the study of iterated functions and dynamical systems, a periodic point of a function is a point which the system returns to after a certain number of function iterations or a certain amount of time.
Iterated functions
Given a ...
. Eventually the system gets far enough away from the periodic orbit to be affected by chaotic dynamics in the rest of the state space
A state space is the set of all possible configurations of a system. It is a useful abstraction for reasoning about the behavior of a given system and is widely used in the fields of artificial intelligence and game theory.
For instance, the toy ...
, until it gets close to the orbit again and returns to the nearly periodic behaviour. Since the time spent near the periodic orbit depends sensitively on how closely the system entered its vicinity (in turn determined by what happened during the chaotic period) the length of each phase is unpredictable.
Another kind, on-off intermittency, occurs when a previously transversally stable chaotic attractor with dimension less than the embedding space begins to lose stability. Near unstable orbits within the attractor orbits can escape into the surrounding space, producing a temporary burst before returning to the attractor.
In crisis-induced intermittency a chaotic attractor suffers a crisis
A crisis ( : crises; : critical) is either any event or period that will (or might) lead to an unstable and dangerous situation affecting an individual, group, or all of society. Crises are negative changes in the human or environmental affair ...
, where two or more attractors cross the boundaries of each other's basin of attraction
In the mathematical field of dynamical systems, an attractor is a set of states toward which a system tends to evolve, for a wide variety of starting conditions of the system. System values that get close enough to the attractor values remain ...
. As an orbit moves through the first attractor it can cross over the boundary and become attracted to the second attractor, where it will stay until its dynamics moves it across the boundary again.
Intermittent behaviour is commonly observed in fluid flows that are turbulent
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between t ...
or near the transition to turbulence. In highly turbulent
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between t ...
flows, intermittency is seen in the irregular dissipation of kinetic energy and the anomalous scaling of velocity increments.F. Anselmet, Y. Gagne, E.J. Hopfinger, R.A. Antonia, High-order velocity structure functions in turbulent shear flows, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, vol. 140, 1984, pp. 63-89 It is also seen in the irregular alternation between turbulent and non-turbulent fluid that appear in turbulent jets and other turbulent free shear flows. In pipe flow
In fluid mechanics, pipe flow is a type of liquid flow within a closed conduit, such as a pipe or tube. The other type of flow within a conduit is open channel flow.
These two types of flow are similar in many ways, but differ in one important ...
and other wall bounded shear flows, there are intermittent puffs that are central to the process of transition from laminar to turbulent flow. Intermittent behavior has also been experimentally demonstrated in circuit oscillators and chemical reactions.
See also
* Pomeau–Manneville scenario *Crisis (dynamical systems)
In applied mathematics and astrodynamics, in the theory of dynamical systems, a crisis is the sudden appearance or disappearance of a strange attractor as the parameters of a dynamical system are varied. This global bifurcation occurs when a ch ...
*Turbulent flow
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between ...
*Fluorescence intermittency Fluorescence intermittency, or blinking, is the phenomenon of random switching between ON (bright) and OFF (dark) states of the emitter under its continuous excitation. It is a common property of the nanoscale emitters (molecular fluorophores, coll ...
(blinking) of organic molecules and colloidal quantum dots (nanocrystals)
References
* *{{cite book , last = Vassilicos , first=J. C. , year = 2000 , title = Intermittency in turbulent flows , page = 288 , publisher =Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press
A university press is an academic publishing hou ...
, bibcode=2000itf..book.....V
, isbn = 0-521-79221-5
External links
Transition to chaos through intermittency
Dynamical systems