Instrumentation in petrochemical industries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Instrumentation is used to monitor and control the process plant in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. Instrumentation ensures that the plant operates within defined parameters to produce materials of consistent quality and within the required specifications. It also ensures that the plant is operated safely and acts to correct out of tolerance operation and to automatically shut down the plant to prevent hazardous conditions from occurring. Instrumentation comprises sensor elements, signal transmitters, controllers, indicators and alarms, actuated valves, logic circuits and operator interfaces.
An outline of key instrumentation is shown on Process Flow Diagrams (PFD) which indicate the principal equipment and the flow of fluids in the plant. Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID) provide details of all the equipment (vessels, pumps, etc), piping and instrumentation on the plant in a symbolic and diagrammatic form.
Instrumentation is used to monitor and control the process plant in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. Instrumentation ensures that the plant operates within defined parameters to produce materials of consistent quality and within the required specifications. It also ensures that the plant is operated safely and acts to correct out of tolerance operation and to automatically shut down the plant to prevent hazardous conditions from occurring. Instrumentation comprises sensor elements, signal transmitters, controllers, indicators and alarms, actuated valves, logic circuits and operator interfaces.
An outline of key instrumentation is shown on Process Flow Diagrams (PFD) which indicate the principal equipment and the flow of fluids in the plant. Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID) provide details of all the equipment (vessels, pumps, etc), piping and instrumentation on the plant in a symbolic and diagrammatic form.
 Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific temperatures.
*Measurement of temperature of fluids in the petrochemical industry is undertaken by temperature elements (TE). These can be
Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific temperatures.
*Measurement of temperature of fluids in the petrochemical industry is undertaken by temperature elements (TE). These can be
 Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific operating pressures.
*Pressure is measured by pressure sensors (PE) which send pressure (PT) signals to pressure controllers (PIC). Pressure vessels and tanks are fitted with local pressure indicators (PI).
* In the petrochemical industry pressure is controlled by maintaining a constant pressure in the upper gas space of a vessel. A pressure controller (PIC) adjusts the setting on a pressure control valve (PCV) that feeds gas forward to the next stage of the process. A rising pressure in the vessel results in the PCV opening to feed more gas forward. If the pressure continues to rise some controllers then act to open a second PCV that feeds excess gas to the flare system. The pressure transmitter is configured to provide warning alarms (PAL and PAH) if the pressure exceeds set high and low limits. If these limits are exceeded (PALL and PAHH) an automatic shutdown of the system is initiated which includes closure of the inlet valves of the vessel. The pressure sensor (PT) that initiates a shutdown is a separate instrument loop from the PT associated with the pressure control loop to mitigate common mode failures and to ensure greater reliability of the shutdown function.
* The operation of
Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific operating pressures.
*Pressure is measured by pressure sensors (PE) which send pressure (PT) signals to pressure controllers (PIC). Pressure vessels and tanks are fitted with local pressure indicators (PI).
* In the petrochemical industry pressure is controlled by maintaining a constant pressure in the upper gas space of a vessel. A pressure controller (PIC) adjusts the setting on a pressure control valve (PCV) that feeds gas forward to the next stage of the process. A rising pressure in the vessel results in the PCV opening to feed more gas forward. If the pressure continues to rise some controllers then act to open a second PCV that feeds excess gas to the flare system. The pressure transmitter is configured to provide warning alarms (PAL and PAH) if the pressure exceeds set high and low limits. If these limits are exceeded (PALL and PAHH) an automatic shutdown of the system is initiated which includes closure of the inlet valves of the vessel. The pressure sensor (PT) that initiates a shutdown is a separate instrument loop from the PT associated with the pressure control loop to mitigate common mode failures and to ensure greater reliability of the shutdown function.
* The operation of
 The throughput of a petrochemical plant is measured and controlled by flow instrumentation.
* Flow measuring devices devices (FE) include
The throughput of a petrochemical plant is measured and controlled by flow instrumentation.
* Flow measuring devices devices (FE) include  * The flow through compressors, see schematic, is controlled by measuring the flow (FT) through the machine at the suction and controlling the speed (SC) of the prime mover (
* The flow through compressors, see schematic, is controlled by measuring the flow (FT) through the machine at the suction and controlling the speed (SC) of the prime mover ( * Large process pumps are provided with minimum flow protection. This comprises measurement of flow (FE) at the pump discharge, this measurement is an input to a flow controller (FIC) whose set point is the minimum flow required through the pump(see diagram). As the flow reduces to the minimum flow value the controller acts to open a flow control valve (FCV) to recycle fluid from the discharge back to the suction of the pump.
* Flow metering (FIQ) is required where custody transfer of fluids takes place, such as an outgoing pipeline or at a tanker loading station. Accurate measurement of the flow is essential and parameters such as liquid density are measured.
* Flare and vent systems are purged to prevent air ingress and the formation of potentially explosive mixtures.American Petroleum Institute, Recommended Practice RP 521 Guide for Pressure-Relieving and Depressuring Systems The flowrate of purge gas is set by rotameter (FIC) or fixed orifice plate (FO). A low flow alarm (FAL) warns operating personnel that the purge flow has reduced significantly.
* Pipelines are monitored by measuring the flowrate of fluid at each end, a discrepancy (FDA) may indicate a leak in the pipeline.
* Large process pumps are provided with minimum flow protection. This comprises measurement of flow (FE) at the pump discharge, this measurement is an input to a flow controller (FIC) whose set point is the minimum flow required through the pump(see diagram). As the flow reduces to the minimum flow value the controller acts to open a flow control valve (FCV) to recycle fluid from the discharge back to the suction of the pump.
* Flow metering (FIQ) is required where custody transfer of fluids takes place, such as an outgoing pipeline or at a tanker loading station. Accurate measurement of the flow is essential and parameters such as liquid density are measured.
* Flare and vent systems are purged to prevent air ingress and the formation of potentially explosive mixtures.American Petroleum Institute, Recommended Practice RP 521 Guide for Pressure-Relieving and Depressuring Systems The flowrate of purge gas is set by rotameter (FIC) or fixed orifice plate (FO). A low flow alarm (FAL) warns operating personnel that the purge flow has reduced significantly.
* Pipelines are monitored by measuring the flowrate of fluid at each end, a discrepancy (FDA) may indicate a leak in the pipeline.
 The
The
 *
*
 Instrumentation is used to monitor and control the process plant in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. Instrumentation ensures that the plant operates within defined parameters to produce materials of consistent quality and within the required specifications. It also ensures that the plant is operated safely and acts to correct out of tolerance operation and to automatically shut down the plant to prevent hazardous conditions from occurring. Instrumentation comprises sensor elements, signal transmitters, controllers, indicators and alarms, actuated valves, logic circuits and operator interfaces.
An outline of key instrumentation is shown on Process Flow Diagrams (PFD) which indicate the principal equipment and the flow of fluids in the plant. Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID) provide details of all the equipment (vessels, pumps, etc), piping and instrumentation on the plant in a symbolic and diagrammatic form.
Instrumentation is used to monitor and control the process plant in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. Instrumentation ensures that the plant operates within defined parameters to produce materials of consistent quality and within the required specifications. It also ensures that the plant is operated safely and acts to correct out of tolerance operation and to automatically shut down the plant to prevent hazardous conditions from occurring. Instrumentation comprises sensor elements, signal transmitters, controllers, indicators and alarms, actuated valves, logic circuits and operator interfaces.
An outline of key instrumentation is shown on Process Flow Diagrams (PFD) which indicate the principal equipment and the flow of fluids in the plant. Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&ID) provide details of all the equipment (vessels, pumps, etc), piping and instrumentation on the plant in a symbolic and diagrammatic form.
The elements of instrumentation
Instrumentation includes sensing devices to measure process parameters such aspressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
, temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
, liquid level
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
, flow, velocity, composition, density, weight; and mechanical and electrical parameters such as vibration, position, power, current and voltage.
* The measured value of a parameter is displayed and recorded locally and/or in a control room
A control room or operations room is a central space where a large physical facility or physically dispersed service can be monitored and controlled. It is often part of a larger command center.
Overview
A control room's purpose is produc ...
. If the measured variable exceeds pre-defined limits an alarm warns the operating personnel of a potential problem. Automatic executive action is taken by the instrumentation to close or open shutdown valves and dampers, or to trip (stop) pumps and compressors, to move the plant to a safe condition.
* Correct operation of the petrochemical process plant is achieved through the action of control loop
A control loop is the fundamental building block of industrial control systems. It consists of all the physical components and control functions necessary to automatically adjust the value of a measured process variable (PV) to equal the value of ...
s. These automatically maintain and control the pressure, temperature, liquid level and flowrate of fluid in vessels and piping. Control loops compare the measured value of a parameter on the plant, eg. pressure, with a pre-determined set point. A difference between the measured variable and the set point generates a signal which modulates the position of a control valve
A control valve is a valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow passage as directed by a signal from a controller. This enables the direct control of flow rate and the consequential control of process quantities such as pressu ...
(the final element) to maintain the measured variable at the set point.
* Valves are actuated by an electric motor, hydraulic fluid or air. For air-operated control valves, electrical signals from the control system are converted to an air pressure for the valve actuator in a current/pneumatic I/P converter. Upon loss of pneumatic or hydraulic pressure valves may fail to an open (FO) or fail to a closed (FC) position.
* Some instrumentation is self actuating. For example, pressure regulator
A pressure regulator is a valve that controls the pressure of a fluid or gas to a desired value, using negative feedback from the controlled pressure. Regulators are used for gases and liquids, and can be an integral device with a pressure setti ...
s maintain a constant pre-set pressure, and rupture disc
A rupture disk, also known as a pressure safety disc, burst disc, bursting disc, or burst diaphragm, is a non-reclosing pressure relief safety device that, in most uses, protects a pressure vessel, equipment or system from overpressurization ...
s and pressure safety valves open at pre-set pressures.American Petroleum Institute, Recommended Practice API RP 520 Sizing, Selection, and Installation of Pressure-Relieving Devices in Refineries
* Instrumentation includes facilities for operating personnel to intervene in the plant either locally or from a control room. Personnel can open or close valves, change set points, start and stop pumps or compressors, and over-ride shutdown functions (in specific controlled circumstances such as during start-up).
Temperature instrumentation
 Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific temperatures.
*Measurement of temperature of fluids in the petrochemical industry is undertaken by temperature elements (TE). These can be
Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific temperatures.
*Measurement of temperature of fluids in the petrochemical industry is undertaken by temperature elements (TE). These can be Thermocouple
A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of th ...
s or Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Pla ...
Resistance Temperature Detector
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a heat-resistant ceramic or glass core but other constructi ...
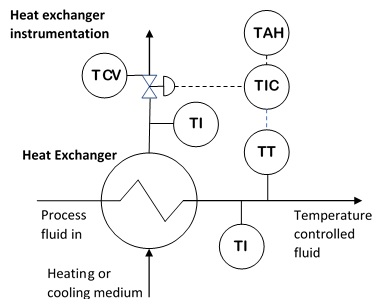
s (RTDs). The latter are used for their good temperature response. Local temperature indicators (TI) are located on the inlet and outlet streams of heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct conta ...
s to monitor the performance of the exchanger.P&IDS NW Hutton 1988
* In industrial applications gaseous or liquid fluids may be heated or cooled. This duty is undertaken in a heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct conta ...
, whereby the fluid is heated or cooled by heat transfer with a second fluid such as water, glycol, hot oil or another process fluid (the heating or cooling medium). Temperature control is used to maintain the desired temperature of the first fluid. A temperature sensor transmitter (TT) is located in the first fluid at its outlet from the heat exchanger. This measured temperature is fed to the temperature controller (TIC) where it is compared to the desired set point temperature. The output of the controller, which is related to the difference between the measured variable and the set point, is fed to a control valve (TCV) in the second fluid to adjust the flow of the heating or cooling medium. In the case of a fluid being cooled, if the temperature of the fluid rises the temperature controller acts to open the TCV increasing the flow of the cooling medium which increases the heat transfer and reduces the temperature of the first fluid. Conversely if the temperature falls the controller acts to close the TCV which reduces the heat transfer increasing the temperature of the first fluid. In the case of heating medium with the falling temperature of the first fluid the controller would act to open the TCV to increase the flow of heating medium thereby raising the temperature of the first fluid. The controller (TIC) may also generate high (TAH) and low temperature (TAL) alarms to warn operating personnel of a potential problem.
* Fin fan coolers use air to cool gases and liquids. The temperature of fluid is controlled (TIC) by opening or closing dampers on the cooler or adjusting the speed of the fan or the pitch angle of the fan blades thereby increasing or decreasing the flow of air.
* Temperature monitoring and control instrumentation is used in fired heaters and furnaces to adjust the fuel flow valve (FCV) to maintain a desired thermal output. Waste heat recovery unit
A waste heat recovery unit (WHRU) is an energy recovery heat exchanger that transfers heat from process outputs at high temperature to another part of the process for some purpose, usually increased efficiency. The WHRU is a tool involved in cogen ...
s (WHRU) are used to extract heat from the flow of hot exhaust gases from a gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
to heat a fluid (heating medium). Instrumentation includes controllers to maintain a desired temperature of the heating medium by closing or opening dampers in the exhaust gas flow.
* Low temperature alarms (TSL) are used where cold fluids could be routed to pipework which is not suitable for cold service. Instrumentation may include an initial alarm (TAL) and then a shutdown action (TSLL) to close a shutdown valve (XV).
* Temperature sensors (TE) are used to indicate that plant flares have been unintentionally extinguished (BAL), perhaps due to insufficient flowrate of gases to maintain a flame.
Pressure instrumentation
 Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific operating pressures.
*Pressure is measured by pressure sensors (PE) which send pressure (PT) signals to pressure controllers (PIC). Pressure vessels and tanks are fitted with local pressure indicators (PI).
* In the petrochemical industry pressure is controlled by maintaining a constant pressure in the upper gas space of a vessel. A pressure controller (PIC) adjusts the setting on a pressure control valve (PCV) that feeds gas forward to the next stage of the process. A rising pressure in the vessel results in the PCV opening to feed more gas forward. If the pressure continues to rise some controllers then act to open a second PCV that feeds excess gas to the flare system. The pressure transmitter is configured to provide warning alarms (PAL and PAH) if the pressure exceeds set high and low limits. If these limits are exceeded (PALL and PAHH) an automatic shutdown of the system is initiated which includes closure of the inlet valves of the vessel. The pressure sensor (PT) that initiates a shutdown is a separate instrument loop from the PT associated with the pressure control loop to mitigate common mode failures and to ensure greater reliability of the shutdown function.
* The operation of
Oil, gas and petrochemical processes are undertaken at specific operating pressures.
*Pressure is measured by pressure sensors (PE) which send pressure (PT) signals to pressure controllers (PIC). Pressure vessels and tanks are fitted with local pressure indicators (PI).
* In the petrochemical industry pressure is controlled by maintaining a constant pressure in the upper gas space of a vessel. A pressure controller (PIC) adjusts the setting on a pressure control valve (PCV) that feeds gas forward to the next stage of the process. A rising pressure in the vessel results in the PCV opening to feed more gas forward. If the pressure continues to rise some controllers then act to open a second PCV that feeds excess gas to the flare system. The pressure transmitter is configured to provide warning alarms (PAL and PAH) if the pressure exceeds set high and low limits. If these limits are exceeded (PALL and PAHH) an automatic shutdown of the system is initiated which includes closure of the inlet valves of the vessel. The pressure sensor (PT) that initiates a shutdown is a separate instrument loop from the PT associated with the pressure control loop to mitigate common mode failures and to ensure greater reliability of the shutdown function.
* The operation of hydrocyclone Hydrocyclones are a type of cyclonic separators that separate product phases mainly on basis of differences in gravity with aqueous solutions as the primary feed fluid.
As opposed to dry or dust cyclones, which separate solids from gasses, hydrocy ...
s is controlled by pressure instrumentation that maintains fixed differential pressures between the inlet and the oil and water outlets.
* Turbo-expanders are controlled by maintaining the inlet pressure (PIC) at a constant value by controlling the angle of the expander inlet vanes. A split range pressure controller may also modulate a Joule-Thomson valve across the turbo-expander.
* Pressure in blanketed tanks is maintained by self actuating pressure control valves (PCVs). As liquid is withdrawn from the tank the pressure in the gas space falls. The blanket gas supply valve opens to maintain the pressure. As the tank fills with liquid the pressure rises and a vent gas valve open to vent gas to atmosphere or a vent system.
* Rupture (bursting) discs (PSE) and pressure relief or pressure safety valves (PSV) are important pressure control devices. Both are self-actuating and are designed to open at a preset pressure to provide an essential safety function on the petrochemical plant.
Flow instrumentation
 The throughput of a petrochemical plant is measured and controlled by flow instrumentation.
* Flow measuring devices devices (FE) include
The throughput of a petrochemical plant is measured and controlled by flow instrumentation.
* Flow measuring devices devices (FE) include vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in ...
, positive displacement (PD), differential pressure (DP), coriolis, ultrasonic,
and rotameters.
 * The flow through compressors, see schematic, is controlled by measuring the flow (FT) through the machine at the suction and controlling the speed (SC) of the prime mover (
* The flow through compressors, see schematic, is controlled by measuring the flow (FT) through the machine at the suction and controlling the speed (SC) of the prime mover (electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate for ...
or gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
) that is driving the compressor. Anti-surge control ensures a minimum flow of fluid through the compressor. The flow (FT) at the discharge and measurements of the suction and discharge pressures (PT) and temperatures (TT) of the fluid flowing through the compressor are measured. The anti-surge controller (FIC) modulates a control valve (FCV) which recycles cooled gas from downstream of the compressor after-cooler back to the suction of the compressor. Low flow alarms (FAL) provide a warning indication to operating personnel.
 * Large process pumps are provided with minimum flow protection. This comprises measurement of flow (FE) at the pump discharge, this measurement is an input to a flow controller (FIC) whose set point is the minimum flow required through the pump(see diagram). As the flow reduces to the minimum flow value the controller acts to open a flow control valve (FCV) to recycle fluid from the discharge back to the suction of the pump.
* Flow metering (FIQ) is required where custody transfer of fluids takes place, such as an outgoing pipeline or at a tanker loading station. Accurate measurement of the flow is essential and parameters such as liquid density are measured.
* Flare and vent systems are purged to prevent air ingress and the formation of potentially explosive mixtures.American Petroleum Institute, Recommended Practice RP 521 Guide for Pressure-Relieving and Depressuring Systems The flowrate of purge gas is set by rotameter (FIC) or fixed orifice plate (FO). A low flow alarm (FAL) warns operating personnel that the purge flow has reduced significantly.
* Pipelines are monitored by measuring the flowrate of fluid at each end, a discrepancy (FDA) may indicate a leak in the pipeline.
* Large process pumps are provided with minimum flow protection. This comprises measurement of flow (FE) at the pump discharge, this measurement is an input to a flow controller (FIC) whose set point is the minimum flow required through the pump(see diagram). As the flow reduces to the minimum flow value the controller acts to open a flow control valve (FCV) to recycle fluid from the discharge back to the suction of the pump.
* Flow metering (FIQ) is required where custody transfer of fluids takes place, such as an outgoing pipeline or at a tanker loading station. Accurate measurement of the flow is essential and parameters such as liquid density are measured.
* Flare and vent systems are purged to prevent air ingress and the formation of potentially explosive mixtures.American Petroleum Institute, Recommended Practice RP 521 Guide for Pressure-Relieving and Depressuring Systems The flowrate of purge gas is set by rotameter (FIC) or fixed orifice plate (FO). A low flow alarm (FAL) warns operating personnel that the purge flow has reduced significantly.
* Pipelines are monitored by measuring the flowrate of fluid at each end, a discrepancy (FDA) may indicate a leak in the pipeline.
Level instrumentation
 The
The level measurement
Level sensors detect the level of liquids and other fluids and fluidized solids, including slurries, granular materials, and powders that exhibit an upper free surface. Substances that flow become essentially horizontal in their containers (or ...
of liquids in pressure vessels and tanks in the petrochemical industry is undertaken by differential pressure level meters, radar, magnetostrictive, nucleonic, magnetic float and pneumatic bubbler instruments.
* Level instrumentation determines the height of liquids by measuring the position of a gas/liquid or liquid/liquid interface within the vessel or tank. Such interfaces include oil/gas, oil/water, condensate/water, glycol/condensate, etc. Local indication (LI) includes sight glasses which show the liquid level directly through a vertical glass tube attached to the vessel/tank.
* Phase interfaces are maintained at a constant level by level transmitters (LT) transmitting a signal to a level controller (LIC) which compares the measured value with the desired set point. The difference is sent as a signal to a level control valve (LCV) on the liquid outlet from the vessel. As the level rises the controller acts to open the valve to draw off liquid to reduce the level. Similarly as the levels fall the controller acts to close the LCV to reduce outflow of fluid.
* Some vessels store liquid until it is pumped out. The controller (LIC) acts to start and stop the pump within a specified band. For example, start the pump when the level rises to 0.6m, stop the pump when the level falls to 0.4m.
* High and low level alarms (LAH and LAL) warn operating personnel that levels are outside predefined limits. Further deviation (LAHH and LALL) initiates a shutdown either to close emergency shutdown valves (ESDV) on the inlet to the vessel or on the liquid outlet lines. As with high and low pressure instrumentation the shutdown function comprises an independent measurement loop to prevent a common mode failure. Loss of liquid level in the vessel may lead to gas blowby where high pressure gas flows to the downstream vessel through the liquid outlet line. The structural integrity of the downstream vessel can be compromised. In addition high liquid level in the vessel may lead to carryover of liquid into the gas outlet may damage downstream equipment such as gas compressors.
* High liquid level in a flare drum can lead to undesirable carryover of liquid to the flare. A high-high liquid level (LSHH) in the flare drum initiates a plant shutdown.
* One of the problems with a significant number of technologies is that they are installed through a nozzle and are exposed to products. This can create several problems, especially when retrofitting new equipment to vessels that have already been stress relieved, as it may not be possible to fit the instrument at the location required. Also, as the measuring element is exposed to the contents within the vessel, it may either attack or coat the instrument causing it to fail in service. One of the most reliable methods for measuring level is using a Nuclear gauge, as it is installed outside the vessel and doesn't normally require a nozzle for bulk level measurement. The measuring element is installed outside the process and can be maintained in normal operation without taking a shutdown. Shutdown is only required for an accurate calibration.
Analyser instrumentation
A wide range of analysis instruments are used in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. *Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system ( ...
– to measure the quality of product or reactants
* Density (oil) – for custody metering of liquids
* Dewpoint
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will co ...
(water dewpoint and hydrocarbon dewpoint) to check the efficiency of dehydration or dewpoint control plant
* Electrical conductivity – to measure the effectiveness of potable water reverse osmosis plant
* Oil-in-water – prior to discharge of water into the environment
* pH of reactants and products
* Sulphur content – to check the efficiency of gas sweetening
Amine gas treating, also known as amine scrubbing, gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and ...
plant
Most instruments function continuously and provide a log of data and trends. Some analyser instruments are configured to alarm (AAH) if a measurement reaches a critical level.
Other instrumentation
*Major pumps and compressors are provided with vibration sensors (VT) to give operating personnel a warning (VA) of potential mechanical problems with the machine. * Rupture discs (PSE) and pressure safety valves (PSV) are self-actuated and provide no immediate indication that they have ruptured or lifted. Instrumentation such as pressure alarms (PXA) or movement alarms (PZA) may be fitted to indicate that they have operated. * Corrosion coupons and corrosion probes provide a local indication of corrosion rates of fluids flowing in piping. *
* Pipeline
Pipeline may refer to:
Electronics, computers and computing
* Pipeline (computing), a chain of data-processing stages or a CPU optimization found on
** Instruction pipelining, a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a s ...
pig launchers and receivers are provided with a pig signaller (XA) to indicate that a pig has been launched or has arrived.
* Packaged items of equipment ( compressors, diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-ca ...
s, electricity generators, etc) are fitted with local vendor supplied instrumentation. When equipment malfunctions a multivariable signal (UA) is sent to the control room.
* The fire and gas detection system comprises local sensors to detect the presence of gas, smoke or fire. These initiate alarms in the control room. Simultaneous detection of multiple sensors initiates action to start firewater pumps and close fire dampers in enclosed spaces.
* The petrochemical plant may have several levels of shutdown. A unit shutdown (USD) entails shutdown of one limited unit with the rest of the plant remaining in operation. A production shutdown (PSD) entails shutdown of the entire process plant. An emergency shutdown (ESD) entails complete shutdown of the plant.
* Older plant may have local control loops which operate pneumatic (3 – 15 psia) final element actuators. Sensors may also transmit electrical signals (4 – 20mA). Conversion between pneumatic and electrical signals is undertaken by P/I and I/P converters. Control of modern plant is based on a Distributed Control Systems using Fieldbus
Fieldbus is the name of a family of industrial computer networks used for real-time distributed control. Fieldbus profiles are standardized by the
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61784/61158.
A complex automated industrial ...
digital protocols.
See also
*Petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable so ...
* Instrument and control engineering
* Process flow diagram
*Piping and instrumentation diagram
A piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID or PID) is a detailed diagram in the process industry which shows the piping and process equipment together with the instrumentation and control devices.
Superordinate to the P&ID is the process flow di ...
*Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
*Control engineering
Control engineering or control systems engineering is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with desired behaviors in control environments. The discipline of controls o ...
* Petroleum products
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Instrumentation In Petrochemical Industries Petroleum products Applied and interdisciplinary physics Process engineering Measuring instruments Control engineering Industrial automation