Hidradenitis suppurativa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


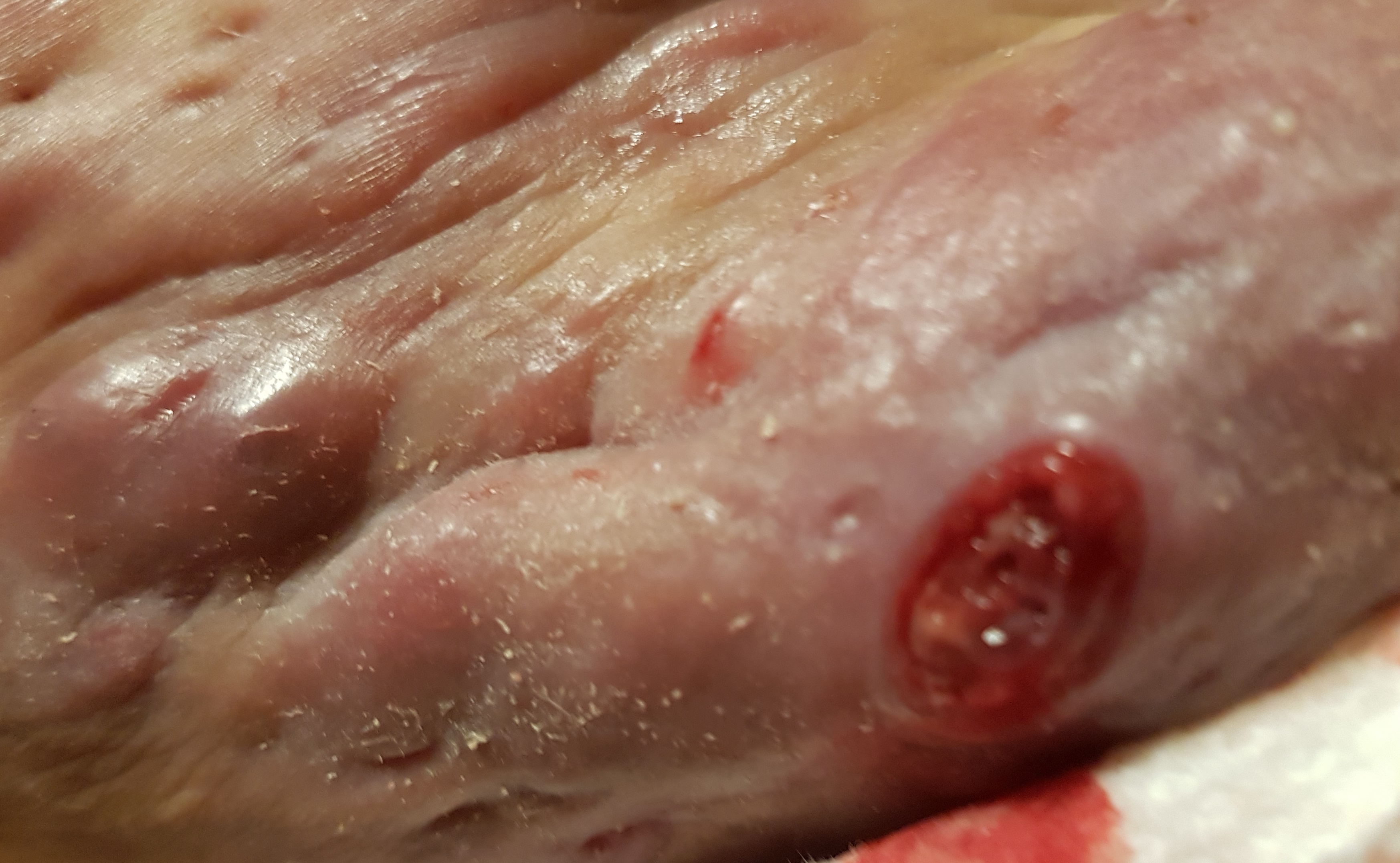
 Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), sometimes known as acne inversa or Verneuil's disease, is a long-term
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), sometimes known as acne inversa or Verneuil's disease, is a long-term
(Seminal paper, SCMS Journal); ''NIH, National Library of Medicine, NCBI''; 2017 Jun, 36(2):47–54. The sweat glands themselves may or may not be inflamed. Diagnosis is based on the symptoms. No cure is known. Warm baths may be tried in those with mild disease. Cutting open the lesions to allow them to drain does not result in significant benefit. While


 Hidradenitis suppurativa presents itself in three stages. Due to the large spectrum of clinical severity and the severe impact on
Hidradenitis suppurativa presents itself in three stages. Due to the large spectrum of clinical severity and the severe impact on
Medline: What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (2004) Prof J. Revuz
{{Use dmy dates, date=August 2019 Acneiform eruptions Inflammations Rare diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate



 Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), sometimes known as acne inversa or Verneuil's disease, is a long-term
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), sometimes known as acne inversa or Verneuil's disease, is a long-term dermatological
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical ...
condition characterized by the occurrence of inflamed and swollen lumps. These are typically painful and break open, releasing fluid or pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
. The areas most commonly affected are the underarms
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorl ...
, under the breasts, and the groin
In human anatomy, the groin (the adjective is ''inguinal'', as in inguinal canal) is the junctional area (also known as the inguinal region) between the abdomen and the thigh on either side of the pubic bone. This is also known as the medial comp ...
. Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a n ...
tissue remains after healing. HS may significantly limit many everyday activities, for instance, walking, hugging, moving, and sitting down. Sitting disability
A sitting disability is a condition in which a person has difficulties sitting or is unable to do so at all; usually due to pain. This can affect people who face little or no chronic problems with standing, as well as those who do, such as mobi ...
may occur in patients with lesions in sacral, gluteal, perineal, femoral, groin or genital regions; and prolonged periods of sitting down itself can also worsen the condition of the skin of these patients.
The exact cause is usually unclear, but believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. About a third of people with the disease have an affected family member. Other risk factors include obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
and smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
. The condition is not caused by an infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
, poor hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
, or the use of deodorant
A deodorant is a substance applied to the body to prevent or mask body odor due to bacterial breakdown of perspiration or vaginal secretions, for example in the armpits, groin, or feet. A subclass of deodorants, called antiperspirants, prevents ...
. Instead, it is believed to be caused by hair follicles being obstructed, with the nearby apocrine sweat glands
An apocrine sweat gland (; from Greek ''apo'' 'away' and ''krinein'' 'to separate') is composed of a coiled secretory portion located at the junction of the dermis and subcutaneous fat, from which a straight portion inserts and secretes into the ...
being strongly implicated in this obstruction.Pathophysiology of hidradenitis suppurativa(Seminal paper, SCMS Journal); ''NIH, National Library of Medicine, NCBI''; 2017 Jun, 36(2):47–54. The sweat glands themselves may or may not be inflamed. Diagnosis is based on the symptoms. No cure is known. Warm baths may be tried in those with mild disease. Cutting open the lesions to allow them to drain does not result in significant benefit. While
antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
are commonly used, evidence for their use is poor. Immunosuppressive medication
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into ...
may also be tried. In those with more severe disease, laser therapy
Laser medicine consists in the use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as laser photodynamic therapy, photorejuvenation, and laser surgery.
Lasers
Lasers used in medicine include in principle any type of laser, but ...
or surgery to remove the affected skin may be viable. Rarely, a skin lesion may develop into skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC) ...
.
If mild cases of HS are included, then the estimate of its frequency is from 1–4% of the population. Women are three times more likely to be diagnosed with it than men. Onset is typically in young adulthood and may become less common after 50 years old. It was first described between 1833 and 1839 by French anatomist Alfred Velpeau.

Causes
The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa remains unknown, and there has, in the recent past, been notable disagreement among experts in this regard. The condition, however, likely stems from both genetic and environmental causes. Specifically, an immune-mediated pathology has been proposed, although there have been sources that have already contradicted the probable likelihood of such an idea. Lesions will occur in any body areas with hair follicles, although areas such as the axilla, groin, and perineal region are more commonly involved. This theory includes most of these potential indicators:Schawartz's principles of surgery, 8th edition, self assessment and board review, chapter 15, the skin and subcutaneous tissue, question 16 * Post-pubescent individuals * Blocked hair follicles or blocked apocrine sweat glands * Excessive sweating *Androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
dysfunction
* Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
s that alter cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
structure
* Patients with more advanced cases may find exercise intolerably painful, which may increase their rate of obesity.
The historical understanding of the disease suggests dysfunctional apocrine glands or dysfunctional hair follicles, possibly triggered by a blocked gland, which creates inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
, pain, and a swollen lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
.

Triggering factors
Several triggering factors should be taken into consideration: *Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
is an exacerbating rather than a triggering factor,Jemec GBE. Body weight in hidradenitis suppurativa. In: Marks R, Plewig G, editors. Acne and Related disorders. London: Martin Dunitz; 1989. pp. 375–6. through mechanical irritation, occlusion
Occlusion may refer to:
Health and fitness
* Occlusion (dentistry), the manner in which the upper and lower teeth come together when the mouth is closed
* Occlusion miliaria, a skin condition
* Occlusive dressing, an air- and water-tight trauma ...
, and skin maceration
Maceration is defined as the softening and breaking down of skin resulting from prolonged exposure to moisture. It was first described by Jean-Martin Charcot in 1877. Maceration is caused by excessive amounts of fluid remaining in contact with th ...
.
* Tight clothing, and clothing made of heavy, nonbreathable materials
* Deodorants
A deodorant is a substance applied to the body to prevent or mask body odor due to bacterial breakdown of perspiration or vaginal secretions, for example in the armpits, groin, or feet. A subclass of deodorants, called antiperspirants, prevents ...
, depilation
Hair removal, also known as epilation or depilation, is the deliberate removal of body hair or head hair.
Hair typically grows all over the human body and can vary in thickness and length across human populations. Hair can become more visible ...
products, shaving
Shaving is the removal of hair, by using a razor or any other kind of bladed implement, to slice it down—to the level of the skin or otherwise. Shaving is most commonly practiced by men to remove their facial hair and by women to remove th ...
of the affected area – their association with HS is still an ongoing debate among researchers.
* Drugs
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalat ...
, in particular oral contraceptive pill Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control.
Female
Two types of female oral contraceptive pill, taken once per day, are widely available:
* The combin ...
s and lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
.
* Hot and especially humid climates.
Predisposing factors
* Genetic factors: anautosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, Title (property), titles, debts, entitlements, Privilege (law), privileges, rights, and Law of obligations, obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ ...
pattern has been proposed.
* Endocrine factors: sex hormones, especially an excess of androgens
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This in ...
, are thought to be involved, although the apocrine glands are not sensitive to these hormones. Women often have outbreaks before their menstrual period
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs ...
and after pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
; HS severity usually decreases during pregnancy and after menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often ...
.
Some cases have been found to result from mutations in the '' NCSTN'', '' PSEN1'', or '' PSENEN'' genes. The genes produce proteins that are all components of a complex called gamma- (γ-) secretase. This complex cuts apart (cleaves) many different proteins, which is an important step in several chemical signaling pathways
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
. One of these pathways, known as notch signaling
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cell signaling system present in most animals. Mammals possess four different notch receptors, referred to as NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, and NOTCH4. The notch receptor is a single-pass transme ...
, is essential for the normal maturation and division of hair follicle cells and other types of skin cells. Notch signaling is also involved in normal immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
function. Studies suggest that mutations in the ''NCSTN'', ''PSEN1'', or ''PSENEN'' gene impair notch signaling in hair follicles. Although little is known about the mechanism, abnormal notch signaling appears to promote the development of nodules and to lead to inflammation in the skin. In addition, the composition of the intestinal microflora and as a consequence dietary patterns appear to play a role. Although dysbiosis of the cutaneous microbiome apparent in HS is not observed, the concurrent existence of inflammatory gut and skin diseases has led to the postulation of a gut-skin axis in which gut microbiota is implicated. Indeed, analysis of bacterial taxa in fecal samples from HS patients support the possibility of a role for intestinal microbial alterations in this chronic inflammatory skin disease.
Diagnosis
Stages

 Hidradenitis suppurativa presents itself in three stages. Due to the large spectrum of clinical severity and the severe impact on
Hidradenitis suppurativa presents itself in three stages. Due to the large spectrum of clinical severity and the severe impact on quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, a reliable method for evaluating HS severity is needed.
Hurley's staging system
Hurley's staging system was the first classification system proposed, and is still in use for the classification of patients with skin diseases (i.e.,psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete ...
, HS, acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
). Hurley separated patients into three groups based largely on the presence and extent of cicatrization and sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
. It has been used as a basis for clinical trials in the past and is a useful basis to approach therapy for patients. These three stages are based on Hurley's staging system, which is simple and relies on the subjective extent of the diseased tissue the patient has. Hurley's three stages of hidradenitis suppurativa are:
Sartorius staging system
The Sartorius staging system is more sophisticated than Hurley's. Sartorius ''et al.'' suggested that the Hurley system is not sophisticated enough to assess treatment effects in clinical trials during research. This classification allows for better dynamic monitoring of the disease severity in individual patients. The elements of this staging system are: *Anatomic
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
regions involved (axilla, groin gluteal, or other region or inframammary region left or right)
* Number and types of lesions
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
involved (abscesses, nodules, fistulas
A fistula (plural: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") in anatomy is an abnormal connection between two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow or ...
or sinuses, scars, points for lesions of all regions involved)
* The distance between lesions, in particular the longest distance between two relevant lesions (i.e., nodules and fistulas in each region or size if only one lesion present)
* The presence of normal skin in between lesions (i.e., if all lesions are clearly separated by normal skin)
Points are accumulated in each of the above categories, and added to give both a regional and total score. In addition, the authors recommend adding a visual analog scale for pain or using the dermatology life quality index
The Dermatology life Quality Index (DLQI) is a ten-question questionnaire used to measure the impact of skin disease on the quality of life of an affected person. It is designed for people aged 16 years and above.
History
The DLQI was created b ...
(DLQI, or the 'skindex') when assessing HS.
Treatment
Treatment depends upon presentation and severity of the disease. Due to the poorly studied nature of the disease, the effectiveness of the drugs and therapies listed below is unclear. Possible treatments include the following:Lifestyle
Warm baths may be tried in those with mild disease. Weight loss and the cessation of smoking are also recommended.Medication
*Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
: taken by mouth, these are used for their anti-inflammatory properties rather than to treat infection. Most effective is a combination of rifampicin and clindamycin given concurrently for 2–3 months. Popular antibiotics also include tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
Common side effects in ...
and minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as pneumonia. It is generally less preferred than the tetracycline doxycycline. It is also ...
. Topical clindamycin has been shown to have an effect in double-blind placebo controlled studies.
* Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
injections, also known as intralesional steroids, can be particularly useful for localized disease, if the drug can be prevented from escaping via the sinuses.
* Antiandrogen
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the ...
therapy, hormonal therapy with antiandrogenic medications such as spironolactone
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood press ...
, flutamide
Flutamide, sold under the brand name Eulexin among others, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) which is used primarily to treat prostate cancer. It is also used in the treatment of androgen-dependent conditions like acne, excessive hair grow ...
, cyproterone acetate
Cyproterone acetate (CPA), sold alone under the brand name Androcur or with ethinylestradiol under the brand names Diane or Diane-35 among others, is an antiandrogen and progestin medication used in the treatment of androgen-dependent condition ...
, ethinylestradiol
Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disord ...
, finasteride, dutasteride
Dutasteride, sold under the brand name Avodart among others, is a medication primarily used to treat the symptoms of a benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), an enlarged prostate not associated with cancer. A few months may be required before benefi ...
, and metformin
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome. ...
, have been found to be effective in clinical studies. However, the quality of available evidence is low and does not presently allow for robust evidence-based recommendations.
* Intravenous infusion or subcutaneous injection of anti-inflammatory (TNF inhibitor
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ...
s; anti-TNF-alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
) drugs such as infliximab
Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spon ...
, and etanercept
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. It ...
This use of these drugs is not currently Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) approved and is somewhat controversial, so may not be covered by insurance.
* TNF inhibitor
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ...
: Studies have supported that various TNF inhibitors have a positive effect on HS lesions. Specifically adalimumab
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira, among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurati ...
at weekly intervals is useful. Adalimumab is the only medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of HS as of 2021.
* Topical isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers ( squamous-cell carcinoma), and in t ...
is usually ineffective in people with HS, and is more commonly known as a medication for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Individuals affected by HS who responded to isotretinoin treatment tended to have milder cases of the condition.
Surgery
When the process becomes chronic, wide surgical excision is the procedure of choice. Wounds in the affected area do not heal bysecondary intention
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue.
In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier agains ...
, and immediate or delayed application of a split-thickness skin graft
Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft.
Surgeons may use skin grafting to treat:
* extensive wounding or trauma
* burns
* areas of extensive skin loss du ...
is an option.
Another option is covering the defect with a perforator flap. With this technique, the (mostly totally excised) defect is covered with tissue from an area nearby. For example, the axilla with a fully excised defect of 15 × 7 cm can be covered with a thoracodorsal artery perforator flap.
Laser hair removal
The 1064- nmwavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
laser for hair removal may aid in the treatment of HS. A randomized control study has shown improvement in HS lesions with the use of an Nd:YAG laser.
Prognosis
In stage III disease, as classified by the Hurley's staging system, fistulae left undiscovered, undiagnosed, or untreated, can rarely lead to the development of squamous cell carcinoma in the anus or other affected areas. Other stage III chronic sequelae may also includeanemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
, multilocalized infections
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
, amyloidosis, and arthropathy
An arthropathy is a disease of a joint. Types
Arthritis is a form of arthropathy that involves inflammation of one or more joints, while the term arthropathy may be used regardless of whether there is inflammation or not.
Joint diseases can be ...
. Stage III complications have been known to lead to sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, but clinical data are still uncertain.
Potential complications
*Contractures
In pathology, a contracture is a permanent shortening of a muscle or joint. It is usually in response to prolonged hypertonia, hypertonic spasticity in a concentrated muscle area, such as is seen in the tightest muscles of people with conditions ...
and reduced mobility of the lower limbs and axillae
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superio ...
due to fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
and scarring occur. Severe lymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fl ...
may develop in the lower limbs.
* Local and systemic infections
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
( meningitis, bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
, etc.), are seen, which may even progress to sepsis.
* Interstitial keratitis
Interstitial keratitis (IK) is corneal scarring due to chronic inflammation of the corneal stroma. Interstitial means space between cells i.e. corneal stroma which lies between the epithelium and the endothelium. Keratitis means corneal inflammati ...
* Anal, rectal, or urethral fistulae
A fistula (plural: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") in anatomy is an abnormal connection between two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow or ...
* Normochromic or hypochromic anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
* People with HS may be at increased risk for autoimmune disorders including ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hi ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
, and psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. Th ...
.
* Squamous cell carcinoma has been found on rare occasions in chronic hidradenitis suppurativa of the anogenital region. The mean time to the onset of this type of lesion is 10 years or more and the tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
are usually highly aggressive.
* Tumors of the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
and oral cavity
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on t ...
, and liver cancer
* Hypoproteinemia
Hypoproteinemia is a condition where there is an abnormally low level of protein in the blood. There are several causes that all result in edema once serum protein levels fall below a certain threshold.
Causes
# Nutritional hypoproteinemia is due ...
and amyloidosis, which can lead to kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
and death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
* Seronegative and usually asymmetric arthropathy
An arthropathy is a disease of a joint. Types
Arthritis is a form of arthropathy that involves inflammation of one or more joints, while the term arthropathy may be used regardless of whether there is inflammation or not.
Joint diseases can be ...
: pauciarticular arthritis, polyarthritis
Polyarthritis is any type of arthritis that involves 5 or more joints simultaneously. It is usually associated with autoimmune conditions and may be experienced at any age and is not sex specific.
Causes
Polyarthritis is most often caused by an au ...
/polyarthralgia
Arthralgia (from Greek ''arthro-'', joint + ''-algos'', pain) literally means ''joint pain''. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication.
According to MeS ...
syndrome
History
* From 1833 to 1839, in a series of three publications, Velpeau identified and described a disease now known as hidradenitis suppurativa. * In 1854, Verneuil described hidradenitis suppurativa as ''hidrosadénite Phlegmoneuse''. This is how HS obtained its alternate name "Verneuil's disease". * In 1922, Schiefferdecker hypothesized a pathogenic link between "acne inversa" and human sweat glands. * In 1956, Pillsbury ''et al''. coined the term '' follicular occlusion triad'' for the common association of hidradenitis suppurativa,acne conglobata
Acne conglobata is a highly inflammatory disease presenting with comedones, nodules, abscesses, and draining sinus tracts.
This condition generally begins between the ages of 18 and 30. It usually persists for a very long time, and often until t ...
and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp
Dissecting cellulitis of the scalp, also known as dissecting folliculitis, perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens of Hoffman, perifolliculitis abscedens et suffodiens, or folliculitis abscedens et suffodiens, is an inflammatory condition ...
. Modern clinical research still employs Pillsbury's terminology for these conditions' descriptions.
* In 1975, Plewig and Kligman, following Pillsbury's research path, modified the "acne triad", replacing it with the "acne tetrad: acne triad, plus pilonidal sinus
Pilonidal disease is a type of skin infection which typically occurs as a cyst Intergluteal cleft, between the cheeks of the buttocks and often at the upper end. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and redness. There may also be drainage of flui ...
". Plewig and Kligman's research follows in Pillsbury's footsteps, offering explanations of the symptoms associated with hidradenitis suppurativa.
* In 1989, Plewig and Steger's research led them to rename hidradenitis suppurativa, calling it "acne inversa" – which is not still used today in medical terminology, although some individuals still use this outdated term.
A surgeon from Paris, Velpeau described an unusual inflammatory process with formation of superficial axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superior ...
ry, submammary
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in prima ...
, and perianal
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
abscesses, in a series of three publications from 1833 to 1839. One of his colleagues, also located in Paris, named Verneuil, coined the term ''hidrosadénite phlegmoneuse'' about 15 years later. This name for the disease reflects the former pathogenetic model of acne inversa, which is considered inflammation of sweat glands as the primary cause of hidradenitis suppurativa. In 1922, Schiefferdecker suspected a pathogenic association between acne inversa and apocrine sweat glands. In 1956, Pillsbury postulated follicular occlusion as the cause of acne inversa, which they grouped together with acne conglobata and ''perifolliculitis capitis abscendens et suffodiens'' ("dissecting cellulitis of the scalp") as the "acne triad". Plewig and Kligman added another element to their acne triad, pilonidal sinus
Pilonidal disease is a type of skin infection which typically occurs as a cyst Intergluteal cleft, between the cheeks of the buttocks and often at the upper end. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and redness. There may also be drainage of flui ...
. Plewig ''et al.'' noted that this new "acne tetrad" includes all the elements found in the original "acne triad", in addition to a fourth element, pilonidal sinus. In 1989, Plewig and Steger introduced the term "acne inversa", indicating a follicular source of the disease and replacing older terms such as "Verneuil disease".
Other names
Hidradenitis suppurativa has been referred to by multiple names in the literature, as well as in various cultures. Some of these are also used to describe different diseases, or specific instances of this disease. * Acne conglobata – not really a synonym – this is a similar process, but in classic acne areas of chest and back * Acne inversa – a proposed new term which has not gained widespread favor. * Apocrine acne – an outdated term based on the disproven concept that apocrine glands are primarily involved, though many do have apocrine gland infection * Apocrinitis – another outdated term based on the same thesis * Fox-den disease – a term not used in medical literature, based on the deepfox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
den–like sinuses
* Hidradenitis supportiva – a misspelling
* Pyodermia fistulans significa – now considered archaic
* Verneuil's disease – recognizing the surgeon whose name is most often associated with the disorder as a result of his 1854–1865 studies
Histology
Terminology
Although hidradenitis suppurativa is often referred to as acne inversa, it is not a form of acne, and lacks the core defining features of acne such as the presence of closedcomedone
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin (skin debris) combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word "comedo" comes from the ...
s and increased sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
production.
References
External links
Medline: What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (2004) Prof J. Revuz
{{Use dmy dates, date=August 2019 Acneiform eruptions Inflammations Rare diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate