Front legs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
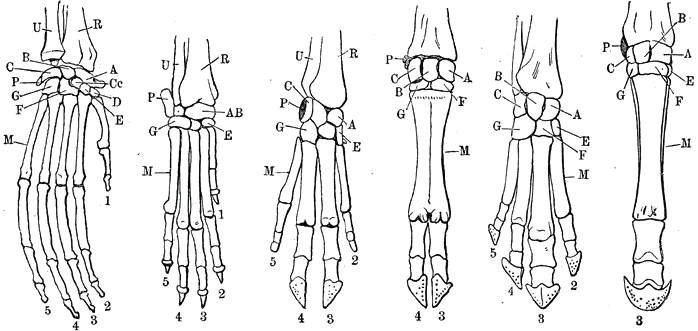 A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired
Evolution of chameleon locomotion: or how to become arboreal as a reptile
{{fins, limbs and wings Limbs (anatomy) Vertebrate anatomy Animal morphology
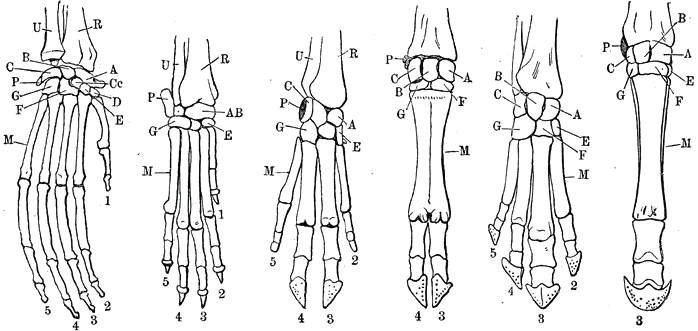 A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated
An articulated vehicle is a vehicle which has a permanent or semi-permanent pivot joint in its construction, allowing it to turn more sharply. There are many kinds, from heavy equipment to buses, trams and trains. Steam locomotives were sometim ...
appendages (limb
Limb may refer to:
Science and technology
*Limb (anatomy), an appendage of a human or animal
*Limb, a large or main branch of a tree
*Limb, in astronomy, the curved edge of the apparent disk of a celestial body, e.g. lunar limb
*Limb, in botany, ...
s) attached on the cranial
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
( anterior) end of a terrestrial
Terrestrial refers to things related to land or the planet Earth.
Terrestrial may also refer to:
* Terrestrial animal, an animal that lives on land opposed to living in water, or sometimes an animal that lives on or near the ground, as opposed to ...
tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
's torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a huma ...
. With reference to quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor' ...
s, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. In bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
animals with an upright
Body relative directions (also known as egocentric coordinates) are geometrical orientations relative to a body such as a human person's.
The most common ones are: left and right; forward(s) and backward(s); up and down.
They form three pairs ...
posture (e.g. humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
and some primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s), the term upper limb
The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shou ...
is often used.
A forelimb is not to be confused with a forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
, which is a distal portion of the human upper limb between the elbow
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the me ...
and the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
.
All vertebrate forelimbs are homologous, meaning that they all evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
from the same structures. For example, the flipper of a turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked t ...
or of a dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
, the arm of a human, the foreleg of a horse, and the wings
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expre ...
of both bats and birds are ultimately homologous, despite the large differences between them.
Specific uses of the forelimbs may be analogous if they evolved from different sub-structures of the forelimb, such as the flippers of turtles and dolphins, and the wings of birds and bats.
Evolution of forelimbs
Evolution of the forelimb may be characterized by many trends. The number of digits, their characteristics, as well as the shape and alignment ofradius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
, ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
, and humerus, have had major evolutionary implications.
Changes in body size, foot posture, habitat, and substrate are frequently found to influence one another (and to connect to broader potential drivers, such as changing climate).
Shape
A number of factors can influence the evolution of forelimb long bone shape, such as body mass, lifestyle, predatory behavior, or relative prey size. A general pattern is for heavier species to have more robust radii, ulnas, and humeri. Musteloid carnivorans that have an arboreal lifestyle tend to have long and slender forelimb long bones, which allow for improved movement and flexibility. Semi-fossorial and aquatic musteloid species tend to have short and robust forelimb long bones to deal with the strain from digging and swimming. In the order Carnivora, felids, which usually ambush and grapple with their prey, have shorter and more robust limbs. Their forelimbs are used for both short sprints and grappling, which means that they need to be flexible and durable. In contrast, canids, which often pursue their prey over greater distances, have longer, more gracile limbs. Running is pretty much the only use for their forelimbs, so they don't need to be adapted for anything else and can be less flexible. Predators hunting prey that is half their body weight or greater evolved shorter and more sturdy radii, ulnas, and humeri to decrease the likelihood of the bone breaking or fracturing while hunting. Predators hunting prey less than half their body weight tended to have longer and more slender forelimb long bones to improve energetic efficiency.Polydactyly
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s were initially understood to have first developed five digits as an ancestral characteristic, which were then reduced or specialized into a number of uses. Certain animals retained 'primitive' forelimbs, such as pentadactylous
In biology, dactyly is the arrangement of digits (fingers and toes) on the hands, feet, or sometimes wings of a tetrapod animal. It comes from the Greek word δακτυλος (''dáktylos'') = "finger".
Sometimes the ending "-dactylia" is use ...
(five-fingered) reptiles and primates. This has mostly held true, but the earliest tetrapod or " fishapod" ancestors may have had more than five digits. This was notably challenged by Stephen Jay Gould in his 1991 essay "Eight (Or Fewer) Little Piggies".
Polydactyly in early tetrapods should be understood as having more than five digits to the finger or foot, a condition that was the natural state of affairs in the very first tetrapods. Early groups like ''Acanthostega
''Acanthostega'' (meaning "spiny roof") is an extinct genus of stem-tetrapod, among the first vertebrate animals to have recognizable limbs. It appeared in the late Devonian period (Famennian age) about 365 million years ago, and was anatomic ...
'' had eight digits, while the more derived '' Ichthyostega'' had seven digits, the yet-more derived '' Tulerpeton'' had six toes.
Tetrapods evolved from animals with fins such as found in lobe-finned fish
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass includ ...
es. From this condition a new pattern of limb formation evolved, where the development axis of the limb rotated to sprout secondary axes along the lower margin, giving rise to a variable number of very stout skeletal supports for a paddle-like foot.
Digit specialization
Digits may be specialized for different forms of locomotion. A classic example is the horse's development of a single toe (monodactyly). Other hooves, like those of even-toed andodd-toed ungulate
Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Perissodactyla (, ), are animals—ungulates—who have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three (rhinoceroses and tapirs, with tapirs still using four toes on the front legs) o ...
s, and even the hoof-like foot of extinct hadrosaurs
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which incl ...
, may be regarded as similar specializations.
To bear their immense weight, sauropods
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
, the most derived being titanosaurs
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still th ...
, developed a tubular manus (front foot) and gradually lost their digits, standing on their metacarpals. The stegosaurian forelimb has evidence for a sauropod−like metacarpal configuration This was a different evolutionary strategy than megafaunal mammals such as modern elephants.
Therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more ...
s started evolving diverse and specialized forelimbs 270 million years ago, during the Permian.
Opposable thumbs
Modern humans are unique in the musculature of the forearm and hand, though opposable thumbs or structures like them have arisen in a few animals. In dinosaurs, a primitive autonomization of the firstcarpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometaca ...
(CMC) may have occurred. In primates, a real differentiation appeared perhaps 70 mya, while the shape of the human thumb CMC finally appears about 5 mya.
* Primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s fall into one of four groups:
** Nonopposable thumbs: tarsiers and marmoset
The marmosets (), also known as zaris or sagoin, are 22 New World monkey species of the genera '' Callithrix'', '' Cebuella'', '' Callibella'', and ''Mico''. All four genera are part of the biological family Callitrichidae. The term "marmoset" ...
s
** Pseudo-opposable thumbs: all strepsirrhine
Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini (; ) is a suborder of primates that includes the lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Africa, and the lorises from India and southeast Asia. Colle ...
s and Cebidae
** Opposable thumbs: Old World monkey
Old World monkey is the common English name for a family of primates known taxonomically as the Cercopithecidae (). Twenty-four genera and 138 species are recognized, making it the largest primate family. Old World monkey genera include baboons ...
s and all great apes
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the ...
** Opposable with comparatively long thumbs: gibbons (or lesser apes)
Pandas have evolved pseudo-opposable thumbs by extension of the sesamoid bone, which is not a true digit.
Pronation and supination
The ability to pronate the manus (hand) and forearm intherian mammals
Theria (; Greek: , wild beast) is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes.
...
is achieved by a rounded head of the radius, which allows it to swivel across the ulna. Supination requires a dorsal glide of the distal radius and pronation a palmar glide in relation to the distal ulna.
Pronation has evolved multiple times, among mammals, chameleons, and varanids
The Varanidae are a family of lizards in the superfamily Varanoidea within the Anguimorpha group. The family, a group of carnivorous and frugivorous lizards, includes the living genus '' Varanus'' and a number of extinct genera more closely re ...
. However, the more basal condition is to be unable to pronate. Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s were not capable of more than semi-pronation of the wrist, though bipedal origins of all quadrupedal dinosaur clades could have allowed for greater disparity in forelimb posture than often considered. Monotremes have forearms that are not as dexterous as therians. Monotremes have a sprawling posture, and multiple elements in their pectoral girdles, which are ancestral traits for mammals.
In birds, the forearm muscles supinate, pronate, flex and extend the distal wing.
Wings
All tetrapod forelimbs are homologous, evolving from the same initial structures inlobe-finned fish
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass includ ...
. However, another distinct process may be identified, convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
, by which the wings of bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
s, and extinct pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 ...
s evolved the same purpose in drastically different ways. These structures have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor
In biology and genetic genealogy, the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as the last common ancestor (LCA) or concestor, of a set of organisms is the most recent individual from which all the organisms of the set are descended. The ...
of those groups.
Bat wings are composed largely of a thin membrane of skin supported on the five fingers, whereas bird wings are composed largely of feathers supported on much reduced fingers, with finger 2 supporting the alula
The alula , or bastard wing, (plural ''alulae'') is a small projection on the anterior edge of the wing of modern birds and a few non-avian dinosaurs. The word is Latin and means "winglet"; it is the diminutive of ''ala'', meaning "wing". The al ...
and finger 4 the primary feathers of the wing; there are only distant homologies between birds and bats, with much closer homologies between any pair of bird species, or any pair of bat species.
Flippers
Marine mammals have evolved several times. Over the course of their evolution, they develop streamlined hydrodynamic bodies. The forelimb thus develops into a flipper. The forelimbs of cetaceans, pinnipeds, and sirenians presents a classic example of convergent evolution. There is widespread convergence at the gene level. Distinct substitutions in common genes created various aquatic adaptations, most of which constituteparallel evolution
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.Zhang, J. and Kumar, S. 1997Detection of convergent and paral ...
because the substitutions in question are not unique to those animals.
When comparing cetaceans to pinnipeds to sirenians, 133 parallel amino acid substitutions occur. Comparing and contrasting cetaceans-pinnipeds, cetaceans-sirenians, and pinnipeds-sirenians, 2,351, 7,684, and 2,579 substitutions occur, respectively.
See also
* Hindlimb *Anatomical terms of motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relati ...
Bibliography
*References
External links
Evolution of chameleon locomotion: or how to become arboreal as a reptile
{{fins, limbs and wings Limbs (anatomy) Vertebrate anatomy Animal morphology