|
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onychodontiformes
Onychodontiformes (also known as Onychodontida and Struniiformes) is an order of prehistoric sarcopterygian fish that lived during the Devonian period. The onychodontiforms are generally regarded as early-diverging members of the coelacanth lineage. Phylogeny The following cladogram is adapted from Mondéjar-Fernández (2020). The study recovered Onychodontiformes as a paraphyletic In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ... group, which is shown in green: References External links Onychodontiformes at Palaeos Prehistoric lobe-finned fish Prehistoric fish orders Devonian bony fish Early Devonian first appearances Famennian extinctions Paraphyletic groups {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorph
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipnomorpha
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but this te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indian Ocean Coelacanth
The West Indian Ocean coelacanth (''Latimeria chalumnae'') (sometimes known as gombessa, African coelacanth, or simply coelacanth) is a crossopterygian, one of two extant species of coelacanth, a rare order of vertebrates more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods than to the common ray-finned fishes. The other extant species is the Indonesian coelacanth (''L. menadoensis''). The West Indian Ocean coelacanth was historically known by fishermen around the Comoro Islands (where it is known as ''gombessa''), Madagascar, and Mozambique in the western Indian Ocean, but first scientifically recognised from a specimen collected in South Africa in 1938. This coelacanth was once thought to be evolutionarily conservative, but discoveries have shown initial morphological diversity. It has a vivid blue pigment, and is the better known of the two extant species. The species has been assessed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List. Anatomy and physiology The average weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
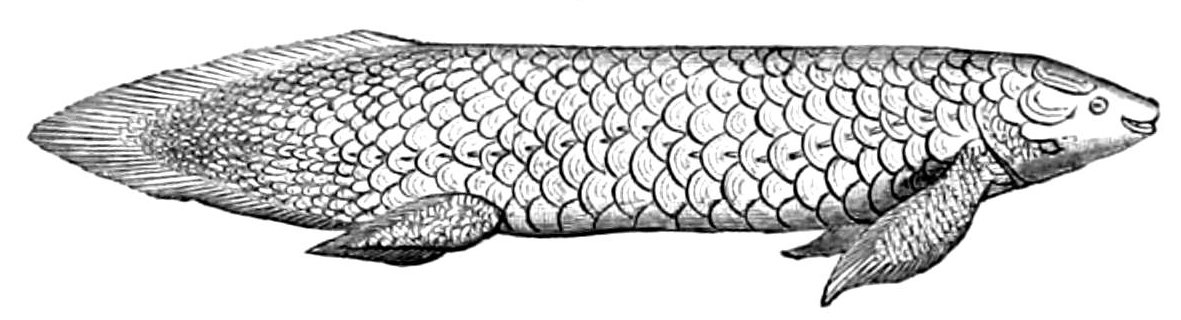
Australian Lungfish
The Australian lungfish (''Neoceratodus forsteri''), also known as the Queensland lungfish, Burnett salmon and barramunda, is the only surviving member of the family Neoceratodontidae. It is one of only six extant lungfish species in the world. Endemic to Australia, the Neoceratodontidae are an ancient family belonging to the class Sarcopterygii, or lobe-finned fishes. Fossil records of this group date back 380 million years, around the time when the higher vertebrate classes were beginning to evolve. Fossils of lungfish almost identical to this species have been uncovered in northern New South Wales, indicating that ''Neoceratodus'' has remained virtually unchanged for well over 100 million years, making it a living fossil and one of the oldest living vertebrate genera on the planet. It is one of six extant representatives of the ancient air-breathing Dipnoi (lungfishes) that flourished during the Devonian period (about 413–365 million years ago) and is the outgroup to al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptiles and birds. The group includes mammals and every animal more closely related to mammals than to sauropsids. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye orbit, leaving a bony arch beneath each; this accounts for their name. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals. Traditionally, non-mammalian synapsids were believed to have evolved from reptiles, and therefore described as mammal-like reptiles in classical systematics, and primitive synapsids were also referred to as pelycosaurs, or pelyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludlow Epoch
In the geological timescale, the Ludlow Epoch (from 427.4 ± 0.5 million years ago to 423.0 ± 2.3 million years ago) occurred during the Silurian Period, after the end of the Homerian Age. It is named for the town of Ludlow in Shropshire, England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe .... The Ludlow Epoch is subdivided into two stages: Gorstian and Ludfordian. Paleontology Arthropods See also * Ludlow Group References *03 Geological epochs {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
