Flota system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
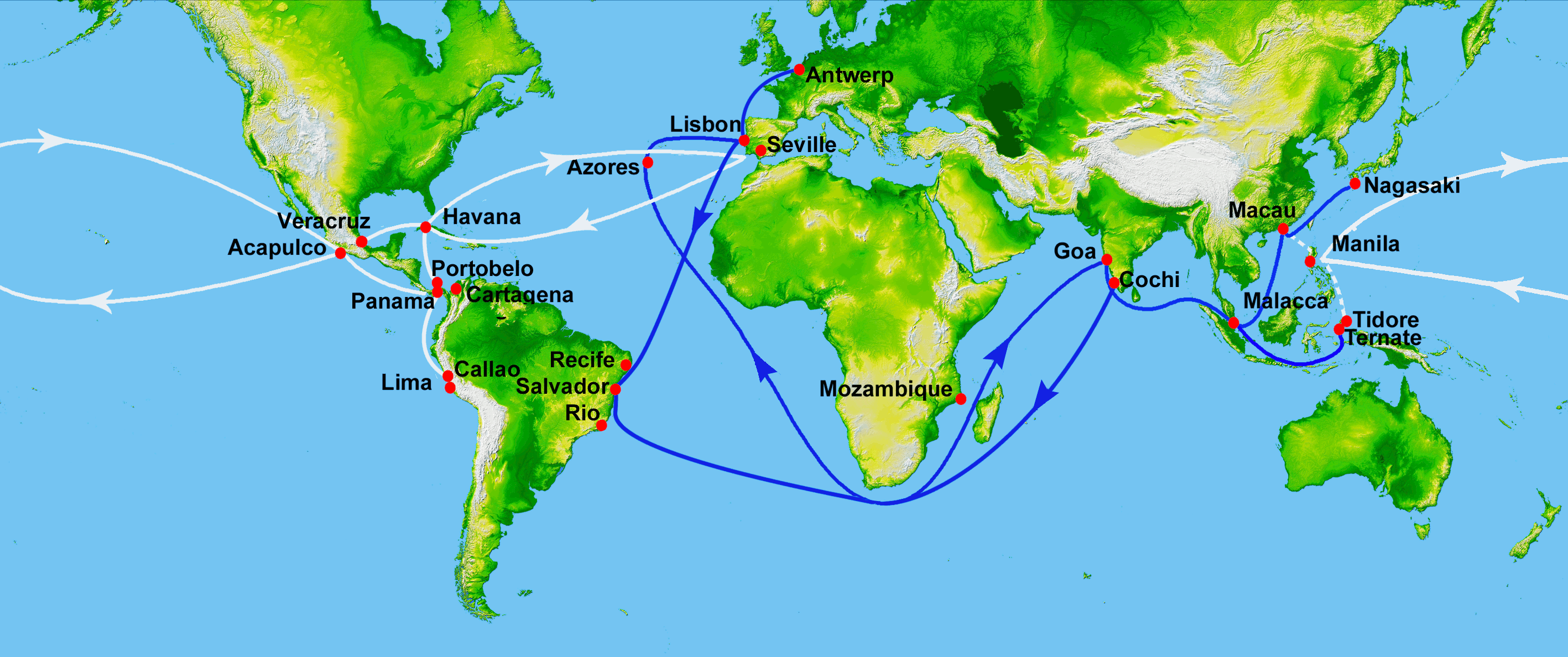 The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a
 Spanish ships had carried goods from the
Spanish ships had carried goods from the
 Spain controlled the trade through the ''
Spain controlled the trade through the ''
 Every year, two fleets left Spain loaded with European goods in demand in Spanish America; they were guarded by military vessels. Valuable cargo from the Americas, most significantly silver from
Every year, two fleets left Spain loaded with European goods in demand in Spanish America; they were guarded by military vessels. Valuable cargo from the Americas, most significantly silver from
 Walton gives the following figures in pesos. For the 300-year period the
Walton gives the following figures in pesos. For the 300-year period the
 Despite the general perception that many Spanish galleons were captured by foreign
Despite the general perception that many Spanish galleons were captured by foreign
''The Spanish Mariners: From the Discovery of America to Trafalgar. 1492–1805. Observations and Reflections.'' Mexico, 1976
* Schurz, William Lytle. ''The Manila Galleon''. New York: E. P. Dutton & Co., Inc., 1939. * Walton, Timothy R.: ''The Spanish Treasure Fleets.'' Pineapple Press Inc, 2002. * Wyatt, Jack J.: ''Lions in the Water.'' Unrest Adventures, 2020. * Zarin, Cynthia. "Green Dreams", ''
www.newyorker.com
* ttp://www.carolinacoastonline.com/news_times/news/article_66e266e6-2f9b-5fba-9ff4-38503c5f0e6e.html Two firms seek ship Carolina Coast Online
Treasure hunter in race to uncover ship of riches
Google
New York Times
Shipwrecks and Treasure: the Spanish Treasure Fleet of 1750
Fayetteville Observer
News & Observer
Photographer suing state over Blackbeard shipwreck footage
WRAL-TV
News & Record
Controversy Over Blackbeard's Queen Anne's Revenge Continues
Public Radio East
Courthouse News
Plunder disputes plague the wreck of Blackbeard’s ship
Soundings {{DEFAULTSORT:Spanish Treasure Fleet Treasure fleet Treasure fleet Treasure fleet Sea lanes History of New Spain History of the Atlantic Ocean Naval warfare Anti-piracy History of international trade Age of Sail 17th century in Spain 18th century in Spain
 The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used ...
system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
from 1566 to 1790, which linked Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
with its territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
across the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
. The convoys were general purpose cargo fleets used for transporting a wide variety of items, including agricultural goods, lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
, various metal resources such as silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, gems, pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
s, spice
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spice ...
s, sugar, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
, and other exotic goods from the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
to the Spanish mainland. Spanish goods such as oil, wine, textiles, books and tools were transported in the opposite direction.
The West Indies fleet was the first permanent transatlantic trade route in history. Similarly, the related Manila galleon trade was the first permanent trade route across the Pacific. The Spanish West and East Indies fleets are considered among the most successful naval operations in history and, from a commercial point of view, they made possible key components of today's global economic system.
History
Origin
 Spanish ships had carried goods from the
Spanish ships had carried goods from the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
since Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
's first expedition of 1492. The organized system of convoys dates from 1564, but Spain sought to protect shipping prior to that by organizing protection around the largest Caribbean island, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, and the maritime region of southern Spain and the Canary Islands because of attacks by pirates and foreign navies. In the 1560s, the Spanish government created a system of convoys in response to the sacking of Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
by French privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s.
The main procedures were established based on the recommendations of Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, an experienced admiral and personal adviser of King Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
.Walton, pp. 46–47 The treasure fleets sailed along two sea lanes. The main one was the Caribbean Spanish West Indies
The Spanish West Indies or the Spanish Antilles (also known as "Las Antillas Occidentales" or simply "Las Antillas Españolas" in Spanish) were Spanish colonies in the Caribbean. In terms of governance of the Spanish Empire, The Indies was the d ...
fleet or ''Flota de Indias'', which departed in two convoys from Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula ...
, where the ''Casa de Contratación
The ''Casa de Contratación'' (, House of Trade) or ''Casa de la Contratación de las Indias'' ("House of Trade of the Indies") was established by the Crown of Castile, in 1503 in the port of Seville (and transferred to Cádiz in 1717) as a cr ...
'' was based, bound for ports such as Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, Portobelo and Cartagena before making a rendezvous at Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
in order to return together to Spain. A secondary route was that of the Manila Galleon
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire ...
s or ''Galeón de Manila'', which linked the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
to Acapulco in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
across the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. From Acapulco, the Asian goods were transhipped by mule train
"Mule Train" is a popular song written by Johnny Lange, Hy Heath, Ramblin' Tommy Scott and Fred Glickman. It is a cowboy song, with the singer filling the role of an Old West wagon driver, spurring on his team of mules pulling a delivery wagon. ...
to Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
to be loaded onto the Caribbean treasure fleet for shipment to Spain. To better defend this trade, Pedro Menéndez de Avilés and Álvaro de Bazán designed the definitive model of the galleon
Galleons were large, multi-decked sailing ships first used as armed cargo carriers by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries during the age of sail and were the principal vessels drafted for use as warships until the Anglo-Dutch W ...
in the 1550s.
''Casa de Contratación''
Casa de Contratación
The ''Casa de Contratación'' (, House of Trade) or ''Casa de la Contratación de las Indias'' ("House of Trade of the Indies") was established by the Crown of Castile, in 1503 in the port of Seville (and transferred to Cádiz in 1717) as a cr ...
'' based in Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula ...
, a river port in southern Spain. By law, the colonies could trade only with Seville, the one designated port in the mother country. Maritime archaeology
Maritime archaeology (also known as marine archaeology) is a discipline within archaeology as a whole that specifically studies human interaction with the sea, lakes and rivers through the study of associated physical remains, be they vessels, s ...
has shown that the quantity of goods transported was sometimes higher than that recorded at the ''Archivo General de Indias
The Archivo General de Indias (, "General Archive of the Indies"), housed in the ancient merchants' exchange of Seville, Spain, the ''Casa Lonja de Mercaderes'', is the repository of extremely valuable archival documents illustrating the history ...
''. Spanish merchants and Spaniards acting as fronts (''cargadores'') for foreign merchants sent their goods on these fleets to the New World. Some resorted to contraband to transport their cargoes untaxed. The Crown of Spain
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
taxed the wares and precious metals of private merchants at a rate of 20%, a tax known as the ''quinto real
The ''quinto real'' or the quinto del rey, the "King's fifth", was a 20% tax established in 1504 that Spain levied on the mining of precious metals. The tax was a major source of revenue for the Spanish monarchy. In 1723 the tax was reduced to 10%. ...
'' or royal fifth.
By the end of the 16th century, Spain became the richest country in Europe. Much of the wealth from this trade was used by the Spanish Habsburgs to finance armies to protect its European territories in the 16th and 17th centuries against the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and most of the major European powers. The flow of precious metals in and out of Spain also stimulated the European economy as a whole.
The flow of precious metals made many traders wealthy, both in Spain and abroad. As a result of the discovery of precious metals in Spanish America, Spain's money supply increased tenfold. The increase in gold and silver on the Iberian market caused high inflation in the 17th century, affecting the Spanish economy. As a consequence, the Crown was forced to delay the payment of some major debts, which had negative consequences for its creditors, mostly foreign bankers. By 1690 some of these creditors could no longer offer financial support to the Crown. The Spanish monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a speci ...
over its West and East Indies colonies lasted for over two centuries.
Decline, revival and abolition
The economic importance of exports later declined with the drop in production of the American precious metal mines, such as Potosí. However, the growth in trade was strong in the early years. Numbering 17 ships in 1550, the fleets expanded to more than 50 much larger vessels by the end of the century. By the second half of the 17th century, that number had dwindled to less than half of its peak. As economic conditions gradually recovered from the last decades of the 17th century, fleet operations slowly expanded again, once again becoming prominent during the reign of the Bourbons in the 18th century. The Spanish trade of goods was sometimes threatened by its colonial rivals, who tried to seize islands as bases along the Spanish Main and in theSpanish West Indies
The Spanish West Indies or the Spanish Antilles (also known as "Las Antillas Occidentales" or simply "Las Antillas Españolas" in Spanish) were Spanish colonies in the Caribbean. In terms of governance of the Spanish Empire, The Indies was the d ...
. However, the Atlantic trade was largely unharmed. The English acquired small islands like St Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially the Saint Christopher Island, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis cons ...
in 1624; expelled in 1629, they returned in 1639 and seized Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
in 1655. French pirates established themselves in Saint-Domingue in 1625, were expelled, only to return later, and the Dutch occupied Curaçao in 1634. Other losses to foreign powers came later. In 1713 as part of the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne ...
after the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
, the Spanish crown was forced to make concessions which included trading privileges for England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
that violated the previous Spanish monopoly on legal trade to its colonial holdings. In 1739 during the War of Jenkin's Ear
The War of Jenkins' Ear, or , was a conflict lasting from 1739 to 1748 between Britain and the Spanish Empire. The majority of the fighting took place in New Granada and the Caribbean Sea, with major operations largely ended by 1742. It is cons ...
, the British admirals Francis Hosier and later Edward Vernon blockaded Portobello in an attempt to prevent the return sailing of the treasure fleet. In 1741 Vernon's campaign against Cartagena de Indias ended in defeat, with high losses of men and ships. Spain dealt with the temporary British seizures of Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
and Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
(1762–4), during the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
, by using a larger number of smaller fleets visiting a greater variety of ports.
The end of the War of the Spanish Succession in 1713 marked the beginning of the rule of the Bourbon dynasty over the Spanish Empire, which brought with it the Bourbon Reforms
The Bourbon Reforms ( es, Reformas Borbónicas) consisted of political and economic changes promulgated by the Spanish Monarchy, Spanish Crown under various kings of the House of Bourbon, since 1700, mainly in the 18th century. The beginning of ...
. These reforms, designed to halt Spain's decline and increase tax revenue, resulted in a series of changes to the fleet system throughout the 18th century. Philip V began the reforms by sending investigators to report on conditions in Spanish America, who brought back evidence of fraud. He and following Bourbon kings, notably including Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person t ...
, would make a concerted effort to centralize the administration of Spanish America and more efficiently tax profits from overseas trade. One of these reforms was the granting of trading monopolies for certain regions to trading companies ran by peninsulares
In the context of the Spanish Empire, a ''peninsular'' (, pl. ''peninsulares'') was a Spaniard born in Spain residing in the New World, Spanish East Indies, or Spanish Guinea. Nowadays, the word ''peninsulares'' makes reference to Peninsular ...
, such as the Guipuzcoan Company. Another involved the increased use of registered ships, or ''navíos de registro'', traveling solo outside the fleet system to transport goods. These reforms gradually decreased reliance on the escorted convoys of the fleet system. In the 1780s, Spain opened its colonies to freer trade. In 1790, the ''Casa de Contratación
The ''Casa de Contratación'' (, House of Trade) or ''Casa de la Contratación de las Indias'' ("House of Trade of the Indies") was established by the Crown of Castile, in 1503 in the port of Seville (and transferred to Cádiz in 1717) as a cr ...
'' was abolished, bringing to an end the great general purpose fleets. Thereafter small groups of naval frigates were assigned specifically to transferring goods or bullion as required.
The fleets
 Every year, two fleets left Spain loaded with European goods in demand in Spanish America; they were guarded by military vessels. Valuable cargo from the Americas, most significantly silver from
Every year, two fleets left Spain loaded with European goods in demand in Spanish America; they were guarded by military vessels. Valuable cargo from the Americas, most significantly silver from Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, were sent back to Spain. Fleets of fifty or more ships sailed from Spain, one bound for the Mexican port of Veracruz and the other for Panama and Cartagena. From the Spanish ports of Seville or Cádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia.
Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, ...
, the two fleets bound for the Americas sailed together down the coast of Africa, and stopped at the Spanish territory of the Canary Islands for provisions before the voyage across the Atlantic. Once the two fleets reached the Caribbean, the fleets separated. The New Spain fleet sailed to Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
in Mexico to load not only silver and the valuable red dye cochineal
The cochineal ( , ; ''Dactylopius coccus'') is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessile parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America through North Americ ...
, but also porcelain and silk shipped from China on the Manila galleon
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire ...
s. The Asian goods were carried overland from Acapulco to Veracruz by mule train.
The '' Tierra Firme'' fleet, or galeones, sailed to Cartagena to load South American products, especially silver from Potosí. Some ships went to Portobello
Portobello, Porto Bello, Porto Belo, Portabello, or Portabella may refer to:
Places Brazil
* Porto Belo
Ireland
* Portobello, Dublin
* Cathal Brugha Barracks, Dublin formerly ''Portobello Barracks''
New Zealand
* Portobello, New Zealand, on Ot ...
on the Caribbean coast of Panama to load Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
vian silver. This had been shipped from the Pacific coast port of Callao and transported across the isthmus of Panama by mule. Other ships went to the Caribbean island of Margarita
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the northeastern coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island.
History
...
, off the coast of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, to collect pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
s which had been harvested from offshore oyster beds. After loading was complete, both fleets sailed for Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
, Cuba, to rendezvous for the journey back to Spain.
The overland journey by mule train, as well as supplies provided by local farmers to prepare the fleets for long ocean voyages, invigorated the economy of colonial Spanish America. Preparation and the transport of goods required porters, innkeepers, and foodstuffs to help facilitate travel. However, in Mexico in 1635, there was an increase of the sales tax levied to finance the fleet, the Armada de Barlovento.
Between 1703 and 1705 Spanish corsair Amaro Pargo began to participate in the West Indies Fleet. In this period he was the owner and captain of the frigate ''El Ave María y Las Ánimas'', a ship which he sailed from the port of Santa Cruz de Tenerife
The Port of Santa Cruz de Tenerife ( es, link=no, 'Puerto de Santa Cruz de Tenerife') in Santa Cruz de Tenerife, is used by fishing boats, commercial and passenger ships, and sports. Located on the Atlantic Ocean, it is managed by the Port Auth ...
to Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
. He reinvested the benefits of the Canarian-American trade in his estates, devoted to the cultivation of the grapevines of Malvasía and Vidueño, whose wine products (mainly Vidueño) were sent to America.
The flow of Spanish treasure
 Walton gives the following figures in pesos. For the 300-year period the
Walton gives the following figures in pesos. For the 300-year period the peso
The peso is the monetary unit of several countries in the Americas, and the Philippines. Originating in the Spanish Empire, the word translates to "weight". In most countries the peso uses the same sign, "$", as many currencies named "dollar" ...
or piece of eight
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
had about 25 grams of silver, about the same as the German thaler and Dutch rijksdaalder. A single galleon might carry 2 million pesos. The modern approximate value of the estimated 4 billion pesos produced during the period would come to $530 billion or €470 billion (based on silver bullion prices of May 2015). Of the 4 billion pesos produced, 2.5 billion was shipped to Europe, of which 500 million was shipped around Africa to Asia. Of the remaining 1.5 billion 650 million went directly to Asia from Acapulco and 850 million remained in the Western Hemisphere. Little of the wealth stayed in Spain. Of the 11 million arriving in 1590, 2 million went to France for imports, 6 million to Italy for imports and military expenses, of which 2.5 went up the Spanish road
The Spanish Road ( Spanish: ''Camino Español'', German: ''Spanische Straße'') was a military road and trade route in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries, linking the Duchy of Milan, the Franche-Comté and the Spanish Netherlands, ...
to the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
and 1 million to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. 1.5 million was shipped from Portugal to Asia. Of the 2 million pesos reaching the Dutch Republic in that year, 75% went to the Baltic for naval stores and 25% went to Asia. The income of the Spanish crown from all sources was about 2.5 million pesos in 1550, 14 million in the 1590s, about 15 million in 1760 and 30 million in 1780. In 1665 the debts of the Spanish crown were 30 million pesos short-term and 300 million long-term. Most of the New World production was silver, but Colombian mines produced mostly gold. The following table gives the estimated legal production. It necessarily excludes smuggling, which was increasingly important after 1600. The crown legally took one fifth (quinto real
The ''quinto real'' or the quinto del rey, the "King's fifth", was a 20% tax established in 1504 that Spain levied on the mining of precious metals. The tax was a major source of revenue for the Spanish monarchy. In 1723 the tax was reduced to 10%. ...
) at the source and obtained more through other taxes.
Losses
 Despite the general perception that many Spanish galleons were captured by foreign
Despite the general perception that many Spanish galleons were captured by foreign privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s and pirates, few fleets were actually lost to enemies in the course of the ''flota's'' two and a half centuries of operation. Only the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
admiral Piet Hein managed to capture an entire fleet, in the Battle in the Bay of Matanzas in 1628, after which its cargo was taken to the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
. The English admiral Robert Blake Robert Blake may refer to:
Sportspeople
* Bob Blake (American football) (1885–1962), American football player
* Robbie Blake (born 1976), English footballer
* Bob Blake (ice hockey) (1914–2008), American ice hockey player
* Rob Blake (born 196 ...
twice attacked the fleet, in the Battle of Cádiz in 1656 and in the Battle of Santa Cruz de Tenerife in 1657, but he managed to capture only a single galleon and Spanish officers managed to prevent most of the silver from falling into English hands. The West Indies fleet was destroyed in the Battle of Vigo Bay in 1702 during the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
, when it was surprised in port unloading its goods, but the Spanish sailors had already unloaded most of its cargo. None of these attacks took place in open seas. In the case of the Manila galleons, only four were ever captured by British warships in nearly three centuries: the ''Santa Anna'' by Thomas Cavendish
Sir Thomas Cavendish (1560 – May 1592) was an English explorer and a privateer known as "The Navigator" because he was the first who deliberately tried to emulate Sir Francis Drake and raid the Spanish towns and ships in the Pacific and retu ...
in 1589, the ''Encarnación'' by Woodes Rogers
Woodes Rogers ( 1679 – 15 July 1732) was an English sea captain, privateer, slave trader and, from 1718, the first Royal Governor of the Bahamas. He is known as the captain of the vessel that rescued marooned Alexander Selkirk, whose ...
in 1709, the ''Covadonga'' by George Anson in 1743, and the '' Santísima Trinidad'' in 1762. Two other British attempts were foiled by the ''Rosario'' in 1704 and the ''Begonia'' in 1710. These losses and others due to hurricanes were significant economic blows to trade.
Famous shipwrecks
Wrecks of Spanish treasure ships, whether sunk innaval combat
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river. Mankind has fought battles on the sea for more than 3,000 years. Even in the interior of large la ...
or, as was more usually the case, by storms (with the ones which occurred 1622, 1715
Events
For dates within Great Britain and the British Empire, as well as in the Russian Empire, the "old style" Julian calendar was used in 1715, and can be converted to the "new style" Gregorian calendar (adopted in the British Empire i ...
, 1733 and 1750 being among the worst), are a prime target for modern treasure hunters. Many, such as the ''Nuestra Señora de Atocha
''Nuestra Señora de Atocha'' ( es, Our Lady of Atocha) was a Spanish treasure galleon and the most widely known vessel of a fleet of ships that sank in a hurricane off the Florida Keys in 1622. At the time of her sinking, ''Nuestra Señora de ...
'', and the '' Santa Margarita'' have been salvaged. In August 1750, at least three Spanish merchantmen ran aground in North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
during a hurricane. The '' El Salvador'' sank near Cape Lookout, the ''Nuestra Señora De Soledad'' went ashore near present-day Core Banks
The Core Banks are barrier islands in North Carolina, part of the Outer Banks and Cape Lookout National Seashore. Named after the Coree tribe, they extend from Ocracoke Inlet to Cape Lookout, and consist of two low-relief narrow islands, North ...
and the ''Nuestra Señora De Guadalupe'' went ashore near present-day Ocracoke.
Encarnación
The wreck of the Spanishmerchant ship
A merchant ship, merchant vessel, trading vessel, or merchantman is a watercraft that transports cargo or carries passengers for hire. This is in contrast to pleasure craft, which are used for personal recreation, and naval ships, which are ...
'' Encarnación'', part of the Tierra Firme fleet, was discovered in 2011 with much of its cargo still aboard and part of its hull intact. The ''Encarnación'' sank in 1681 during a storm near the mouth of the Chagres River on the Caribbean side of Panama. The ''Encarnación'' sank in less than 40 feet of water. The remains of the '' Urca de Lima'' from the 1715 fleet and the '' San Pedro'' from the 1733 fleet, after being found by treasure hunters, are now protected as Florida Underwater Archaeological Preserves.
Capitana
The ''Capitana'' (El Rubi) was the flagship of the 1733 fleet; it ran aground during a hurricane nearUpper Matecumbe Key
Upper Matecumbe Key is an island in the upper Florida Keys.
U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway) crosses the key at approximately mile markers 79–83.5, between Windley Key and Lower Matecumbe Key.
All of the key is within the Village of Islamorada ...
, then sank. Three men died during the storm. Afterward, divers recovered most of the treasure aboard.
The ''Capitana'' was the first of the 1733 ships to be found again in 1938. Salvage workers recovered items from the sunken ship over more than 10 years. Additional gold was recovered in June 2015. The ship's location: is 24° 55.491' north, 80° 30.891' west.
San José
The '' San José'' was sunk in 1708 by British forces near Colombian's coasts. Its wreckage was discovered in 2015 and is believed to contain the record 17B US$ in gold, silver, and other precious stones. Its place is a national secret.Nuestra Señora de las Maravillas
The '' Nuestra Señora de las Maravillas'' ( de) ( en, Our Lady of Miracles) which had collided with another ship in the fleet suffered damage to its hull and sunk into a coral reef off theBahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
in January 1656. The ship's cargo with almost 3.5 million items was recovered between 1650s and 1990s, while latest discoveries would be exhibited at the Bahamas Maritime Museum.
See also
* '' Asiento de Negros'' * Álvaro de Bazán * List of Atlantic hurricanes before 1600 * Luis Fajardo *Manila galleon
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and Acapulco
, location = New Spain (Spanish Empire ...
* Piracy in the Caribbean
]The era of piracy in the Caribbean began in the 1500s and phased out in the 1830s after the navies of the nations of Western Europe and North America with colonies in the Caribbean began combating pirates. The period during which pirates were ...
* Portuguese India Armadas
The Portuguese Indian Armadas ( pt, Armadas da Índia) were the fleets of ships funded by the Crown of Portugal, and dispatched on an annual basis from Portugal to India. The principal destination was Goa, and previously Cochin. These armada ...
* ''San Esteban''
Notes
Further reading
* Andrews, Kenneth R. ''The Spanish Caribbean: Trade and Plunder, 1530–1630''. 1978. * Fish, Shirley. ''The Manila-Acapulco Galleons: The Treasure Ships of the Pacific, with an Annotated List of the Transpacific Galleons 1565–1815''. Central Milton Keynes, England: Authorhouse 2011. * Fisher, John R. "Fleet System (Flota)" in ''Encyclopedia of Latin American History and Culture'', vol. 2, p. 575. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons 1996. * Haring, Clarence. ''Trade and Navigation between Spain and the Indies in the Time of the Habsburgs'' (1918) * Haring, Clarence. ''The Spanish Empire in America'' New York: Oxford University Press 1947 * Murray, Paul''The Spanish Mariners: From the Discovery of America to Trafalgar. 1492–1805. Observations and Reflections.'' Mexico, 1976
* Schurz, William Lytle. ''The Manila Galleon''. New York: E. P. Dutton & Co., Inc., 1939. * Walton, Timothy R.: ''The Spanish Treasure Fleets.'' Pineapple Press Inc, 2002. * Wyatt, Jack J.: ''Lions in the Water.'' Unrest Adventures, 2020. * Zarin, Cynthia. "Green Dreams", ''
The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American weekly magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. Founded as a weekly in 1925, the magazine is published 47 times annually, with five of these issues ...
'', November 21, 2005, pp. 76–8www.newyorker.com
External links
* ttp://www.carolinacoastonline.com/news_times/news/article_66e266e6-2f9b-5fba-9ff4-38503c5f0e6e.html Two firms seek ship Carolina Coast Online
Treasure hunter in race to uncover ship of riches
New York Times
Shipwrecks and Treasure: the Spanish Treasure Fleet of 1750
Fayetteville Observer
News & Observer
Photographer suing state over Blackbeard shipwreck footage
WRAL-TV
News & Record
Controversy Over Blackbeard's Queen Anne's Revenge Continues
Public Radio East
Courthouse News
Plunder disputes plague the wreck of Blackbeard’s ship
Soundings {{DEFAULTSORT:Spanish Treasure Fleet Treasure fleet Treasure fleet Treasure fleet Sea lanes History of New Spain History of the Atlantic Ocean Naval warfare Anti-piracy History of international trade Age of Sail 17th century in Spain 18th century in Spain