Fishing industry in the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
As with other countries, the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off the coast of the
 On the
On the
 Until the late 19th century, the U.S. fishing fleet used sailing vessels. By the early 20th century, fishing vessels were built as steam boats with steam engines, or as schooners with auxiliary gasoline engines. By the 1930s the fleet was almost completely converted to diesel vessels. Fishing gear became more technical: Alaska
Until the late 19th century, the U.S. fishing fleet used sailing vessels. By the early 20th century, fishing vessels were built as steam boats with steam engines, or as schooners with auxiliary gasoline engines. By the 1930s the fleet was almost completely converted to diesel vessels. Fishing gear became more technical: Alaska
 By 2003,
By 2003,
Fisheries of the United States, 2003
 A marine protected area (MPA) is federally defined as: "any area of the marine environment that has been reserved by federal, state, tribal, territorial, or local laws or regulations to provide lasting protection for part or all of the natural and cultural resources therein."
Fourteen MPAs covering have been federally designated as
A marine protected area (MPA) is federally defined as: "any area of the marine environment that has been reserved by federal, state, tribal, territorial, or local laws or regulations to provide lasting protection for part or all of the natural and cultural resources therein."
Fourteen MPAs covering have been federally designated as
Federal Fisheries Investment Task Force
Report to Congress, July 1999.
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service.
Commercial Fishing Safety in the US
''
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
gives its fishing industry
The fishing industry includes any industry or activity concerned with taking, culturing, processing, preserving, storing, transporting, marketing or selling fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including ...
special fishing rights. It covers 11.4 million square kilometres (4.38 million sq mi), which is the second largest zone in the world, exceeding the land area of the United States.
According to the FAO, in 2005, the United States harvested 4,888,621 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of fish from wild fisheries, and another 471,958 tonnes from aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
. This made the United States the fifth leading producer of fish, after China, Peru, India, and Indonesia, with 3.8 percent of the world total.
Management
Historically,fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ...
developed in the U.S. as each area was settled. Concern for the sustainability of fishery resources was evident as early as 1871, when Congress wrote that "... the most valuable food fishes of the coast and the lakes of the U.S. are rapidly diminishing in number, to the public injury, and so as materially to affect the interests of trade and commerce..." However, it was not until 1976, with the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act, that the federal government began actively managing fisheries.
Today, inland fisheries and nearshore marine fisheries are managed by state (or regional or county) fisheries commissions. State jurisdictions usually extend out to sea. Coastal fisheries in the EEZ beyond state jurisdictions are the responsibility of the federal system. The primary institutions of the federal system are eight regional fishery management councils and the National Marine Fisheries Service
The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), informally known as NOAA Fisheries, is a United States federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) that is responsible for the stew ...
(NMFS), also known as NOAA Fisheries. NMFS works in partnership with industry, universities, and state, local, and tribal agencies to collect data about commercial species. Fisheries observer
A fisheries observer is an independent specialist who serves on board commercial fishing vessels, or in fish processing plants and other platforms, and is employed by a fisheries observer program, either directly by a government agency or by a t ...
s on fishing vessels, transmit real time data electronically to NMFS.
NMFS works in partnership with the regional fishery management councils to prevent overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
, and restore overfished stocks. Objectives are to reduce fishing intensity, monitor the fisheries, and implement measures to reduce bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
and protect essential fish habitat. NMFS is establishing marine protected areas and individual fishing quotas, and implementing ecosystem based fishery
The goal of fisheries management is to produce sustainable biological, environmental and socioeconomic benefits from renewable aquatic resources. Wild fisheries are classified as renewable when the organisms of interest (e.g., fish, shellfish, am ...
management.
Wild fisheries
EEZ
The U.S. EEZ is the second largest in the world, 1.7 times the land area of the US, and includes eightlarge marine ecosystem
Large marine ecosystems (LMEs) are regions of the world's oceans, encompassing coastal areas from river basins and estuaries to the seaward boundaries of continental shelves and the outer margins of the major ocean current systems. They are relat ...
s:
* Northeast U.S. Continental Shelf
* Southeast U.S. Continental Shelf
* Caribbean Sea
* Gulf of Mexico
* California Current
* Insular Pacific- Hawaiian
* Gulf of Alaska
* Eastern Bering Sea
The Bering Sea (, ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Ameri ...
Catch profile

Nearshore fisheries
Nearshore fishing areas consist of estuaries and coastal areas that lie within of the shoreline. These are under the control of the relevant coastal state rather than underfederal
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
or NMFS control. They vary widely in species diversity and abundance. Many species are highly prized game fish, while others are small forage fish used for bait, animal food, and industrial products. Those of greatest interest include invertebrate species like crabs, shrimps, abalones, clams, oysters, and scallops. Many species are of unknown status because it is difficult to assess their condition. There are no firm estimates exist for long term potential yield.
Management is spread out among the coastal states and other local authorities, and a comprehensive treatment of the fisheries has not been attempted. Traditional techniques are usually employed, including size limits, catch limits, method restrictions, and area and time closures.
Coastal fisheries
The coastal fisheries are the fisheries that lie within of the coast that defines the exclusive economic zone, but outside the distance that defines the nearshore fisheries. Coastal fisheries are under federal control in the form of NMFS, as well as under the control of one of the eight regional fishery management councils.Northeast
Traditionally the most valued fishery for the northeast region has beengroundfish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
. However, the groundfish, especially haddock, yellowtail flounder
The yellowtail flounder (''Limanda ferruginea''), also known as the rusty dab, is a species of flatfish in the family Pleuronectidae (righteye flounders). Reaching in length, it has reddish brown upperparts, pale underparts and yellow fins. Bot ...
, and cod
Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus '' Gadus'', belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not call ...
, have been overfished. Record-low spawning biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
levels occurred in 1993–1994, but these are now recovering. Dogfish and skate
Skate or Skates may refer to: Fish
*Skate (fish), several genera of fish belonging to the family Rajidae
* Pygmy skates, several genera of fish belonging to the family Gurgesiellidae
* Smooth skates or leg skates, several genera of fish belongin ...
rebounded in the 1970s, while groundfish and flounder declined. These fish are an important part of the Georges Bank.
The next most important fishery by value is American lobster
The American lobster (''Homarus americanus'') is a species of lobster found on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of North America, chiefly from Labrador to New Jersey. It is also known as Atlantic lobster, Canadian lobster, true lobster, norther ...
and Atlantic sea scallop
''Placopecten magellanicus'', previously listed as ''Pecten tenuicostatus'' and as ''Pecten grandis'' and once referred to as the "giant scallop", common names Atlantic deep-sea scallop, deep sea scallop, North Atlantic sea scallop, American ...
. The Port of New Bedford, Massachusetts is America's #1 Fishing Port with fish landings valued at $369 million. Each year, there are nearly 50 million pounds of sea scallops landed there. The striped bass
The striped bass (''Morone saxatilis''), also called the Atlantic striped bass, striper, linesider, rock, or rockfish, is an anadromous perciform fish of the family Moronidae found primarily along the Atlantic coast of North America. It has al ...
was driven to low levels early in the 1980s. Catch restrictions were applied in the mid 1980s, and by 1995, this species of fish had recovered. The region has valuable mollusk fisheries too. Offshore are sea scallops, surfclams, American lobsters, and ocean quahog
The ocean quahog (''Arctica islandica'') is a species of edible clam, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Arcticidae. This species is native to the North Atlantic Ocean, and it is harvested commercially as a food source. This species is ...
. Inshore are oysters, blue mussels, blue crab Blue crab may refer to:
* Blue Crab 11, an American sailboat design
* ''Callinectes sapidus'' – Chesapeake or Atlantic blue crab of the West Atlantic, introduced elsewhere
* ''Cardisoma guanhumi'' – blue land crab of the West Atlantic
* '' Disc ...
s, and clam fisheries. These fisheries are pretty much fully exploited.
The fisheries in the Northeast Region are governed mostly by Fishery Management Plans (FMPs). An example of successful regulation is the 1994 Amendment 4 to the Sea Scallop FMP. This set out to control scallop fishing effort by not accepting more entrants, by restricting the time vessels could fish each day, and by requiring bigger mesh sizes on dredges
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
. Additional protection for scallops was given closing parts of Georges Bank to groundfish fishing. The scallops recovered.
Southeast
The Southeast region spans the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea and the US Southeast Atlantic. Important species are menhaden,drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a she ...
, croaker, invertebrates, highly migratory species
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousan ...
, reef fish, and other nearshore species.
Overfishing of king and Spanish mackerel occurred in the 1980s. Regulations were introduced to restrict the size, amount of catch, fishing locations, and bag limits for recreational fishers as well as commercial fishers. Gillnet
Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is ...
s were banned in waters off Florida. By 2001, the mackerel stocks had bounced back.
Menhaden and stone crabs and the three major species of shrimp - ( pink, brown, and white) - are fully exploited. Spiny lobster are over-exploited. Better data is needed if stocks are to be assessed accurately.
Until 2016, commercial fish farming was prohibited in federal waters, meaning that the Gulf of Mexico was closed to the practice. NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
announced in January 2016, however, that companies can now set up commercial aquaculture in the Gulf. This is the first opening of federal waters to fish farming, which NOAA hopes will increase production and reduce the US's dependence on foreign fish imports.
Pacific Coast
 On the
On the Pacific Coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
, important rich resources and species are chum
Chum may refer to:
Broadcasting
* CHUM Limited, a defunct Canadian media company
* CHUM Radio, now Bell Media Radio, a Canadian radio broadcasting company
* CHUM (AM), a Toronto radio station
* CHUM-FM, a Toronto radio station
* CHUM Chart, a C ...
, Pacific halibut, Pacific salmon, shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater envir ...
, groundfish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
, flatfish
A flatfish is a member of the Ray-finned fish, ray-finned demersal fish order (biology), order Pleuronectiformes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the ...
, pelagic fishes, herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
, and nearshore species. The stocks are mostly overfished or fully exploited.
* Salmon: Salmon production has decreased since the late 1970s, partly due to habitat degradation.
* Groundfish: this harvest is dominated by Pacific whiting. Some stocks need rebuilding. Rockfish can live as long as 100 years, and grow and reproduce very slowly. This makes stock recovery very slow. In 2004, plans for rebuilding several overfished groundfish species were approved.
* Shellfish: Shellfish, such as crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s, clams, shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
, and abalone
Abalone ( or ; via Spanish , from Rumsen ''aulón'') is a common name for any of a group of small to very large marine gastropod molluscs in the family (biology), family Haliotidae. Other common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon o ...
, sell for high prices, so their fisheries can be small by volume, but high by value. These fisheries are mostly fully exploited. Recreational fishers catch more of some species than the commercial fishers.
* Recovering stocks: After decades of decline, Pacific sardine
''Sardinops'' is a monotypic genus of sardines of the family Clupeidae. The only member of the genus is ''Sardinops sagax''. It is found in the Indo-Pacific and East Pacific oceans. Its length is up to . It has numerous common or vernacular names ...
populations are recovering. In 2004, the NMFS declared that, due to reduced harvest and bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
, Pacific whiting were recovering.
In Alaska, the Aleutian Islands, a series of over 300 rocky islands, stretch over from southwest Alaska to Russia. They are home to the largest fishing port in the U.S., Dutch Harbor. The primary target species is pollock, but crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s, salmon, and groundfish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
are also important. Between 1997 and 2001, groundfish were caught by bottom trawling, a fishing method which destroys the habitat of the groundfish, the ocean floor coral, and sponge communities. In 2005, about 80,000 km2 (30,000 sq mi) of seafloor around the Aleutian Islands were permanently closed to destructive fishing gears. In 2008, NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
fisheries created the Aleutian Islands Habitat Conservation Area (AIHCA), most of which is closed to bottom trawling. At 725,000 km2 (280,000 sq mi), the AIHCA is the largest marine protected area in the USA.
Western Pacific
The Western Pacific region includes the western and central Pacific, theHawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
, and the islands of the Northern Marianas, Guam, and American Samoa. These are tropical or subtropical waters. They have large species diversity, but, because ocean nutrients are not rich, the sustainable yields is low. Pelagic armorhead
Pentacerotidae or armourheads are a small family of fishes in the order Perciformes. They are native to the Indian Ocean, western and central Pacific, and southwestern Atlantic. They are generally found at rocky reefs below normal scuba diving d ...
is the only overfished stock.
* Groundfish fisheries: Groundfish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
, such as snapper, jacks, emperors, and grouper, are harvested from coral and rock habitats, mostly around the Hawaiian Islands. While some stocks are under-utilized, other important species have declined to 30 percent of their earlier stock levels.
* Invertebrate fisheries: The main invertebrate fisheries are in the north west Hawaiian Islands for slipper and spiny lobster. This fishery started in 1977, peaked in the mid 1980s, and then declined. The decline is thought to stem from oceanographic changes. Some recovery has occurred since 1991, due to entry and harvest restrictions.
* Highly migratory species
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousan ...
account for 99 percent catch in this region, and are discussed below.
High sea fisheries
The high seas, or international waters, are the waters outside the jurisdiction of the EEZ of any country. U. S. distant fisheries operate in some of these waters, alongside other nations, beyond the jurisdiction of any nation's coastal fisheries.Highly migratory species
The main commercial species in the high seas are thehighly migratory species
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousan ...
. These fish make long migrations across the high seas, and are fished by many nations. Highly migratory fish also cross boundaries without regard for international laws. In particular, they enter the EEZ zones of the U.S., which means they become important species also for U.S. coastal fisheries.
In the Atlantic, overfished species include:
* Tuna: bigeye in the Atlantic, albacore in the North Atlantic, and bluefin Bluefin or Blue Fin and variants may refer to:
Fish
* Bluefin tuna, multiple species of tuna
* Bluefin damsel (''Neoglyphidodon melas''), damselfish
* Bluefin driftfish (''Psenes pellucidus'')
* Bluefin gurnard (''Chelidonichthys kumu''), fish in t ...
in the West Atlantic, with yellowfin tuna close to being overfished.
* Blue marlin
''Makaira'' (Latin via Greek: ''μαχαίρα'' "sword") is a genus of marlin in the family Istiophoridae. It includes the Atlantic blue, and Indo-Pacific blue marlins. In the past, the black marlin was also included in this genus, but today ...
, white marlin, and sailfish.
* Sharks: bull, dusky, bignose, night, Caribbean reef, spinner, silky, tiger, lemon, sand, nurse, scalloped, smooth hammerhead
The smooth hammerhead (''Sphyrna zygaena'') is a species of hammerhead shark, and part of the family Sphyrnidae. This species is named "smooth hammerhead" because of the distinctive shape of the head, which is flattened and laterally extended int ...
, and white shark
The great white shark (''Carcharodon carcharias''), also known as the white shark, white pointer, or simply great white, is a species of large mackerel shark which can be found in the coastal surface waters of all the major oceans. It is nota ...
.
The biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
of swordfish
Swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as broadbills in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category, though elusive. Swordfis ...
in the North Atlantic has increased, probably due to catch reduction and strong recruitment.
In the Pacific, these transboundary fisheries are also important to other Pacific Rim
The Pacific Rim comprises the lands around the rim of the Pacific Ocean. The ''Pacific Basin'' includes the Pacific Rim and the islands in the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Rim roughly overlaps with the geologic Pacific Ring of Fire.
List of co ...
nations, and to U.S. fleets fishing within and beyond the EEZ. The major U.S. catch stock is tuna, though billfish, swordfish, and shark are also caught. These stocks account for 99 percent of the Western Pacific region's catch.
Seamounts
Aseamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach the ocean surface. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise at least 1,000 meters above the seafloor. Seamounts became interesting during the 1960s, when it was discovered that they can maintain large stocks of commercially important fishes and invertebrates. From 1968 to about 1990, foreign fleets harvested pelagic armorhead
Pentacerotidae or armourheads are a small family of fishes in the order Perciformes. They are native to the Indian Ocean, western and central Pacific, and southwestern Atlantic. They are generally found at rocky reefs below normal scuba diving d ...
across seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abru ...
s in the Hawaiian Ridge. Since 1984, fishing has been prohibited there so the stock can recover.
Generally, seamounts are found in the high seas, outside the continental shelves, and outside the jurisdiction of any nation's EEZ. However, the U.S. Pacific Coast region has an unusually small continental shelf, while the Western Coast region contains islands with no continental shelf. As a result, there are some seamounts within U.S. jurisdiction.
Inland fisheries
Fisheries in inland waters of the United States are small compared to marine fisheries. The largest fisheries are the landings from the Great Lakes, worth about $13 million in 2003, with a similar amount from the Mississippi River basin. This is less than one percent of the dollar value of the marine fisheries.Fishing fleet
 Until the late 19th century, the U.S. fishing fleet used sailing vessels. By the early 20th century, fishing vessels were built as steam boats with steam engines, or as schooners with auxiliary gasoline engines. By the 1930s the fleet was almost completely converted to diesel vessels. Fishing gear became more technical: Alaska
Until the late 19th century, the U.S. fishing fleet used sailing vessels. By the early 20th century, fishing vessels were built as steam boats with steam engines, or as schooners with auxiliary gasoline engines. By the 1930s the fleet was almost completely converted to diesel vessels. Fishing gear became more technical: Alaska purse seiner
A fishing vessel is a boat or ship used to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Many different kinds of vessels are used in commercial, artisanal and recreational fishing.
The total number of fishing vessels in the world in 2016 was es ...
s were in use by 1870, longliners were introduced in 1885; otter trawl
Bottom trawling is trawling (towing a trawl, which is a fishing net) along the seafloor. It is also referred to as "dragging". The scientific community divides bottom trawling into benthic trawling and demersal trawling. Benthic trawling is towin ...
s were operating in the groundfish
Demersal fish, also known as groundfish, live and feed on or near the bottom of seas or lakes (the demersal zone).Walrond Carl . "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009 They occ ...
and shrimp fisheries
The shrimp fishery is a major global industry, with more than 3.4 million tons caught per year, chiefly in Asia. Rates of bycatch are unusually high for shrimp fishing, with the capture of sea turtles being especially contentious.
A shrimper is a ...
by the early 20th century. In the late 1960s, factory ships from other countries started fishing haddock, herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
, salmon, and halibut on traditional U.S. fishing grounds.
Technological advances have played an important role in the development of U.S. fisheries.
Increases in size and speed allowed vessels to fish in more distant waters. Advances include double trawls, the Puretic power block
The Puretic power block is a special kind of mechanised winch used to haul nets on fishing vessels. The power block is a large powered aluminium pulley with a hard rubber-coated sheave. While many men were needed for the back-breaking work of ha ...
s for retrieving seine nets, refrigerated holds, durable synthetic fibres
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling differences) are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants (like cotton) ...
for lines
Line most often refers to:
* Line (geometry), object with zero thickness and curvature that stretches to infinity
* Telephone line, a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system
Line, lines, The Line, or LINE may also refer to:
Arts ...
and nets, GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
to navigate and locate fishing grounds, fishfinders for the location of fish, and spotter plane
A surveillance aircraft is an aircraft used for surveillance. They are operated by military forces and other government agencies in roles such as intelligence gathering, battlefield surveillance, airspace surveillance, reconnaissance, observat ...
s to locate fish schools.
The vessel size and gear types of the U.S. fishing fleet varies geographically and between fisheries. Because of this, management of U.S. fisheries with a single policy is not feasible. Individual fisheries have their own biological, economic, and sociological characteristics which make broad policies impractical. On the other hand, ad hoc regulations for individual fisheries is not practical either.
U.S. fisheries use most fishing gear types. Vessels are often configured so they can change rapidly between two or more gear types, such as lobster pots to bottom trawls to scallop dredges. The main techniques are purse seining
Seine fishing (or seine-haul fishing; ) is a method of fishing that employs a surrounding net, called a seine, that hangs vertically in the water with its bottom edge held down by weights and its top edge buoyed by floats. Seine nets can be de ...
and trawling. Some vessels freeze their catch at sea, such as factory trawler
A factory ship, also known as a fish processing vessel, is a large ocean-going vessel with extensive on-board facilities for Fish processing, processing and freezing caught fish or whales. Modern factory ships are automated and enlarged versions ...
s, tuna boats, Alaskan crab pot vessels, and some southeast shrimp trawlers. Vessels usually land their catches near their homeports.
Bycatch mitigation
Based in Hawaii, alongline Long line or longline may refer to:
*''Long Line'', an album by Peter Wolf
*Long line (topology), or Alexandroff line, a topological space
*Long line (telecommunications), a transmission line in a long-distance communications network
*Longline fish ...
fishery for tuna and billfish were popular. Now, new management approaches, including placing fisheries observer
A fisheries observer is an independent specialist who serves on board commercial fishing vessels, or in fish processing plants and other platforms, and is employed by a fisheries observer program, either directly by a government agency or by a t ...
s on vessels to observe what is happening with protected species such as albatross and leatherback, loggerhead and green sea turtles, is expected to reduce incidental catch.
Overfished stocks
 By 2003,
By 2003, overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing fish stock), resulting in th ...
had occurred on 60 stocks. Another 232 stocks were not overfished. Overfishing had been stopped on 31 stocks, and a gain was made of 13 stocks that had been fully rebuilt. There were 617 other stocks which have limited data or for which criteria for overfishing had not been defined. These stocks mostly have harvests which are not significant, so they are not allocated research funding. Their assessment can be expensive, and there is no evidence of overfishing. Rebuilding strategies are operating or are being developed for most stocks which are overfished.
There were 267 major stocks, that is, stocks with at least 200,000 pounds (91,000 kg) in annual landings. Of these, 40 were overfished, 147 were not, and it was not known whether the remaining 80 stocks were overfished. There were 642 minor stocks, of which 20 were overfished, 85 were not, and the remainder had an overfishing status which is unknown or is undefined.
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
/ NMFS: (2004Fisheries of the United States, 2003
Marine protected areas
 A marine protected area (MPA) is federally defined as: "any area of the marine environment that has been reserved by federal, state, tribal, territorial, or local laws or regulations to provide lasting protection for part or all of the natural and cultural resources therein."
Fourteen MPAs covering have been federally designated as
A marine protected area (MPA) is federally defined as: "any area of the marine environment that has been reserved by federal, state, tribal, territorial, or local laws or regulations to provide lasting protection for part or all of the natural and cultural resources therein."
Fourteen MPAs covering have been federally designated as National Marine Sanctuaries
A U.S. National Marine Sanctuary is a zone within United States waters where the marine environment enjoys special protection. The program began in 1972 in response to public concern about the plight of marine ecosystems.
A U.S. National Marine ...
, and are administered by a division of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
In practice, these MPAs are defined areas where natural and/or cultural resources are given more protection than occurs in the surrounding waters. United States MPAs cover many habitats including the open ocean, coastal areas, intertidal zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species o ...
s, estuaries, and the Great Lakes. They vary in purpose, legal authorities, agencies, management approaches, level of protection, and restrictions on human uses.
Aquaculture
The value ofaquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
products grew from $45 million in 1974 to about $866 million (393,400 tonnes) in 2003.
Aquaculture, in the United States, includes the farming of hatchery fish and shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater envir ...
which are grown to market size in ponds, tanks, cages, or raceway
RaceTrac, Inc. is an American corporation that operates a chain of gasoline service stations across the Southern United States. The firm is Georgia's third largest private company, with sales of $9.1 billion in 2013.
History
The company was fou ...
s, and released into the wild. Aquaculture is also used to support commercial and recreational marine fisheries by enhancing or rebuilding wild stock populations. It also includes the cultivation of ornamental fish for the aquarium
An aquarium (plural: ''aquariums'' or ''aquaria'') is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aq ...
trade, as well as plant species used in various pharmaceutical, nutritional, and biotechnology products.Aquaculture in the United StatesNOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
Aquaculture Program. Retrieved 4 January 2009.
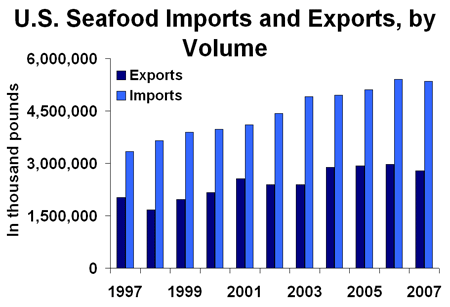
According to the FAO, in 2004 the United States ranked 10th in total aquaculture production, behind China, India, Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Japan, Chile, and Norway. The United States imports aquaculture products from these and other countries, and operates an annual seafood trade deficit of over $9 billion.
Shellfish ( oysters, clams, mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
s), account for two-thirds of marine aquaculture production, followed by salmon (25 percent) and shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are refer ...
(10 percent). Production occurs mainly on land, in ponds, and in coastal waters under state jurisdiction. As a result of recent advances in offshore aquaculture technology, commercial finfish and shellfish operations have been established in more exposed, open ocean locations in state waters in New Hampshire, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico.
Total U.S. aquaculture production, including aquatic plants
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments (saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that ...
, is about $1 billion annually, compared to the total world production of about $70 billion. Only about 20 percent of U.S. aquaculture production is from marine species. NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
estimates that the annual U.S. domestic aquaculture production of all species could increase from about 0.5 million tons to 1.5 million tons by 2025.
Environmental regulations
Large aquaculture facilities (i.e. those producing per year) which discharge wastewater are required to obtain permits pursuant to theClean Water Act
The Clean Water Act (CWA) is the primary federal law in the United States governing water pollution. Its objective is to restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters; recognizing the responsibiliti ...
. Facilities that produce at least of fish, molluscs or crustaceans a year are subject to specific national discharge standards. Other permitted facilities are subject to effluent limitations that are developed on a case-by-case basis.
Subsidies
In a study of federal investment in the fishery sector in 1999, most aspects of United States tax, fisheries, and societal policies were examined to see whether they createdsubsidies for the fishing industry A fisheries subsidy is a government action that confers an advantage on consumers or extractors of fish in order to supplement their income or lower their cost. Fisheries subsidy are addressed in sustainable development goal 14 where target 14.6 wo ...
and whether these subsidies had impacts. The gross value of direct U.S. subsidies was about 0.5% of the gross ex-vessel value of commercial landings. There are no major ship construction subsidies, market development, or other forms of assistance that often exist in developed and developing fishing industries around the world.Report to Congress, July 1999.
Recreational
In 2006, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service estimated that 30.0 million U.S. anglers, 16 years old and older, took 403 million fishing trips, spending $42.0 billion in fishing related expenses. Of these, 25.4 million were freshwater anglers who took 337 million trips and spent $26.3 billion. Saltwater fishing attracted 7.7 million anglers who took 67 million trips and spent $8.9 billion.2006 National Survey of Fishing, Hunting, and Wildlife-Associated RecreationU.S. Fish & Wildlife Service.
See also
* Magnuson-Stevens Fisheries Conservation and Management Act of 1976 * Tidelands *Continental shelf of the United States
The continental shelf of the United States is the total of the continental shelves adjacent to the United States. In the context of the international law as defined by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, it is seabed and subsoil ...
References
External links
Commercial Fishing Safety in the US
''
CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency, under the United S ...
''.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fishing Industry in the United States