Tachyglossus aculeatus side on.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The short-beaked echidna (''Tachyglossus aculeatus''), also called the short-nosed echidna, is one of four living species of echidna and the only member of the genus ''Tachyglossus''. It is covered in fur and spines and has a distinctive
 The short-beaked echidna was commonly called the spiny anteater in older books, though this term has fallen out of fashion since the echidna bears no relation to the true anteaters. It has a variety of names in the indigenous languages of the regions where it is found. The
The short-beaked echidna was commonly called the spiny anteater in older books, though this term has fallen out of fashion since the echidna bears no relation to the true anteaters. It has a variety of names in the indigenous languages of the regions where it is found. The

 Short-beaked echidnas are typically in length, with of snout, and weigh between .Egerton, p. 38. However, the Tasmanian subspecies, ''T. a. setosus'', is smaller than its Australian mainland counterparts.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 6. Because the neck is not externally visible, the head and body appear to merge. The earholes are on either side of the head, with no external pinnae. The eyes are small, about in diameter and at the base of the wedge-shaped snout.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 55. The nostrils and the mouth are at the distal end of the snout;Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 2. the mouth cannot open wider than . The body of the short-beaked echidna is, with the exception of the underside, face and legs, covered with cream-coloured spines. The spines, which may be up to long, are modified hairs, mostly made of keratin.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 35. Insulation is provided by fur between the spines, which ranges in colour from honey to a dark reddish-brown and even black; the underside and short tail are also covered in fur.
The echidna's fur may be infested with what is said to be one of the world's largest fleas, '' Bradiopsylla echidnae'', which is about long.
The limbs of the short-beaked echidna are adapted for rapid digging; they are short and have strong claws. Their strong and stout limbs allow it to tear apart large logs and move paving stones, and one has been recorded moving a 13.5-kg (30-lb) stone; a scientist also reported that a captive echidna moved a refrigerator around the room in his home.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 100. The power of the limbs is based on strong musculature, particularly around the shoulder and torso areas. The mechanical advantage of its arm is greater than that of humans, as its biceps connects the shoulder to the forearm at a point further down than for humans, and the chunky
Short-beaked echidnas are typically in length, with of snout, and weigh between .Egerton, p. 38. However, the Tasmanian subspecies, ''T. a. setosus'', is smaller than its Australian mainland counterparts.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 6. Because the neck is not externally visible, the head and body appear to merge. The earholes are on either side of the head, with no external pinnae. The eyes are small, about in diameter and at the base of the wedge-shaped snout.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 55. The nostrils and the mouth are at the distal end of the snout;Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 2. the mouth cannot open wider than . The body of the short-beaked echidna is, with the exception of the underside, face and legs, covered with cream-coloured spines. The spines, which may be up to long, are modified hairs, mostly made of keratin.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 35. Insulation is provided by fur between the spines, which ranges in colour from honey to a dark reddish-brown and even black; the underside and short tail are also covered in fur.
The echidna's fur may be infested with what is said to be one of the world's largest fleas, '' Bradiopsylla echidnae'', which is about long.
The limbs of the short-beaked echidna are adapted for rapid digging; they are short and have strong claws. Their strong and stout limbs allow it to tear apart large logs and move paving stones, and one has been recorded moving a 13.5-kg (30-lb) stone; a scientist also reported that a captive echidna moved a refrigerator around the room in his home.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 100. The power of the limbs is based on strong musculature, particularly around the shoulder and torso areas. The mechanical advantage of its arm is greater than that of humans, as its biceps connects the shoulder to the forearm at a point further down than for humans, and the chunky  The musculature of the short-beaked echidna has a number of unusual aspects. The
The musculature of the short-beaked echidna has a number of unusual aspects. The 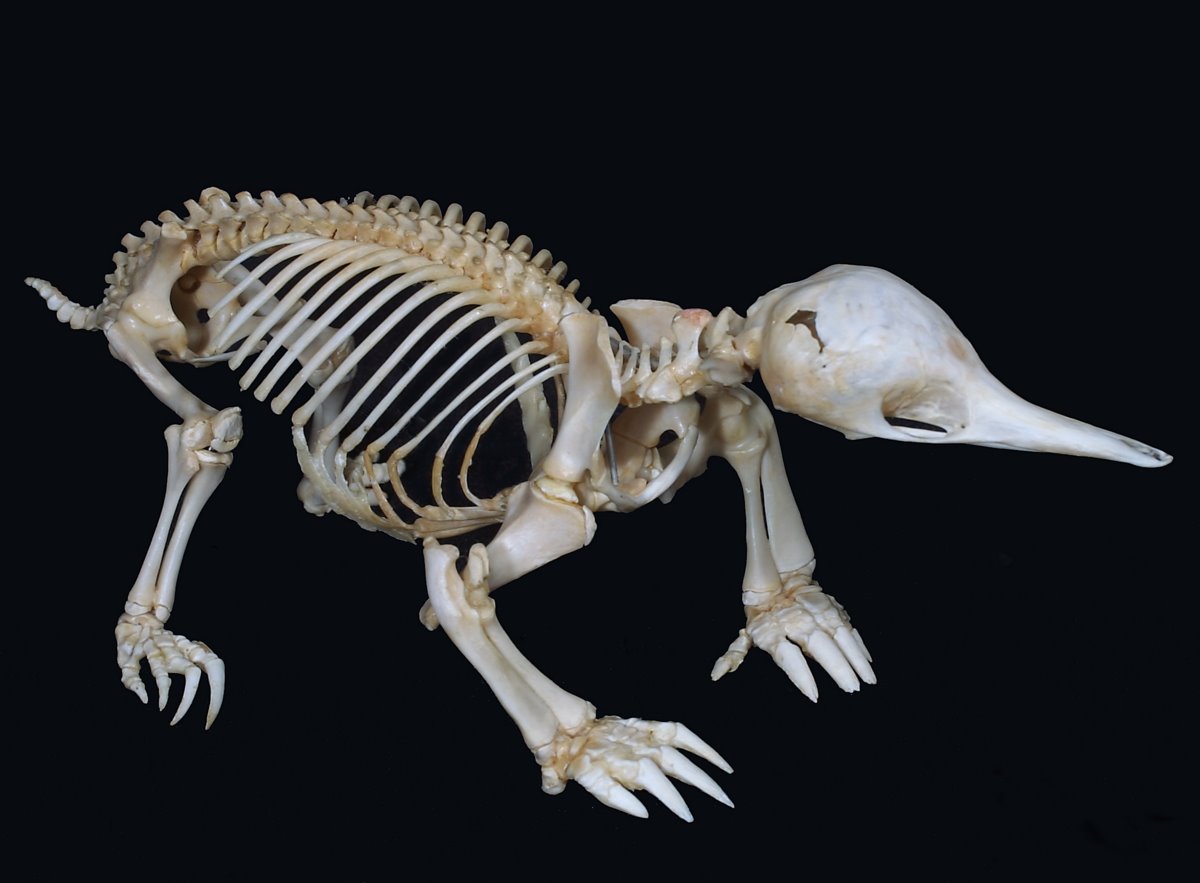 The leathery snout is keratinised and covered in mechano- and thermoreceptors, which provide information about the surrounding environment.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 66. These nerves protrude through microscopic holes at the end of the snout,Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 68. which also has mucus glands on the end that act as electroreceptors. Echidnas can detect
The leathery snout is keratinised and covered in mechano- and thermoreceptors, which provide information about the surrounding environment.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 66. These nerves protrude through microscopic holes at the end of the snout,Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 68. which also has mucus glands on the end that act as electroreceptors. Echidnas can detect
figure
ref name = "Rensetal2007"/>), while females are X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5. Weak identity between chromosomes results in meiotic pairing that yields only two possible
 The short-beaked echidna is common throughout most of temperate Australia and lowland New Guinea, and is not listed as endangered. In Australia, it remains widespread across a wide range of conditions, including urban outskirts, coastal forests and dry inland areas, and is especially widespread in Tasmania and on Kangaroo Island.
The most common threats to the animal in Australia are motor vehicles and habitat destruction, which have led to localized extinctions.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 120. In Australia, the number of short-beaked echidnas has been less affected by land clearance than have some other species, since they do not require a specialized habitat beyond a good supply of ants and termites. As a result, they can survive in cleared land if the cut-down wood is left in the area, as the logs can be used as shelters and sources of insects. However, areas where the land has been completely cleared for single crops that can be mechanically harvested, such as wheat fields, have seen extinctions. Over a decade-long period, around one-third of echidna deaths reported to wildlife authorities in Victoria were due to motor vehicles, and the majority of wounded animals handed in were traffic accident victims. Studies have shown they often choose to traverse drainage culverts under roads, so this is seen as a viable means of reducing deaths on busy roads in rural areas or national parks where the animals are more common.
Despite their spines, they are preyed on by birds of prey, the
The short-beaked echidna is common throughout most of temperate Australia and lowland New Guinea, and is not listed as endangered. In Australia, it remains widespread across a wide range of conditions, including urban outskirts, coastal forests and dry inland areas, and is especially widespread in Tasmania and on Kangaroo Island.
The most common threats to the animal in Australia are motor vehicles and habitat destruction, which have led to localized extinctions.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 120. In Australia, the number of short-beaked echidnas has been less affected by land clearance than have some other species, since they do not require a specialized habitat beyond a good supply of ants and termites. As a result, they can survive in cleared land if the cut-down wood is left in the area, as the logs can be used as shelters and sources of insects. However, areas where the land has been completely cleared for single crops that can be mechanically harvested, such as wheat fields, have seen extinctions. Over a decade-long period, around one-third of echidna deaths reported to wildlife authorities in Victoria were due to motor vehicles, and the majority of wounded animals handed in were traffic accident victims. Studies have shown they often choose to traverse drainage culverts under roads, so this is seen as a viable means of reducing deaths on busy roads in rural areas or national parks where the animals are more common.
Despite their spines, they are preyed on by birds of prey, the
Echidna : extraordinary egg-laying mammal
'. Collingwood, Victoria, CSIRO Publishing * Egerton, L. ed. 2005. ''Encyclopedia of Australian wildlife''. Reader's Digest
Tachyglossidae
pp. 407–435 in ''Fauna of Australia'' (D. W. Walton and B. J. Richardson, eds.). Mammalia, Canberra, Australian Capital Territory 1B:1–1227.
Tasmanian Department of Water, Primary Industries and Environment – Short-beaked echidna
article with sound clips and images of puggles {{Taxonbar, from=Q193182, from2=Q12902259 Mammals of South Australia Mammals of Tasmania Mammals of Western Australia Mammals of the Northern Territory Mammals of New South Wales Mammals of Queensland Mammals of Victoria (Australia) Mammals of Papua New Guinea Mammals of Western New Guinea Monotremes of New Guinea
snout
A snout is the protruding portion of an animal's face, consisting of its nose, mouth, and jaw. In many animals, the structure is called a muzzle, rostrum, or proboscis. The wet furless surface around the nostrils of the nose of many mammals is c ...
and a specialized tongue, which it uses to catch its insect prey at a great speed. Like the other extant monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brain ...
s, the short-beaked echidna lays eggs; the monotremes are the only living group of mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s to do so.
The short-beaked echidna has extremely strong front limbs and claws, which allow it to burrow quickly with great power. As it needs to be able to survive underground, it has a significant tolerance to high levels of carbon dioxide and low levels of oxygen. It has no weapons or fighting ability but repels predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
by curling into a ball and deterring them with its spines. It lacks the ability to sweat and cannot deal with heat well, so it tends to avoid daytime activity in hot weather. It can swim if needed. The snout has mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are innervated by sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals that, in animals, ...
s and electroreceptors
Electroreception and electrogenesis are the closely-related biological abilities to perceive electrical stimuli and to generate electric fields. Both are used to locate prey; stronger electric discharges are used in a few groups of fishes to stu ...
that help the echidna to detect its surroundings.
During the Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
n winter, it goes into deep torpor and hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
, reducing its metabolism to save energy. As the temperature increases, it emerges to mate
Mate may refer to:
Science
* Mate, one of a pair of animals involved in:
** Mate choice, intersexual selection
** Mating
* Multi-antimicrobial extrusion protein, or MATE, an efflux transporter family of proteins
Person or title
* Friendship ...
. Female echidnas lay one egg a year and the mating period is the only time the otherwise solitary animals meet one another; the male has no further contact with the female or his offspring after mating. A newborn echidna is the size of a grape but grows rapidly on its mother's milk, which is very rich in nutrients. Baby echidnas eventually grow too large and spiky to stay in the pouch and, around seven weeks after hatching, are expelled from the pouch into the mother's burrow. At around six months of age, they leave the burrow and have no more contact with their mothers.
The species is found throughout Australia, where it is the most widespread native mammal, and in coastal and highland regions of eastern New Guinea, where it is known as the ''mungwe'' in the Daribi
Dadibi (also Daribi or Karimui) is a language of eastern Papua New Guinea. In 2001, the Bible (including the Old Testament) was translated into Dadibi.
Distribution
Dadibi is spoken in:
*Chimbu Province: Karimui-Nomane District, Tua River syste ...
and Chimbu languages.Flannery, T. 1990. ''Mammals of New Guinea'' Robert Brown & Associates It is not threatened with extinction, but human activities, such as hunting, habitat destruction, and the introduction
Introduction, The Introduction, Intro, or The Intro may refer to:
General use
* Introduction (music), an opening section of a piece of music
* Introduction (writing), a beginning section to a book, article or essay which states its purpose and g ...
of foreign predatory species and parasites, have reduced its distribution in Australia.
Taxonomy and naming
The short-beaked echidna was first described byGeorge Shaw George Shaw may refer to:
* George Shaw (biologist) (1751–1813), English botanist and zoologist
* George B. Shaw (1854–1894), U.S. Representative from Wisconsin
* George Bernard Shaw (1856–1950), Irish playwright
* George C. Shaw (1866–196 ...
in 1792. He named the species ''Myrmecophaga aculeata'', thinking that it might be related to the giant anteater. Since Shaw first described the species, its name has undergone four revisions: from ''M. aculeata'' to ''Ornithorhynchus hystrix'', ''Echidna hystrix'', ''Echidna aculeata'' and finally, ''Tachyglossus aculeatus''. The name ''Tachyglossus'' means "quick tongue", in reference to the speed with which the echidna uses its tongue to catch ants and termites, and ''aculeatus'' means "spiny" or "equipped with spines".Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 5.
The short-beaked echidna is the only member of its genus, sharing the family Tachyglossidae with the extant species of the genus ''Zaglossus
The long-beaked echidnas (genus ''Zaglossus'') make up one of the two extant genus, genera of echidnas, spiny monotremes that live in New Guinea; the other being the short-beaked echidna. There are three living species and one extinct species in ...
'' that occur in New Guinea. ''Zaglossus'' species, which include the western long-beaked, Sir David's long-beaked and eastern long-beaked echidnas
The eastern long-beaked echidna (''Zaglossus bartoni''), also known as Barton's long-beaked echidna, is one of three species from the genus ''Zaglossus'' to occur in New Guinea. It is found mainly in the eastern half at elevations between .
Desc ...
, are all significantly larger than ''T. aculeatus'', and their diets consist mostly of worms and grubs rather than ants and termites. Species of the Tachyglossidae are egg-laying mammals; together with the related family Ornithorhynchidae, they are the only extant monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brain ...
s in the world.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 10.
The five subspecies of the short-beaked echidna are each found in different geographical locations. The subspecies also differ from one another in their hairiness, spine length and width, and the size of the grooming claws on their hind feet.Augee, Gooden and Musser, pp. 6–7.
* ''T. a. acanthion'' is found in Northern Territory and Western Australia.
* ''T. a. aculeatus'' is found in Queensland, New South Wales, South Australia and Victoria.
* ''T. a. lawesii'' is found in coastal regions and the highlands of New Guinea, and possibly in the rainforests of Northeast Queensland.
* ''T. a. multiaculeatus'' is found on Kangaroo Island.
* '' T. a. setosus'' is found on Tasmania and some islands in Bass Strait
Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The strait provides the most direct waterwa ...
.
The earliest fossils of the short-beaked echidna date back around 15 million years ago to the Miocene epoch, and the oldest specimens were found in caves in South Australia, often with fossils of the long-beaked echidna from the same period. The ancient short-beaked echidnas are considered to be identical to their contemporary descendants except the ancestors are around 10% smaller.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 16. This "post-Pleistocene dwarfing" affects many Australian mammals. Part of the last radiation of monotreme mammals, echidnas are believed to have evolutionally diverged from the platypus around 66 million years ago, between the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods. However, the echidna's pre-Pleistocene heritage has not been traced yet, and the lack of teeth on the fossils found thus far have made it impossible to use dental evidence.
 The short-beaked echidna was commonly called the spiny anteater in older books, though this term has fallen out of fashion since the echidna bears no relation to the true anteaters. It has a variety of names in the indigenous languages of the regions where it is found. The
The short-beaked echidna was commonly called the spiny anteater in older books, though this term has fallen out of fashion since the echidna bears no relation to the true anteaters. It has a variety of names in the indigenous languages of the regions where it is found. The Noongar people
The Noongar (, also spelt Noongah, Nyungar , Nyoongar, Nyoongah, Nyungah, Nyugah, and Yunga ) are Aboriginal Australian peoples who live in the south-west corner of Western Australia, from Geraldton on the west coast to Esperance on the so ...
from southwestern Western Australia call it the . In Central Australia
Central Australia, also sometimes referred to as the Red Centre, is an inexactly defined region associated with the geographic centre of Australia. In its narrowest sense it describes a region that is limited to the town of Alice Springs and i ...
southwest of Alice Springs
Alice Springs ( aer, Mparntwe) is the third-largest town in the Northern Territory of Australia. Known as Stuart until 31 August 1933, the name Alice Springs was given by surveyor William Whitfield Mills after Alice, Lady Todd (''née'' Al ...
, the Pitjantjatjara term is or , from the word for spike of porcupine grass ''(Triodia irritans
''Triodia irritans'' is a species of plant that forms low and dense mounds of tough grassy vegetation. It is found on sandplains in arid regions of southern and central Australia.
The species was first described by Robert Brown in 1810. A comm ...
)''. The word can also mean 'slowpoke'. In the Wiradjuri language of Central NSW, it is called ''.''
In central Cape York Peninsula, it is called in Pakanh
Pakanha (Bakanha), or Ayabakan, is a nearly extinct Paman language spoken on the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia. In 1981, there were 10 speakers of the language, originally spoken by the aboriginal Pakanha people in the central part ...
, where is a qualifier meaning 'meat' or 'animal', in Uw Oykangand and in Uw Olkola, where is a qualifier meaning 'meat' or 'animal'. In the highland regions of southwestern New Guinea, it is known as the in the Daribi
Dadibi (also Daribi or Karimui) is a language of eastern Papua New Guinea. In 2001, the Bible (including the Old Testament) was translated into Dadibi.
Distribution
Dadibi is spoken in:
*Chimbu Province: Karimui-Nomane District, Tua River syste ...
and Chimbu languages. The short-beaked echidna is called in the Motu language of Papua New Guinea.
Description

humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
allows more muscle to form.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 102.
The claws on the hind feet are elongated and curved backward to enable cleaning and grooming between the spines. Like the platypus, the echidna has a low body temperature—between 30 and 32 °C (86 and 90 °F)—but, unlike the platypus, which shows no evidence of torpor or hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
, the body temperature of the echidna may fall as low as 5 °C (41 °F). The echidna does not pant or sweat and normally seeks shelter in hot conditions.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 91. Despite their inability to sweat, echidnas still lose water as they exhale. The snout is believed to be crucial in restricting this loss to sustainable levels, through a bony labyrinth that has a refrigerator effect and helps to condense water vapour in the breath.Augee, Gooden and Musser, pp. 114–115. The echidna does not have highly concentrated urine, and around half of the estimated daily water loss of occurs in this manner, while most of the rest is through the skin and respiratory system.Augee, Gooden and Musser, pp. 115. Most of this is replenished by its substantial eating of termites—one laboratory study reported ingestion of around a day, most of which was water. This can be supplemented by drinking water, if available, or licking morning dew from flora.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 116.
In the Australian autumn and winter, the echidna enters periods of torpor or deep hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
. Because of its low body temperature, it becomes sluggish in very hot and very cold weather.
Like all monotremes, it has one orifice,Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 3. the cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
, for the passage of faeces, urine and reproductive products. The male has internal testes, no external scrotum and a highly unusual penis with four knobs on the tip,Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 79. which is nearly a quarter of his body length when erect. The gestating female develops a pouch on her underside, where she raises her young.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 4.
 The musculature of the short-beaked echidna has a number of unusual aspects. The
The musculature of the short-beaked echidna has a number of unusual aspects. The panniculus carnosus
The panniculus carnosus is a part of the subcutaneous tissues in vertebrates. It is a layer of striated muscle deep to the panniculus adiposus.McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Pope, F.M. (2004). ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology'' (Seventh Edition). Black ...
, an enormous muscle just beneath the skin, covers the entire body. By contraction of various parts of the panniculus carnosus, the short-beaked echidna can change shape, the most characteristic shape change being achieved by rolling itself into a ball when threatened, so protecting its belly and presenting a defensive array of sharp spines. It has one of the shortest spinal cords of any mammal, extending only as far as the thorax. Whereas the human spinal cord ends at the first or second lumbar vertebra, for the echidna it occurs at the seventh thoracic vertebra.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 53. The shorter spinal cord is thought to allow flexibility to enable wrapping into a ball.
The musculature of the face, jaw and tongue is specialised for feeding. The tongue is the animal's sole means of catching prey, and can protrude up to outside the snout. The snout's shape, resembling a double wedge, gives it a significant mechanical advantage in generating a large moment, so makes it efficient for digging to reach prey or to build a shelter. The tongue is sticky because of the presence of glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
-rich mucus, which both lubricates movement in and out of the snout and helps to catch ants and termites, which adhere to it. The tongue is protruded by contracting circular muscles that change the shape of the tongue and force it forwards and contracting two genioglossal muscles attached to the caudal end of the tongue and to the mandible. The protruded tongue is stiffened by a rapid flow of blood, which allows it to penetrate wood and soil. Retraction requires the contraction of two internal longitudinal muscles, known as the sternoglossi. When the tongue is retracted, the prey is caught on backward-facing keratinous "teeth", located along the roof of the buccal cavity, allowing the animal both to capture and grind food. The tongue moves with great speed, and has been measured to move in and out of the snout 100 times a minute. This is partly achieved through the elasticity of the tongue and the conversion of elastic potential energy into kinetic energy. The tongue is very flexible, particularly at the end, allowing it to bend in U-turns and catch insects attempting to flee in their labyrinthine nests or mounds.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 104. The tongue also has an ability to avoid picking up splinters while foraging in logs; the factors behind this ability are unknown.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 105. It can eat quickly; a specimen of around can ingest of termites in 10 minutes.
The echidna's stomach is quite different from other mammals. It is devoid of secretory glands and has a cornified stratified epithelium, which resembles horny skin.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 106. Unlike other mammals, which typically have highly acidic stomachs, the echidna has low levels of acidity, almost neutral, with pH in the 6.2–7.4 range. The stomach is elastic, and gastric peristalsis grinds soil particulates and shredded insects together. Digestion occurs in the small intestine, which is around in length. The insect exoskeletons and soil are not digested, being ejected in the waste.
Numerous physiological adaptations aid the lifestyle of the short-beaked echidna. Because the animal burrows, it must tolerate very high levels of carbon dioxide in inspired air, and will voluntarily remain in situations where carbon dioxide concentrations are high. It can dig up to a metre into the ground to retrieve ants or evade predators, and can survive with low oxygen when the area is engulfed by bushfires. The echidna can also dive underwater, which can help it to survive sudden floods. During these situations, the heart rate drops to around 12 beats per minute, around one-fifth of the rate at rest. This process is believed to save oxygen for the heart and brain, which are the most sensitive organs to such a shortage; laboratory testing has revealed the echidna's cardiovascular system is similar to that of the seal. Following the devastation of a bushfire, echidnas can compensate for the lack of food by reducing their daytime body temperature and activity through use of torpor, for a period of up to three weeks.
The echidna's optical system is an uncommon hybrid of both mammalian and reptilian characteristics. The cartilaginous layer beneath the sclera of the eyeball is similar to that of reptiles and avians. The small corneal surface is keratinised and hardened, possibly to protect it from chemicals secreted by prey insects or self-impalement when it rolls itself up, which has been observed.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 56. The echidna has the flattest lens of any animal, giving it the longest focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative foca ...
. This similarity to primates and humans allows it to see distant objects clearly.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 57. Unlike placental mammals, including humans, the echidna does not have a ciliary muscle to distort the geometry of the lens and thereby change the focal length and allow objects at different distances to be viewed clearly; the whole eye is believed to distort, so the distance between the lens and retina instead changes to allow focusing. The visual ability of an echidna is not great, and it is not known whether it can perceive colour; however, it can distinguish between black and white, and horizontal and vertical stripes. Eyesight is not a crucial factor in the animal's ability to survive, as blind echidnas are able to live healthily.
Its ears are sensitive to low- frequency sound, which may be ideal for detecting sounds emitted by termites and ants underground. The pinnae are obscured and covered by hair, so predators cannot grab them in an attack, and prey or foreign material cannot enter, although ticks are known to reside there.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 58. The macula of the ear is very large compared to other animals, and is used as a gravity sensor to orient the echidna. The large size may be important for burrowing downwards.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 65.
 The leathery snout is keratinised and covered in mechano- and thermoreceptors, which provide information about the surrounding environment.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 66. These nerves protrude through microscopic holes at the end of the snout,Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 68. which also has mucus glands on the end that act as electroreceptors. Echidnas can detect
The leathery snout is keratinised and covered in mechano- and thermoreceptors, which provide information about the surrounding environment.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 66. These nerves protrude through microscopic holes at the end of the snout,Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 68. which also has mucus glands on the end that act as electroreceptors. Echidnas can detect electric field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field fo ...
s of 1.8 mV/cm—1000 times more sensitive than humans—and dig up buried batteries. A series of push rods protrude from the snout. These are columns of flattened, spinous cells, with roughly an average diameter of 50 micrometres and a length of 300 micrometres. The number of push rods per square millimetre of skin is estimated to be 30 to 40. Longitudinal waves
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical wave, Mechanical l ...
are believed to be picked up and transmitted through the rods, acting as mechanical sensors, to allow prey detection.
A well-developed olfactory system may be used to detect mates and prey. A highly sensitive optic nerve has been shown to have visual discrimination and spatial memory
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is a form of memory responsible for the recording and recovery of information needed to plan a course to a location and to recall the location of an object or the occurrence of an event. Sp ...
comparable to those of a rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
. The brain and central nervous system have been extensively studied for evolutionary comparison with placental mammals, particularly with its fellow monotreme, the platypus. The average brain volume is 25 ml, similar to a cat of approximately the same size;Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 45. while the platypus has a largely smooth brain, the echidna has a heavily folded and fissured, gyrencephalic brain similar to humans, which is seen as a sign of a highly neurologically advanced animal.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 47. The cerebral cortex is thinner, and the brain cells are larger and more densely packed and organised in the echidna than the platypus, suggesting evolutionary divergence must have occurred long ago. Almost half of the sensory area in the brain is devoted to the snout and tongue, and the part devoted to smell is relatively large compared to other animals.
The short-beaked echidna has the largest prefrontal cortex relative to body size of any mammal, taking up 50% of the volume in comparison to 29% for humans.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 48. This part of the brain in humans is thought to be used for planning and analytical behaviour, leading to debate as to whether the echidna has reasoning and strategising ability. Experiments in a simple maze and with a test on opening a trap door to access food, and the echidna's ability to remember what it has learnt for over a month, has led scientists to conclude its learning ability is similar to that of a cat or a rat.
The echidna shows rapid eye movement during sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream ...
, usually around its thermoneutral temperature of 25 °C, and this effect is suppressed at other temperatures. Its brain has been shown to contain a claustrum similar to that of placental mammals, linking this structure to their common ancestor.
Ecology and behaviour
No systematic study of the ecology of the short-beaked echidna has been published, but studies of several aspects of their ecological behaviour have been conducted. They live alone, and, apart from the burrow created for rearing young, they have no fixed shelter or nest site. They do not have a home territory they defend against other echidnas, but range over a wide area. The range area has been observed to be between 21 and 93 ha, although one study in Kangaroo Island found the animals there covered an area between 9 and 192 ha. Overall, the mean range areas across the various regions of Australia were 40–60 ha. There was no correlation between sex and range area, but a weak one with size. Echidnas can share home ranges without incident, and sometimes share shelter sites if not enough are available for each animal to have one individually. Short-beaked echidnas are typically active in the daytime, though they are ill-equipped to deal with heat because they have nosweat gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial sur ...
s and do not pant. Therefore, in warm weather, they change their patterns of activity, becoming crepuscular
In zoology, a crepuscular animal is one that is active primarily during the twilight period, being matutinal, vespertine, or both. This is distinguished from diurnal and nocturnal behavior, where an animal is active during the hours of daylig ...
or nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
. Body temperatures above 34 °C (93 °F) are believed to be fatal, and in addition to avoiding heat, the animal adjusts its circulation to maintain a sustainable temperature by moving blood to and from the skin to increase or lower heat loss. In areas where water is present, they can also swim to keep their body temperatures low. The "thermoneutral zone" for the environment is around 25 °C (77 °F), at which point the metabolism needed to maintain body temperature is minimized. The echidna is endothermic, and can maintain body temperatures of around 32 °C.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 112. It can also reduce its metabolism and heart rate and body temperature.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 107. In addition to brief and light bouts of torpor throughout the year, the echidna enters periods during the Australian winter when it hibernates,Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 108. both in cold regions and in regions with more temperate climates. During hibernation, the body temperature drops to as low as 4 °C (39 °F). The heart rate falls to four to seven beats per minute—down from 50 to 68 at rest—and the echidna can breathe as infrequently as once every three minutes, 80 to 90% slower than when it is active. Metabolism can drop to one-eighth of the normal rate.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 109. Echidnas begin to prepare for hibernation between February and April, when they reduce their consumption and enter brief periods of torpor. Males begin hibernating first, while females that have reproduced start later. During periods of hibernation, the animals average 13 separate bouts of torpor, which are broken up by periods of arousal lasting 1.2 days on average. These interruptions tend to coincide with warmer periods. Males end their hibernation period in mid-June, while reproductive females return to full activity in July and August; nonreproductive females and immature echidnas may not end hibernation until two months later. During euthermia
Normal human body-temperature (normothermia, euthermia) is the typical temperature range found in humans. The normal human body temperature range is typically stated as .
Human body temperature varies. It depends on sex, age, time of day, exert ...
, the body temperature can vary by 4 °C per day. The metabolic rate is around 30% of that of placental mammals, making it the lowest energy-consuming mammal. This figure is similar to that of other animals that eat ants and termites;Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 113. burrowing animals also tend to have low metabolism generally.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 114.
Echidnas hibernate even though it is seemingly unnecessary for survival; they begin their hibernation period while the weather is still warm, and food is generally always plentiful.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 110. One explanation is that echidnas maximize their foraging productivity by exercising caution with their energy reserves. Another hypothesis is that they are descended from ectothermic ancestors, but have taken to periodic endothermy for reproductive reasons, so that the young can develop more quickly. Supporters of this theory argue that males hibernate earlier than females because they finish their contribution to reproduction first, and they awake earlier to undergo spermatogenesis in preparation for mating, while females and young lag in their annual cycle. During the hibernation period, the animals stay in entirely covered shelter.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 111.
Short-beaked echidnas can live anywhere with a good supply of food, and regularly feast on ants and termites. They are believed to locate food by smell, using sensors in the tips of their snouts, by shuffling around seemingly arbitrarily, and using their snout in a probing manner. A study of echidnas in New England (New South Wales) has shown that they tend to dig up scarab beetle larvae in spring when the prey are active, but eschew this prey when it is inactive, leading to the conjecture that echidnas detect prey using hearing.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 99. Vision is not believed to be significant in hunting, as blind animals have been observed to survive in the wild.
Echidnas use their strong claws to pull apart nests and rotting logs to gain access to their prey.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 95. They avoid ants and termites that secrete repulsive liquids, and have a preference for the eggs, pupae and winged phases of the insects. Echidnas hunt most vigorously towards the end of the southern winter and early in spring, when their fat reserves have been depleted after hibernation and nursing.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 97. At this time, ants have high body fat, and the echidna targets their mounds. The animal also hunts beetles and earthworms, providing they are small enough to fit in a 5-mm gap. The proportion of ants and termites in their diets depends on the availability of prey, and termites make up a larger part in drier areas where they are more plentiful.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 98. However, termites are preferred, if available, as their bodies contain a smaller proportion of indigestible exoskeleton. Termites from the Rhinotermitidae family are avoided due to their chemical defences. Scarab beetle larvae are also a large part of the diet when and where available. In the New England study, 37% of the food intake consisted of beetle larvae, although the echidna had to squash the prey in its snout as it ingested it, due to size.
Echidnas are powerful diggers, using their clawed front paws to dig out prey and create burrows for shelter. They may rapidly dig themselves into the ground if they cannot find cover when in danger. They bend their belly together to shield the soft, unprotected part, and can also urinate, giving off a pungent liquid, in an attempt to deter attackers. Males also have single small spurs on each rear leg, believed to be a defensive weapon that has since been lost through evolution. Echidnas typically try to avoid confrontation with predators. Instead, they use the colour of their spines, which is similar to the vegetation of the dry Australian environment, to avoid detection. They have good hearing and tend to become stationary if sound is detected.
It is likely that echidnas are keystone species in the ecosystem health in Australia, due to their contribution through bioturbation
Bioturbation is defined as the reworking of soils and sediments by animals or plants. It includes burrowing, ingestion, and defecation of sediment grains. Bioturbating activities have a profound effect on the environment and are thought to be a pr ...
, the reworking of soils through their digging activity. This is based on the estimation that a single echidna will move up to 204 m3 of soil a year, that it is the most widespread of any terrestrial Australian species, is relatively common, and that other bioturbators have been heavily impacted by human settlement.
In Australia, they are most common in forested areas with abundant, termite-filled, fallen logs. In agricultural areas, they are most likely to be found in uncleared scrub; they may be found in grassland, arid areas, and in the outer suburbs of the capital cities. Little is known about their distribution in New Guinea. They have been found in southern New Guinea between Merauke in the west and the Kelp Welsh River, east of Port Moresby, in the east, where they may be found in open woodland.
Echidnas have the ability to swim, and have been seen cooling off near dams during high temperatures. They have also been seen crossing streams and swimming for brief periods in seas off Kangaroo Island. They swim with only the snout above water, using it as a snorkel.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 92.
Reproduction
The solitary short-beaked echidna looks for a mate between May and September; the precise timing of the mating season varies with geographic location.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 77. In the months before the mating season, the size of the male's testes increases by a factor of three or more before spermatogenesis occurs.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 80. Both males and females give off a strong, musky odour during the mating season, by turning theircloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
s inside out and wiping them on the ground, secreting a glossy liquid believed to be an aphrodisiac. During courtship—observed for the first time in 1989—males locate and pursue females. Trains of up to 10 males, often with the youngest and smallest male at the end of the queue, may follow a single female in a courtship ritual that may last for up to four weeks; the duration of the courtship period varies with location. During this time, they forage for food together, and the train often changes composition, as some males leave and other join the pursuit.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 78. In cooler parts of their range, such as Tasmania, females may mate within a few hours of arousal from hibernation.
Before mating, the male smells the female, paying particular attention to the cloaca. This process can take a few hours, and the female can reject the suitor by rolling herself into a ball. After prodding and sniffing her back, the male is often observed to roll the female onto her side and then assume a similar position himself so the two animals are abdomen to abdomen, having dug a small crater in which to lie. They can lie with heads facing one another, or head to rear.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 81. If more than one male is in the vicinity, fighting over the female may occur. Each side of the bilaterally symmetrical, rosette-like, four-headed penis (similar to that of reptiles and in length) is used alternately, with the other half being shut down between ejaculations. Sperm bundles of around 100 each appear to confer increased sperm motility, which may provide the potential for sperm competition between males. This process takes between a half and three hours. Each mating results in the production of a single egg, and females are known to mate only once during the breeding season; each mating is successful.
Fertilisation occurs in the oviduct. Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
takes between 21 and 28 days after copulation, during which time the female constructs a nursery burrow. Following the gestation period, a single, rubbery-skinned egg between in diameter and in weightAugee, Gooden and Musser, p. 84. is laid from her cloaca directly into a small, backward-facing pouch that has developed on her abdomen. The egg is ovoid, leathery, soft, and cream-coloured. Between laying and hatching, some females continue to forage for food, while others dig burrows and rest there until hatching. Ten days after it is laid, the egg hatches within the pouch. The embryo develops an egg tooth during incubation, which it uses to tear open the egg; the tooth disappears soon after hatching.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 85.
Hatchlings are about long and weigh between . After hatching, young echidnas are known as "puggles". Although newborns are still semitranslucent and still surrounded by the remains of the egg yolk, and the eyes are still barely developed, they already have well-defined front limbs and digits that allow them to climb on their mothers' bodies. Hatchlings attach themselves to their mothers' milk areolae, specialised patches on the skin that secrete milk—monotremes lack nipples—through about 100–150 pores. The puggles were thought to have imbibed the milk by licking the mother's skin, but they are now thought to feed by sucking the areolae.
They have been observed ingesting large amounts during each feeding period, and mothers may leave them unattended in the burrow for between five and ten days to find food.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 86. Studies of captives have shown they can ingest milk once every two or three days and then increase their mass by 20% in one milk-drinking session lasting between one and two hours. Around 40% of the milk weight is converted into body mass, and as such, a high proportion of milk is converted into growth; a correlation with the growth of the puggle and its mother's size has been observed. By the time the puggle is around , it is left in the burrow while the mother forages for food, and it reaches around after around two months. Juveniles are eventually ejected from the pouch at around two to three months of age, because of the continuing growth in the length of their spines. During this period, the young are left in covered burrows while the mothers forage, and the young are often preyed upon. Suckling gradually decreases until juveniles are weaned at about six months of age. The duration of lactation is about 200 days, and the young leave the burrow after 180 to 205 days, usually in January or February, at which time they weigh around . There is no contact between the mother and young after this point.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 88.
The composition of the milk secreted by the mother changes over time. At the moment of birth, the solution is dilute and contains 1.25% fat, 7.85% protein, and 2.85% carbohydrates and minerals. Mature milk has much more concentrated nutrients, with 31.0, 12.4 and 2.8% of the aforementioned nutrients, respectively. Near weaning, the protein level continues to increase; this may be due to the need for keratin synthesis for hair and spines, to provide defences against the cold weather and predators.
The principal carbohydrate components of the milk are fucosyllactose and saialyllactose; it has a high iron content, which gives it a pink colour.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 87. The high iron content and low levels of free lactose differ from eutherian mammals. Lactose production is believed to proceed along the same lines as in the platypus.
The age of sexual maturity is uncertain, but may be four to five years. A 12-year field study found the short-beaked echidna reaches sexual maturity between five and 12 years of age, and the frequency of reproduction varies from once every two years to once every six years. In the wild, the short-beaked echidna has an average lifespan of 10 years, though they can live as long as 40. The longest-lived specimen reached 49 years of age in a zoo in Philadelphia.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 93. In contrast to other mammals, echidna rates of reproduction and metabolism are lower, and they live longer, as though in slow motion, something caused, at least in part, by their low body temperature, which rarely exceeds 33 °C, even when they are not hibernating.
Like its fellow monotreme the platypus, the short-beaked echidna has a system of multiple sex chromosomes, in which males have four Y chromosomes and five X chromosomes. Males appear to be X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5figure
ref name = "Rensetal2007"/>), while females are X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5. Weak identity between chromosomes results in meiotic pairing that yields only two possible
genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
s of sperm, X1X2X3X4X5 or Y1Y2Y3Y4, thus preserving this complex system.
Conservation status
 The short-beaked echidna is common throughout most of temperate Australia and lowland New Guinea, and is not listed as endangered. In Australia, it remains widespread across a wide range of conditions, including urban outskirts, coastal forests and dry inland areas, and is especially widespread in Tasmania and on Kangaroo Island.
The most common threats to the animal in Australia are motor vehicles and habitat destruction, which have led to localized extinctions.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 120. In Australia, the number of short-beaked echidnas has been less affected by land clearance than have some other species, since they do not require a specialized habitat beyond a good supply of ants and termites. As a result, they can survive in cleared land if the cut-down wood is left in the area, as the logs can be used as shelters and sources of insects. However, areas where the land has been completely cleared for single crops that can be mechanically harvested, such as wheat fields, have seen extinctions. Over a decade-long period, around one-third of echidna deaths reported to wildlife authorities in Victoria were due to motor vehicles, and the majority of wounded animals handed in were traffic accident victims. Studies have shown they often choose to traverse drainage culverts under roads, so this is seen as a viable means of reducing deaths on busy roads in rural areas or national parks where the animals are more common.
Despite their spines, they are preyed on by birds of prey, the
The short-beaked echidna is common throughout most of temperate Australia and lowland New Guinea, and is not listed as endangered. In Australia, it remains widespread across a wide range of conditions, including urban outskirts, coastal forests and dry inland areas, and is especially widespread in Tasmania and on Kangaroo Island.
The most common threats to the animal in Australia are motor vehicles and habitat destruction, which have led to localized extinctions.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 120. In Australia, the number of short-beaked echidnas has been less affected by land clearance than have some other species, since they do not require a specialized habitat beyond a good supply of ants and termites. As a result, they can survive in cleared land if the cut-down wood is left in the area, as the logs can be used as shelters and sources of insects. However, areas where the land has been completely cleared for single crops that can be mechanically harvested, such as wheat fields, have seen extinctions. Over a decade-long period, around one-third of echidna deaths reported to wildlife authorities in Victoria were due to motor vehicles, and the majority of wounded animals handed in were traffic accident victims. Studies have shown they often choose to traverse drainage culverts under roads, so this is seen as a viable means of reducing deaths on busy roads in rural areas or national parks where the animals are more common.
Despite their spines, they are preyed on by birds of prey, the Tasmanian devil
The Tasmanian devil (''Sarcophilus harrisii'') (palawa kani: purinina) is a carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae. Until recently, it was only found on the island state of Tasmania, but it has been reintroduced to New South Wales in ...
, dingo
The dingo (''Canis familiaris'', ''Canis familiaris dingo'', ''Canis dingo'', or ''Canis lupus dingo'') is an ancient (Basal (phylogenetics), basal) lineage of dog found in Australia (continent), Australia. Its taxonomic classification is de ...
es, snakes, lizards, goannas, cats, and foxes,Augee, Gooden and Musser, pp. 120–121. although almost all victims are young. Goannas are known for their digging abilities and strong sense of smell, and are believed to have been the main predators of the echidna before the introduction of eutherian mammals. Dingoes are known to kill echidnas by rolling them over onto their backs and attacking their underbellies. A tracking study of a small number of echidnas on Kangaroo Island concluded that goannas and cats were the main predators, although foxes—absent in Kangaroo Island—would be expected to be a major threat.
They were eaten by indigenous Australians and the early European settlers of Australia. Hunting and eating of the echidna in New Guinea has increased over time and caused a decline in the population and distribution areas; it is now believed to have disappeared from highland areas. The killing of echidnas was a taboo in traditional culture, but since the tribespeople have become increasingly Westernised, hunting has increased, and the animals have been more easily tracked down due to the use of dogs.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 119.
Infection with the introduced parasitic tapeworm ''Spirometra erinaceieuropaei
''Spirometra erinaceieuropaei'' is a parasitic tapeworm that infects domestic animals and humans. The medical term for this infection in humans and other animals is sparganosis. Morphologically, these worms are similar to other worms in the genus ...
'' is considered fatal for the echidna. This waterborne infection is contracted through sharing drinking areas with infected dogs, foxes, cats, and dingos, which do not die from the parasite. The infection is seen as being more dangerous in drier areas, where more animals are sharing fewer bodies of water, increasing the chance of transmission.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 121. The Wildlife Preservation Society of Queensland runs an Australia-wide survey, called Echidna Watch, to monitor the species. Echidnas are also known to be affected by other tapeworms, protozoans and herpes-like viral infections, but little is known of how the infections affect the health of the animals or the populations.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 122.
Although it is considered easy to keep echidnas healthy in captivity, breeding is difficult, partly due to the relatively infrequent cycle. In 2009, Perth Zoo managed to breed some captive short-beaked echidnas, and in 2015 the first zoo-born echidnas were successfully bred there. Until 2006, only five zoos have managed to breed short-beaked echidnas, but no captive-bred young have survived to maturity.Augee, Gooden and Musser, p. 126. Of these five institutions, only one in Australia—Sydney's Taronga Zoo—managed to breed echidnas, in 1977. The other four cases occurred in the Northern Hemisphere, two in the United States and the others in western Europe. In these cases, breeding occurred six months out of phase compared to Australia, after the animals had adapted to Northern Hemisphere seasons. The failure of captive breeding programs has conservation implications for the endangered species of echidna from the genus ''Zaglossus'', and to a lesser extent for the short-beaked echidna.
Cultural references
Short-beaked echidnas feature in the animistic culture of indigenous Australians, including their visual arts and stories. The species was a totem for some groups, including theNoongar people
The Noongar (, also spelt Noongah, Nyungar , Nyoongar, Nyoongah, Nyungah, Nyugah, and Yunga ) are Aboriginal Australian peoples who live in the south-west corner of Western Australia, from Geraldton on the west coast to Esperance on the so ...
from Western Australia. Many groups have myths about the animal; one myth explains it was created when a group of hungry young men went hunting at night and stumbled across a wombat. They threw spears at the wombat, but lost sight of it in the darkness. The wombat adapted the spears for its own defence and turned into an echidna.
The short-beaked echidna is an iconic animal in contemporary Australia, notably appearing on the five-cent coin A five-cent coin or five-cent piece is a small-value coin minted for various decimal currencies using the cent as their hundredth subdivision.
Examples include:
* the United States five-cent coin, better known as the US nickel
* the Canadian five ...
(the smallest denomination), and on a $200 commemorative coin released in 1992. The anthropomorphic echidna ''Millie'' was a mascot for the 2000 Summer Olympics
The 2000 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXVII Olympiad and also known as Sydney 2000 (Dharug: ''Gadigal 2000''), the Millennium Olympic Games or the Games of the New Millennium, was an international multi-sport event held from 1 ...
.
See also
* Echidna *Fauna of Australia
The fauna of Australia consists of a huge variety of animals; some 46% of birds, 69% of mammals, 94% of amphibians, and 93% of reptiles that inhabit the continent are endemic to it. This high level of endemism can be attributed to the continent ...
* List of monotremes and marsupials
Cited references
Works cited
* Augee, M. L., Gooden, B. A. and Musser, A. 2006.Echidna : extraordinary egg-laying mammal
'. Collingwood, Victoria, CSIRO Publishing * Egerton, L. ed. 2005. ''Encyclopedia of Australian wildlife''. Reader's Digest
General references
* Augee, M. L. and Gooden, B. A. 1993. ''Echidnas of Australia and New Guinea''. Australian National History Press, Sydney * Augee, M. L. 1983. R. Strahan Ed. ''The Australian Museum Complete Book of Australian Mammals''. pp. 8–9. Angus & Robertson * Griffiths, M. 1989Tachyglossidae
pp. 407–435 in ''Fauna of Australia'' (D. W. Walton and B. J. Richardson, eds.). Mammalia, Canberra, Australian Capital Territory 1B:1–1227.
External links
* *Tasmanian Department of Water, Primary Industries and Environment – Short-beaked echidna
article with sound clips and images of puggles {{Taxonbar, from=Q193182, from2=Q12902259 Mammals of South Australia Mammals of Tasmania Mammals of Western Australia Mammals of the Northern Territory Mammals of New South Wales Mammals of Queensland Mammals of Victoria (Australia) Mammals of Papua New Guinea Mammals of Western New Guinea Monotremes of New Guinea
Myrmecophagous mammals
Myrmecophagy is a feeding behavior defined by the consumption of termites or ants, particularly as pertaining to those animal species whose diets are largely or exclusively composed of said insect types. Literally, myrmecophagy means "ant eating" ...
Articles containing video clips
Mammals described in 1792
Taxa named by George Shaw