Spacelab 2 mission.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by
 In August 1973, NASA and
In August 1973, NASA and 
 In the early 1970s NASA shifted its focus from the Lunar missions to the Space Shuttle, and also space research. The Administrator of NASA at the time moved the focus from a new space station to space laboratory for planned Space Shuttle. This would allow technologies for future space stations to be researched and harness the capabilities of the Space Shuttle for research.
Spacelab was produced by European Space Research Organisation (ESRO), a consortium of ten European countries including:
* Austria
* Belgium
* Denmark
* France
* West Germany/ Germany
* Italy
* Netherlands
* Spain
*
In the early 1970s NASA shifted its focus from the Lunar missions to the Space Shuttle, and also space research. The Administrator of NASA at the time moved the focus from a new space station to space laboratory for planned Space Shuttle. This would allow technologies for future space stations to be researched and harness the capabilities of the Space Shuttle for research.
Spacelab was produced by European Space Research Organisation (ESRO), a consortium of ten European countries including:
* Austria
* Belgium
* Denmark
* France
* West Germany/ Germany
* Italy
* Netherlands
* Spain
*
 In addition to the laboratory module, the complete set also included five external pallets for experiments in vacuum built by British Aerospace (BAe) and a pressurized "Igloo" containing the subsystems needed for the pallet-only flight configuration operation. Eight flight configurations were qualified, though more could be assembled if needed.
The system had some unique features including an intended two-week turn-around time (for the original Space Shuttle launch turn-around time) and the roll-on-roll-off for loading in aircraft (Earth-transportation).
Spacelab consisted of a variety of interchangeable components, with the major one being a crewed laboratory that could be flown in Space Shuttle orbiter's bay and returned to Earth. However, the habitable module did not have to be flown to conduct a Spacelab-type mission and there was a variety of pallets and other hardware supporting space research. The habitable module expanded the volume for astronauts to work in a
In addition to the laboratory module, the complete set also included five external pallets for experiments in vacuum built by British Aerospace (BAe) and a pressurized "Igloo" containing the subsystems needed for the pallet-only flight configuration operation. Eight flight configurations were qualified, though more could be assembled if needed.
The system had some unique features including an intended two-week turn-around time (for the original Space Shuttle launch turn-around time) and the roll-on-roll-off for loading in aircraft (Earth-transportation).
Spacelab consisted of a variety of interchangeable components, with the major one being a crewed laboratory that could be flown in Space Shuttle orbiter's bay and returned to Earth. However, the habitable module did not have to be flown to conduct a Spacelab-type mission and there was a variety of pallets and other hardware supporting space research. The habitable module expanded the volume for astronauts to work in a
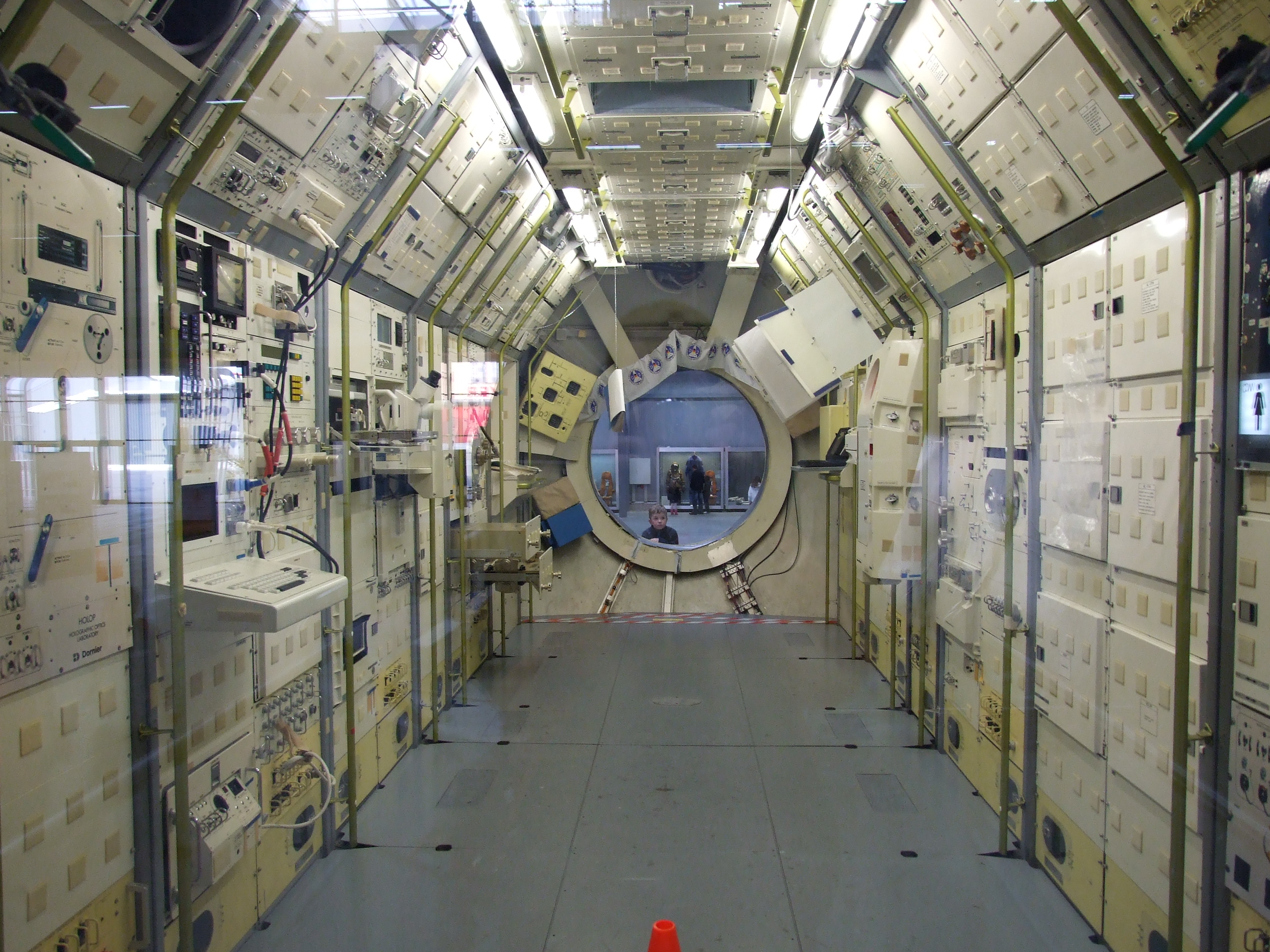
 The habitable Spacelab laboratory module comprised a cylindrical environment in the rear of the Space Shuttle orbiter payload bay, connected to the orbiter crew compartment by a tunnel. The laboratory had an outer diameter of , and each segment a length of . The laboratory module consisted at minimum of a core segment, which could be used alone in a ''short module'' configuration. The ''long module'' configuration included an additional experiment segment. It was also possible to operate Spacelab experiments from the orbiter's aft flight deck.
The pressurized tunnel had its connection point at the orbiter's mid-deck. There were two different length tunnels depending on the location of the habitable module in the payload bay. When the laboratory module was not used, but additional space was needed for support equipment, another structure called the ''Igloo'' could be used.
Two laboratory modules were built, identified as LM1 and LM2. LM1 is on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum behind the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. LM2 was on display in the ''Bremenhalle'' exhibition in the Bremen Airport of
The habitable Spacelab laboratory module comprised a cylindrical environment in the rear of the Space Shuttle orbiter payload bay, connected to the orbiter crew compartment by a tunnel. The laboratory had an outer diameter of , and each segment a length of . The laboratory module consisted at minimum of a core segment, which could be used alone in a ''short module'' configuration. The ''long module'' configuration included an additional experiment segment. It was also possible to operate Spacelab experiments from the orbiter's aft flight deck.
The pressurized tunnel had its connection point at the orbiter's mid-deck. There were two different length tunnels depending on the location of the habitable module in the payload bay. When the laboratory module was not used, but additional space was needed for support equipment, another structure called the ''Igloo'' could be used.
Two laboratory modules were built, identified as LM1 and LM2. LM1 is on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum behind the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. LM2 was on display in the ''Bremenhalle'' exhibition in the Bremen Airport of 
 The Spacelab Pallet is a U-shaped platform for mounting instrumentation, large instruments, experiments requiring exposure to space, and instruments requiring a large field of view, such as telescopes. The pallet has several hard points for mounting heavy equipment. The pallet can be used in single configuration or stacked end to end in double or triple configurations. Up to five pallets can be configured in the Space Shuttle cargo bay by using a double pallet plus triple pallet configurations.
The Spacelab Pallet used to transport both
The Spacelab Pallet is a U-shaped platform for mounting instrumentation, large instruments, experiments requiring exposure to space, and instruments requiring a large field of view, such as telescopes. The pallet has several hard points for mounting heavy equipment. The pallet can be used in single configuration or stacked end to end in double or triple configurations. Up to five pallets can be configured in the Space Shuttle cargo bay by using a double pallet plus triple pallet configurations.
The Spacelab Pallet used to transport both
/ref> IRT collected infrared data on 60% of the galactic plane.
Spacelab IPS.jpg, Instrument Pointing System (IPS)
Astro2 sts67 big.jpg, IPS at work above the sky on Astro-2, 1995
Spacelab Instrument Pointing System at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Dec 2017.jpg, Dornier Instrument Pointing System at the Smithsonian Museum (Udvar Hazy Center)

 Examples of Spacelab components or hardware:
* EVA Airlock
* Tunnel
* Tunnel adapter
* Igloo
* Spacelab module
** Forward end cone
** Aft end cone
** Core segment/module
** Experiment racks
** Experiment segment/module
* Electrical Ground Support Equipment
* Mechanical Ground Support Equipment
* Electrical Power Distribution Subsystem
* Command and Data Management Subsystem
* Environmental Control Subsystem
* Instrument Pointing System
* Pallet Structure
* Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure (MPESS)
The Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) assembly was not Spacelab hardware, strictly speaking. However, it was used most often on Spacelab flights. Also, NASA later used it with the SpaceHab modules.
Examples of Spacelab components or hardware:
* EVA Airlock
* Tunnel
* Tunnel adapter
* Igloo
* Spacelab module
** Forward end cone
** Aft end cone
** Core segment/module
** Experiment racks
** Experiment segment/module
* Electrical Ground Support Equipment
* Mechanical Ground Support Equipment
* Electrical Power Distribution Subsystem
* Command and Data Management Subsystem
* Environmental Control Subsystem
* Instrument Pointing System
* Pallet Structure
* Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure (MPESS)
The Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) assembly was not Spacelab hardware, strictly speaking. However, it was used most often on Spacelab flights. Also, NASA later used it with the SpaceHab modules.



 Spacelab components flew on 22 Space Shuttle missions from November 1983 to April 1998. The Spacelab components were decommissioned in 1998, except the Pallets. Science work was moved to the International Space Station (ISS) and Spacehab module, a pressurized carrier similar to the Spacelab Module. A Spacelab Pallet was recommissioned in 2000 for flight on STS-99. The "Spacelab Pallet – Deployable 1 (SLP-D1) with Canadian Dextre (Purpose Dexterous Manipulator)" was launched on
Spacelab components flew on 22 Space Shuttle missions from November 1983 to April 1998. The Spacelab components were decommissioned in 1998, except the Pallets. Science work was moved to the International Space Station (ISS) and Spacehab module, a pressurized carrier similar to the Spacelab Module. A Spacelab Pallet was recommissioned in 2000 for flight on STS-99. The "Spacelab Pallet – Deployable 1 (SLP-D1) with Canadian Dextre (Purpose Dexterous Manipulator)" was launched on  The first West German mission ''Deutschland 1'' (Spacelab-D1, DLR-1, NASA designation
The first West German mission ''Deutschland 1'' (Spacelab-D1, DLR-1, NASA designation
Sunrise over Spacelab.jpg, Spacelab in payload bay during STS-90
STS-9 Spacelab 1.jpg, Shuttle ''Columbia'' during
 The legacy of Spacelab lives on in the form of the MPLMs and the systems derived from it. These systems include the
The legacy of Spacelab lives on in the form of the MPLMs and the systems derived from it. These systems include the

Spacelab history on NASA.gov
* ttps://history.nasa.gov/NP-119/contents.htm Science in Orbit: The Shuttle & Spacelab Experience, 1981–1986, NASA-NP-119 on NASA.gov
Spacelab Payloads on Shuttle Flights on NASA.gov
James Downey Collection, UAH Archives and Special Collections
files of James A. Downey III, project manager for Spacelab payloads * Lord, Douglas R
''Spacelab An international success story'', NASA-SP-487
NASA, January 1, 1987 * SLP/2104-2: Spacelab Payload Accommodation Handbook {{Orbital launches in 2008 Crewed space observatories Space hardware returned to Earth intact Space science Space Shuttle program


 Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
(ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, and other related hardware housed in the Shuttle's cargo bay. The components were arranged in various configurations to meet the needs of each spaceflight.
Spacelab components flew on a total of about 32 Shuttle missions, depending on how such hardware and missions are tabulated. Spacelab allowed scientists to perform experiments in microgravity
The term micro-g environment (also μg, often referred to by the term microgravity) is more or less synonymous with the terms ''weightlessness'' and ''zero-g'', but emphasising that g-forces are never exactly zero—just very small (on the I ...
in geocentric orbit. There was a variety of Spacelab-associated hardware, so a distinction can be made between the major Spacelab program missions with European scientists running missions in the Spacelab habitable module, missions running other Spacelab hardware experiments, and other Space Transportation System
The Space Transportation System (STS), also known internally to NASA as the Integrated Program Plan (IPP), was a proposed system of reusable crewed space vehicles envisioned in 1969 to support extended operations beyond the Apollo program. ...
(STS) missions that used some component of Spacelab hardware. There is some variation in counts of Spacelab missions, in part because there were different types of Spacelab missions with a large range in the amount of Spacelab hardware flown and the nature of each mission. There were at least 22 major Spacelab missions between 1983 and 1998, and Spacelab hardware was used on a number other missions, with some of the Spacelab pallets being flown as late as 2008.
Background and history
 In August 1973, NASA and
In August 1973, NASA and European Space Research Organisation
The European Space Research Organisation (ESRO) was an international organisation founded by 10 European nations with the intention of jointly pursuing scientific research in space. It was founded in 1964. As an organisation ESRO was based on a ...
(ESRO), now European Space Agency or ESA, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to build a science laboratory for use on Space Shuttle flights. Construction of Spacelab was started in 1974 by Entwicklungsring Nord (ERNO), a subsidiary of VFW-Fokker GmbH
VFW-Fokker GmbH was a joint venture of Fokker and Vereinigte Flugtechnische Werke (VFW) started in 1969 that, from then on, controlled the ERNO initiative.
The Entwicklungsring Nord (Northern development circle) — abbreviated ERNO — was a ...
, after merger with Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB) was a West German aerospace manufacturer. It was formed during the late 1960s as the result of efforts to consolidate the West German aerospace industry; aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt AG merged with the civi ...
(MBB) named MBB/ERNO, and merged into EADS SPACE Transportation in 2003. The first lab module, ''LM1'', was donated to NASA in exchange for flight opportunities for European astronauts. A second module, ''LM2'', was bought by NASA for its own use from ERNO.
Construction on the Spacelab modules began in 1974 by what was then the company ERNO-VFW-Fokker.

 In the early 1970s NASA shifted its focus from the Lunar missions to the Space Shuttle, and also space research. The Administrator of NASA at the time moved the focus from a new space station to space laboratory for planned Space Shuttle. This would allow technologies for future space stations to be researched and harness the capabilities of the Space Shuttle for research.
Spacelab was produced by European Space Research Organisation (ESRO), a consortium of ten European countries including:
* Austria
* Belgium
* Denmark
* France
* West Germany/ Germany
* Italy
* Netherlands
* Spain
*
In the early 1970s NASA shifted its focus from the Lunar missions to the Space Shuttle, and also space research. The Administrator of NASA at the time moved the focus from a new space station to space laboratory for planned Space Shuttle. This would allow technologies for future space stations to be researched and harness the capabilities of the Space Shuttle for research.
Spacelab was produced by European Space Research Organisation (ESRO), a consortium of ten European countries including:
* Austria
* Belgium
* Denmark
* France
* West Germany/ Germany
* Italy
* Netherlands
* Spain
* Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
* United Kingdom
Components
 In addition to the laboratory module, the complete set also included five external pallets for experiments in vacuum built by British Aerospace (BAe) and a pressurized "Igloo" containing the subsystems needed for the pallet-only flight configuration operation. Eight flight configurations were qualified, though more could be assembled if needed.
The system had some unique features including an intended two-week turn-around time (for the original Space Shuttle launch turn-around time) and the roll-on-roll-off for loading in aircraft (Earth-transportation).
Spacelab consisted of a variety of interchangeable components, with the major one being a crewed laboratory that could be flown in Space Shuttle orbiter's bay and returned to Earth. However, the habitable module did not have to be flown to conduct a Spacelab-type mission and there was a variety of pallets and other hardware supporting space research. The habitable module expanded the volume for astronauts to work in a
In addition to the laboratory module, the complete set also included five external pallets for experiments in vacuum built by British Aerospace (BAe) and a pressurized "Igloo" containing the subsystems needed for the pallet-only flight configuration operation. Eight flight configurations were qualified, though more could be assembled if needed.
The system had some unique features including an intended two-week turn-around time (for the original Space Shuttle launch turn-around time) and the roll-on-roll-off for loading in aircraft (Earth-transportation).
Spacelab consisted of a variety of interchangeable components, with the major one being a crewed laboratory that could be flown in Space Shuttle orbiter's bay and returned to Earth. However, the habitable module did not have to be flown to conduct a Spacelab-type mission and there was a variety of pallets and other hardware supporting space research. The habitable module expanded the volume for astronauts to work in a shirt-sleeve environment
"Shirt-sleeve environment" is a term used in aircraft design to describe the interior of an aircraft in which no special clothing need be worn. Early aircraft had no internal pressurization, so the crews of those that reached the stratosphere ...
and had space for equipment racks and related support equipment. When the habitable module was not used, some of the support equipment for the pallets could instead be housed in the smaller Igloo
An igloo (Inuit languages: , Inuktitut syllabics (plural: )), also known as a snow house or snow hut, is a type of shelter built of suitable snow.
Although igloos are often associated with all Inuit, they were traditionally used only b ...
, a pressurized cylinder connected to the Space Shuttle orbiter crew area.
Spacelab mission typically supported multiple experiments, and the Spacelab 1 mission had experiments in the fields of space plasma physics, solar physics, atmospheric physics, astronomy, and Earth observation. The selection of appropriate modules was part of mission planning for Spacelab Shuttle missions, and for example, a mission might need less habitable space and more pallets, or vice versa.
Habitable module
 The habitable Spacelab laboratory module comprised a cylindrical environment in the rear of the Space Shuttle orbiter payload bay, connected to the orbiter crew compartment by a tunnel. The laboratory had an outer diameter of , and each segment a length of . The laboratory module consisted at minimum of a core segment, which could be used alone in a ''short module'' configuration. The ''long module'' configuration included an additional experiment segment. It was also possible to operate Spacelab experiments from the orbiter's aft flight deck.
The pressurized tunnel had its connection point at the orbiter's mid-deck. There were two different length tunnels depending on the location of the habitable module in the payload bay. When the laboratory module was not used, but additional space was needed for support equipment, another structure called the ''Igloo'' could be used.
Two laboratory modules were built, identified as LM1 and LM2. LM1 is on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum behind the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. LM2 was on display in the ''Bremenhalle'' exhibition in the Bremen Airport of
The habitable Spacelab laboratory module comprised a cylindrical environment in the rear of the Space Shuttle orbiter payload bay, connected to the orbiter crew compartment by a tunnel. The laboratory had an outer diameter of , and each segment a length of . The laboratory module consisted at minimum of a core segment, which could be used alone in a ''short module'' configuration. The ''long module'' configuration included an additional experiment segment. It was also possible to operate Spacelab experiments from the orbiter's aft flight deck.
The pressurized tunnel had its connection point at the orbiter's mid-deck. There were two different length tunnels depending on the location of the habitable module in the payload bay. When the laboratory module was not used, but additional space was needed for support equipment, another structure called the ''Igloo'' could be used.
Two laboratory modules were built, identified as LM1 and LM2. LM1 is on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum behind the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. LM2 was on display in the ''Bremenhalle'' exhibition in the Bremen Airport of Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
, Germany from 2000 to 2010. It resides in building 4c at the nearby Airbus Defence and Space
Airbus Defence and Space is the division of Airbus SE responsible for the development and manufacturing of the corporation's defence and space products, while also providing related services. The division was formed in January 2014 during the ...
plant since 2010 and can only be viewed during guided tours.

Pallet
 The Spacelab Pallet is a U-shaped platform for mounting instrumentation, large instruments, experiments requiring exposure to space, and instruments requiring a large field of view, such as telescopes. The pallet has several hard points for mounting heavy equipment. The pallet can be used in single configuration or stacked end to end in double or triple configurations. Up to five pallets can be configured in the Space Shuttle cargo bay by using a double pallet plus triple pallet configurations.
The Spacelab Pallet used to transport both
The Spacelab Pallet is a U-shaped platform for mounting instrumentation, large instruments, experiments requiring exposure to space, and instruments requiring a large field of view, such as telescopes. The pallet has several hard points for mounting heavy equipment. The pallet can be used in single configuration or stacked end to end in double or triple configurations. Up to five pallets can be configured in the Space Shuttle cargo bay by using a double pallet plus triple pallet configurations.
The Spacelab Pallet used to transport both Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supp ...
and Dextre to the International Space Station is currently at the Canada Aviation and Space Museum
The Canada Aviation and Space Museum (french: link=no, Musée de l'Aviation et de l'Espace du Canada) (formerly the Canada Aviation Museum and National Aeronautical Collection) is Canada's national aviation history museum. The museum is located ...
, on loan from NASA through the Canadian Space Agency
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA; french: Agence spatiale canadienne, ASC) is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the ''Canadian Space Agency Act''.
The president is Lisa Campbell, who took the position on September 3, 2020 ...
(CSA).
A Spacelab Pallet was transferred to the Swiss Museum of Transport for permanent display on 5 March 2010. The Pallet, nicknamed ''Elvis'', was used during the eight-day STS-46 mission, 31 July – 8 August 1992, when ESA astronaut Claude Nicollier was on board Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' to deploy ESA's European Retrievable Carrier
The European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA) was an unmanned 4.5-tonne satellite with 15 experiments. It was a European Space Agency (ESA) mission and the acronym was derived from Archimedes' bathtub revelation " Eureka!".
It was built by the Germa ...
(Eureca) scientific mission and the joint NASA/ASI ( Italian Space Agency) Tethered Satellite System
Space tethers are long cables which can be used for propulsion, momentum exchange, stabilization and attitude control, or maintaining the relative positions of the components of a large dispersed satellite/spacecraft sensor system. Depending on t ...
(TSS-1). The Pallet carried TSS-1 in the Shuttle's cargo bay.
Another Spacelab Pallet is on display at the U.S. National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the Nat ...
in Washington, D.C. There was a total of ten space-flown Spacelab pallets.
Igloo
On spaceflight where a habitable module was not flown, but pallets were flown, a pressurized cylinder known as the ''Igloo'' carried the subsystems needed to operate the Spacelab equipment. The Igloo was tall, had a diameter of , and weighed . Two Igloo units were manufactured, both by Belgium companySABCA
SABCA (Sociétés Anonyme Belge de Constructions Aéronautiques) is a Belgian aerospace company. Its main sectors of activity are civil aviation, space and defence.
SABCA was established during 1920. Presently, it is owned by the French aircraf ...
, and both were used on spaceflight. An Igloo component was flown on Spacelab 2
STS-51-F (also known as Spacelab 2) was the 19th flight of NASA's Space Shuttle program and the eighth flight of Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. It launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on July 29, 1985, and landed eight days later on Aug ...
, ASTRO-1, ATLAS-1, ATLAS-2, ATLAS-3, and ASTRO-2.
A Spacelab Igloo is on display at the James S. McDonnell Space Hangar at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in the US.
Instrument Pointing System
The IPS was a gimbaled pointing device, capable of aiming telescopes, cameras, or other instruments. IPS was used on three different Space Shuttle missions between 1985 and 1995. IPS was manufactured by Dornier, and two units were made. The IPS was primarily constructed out of aluminum, steel, and multi-layer insulation. IPS would be mounted inside the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter, and could provide gimbaled 3-axis pointing. It was designed for a pointing accuracy of less than 1 arcsecond (a unit of degree), and three pointing modes including Earth, Sun, and Stellar focused modes. The IPS was mounted on a pallet exposed to outer space in the payload bay. IPS missions: * Spacelab 2, a.k.a. STS-51-F launched 1985 * Astro-1, a.k.a. STS-35 launched in 1990 * Astro-2, a.k.a.STS-67
STS-67 was a human spaceflight mission using that launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida on 2 March 1995.
Crew
Mission highlights
Ultraviolet Imaging Experiments
Astro-2 was the second dedicated Spacelab mission to conduct astronom ...
launched in 1995
The Spacelab 2 mission flew the Infrared Telescope (IRT), which was a aperture helium-cooled infrared telescope, observing light between wavelengths of 1.7 to 118 μm.Kent, et al. – ''Galactic structure from the Spacelab infrared telescope'' (1992)/ref> IRT collected infrared data on 60% of the galactic plane.
List of parts

 Examples of Spacelab components or hardware:
* EVA Airlock
* Tunnel
* Tunnel adapter
* Igloo
* Spacelab module
** Forward end cone
** Aft end cone
** Core segment/module
** Experiment racks
** Experiment segment/module
* Electrical Ground Support Equipment
* Mechanical Ground Support Equipment
* Electrical Power Distribution Subsystem
* Command and Data Management Subsystem
* Environmental Control Subsystem
* Instrument Pointing System
* Pallet Structure
* Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure (MPESS)
The Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) assembly was not Spacelab hardware, strictly speaking. However, it was used most often on Spacelab flights. Also, NASA later used it with the SpaceHab modules.
Examples of Spacelab components or hardware:
* EVA Airlock
* Tunnel
* Tunnel adapter
* Igloo
* Spacelab module
** Forward end cone
** Aft end cone
** Core segment/module
** Experiment racks
** Experiment segment/module
* Electrical Ground Support Equipment
* Mechanical Ground Support Equipment
* Electrical Power Distribution Subsystem
* Command and Data Management Subsystem
* Environmental Control Subsystem
* Instrument Pointing System
* Pallet Structure
* Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure (MPESS)
The Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) assembly was not Spacelab hardware, strictly speaking. However, it was used most often on Spacelab flights. Also, NASA later used it with the SpaceHab modules.
Spacelab missions


 Spacelab components flew on 22 Space Shuttle missions from November 1983 to April 1998. The Spacelab components were decommissioned in 1998, except the Pallets. Science work was moved to the International Space Station (ISS) and Spacehab module, a pressurized carrier similar to the Spacelab Module. A Spacelab Pallet was recommissioned in 2000 for flight on STS-99. The "Spacelab Pallet – Deployable 1 (SLP-D1) with Canadian Dextre (Purpose Dexterous Manipulator)" was launched on
Spacelab components flew on 22 Space Shuttle missions from November 1983 to April 1998. The Spacelab components were decommissioned in 1998, except the Pallets. Science work was moved to the International Space Station (ISS) and Spacehab module, a pressurized carrier similar to the Spacelab Module. A Spacelab Pallet was recommissioned in 2000 for flight on STS-99. The "Spacelab Pallet – Deployable 1 (SLP-D1) with Canadian Dextre (Purpose Dexterous Manipulator)" was launched on STS-123
STS-123 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which was flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. STS-123 was the 1J/A ISS assembly mission. The original launch target date was 14 February 2008 but after the delay of ...
. The Spacelab components were used on 41 Shuttle missions in total.
The habitable modules were flown on 16 Space Shuttle missions in the 1980s and 1990s. Spacelab Pallet missions were flown 6 times and Spacelab Pallets were flown on other missions 19 times.
Mission name acronyms:
* ATLAS: Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science
* ASTRO: Not an acronym; abbreviation for "astronomy"
* IML: International Microgravity Laboratory
* LITE: Lidar In-space Technology Experiment
* LMS: Life and Microgravity Sciences
* MSL: Materials Science Laboratory
* SLS: Spacelab Life Sciences
* SRL: Space Radar Laboratory
* TSS: Tethered Satellite System
* USML: U.S. Microgravity Laboratory
* USMP: U.S. Microgravity Payload
Besides contributing to ESA missions, Germany and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
each funded their own Space Shuttle and Spacelab missions. Although superficially similar to other flights, they were actually the first and only non-U.S. and non-European human space missions with complete German and Japanese control.
 The first West German mission ''Deutschland 1'' (Spacelab-D1, DLR-1, NASA designation
The first West German mission ''Deutschland 1'' (Spacelab-D1, DLR-1, NASA designation STS-61-A
STS-61-A (also known as Spacelab D-1) was the 22nd mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program. It was a scientific Spacelab mission, funded and directed by West Germany – hence the non-NASA designation of D-1 (for Deutschland-1). STS-61-A was th ...
) took place in 1985. A second similar mission, ''Deutschland 2'' (Spacelab-D2, DLR-2, NASA designation STS-55
STS-55, or Deutschland 2 (D-2), was the 55th overall flight of the NASA Space Shuttle and the 14th flight of Shuttle '' Columbia''. This flight was a multinational Spacelab flight involving 88 experiments from eleven different nations. The expe ...
), was first planned for 1988, but due to the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' disaster, was delayed until 1993. It became the first German human space mission after German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
.
The only Japan mission, Spacelab-J
STS-47 was the 50th NASA Space Shuttle mission of the program, as well as the second mission of the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. The mission mainly involved conducting experiments in life and material sciences inside Spacelab-J, a collaborati ...
(NASA designation STS-47
STS-47 was the 50th NASA Space Shuttle mission of the program, as well as the second mission of the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. The mission mainly involved conducting experiments in life and material sciences inside Spacelab-J, a collaborativ ...
), took place in 1992.
Other missions
*STS-92
STS-92 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Discovery''. STS-92 marked the 100th mission of the Space Shuttle. It was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, 11 October 2000.
Crew
...
, October 2000, PMA-3, ()
* STS-108
STS-108 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. Its primary objective was to deliver supplies to and help maintain the ISS.
STS-108 was the 12th shuttle flight to visit the In ...
, December 2001, Lightweight Mission Peculiar Support Structure Carrier (LMC) ()
* STS-123
STS-123 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which was flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. STS-123 was the 1J/A ISS assembly mission. The original launch target date was 14 February 2008 but after the delay of ...
, March 2008, Pallet (), Dextre
Cancelled missions
Spacelab-4, Spacelab-5, and other planned Spacelab missions were cancelled due to the late development of the Shuttle and the ''Challenger'' disaster.Gallery
STS-9
STS-9 (also referred to Spacelab 1) was the ninth NASA Space Shuttle mission and the sixth mission of the Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. Launched on 28 November 1983, the ten-day mission carried the first Spacelab laboratory module into orbit.
...
with Spacelab Module LM1 and tunnel in its cargo bay
Spacelab-in-shuttle.jpg, Illustrated cutaway of orbiter and lab
Legacy
 The legacy of Spacelab lives on in the form of the MPLMs and the systems derived from it. These systems include the
The legacy of Spacelab lives on in the form of the MPLMs and the systems derived from it. These systems include the ATV
ATV may refer to:
Broadcasting
* Amateur television
*Analog television
Television stations and companies
* Ràdio i Televisió d'Andorra
* ATV (Armenia)
* ATV (Aruba), NBC affiliate
* ATV (Australian TV station), Melbourne
* ATV (Austria)
* AT ...
and Cygnus spacecraft used to transfer payloads to the International Space Station, and the Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, Harmony
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However ...
and Tranquility
Tranquillity (also spelled tranquility) is the quality or state of being tranquil; that is, calm, serene, and worry-free. The word tranquillity appears in numerous texts ranging from the religious writings of Buddhism, where the term ''passaddhi'' ...
modules of the International Space Station.
The Spacelab 2 mission surveyed 60% of the galactic plane in infrared in 1985.
Spacelab was an extremely large program, and this was enhanced by different experiments and multiple payloads and configurations over two decades. For example, in a subset of just one part of the Spacelab 1 (STS-9) mission, no less than eight different imaging systems were flown into space. Including those experiments, there was a total of 73 separate experiments across different disciplines on the Spacelab 1 flight alone. Spacelab missions conducted experiments in materials, life, solar, astrophysics, atmospheric, and Earth science.
Diagram, Spacelab Module and Pallet
See also
* Columbus Man-Tended Free Flyer * Hermes (spacecraft) * International Space Station ** ''Columbus'' (ISS module) *Space Shuttle retirement
The retirement of NASA's Space Shuttle fleet took place from March to July 2011. ''Discovery'' was the first of the three active Space Shuttles to be retired, completing its final mission on March 9, 2011; '' Endeavour'' did so on June 1. The ...
* Space Station Freedom
* Spacehab module
Astrotech Corporation, formerly Spacehab Inc., is a technology incubator headquartered in Austin, Texas. Astrotech uses technology sourced internally and from research institutions, government laboratories, and universities to fund, manage and s ...
(various, not to be confused with Spacelab)
* Spacelab, a 1978 song by Kraftwerk
Kraftwerk (, "power station") is a German band formed in Düsseldorf in 1970 by Ralf Hütter and Florian Schneider. Widely considered innovators and pioneers of electronic music, Kraftwerk were among the first successful acts to popularize the ...
References
External links
Spacelab history on NASA.gov
* ttps://history.nasa.gov/NP-119/contents.htm Science in Orbit: The Shuttle & Spacelab Experience, 1981–1986, NASA-NP-119 on NASA.gov
Spacelab Payloads on Shuttle Flights on NASA.gov
James Downey Collection, UAH Archives and Special Collections
files of James A. Downey III, project manager for Spacelab payloads * Lord, Douglas R
''Spacelab An international success story'', NASA-SP-487
NASA, January 1, 1987 * SLP/2104-2: Spacelab Payload Accommodation Handbook {{Orbital launches in 2008 Crewed space observatories Space hardware returned to Earth intact Space science Space Shuttle program