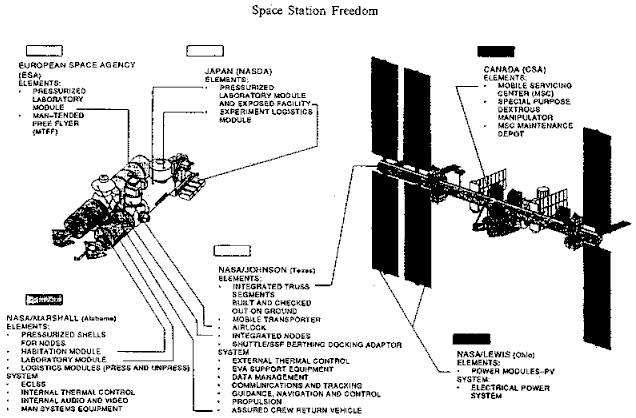
|
Pressurized Mating Adapter
A Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA) is a component used on the International Space Station (ISS) to convert the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) interface used to connect ISS modules to an APAS-95 spacecraft docking port. Three PMAs are attached to the US Orbital Segment of ISS. PMA-1 and PMA-2 were launched along with the ''Unity'' module in 1998 aboard STS-88; PMA-3 was launched in 2000 aboard STS-92. PMA-1 permanently connects the ''Unity'' and '' Zarya'' modules. International Docking Adapters were permanently installed on PMA-2 and PMA-3 in 2017 to convert them from the APAS-95 standard to the newer International Docking System Standard (IDSS). Design and history Its origins lie in designs for the Pressurized Docking Mast, consisting of an off-axis frustoconical docking tunnel contained within a framework and a retractable coupling mechanism, later part of the Pressurized Berthing Adapter assembly that appeared in designs for Space Station Freedom 1987, and the reduced d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destiny (ISS Module)
The ''Destiny'' module, also known as the U.S. Lab, is the primary operating facility for United States, U.S. research payloads aboard the International Space Station (ISS). It was berthed to the forward port of the ''Unity (ISS module), Unity'' module and activated over a period of five days in February, 2001. ''Destiny'' is NASA's first permanent operating orbital research station since Skylab was vacated in February 1974. The Boeing Company began construction of the research laboratory in 1995 at the Michoud Assembly Facility and then the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville, Alabama. ''Destiny'' was shipped to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in 1998, and was turned over to NASA for pre-launch preparations in August 2000. It launched on February 7, 2001 aboard the on STS-98. Astronauts work inside the pressurized facility to conduct research in numerous scientific fields. Scientists throughout the world would use the results to enhance their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IDA Planned Locations On ISS
Ida or IDA may refer to: People *Ida (given name), including people so named * Ida (surname), a list of people so named Astronomy * Ida Facula, a mountain on Amalthea, a moon of Jupiter *243 Ida, an asteroid *International Docking Adapter, a docking adapter for the International Space Station Computing * Intel Dynamic Acceleration, a technology for increasing single-threaded performance on multi-core processors *Interactive Disassembler (now ''IDA Pro''), a popular software disassembler tool for reverse engineering *Interactive Data Analysis, a software package for SPSS *Interchange of Data across Administrations (IDA), a predecessor programme to the IDABC in European eGovernment Film and television *'' ID:A'', a 2011 Danish film * ''Ida'' (film), a 2013 Polish film * Ida Galaxy, a fictional galaxy in the ''Stargate'' TV series Greek mythology * Ida (mother of Minos), daughter of Corybas, the wife of Lycastus king of Crete, and the mother of the "second" king Minos of Crete * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Truss Structure
The Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) of the International Space Station (ISS) consists of a linear arranged sequence of connected trusses on which various unpressurized components are mounted such as logistics carriers, radiators, ISS Solar Arrays, solar arrays, and other equipment. It supplies the ISS with a Spacecraft bus, bus architecture. It is approximately 110 meters long and is made from aluminium and stainless steel. Truss components All truss components were named after their planned end-positions: Z for zenith, S for starboard and P for port, with the number indicating the sequential position. The S0 truss might be considered a misnomer, as it is mounted centrally on the zenith position of ''Destiny'' and is neither starboard nor port side. Manufacturing ISS truss segments were Manufacturing of the International Space Station, fabricated by Boeing in its facilities at Huntington Beach, California (formerly McDonnell Douglas), Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orlean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-97
STS-97 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. The crew installed the first set of solar arrays to the ISS, prepared a docking port for arrival of the Destiny Laboratory Module, and delivered supplies for the station's crew. It was the last human spaceflight of the 20th century. Crew Spacewalks ;EVA 1 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 1 Start: 3 December 2000 – 18:35 UTC *EVA 1 End: 4 December 2000 – 02:08 UTC *Duration: 7 hours, 33 minutes ;EVA 2 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 2 Start: 5 December 2000 – 17:21 UTC *EVA 2 End: 5 December 2000 – 23:58 UTC *Duration: 6 hours, 37 minutes ;EVA 3 – Tanner and Noriega *EVA 3 Start: 7 December 2000 – 16:13 UTC *EVA 3 End: 7 December 2000 – 21:23 UTC *Duration: 5 hours, 10 minutes Crew seat assignments Mission highlights During the 11-day mission, the primary objective was completed, which was to deliver and connect the first set of U.S.-provided sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nadir
The nadir is the direction pointing directly ''below'' a particular location; that is, it is one of two vertical directions at a specified location, orthogonal to a horizontal flat surface. The direction opposite of the nadir is the zenith. Etymology Although it entered English via other European languages, the word “nadir” is ultimately an Arabic loanword. It comes from the Arabic word “nazir”, meaning “opposite to”. More specifically, it originated from the Arabic phrase “nazir as-samt”, meaning “ heopposite direction”. Hebrew (whether ancient or modern) is a related language to Arabic, as they are both Semitic languages. Hebrew also has a word “nadir” (נדיר), but with a somewhat different meaning: it is an adjective meaning “rare”. However, the same word also has a specialized usage to match its meaning in other languages like English. Definitions Space science Since the concept of ''being below'' is itself somewhat vague, scientists define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, and other related hardware housed in the Shuttle's cargo bay. The components were arranged in various configurations to meet the needs of each spaceflight. Spacelab components flew on a total of about 32 Shuttle missions, depending on how such hardware and missions are tabulated. Spacelab allowed scientists to perform experiments in micro-g environment , microgravity in geocentric orbit. There was a variety of Spacelab-associated hardware, so a distinction can be made between the major Spacelab program missions with European scientists running missions in the Spacelab habitable module, missions running other Spacelab hardware experiments, and other Space Transportation System (STS) missions that used some component of Spacelab hardware. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iss072e143839 (Nov 3, 2024) --- The Unoccupied Space-facing Port On The International Space Station's Harmony Module Is Pictured Several Hours Before The SpaceX Dragon Freedom Spacecraft Would Relocate There After Und
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, storage, spacecraft control, and airlock operations. The ISS has eight docking and berthing ports for visiting spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX CRS-9
SpaceX CRS-9, also known as SpX-9, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station which launched on 18 July 2016. The mission was contracted by NASA and was operated by SpaceX using a Dragon capsule. The cargo was successfully carried aboard SpaceX's Falcon 9 Flight 27. Launch and operations history A July 2014 NASA Flight Planning Integration Panel (FPIP) presentation had this mission scheduled no earlier than (NET) 7 December 2015. By December 2014, the launch had been pushed back to NET 9 December 2015. Following the failure of SpaceX CRS-7 on 28 June 2015, the launch date was left open and, in September 2015, was moved to NET 21 March 2016. The flight was later pushed to 24 June, 27 June, 16 July, and finally 18 July 2016, as the crewed mission Soyuz MS-01 took the 24 June slot. CRS-9 launched on 18 July 2016 at 04:44 UTC from Cape Canaveral SLC-40 aboard a Falcon 9 launch vehicle. After 9 minutes and 37 seconds the Dragon spacecr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS) is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supports astronauts working in space, services instruments and other payloads attached to the ISS, and is used for external maintenance. Astronauts receive specialized training to perform these functions with the various systems of the MSS. The MSS is composed of three components: * the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), known as Canadarm2. * the Mobile Remote Servicer Base System (MBS). * the Dextre, Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (SPDM, also known as "Dextre" or "Canada hand"). The system can move along rails on the Integrated Truss Structure on top of the US-provided Mobile Transporter cart, which hosts the MRS Base System. The system's control software was written in the Ada (programming language), Ada 95 programming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-120
STS-120 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) that launched on October 23, 2007, from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The mission is also referred to as ISS-10A by the ISS program. STS-120 delivered the ''Harmony (ISS module), Harmony'' module and reconfigured a portion of the station in preparation for future assembly missions. STS-120 was flown by , and was the twenty-third Space Shuttle mission to the ISS. It was Discovery's 34th flight. Crew Crew notes As commander of STS-120, Pamela Melroy became the second woman (after Eileen Collins) to command a Space Shuttle mission. Additionally, the Expedition 16 crew that received STS-120 was commanded by Peggy Whitson, the first female ISS commander. The flight of STS-120 thus became the first time two female mission commanders were in space at the same time. Crew prior to the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster Prior to the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z1 Truss
The Integrated Truss Structure (ITS) of the International Space Station (ISS) consists of a linear arranged sequence of connected trusses on which various unpressurized components are mounted such as logistics carriers, radiators, solar arrays, and other equipment. It supplies the ISS with a bus architecture. It is approximately 110 meters long and is made from aluminium and stainless steel. Truss components All truss components were named after their planned end-positions: Z for zenith, S for starboard and P for port, with the number indicating the sequential position. The S0 truss might be considered a misnomer, as it is mounted centrally on the zenith position of ''Destiny'' and is neither starboard nor port side. Manufacturing ISS truss segments were fabricated by Boeing in its facilities at Huntington Beach, California (formerly McDonnell Douglas), Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana, Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, and in Tulsa, O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-98
STS-98 was a 2001 Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle Atlantis, Space Shuttle '' Atlantis''. It was the first human spaceflight launch of the 21st century. STS-98 delivered to the station the Destiny (ISS module), ''Destiny'' Laboratory Module. All mission objectives were completed and the shuttle reentered and landed safely at Edwards Air Force Base on 20 February 2001, after twelve days in space, six of which were spent docked to the ISS. Crew Crew seat assignments Launch attempts Mission highlights The crew continued the task of building and enhancing the International Space Station by delivering the U.S. Destiny Laboratory Module, ''Destiny'' Laboratory Module. It was the first NASA lab to be permanently used since the days of Skylab nearly three Decade, decades earlier. It was manufactured by Boeing at the Michoud Assembly Facility and the Marshall Space Flight Center in 1997. Upon transport to Kennedy Space Cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |