Housefly mating.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The housefly (''Musca domestica'') is a
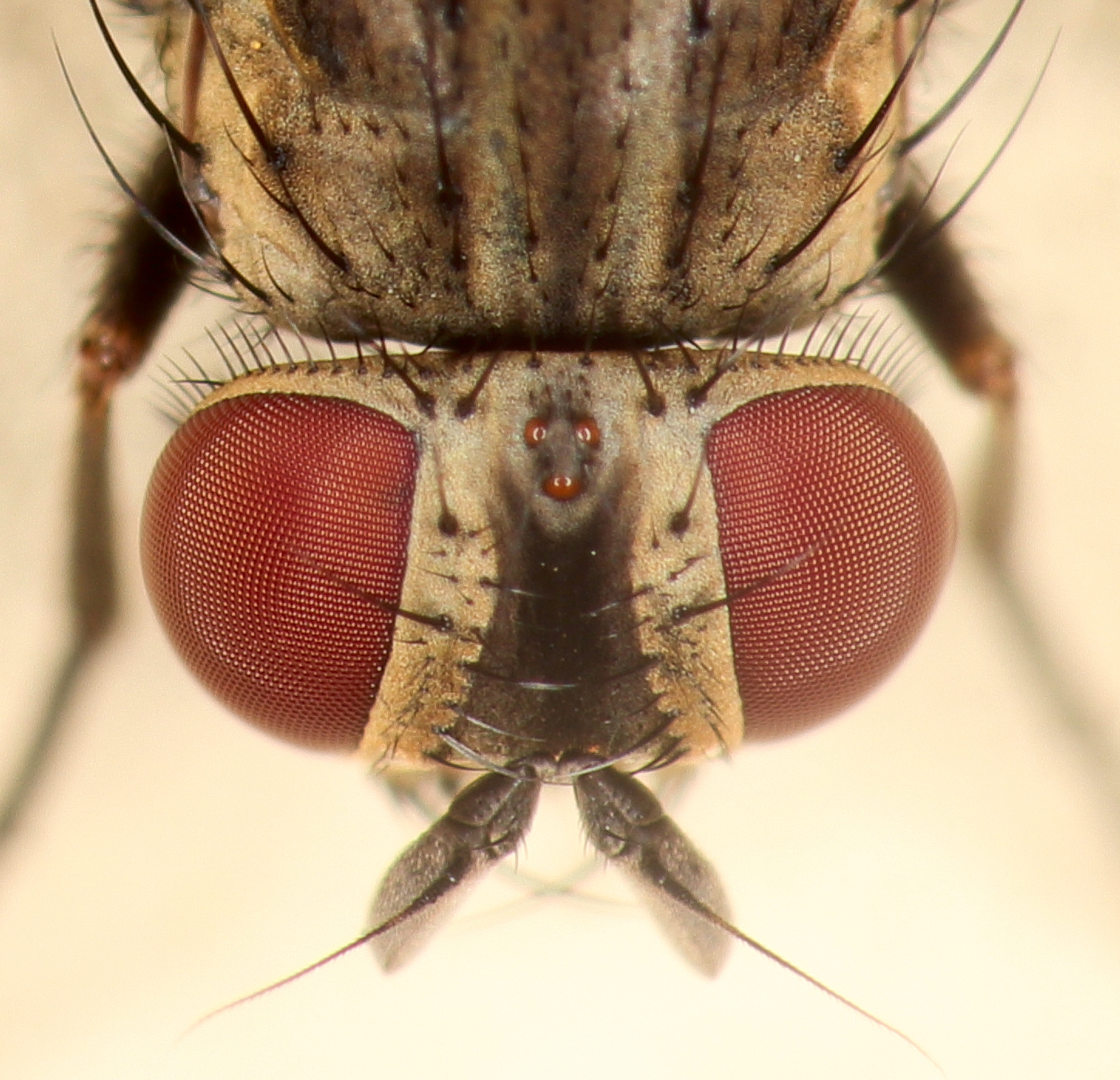 Adult houseflies are usually long with a wingspan of . The females tend to be larger winged than males, while males have relatively longer legs. Females tend to vary more in size and there is geographic variation with larger individuals in higher latitudes. The head is strongly convex in front and flat and slightly conical behind. The pair of large compound eyes almost touch in the male, but are more widely separated in the female. They have three simple eyes ( ocelli) and a pair of short antennae. Houseflies process visual information around seven times more quickly than humans, enabling them to identify and avoid attempts to catch or swat them, since they effectively see the human's movements in slow motion with their higher flicker fusion rate.
Adult houseflies are usually long with a wingspan of . The females tend to be larger winged than males, while males have relatively longer legs. Females tend to vary more in size and there is geographic variation with larger individuals in higher latitudes. The head is strongly convex in front and flat and slightly conical behind. The pair of large compound eyes almost touch in the male, but are more widely separated in the female. They have three simple eyes ( ocelli) and a pair of short antennae. Houseflies process visual information around seven times more quickly than humans, enabling them to identify and avoid attempts to catch or swat them, since they effectively see the human's movements in slow motion with their higher flicker fusion rate.
 The mouthparts are specially adapted for a liquid diet; the mandibles and maxillae are reduced and not functional, and the other mouthparts form a retractable, flexible proboscis with an enlarged, fleshy tip, the labellum. This is a sponge-like structure that is characterized by many grooves, called pseudotracheae, which suck up fluids by capillary action. It is also used to distribute saliva to soften solid foods or collect loose particles. Houseflies have chemoreceptors, organs of taste, on the tarsi of their legs, so they can identify foods such as sugars by walking over them. Houseflies are often seen cleaning their legs by rubbing them together, enabling the chemoreceptors to taste afresh whatever they walk on next. At the end of each leg is a pair of claws, and below them are two adhesive pads,
The mouthparts are specially adapted for a liquid diet; the mandibles and maxillae are reduced and not functional, and the other mouthparts form a retractable, flexible proboscis with an enlarged, fleshy tip, the labellum. This is a sponge-like structure that is characterized by many grooves, called pseudotracheae, which suck up fluids by capillary action. It is also used to distribute saliva to soften solid foods or collect loose particles. Houseflies have chemoreceptors, organs of taste, on the tarsi of their legs, so they can identify foods such as sugars by walking over them. Houseflies are often seen cleaning their legs by rubbing them together, enabling the chemoreceptors to taste afresh whatever they walk on next. At the end of each leg is a pair of claws, and below them are two adhesive pads,  The thorax is a shade of gray, sometimes even black, with four dark, longitudinal bands of even width on the dorsal surface. The whole body is covered with short hairs. Like other
The thorax is a shade of gray, sometimes even black, with four dark, longitudinal bands of even width on the dorsal surface. The whole body is covered with short hairs. Like other 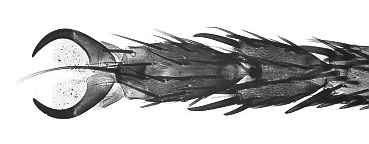 A variety of species around the world appear similar to the housefly, such as the
A variety of species around the world appear similar to the housefly, such as the
 Each female housefly can lay up to 500
Each female housefly can lay up to 500
 Houseflies play an important ecological role in breaking down and recycling organic matter. Adults are mainly
Houseflies play an important ecological role in breaking down and recycling organic matter. Adults are mainly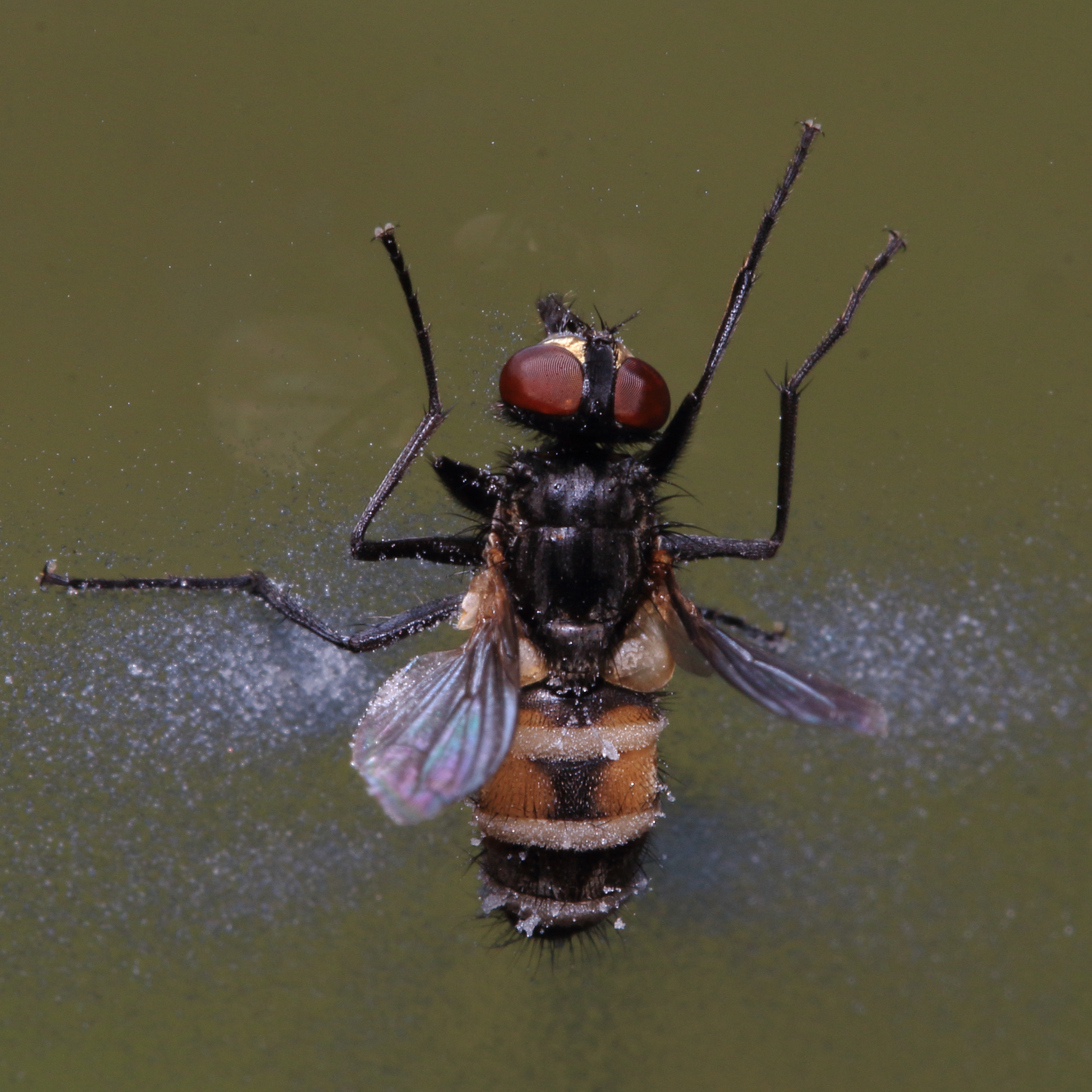  Houseflies sometimes carry
Houseflies sometimes carry
 Houseflies can fly for several kilometers from their breeding places, carrying a wide variety of organisms on their hairs, mouthparts, vomitus, and feces. Parasites carried include cysts of
Houseflies can fly for several kilometers from their breeding places, carrying a wide variety of organisms on their hairs, mouthparts, vomitus, and feces. Parasites carried include cysts of
 During the Second World War, the Japanese worked on
During the Second World War, the Japanese worked on
 Houseflies can be controlled, at least to some extent, by physical, chemical, or biological means. Physical controls include screening with small mesh or the use of vertical strips of plastic or strings of beads in doorways to prevent entry of houseflies into buildings. Fans to create air movement or air barriers in doorways can deter houseflies from entering, and food premises often use fly-killing devices; sticky
Houseflies can be controlled, at least to some extent, by physical, chemical, or biological means. Physical controls include screening with small mesh or the use of vertical strips of plastic or strings of beads in doorways to prevent entry of houseflies into buildings. Fans to create air movement or air barriers in doorways can deter houseflies from entering, and food premises often use fly-killing devices; sticky
 The ease of culturing houseflies, and the relative ease of handling them when compared to the fruit fly '' Drosophila'', have made them useful as model organism for use in laboratories. The American entomologist
The ease of culturing houseflies, and the relative ease of handling them when compared to the fruit fly '' Drosophila'', have made them useful as model organism for use in laboratories. The American entomologist
How to control house and stable flies without using pesticides. Agriculture Information Bulletin Number 673
on the UF/
''The House Fly and How to Suppress It'', by L. O. Howard and F. C. Bishopp. U.S. Department of Agriculture Bulletin No. 1408, 1928
from Project Gutenberg. {{Authority control Cosmopolitan arthropods Flies and humans Household pest insects Insect common names Insect vectors of human pathogens Flies described in 1758 Insects in culture Insects as feed Muscidae Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
fly
Flies are insects of the Order (biology), order Diptera, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwing ...
of the suborder Cyclorrhapha
Cyclorrhapha is an unranked taxon within the infraorder Muscomorpha. They are called "Cyclorrhapha" ('circular-seamed flies') with reference to the circular aperture through which the adult escapes the puparium. This is a circumscriptional name t ...
. It is believed to have evolved in the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
Era, possibly in the Middle East, and has spread all over the world as a commensal of humans. It is the most common fly species found in house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
s. Adults are gray to black, with four dark, longitudinal lines on the thorax, slightly hairy bodies, and a single pair of membranous wings. They have red eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and conv ...
s, set farther apart in the slightly larger female.
The female housefly usually mates only once and stores the sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, whi ...
for later use. She lays batches of about 100 eggs on decaying organic matter such as food waste, carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
, or feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
. These soon hatch into legless white larvae
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
The ...
, known as maggots. After two to five days of development, these metamorphose into reddish-brown pupae, about long. Adult flies normally live for two to four weeks, but can hibernate during the winter. The adults feed on a variety of liquid or semi-liquid substances, as well as solid materials which have been softened by their saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
. They can carry pathogens on their bodies and in their feces, contaminate food, and contribute to the transfer of food-borne illness
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease) ...
es, while, in numbers, they can be physically annoying. For these reasons, they are considered pest
Pest or The Pest may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Pest (organism), an animal or plant deemed to be detrimental to humans or human concerns
** Weed, a plant considered undesirable
* Infectious disease, an illness resulting from an infection
** ...
s.
Houseflies have been used in the laboratory in research into aging and sex determination. Houseflies appear in literature from Ancient Greek myth and Aesop's '' The Impertinent Insect'' onwards. Authors sometimes choose the housefly to speak of the brevity of life, as in William Blake's 1794 poem " The Fly", which deals with mortality subject to uncontrollable circumstances.
Description
 Adult houseflies are usually long with a wingspan of . The females tend to be larger winged than males, while males have relatively longer legs. Females tend to vary more in size and there is geographic variation with larger individuals in higher latitudes. The head is strongly convex in front and flat and slightly conical behind. The pair of large compound eyes almost touch in the male, but are more widely separated in the female. They have three simple eyes ( ocelli) and a pair of short antennae. Houseflies process visual information around seven times more quickly than humans, enabling them to identify and avoid attempts to catch or swat them, since they effectively see the human's movements in slow motion with their higher flicker fusion rate.
Adult houseflies are usually long with a wingspan of . The females tend to be larger winged than males, while males have relatively longer legs. Females tend to vary more in size and there is geographic variation with larger individuals in higher latitudes. The head is strongly convex in front and flat and slightly conical behind. The pair of large compound eyes almost touch in the male, but are more widely separated in the female. They have three simple eyes ( ocelli) and a pair of short antennae. Houseflies process visual information around seven times more quickly than humans, enabling them to identify and avoid attempts to catch or swat them, since they effectively see the human's movements in slow motion with their higher flicker fusion rate.
 The mouthparts are specially adapted for a liquid diet; the mandibles and maxillae are reduced and not functional, and the other mouthparts form a retractable, flexible proboscis with an enlarged, fleshy tip, the labellum. This is a sponge-like structure that is characterized by many grooves, called pseudotracheae, which suck up fluids by capillary action. It is also used to distribute saliva to soften solid foods or collect loose particles. Houseflies have chemoreceptors, organs of taste, on the tarsi of their legs, so they can identify foods such as sugars by walking over them. Houseflies are often seen cleaning their legs by rubbing them together, enabling the chemoreceptors to taste afresh whatever they walk on next. At the end of each leg is a pair of claws, and below them are two adhesive pads,
The mouthparts are specially adapted for a liquid diet; the mandibles and maxillae are reduced and not functional, and the other mouthparts form a retractable, flexible proboscis with an enlarged, fleshy tip, the labellum. This is a sponge-like structure that is characterized by many grooves, called pseudotracheae, which suck up fluids by capillary action. It is also used to distribute saliva to soften solid foods or collect loose particles. Houseflies have chemoreceptors, organs of taste, on the tarsi of their legs, so they can identify foods such as sugars by walking over them. Houseflies are often seen cleaning their legs by rubbing them together, enabling the chemoreceptors to taste afresh whatever they walk on next. At the end of each leg is a pair of claws, and below them are two adhesive pads, pulvilli Pulvilli are soft, cushionlike pads on the feet of insects and other arthropods, such as the housefly and ixodid ticks. They are located at the base of the claws (#2 in the figure at right).
The pulvilli function as an adhesive system. Their sti ...
, enabling the housefly to walk up smooth walls and ceilings using Van der Waals forces. The claws help the housefly to unstick the foot for the next step. Houseflies walk with a common gait on horizontal and vertical surfaces with three legs in contact with the surface and three in movement. On inverted surfaces, they alter the gait to keep four feet stuck to the surface. Houseflies land on a ceiling by flying straight towards it; just before landing, they make a half roll and point all six legs at the surface, absorbing the shock with the front legs and sticking a moment later with the other four.
 The thorax is a shade of gray, sometimes even black, with four dark, longitudinal bands of even width on the dorsal surface. The whole body is covered with short hairs. Like other
The thorax is a shade of gray, sometimes even black, with four dark, longitudinal bands of even width on the dorsal surface. The whole body is covered with short hairs. Like other Diptera
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
, houseflies have only one pair of wings; what would be the hind pair is reduced to small halteres that aid in flight stability. The wings are translucent with a yellowish tinge at their base. Characteristically, the medial vein (M1+2 or fourth long vein) shows a sharp upward bend. Each wing has a lobe at the back, the calypter
A calypter is either of two posterior lobes of the posterior margin of the forewing of flies between the extreme posterior wing base and the alula, which covers the halteres.
The lower calypter is the proximal calypter (synonyms: squama (of som ...
, covering the haltere. The abdomen is gray or yellowish with a dark stripe and irregular dark markings at the side. It has 10 segments which bear spiracles for respiration. In males, the ninth segment bears a pair of claspers for copulation, and the 10th bears anal cerci in both sexes.
 A variety of species around the world appear similar to the housefly, such as the
A variety of species around the world appear similar to the housefly, such as the lesser house fly
The lesser house fly or little house fly, ''Fannia canicularis'', is somewhat smaller () than the common housefly. It is best known for its habit of entering buildings and flying in jagged patterns in the middle of a room. It is slender, and the ...
, ''Fannia canicularis''; the stable fly
''Stomoxys calcitrans'' is commonly called the stable fly, barn fly, biting house fly, dog fly, or power mower fly. Unlike most members of the family Muscidae, ''Stomoxys calcitrans'' ('sharp mouth' + 'kicking') and others of its genus suck bl ...
, ''Stomoxys calcitrans''; and other members of the genus ''Musca'' such as '' M. vetustissima'', the Australian bush fly and several closely related taxa that include ''M. primitiva'', ''M. shanghaiensis'', ''M. violacea'', and ''M. varensis''. The systematic identification of species may require the use of region-specific taxonomic keys and can require dissections of the male reproductive parts for confirmation.
Distribution
The housefly is probably the insect with the widest distribution in the world; it is largely associated with humans and has accompanied them around the globe. It is present in the Arctic, as well as in the tropics, where it is abundant. It is present in all populated parts of Europe, Asia, Africa, Australasia, and theAmericas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
.
Evolution and taxonomy
Though the order of flies (Diptera) is much older, true houseflies are believed to have evolved in the beginning of theCenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
Era. The housefly's superfamily, Muscoidea, is most closely related to the Oestroidea (blow flies, flesh flies and allies), and more distantly to the Hippoboscoidea (louse flies, bat flies and allies). They are thought to have originated in the southern Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Sibe ...
region, particularly the Middle East. Because of their close, commensal relationship with humans, they probably owe their worldwide dispersal to co-migration with humans.
The housefly was first described as ''Musca domestica'' in 1758 based on the common European specimens by the Swedish botanist and zoologist Carl Linnaeus in his ''Systema naturae'' and continues to be classified under that name. A more detailed description was given in 1776 by the Danish entomologist Johan Christian Fabricius in his ''Genera Insectorum''.
Life cycle
 Each female housefly can lay up to 500
Each female housefly can lay up to 500 egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
s in her lifetime, in several batches of about 75 to 150. The eggs are white and are about in length, and they are deposited by the fly in a suitable place, usually dead and decaying organic matter, such as food waste, carrion, or feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
. Within a day, larvae ( maggots) hatch from the eggs; they live and feed where they were laid. They are pale-whitish, long, thinner at the mouth end, and legless. Larval development takes from two weeks, under optimal conditions, to 30 days or more in cooler conditions. The larvae avoid light; the interiors of heaps of animal manure provide nutrient-rich sites and ideal growing conditions, warm, moist, and dark.
At the end of their third instar, the larvae crawl to a dry, cool place and transform into pupae. The pupal case is cylindrical with rounded ends, about long, and formed from the last shed larval skin. It is yellowish at first, darkening through red and brown to nearly black as it ages. Pupae complete their development in two to six days at , but may take 20 days or more at .
When metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
is complete, the adult housefly emerges from the pupa. To do this, it uses the ptilinum
The ptilinum is an eversible pouch on the head, above the base of the antenna in schizophoran flies (a section
Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Section (music), a complete, but not independent, ...
, an eversible pouch on its head, to tear open the end of the pupal case. The adult housefly lives from two weeks to one month in the wild, or longer in benign laboratory conditions. Having emerged from the pupa, it ceases to grow; a small fly is not necessarily a young fly, but is instead the result of getting insufficient food during the larval stage.
Male houseflies are sexually mature after 16 hours and females after 24. Females produce a pheromone, (Z)-9-tricosene (muscalure). This cuticular hydrocarbon is not released into the air and males sense it only on contact with females; it has found use as in pest control, for luring males to fly traps. The male initiates the mating by bumping into the female, in the air or on the ground, known as a "strike". He climbs on to her thorax, and if she is receptive, a courtship period follows, in which the female vibrates her wings and the male strokes her head. The male then reverses onto her abdomen and the female pushes her ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typical ...
into his genital opening; copulation, with sperm transfer, lasts for several minutes. Females normally mate only once and then reject further advances from males, while males mate multiple times. A volatile semiochemical that is deposited by females on their eggs attracts other gravid females and leads to clustered egg deposition.
The larvae depend on warmth and sufficient moisture to develop; generally, the warmer the temperature, the faster they grow. In general, fresh swine and chicken manures present the best conditions for the developing larvae, reducing the larval period and increasing the size of the pupae. Cattle, goat, and horse manures produce fewer, smaller pupae, while mature swine manure composted with water content under 30%, approached 100% mortality of the larvae. Pupae can range from about in weight under different conditions.
The life cycle can be completed in seven to ten days under optimal conditions, but may take up to two months in adverse circumstances. In temperate regions, 12 generations may occur per year, and in the tropics and subtropics, more than 20.
Ecology
 Houseflies play an important ecological role in breaking down and recycling organic matter. Adults are mainly
Houseflies play an important ecological role in breaking down and recycling organic matter. Adults are mainly carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other sof ...
; their primary food is animal matter, carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, c ...
, and feces
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
, but they also consume milk, sugary substances, and rotting fruit and vegetables. Solid foods are softened with saliva before being sucked up. They can be opportunistic blood feeders. Houseflies have a mutualistic relationship with the bacterium '' Klebsiella oxytoca'', which can live on the surface of housefly eggs and deter fungi which compete with the housefly larvae for nutrients.
Adult houseflies are diurnal and rest at night. If inside a building after dark, they tend to congregate on ceilings, beams, and overhead wires, while out of doors, they crawl into foliage or long grass, or rest in shrubs and trees or on wires. In cooler climates, some houseflies hibernate
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
in winter, choosing to do so in cracks and crevices, gaps in woodwork, and the folds of curtains. They arouse in the spring when the weather warms up, and search out a place to lay their eggs.
Houseflies have many predators, including birds, reptiles, amphibians, various insects, and spiders. The eggs, larvae, and pupae have many species of stage-specific parasites and parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable str ...
s. Some of the more important are the parasitic wasps ''Muscidifurax uniraptor
''Muscidifurax uniraptor'' is a species of wasp (the taxonomic order Hymenoptera) in the family Pteromalidae. The species does not currently have a common name. ''M. uniraptor'' is a pupal parasitoid of synanthropic filth-breeding Diptera and ...
'' and ''Spalangia cameroni
''Spalangia cameroni'' is a species of parasitic wasp in the genus '' Spalangia'' that feeds on houseflies
The housefly (''Musca domestica'') is a fly of the suborder Cyclorrhapha. It is believed to have evolved in the Cenozoic Era, po ...
''; these lay their eggs in the housefly larvae tissue and their offspring complete their development before the adult houseflies can emerge from the pupae. Hister beetles feed on housefly larvae in manure heaps and the predatory mite ''Macrocheles muscae domesticae'' consumes housefly eggs, each mite eating 20 eggs per day.
 Houseflies sometimes carry
Houseflies sometimes carry phoretic
Phoresis or phoresy is a non-permanent, commensalistic interaction in which one organism (a phoront or phoretic) attaches itself to another (the host) solely for the purpose of travel. Phoresis has been observed directly in ticks and mites s ...
(nonparasitic) passengers, including mites such as ''Macrocheles muscaedomesticae
''Macrocheles muscaedomesticae'' is a species of mite in the family Macrochelidae. It has a cosmopolitan distribution.
This mite species feeds on flies in their egg, larval and (possibly) adult stages, and also attaches to adult flies for disper ...
'' and the pseudoscorpion ''Lamprochernes chyzeri
''Lamprochernes chyzeri'', also known as Chyzer’s shining claw, is a species of pseudoscorpion in the family Chernetidae. Its range covers most of Europe, including Sweden, Finland, Norway, England, Hungary, Romania and Yugoslavia. It is a phor ...
''.
The pathogenic fungus ''Entomophthora muscae
''Entomophthora muscae'' is a species of pathogenic fungus in the order Entomophthorales which causes a fatal disease in flies. It can cause epizootic outbreaks of disease in houseflies and has been investigated as a potential biological control ...
'' causes a fatal disease in houseflies. After infection, the fungal hyphae grow throughout the body, killing the housefly in about five days. Infected houseflies have been known to seek high temperatures that could suppress the growth of the fungus. Affected females tend to be more attractive to males, but the fungus-host interactions have not been fully understood. The housefly also acts as the alternative host to the parasitic nematode ''Habronema muscae
''Habronema muscae'' is an internal stomach parasite that is most commonly found in horses. It is the most common cause of cutaneous ulcerative granulomas in the horse. It is in genus '' Habronema''.
Life cycle
Eggs
The parasitic adult fema ...
'' that attacks horses. A virus that causes enlargement of the salivary glands, salivary gland hypertrophy virus (SGHV), is spread among houseflies through contact with food and infected female houseflies become sterile.
Relationship with humans
Houseflies are a nuisance, disturbing people while at leisure and at work, but they are disliked principally because of their habits of contaminating foodstuffs. They alternate between breeding and feeding in dirty places with feeding on human foods, during which process they soften the food with saliva and deposit their feces, creating a health hazard. However, housefly larvae are as nutritious asfish meal
Fish meal is a commercial product made from whole wild-caught fish, bycatch and fish by-products to feed farm animals, e.g., pigs, poultry, and farmed fish.R. D. Miles and F. A. Chapman.FA122: The Benefits of Fish Meal in Aquaculture DietsFisheri ...
, and could be used to convert waste to insect-based animal feed for farmed fish and livestock. Housefly larvae have been used in traditional cures since the Ming period in China (1386 AD) for a range of medical conditions and have been considered as a useful source of chitosan, with antioxidant properties, and possibly other proteins and polysaccharides of medical value.
Houseflies have been used in art and artifacts in many cultures. In 16th- and 17th-century European vanitas paintings, houseflies sometimes occur as ''memento mori
''Memento mori'' (Latin for 'remember that you ave todie'Master of Frankfurt
The Master of Frankfurt (1460–c. 1533) was a Flemish Renaissance painter active in Antwerp between about 1480 and 1520.Stephen H. Goddard, "Master of Frankfurt," ''Grove Art Online'', Oxford University Press ccessed 9 April 2008/ref>Kate Chall ...
'' (1496). Housefly amulets were popular in ancient Egypt.
As a disease vector
 Houseflies can fly for several kilometers from their breeding places, carrying a wide variety of organisms on their hairs, mouthparts, vomitus, and feces. Parasites carried include cysts of
Houseflies can fly for several kilometers from their breeding places, carrying a wide variety of organisms on their hairs, mouthparts, vomitus, and feces. Parasites carried include cysts of protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
, e.g. '' Entamoeba histolytica'' and '' Giardia lamblia'' and eggs of helminths; e.g., '' Ascaris lumbricoides'', '' Trichuris trichiura'', ''Hymenolepis nana
Dwarf tapeworm (''Hymenolepis nana'', also known as ''Rodentolepis nana'', ''Vampirolepis nana'', ''Hymenolepis fraterna'', and ''Taenia nana'') is a cosmopolitan species though most common in temperate zones, and is one of the most common ces ...
'', and '' Enterobius vermicularis''. Houseflies do not serve as a secondary host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include a ...
or act as a reservoir of any bacteria of medical or veterinary importance, but they do serve as mechanical vectors to over 100 pathogens, such as those causing typhoid, cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
, salmonellosis, bacillary dysentery, tuberculosis, anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium ''Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The sk ...
, ophthalmia, and pyogenic cocci, making them especially problematic in hospitals and during outbreaks of certain diseases. Disease-causing organisms on the outer surface of the housefly may survive for a few hours, but those in the crop or gut can be viable for several days. Usually, too few bacteria are on the external surface of the houseflies (except perhaps for '' Shigella'') to cause infection, so the main routes to human infection are through the housefly's regurgitation and defecation. A number of bacterial endosymbionts have however been detected in sequence-based identification from whole genome sequences extracted from flies, the greatest numbers being detected in the abdomen.
In the early 20th century, Canadian public health workers believed that the control of houseflies was important in controlling the spread of tuberculosis. A "swat that fly" contest was held for children in Montreal in 1912. Houseflies were targeted in 1916, when a polio epidemic broke out in the eastern United States. The belief that housefly control was the key to disease control continued, with extensive use of insecticidal spraying well until the mid-1950s, declining only after the introduction of Salk's vaccine. In China, Mao Zedong's Four Pests Campaign between 1958 and 1962 exhorted the people to catch and kill houseflies, along with rats, mosquitoes, and sparrows.
In warfare
 During the Second World War, the Japanese worked on
During the Second World War, the Japanese worked on entomological warfare
Entomological warfare (EW) is a type of biological warfare that uses insects to interrupt supply lines by damaging crops, or to directly harm enemy combatants and civilian populations. There have been several programs which have attempted to instit ...
techniques under Shirō Ishii. Japanese Yagi bombs developed at Pingfan consisted of two compartments, one with houseflies and another with a bacterial slurry that coated the houseflies prior to release. '' Vibrio cholerae'', which causes cholera, was the bacterium of choice, and was used in China in Baoshan in 1942, and in northern Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
in 1943. Baoshan had been used by the Allies and bombing produced epidemics that killed 60,000 people in the initial stages, reaching a radius of which finally took a toll of 200,000 victims. The Shandong attack killed 210,000; the occupying Japanese troops had been vaccinated in advance.
In waste management
The ability of housefly larvae to feed and develop in a wide range of decaying organic matter is important for recycling of nutrients in nature. This could be exploited to combat ever-increasing amounts of waste. Housefly larvae can be mass-reared in a controlled manner in animal manure, reducing the bulk of waste and minimizing environmental risks of its disposal. Harvested maggots may be used as feed for animal nutrition.Control
 Houseflies can be controlled, at least to some extent, by physical, chemical, or biological means. Physical controls include screening with small mesh or the use of vertical strips of plastic or strings of beads in doorways to prevent entry of houseflies into buildings. Fans to create air movement or air barriers in doorways can deter houseflies from entering, and food premises often use fly-killing devices; sticky
Houseflies can be controlled, at least to some extent, by physical, chemical, or biological means. Physical controls include screening with small mesh or the use of vertical strips of plastic or strings of beads in doorways to prevent entry of houseflies into buildings. Fans to create air movement or air barriers in doorways can deter houseflies from entering, and food premises often use fly-killing devices; sticky fly paper
Flypaper (also known as a fly ribbon, fly strip, fly capture tape, or fly catcher) is a fly-killing device made of paper coated with a sweetly fragrant, but extremely sticky and sometimes poisonous substance that traps flies and other flying inse ...
s hanging from the ceiling are effective, but electric " bug zappers" should not be used directly above food-handling areas because of scattering of contaminated insect parts. Another approach is the elimination as far as possible of potential breeding sites. Keeping garbage in lidded containers and collecting it regularly and frequently, prevents any eggs laid from developing into adults. Unhygienic rubbish tips are a prime housefly-breeding site, but if garbage is covered by a layer of soil, preferably daily, this can be avoided.
Insecticides can be used. Larvicides kill the developing larvae, but large quantities may need to be used to reach areas below the surface. Aerosols can be used in buildings to "zap" houseflies, but outside applications are only temporarily effective. Residual sprays on walls or resting sites have a longer-lasting effect. Many strains of housefly have become immune to the most commonly used insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
s. Resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
to carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally o ...
s and organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered a ...
s is conferred by variation in acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that a ...
genes. ''M. domestica'' has achieved a high degree of resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
. Resistance monitoring is vital to avoid continued use of ineffective a.i.s such as found in the notably severe example of Freeman et al 2019 in Kansas and Maryland, USA.
Several means of biological pest control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also invo ...
have been investigated. These include the introduction of another species, the black soldier fly (''Hermetia illucens''), whose larvae compete with those of the housefly for resources. The introduction of dung beetles to churn up the surface of a manure heap and render it unsuitable for breeding is another approach. Augmentative biological control by releasing parasitoids can be used, but houseflies breed so fast that the natural enemies are unable to keep up.
In science
 The ease of culturing houseflies, and the relative ease of handling them when compared to the fruit fly '' Drosophila'', have made them useful as model organism for use in laboratories. The American entomologist
The ease of culturing houseflies, and the relative ease of handling them when compared to the fruit fly '' Drosophila'', have made them useful as model organism for use in laboratories. The American entomologist Vincent Dethier
Vincent Gaston Dethier (February 20, 1915 – September 8, 1993) was an American physiologist and entomologist. Considered a leading expert in his field, he was a pioneer in the study of insect-plant interactions and wrote more than 170 academic ...
, in his humorous ''To Know A Fly'' (1962), pointed out that as a laboratory animal, houseflies did not trouble anyone sensitive to animal cruelty. Houseflies have a small number of chromosomes, haploid 6 or diploid 12. Because the somatic tissue of the housefly consists of long-lived postmitotic cells, it can be used as an informative model system for understanding cumulative age-related cellular alterations. Oxidative DNA damage 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in houseflies was found in one study to increase with age and reduce life expectancy supporting the hypothesis that oxidative molecular damage is a causal factor in senescence (aging).
The housefly is an object of biological research, partly for its variable sex-determination mechanism. Although a wide variety of sex-determination mechanisms exists in nature (e.g. male and female heterogamy
Heterogamy is a term applied to a variety of distinct phenomena in different scientific domains. Usually having to do with some kind of difference, "hetero", in reproduction, "gamy". See below for more specific senses.
Science Reproductive biolog ...
, haplodiploidy, environmental factors), the way sex is determined is usually fixed within a species. The housefly is, however, thought to exhibit multiple mechanisms for sex determination, such as male heterogamy (like most insects and mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s), female heterogamy (like birds), and maternal control over offspring sex. This is because a male-determining gene (''Mdmd'') can be found on most or all housefly chromosomes. Sexual differentiation is controlled, as in other insects, by an ancient developmental switch, doublesex, which is regulated by the transformer protein in many different insects. ''Mdmd'' causes male development by negatively regulating ''transformer''. There is also a female-determining allele of ''transformer'' that is not sensitive to the negative regulation of ''Mdmd.''
The antimicrobial peptides produced by housefly maggots are of pharmacological interest.
In the 1970s, the aircraft modeler Frank Ehling constructed miniature balsa-wood aircraft powered by live houseflies. Studies of tethered houseflies have helped in the understanding of insect vision, sensory perception, and flight control.
In literature
'' The Impertinent Insect'' is a group of five fables, sometimes ascribed to Aesop, concerning an insect, in one version a fly, which puffs itself up to seem important. In the Biblical fourth plague of Egypt, flies represent death and decay, while thePhilistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
god Beelzebub's name may mean "lord of the flies". In Greek mythology, Myiagros
In ancient Greek religion, Myiagros ("He Who Chases the Flies") or Myacoris was a cult title for a divine figure who warded off flies. It could be used as an epithet for either a divinity or a hero.
Pausanias characterizes Myiagros as a diviniz ...
was a god who chased away flies during the sacrifices to Zeus and Athena; Zeus sent a fly to bite Pegasus
Pegasus ( grc-gre, Πήγασος, Pḗgasos; la, Pegasus, Pegasos) is one of the best known creatures in Greek mythology. He is a winged divine stallion usually depicted as pure white in color. He was sired by Poseidon, in his role as hor ...
, causing Bellerophon
Bellerophon (; Ancient Greek: Βελλεροφῶν) or Bellerophontes (), born as Hipponous, was a hero of Greek mythology. He was "the greatest hero and slayer of monsters, alongside Cadmus and Perseus, before the days of Heracles", and his ...
to fall back to Earth when he attempted to ride the winged steed to Mount Olympus. In the traditional Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United ...
religion, Big Fly is an important spirit being.
William Blake's 1794 poem "The Fly", part of his collection ''Songs of Experience
''Songs of Innocence and of Experience'' is a collection of illustrated poems by William Blake. It appeared in two phases: a few first copies were printed and illuminated by Blake himself in 1789; five years later, he bound these poems with a ...
'', deals with the insect's mortality, subject to uncontrollable circumstances, just like humans. Emily Dickinson's 1855 poem "I Heard a Fly Buzz When I Died" speaks of flies in the context of death. In William Golding
Sir William Gerald Golding (19 September 1911 – 19 June 1993) was a British novelist, playwright, and poet. Best known for his debut novel ''Lord of the Flies'' (1954), he published another twelve volumes of fiction in his lifetime. In 1980 ...
's 1954 novel '' Lord of the Flies'', the fly is, however, a symbol of the children involved.
Ogden Nash's humorous two-line 1942 poem "God in His wisdom made the fly/And then forgot to tell us why." indicates the debate about the value of biodiversity, given that even those considered by humans as pests have their place in the world's ecosystems.
References
External links
* The house-fly, ''Musca domestica'' Linn. : its structure, habits, development, relation to disease and control by C. Gordon Hewitt (1914)How to control house and stable flies without using pesticides. Agriculture Information Bulletin Number 673
on the UF/
IFAS IFAS may refer:
* Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences
* Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge, a sewage treatment process
* International French adjectival system
In rock climbing, mountaineering, and other climbing disciplines, clim ...
Featured Creatures Web site
''The House Fly and How to Suppress It'', by L. O. Howard and F. C. Bishopp. U.S. Department of Agriculture Bulletin No. 1408, 1928
from Project Gutenberg. {{Authority control Cosmopolitan arthropods Flies and humans Household pest insects Insect common names Insect vectors of human pathogens Flies described in 1758 Insects in culture Insects as feed Muscidae Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus