Gutenberg bible Old Testament Epistle of St Jerome.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg (; – 3 February 1468) was a German inventor and craftsman who introduced letterpress
 Johannes Gutenberg was born in
Johannes Gutenberg was born in
 Some time in 1456, there was a dispute between Gutenberg and Fust, and Fust demanded his money back, accusing Gutenberg of misusing the funds. Gutenberg's two rounds of financing from Fust, a total of 1,600 guilders at 6% interest, now amounted to 2,026 guilders. Fust sued at the archbishop's court. A November 1455 legal document records that there was a partnership for a "project of the books," the funds for which Gutenberg had used for other purposes, according to Fust. The court decided in favor of Fust, giving him control over the Bible printing workshop and half of all printed Bibles.
Thus Gutenberg was effectively bankrupt, but it appears he retained (or restarted) a small printing shop, and participated in the printing of a Bible in the town of Bamberg around 1459, for which he seems at least to have supplied the type. But since his printed books never carry his name or a date, it is difficult to be certain, and there is consequently a considerable scholarly debate on this subject. It is also possible that the large Catholicon (trilingual dictionary), ''Catholicon'' dictionary, 300 copies of 754 pages, printed in Mainz in 1460, was executed in his workshop.
Meanwhile, the Fust–Schöffer shop was the first in Europe to bring out a book with the printer's name and date, the ''Mainz Psalter'' of August 1457, and while proudly proclaiming the mechanical process by which it had been produced, it made no mention of Gutenberg.
Some time in 1456, there was a dispute between Gutenberg and Fust, and Fust demanded his money back, accusing Gutenberg of misusing the funds. Gutenberg's two rounds of financing from Fust, a total of 1,600 guilders at 6% interest, now amounted to 2,026 guilders. Fust sued at the archbishop's court. A November 1455 legal document records that there was a partnership for a "project of the books," the funds for which Gutenberg had used for other purposes, according to Fust. The court decided in favor of Fust, giving him control over the Bible printing workshop and half of all printed Bibles.
Thus Gutenberg was effectively bankrupt, but it appears he retained (or restarted) a small printing shop, and participated in the printing of a Bible in the town of Bamberg around 1459, for which he seems at least to have supplied the type. But since his printed books never carry his name or a date, it is difficult to be certain, and there is consequently a considerable scholarly debate on this subject. It is also possible that the large Catholicon (trilingual dictionary), ''Catholicon'' dictionary, 300 copies of 754 pages, printed in Mainz in 1460, was executed in his workshop.
Meanwhile, the Fust–Schöffer shop was the first in Europe to bring out a book with the printer's name and date, the ''Mainz Psalter'' of August 1457, and while proudly proclaiming the mechanical process by which it had been produced, it made no mention of Gutenberg.
 Between 1450 and 1455, Gutenberg printed several texts, some of which remain unidentified; his texts did not bear the printer's name or date, so attribution is possible only from typographical evidence and external references. Certainly several church documents including a papal letter and two 31-line Indulgence, indulgences were printed, one of which was issued in Mainz. In view of the value of printing in quantity, seven editions in two styles were ordered, resulting in several thousand copies being printed. Some printed editions of ''Ars Minor'', a schoolbook on Latin grammar by Aelius Donatus, may have been printed by Gutenberg; these have been dated either 1451–52 or 1455.
In 1455, Gutenberg completed copies of a beautifully executed folio Bible (''Biblia Sacra''), with 42 lines on each page. Copies sold for 30 Florin (Italian coin), florins each, which was roughly three years' wages for an average clerk. Nonetheless, it was much cheaper than a manuscript Bible that could take a single scribe over a year to prepare. After printing, some copies were Rubrication, rubricated or Illuminated manuscript, hand-illuminated in the same elegant way as manuscript Bibles from the same period.
48 substantially complete copies are known to survive, including two at the British Library that can be viewed and compared online. The text lacks modern features such as page numbers, Indentation (typesetting), indentations, and paragraph breaks.
An undated 36-line Bible, 36-line edition of the Bible was printed, probably in Bamberg in 1458–60, possibly by Gutenberg. A large part of it was shown to have been set from a copy of Gutenberg's Bible, thus disproving earlier speculation that it was the earlier of the two.
Between 1450 and 1455, Gutenberg printed several texts, some of which remain unidentified; his texts did not bear the printer's name or date, so attribution is possible only from typographical evidence and external references. Certainly several church documents including a papal letter and two 31-line Indulgence, indulgences were printed, one of which was issued in Mainz. In view of the value of printing in quantity, seven editions in two styles were ordered, resulting in several thousand copies being printed. Some printed editions of ''Ars Minor'', a schoolbook on Latin grammar by Aelius Donatus, may have been printed by Gutenberg; these have been dated either 1451–52 or 1455.
In 1455, Gutenberg completed copies of a beautifully executed folio Bible (''Biblia Sacra''), with 42 lines on each page. Copies sold for 30 Florin (Italian coin), florins each, which was roughly three years' wages for an average clerk. Nonetheless, it was much cheaper than a manuscript Bible that could take a single scribe over a year to prepare. After printing, some copies were Rubrication, rubricated or Illuminated manuscript, hand-illuminated in the same elegant way as manuscript Bibles from the same period.
48 substantially complete copies are known to survive, including two at the British Library that can be viewed and compared online. The text lacks modern features such as page numbers, Indentation (typesetting), indentations, and paragraph breaks.
An undated 36-line Bible, 36-line edition of the Bible was printed, probably in Bamberg in 1458–60, possibly by Gutenberg. A large part of it was shown to have been set from a copy of Gutenberg's Bible, thus disproving earlier speculation that it was the earlier of the two.
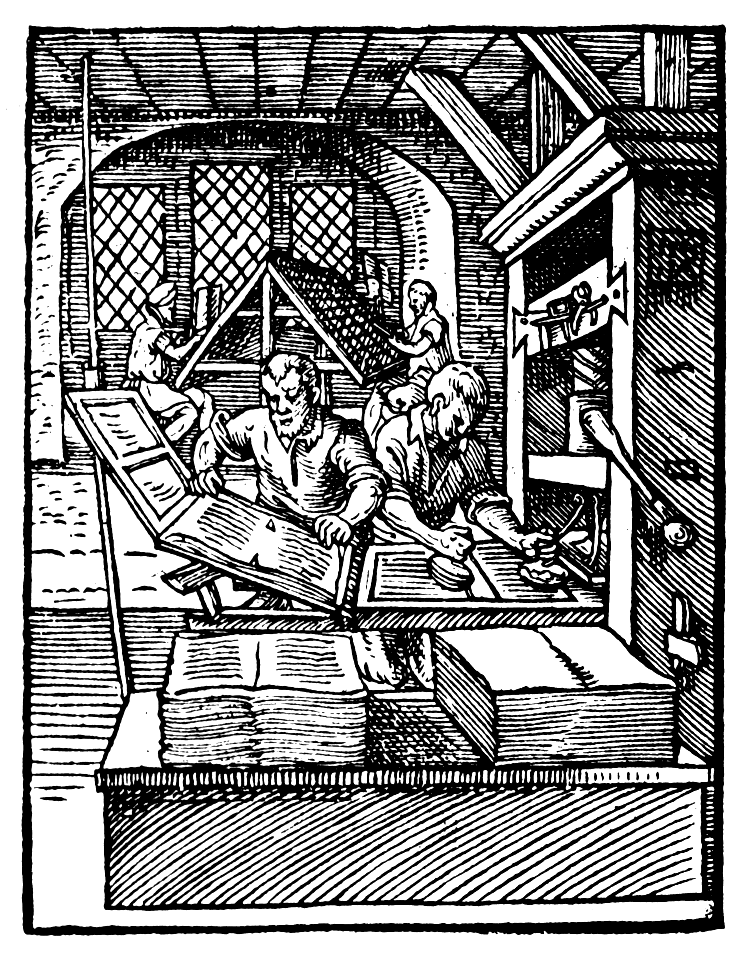 Gutenberg's early printing process, and what texts he printed with movable type, are not known in great detail. His later Bibles were printed in such a way as to have required large quantities of type, some estimates suggesting as many as 100,000 individual sorts. Setting each page would take, perhaps, half a day, and considering all the work in loading the press, inking the type, pulling the impressions, hanging up the sheets, distributing the type, etc., it is thought that the Gutenberg–Fust shop might have employed as many as 25 craftsmen.
Gutenberg's technique of making movable type remains unclear. In the following decades, Punch (typography), punches and copper matrices became standardized in the rapidly disseminating printing presses across Europe. Whether Gutenberg used this sophisticated technique or a somewhat primitive version has been the subject of considerable debate.
In the standard process of making type, a hard metal punch (made by punchcutting, with the letter carved back to front) is hammered into a softer copper bar, creating a ''matrix (printing), matrix''. This is then placed into a hand mould, hand-held mould and a piece of type, or "sort", is cast by filling the mould with molten type-metal; this cools almost at once, and the resulting piece of type can be removed from the mould. The matrix can be reused to create hundreds, or thousands, of identical sorts so that the same character appearing anywhere within the book will appear very uniform, giving rise, over time, to the development of distinct styles of typefaces or fonts. After casting, the sorts are arranged into type cases, and used to make up pages which are inked and printed, a procedure which can be repeated hundreds, or thousands, of times. The sorts can be reused in any combination, earning the process the name of "movable type".
The invention of the making of types with punch, matrix and mold has been widely attributed to Gutenberg. However, recent evidence suggests that Gutenberg's process was somewhat different. If he used the punch and matrix approach, all his letters should have been nearly identical, with some variation due to miscasting and inking. However, the type used in Gutenberg's earliest work shows other variations.
Gutenberg's early printing process, and what texts he printed with movable type, are not known in great detail. His later Bibles were printed in such a way as to have required large quantities of type, some estimates suggesting as many as 100,000 individual sorts. Setting each page would take, perhaps, half a day, and considering all the work in loading the press, inking the type, pulling the impressions, hanging up the sheets, distributing the type, etc., it is thought that the Gutenberg–Fust shop might have employed as many as 25 craftsmen.
Gutenberg's technique of making movable type remains unclear. In the following decades, Punch (typography), punches and copper matrices became standardized in the rapidly disseminating printing presses across Europe. Whether Gutenberg used this sophisticated technique or a somewhat primitive version has been the subject of considerable debate.
In the standard process of making type, a hard metal punch (made by punchcutting, with the letter carved back to front) is hammered into a softer copper bar, creating a ''matrix (printing), matrix''. This is then placed into a hand mould, hand-held mould and a piece of type, or "sort", is cast by filling the mould with molten type-metal; this cools almost at once, and the resulting piece of type can be removed from the mould. The matrix can be reused to create hundreds, or thousands, of identical sorts so that the same character appearing anywhere within the book will appear very uniform, giving rise, over time, to the development of distinct styles of typefaces or fonts. After casting, the sorts are arranged into type cases, and used to make up pages which are inked and printed, a procedure which can be repeated hundreds, or thousands, of times. The sorts can be reused in any combination, earning the process the name of "movable type".
The invention of the making of types with punch, matrix and mold has been widely attributed to Gutenberg. However, recent evidence suggests that Gutenberg's process was somewhat different. If he used the punch and matrix approach, all his letters should have been nearly identical, with some variation due to miscasting and inking. However, the type used in Gutenberg's earliest work shows other variations.
 In 2001, the physicist Blaise Agüera y Arcas and Princeton University, Princeton librarian Paul Needham, used digital scans of a Papal bull in the Scheide Library, Princeton, to carefully compare the same letters (types) appearing in different parts of the printed text. The irregularities in Gutenberg's type, particularly in simple characters such as the hyphen, suggested that the variations could not have come either from ink smear or from wear and damage on the pieces of metal on the types themselves. Although some identical types are clearly used on other pages, other variations, subjected to detailed image analysis, suggested that they could not have been produced from the same matrix. Transmitted light pictures of the page also appeared to reveal substructures in the type that could not arise from traditional punchcutting techniques. They hypothesized that the method involved impressing simple shapes to create alphabets in "cuneiform" style in a matrix made of some soft material, perhaps sand. Casting the type would destroy the mould, and the matrix would need to be recreated to make each additional sort. This could explain the variations in the type, as well as the substructures observed in the printed images.
Thus, they speculated that "the decisive factor for the birth of typography", the use of reusable moulds for casting type, was a more progressive process than was previously thought. They suggested that the additional step of using the punch to create a mould that could be reused many times was not taken until twenty years later, in the 1470s. Others have not accepted some or all of their suggestions, and have interpreted the evidence in other ways, and the truth of the matter remains uncertain.
A 1568 book ''Batavia'' by Hadrianus Junius from Holland claims that the idea of the movable type came to Gutenberg from Laurens Janszoon Coster via Fust, who was apprenticed to Coster in the 1430s and may have brought some of his equipment from Haarlem to Mainz. While Coster appears to have experimented with moulds and castable metal type, there is no evidence that he had actually printed anything with this technology. He was an inventor and a goldsmith. However, there is one indirect supporter of the claim that Coster might be the inventor. The author of the ''Cologne Chronicle of 1499'' quotes Ulrich Zell, the first printer of Cologne, that printing was performed in
In 2001, the physicist Blaise Agüera y Arcas and Princeton University, Princeton librarian Paul Needham, used digital scans of a Papal bull in the Scheide Library, Princeton, to carefully compare the same letters (types) appearing in different parts of the printed text. The irregularities in Gutenberg's type, particularly in simple characters such as the hyphen, suggested that the variations could not have come either from ink smear or from wear and damage on the pieces of metal on the types themselves. Although some identical types are clearly used on other pages, other variations, subjected to detailed image analysis, suggested that they could not have been produced from the same matrix. Transmitted light pictures of the page also appeared to reveal substructures in the type that could not arise from traditional punchcutting techniques. They hypothesized that the method involved impressing simple shapes to create alphabets in "cuneiform" style in a matrix made of some soft material, perhaps sand. Casting the type would destroy the mould, and the matrix would need to be recreated to make each additional sort. This could explain the variations in the type, as well as the substructures observed in the printed images.
Thus, they speculated that "the decisive factor for the birth of typography", the use of reusable moulds for casting type, was a more progressive process than was previously thought. They suggested that the additional step of using the punch to create a mould that could be reused many times was not taken until twenty years later, in the 1470s. Others have not accepted some or all of their suggestions, and have interpreted the evidence in other ways, and the truth of the matter remains uncertain.
A 1568 book ''Batavia'' by Hadrianus Junius from Holland claims that the idea of the movable type came to Gutenberg from Laurens Janszoon Coster via Fust, who was apprenticed to Coster in the 1430s and may have brought some of his equipment from Haarlem to Mainz. While Coster appears to have experimented with moulds and castable metal type, there is no evidence that he had actually printed anything with this technology. He was an inventor and a goldsmith. However, there is one indirect supporter of the claim that Coster might be the inventor. The author of the ''Cologne Chronicle of 1499'' quotes Ulrich Zell, the first printer of Cologne, that printing was performed in
 There are many statues of Gutenberg in Germany, including the famous one by Bertel Thorvaldsen (1837) at Gutenbergplatz (Mainz), Gutenbergplatz in Mainz, home to the eponymous Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz and the
There are many statues of Gutenberg in Germany, including the famous one by Bertel Thorvaldsen (1837) at Gutenbergplatz (Mainz), Gutenbergplatz in Mainz, home to the eponymous Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz and the
Gutenberg-Museum Mainz, Germany
– English homepage
Gutenberg Bible
at the British Library {{DEFAULTSORT:Gutenberg, Johannes Johannes Gutenberg, 1398 births 1468 deaths 15th-century German businesspeople 15th-century German inventors 15th-century printers Businesspeople from Mainz German goldsmiths German printers German Roman Catholics German typographers and type designers History of printing People from the Electoral Palatinate Printers of incunabula University of Erfurt alumni
printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
to Europe with his movable-type printing press. Though not the first of its kind, earlier designs were restricted to East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
, and Gutenberg's version was the first to spread across the world. His work led to an information revolution
The term information revolution describes current economic, social and technological trends beyond the Industrial Revolution.
Many competing terms have been proposed that focus on different aspects of this societal development.
The British polymat ...
and the unprecedented mass-spread of literature throughout Europe. It also had a direct impact on the development of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
and humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
movement, ushering in the modern period of human history.
His many contributions to printing include the invention of a process for mass-producing movable type; the use of oil-based ink
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker ...
for printing books; adjustable molds; mechanical movable type; and the use of a wooden printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
similar to the agricultural screw press
A screw press is a type of machine press in which the ram is driven up and down by a screw. The screw shaft can be driven by a handle or a wheel. It works by using a coarse screw to convert the rotation of the handle or drive-wheel into a small d ...
es of the period. Gutenberg's method for making type is traditionally considered to have included a type metal
In printing, type metal refers to the metal alloys used in traditional typefounding and hot metal typesetting. Historically, type metal was an alloy of lead, tin and antimony in different proportions depending on the application, be it individ ...
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
and a hand mould
A hand mold is a simple mold used for low quantity work. It is used in the injection molding and the printing industry.
It is made by a hand injection molding machine. It is a simple machine which contains a barrel, handle, nozzle, mold and heater ...
for casting type. The alloy was a mixture of lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, and antimony
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from la, stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
that melted at a relatively low temperature for faster and more economical casting, cast well, and created a durable type. His major work, the Gutenberg Bible
The Gutenberg Bible (also known as the 42-line Bible, the Mazarin Bible or the B42) was the earliest major book printed using mass-produced movable metal type in Europe. It marked the start of the " Gutenberg Revolution" and the age of printed ...
, was the first printed version of the Bible and has been acclaimed for its high aesthetic and technical quality.
Described as the "man of the millennium", Gutenberg is often cited as among the most influential figures in human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied throug ...
. He has been commemorated around the world and is a frequent namesake. To celebrate the 400th anniversary of his death in 1900, the Gutenberg Museum
The Gutenberg Museum is one of the oldest museums of printing in the world, located opposite the cathedral in the old part of Mainz, Germany. It is named after Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of printing from movable metal type in Western Euro ...
was founded in his hometown of Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
.
Life and career
Early life
 Johannes Gutenberg was born in
Johannes Gutenberg was born in Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
(in modern-day Germany), a wealthy city along the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, between the 14th and 15th centuries. His exact year of birth is unknown; on the basis of a later document indicating that he came of age by 1420, scholarly estimates have ranged from 1393 to 1406. The year 1400 is commonly assigned to Gutenberg, "for the sake of convenience". Tradition also holds his birthdate to be on the feast day of Saint John the Baptist, 24 June, since children of the time were often named after their birthday's patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
. There is no verification for this assumption, since the name "Johannes"—and variants such as "Johann", "Henne", "Hengin" and "Henchen"—was widely popular at the time. In full, Johannes Gutenberg's name was 'Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg', with "Laden" and "Gutenberg" being adopted from the family's residences in Mainz. The latter refers to the ''Hof zum Gutenberg'', a large and now destroyed Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
-style residence inherited by Gutenberg's father. Gutenberg probably spent his earliest years at the manor, which existed beside St. Christoph's.
His father Friele Gensfleisch zur Laden was a patrician
Patrician may refer to:
* Patrician (ancient Rome), the original aristocratic families of ancient Rome, and a synonym for "aristocratic" in modern English usage
* Patrician (post-Roman Europe), the governing elites of cities in parts of medieval ...
and merchant, likely in the cloth trade. Friele later served among the "master of the accounts" for the city and was a (), apart of the mint
MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaA ...
's companionship. In 1386 Friele married his second wife, Else Wyrich, the daughter of a shopkeeper; Johannes was probably the youngest of the couple's three children, after his brother Friele ( ) and sister Else ( ). Scholars commonly assume that the marriage of Friele to Else, who was not of patrician lineage, complicated Gutenberg's future. Because of his mother's commoner status, Gutenberg would never be able to succeed his father at the mint; according to the historian this disconnect may have disillusioned him from high society and encouraged his unusual career as an inventor.
No documents survive concerning Gutenberg's childhood. The biographer remarked that "most books on Gutenberg pass over this period with the remark that not a single fact is known". As the son of a patrician, education in reading and arithmetic would have been expected. A knowledge of Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
—a prerequisite for universities—is also probable, though it is unknown whether he attended a Mainz parish school
A parochial school is a private primary or secondary school affiliated with a religious organization, and whose curriculum includes general religious education in addition to secular subjects, such as science, mathematics and language arts. The ...
, was educated in Eltville
Eltville am Rhein (from ''Alta Villa'', Latin for "high estate, high town", corrupted to ''Eldeville'', ''Elfeld'' and later Eltville, ) is a town in the Rheingau-Taunus-Kreis in the ''Regierungsbezirk'' of Darmstadt in Hesse, Germany. It lies on ...
or had a private tutor. Gutenberg may have initially pursued a religious career, as was common with the youngest sons of patricians, since the proximity of many churches and monasteries made it a safe prospect. It has been speculated that he attended the south of Mainz (near ), as he would later join their brotherhood. It was the site of a well-regarded school and his family had connections there, though his actual attendance remains speculative.
Eltville and Strasbourg
In 1411, there was an uprising in Mainz against the patricians, and more than a hundred families were forced to leave. As a result, the Gutenbergs are thought to have moved toEltville am Rhein
Eltville am Rhein (from ''Alta Villa'', Latin for "high estate, high town", corrupted to ''Eldeville'', ''Elfeld'' and later Eltville, ) is a town in the Rheingau-Taunus-Kreis in the ''Regierungsbezirk'' of Darmstadt in Hesse, Germany. It lies on ...
(Alta Villa), where his mother had an inherited estate. He is assumed to have studied at the University of Erfurt, where there is a record of the enrollment of a student called Johannes de Altavilla in 1418—Altavilla is the Latin form of Eltville am Rhein.
Nothing is now known of Gutenberg's life for the next fifteen years, but in March 1434, a letter by him indicates that he was living in Strasbourg, where he had some relatives on his mother's side. He also appears to have been a goldsmith member enrolled in the Strasbourg militia. In 1437, there is evidence that he was instructing a wealthy tradesman on polishing gems, but where he had acquired this knowledge is unknown. In 1436/37 his name also comes up in court in connection with a broken promise of marriage to a woman from Strasbourg, Ennelin. Whether the marriage actually took place is not recorded. Following his father's death in 1419, he is mentioned in the inheritance proceedings.
Printing press
Around 1439, Gutenberg was involved in a financial misadventure making polished metal mirrors (which were believed to capture holy light from religious relics) for sale to pilgrims to Aachen: in 1439 the city was planning to exhibit its collection of relics from Charlemagne, Emperor Charlemagne but the event was delayed by one year due to a severe flood and the capital already spent could not be repaid. Until at least 1444 Gutenberg lived in Strasbourg, most likely in the Saint Arbogast, St. Arbogast parish. It was in Strasbourg in 1440 that he is said to have perfected and unveiled the secret of printing based on his research, mysteriously entitled ''Aventur und Kunst'' (enterprise and art). It is not clear what work he was engaged in, or whether some early trials with printing from movable type were conducted there. After this, there is a gap of four years in the record. In 1448, he was back in Mainz, where he took out a loan from his brother-in-law Arnold Gelthus, quite possibly for a printing press or related paraphernalia. By this date, Gutenberg may have been familiar with Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio printing; it is claimed that he had worked on copper engravings with an artist known as the Master of Playing Cards. By 1450, the press was in operation, and a German language, German poem had been printed, possibly the first item to be printed there. Gutenberg was able to convince the wealthy moneylender Johann Fust for a loan of 800 guilders. Peter Schöffer, who became Fust's son-in-law, also joined the enterprise. Schöffer had worked as a scribe in Paris and is believed to have designed some of the first typefaces. Gutenberg's workshop was set up at Humbrechthof, a property belonging to a distant relative. It is not clear when Gutenberg conceived the Bible project, but for this he borrowed another 800 guilders from Fust, and work commenced in 1452. At the same time, the press was also printing other, more lucrative texts (possiblyLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
grammars). There is also some speculation that there were two presses: one for the pedestrian texts and one for the Bible. One of the profit-making enterprises of the new press was the printing of thousands of indulgences for the church, documented from 1454 to 1455.
In 1455 Gutenberg completed his ''42-line Bible'', known as the Gutenberg Bible
The Gutenberg Bible (also known as the 42-line Bible, the Mazarin Bible or the B42) was the earliest major book printed using mass-produced movable metal type in Europe. It marked the start of the " Gutenberg Revolution" and the age of printed ...
. About 180 copies were printed on vellum.
Court case
 Some time in 1456, there was a dispute between Gutenberg and Fust, and Fust demanded his money back, accusing Gutenberg of misusing the funds. Gutenberg's two rounds of financing from Fust, a total of 1,600 guilders at 6% interest, now amounted to 2,026 guilders. Fust sued at the archbishop's court. A November 1455 legal document records that there was a partnership for a "project of the books," the funds for which Gutenberg had used for other purposes, according to Fust. The court decided in favor of Fust, giving him control over the Bible printing workshop and half of all printed Bibles.
Thus Gutenberg was effectively bankrupt, but it appears he retained (or restarted) a small printing shop, and participated in the printing of a Bible in the town of Bamberg around 1459, for which he seems at least to have supplied the type. But since his printed books never carry his name or a date, it is difficult to be certain, and there is consequently a considerable scholarly debate on this subject. It is also possible that the large Catholicon (trilingual dictionary), ''Catholicon'' dictionary, 300 copies of 754 pages, printed in Mainz in 1460, was executed in his workshop.
Meanwhile, the Fust–Schöffer shop was the first in Europe to bring out a book with the printer's name and date, the ''Mainz Psalter'' of August 1457, and while proudly proclaiming the mechanical process by which it had been produced, it made no mention of Gutenberg.
Some time in 1456, there was a dispute between Gutenberg and Fust, and Fust demanded his money back, accusing Gutenberg of misusing the funds. Gutenberg's two rounds of financing from Fust, a total of 1,600 guilders at 6% interest, now amounted to 2,026 guilders. Fust sued at the archbishop's court. A November 1455 legal document records that there was a partnership for a "project of the books," the funds for which Gutenberg had used for other purposes, according to Fust. The court decided in favor of Fust, giving him control over the Bible printing workshop and half of all printed Bibles.
Thus Gutenberg was effectively bankrupt, but it appears he retained (or restarted) a small printing shop, and participated in the printing of a Bible in the town of Bamberg around 1459, for which he seems at least to have supplied the type. But since his printed books never carry his name or a date, it is difficult to be certain, and there is consequently a considerable scholarly debate on this subject. It is also possible that the large Catholicon (trilingual dictionary), ''Catholicon'' dictionary, 300 copies of 754 pages, printed in Mainz in 1460, was executed in his workshop.
Meanwhile, the Fust–Schöffer shop was the first in Europe to bring out a book with the printer's name and date, the ''Mainz Psalter'' of August 1457, and while proudly proclaiming the mechanical process by which it had been produced, it made no mention of Gutenberg.
Later life
In 1462, during the devastating Mainz Diocesan Feud, Mainz was sacked by Archbishop Adolph II of Nassau, Adolph von Nassau. On 18 January 1465, Gutenberg's achievements were recognized by Archbishop von Nassau. He was given the title ''Hofmann'' (gentleman of the court). This honor included a stipend and an annual court outfit, as well as 2,180 litres of grain and 2,000 litres of wine tax-free. Gutenberg died in 1468 and was buried likely as a Third order, tertiary in the Franciscans, Franciscan church at Mainz. This church and the cemetery were later destroyed, and Gutenberg's grave is now lost. In 1504, he was mentioned as the inventor of typography in a book by Professor Ivo Wittig. It was not until 1567 that the first portrait of Gutenberg, almost certainly an imaginary reconstruction, appeared in Heinrich Pantaleon's biography of famous Germans.Printed books
 Between 1450 and 1455, Gutenberg printed several texts, some of which remain unidentified; his texts did not bear the printer's name or date, so attribution is possible only from typographical evidence and external references. Certainly several church documents including a papal letter and two 31-line Indulgence, indulgences were printed, one of which was issued in Mainz. In view of the value of printing in quantity, seven editions in two styles were ordered, resulting in several thousand copies being printed. Some printed editions of ''Ars Minor'', a schoolbook on Latin grammar by Aelius Donatus, may have been printed by Gutenberg; these have been dated either 1451–52 or 1455.
In 1455, Gutenberg completed copies of a beautifully executed folio Bible (''Biblia Sacra''), with 42 lines on each page. Copies sold for 30 Florin (Italian coin), florins each, which was roughly three years' wages for an average clerk. Nonetheless, it was much cheaper than a manuscript Bible that could take a single scribe over a year to prepare. After printing, some copies were Rubrication, rubricated or Illuminated manuscript, hand-illuminated in the same elegant way as manuscript Bibles from the same period.
48 substantially complete copies are known to survive, including two at the British Library that can be viewed and compared online. The text lacks modern features such as page numbers, Indentation (typesetting), indentations, and paragraph breaks.
An undated 36-line Bible, 36-line edition of the Bible was printed, probably in Bamberg in 1458–60, possibly by Gutenberg. A large part of it was shown to have been set from a copy of Gutenberg's Bible, thus disproving earlier speculation that it was the earlier of the two.
Between 1450 and 1455, Gutenberg printed several texts, some of which remain unidentified; his texts did not bear the printer's name or date, so attribution is possible only from typographical evidence and external references. Certainly several church documents including a papal letter and two 31-line Indulgence, indulgences were printed, one of which was issued in Mainz. In view of the value of printing in quantity, seven editions in two styles were ordered, resulting in several thousand copies being printed. Some printed editions of ''Ars Minor'', a schoolbook on Latin grammar by Aelius Donatus, may have been printed by Gutenberg; these have been dated either 1451–52 or 1455.
In 1455, Gutenberg completed copies of a beautifully executed folio Bible (''Biblia Sacra''), with 42 lines on each page. Copies sold for 30 Florin (Italian coin), florins each, which was roughly three years' wages for an average clerk. Nonetheless, it was much cheaper than a manuscript Bible that could take a single scribe over a year to prepare. After printing, some copies were Rubrication, rubricated or Illuminated manuscript, hand-illuminated in the same elegant way as manuscript Bibles from the same period.
48 substantially complete copies are known to survive, including two at the British Library that can be viewed and compared online. The text lacks modern features such as page numbers, Indentation (typesetting), indentations, and paragraph breaks.
An undated 36-line Bible, 36-line edition of the Bible was printed, probably in Bamberg in 1458–60, possibly by Gutenberg. A large part of it was shown to have been set from a copy of Gutenberg's Bible, thus disproving earlier speculation that it was the earlier of the two.
Printing method with movable type
 Gutenberg's early printing process, and what texts he printed with movable type, are not known in great detail. His later Bibles were printed in such a way as to have required large quantities of type, some estimates suggesting as many as 100,000 individual sorts. Setting each page would take, perhaps, half a day, and considering all the work in loading the press, inking the type, pulling the impressions, hanging up the sheets, distributing the type, etc., it is thought that the Gutenberg–Fust shop might have employed as many as 25 craftsmen.
Gutenberg's technique of making movable type remains unclear. In the following decades, Punch (typography), punches and copper matrices became standardized in the rapidly disseminating printing presses across Europe. Whether Gutenberg used this sophisticated technique or a somewhat primitive version has been the subject of considerable debate.
In the standard process of making type, a hard metal punch (made by punchcutting, with the letter carved back to front) is hammered into a softer copper bar, creating a ''matrix (printing), matrix''. This is then placed into a hand mould, hand-held mould and a piece of type, or "sort", is cast by filling the mould with molten type-metal; this cools almost at once, and the resulting piece of type can be removed from the mould. The matrix can be reused to create hundreds, or thousands, of identical sorts so that the same character appearing anywhere within the book will appear very uniform, giving rise, over time, to the development of distinct styles of typefaces or fonts. After casting, the sorts are arranged into type cases, and used to make up pages which are inked and printed, a procedure which can be repeated hundreds, or thousands, of times. The sorts can be reused in any combination, earning the process the name of "movable type".
The invention of the making of types with punch, matrix and mold has been widely attributed to Gutenberg. However, recent evidence suggests that Gutenberg's process was somewhat different. If he used the punch and matrix approach, all his letters should have been nearly identical, with some variation due to miscasting and inking. However, the type used in Gutenberg's earliest work shows other variations.
Gutenberg's early printing process, and what texts he printed with movable type, are not known in great detail. His later Bibles were printed in such a way as to have required large quantities of type, some estimates suggesting as many as 100,000 individual sorts. Setting each page would take, perhaps, half a day, and considering all the work in loading the press, inking the type, pulling the impressions, hanging up the sheets, distributing the type, etc., it is thought that the Gutenberg–Fust shop might have employed as many as 25 craftsmen.
Gutenberg's technique of making movable type remains unclear. In the following decades, Punch (typography), punches and copper matrices became standardized in the rapidly disseminating printing presses across Europe. Whether Gutenberg used this sophisticated technique or a somewhat primitive version has been the subject of considerable debate.
In the standard process of making type, a hard metal punch (made by punchcutting, with the letter carved back to front) is hammered into a softer copper bar, creating a ''matrix (printing), matrix''. This is then placed into a hand mould, hand-held mould and a piece of type, or "sort", is cast by filling the mould with molten type-metal; this cools almost at once, and the resulting piece of type can be removed from the mould. The matrix can be reused to create hundreds, or thousands, of identical sorts so that the same character appearing anywhere within the book will appear very uniform, giving rise, over time, to the development of distinct styles of typefaces or fonts. After casting, the sorts are arranged into type cases, and used to make up pages which are inked and printed, a procedure which can be repeated hundreds, or thousands, of times. The sorts can be reused in any combination, earning the process the name of "movable type".
The invention of the making of types with punch, matrix and mold has been widely attributed to Gutenberg. However, recent evidence suggests that Gutenberg's process was somewhat different. If he used the punch and matrix approach, all his letters should have been nearly identical, with some variation due to miscasting and inking. However, the type used in Gutenberg's earliest work shows other variations.
 In 2001, the physicist Blaise Agüera y Arcas and Princeton University, Princeton librarian Paul Needham, used digital scans of a Papal bull in the Scheide Library, Princeton, to carefully compare the same letters (types) appearing in different parts of the printed text. The irregularities in Gutenberg's type, particularly in simple characters such as the hyphen, suggested that the variations could not have come either from ink smear or from wear and damage on the pieces of metal on the types themselves. Although some identical types are clearly used on other pages, other variations, subjected to detailed image analysis, suggested that they could not have been produced from the same matrix. Transmitted light pictures of the page also appeared to reveal substructures in the type that could not arise from traditional punchcutting techniques. They hypothesized that the method involved impressing simple shapes to create alphabets in "cuneiform" style in a matrix made of some soft material, perhaps sand. Casting the type would destroy the mould, and the matrix would need to be recreated to make each additional sort. This could explain the variations in the type, as well as the substructures observed in the printed images.
Thus, they speculated that "the decisive factor for the birth of typography", the use of reusable moulds for casting type, was a more progressive process than was previously thought. They suggested that the additional step of using the punch to create a mould that could be reused many times was not taken until twenty years later, in the 1470s. Others have not accepted some or all of their suggestions, and have interpreted the evidence in other ways, and the truth of the matter remains uncertain.
A 1568 book ''Batavia'' by Hadrianus Junius from Holland claims that the idea of the movable type came to Gutenberg from Laurens Janszoon Coster via Fust, who was apprenticed to Coster in the 1430s and may have brought some of his equipment from Haarlem to Mainz. While Coster appears to have experimented with moulds and castable metal type, there is no evidence that he had actually printed anything with this technology. He was an inventor and a goldsmith. However, there is one indirect supporter of the claim that Coster might be the inventor. The author of the ''Cologne Chronicle of 1499'' quotes Ulrich Zell, the first printer of Cologne, that printing was performed in
In 2001, the physicist Blaise Agüera y Arcas and Princeton University, Princeton librarian Paul Needham, used digital scans of a Papal bull in the Scheide Library, Princeton, to carefully compare the same letters (types) appearing in different parts of the printed text. The irregularities in Gutenberg's type, particularly in simple characters such as the hyphen, suggested that the variations could not have come either from ink smear or from wear and damage on the pieces of metal on the types themselves. Although some identical types are clearly used on other pages, other variations, subjected to detailed image analysis, suggested that they could not have been produced from the same matrix. Transmitted light pictures of the page also appeared to reveal substructures in the type that could not arise from traditional punchcutting techniques. They hypothesized that the method involved impressing simple shapes to create alphabets in "cuneiform" style in a matrix made of some soft material, perhaps sand. Casting the type would destroy the mould, and the matrix would need to be recreated to make each additional sort. This could explain the variations in the type, as well as the substructures observed in the printed images.
Thus, they speculated that "the decisive factor for the birth of typography", the use of reusable moulds for casting type, was a more progressive process than was previously thought. They suggested that the additional step of using the punch to create a mould that could be reused many times was not taken until twenty years later, in the 1470s. Others have not accepted some or all of their suggestions, and have interpreted the evidence in other ways, and the truth of the matter remains uncertain.
A 1568 book ''Batavia'' by Hadrianus Junius from Holland claims that the idea of the movable type came to Gutenberg from Laurens Janszoon Coster via Fust, who was apprenticed to Coster in the 1430s and may have brought some of his equipment from Haarlem to Mainz. While Coster appears to have experimented with moulds and castable metal type, there is no evidence that he had actually printed anything with this technology. He was an inventor and a goldsmith. However, there is one indirect supporter of the claim that Coster might be the inventor. The author of the ''Cologne Chronicle of 1499'' quotes Ulrich Zell, the first printer of Cologne, that printing was performed in Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
in 1450, but that some type of printing of lower quality had previously occurred in the Netherlands. However, the chronicle does not mention the name of Coster, while it actually credits Gutenberg as the "first inventor of printing" in the very same passage (fol. 312). The first securely dated book by Dutch printers is from 1471, and the Coster connection is today regarded as a mere legend.
The 19th-century printer and typefounder Fournier Le Jeune suggested that Gutenberg was not using type cast with a reusable matrix, but wooden types that were carved individually. A similar suggestion was made by Nash in 2004. This remains possible, albeit entirely unproven.
Legacy
Influence
Gutenberg's invention had an enormous impact on subsequenthuman history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied throug ...
, both on cultural and social matters. His design directly impacted the mass spread of books across Europe, causing an information revolution
The term information revolution describes current economic, social and technological trends beyond the Industrial Revolution.
Many competing terms have been proposed that focus on different aspects of this societal development.
The British polymat ...
. As a result, Venzke describes the inauguration of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
and humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
movement as "unthinkable" without Gutenberg's influence. Described as "one of the most recognized names in the world", a team of US journalists voted Gutenberg as the "man of the millennium" in 1999. Similarly, in 1999 the A&E Network ranked Gutenberg the No. 1 most influential person of the second millennium on their "Biographies of the Millennium" countdown, while ''Time–Life'' magazine picked Gutenberg's invention as the most important of the second millennium in 1997. The scholar of paper history, Thomas Francis Carter, drew parallels between Cai Lun, the traditional inventor of paper during the Eastern Han dynasty, and Gutenberg, calling them "spiritual father and son" respectively. In his 1978 book, ''The 100: A Ranking of the Most Influential Persons in History'', Michael H. Hart ranked him 8th, below Cai but above figures such as Christopher Columbus, Albert Einstein and Charles Darwin.
The capital of printing in Europe shifted to Venice, where visionary printers like Aldus Manutius ensured widespread availability of the major Greek language, Greek and Latin texts. The claims of an Italian origin for movable type have also focused on this rapid rise of Italy in movable-type printing. This may perhaps be explained by the prior eminence of Italy in the paper and printing trade. Additionally, Italy's economy was growing rapidly at the time, facilitating the spread of literacy. Christopher Columbus had a geography book (printed with movable type) bought by his father. That book is in a Spanish museum, the Institución Colombina#Biblioteca Colombina, Biblioteca Colombina in Seville. Finally, the city of Mainz was sacked in 1462, driving many (including a number of printers and punch cutters) into exile.
Printing was also a factor in the Protestant Reformation, Reformation. Martin Luther's ''Ninety-five Theses'' were printed and circulated widely; subsequently he issued broadsheets outlining his anti-indulgences position (certificates of indulgences were one of the first items Gutenberg had printed). Due to this, Gutenberg would also be viewed as a proto Protestant. The broadsheet contributed to the development of the newspaper.
Memorials and monuments
Gutenberg Museum
The Gutenberg Museum is one of the oldest museums of printing in the world, located opposite the cathedral in the old part of Mainz, Germany. It is named after Johannes Gutenberg, the inventor of printing from movable metal type in Western Euro ...
on the history of early printing. The latter publishes the ''Gutenberg-Jahrbuch'', the leading periodical in the field.
In 1952, the United States Postal Service issued a five hundredth anniversary stamp commemorating Johannes Gutenberg invention of the movable-type printing press. In space, he is commemorated in the name of the asteroid 777 Gutemberga. Two operas based on Gutenberg are ''G, Being the Confession and Last Testament of Johannes Gensfleisch, also known as Gutenberg, Master Printer, formerly of Strasbourg and Mainz'', from 2001, with music by Gavin Bryars; and ''La Nuit de Gutenberg'', with music by Philippe Manoury, premiered in 2011 in Strasbourg. Project Gutenberg, the oldest digital library, commemorates Gutenberg's name. The Johannisnacht, Mainz, Mainzer Johannisnacht commemorates the person Johannes Gutenberg in his native city since 1968.
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
Gutenberg-Museum Mainz, Germany
– English homepage
Gutenberg Bible
at the British Library {{DEFAULTSORT:Gutenberg, Johannes Johannes Gutenberg, 1398 births 1468 deaths 15th-century German businesspeople 15th-century German inventors 15th-century printers Businesspeople from Mainz German goldsmiths German printers German Roman Catholics German typographers and type designers History of printing People from the Electoral Palatinate Printers of incunabula University of Erfurt alumni