Fokker F.27-100 VH-TFF TAA ESS 24.09.70 edited-3.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fokker was a Dutch aircraft manufacturer named after its founder,

 Fitted with a developed version of this gear, the M.5 became the Fokker Eindecker, which due to its revolutionary armament, became one of the most feared aircraft over the western front, its introduction leading to a period of German air superiority known as the Fokker Scourge which only ended with the introduction of new aircraft such as the
Fitted with a developed version of this gear, the M.5 became the Fokker Eindecker, which due to its revolutionary armament, became one of the most feared aircraft over the western front, its introduction leading to a period of German air superiority known as the Fokker Scourge which only ended with the introduction of new aircraft such as the
 In the 1920s, Fokker entered its glory years, becoming the world's largest aircraft manufacturer by the late 1920s. Its greatest success was the 1925 F.VIIa/3m trimotor passenger aircraft, which was used by 54
In the 1920s, Fokker entered its glory years, becoming the world's largest aircraft manufacturer by the late 1920s. Its greatest success was the 1925 F.VIIa/3m trimotor passenger aircraft, which was used by 54
 Rebuilding after the war proved difficult. The market was flooded with cheap surplus planes from the war. The company cautiously started building gliders and autobuses and converting Dakota transport planes to civilian versions. A few F25s were built. Nevertheless, the S-11 trainer was a success, being purchased by several air forces. The S-14 Machtrainer became one of the first
Rebuilding after the war proved difficult. The market was flooded with cheap surplus planes from the war. The company cautiously started building gliders and autobuses and converting Dakota transport planes to civilian versions. A few F25s were built. Nevertheless, the S-11 trainer was a success, being purchased by several air forces. The S-14 Machtrainer became one of the first  In 1958, the F-27 Friendship was introduced, Fokker's most successful postwar airliner. The Dutch government contributed 27 million guilders to its development. Powered by the Rolls-Royce Dart, it became the world's best-selling turboprop airliner, reaching almost 800 units sold by 1986, including 206 under licence by Fairchild. Also, a military version of the F-27, the F-27 Troopship, was built.
In 1962, the F-27 was followed by the jet-powered F-28 Fellowship. Until production stopped in 1987, a total of 241 were built in various versions. Both an F-27 and later an F-28 served with the
In 1958, the F-27 Friendship was introduced, Fokker's most successful postwar airliner. The Dutch government contributed 27 million guilders to its development. Powered by the Rolls-Royce Dart, it became the world's best-selling turboprop airliner, reaching almost 800 units sold by 1986, including 206 under licence by Fairchild. Also, a military version of the F-27, the F-27 Troopship, was built.
In 1962, the F-27 was followed by the jet-powered F-28 Fellowship. Until production stopped in 1987, a total of 241 were built in various versions. Both an F-27 and later an F-28 served with the  Fokker was one of the main partners in the
Fokker was one of the main partners in the
 After a brief and unsuccessful collaboration effort with McDonnell Douglas in 1981, Fokker began an ambitious project to develop two new aircraft concurrently. The
After a brief and unsuccessful collaboration effort with McDonnell Douglas in 1981, Fokker began an ambitious project to develop two new aircraft concurrently. The
 * In 1915, the Fokker E.I was the first fighter armed with a synchronized machine gun firing through the propeller, achieving
* In 1915, the Fokker E.I was the first fighter armed with a synchronized machine gun firing through the propeller, achieving
Fokker Technologies Official company website
Pictures of the Fokker fleet
Rekkof official website
Fokker, a living history
FokkerPilot.net
Fokker aircraft website
The assembly-hall at Fokker with many F-16s
{{Economic history of the Netherlands Manufacturing companies established in 1912 Defunct aircraft manufacturers of the Netherlands Science and technology in the Netherlands Manufacturing companies disestablished in 1996 Defunct aircraft manufacturers of Germany 1912 establishments in Germany Dutch brands Dutch companies disestablished in 1996 German companies established in 1912 Defence companies of the Netherlands
Anthony Fokker
Anton Herman Gerard "Anthony" Fokker (6 April 1890 – 23 December 1939) was a Dutch aviation pioneer, aviation entrepreneur, aircraft designer, and aircraft manufacturer. He produced fighter aircraft in Germany during the First World War such ...
. The company operated under several different names. It was founded in 1912 in Berlin, Germany, and became famous for its fighter aircraft in World War I. In 1919 the company moved its operations to the Netherlands.
During its most successful period in the 1920s and 1930s, it dominated the civil aviation market. Fokker went into bankruptcy in 1996, and its operations were sold to competitors.
History

Fokker in Germany
At age 20, while studying in Germany, Anthony Fokker built his initial aircraft, the ''Spin'' (Spider)—the first Dutch-built plane to fly in his home country. Taking advantage of better opportunities in Germany, he moved to Berlin, where in 1912, he founded his first company, Fokker Aeroplanbau, later moving to the Görries suburb just southwest of Schwerin (at ), where the current company was founded, as Fokker Aviatik GmbH, on 12 February 1912.World War I
Fokker capitalized on having sold severalFokker Spin
The Fokker ''Spin'' was the first airplane built by Dutch aviation pioneer Anthony Fokker. The many bracing wires used to strengthen the aircraft made it resemble a giant spider, hence its name ''Spin'', Dutch for "spider".
Fokker built the ''Spi ...
monoplanes to the German government and set up a factory in Germany to supply the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
in World War I. His first new design for the Germans to be produced in any numbers was the Fokker M.5
The Fokker M.5 was an unarmed single-seat monoplane aircraft designed and built by Anthony Fokker in 1913. It served as a light reconnaissance aircraft with the German army at the outbreak of World War I and was the basis for the first successfu ...
, which was little more than a copy of the Morane-Saulnier G, built with steel tube instead of wood for the fuselage, and with minor alterations to the outline of the rudder and undercarriage and a new aerofoil section.Weyl 1965, pp. 65–67. When it was realized that arming these scouts with a machine gun firing through the arc of the propeller was desirable, Fokker developed a synchronization gear
A synchronization gear (also known as a gun synchronizer or interrupter gear) was a device enabling a single-engine tractor configuration aircraft to fire its forward-firing armament through the arc of its spinning propeller without bullets strik ...
similar to that patented by Franz Schneider.Weyl 1965, p. 96.
 Fitted with a developed version of this gear, the M.5 became the Fokker Eindecker, which due to its revolutionary armament, became one of the most feared aircraft over the western front, its introduction leading to a period of German air superiority known as the Fokker Scourge which only ended with the introduction of new aircraft such as the
Fitted with a developed version of this gear, the M.5 became the Fokker Eindecker, which due to its revolutionary armament, became one of the most feared aircraft over the western front, its introduction leading to a period of German air superiority known as the Fokker Scourge which only ended with the introduction of new aircraft such as the Nieuport 11
The Nieuport 11 (or Nieuport XI C.1 in contemporary sources), nicknamed the ''Bébé'', was a French World War I single seat sesquiplane fighter aircraft, designed by Gustave Delage. It was the primary aircraft that ended the Fokker Scourge in ...
and Airco DH.2
The Airco DH.2 was a single-seat pusher biplane fighter aircraft which operated during the First World War. It was the second pusher design by aeronautical engineer Geoffrey de Havilland for Airco, based on his earlier DH.1 two-seater.
The d ...
.
During World War I, Fokker engineers worked on the Fokker-Leimberger
The Fokker-Leimberger was an externally powered, 12-barrel rifle-caliber rotary gun developed in Germany during the First World War. The action of the Fokker-Leimberger differed from that of a Gatling in that it employed a rotary split-breech des ...
, an externally powered 12-barrel Gatling gun
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon.
The Gatling gun's operation centered on a cyc ...
in the 7.92×57mm round claimed to be capable of firing over 7200 rounds per minute.
Later in the war, after the Fokker D.V
The Fokker D.V (Fokker designation M.22) was a German biplane fighter of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included mu ...
(the last design by earlier chief designer Martin Kreutzer), had failed to gain acceptance with the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' the German government forced Fokker (for their aircraft production expertise) and Junkers
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (JFM, earlier JCO or JKO in World War I, English: Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works) more commonly Junkers , was a major German aircraft and aircraft engine manufacturer. It was founded there in Dessau, Germ ...
(for their pioneering all-metal airframe construction techniques, and advanced design concepts) to cooperate more closely, which resulted in the foundation of the Junkers-Fokker Aktiengesellschaft, or Jfa, on 20 October 1917. As this partnership proved to be troublesome, it was eventually dissolved. By then, former Fokker welder and new designer Reinhold Platz
Reinhold Platz (16 January 1886 – 15 September 1966) was a German aircraft designer and manufacturer in service of the Dutch company Fokker.
Platz was hired by Fokker in 1912 as a welder. His first hands-on projects were to weld the frame pa ...
, who had taken the late Martin Kreutzer's place with the firm, had adapted some of Prof. Junkers' design concepts, that resulted in a visual similarity between the aircraft of those two manufacturers during the next decade.
Some of the noteworthy types produced by Fokker during the second half of the war, all designed primarily by Platz, included the Fokker D.VI
The Fokker D.VI was a German fighter aircraft built in limited numbers at the end of World War I. The D.VI served in the German and Austro-Hungarian air services.
Design and development
In late 1917, Fokker-Flugzeugwerke built two small biplane ...
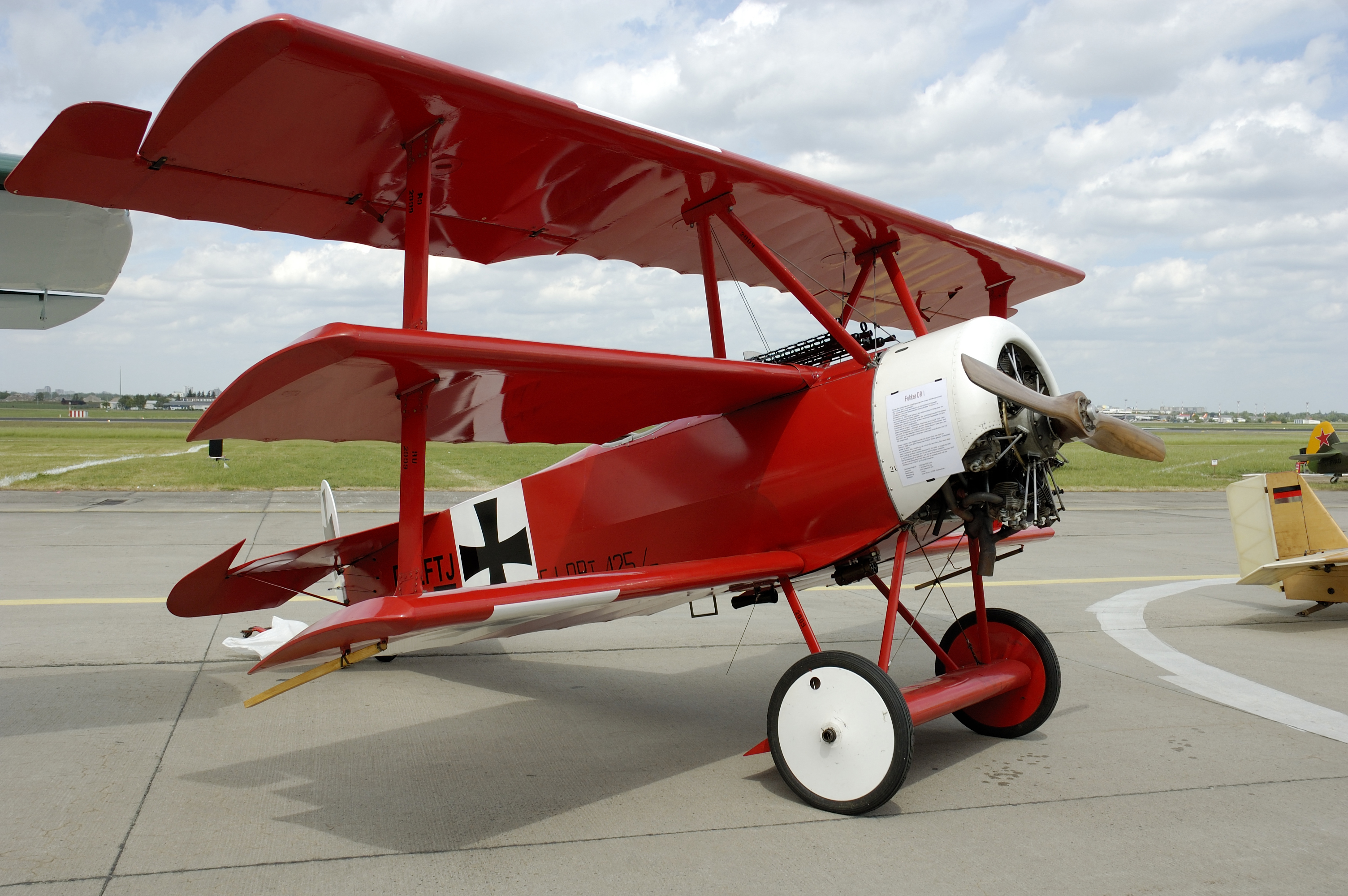
biplane, Fokker Dr.I
The Fokker Dr.I (''Dreidecker'', "triplane" in German), often known simply as the Fokker Triplane, was a World War I fighter aircraft built by Fokker-Flugzeugwerke. The Dr.I saw widespread service in the spring of 1918. It became famous as the ...
triplane or ''Dreidecker'' (remembered as a mount of the Red Baron), Fokker D.VII
The Fokker D.VII was a German World War I fighter aircraft designed by Reinhold Platz of the Fokker-Flugzeugwerke. Germany produced around 3,300 D.VII aircraft in the second half of 1918. In service with the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the D.VII qu ...
biplane (the only aircraft ever referred to directly in a treaty: all D.VII's were singled out for handover to the allies in their terms of the armistice agreement) and the Fokker D.VIII
The Fokker E.V was a German parasol-monoplane fighter aircraft designed by Reinhold Platz and built by Fokker-Flugzeugwerke. The E.V was the last Fokker design to become operational with the ''Luftstreitkräfte,'' entering service in the last mon ...
parasol monoplane.
Return to the Netherlands
In 1919, Fokker, owing large sums in back taxes (including 14,250,000 marks of income tax),Weyl 1965, p.354. returned to the Netherlands and founded a new company near Amsterdam with the support of Steenkolen Handels Vereniging, now known as SHV Holdings. He chose the name Nederlandse Vliegtuigenfabriek (Dutch Aircraft Factory) to conceal the Fokker brand because of his involvement in World War I. Despite the strict disarmament conditions of the Treaty of Versailles, Fokker did not return home empty-handed. In 1919, he arranged an export permit and brought six entire trains of parts, and 180 types of aircraft across the Dutch-German border, among them 117 Fokker C.Is, D.VIIs, and D.VIIIs. This initial stock enabled him to set up shop quickly. After his company's relocation, many FokkerC.I
C1, C01, C.I or C-1 may refer to:
Arts and media
* C1, a note-octave in music
* C1 Television, a Mongolian television channel
* Schecter C-1 Hellraiser FR, a guitar model
* A Yamaha grand piano model
* "C1", a slang expression in the video game ...
and C.IV military airplanes were delivered to Russia, Romania, and the still-clandestine German air force. Success came on the commercial market, too, with the development of the Fokker F.VII
The Fokker F.VII, also known as the Fokker Trimotor, was an airliner produced in the 1920s by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker, Fokker's American subsidiary Atlantic Aircraft Corporation, and other companies under licence.
Design and dev ...
, a high-winged aircraft capable of taking on various types of engines. Fokker continued to design and build military aircraft, delivering planes to the Royal Netherlands Air Force
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march = ''Parade March of the Royal Netherlands Air Force''
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, equipment ...
. Foreign military customers eventually included Finland, Sweden, Denmark, Norway, Switzerland, Hungary, and Italy. These countries bought substantial numbers of the Fokker C.V reconnaissance aircraft, which became Fokker's main success in the late 1920s and early 1930s.
1920s and 30s: Fokker's glory period
 In the 1920s, Fokker entered its glory years, becoming the world's largest aircraft manufacturer by the late 1920s. Its greatest success was the 1925 F.VIIa/3m trimotor passenger aircraft, which was used by 54
In the 1920s, Fokker entered its glory years, becoming the world's largest aircraft manufacturer by the late 1920s. Its greatest success was the 1925 F.VIIa/3m trimotor passenger aircraft, which was used by 54 airline companies
An airline is a company that provides air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines use aircraft to supply these services and may form partnerships or alliances with other airlines for codeshare agreements, in which ...
worldwide and captured 40% of the American market in 1936. It shared the European market with the Junkers all-metal aircraft, but dominated the American market until the arrival of the Ford Trimotor
The Ford Trimotor (also called the "Tri-Motor", and nicknamed the "Tin Goose") is an American three-engined transport aircraft. Production started in 1925 by the companies of Henry Ford and ended on June 7, 1933, after 199 had been made. It w ...
which copied the aerodynamic features of the Fokker F.VII, and Junkers structural concepts.
In 1923, Anthony Fokker moved to the United States, where in 1927, he established an American branch of his company, the Atlantic Aircraft
Atlantic Aircraft Corporation, also known as Fokker-America and Atlantic-Fokker, was a US subsidiary of the Dutch Fokker company, responsible for sales and information about Fokker imports, and eventually constructing various Fokker designs."The ...
Corporation, which was renamed the Fokker Aircraft Corporation of America. In 1930, this company merged with General Motors Corporation and the company's name became General Aviation Manufacturing Corporation, which in turn merged with North American Aviation
North American Aviation (NAA) was a major American aerospace manufacturer that designed and built several notable aircraft and spacecraft. Its products included: the T-6 Texan trainer, the P-51 Mustang fighter, the B-25 Mitchell bomber, the F ...
and was divested by GM in 1948. In 1931, discontented at being totally subordinate to GM management, Fokker resigned.
A serious blow to Fokker's reputation came after the 1931 crash of a Transcontinental & Western Air Fokker F-10 in Kansas, when it became known that the crash was caused by a structural failure caused by wood rot. Notre Dame
Notre Dame, French for "Our Lady", a title of Mary, mother of Jesus, most commonly refers to:
* Notre-Dame de Paris, a cathedral in Paris, France
* University of Notre Dame, a university in Indiana, United States
** Notre Dame Fighting Irish, th ...
legendary football coach Knute Rockne
Knut (Norwegian and Swedish), Knud (Danish), or Knútur (Icelandic) is a Scandinavian, German, and Dutch first name, of which the anglicised form is Canute. In Germany both "Knut" and "Knud" are used. In Spanish and Portuguese Canuto is used whi ...
was among the fatalities, prompting extensive media coverage and technical investigation. As a result, all Fokkers were grounded in the US, along with many other types that had copied Fokker's wings.
In 1934 Nevil Shute of Airspeed Ltd (England) negotiated with Fokker himself for a manufacturing licensing agreement. In January 1935 Airspeed signed an agreement
for the Douglas DC-2
The Douglas DC-2 is a 14-passenger, twin-engined airliner that was produced by the American company Douglas Aircraft Company starting in 1934. It competed with the Boeing 247. In 1935, Douglas produced a larger version called the DC-3, which b ...
and a number of Fokker types, with Fokker to be a consultant for seven years. Shute found him "genial, shrewd and helpful" but "already a sick man"; and he was difficult to deal with as "his domestic life was irregular". Airspeed considered making the Fokker D.XVII
Fokker D.XVII (sometimes written as Fokker D.17), was a 1930s Dutch sesquiplane developed by Fokker. It was the last fabric-covered biplane fighter they developed in a lineage that extended back to the First World War Fokker D.VII.
Design and d ...
for Greece, as Greece wanted to buy from Britain for currency reasons, but the proposal did not "come off"; Shute recommended reading his novel '' Ruined City'' on Balkan methods of business. And after a year the drift to war meant that Dutchmen could not go to the Airspeed factory or to board meetings.
On December 23, 1939, Fokker died in New York City after a three-week illness.
World War II
At the outset of World War II, the few G.Is and D.XXIs of the Dutch Air Force were able to score a respectable number of victories against the ''Luftwaffe'', but many were destroyed on the ground before they could be used. The Fokker factories were confiscated by the Germans and were used to build Bücker Bü 181 Bestmann trainers and parts for theJunkers Ju 52
The Junkers Ju 52/3m (nicknamed ''Tante Ju'' ("Aunt Ju") and ''Iron Annie'') is a transport aircraft that was designed and manufactured by German aviation company Junkers.
Development of the Ju 52 commenced during 1930, headed by German Aeros ...
transport. At the end of the war, the factories were completely stripped by the Germans and destroyed by Allied bombing.
Post-World War II rebuilding
 Rebuilding after the war proved difficult. The market was flooded with cheap surplus planes from the war. The company cautiously started building gliders and autobuses and converting Dakota transport planes to civilian versions. A few F25s were built. Nevertheless, the S-11 trainer was a success, being purchased by several air forces. The S-14 Machtrainer became one of the first
Rebuilding after the war proved difficult. The market was flooded with cheap surplus planes from the war. The company cautiously started building gliders and autobuses and converting Dakota transport planes to civilian versions. A few F25s were built. Nevertheless, the S-11 trainer was a success, being purchased by several air forces. The S-14 Machtrainer became one of the first jet trainers
A jet trainer is a jet aircraft for use as a trainer, whether for basic or advanced flight training. Jet trainers are either custom designs or modifications of existing aircraft. With the introduction of military jet-powered aircraft towards the e ...
, and although not an export success, it served for over a decade with the Royal Netherlands Air Force
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march = ''Parade March of the Royal Netherlands Air Force''
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, equipment ...
.
A new factory was built next to Schiphol Airport near Amsterdam in 1951. A number of military planes were built there under license, among them the Gloster Meteor twin-jet fighter and Lockheed's F-104 Starfighter
The Lockheed F-104 Starfighter is an American single-engine, supersonic air superiority fighter which was extensively deployed as a fighter-bomber during the Cold War. Created as a day fighter by Lockheed as one of the "Century Series" of fi ...
. A second production and maintenance facility was established at Woensdrecht.
 In 1958, the F-27 Friendship was introduced, Fokker's most successful postwar airliner. The Dutch government contributed 27 million guilders to its development. Powered by the Rolls-Royce Dart, it became the world's best-selling turboprop airliner, reaching almost 800 units sold by 1986, including 206 under licence by Fairchild. Also, a military version of the F-27, the F-27 Troopship, was built.
In 1962, the F-27 was followed by the jet-powered F-28 Fellowship. Until production stopped in 1987, a total of 241 were built in various versions. Both an F-27 and later an F-28 served with the
In 1958, the F-27 Friendship was introduced, Fokker's most successful postwar airliner. The Dutch government contributed 27 million guilders to its development. Powered by the Rolls-Royce Dart, it became the world's best-selling turboprop airliner, reaching almost 800 units sold by 1986, including 206 under licence by Fairchild. Also, a military version of the F-27, the F-27 Troopship, was built.
In 1962, the F-27 was followed by the jet-powered F-28 Fellowship. Until production stopped in 1987, a total of 241 were built in various versions. Both an F-27 and later an F-28 served with the Dutch Royal Flight
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, Prince Bernhard himself being a pilot.
In 1969, Fokker agreed to an alliance with Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
-based Vereinigte Flugtechnische Werke under control of a transnational holding company. They collaborated on an unsuccessful regional jetliner
A jet airliner or jetliner is an airliner powered by jet engines (passenger jet aircraft). Airliners usually have two or four jet engines; three-engined designs were popular in the 1970s but are less common today. Airliners are commonly clas ...
, the VFW-614
The VFW-Fokker 614 (also VFW 614) was a twin-engined jetliner designed and constructed by West German aviation company VFW-Fokker. It is the first jet-powered passenger liner to be developed and produced in West Germany (the East German Baade 152 ...
, of which only 19 were sold. This collaboration ended in early 1980.
 Fokker was one of the main partners in the
Fokker was one of the main partners in the F-16 Fighting Falcon
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful ...
consortium (European Participating Air Forces), which was responsible for the production of these fighters for the Belgian, Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish ance ...
, Dutch and Norwegian Air Forces. It consisted of companies and government agencies from these four countries and the United States. F-16s were assembled at Fokker and at SABCA
SABCA (Sociétés Anonyme Belge de Constructions Aéronautiques) is a Belgian aerospace company. Its main sectors of activity are civil aviation, space and defence.
SABCA was established during 1920. Presently, it is owned by the French aircraf ...
in Belgium with parts from the five countries involved.
Aerospace
In 1967, Fokker started a modest space division building parts for European satellites. A major advance came in 1968 when Fokker developed the first Dutch satellite (the Astronomical Netherlands Satellite) together with Philips and Dutch universities. This was followed by a second major satellite project, IRAS, successfully launched in 1983. TheEuropean Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
in June 1974 named a consortium headed by ERNO-VFW-Fokker GmbH
VFW-Fokker GmbH was a joint venture of Fokker and Vereinigte Flugtechnische Werke (VFW) started in 1969 that, from then on, controlled the ERNO initiative.
The Entwicklungsring Nord (Northern development circle) — abbreviated ERNO — was a ...
to build pressurized modules for Spacelab.
Subsequently, Fokker contributed to many European satellite projects, as well as to the Ariane rocket in its various models. Together with a Russian contractor, they developed the huge parachute system for the Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It is launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) in French Guiana. It has been used to deliver payloads int ...
rocket boosters which would allow the boosters to return to Earth safely and be reused.
The space division became more and more independent, until just before Fokker's bankruptcy in 1996, it became a fully stand-alone corporation, known successively as Fokker Space and Systems, Fokker Space, and Dutch Space. On 1 January 2006, it was taken over by EADS
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft throughout the world. The company has three divisions: '' ...
-Space Transportation.
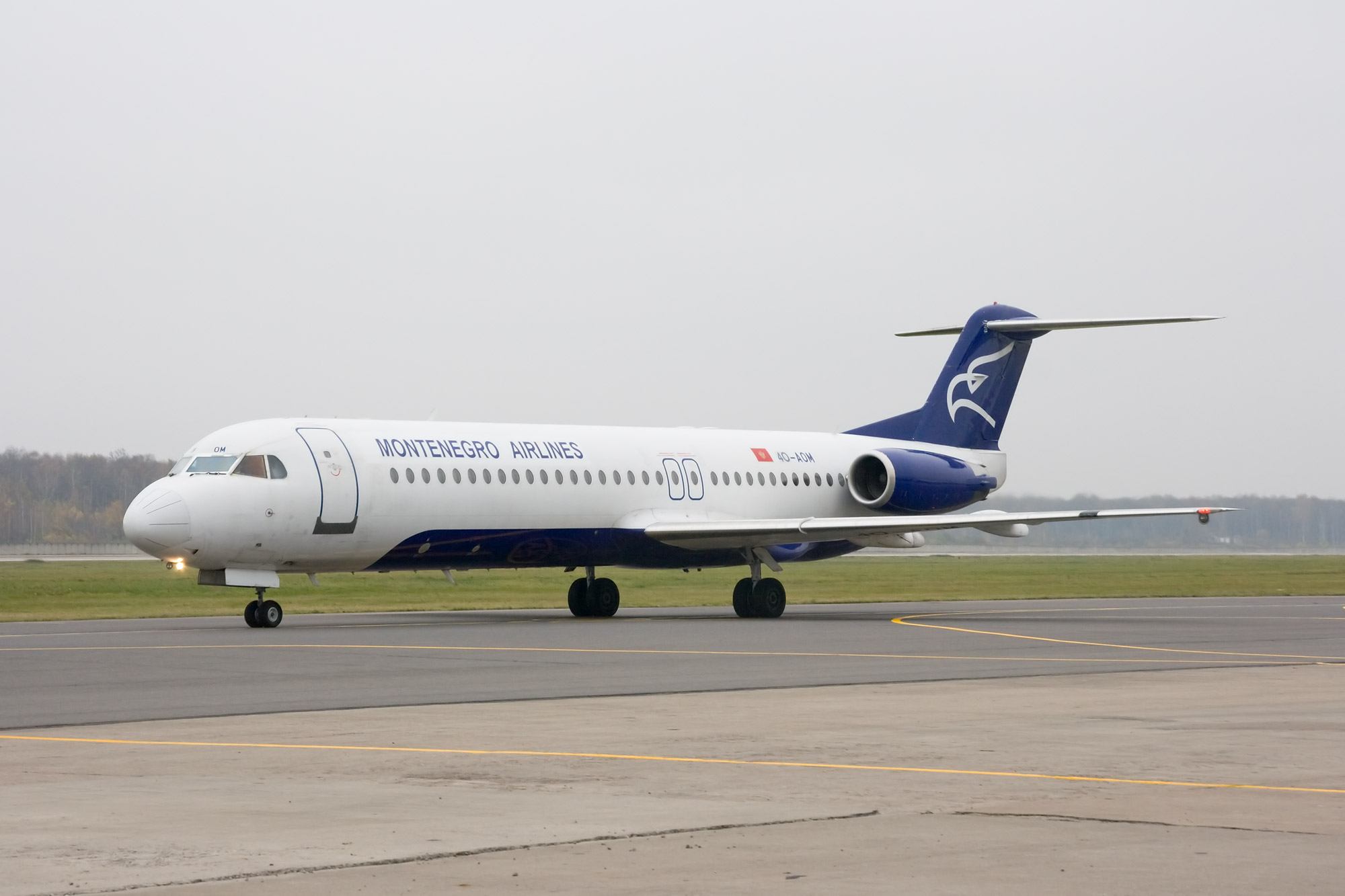
Fokker 50, Fokker 100, and Fokker 70

 After a brief and unsuccessful collaboration effort with McDonnell Douglas in 1981, Fokker began an ambitious project to develop two new aircraft concurrently. The
After a brief and unsuccessful collaboration effort with McDonnell Douglas in 1981, Fokker began an ambitious project to develop two new aircraft concurrently. The Fokker 50
The Fokker 50 is a turboprop-powered airliner, designed as an improved version of the successful Fokker F27 Friendship. The Fokker 60 is a stretched freighter version of the Fokker 50. Both aircraft were manufactured and supported by Dutch airc ...
was to be a completely modernised version of the F-27, and the Fokker 100 a new airliner based on the F-28. Development costs were allowed to spiral out of control, almost forcing Fokker out of business in 1987. The Dutch government bailed the company out with 212 million guilders, but demanded Fokker look for a "strategic partner", British Aerospace and DASA being named most likely candidates.
Initial sales of the Fokker 100 were good, leading Fokker to begin development of the Fokker 70
The Fokker 70 is a narrow-body, twin-engined, medium-range, turbofan regional airliner designed and produced by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker.
It was developed during the early 1990s as a smaller version of the newly-developed Fokker ...
, a smaller version of the F100, in 1991, but sales of the F70 were below expectations and the F100 had strong competition from Boeing and Airbus by then.
In 1992, after a long and arduous negotiation process, Fokker signed an agreement with DASA. This did not solve Fokker's problems, though, mostly because DASA's parent company Daimler-Benz also had to deal with its own organisational problems.
Bankruptcy
On 22 January 1996, the board of directors of Daimler-Benz decided to focus on its core automobile business and cut ties with Fokker. The next day, an Amsterdam court extended temporary creditor protection. Discussions were initiated with Bombardier on 5 February 1996. After having reviewed and evaluated the opportunities and challenges Fokker represented at the time, Bombardier renounced its acquisition on 27 February. On 15 March, the Fokker company was declared bankrupt. Differences in national culture could have played a role in the failed takeover of Fokker by Deutsche Aerospace (DASA). Those divisions of the company that manufactured parts and carried out maintenance and repair work were taken over by Stork N.V.; it is now known as Stork Aerospace Group. Stork Fokker exists to sustain remarketing of the company's existing aircraft: it refurbishes and resells F 50s and F 100s, and has converted a few F 50s to transport aircraft. Special projects included the development of an F50 maritime patrol variant and an F100 executive jet. For this project, Stork received the 2005 "Aerospace Industry Award" in the Air Transport category from '' Flight International'' magazine. Other divisions of the company that were profitable continued as separate companies: Fokker Space (later Dutch Space) and Fokker Control Systems. In November 2009, Stork Aerospace changed its name to Fokker Aerospace Group. As of 2011, the Fokker Aerospace Group changed its name to Fokker Technologies. The five individual business units within Fokker Technologies all carry the Fokker name: * Fokker Aerostructures * Fokker Landing Gear * Fokker Elmo * Fokker Techniek * Fokker Services The former Fokker aircraft facilities at Schiphol were redeveloped into the Fokker Logistics Park. One of the former Fokker tenants is Fokker Services. Meanwhile, Rekkof Aircraft ("Fokker" backwards) is attempting to restart production of the Fokker F70 and F100, supported by suppliers and airlines. In 2015,GKN
GKN Ltd is a British multinational automotive and aerospace components business headquartered in Redditch, England. It is a long-running business known for many decades as Guest, Keen and Nettlefolds. It can trace its origins back to 1759 an ...
considers Fokker Technologies as a possible acquisition to supply for the hybrid car market. The British automotive and aerospace supplier plans to buy the Netherlands-based Fokker for €706 million.
In 2021, Fokker Services and Fokker Techniek are acquired by Panta Holdings. This acquisition will strengthen the Panta Holdings’, Dutch investment fund, aerospace footprint.
Famous Fokker aircraft and pilots
air superiority
Aerial supremacy (also air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of c ...
during the Fokker Scourge.
* Manfred von Richthofen ("The Red Baron," the top scoring World War I ace) is associated with an all-red Fokker Dr.I
The Fokker Dr.I (''Dreidecker'', "triplane" in German), often known simply as the Fokker Triplane, was a World War I fighter aircraft built by Fokker-Flugzeugwerke. The Dr.I saw widespread service in the spring of 1918. It became famous as the ...
triplane, at least for some of his 80 victories (1917–1918)
* The 1918 Fokker D.VII
The Fokker D.VII was a German World War I fighter aircraft designed by Reinhold Platz of the Fokker-Flugzeugwerke. Germany produced around 3,300 D.VII aircraft in the second half of 1918. In service with the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the D.VII qu ...
performed so well that surrender of all examples of the type was demanded when Germany capitulated.
* In 1923, Oakley George Kelly
Oakley George Kelly (December 3, 1891 – June 5, 1966) was a record setting pilot for the United States Army Air Service.
Biography
He was born on December 3, 1891 in Pennsylvania and grew up in Grove City.
In May 1922, Lieutenant Oakley G. K ...
and John Arthur Macready
John Arthur Macready (October 14, 1887 – September 15, 1979) was an American test pilot and aviator. He was the only three-time recipient of the Mackay Trophy, receiving the trophy three consecutive years. Macready won the MacKay Trophy thr ...
completed the first non-stop flight spanning the North American continent in a Fokker T-2
The Fokker F.IV was an airliner designed in the Netherlands in the early 1920s, with only two ever made, both for the United States Army Air Service (designated T-2).
Design and development
The Fokker F.IV was constructed in typical Fokker styl ...
.
* In 1927, Richard E. Byrd completed his trans-Atlantic flight from New York City to Paris in the Fokker F.VII
The Fokker F.VII, also known as the Fokker Trimotor, was an airliner produced in the 1920s by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker, Fokker's American subsidiary Atlantic Aircraft Corporation, and other companies under licence.
Design and dev ...
''America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
''.
* In 1928, Amelia Earhart
Amelia Mary Earhart ( , born July 24, 1897; disappeared July 2, 1937; declared dead January 5, 1939) was an American aviation pioneer and writer. Earhart was the first female aviator to fly solo across the Atlantic Ocean. She set many oth ...
became the first woman to fly across the Atlantic as a passenger in a Fokker F.VII
The Fokker F.VII, also known as the Fokker Trimotor, was an airliner produced in the 1920s by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker, Fokker's American subsidiary Atlantic Aircraft Corporation, and other companies under licence.
Design and dev ...
.
* In 1928, Charles Kingsford-Smith
Sir Charles Edward Kingsford Smith (9 February 18978 November 1935), nicknamed Smithy, was an Australian aviation pioneer. He piloted the first transpacific flight and the first flight between Australia and New Zealand.
Kingsford Smith was b ...
completed the first trans-Pacific flight in another F.VII, the '' Southern Cross''.
* Finnish pilot Jorma Sarvanto
Jorma Kalevi Sarvanto (22 August 1912 – 16 October 1963) was a Finnish Air Force pilot and the foremost Finnish fighter ace of the Winter War.
Early life
Sarvanto was born and raised in Turku, Finland. He attended high school in Turku and g ...
shot down six Soviet Ilyushin DB-3
The Ilyushin DB-3, where "DB" stands for ''Dalniy Bombardirovschik'' (Russian: Дальний бомбардировщик) meaning "long-range bomber", was a Soviet bomber aircraft of World War II. It was a twin-engined, low-wing monoplane that f ...
s in a quick succession using a Fokker D.XXI
The Fokker D.XXI fighter was designed in 1935 by Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker in response to requirements laid out by the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force (''Militaire Luchtvaart van het Koninklijk Nederlands-Indisch Leger'', M ...
fighter during the Winter War, drawing international attention.
* The 1951 Fokker S.14 Machtrainer was one of the first purpose-built jet training aircraft in the world.
* King Willem-Alexander of the Netherlands was a co-pilot about twice per month for 21 years on commercial KLM Cityhopper
KLM Cityhopper is the regional airline subsidiary of KLM, headquartered in Haarlemmermeer, North Holland, Netherlands. It is based at nearby Amsterdam Airport Schiphol. As a subsidiary of Air France–KLM, it is an affiliate of SkyTeam. The airli ...
and Martinair flights flying Fokker 70
The Fokker 70 is a narrow-body, twin-engined, medium-range, turbofan regional airliner designed and produced by the Dutch aircraft manufacturer Fokker.
It was developed during the early 1990s as a smaller version of the newly-developed Fokker ...
aircraft.
Fokker aircraft
1912–1921
1922–1940
Fokker-Atlantic designs
1945–1996
References
Notes
Bibliography
* Bowers, Peter and Ernest McDowell. ''Triplanes: A Pictorial History of the World's Triplanes and Multiplanes''. St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International, 1993. . * Dierikx, Marc. ''Fokker: A Transatlantic Biography''. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1997. . * * Hegener, Henri. ''Fokker – the man and the aircraft'' Herts, UK: Harleyford Publications, 1961. LCCN 61-10595 * * Molson, K.M. ''Pioneering in Canadian Air Transport''. Winnipeg: James Richardson & Sons, 1974. . * Nevin, David. ''The Pathfinders (The Epic of Flight Series)''. Alexandria, Virginia: Time-Life Books, 1980. . * Postma, Thijs. ''Fokker: Aircraft Builders to the World''. London: Jane's, 1979. . * Weyl, A.R. ''Fokker: The Creative Years''. London: Putnam, 1965.External links
Fokker Technologies Official company website
Pictures of the Fokker fleet
Rekkof official website
Fokker, a living history
FokkerPilot.net
Fokker aircraft website
The assembly-hall at Fokker with many F-16s
{{Economic history of the Netherlands Manufacturing companies established in 1912 Defunct aircraft manufacturers of the Netherlands Science and technology in the Netherlands Manufacturing companies disestablished in 1996 Defunct aircraft manufacturers of Germany 1912 establishments in Germany Dutch brands Dutch companies disestablished in 1996 German companies established in 1912 Defence companies of the Netherlands