Abdominal Organs Anatomy.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and
Sobo 1906 393.png, View of the various organs and blood-vessels in proximity with liver.
Gray1120.png, The relations of the viscera and large vessels of the abdomen, seen from behind.
 Functionally, the human abdomen is where most of the digestive tract is placed and so most of the absorption and digestion of food occurs here. The alimentary tract in the abdomen consists of the lower esophagus, the stomach, the
Functionally, the human abdomen is where most of the digestive tract is placed and so most of the absorption and digestion of food occurs here. The alimentary tract in the abdomen consists of the lower esophagus, the stomach, the
 In the mid-line a slight furrow extends from the xiphoid process above to the pubic symphysis below, representing the linea alba in the abdominal wall. At about its midpoint sits the umbilicus or navel. The rectus abdominis on each side of the linea alba stands out in muscular people. The outline of these muscles is interrupted by three or more transverse depressions indicating the tendinous intersections. There is usually one about the xiphoid process, one at the navel, and one in between. It is the combination of the linea alba and the tendinous intersections which form the abdominal "six-pack" sought after by many people.
The upper lateral limit of the abdomen is the subcostal margin (at or near the '' subcostal plane'') formed by the cartilages of the
In the mid-line a slight furrow extends from the xiphoid process above to the pubic symphysis below, representing the linea alba in the abdominal wall. At about its midpoint sits the umbilicus or navel. The rectus abdominis on each side of the linea alba stands out in muscular people. The outline of these muscles is interrupted by three or more transverse depressions indicating the tendinous intersections. There is usually one about the xiphoid process, one at the navel, and one in between. It is the combination of the linea alba and the tendinous intersections which form the abdominal "six-pack" sought after by many people.
The upper lateral limit of the abdomen is the subcostal margin (at or near the '' subcostal plane'') formed by the cartilages of the
 * The highest of the former is the
* The highest of the former is the
 The abdomen can be divided into quadrants or regions to describe the location of an organ or structure. Classically, quadrants are described as the left upper, left lower, right upper, and right lower. Quadrants are also often used in describing the site of an abdominal pain.
The abdomen can also be divided into nine regions.
These terms stem from "hypo" meaning "below" and "epi" means "above", while "chondron" means "cartilage" (in this case, the cartilage of the rib) and "gaster" means stomach. The reversal of "left" and "right" is intentional, because the anatomical designations reflect the patient's own right and left.)
The "right iliac fossa" (RIF) is a common site of pain and tenderness in patients who have appendicitis. The fossa is named for the underlying iliac fossa of the hip bone, and thus is somewhat imprecise. Most of the anatomical structures that will produce pain and tenderness in this region are not in fact in the concavity of the ileum. However, the term is in common usage.
The abdomen can be divided into quadrants or regions to describe the location of an organ or structure. Classically, quadrants are described as the left upper, left lower, right upper, and right lower. Quadrants are also often used in describing the site of an abdominal pain.
The abdomen can also be divided into nine regions.
These terms stem from "hypo" meaning "below" and "epi" means "above", while "chondron" means "cartilage" (in this case, the cartilage of the rib) and "gaster" means stomach. The reversal of "left" and "right" is intentional, because the anatomical designations reflect the patient's own right and left.)
The "right iliac fossa" (RIF) is a common site of pain and tenderness in patients who have appendicitis. The fossa is named for the underlying iliac fossa of the hip bone, and thus is somewhat imprecise. Most of the anatomical structures that will produce pain and tenderness in this region are not in fact in the concavity of the ileum. However, the term is in common usage.

 In arthropods the abdomen is built up of a series of upper plates known as tergites and lower plates known as
In arthropods the abdomen is built up of a series of upper plates known as tergites and lower plates known as
pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the th ...
. In arthropods it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cepha ...
.
In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint
The lumbosacral joint is a joint of the body, between the last lumbar vertebra and the first sacral segment of the vertebral column. In some ways, calling it a "joint" (singular) is a misnomer, since the lumbosacral junction includes a disc between ...
(the intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold t ...
between L5 and S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the th ...
. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear.
In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at front and to the sides, and by part of the vertebral column at the back. Lower ribs can also enclose ventral and lateral walls. The abdominal cavity is continuous with, and above, the pelvic cavity. It is attached to the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
. Structures such as the aorta, inferior vena cava and esophagus pass through the diaphragm. Both the abdominal and pelvic cavities are lined by a serous membrane known as the parietal peritoneum. This membrane is continuous with the visceral peritoneum lining the organs. The abdomen in vertebrates contains a number of organs belonging to, for instance, the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
, urinary system, and muscular system.
Contents
Theabdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the th ...
contains most organs of the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
, including the stomach, the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
, and the colon with its attached appendix
Appendix, or its plural form appendices, may refer to:
__NOTOC__ In documents
* Addendum, an addition made to a document by its author after its initial printing or publication
* Bibliography, a systematic list of books and other works
* Index (pub ...
. Other digestive organs are known as the accessory digestive organs and include the liver, its attached gallbladder, and the pancreas, and these communicate with the rest of the system via various ducts. The spleen, and organs of the urinary system including the kidneys, and adrenal glands also lie within the abdomen, along with many blood vessels including the aorta and inferior vena cava. The urinary bladder, uterus, fallopian tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ot ...
s, and ovaries may be seen as either abdominal organs or as pelvic organs. Finally, the abdomen contains an extensive membrane called the peritoneum. A fold of peritoneum may completely cover certain organs, whereas it may cover only one side of organs that usually lie closer to the abdominal wall. This is called the retroperitoneum, and the kidneys and ureters are known as ''retroperitoneal'' organs.
Abdominal organs can be highly specialized in some animals. For example, the stomach of ruminants, (a suborder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and ...
of mammals that includes cattle and sheep), is divided into four chambers – rumen, reticulum, omasum and abomasum.
Muscles
There are three layers of muscles in the abdominal wall. They are, from the outside to the inside: external oblique, internal oblique, andtransverse abdominal
The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral (front and side) abdominal wall which is deep to (layered below) t ...
. The first three layers extend between the vertebral column, the lower ribs, the iliac crest and pubis of the hip
In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or "coxa"Latin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
The hip region is ...
. All of their fibers merge towards the midline and surround the rectus abdominis in a sheath before joining up on the opposite side at the linea alba. Strength is gained by the criss-crossing of fibers, such that the external oblique runs downward and forward, the internal oblique upward and forward, and the transverse abdominal horizontally forward.
The transverse abdominal
The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral (front and side) abdominal wall which is deep to (layered below) t ...
muscle is flat and triangular, with its fibers running horizontally. It lies between the internal oblique and the underlying transverse fascia. It originates from the inguinal ligament, costal cartilages 7-12, the iliac crest and thoracolumbar fascia. Inserts into the conjoint tendon, xiphoid process, linea alba and the pubic crest.
The rectus abdominis muscles are long and flat. The muscle is crossed by three fibrous bands called the tendinous intersections. The rectus abdominis is enclosed in a thick sheath, formed as described above, by fibers from each of the three muscles of the lateral abdominal wall. They originate at the pubis bone
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ra ...
, run up the abdomen on either side of the linea alba, and insert into the cartilages of the fifth, sixth, and seventh ribs. In the region of the groin, the inguinal canal, is a passage through the layers. This gap is where the testes can drop through the wall and where the fibrous cord from the uterus in the female runs. This is also where weakness can form, and cause inguinal hernias.
The pyramidalis muscle
The pyramidalis muscle is a small triangular muscle, anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle, and contained in the rectus sheath.
Structure
The pyramidalis muscle is part of the anterior abdominal wall. Inferiorly, the pyramidalis muscle attaches ...
is small and triangular. It is located in the lower abdomen in front of the rectus abdominis. It originates at the pubic bone and is inserted into the linea alba halfway up to the navel.
Function
 Functionally, the human abdomen is where most of the digestive tract is placed and so most of the absorption and digestion of food occurs here. The alimentary tract in the abdomen consists of the lower esophagus, the stomach, the
Functionally, the human abdomen is where most of the digestive tract is placed and so most of the absorption and digestion of food occurs here. The alimentary tract in the abdomen consists of the lower esophagus, the stomach, the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
, the jejunum, ileum, the cecum and the appendix
Appendix, or its plural form appendices, may refer to:
__NOTOC__ In documents
* Addendum, an addition made to a document by its author after its initial printing or publication
* Bibliography, a systematic list of books and other works
* Index (pub ...
, the ascending
''Ascending'' is a science fiction novel by the Canadian writer James Alan Gardner, published in 2001 by HarperCollins Publishers under its various imprints.HarperCollins, Avon, HarperCollins Canada, SFBC/Avon; paperback edition 2001, Eos Books. ...
, transverse
Transverse may refer to:
*Transverse engine, an engine in which the crankshaft is oriented side-to-side relative to the wheels of the vehicle
*Transverse flute, a flute that is held horizontally
* Transverse force (or ''Euler force''), the tangen ...
and descending colon
In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the descending colon is the part of the colon extending from the left colic flexure to the level of the iliac crest (whereupon it transitions into the sigmoid colon). The function of the descendin ...
s, the sigmoid colon
The sigmoid colon (or pelvic colon) is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about in length. The loop is typically shaped like a Greek letter sigma (ς) or Latin letter S (thus ''s ...
and the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the s ...
. Other vital organs inside the abdomen include the liver, the kidneys, the pancreas and the spleen.
The abdominal wall is split into the posterior (back), lateral (sides), and anterior (front) walls.
Movement, breathing and other functions
The abdominal muscles have different important functions. They assist as muscles of exhalation in the breathing process duringforceful exhalation
The muscles of respiration are the muscles that contribute to inhalation and exhalation, by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm and, to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles drive respiration during qu ...
. Moreover, these muscles serve as protection for the inner organs. Furthermore, together with the back muscles they provide postural support and are important in defining the form. When the glottis
The glottis is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing vowels and voiced consonants.
Etymology
From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), va ...
is closed and the thorax and pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
are fixed, they are integral in the cough, urination, defecation
Defecation (or defaecation) follows digestion, and is a necessary process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material known as feces from the digestive tract via the anus. The act has a variety of names ranging f ...
, childbirth, vomit, and singing functions. When the pelvis is fixed, they can initiate the movement of the trunk in a forward motion. They also prevent hyperextension. When the thorax is fixed, they can pull up the pelvis and finally, they can bend the vertebral column sideways and assist in the trunk's rotation.
Posture
The transverse abdominis muscle is the deepest muscle, therefore, it cannot be touched from the outside. It can greatly affect the body's posture. The internal obliques are also deep and also affect body posture. Both of them are involved in rotation and lateral flexion of thespine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Vertebral column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoolog ...
and are used to bend and support the spine from the front. The external obliques are more superficial and they are also involved in rotation and lateral flexion of the spine. Also they stabilize the spine when upright. The rectus abdominis muscle is not the most superficial abdominal muscle. The tendonous sheath extending from the external obliques cover the rectus abdominis. The rectus abdominis is the muscle that very fit people develop into the 6-pack ab look. Although it should really be a 10 pack as there are 5 vertical sections on each side. The 2 bottom sections are just above the pubic bone and usually not visible, hence, the 6 pack abs. The rectus abdominals' function is to bend one's back forward (flexion). The main work of the abdominal muscles is to bend the spine forward when contracting concentrically.
Society and culture
Social and cultural perceptions of the outward appearance of the abdomen has varying significance around the world. Depending on the type of society, excess weight can be perceived as an indicator of wealth and prestige due to excess food, or as a sign of poor health due to lack of exercise. In many cultures, bare abdomens are distinctly sexualized and perceived similarly to breast cleavage.Exercise
Being key elements of spinal support, and contributors to good posture, it is important to properly exercise the abdominal muscles together with the back muscles because when these are weak or overly tight they can suffer painful spasms and injuries. When properly exercised, abdominal muscles contribute to improved posture and balance, reduce the likelihood of back pain episodes, reduce the severity of back pain, protect against injury by responding efficiently to stresses, help avoid some back surgeries, and help with the healing of back problems, or after spine surgery. When strengthened, the abdominal muscles provide flexibility as well. The abdominal muscles can be worked by practicing disciplines of general body strength such as Pilates, yoga, T'ai chi, and jogging. There are also specific routines which target each of these muscles.Clinical significance
Abdominal obesity
Abdominal obesity, also known as central obesity and truncal obesity, is a condition when excessive visceral fat around the stomach and abdomen has built up to the extent that it is likely to have a negative impact on health. Abdominal obesity has ...
is a condition where abdominal fat
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular en ...
or visceral fat, has built up excessively between the abdominal organs. This is associated with a higher risk of heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
, asthma and type 2 diabetes.
Abdominal trauma is an injury to the abdomen and can involve damage to the abdominal organs. There is an associated risk of severe blood loss and infection. Injury to the lower chest can cause injuries to the spleen and liver.
A scaphoid abdomen is when the abdomen is sucked inwards. In a newborn, it may represent a diaphragmatic hernia
Diaphragmatic hernia is a defect or hole in the diaphragm that allows the abdominal contents to move into the chest cavity. Treatment is usually surgical.
Types
* Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
** Morgagni's hernia
** Bochdalek hernia
* Hiatal h ...
. In general, it is indicative of malnutrition.
Disease
Many gastrointestinal diseases affect the abdominal organs. These include stomach disease, liver disease,pancreatic disease Pancreatic diseases are diseases that affect the pancreas, an organ in most vertebrates and in humans and other mammals located in the abdomen. The pancreas plays a role in the digestive and endocrine system, producing enzymes which aid the digesti ...
, gallbladder and bile duct disease; intestinal diseases include enteritis, coeliac disease, diverticulitis
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdominal ...
, and IBS.
Examination
Different medical procedures can be used to examine the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. These include endoscopy,colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (''e. ...
, sigmoidoscopy, enteroscopy
Enteroscopy is the procedure of using an endoscope for the direct visualization of the small bowel. Etymologically, the word could potentially refer to any bowel endoscopy ('' entero-'' + '' -scopy''), but idiomatically it is conventionally restri ...
, oesophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considered ...
and virtual colonoscopy
Virtual colonoscopy (VC, also called CT colonography or CT pneumocolon) is the use of CT scanning or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce two- and three-dimensional images of the colon (large intestine), from the lowest part, the rectum, ...
. There are also a number of medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
techniques that can be used. Surface landmarks are important in the examination of the abdomen.
Surface landmarks
 In the mid-line a slight furrow extends from the xiphoid process above to the pubic symphysis below, representing the linea alba in the abdominal wall. At about its midpoint sits the umbilicus or navel. The rectus abdominis on each side of the linea alba stands out in muscular people. The outline of these muscles is interrupted by three or more transverse depressions indicating the tendinous intersections. There is usually one about the xiphoid process, one at the navel, and one in between. It is the combination of the linea alba and the tendinous intersections which form the abdominal "six-pack" sought after by many people.
The upper lateral limit of the abdomen is the subcostal margin (at or near the '' subcostal plane'') formed by the cartilages of the
In the mid-line a slight furrow extends from the xiphoid process above to the pubic symphysis below, representing the linea alba in the abdominal wall. At about its midpoint sits the umbilicus or navel. The rectus abdominis on each side of the linea alba stands out in muscular people. The outline of these muscles is interrupted by three or more transverse depressions indicating the tendinous intersections. There is usually one about the xiphoid process, one at the navel, and one in between. It is the combination of the linea alba and the tendinous intersections which form the abdominal "six-pack" sought after by many people.
The upper lateral limit of the abdomen is the subcostal margin (at or near the '' subcostal plane'') formed by the cartilages of the false rib
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi ...
s (8, 9, 10) joining one another. The lower lateral limit is the anterior crest of the ilium
Ilium or Ileum may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions
* Ilion (Asia Minor), former name of Troy
* Ilium (Epirus), an ancient city in Epirus, Greece
* Ilium, ancient name of Cestria (Epirus), an ancient city in Epirus, Greece
* Ilium Building, a ...
and Poupart's ligament
The inguinal ligament (), also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may dev ...
, which runs from the anterior superior spine of the ilium to the spine of the pubis. These lower limits are marked by visible grooves. Just above the pubic spines on either side are the external abdominal rings, which are openings in the muscular wall of the abdomen through which the spermatic cord emerges in the male, and through which an inguinal hernia may rupture.
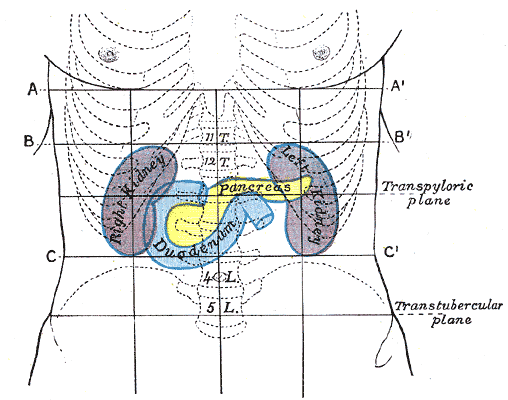
One method by which the location of the abdominal contents can be appreciated is to draw three horizontal and two vertical lines.
=Horizontal lines
= * The highest of the former is the
* The highest of the former is the transpyloric line
The transpyloric plane, also known as Addison's plane, is an imaginary horizontal plane, located halfway between the suprasternal notch of the manubrium and the upper border of the symphysis pubis at the level of the first lumbar vertebrae, L1. I ...
of C. Addison, which is situated halfway between the suprasternal notch and the top of the pubic symphysis, and often cuts the pyloric opening of the stomach an inch to the right of the mid-line. The hilum of each kidney is a little below it, while its left end approximately touches the lower limit of the spleen. It corresponds to the first lumbar vertebra behind.
* The second line is the ''subcostal line
The subcostal plane is a transverse plane which bisects the body at the level of the 10th costal margin and the vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lo ...
'', drawn from the lowest point of the subcostal arch
The costal margin, also known as the costal arch, is the lower edge of the chest (thorax) formed by the bottom edge of the rib cage.
Structure
The costal margin is the medial margin formed by the cartilages of the seventh to tenth ribs. It attac ...
( tenth rib). It corresponds to the upper part of the third lumbar vertebra, and it is an inch or so above the umbilicus. It indicates roughly the transverse colon, the lower ends of the kidneys, and the upper limit of the transverse (3rd) part of the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
.
* The third line is called the '' intertubercular line'', and runs across between the two rough tubercles, which can be felt on the outer lip of the crest of the ilium about from the anterior superior spine. This line corresponds to the body of the fifth lumbar vertebra, and passes through or just above the ileo-caecal valve, where the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
joins the large intestine.
=Vertical lines
= The two vertical or mid-Poupart lines are drawn from the point midway between the anterior superior spine and the pubic symphysis on each side, vertically upward to the costal margin. * The right one is the most valuable, as the ileo-caecal valve is situated where it cuts the intertubercular line. The orifice of theappendix
Appendix, or its plural form appendices, may refer to:
__NOTOC__ In documents
* Addendum, an addition made to a document by its author after its initial printing or publication
* Bibliography, a systematic list of books and other works
* Index (pub ...
lies an inch lower, at McBurney's point. In its upper part, the vertical line meets the transpyloric line at the lower margin of the ribs, usually the ninth, and here the gallbladder is situated.
* The left mid-Poupart line corresponds in its upper three-quarters to the inner edge of the descending colon
In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the descending colon is the part of the colon extending from the left colic flexure to the level of the iliac crest (whereupon it transitions into the sigmoid colon). The function of the descendin ...
.
The right subcostal margin corresponds to the lower limit of the liver, while the right nipple is about half an inch above its upper limit.
Quadrants and regions
 The abdomen can be divided into quadrants or regions to describe the location of an organ or structure. Classically, quadrants are described as the left upper, left lower, right upper, and right lower. Quadrants are also often used in describing the site of an abdominal pain.
The abdomen can also be divided into nine regions.
These terms stem from "hypo" meaning "below" and "epi" means "above", while "chondron" means "cartilage" (in this case, the cartilage of the rib) and "gaster" means stomach. The reversal of "left" and "right" is intentional, because the anatomical designations reflect the patient's own right and left.)
The "right iliac fossa" (RIF) is a common site of pain and tenderness in patients who have appendicitis. The fossa is named for the underlying iliac fossa of the hip bone, and thus is somewhat imprecise. Most of the anatomical structures that will produce pain and tenderness in this region are not in fact in the concavity of the ileum. However, the term is in common usage.
The abdomen can be divided into quadrants or regions to describe the location of an organ or structure. Classically, quadrants are described as the left upper, left lower, right upper, and right lower. Quadrants are also often used in describing the site of an abdominal pain.
The abdomen can also be divided into nine regions.
These terms stem from "hypo" meaning "below" and "epi" means "above", while "chondron" means "cartilage" (in this case, the cartilage of the rib) and "gaster" means stomach. The reversal of "left" and "right" is intentional, because the anatomical designations reflect the patient's own right and left.)
The "right iliac fossa" (RIF) is a common site of pain and tenderness in patients who have appendicitis. The fossa is named for the underlying iliac fossa of the hip bone, and thus is somewhat imprecise. Most of the anatomical structures that will produce pain and tenderness in this region are not in fact in the concavity of the ileum. However, the term is in common usage.
Other animals

sternite
The sternum (pl. "sterna") is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen.
In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the ...
s, the whole being held together by a tough yet stretchable membrane.
The abdomen contains the insect's digestive tract and reproductive organs, it consists of eleven segments in most orders of insects though the eleventh segment is absent in the adult of most higher orders. The number of these segments does vary from species to species with the number of segments visible reduced to only seven in the common honeybee. In the Collembola (Springtails) the abdomen has only six segments.
The abdomen is sometimes highly modified. In Apocrita (bees, ants and wasps), the first segment of the abdomen is fused to the thorax and is called the propodeum. In ants the second segment forms the narrow petiole. Some ants have an additional postpetiole segment, and the remaining segments form the bulbous gaster. The petiole and gaster (abdominal segments 2 and onward) are collectively called the metasoma.
Unlike other arthropods, insects possess no legs on the abdomen in adult form, though the Protura do have rudimentary leg-like appendages on the first three abdominal segments, and Archaeognatha possess small, articulated "styli" which are sometimes considered to be rudimentary appendages. Many larval insects including the Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) is an order (biology), order of insects that includes butterfly, butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 Family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic r ...
and the Symphyta
Sawflies are the insects of the suborder Symphyta within the order Hymenoptera, alongside ants, bees, and wasps. The common name comes from the saw-like appearance of the ovipositor, which the females use to cut into the plants where they lay ...
(Sawflies) have fleshy appendages called prolegs on their abdominal segments (as well as their more familiar thoracic legs), which allow them to grip onto the edges of plant leaves as they walk around.
In arachnids
Arachnida () is a Class (biology), class of joint-legged invertebrate animals (arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, came ...
(spiders, scorpions and relatives), the term "abdomen" is used interchangeably with " opisthosoma" ("hind body"), which is the body section posterior to that bearing the legs and head (the prosoma or cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cepha ...
).
See also
*Abdominal fat
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular en ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Animal anatomy Human anatomy