Ferrovia Centro-AtlûÂntica on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vale S.A., formerly ''Companhia Vale do Rio Doce'' (the Sweet River Valley Company, referring to the
/ref> and its stock to lose nearly 25 percent in value."Vale Denied Having ãUpstreamã Dams Ahead of Deadly Accident"
'' Wall Street Journal'' February 10, 2019. Retrieved February 10, 2019. Vale is considered the most valuable company in Latin America, with an estimated market value of

/ref> Vale's Mariana Hub was the 9th largest iron ore mining center in the world in 2014, with an output of 39 million metric tonnes. Vale's Serra Sul / S11D is the largest mining reserve in the world. The company's iron ore mines are primarily in Brazil. Nickel: Vale is the world's largest nickel producer. Sales of nickel represented 17% of total company revenues in 2014. In 2014, Vale sold 272,000 metric tonnes of nickel. The company owns nickel mines in Canada, Indonesia,
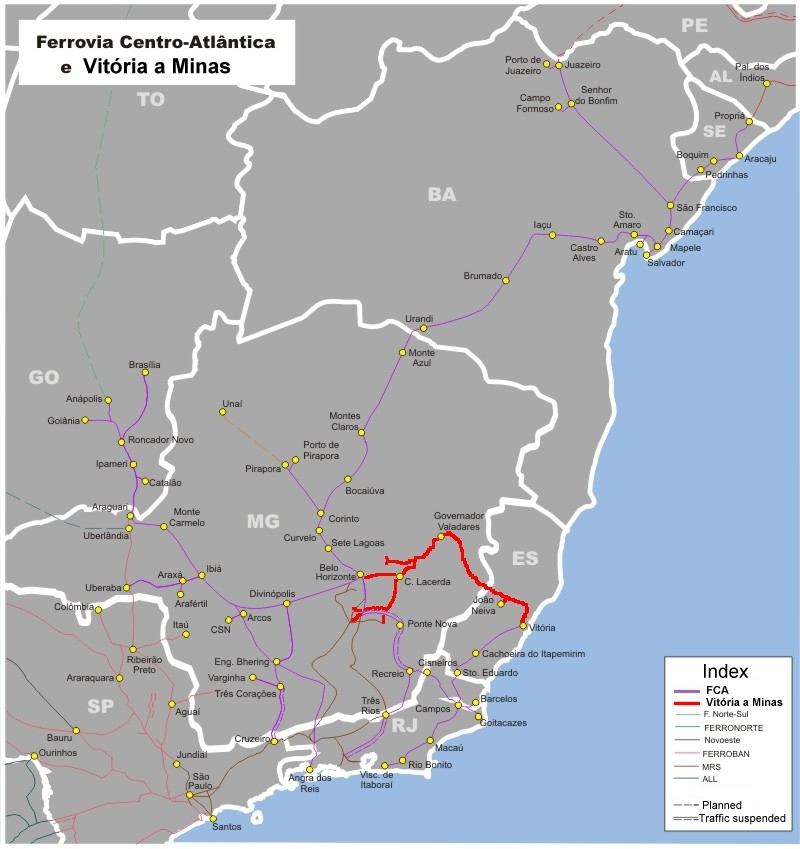 * Vitû°ria a Minas railroad - Vale operates under a 30-year contract this 905 km, railroad, which is used to transport iron from the ''Iron Quadrangle'' in Minas Gerais to the
* Vitû°ria a Minas railroad - Vale operates under a 30-year contract this 905 km, railroad, which is used to transport iron from the ''Iron Quadrangle'' in Minas Gerais to the
/ref> The company also plans to build a 600 MW thermoelectric power plant in the state of ParûÀ.A CVRD Anuncia a ConstruûÏûÈo de uma Tûˋrmica a CarvûÈo - Adriano Pires: O Globo Online
/ref> Vale also operates hydroelectric plants in Canada and Indonesia.
/ref> One year later the ''Vitû°ria a Minas'' railroad was inaugurated. The 1950s marked Companhia Vale do Rio Doce's entry into the global iron ore market, after the company's mine-railroad-port complex was modernized and iron ore prices doubled. At first, sales were mostly to the United States, but exports to Europe increased over the course of the decade.Vale History Book: Chapter 3
/ref> In 1966, the company inaugurated in
/ref> In 1974, Vale became the world's biggest exporter of iron ore, a title which it still holds today. In 1982, Vale began to diversify after it started to produce aluminium in Rio de Janeiro. In the mid 1980s, profits increased considerably under the leadership of Eliezer Batista, father of

/ref> in a wave of red iron ore which destroyed the mine's cafeteria, where many workers were present and lost their lives, and which flooded the town of
/ref> Kt (-1,850 /-15.3% y-o-y). This is a higher rate of decline than over the period since 4Q'18 (-10.9% CAGR).
The company's home page in Portuguese
The company's home page in English
Rheebu Nuu - indigenous group attempting to halt CVRD's mining projects in the South Pacific
Eyewitness Survivor Account and video.
"Brumadinho: novas imagens revelam detalhes da tragûˋdia, ''Jornol O Globo'', February 1, 2019. Retrieved February 10, 2019. * {{Authority control Conglomerate companies of Brazil 1942 establishments in Brazil Aluminium companies of Brazil Coal companies of Brazil Conglomerate companies established in 1942 Railway companies established in 1942 Energy companies established in 1942 Iron ore mining companies Companies listed on B3 (stock exchange) Mining companies of Brazil Multinational companies headquartered in Brazil Railway companies of Brazil Privatized companies of Brazil Non-renewable resource companies established in 1942 Metal companies of Brazil
Doce River
The Doce River (literally the "sweet river"; pt, Rio Doce ) is a river in southeast Brazil with a length of .
The river basin is economically important. In 2015 the collapse of a dam released highly contaminated water from mining into the river ...
) () is a Brazilian multinational corporation engaged in metals and mining and one of the largest logistics operators in Brazil. Vale is the largest producer of iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
and nickel in the world. It also produces manganese, ferroalloy
Ferroalloy refers to various alloys of iron with a high proportion of one or more other elements such as manganese (Mn), aluminium (Al), or silicon (Si). They are used in the production of steels and alloys. The alloys impart distinctive qualitie ...
s, copper, bauxite, potash, kaolin, and cobalt, currently operating nine hydroelectricity plants, and a large network of railroads, ships, and ports used to transport its products.
The company has had two catastrophic tailings dam failure
A tailings dam is typically an earth-fill embankment dam used to store byproducts of mining operations after separating the ore from the gangue. Tailings can be liquid, solid, or a slurry of fine particles, and are usually highly toxic and potent ...
s in Brazil: Mariana
Mariana may refer to:
Literature
* ''Mariana'' (Dickens novel), a 1940 novel by Monica Dickens
* ''Mariana'' (poem), a poem by Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson
* ''Mariana'' (Vaz novel), a 1997 novel by Katherine Vaz
Music
*"Mariana", a so ...
, in 2015, and Brumadinho
Brumadinho () is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Minas Gerais. The city belongs to the Belo Horizonte metropolitan mesoregion and to the microregion of Belo Horizonte. Brumadinho is at an altitude of 880ã₤m. In 2020 the population wa ...
, in 2019; the Brumadinho dam disaster caused the company to lose its license to operate eight tailings dams in Minas Gerais,"Vale ordered to halt operations at Brucutu", by Kelsey Rolfe, ''CIM magazine'', Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum, February 04, 2019. Retrieved February 10, 2019./ref> and its stock to lose nearly 25 percent in value."Vale Denied Having ãUpstreamã Dams Ahead of Deadly Accident"
'' Wall Street Journal'' February 10, 2019. Retrieved February 10, 2019. Vale is considered the most valuable company in Latin America, with an estimated market value of
US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
111 billion in 2021.
Current operations
Although the company's primary operations are in Brazil, Vale has operations in 30 countries, which are detailed below and on the company's website.Ownership structure
The company is listed on the stock exchanges of SûÈo Paulo, New York City,Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
, Paris and Madrid.
Mining business

Iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
: Vale is the world's largest iron ore producer. Sales of iron ore fines and pellets represented 65% of total company revenues in 2014. In 2014, Vale sold 256 million metric tonnes of iron ore fines and 44 million metric tonnes of iron ore pellets.Vale 2014 Form 20-F Annual Report/ref> Vale's Mariana Hub was the 9th largest iron ore mining center in the world in 2014, with an output of 39 million metric tonnes. Vale's Serra Sul / S11D is the largest mining reserve in the world. The company's iron ore mines are primarily in Brazil. Nickel: Vale is the world's largest nickel producer. Sales of nickel represented 17% of total company revenues in 2014. In 2014, Vale sold 272,000 metric tonnes of nickel. The company owns nickel mines in Canada, Indonesia,
New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
and Brazil. Tesla is known to buy the majority of their Nickel from Vale. In May 2022, Vale said that it had signed a long term deal of supplying nickel for Tesla. The agreement involves supplying low-carbon Class 1 nickel which Tesla needs for its electric vehicles' batteries. In line with this, Vale is pushing to increase its exposure to the electric vehicle industry.
Fertilizer products, primarily phosphates and nitrogen: Sales of fertilizer products represented 6% of total company revenues in 2014. In 2014, Vale sold 9 million metric tonnes of fertilizer products.
Copper: Sales of copper concentrate represented 4% of total company revenues in 2014. In 2014, Vale sold 353,000 metric tonnes of copper. The company owns copper mines in Brazil, Canada, Chile and Zambia.
Manganese and alloys: Sales of manganese and alloys represented 1% of total company revenues in 2014. In 2014, Vale sold 2 million metric tonnes of manganese and alloys.
Coal: Sales of coal represented 2% of total company revenues in 2014. In 2014, Vale sold 7.5 million metric tonnes of coal. The company owns coal mines in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and Mozambique.
Logistics
Railroads
From 2000 to 2006, Vale invested more than $1.3 billion on the acquisition of over 361locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
s and around 14,090 freight cars, those locomotives were primarily for iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
transportation, but some were for regular cargo. Some of the locomotives purchased were secondhand for refurbishment but at least 55 of the locomotives acquired were new ones of the model EMD SD70M
The EMD SD70 is a series of diesel-electric locomotives produced by the US company Electro-Motive Diesel in response to the GE Dash 9-44CW. Production commenced in late 1992 and since then over 5,700 units have been produced; most of these are th ...
, each one costing about $2 million.
After those investments, Vale became the owner of over 800 locomotives and more than 35,000 freight cars.
Vale owns the concession of three Brazilian railways: Vitû°ria-Minas Railway (EFVM), Ferrovia Centro-AtlûÂntica (FCA) and CarajûÀs railroad CarajûÀs may refer to:
* CarajûÀs Mine
* CarajûÀs Airport
* CanaûÈ dos CarajûÀs
* Eldorado dos CarajûÀs
* CarajûÀs (proposed Brazilian state)
* ''Carajas'' (spider)
* KarajûÀ
The KarajûÀ, also known as Iny, are an indigenous tribe located in Br ...
(EFC).  * Vitû°ria a Minas railroad - Vale operates under a 30-year contract this 905 km, railroad, which is used to transport iron from the ''Iron Quadrangle'' in Minas Gerais to the
* Vitû°ria a Minas railroad - Vale operates under a 30-year contract this 905 km, railroad, which is used to transport iron from the ''Iron Quadrangle'' in Minas Gerais to the Port of TubarûÈo
The Port of TubarûÈo is a port in Brazil, near the city of Vitû°ria in EspûÙrito Santo. The port was created in 1966 by the Brazilian mining company Vale to export iron ore extracted from the Iron Quadrangle in Minas Gerais. In 2007, the Port o ...
in the state of EspûÙrito Santo . The concession expires in 2027. This railroad also carried 1.1 million passengers in 2006.
*CarajûÀs railroad - The concession of this 892 km, gauge railroad also expires in 2027, it links CarajûÀs iron ore mines in the state of ParûÀ to Ponta da Madeira
Ponta da Madeira is a Brazilian private port, a large iron ore loading port in SûÈo LuûÙs, in the Northern part of Brazil, and one of the only terminals in the country suited for the ultra large Valemax ships. In 2020, the port of Ponta da Mad ...
port terminal in the state of MaranhûÈo. Vale operates a train of 3.2 km and 340 cars on this railroad.
*Ferrovia Centro-AtlûÂntica - Vale controls this railroad through the subsidiary ''FCA''. As it is shown on the ''Vale's operations map'' above, this 7,000 km, railroad extends through 6 Brazilian states, this railroad originally belonged to the RFFSA. Vale's concession of this railroad expires in 2026.
*Vale also has a stake in railway operators in Mozambique and Malawi via the Nacala Logistics Corridor The Nacala Logistics Corridor is a logistical mega-enterprise for connecting areas in Southeast Africa, which includes the creation and management of railways, highways, ports and airports, which directly serve Mozambique and Malawi, and indirectly ...
.
Ports and container terminals
=Brazil
= On February 5, 2019, the state court of the Province of Minas Gerais ordered Vale to halt use of eight of its tailings dams, including the Laranjeiras dam at Brucutu. *Port of TubarûÈo
The Port of TubarûÈo is a port in Brazil, near the city of Vitû°ria in EspûÙrito Santo. The port was created in 1966 by the Brazilian mining company Vale to export iron ore extracted from the Iron Quadrangle in Minas Gerais. In 2007, the Port o ...
- Vale owns and operates this port located in Vitû°ria, Brazil in the state of Espirito Santo. It's the largest iron ore embarking port in the world. Around 80 million metric tons of iron ore (30% of the company's annual production) are shipped through this port.
* Ponta da Madeira
Ponta da Madeira is a Brazilian private port, a large iron ore loading port in SûÈo LuûÙs, in the Northern part of Brazil, and one of the only terminals in the country suited for the ultra large Valemax ships. In 2020, the port of Ponta da Mad ...
- Located in the state of MaranhûÈo, it ships around 70 million metric tons mostly of iron ore, but also of manganese and copper for the company; it is being upgraded for the S11D project
* Port of Sepetiba - Vale operates two maritime terminals in the Port of Sepetiba area located in the state of Rio de Janeiro, together they ship around 60 million metric tons of iron ore.
* Samarco mine ã a joint-venture with BHP and the site of the Mariana dam disaster on 5 November 2015.
* FeijûÈo mine
The Brumadinho dam disaster occurred on 25 January 2019 when Dam I, a tailings dam at the Cû°rrego do FeijûÈo iron ore mine, east of Brumadinho, Minas Gerais, Brazil, suffered a catastrophic failure. The dam is owned by Vale, the same company ...
ã site of the Brumadinho dam disaster
The Brumadinho dam disaster occurred on 25 January 2019 when Dam I, a tailings dam at the Cû°rrego do FeijûÈo iron ore mine, east of Brumadinho, Minas Gerais, Brazil, suffered a catastrophic failure. The dam is owned by Vale, the same company ...
on 25 January 2019.
Vale also operates port terminals in the state of Sergipe and two others in the state of Espirito Santo
''Espirito'' (Brazilian for "Spirit") is the second album by Lawson Rollins. Rollins composed all of the music and co-produced the album with Persian-American musician and producer Shahin Shahida (of Shahin & Sepehr) and multi-platinum producer Do ...
.
=Malaysia
= * Teluk Rubiah Maritime Terminal (TRMT), a state of the art maritime terminal in the state ofPerak
Perak () is a state of Malaysia on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula. Perak has land borders with the Malaysian states of Kedah to the north, Penang to the northwest, Kelantan and Pahang to the east, and Selangor to the south. Thailand's ...
, operates as a distribution centre for iron ore in the Asia Pacific region.
Ships
Vale has also entered the shipping business by ordering 35 Very Large Ore Carriers (VLOC) to transport iron ore between South America and Asia. These , 400,000 DWT ships are the longest and largest dry bulk carriers in the world. The first ship, ''Vale Brasil'', was delivered in March 2011.Energy
Vale's energy business is focused at power production to fulfill the needs of its mining operations, as well as supplying the general Brazilian power grid. In 2005 it consumed 16.9 TWh of electrical power, accounting for 4.4% of Brazil's total consumption in that year. Vale has participation in 8hydroelectric plants
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
, with 7 of these located in the state of Minas Gerais. Vale's investment in hydroelectric power plants totals $880 million.SEC Info - Companhia Vale do Rio Doce, et al. - 20-F - For 12/31/05/ref> The company also plans to build a 600 MW thermoelectric power plant in the state of ParûÀ.A CVRD Anuncia a ConstruûÏûÈo de uma Tûˋrmica a CarvûÈo - Adriano Pires: O Globo Online
/ref> Vale also operates hydroelectric plants in Canada and Indonesia.
Rebranding
In November 2007, the company retired the name ''CVRD'' in favour of simplified company name of ''Vale'', and rebranded.History
Companhia Vale do Rio Doce (widely known as CVRD prior to 2007) (in English, "Doce River
The Doce River (literally the "sweet river"; pt, Rio Doce ) is a river in southeast Brazil with a length of .
The river basin is economically important. In 2015 the collapse of a dam released highly contaminated water from mining into the river ...
Valley Company") was founded in Itabira, Minas Gerais, by the Brazilian Federal Government on 1 June 1942.Vale History Book: Chapter 1/ref> One year later the ''Vitû°ria a Minas'' railroad was inaugurated. The 1950s marked Companhia Vale do Rio Doce's entry into the global iron ore market, after the company's mine-railroad-port complex was modernized and iron ore prices doubled. At first, sales were mostly to the United States, but exports to Europe increased over the course of the decade.Vale History Book: Chapter 3
/ref> In 1966, the company inaugurated in
Espirito Santo
''Espirito'' (Brazilian for "Spirit") is the second album by Lawson Rollins. Rollins composed all of the music and co-produced the album with Persian-American musician and producer Shahin Shahida (of Shahin & Sepehr) and multi-platinum producer Do ...
the Port of TubarûÈo
The Port of TubarûÈo is a port in Brazil, near the city of Vitû°ria in EspûÙrito Santo. The port was created in 1966 by the Brazilian mining company Vale to export iron ore extracted from the Iron Quadrangle in Minas Gerais. In 2007, the Port o ...
, which was to become the most important port for CVRD and is still used to export iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
mined from the ''Iron Quadrangle'' in Minas Gerais.
The company acquired a majority interest in the CarajûÀs Mine, with over 1.5 billion tonnes of iron ore in reserves, in 1970.Vale History Book 5/ref> In 1974, Vale became the world's biggest exporter of iron ore, a title which it still holds today. In 1982, Vale began to diversify after it started to produce aluminium in Rio de Janeiro. In the mid 1980s, profits increased considerably under the leadership of Eliezer Batista, father of
Eike Batista
Eike Fuhrken Batista da Silva (; born 3 November 1956) is a Brazilian-German serial entrepreneur who made and lost a fortune in mining and oil and gas industries. He engaged in a quest to promote Brazil's infrastructure with large-scale project ...
.
In 1985, Vale started to explore the CarajûÀs Mine in the state of ParûÀ just after the gauge CarajûÀs railroad was opened.
In 1986, Ponta Madeira port terminal, which is still used to export iron ore mined at the CarajûÀs Mine, was inaugurated in the state of MaranhûÈo.
In March 2017, Vale SA chose a commodities
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a comm ...
industry veteran, Fabio Schvartsman, as chief executive officer. Schvartsman was CEO
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a central executive officer (CEO), chief administrator officer (CAO) or just chief executive (CE), is one of a number of corporate executives charged with the management of an organization especially ...
of Klabin SA, Brazil's largest paper and cardboard producer, for the previous six years.
Privatization in 1997
In May 1997, despite protests by Vale employees and some politicians, the Brazilian Government auctioned a 41.73% interest in the company, which was sold for R$3.34 billion (US$3.13 billion). The largest interest purchased was a 16.3% stake purchased by Brazilian steel companyCompanhia Siderû¤rgica Nacional
Companhia Siderû¤rgica Nacional (CSN) is the largest fully integrated steel producer in Brazil and one of the largest in Latin America in terms of crude steel production.
.
Sale of wood pulp businesses
In 2001, Vale sold its Cenibra wood pulp business for US$670.5 million to focus on mining and logistics. In 2002, Vale sold 100,000 acres of land and the eucalyptus forests thereon related to its wood pulp business for R$137 million.Sale of steel businesses
In 2000, the company sold its stake in AûÏominas to Gerdau in exchange for preferred shares in Gerdau. In 2001, Vale sold its stake inCompanhia Siderû¤rgica Nacional
Companhia Siderû¤rgica Nacional (CSN) is the largest fully integrated steel producer in Brazil and one of the largest in Latin America in terms of crude steel production.
for R$520 million.
In 2004, Vale sold its stake in CST to Arcelor for US$415.1 million.
In 2006, Vale sold its interest in Siderar to Ternium for US$107.5 million.
In 2006, the company sold 5,362,928 shares in Usiminas for or R$378.6 million. In 2007, the company sold the majority of its stake in Usiminas. In 2009, the company sold its remaining stake in Usiminas.
Acquisitions of Brazilian iron ore companies
In May 2000, the company acquired Sociomex, owner of theGongo SûÇco
Gongo Soco was a gold mine in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil, to the east of Belo Horizonte in the mid-19th century.
It was worked by skilled miners from Cornwall and by less skilled Brazilian labourers and slaves.
Machinery powered by a water ...
Mine, with proven reserves of approximately 75 million tons.
In May 2000, the company also acquired a controlling interest in Samitri, one of the biggest pelletizing companies of Brazil.
In April 2001, the company acquired Ferteco, then the third largest Brazilian producer of iron ore, with a production capacity of 15 million tonnes per year.
In 2006, the company acquired Rio Verde Mineracao for $47 million.
Acquisition of
Caemi
Caemi MineraûÏûÈo e Metallurgia S.A. was a major Brazilian mining holding company that ceased to exist in December 2006 after it was merged into Vale. Caemi means ''Companhia Auxiliar de Empresas de MineraûÏûÈo''.
Operations
The company owned ir ...
and acquisition and partial disposition of MBR
On 1 April 2000, Vale offered to pay Mitsui US$277 million for 50% of the common shares and US$150 million for 40% of the preferred stock in Caemi
Caemi MineraûÏûÈo e Metallurgia S.A. was a major Brazilian mining holding company that ceased to exist in December 2006 after it was merged into Vale. Caemi means ''Companhia Auxiliar de Empresas de MineraûÏûÈo''.
Operations
The company owned ir ...
. Caemi owned MBR, Brazil's second largest iron ore producer, mining over 60 million tonnes per year.
The acquisition was approved by European regulators subject to conditions.
In September 2003, Vale purchased an additional stake in Caemi from Mitsui for US$426.4 million.
On 23 January 2006, the company announced a stock swap
In corporate finance a stock swap is the exchange of one equity-basedô asset for another, where, during the merger or acquisition, the swap provides an opportunity to pay with stock rather than with cash; see .
Overview
The acquiring company e ...
merger to acquire the interest Caemi that it did not already own.
In 2007, increased its ownership in MBR by purchasing additional interests from Mitsui for US$114.5 million.
Also in 2007, Vale announced that it will lease the shares of MBR that it did not already own from their 7 Japanese shareholders for a 30-year period. The agreement required the company to pay a total of US$60.5 million in 2007 and US$48.1 million annually for a 30-year period and gave it total control of MBR.
In 2015, Vale announced the sale of a 36.4% interest in MBR for R$4 billion.
Diversification into non-ferrous metals, coal and phosphate
In 2001, Vale increased its copper mining operations by purchasing the Sossego mine in Carajas, in northern Brazil, for $48.5 million. In 2005, Vale acquired Canico Resource, owner of a nickel mine in Brazil, after increasing its offer to $865 million. In October 2006, Vale acquired Canadian-based nickel producer Inco for $18.9 billion, including $17.7 billion in cash and the assumption of $1.2 billion in debt. To gain approval from Canadian authorities, Vale promised to continue investments in Canada and not lay off people for 3 years after closing. In 2007, Vale made a major entry into coal mining by acquiring AMCI Holdings Australia for AU$835 million. In 2010, Vale launched a public offer to acquire fertilizer and copper producer Paranapanema. In 2010, Vale acquired a controlling interest in Fosfertil via a series of transactions. In June 2011, Jason Chenier and Jordan Fram were killed at the 3,000 foot level of theFrood Mine
Frood-Stobie Mine is a nickel mine in Greater Sudbury, Ontario, named for Thomas Frood, an employee of the federal department of Crown lands who prospected and staked many of the early mining claims in the area. A major arterial road in the city i ...
near Sudbury, Ontario.
In 2011, the company sold its aluminum business to Norsk Hydro in a US$5.27 billion transaction.
In July 2012, Vale sold its ferro-manganese plants in Europe to Glencore
Glencore plc is a Swiss multinational commodity trading and mining company with headquarters in Baar, Switzerland. Glencore's oil and gas head office is in London and its registered office is in Saint Helier, Jersey. The current company was c ...
for $160 million.
In 2014, Vale announced the sale of coal assets in Mozambique to Mitsui in a $950 million transaction.
In 2014, Vale sold its interest in Fosbrasil S.A., a manufacturer of phosphate-based products.
In 2015, the company announced that it would sell a 25% interest in gold produced from its Salobo mine, located in Brazil, to Silver Wheaton
Wheaton Precious Metals Corp. is a Canadian multinational precious metals streaming company. It produces over 26 million ounces and sells over 29 million ounces of silver mined by other companies (including Barrick Gold and Goldcorp) as a by-prod ...
for US$900 million.
In 2015, the company entered into a letter of intent to sell bauxite assets to Norsk Hydro.
On 26 November 2015, Vale announced that it planned to reduce its budget
A budget is a calculation play, usually but not always financial, for a defined period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including time, costs and expenses, environmenta ...
for capital expenditures from US$8 billion in 2015 to US$6.2 billion in 2016, with further reductions to US$4ã5 billion by 2018.
Disasters and Incidents

Bento Rodrigues dam collapse
On 5 November 2015, the Mariana dam disaster caused 19 deaths and massive environmental contamination when a tailings dam collapsed at the Samarco mining site, co-owned by Vale and BHP. Heavy metal contamination of theDoce River
The Doce River (literally the "sweet river"; pt, Rio Doce ) is a river in southeast Brazil with a length of .
The river basin is economically important. In 2015 the collapse of a dam released highly contaminated water from mining into the river ...
caused water emergencies in many downstream cities which depend on the river for drinking water. Activities at the mine were suspended, and the companies agreed to pay compensation of R$4.4 billion (US$1.55 billion).
An investigation into the disaster commissioned by BHP, Vale and Samarco found the collapse was due to a variety of construction and design flaws. In June 2018, Samarco, Vale and BHP signed an agreement to drop a US$7 billion lawsuit and allow two years for the companies to address the greater US$55 billion suit seeking social, environmental and economic compensation.
Brumadinho dam disaster
On 25 January 2019, theBrumadinho dam disaster
The Brumadinho dam disaster occurred on 25 January 2019 when Dam I, a tailings dam at the Cû°rrego do FeijûÈo iron ore mine, east of Brumadinho, Minas Gerais, Brazil, suffered a catastrophic failure. The dam is owned by Vale, the same company ...
occurred at the Cû°rrego do FeijûÈo mine in the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais, releasing 3 billion gallons of mine waste,"Court Orders Vale To Stop Using Tailings Dams As Death Toll Climbs Above 120", by Vanessa Roma, February 4, 2019. Retrieved February 10, 2019./ref> in a wave of red iron ore which destroyed the mine's cafeteria, where many workers were present and lost their lives, and which flooded the town of
Brumadinho
Brumadinho () is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Minas Gerais. The city belongs to the Belo Horizonte metropolitan mesoregion and to the microregion of Belo Horizonte. Brumadinho is at an altitude of 880ã₤m. In 2020 the population wa ...
. Two hundred and seventy people were killed. In 2020, prosecutors found that Vale had falsified safety reports for at least ten of its dams. They later charged sixteen officials of Vale including its CEO, with manslaughter.
In 2021, Vale agreed to pay victims $7 billion. Though substantially deadlier, the environmental devastation was not as severe as with Bento Rodrigues.
Following the Cû°rrego do FeijûÈo disaster, a Brazilian court ordered Vale to stop disposing of tailings at eight dams.
Tax dispute
In 2013, Vale S.A. agreed to pay the equivalent of $9.5 billion to settle a tax dispute with the Brazilian authorities regarding its overseas profits from 2003 to 2012.Totten Mine
On September 28, 2021, thirty-nine miners were trapped underground for 24 hours at the Totten Mine in Ontario after the entrance shaft became obstructed.Criticism
In January 2012, Vale received the "people's choice" Public Eye Award as the corporation with the most "contempt for the environment and human rights" in the world. Vale received 25,000 votes, with theBelo Monte Dam
The Belo Monte Dam (''formerly known as'' KararaûÇ) is a hydroelectric dam complex on the northern part of the Xingu River in the state of ParûÀ, Brazil. After its completion, with the installation of its 18th turbine, in November 2019, the inst ...
cited as a reason.
During the interim between the two dam disasters of 2015 and 2019; Vale had denied owning an upstream tailings waste structure such as collapsed, causing the Brumadinho dam to burst.
Following the 2019 disaster, BBC News reported that "Correspondents say the alarm system the company had installed to warn residents of any risk did not go off."
In February 2021, an agreement was signed that required Vale to pay over $7 billion in compensation to the families of the victims.
Carbon footprint
Vale reported Total CO2e emissions (Direct + Indirect) for 31 December 2020 at 10,250Alt URL/ref> Kt (-1,850 /-15.3% y-o-y). This is a higher rate of decline than over the period since 4Q'18 (-10.9% CAGR).
References
Bibliography
*Michel Braudeau
Michel Braudeau (born 1946 in Niort) is a French writer.http://www.gallimard.fr/Contributeurs/Michel-Braudeau (page visited on 19 August 2013).
He was editor-in-chief of the ''Nouvelle revue franûÏaise'', from 1999 to 2010.
Works
* ''L'Amazo ...
, ô¨ Mourir dans l'or û Serra Pelada ô£, in ''Le rûˆve amazonien'', ûˋditions Gallimard
ûditions Gallimard (; formerly ûditions de la Nouvelle Revue FranûÏaise (1911ã1919) and Librairie Gallimard (1919ã1961) is one of the leading French book publishers. In 2003 it and its subsidiaries published 1,418 titles.
Founded by Gasto ...
, 2004 ().
External links
The company's home page in Portuguese
The company's home page in English
Rheebu Nuu - indigenous group attempting to halt CVRD's mining projects in the South Pacific
Eyewitness Survivor Account and video.
"Brumadinho: novas imagens revelam detalhes da tragûˋdia, ''Jornol O Globo'', February 1, 2019. Retrieved February 10, 2019. * {{Authority control Conglomerate companies of Brazil 1942 establishments in Brazil Aluminium companies of Brazil Coal companies of Brazil Conglomerate companies established in 1942 Railway companies established in 1942 Energy companies established in 1942 Iron ore mining companies Companies listed on B3 (stock exchange) Mining companies of Brazil Multinational companies headquartered in Brazil Railway companies of Brazil Privatized companies of Brazil Non-renewable resource companies established in 1942 Metal companies of Brazil