European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) is a 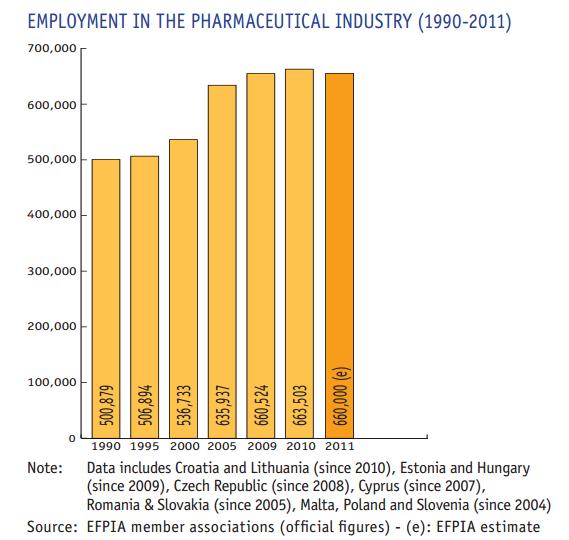 The key contribution of the research-based pharmaceutical industry to medical progress is to turn fundamental research into
innovative treatments that are widely available and accessible to patients, with the goal of helping people live longer and be healthier.
The key contribution of the research-based pharmaceutical industry to medical progress is to turn fundamental research into
innovative treatments that are widely available and accessible to patients, with the goal of helping people live longer and be healthier.
IMS Health
data, 66% of sales of new medicines launched during the period 2004-2008 were generated on the US market, compared with 26% on the European market. Source
EurostatEFPIA
Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI)
is a public-private partnership designed by the European Commission and EFPIA. It is a pan-European collaboration that brings together large biopharmaceutical companies, small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), patient organisations, academia, hospitals and public authorities. The initiative aims to accelerate the discovery and development of better medicines by removing bottlenecks in the drug development process. It focuses on creating better methods and tools that improve and enhance the drug development process, rather than on developing specific, new medicines. The European Commission and EFPIA have jointly established a new-non-profit European Community body. This organisation has a legal mandate to award research grants to European public-private collaborations conducting innovative research projects that focus on implementing the recommendation of the IMI Research Agenda. The IMI Research Agenda was established under the lead of industry following intensive consultations with a broad range of stakeholders from across Europe. It identifies the principal research bottlenecks in the biopharmaceutical R&D process and sets forth recommendations to overcome these bottlenecks by focusing on four areas: * Predicting safety: this addresses bottlenecks related to accurately evaluating the safety of a compound during the pre-clinical phase of the development process, but also impacts the later phases in clinical development. * Predicting efficacy: this addresses bottlenecks in the ability to predict how a drug will interact in humans and how it may produce a change in function. * Knowledge management: this addresses the more effective use of information and data for predicting safety and efficacy. * Education & training: this closes existing training gaps in the drug development process. IMI will make Europe more attractive for biopharmaceutical R&D investments and boost the competitiveness of European life science R&D. By directly addressing the challenges facing the biopharmaceutical sector in Europe, IMI has the potential to: * modernise the development of medicines * expand European expertise and know-how in new technologies to attract biomedical R&D investment to Europe * anchor R&D jobs in Europe and reverse the brain drain * enhance Europe's economy by improving the conditions for the biomedical industry and intensifying the collaboration of all stakeholders.
Ghostarchive
and th
Wayback Machine
European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations - (EFPIA)Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI)
Vaccines Europe (VE)
European Biopharmaceutical Enterprises (EBE)
EFPIA on Twitter
{{DEFAULTSORT:European Federation Of Pharmaceutical Industries And Associations European medical and health organizations Pharmaceutical industry trade groups Pan-European trade and professional organizations Life sciences industry Lobbying organizations in Europe International organisations based in Belgium Organizations established in 1978 1978 establishments in Europe Pharmaceutical industry
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
-based trade association and lobbying
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies. Lobbying, whic ...
organisation, founded in 1978 and representing the research-based pharmaceutical industry operating in Europe. Through its membership of 37 national associations and 38 leading pharmaceutical companies, EFPIA represents 1,900 european companies in the areas of researching, developing and manufacturing new medical treatments.
Figures in 2021 by the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
showed that based on the companies included in its scoreboard Health industries spent 19.9% of all the business research & development in Europe, only surpassed by the Automobiles & Parts industry (33.6%). But the percentage of european spending on R&D in this sector was considerably lower than in the United States.
 The key contribution of the research-based pharmaceutical industry to medical progress is to turn fundamental research into
innovative treatments that are widely available and accessible to patients, with the goal of helping people live longer and be healthier.
The key contribution of the research-based pharmaceutical industry to medical progress is to turn fundamental research into
innovative treatments that are widely available and accessible to patients, with the goal of helping people live longer and be healthier. High blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
and cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
can be controlled with anti-hypertensive medicines and cholesterol-lowering medicines, knee or hip replacements prevent patients from immobility, and some cancers can be controlled or even cured thanks to newer targeted medicines. Yet there remain huge challenges in many disease areas such as Alzheimer
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As t ...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This ...
, many cancers and orphan diseases.
EFPIA also includes two specialised groups focusing on vaccines and biotechnology respectively:
* Vaccines Europe produce approximately 80% of vaccines used worldwide.
* European Biopharmaceutical Enterprises harness biotechnology to develop approximately one-fifth of new medicines.
EFPIA priorities
The industry's efforts are focused around four key areas - the AIMS - Roadmap of priorities Access, Innovation, Mobilization, Security programme. * Access refers to the need to continue to work towards speeding up regulatory approval and reimbursement processes for new medicines; removing government controls on medicines that are not reimbursed; and ensuring that Health Technology Assessment (HTA) does not become a fourth hurdle to market access. * Innovation focuses on efforts towards creating a strong science base in Europe and making Europe an attractive location for the best researchers; ensuring a fair reward for innovation, including incremental innovation and ensuring a high level of protection for Intellectual Property Rights. * Mobilization is about joining forces with key stakeholders to address the challenges of an ageing population and deliver modern and sustainable healthcare; to fight damaging cost-containment policies; to empower patients and citizens to take an active role in managing their health through better access to information from multiple sources; to highlight industry's contribution to access to medicines and to promote new incentives for research into diseases affecting the developing world. * Security refers to the need to strengthen the integrity and transparency of the pharmaceutical supply chain by addressing the safety concerns of parallel trade; raising public awareness on the risk of counterfeits; and increasing the traceability of pharmaceutical products.Research and Development (R&D)
In 2010 the pharmaceutical industry invested about €27,800 million in R&D in Europe. After a decade of strong US market dominance, which led to a significant shift of economic and pharmaceutical research activity towards the US during the period 1995–2005, Europe is now also facing increasing competition from emerging economies. Today there is rapid growth in the market and research environment in emerging economies such as Brazil, China and India, resulting in further migration of economic and research activities outside of Europe to these fast-growing markets. The geographical balance of the pharmaceutical market – and ultimately the R&D base – is likely to shift gradually towards emerging economies. All new medicines introduced into the market are the result of lengthy, costly and risky research and development (R&D) conducted by pharmaceutical companies: * By the time a medicinal product reaches the market, an average of 12–13 years will have elapsed since the first synthesis of the new active substance; * The cost of researching and developing a new chemical or biological entity was estimated at €1,059 million ($1,318 million in year 2005 dollars) in 2005 (Di Masi J., Tufts University, Centre for the Study of Drug Development, 2007); * On average, only one or two of every 10,000 substances synthesised in laboratories, will successfully pass all the stages to become marketable medicines. There is rapid growth in the research environment in emerging economies such as China and India. The current tendency to close R&D sites in Europe and to open new sites in Asia will show dramatic effects to maintain the pharmaceutical discovery expertise in the EU. The United States still dominates the biopharmaceutical field, accounting for the three quarters of the world's biotechnology revenues and R&D spending. In 2007 North America accounted for 45.9% of world pharmaceutical sales against 31.1% for Europe. According tIMS Health
data, 66% of sales of new medicines launched during the period 2004-2008 were generated on the US market, compared with 26% on the European market. Source
Eurostat
Innovative Medicines Initiative
ThInnovative Medicines Initiative (IMI)
is a public-private partnership designed by the European Commission and EFPIA. It is a pan-European collaboration that brings together large biopharmaceutical companies, small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), patient organisations, academia, hospitals and public authorities. The initiative aims to accelerate the discovery and development of better medicines by removing bottlenecks in the drug development process. It focuses on creating better methods and tools that improve and enhance the drug development process, rather than on developing specific, new medicines. The European Commission and EFPIA have jointly established a new-non-profit European Community body. This organisation has a legal mandate to award research grants to European public-private collaborations conducting innovative research projects that focus on implementing the recommendation of the IMI Research Agenda. The IMI Research Agenda was established under the lead of industry following intensive consultations with a broad range of stakeholders from across Europe. It identifies the principal research bottlenecks in the biopharmaceutical R&D process and sets forth recommendations to overcome these bottlenecks by focusing on four areas: * Predicting safety: this addresses bottlenecks related to accurately evaluating the safety of a compound during the pre-clinical phase of the development process, but also impacts the later phases in clinical development. * Predicting efficacy: this addresses bottlenecks in the ability to predict how a drug will interact in humans and how it may produce a change in function. * Knowledge management: this addresses the more effective use of information and data for predicting safety and efficacy. * Education & training: this closes existing training gaps in the drug development process. IMI will make Europe more attractive for biopharmaceutical R&D investments and boost the competitiveness of European life science R&D. By directly addressing the challenges facing the biopharmaceutical sector in Europe, IMI has the potential to: * modernise the development of medicines * expand European expertise and know-how in new technologies to attract biomedical R&D investment to Europe * anchor R&D jobs in Europe and reverse the brain drain * enhance Europe's economy by improving the conditions for the biomedical industry and intensifying the collaboration of all stakeholders.
Controversy
From 1991 to 1998 Emer Cooke worked for the EFPIA. She became Executive Director of theEuropean Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or Eur ...
(EMA), an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products, in November 2020.
In a session of the Austrian Parliament member of parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
Gerald Hauser on 1 April 2021 publicly criticised a potential conflict of interest
A conflict of interest (COI) is a situation in which a person or organization is involved in multiple interests, financial or otherwise, and serving one interest could involve working against another. Typically, this relates to situations i ...
, by her allowing the controversial Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine to be approved, while having worked for the very same industry in the past as a lobbyist of the EFPIA.Archived aGhostarchive
and th
Wayback Machine
See also
* European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP) *EuropaBio
EuropaBio ("The European Association for Bioindustries") is Europe's largest and most influential biotech industry group, whose members include leading large-size healthcare and industrial biotechnology companies. EuropaBio is located in Brussels, ...
* European Federation of Biotechnology
The European Federation of Biotechnology (EFB) was established by European scientists in 1978. It is a non-profit federation of national biotechnology associations, learned societies, universities, scientific institutes, biotechnology companies ...
(EFB)
* International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Associations (IFPMA)
* Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA)
* Pharmaceutical company
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate sympt ...
* Portuguese Pharmaceutical Industry Association The Portuguese Pharmaceutical Industry Association (Associação Portuguesa Da Indústria Farmacêutica) is a trade association based in Lisbon. It was established in 1975, succeeding the National Guild of the Manufacturers of Medicinal Products wh ...
References
External links
European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations - (EFPIA)
Vaccines Europe (VE)
European Biopharmaceutical Enterprises (EBE)
EFPIA on Twitter
{{DEFAULTSORT:European Federation Of Pharmaceutical Industries And Associations European medical and health organizations Pharmaceutical industry trade groups Pan-European trade and professional organizations Life sciences industry Lobbying organizations in Europe International organisations based in Belgium Organizations established in 1978 1978 establishments in Europe Pharmaceutical industry