Environmental issues in Wyoming on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The U.S. state of
The U.S. state of
 Production in Wyoming's oil and gas industry grew from $7.3 billion to $17.6 billion between 2000 and 2006. The
Production in Wyoming's oil and gas industry grew from $7.3 billion to $17.6 billion between 2000 and 2006. The
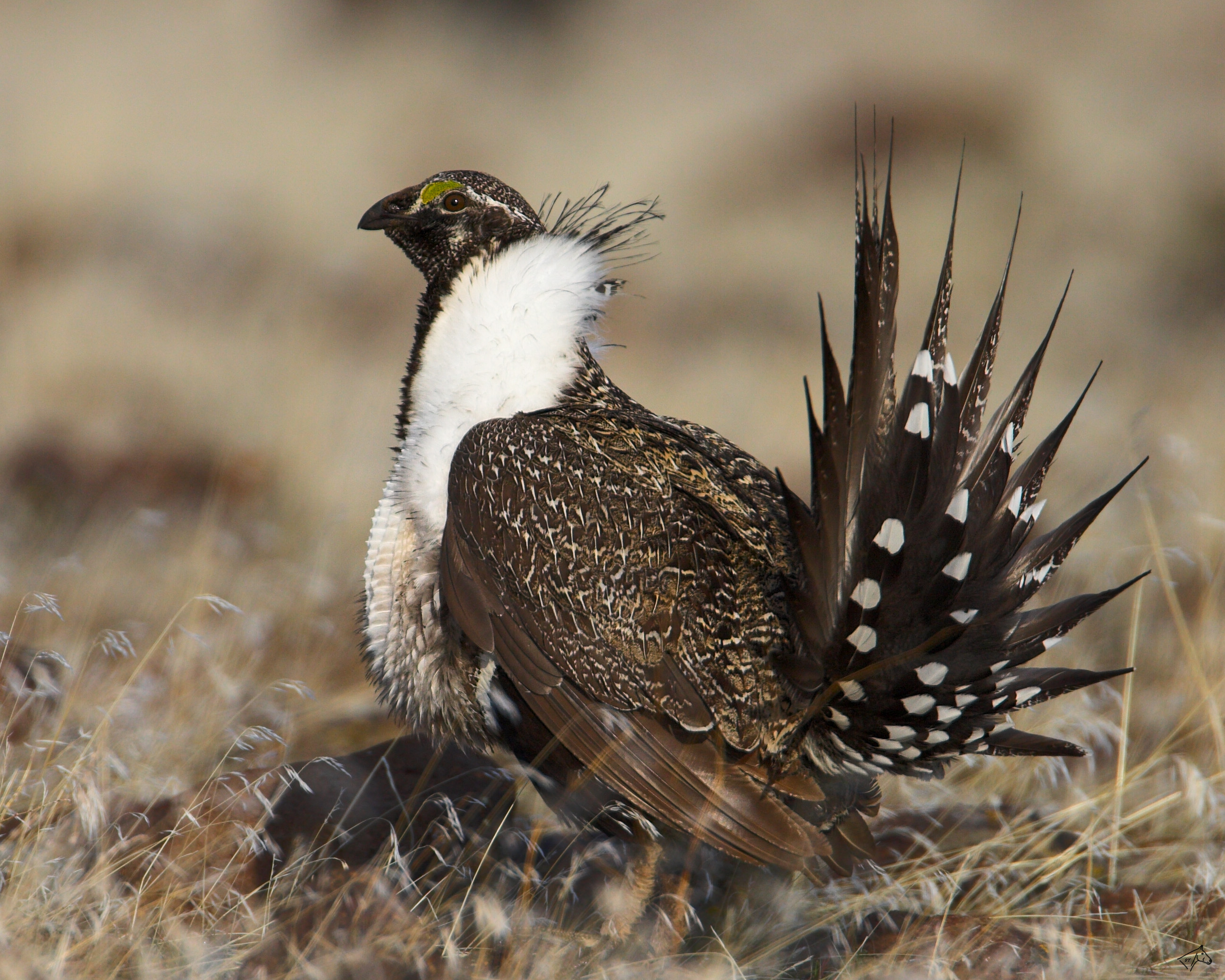


 Dwindling sage grouse populations have sparked heated debate over Wyoming's natural resource industry. The PAPA covers a large portion of the sage grouse's habitat. The area consists of about 200,000 acres of land, much of it covered with sagebrush, the grouse's landscape it requires to survive. The three largest operators in the PAPA are Ultra Resources, Shell Rocky Mountain Production, LLC and Questar Exploration and Production Company. Together these companies funded a five-year sage grouse study examining the impact of natural gas development on the birds’ winter habitat, at a cost of $1.4 million. According to the Greater sage-grouse winter habitat selection 2009 report, the study results suggested that the sage grouse were avoiding industry activity areas with truck traffic, but not avoiding well sites with pipelines, or liquid gathering systems installed. A smaller operator in the PAPA, Devon Energy, reported that oil and gas companies pledged $60 million in 2007 to monitor the sage grouse and its habitat in the vicinities of their well sites.
Wyoming spent at least half a million dollars in 2010 solely to examine and redefine the map of the core areas of sage grouse habitat. In an August 2011 press release from the USDA, Agriculture secretary
Dwindling sage grouse populations have sparked heated debate over Wyoming's natural resource industry. The PAPA covers a large portion of the sage grouse's habitat. The area consists of about 200,000 acres of land, much of it covered with sagebrush, the grouse's landscape it requires to survive. The three largest operators in the PAPA are Ultra Resources, Shell Rocky Mountain Production, LLC and Questar Exploration and Production Company. Together these companies funded a five-year sage grouse study examining the impact of natural gas development on the birds’ winter habitat, at a cost of $1.4 million. According to the Greater sage-grouse winter habitat selection 2009 report, the study results suggested that the sage grouse were avoiding industry activity areas with truck traffic, but not avoiding well sites with pipelines, or liquid gathering systems installed. A smaller operator in the PAPA, Devon Energy, reported that oil and gas companies pledged $60 million in 2007 to monitor the sage grouse and its habitat in the vicinities of their well sites.
Wyoming spent at least half a million dollars in 2010 solely to examine and redefine the map of the core areas of sage grouse habitat. In an August 2011 press release from the USDA, Agriculture secretary
 The
The
 Several agencies such as the Wyoming Game and Fish, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services, and the Cheyenne Mountain Zoo are currently working on saving the species. The primary focus is breeding the toad in captivity and releasing tadpoles in the wild as an attempt to restore the previous populations. No reproduction has been recorded in the wild so far, and it seems that the species are procreating successfully only in captivity. The reason why the Toads are not doing as well in nature remains unknown. Even though the species is protected under the Endangered Species Act, professionals working with the toad also argue that the situation is not well known enough to the public, and believe that the Wyoming Toads deserve more attention.
Several agencies such as the Wyoming Game and Fish, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services, and the Cheyenne Mountain Zoo are currently working on saving the species. The primary focus is breeding the toad in captivity and releasing tadpoles in the wild as an attempt to restore the previous populations. No reproduction has been recorded in the wild so far, and it seems that the species are procreating successfully only in captivity. The reason why the Toads are not doing as well in nature remains unknown. Even though the species is protected under the Endangered Species Act, professionals working with the toad also argue that the situation is not well known enough to the public, and believe that the Wyoming Toads deserve more attention.
 The U.S. state of
The U.S. state of Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to t ...
faces a broad array of environmental issue
Environmental issues are effects of human activity on the biophysical environment, most often of which are harmful effects that cause environmental degradation. Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment o ...
s stemming from natural resource extraction
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
, species extirpation, non-native species introduction
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there ...
, and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, th ...
. Wildlife species that have been affected by these issues include:
* Gray wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
(''Canis lupus''), locally extirpated
* Grizzly bear
The grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), also known as the North American brown bear or simply grizzly, is a population or subspecies of the brown bear inhabiting North America.
In addition to the mainland grizzly (''Ursus arctos horri ...
(''Ursus arctos horribilis'')
* Lodgepole pine
''Pinus contorta'', with the common names lodgepole pine and shore pine, and also known as twisted pine, and contorta pine, is a common tree in western North America. It is common near the ocean shore and in dry montane forests to the subalpin ...
(''Pinus contorta''), affected by mountain pine beetle
The mountain pine beetle (''Dendroctonus ponderosae'') is a species of bark beetle native to the forests of western North America from Mexico to central British Columbia. It has a hard black exoskeleton, and measures approximately , about the siz ...
s, which threaten to disrupt forests in Wyoming
* Greater sage grouse
The greater sage-grouse (''Centrocercus urophasianus''), also known as the sagehen, is the largest grouse (a type of bird) in North America. Its range is sagebrush country in the western United States and southern Alberta and Saskatchewan, Canad ...
(''Centrocercus urophasianus''), affected by natural gas extraction.
* Wyoming toad
The Wyoming toad or Baxter's toad (''Anaxyrus baxteri'') is an extremely rare amphibian that exists only in captivity and within Mortenson Lake National Wildlife Refuge in Wyoming in the United States. The Wyoming toad was listed as an endanger ...
(''Anaxyrus baxteri''), extinct in the wild
Within the state organizations and governments are working to combat these environmental threats and restore balance to the ecology. Protection of some of these species has proven controversial.
Natural resource extraction
Wyoming is a resource rich state with a history of boom and bust cycles. The1970s energy crisis
The 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period wer ...
initiated a coal-mining boom in Wyoming that lasted until the early 80's. The state's latest energy boom (1995–2010) is due to increased development in oil and natural gas production as well as further growth in the coal-mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
industry. Despite the role of natural resource extraction
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
in the economy, growth in Wyoming is characterized by severe environmental consequences.
Industry development
 Production in Wyoming's oil and gas industry grew from $7.3 billion to $17.6 billion between 2000 and 2006. The
Production in Wyoming's oil and gas industry grew from $7.3 billion to $17.6 billion between 2000 and 2006. The U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
recorded a 73.1% increase in the population of Sublette County, Wyoming, from 5,920 to 10,247, between 2000 and 2010.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, Wyoming produces 41% of the nation's coal, or as much as the next seven coal producing states combined.U.S. Energy Information Administration. (2011, February 17). Analysis. In Wyoming. Retrieved November 29, 2011, from http://www.eia.gov/state/state-energy-profiles-analysis.cfm?sid=WY The Wyoming Mining Association (WMA) reports that the coal mining industry alone contributed over $1.15 billion to the state and local governments in 2009.
Two of the nation's largest natural gas fields, Pinedale Anticline and Jonah Field, are located in Sublette County, Wyoming
Sublette County is a county in the U.S. state of Wyoming. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 8,728. The county seat is Pinedale. It is a sparsely populated rural county in western Wyoming, along the Green River.
History
...
. Wyoming accounts for roughly one tenth of U.S. natural gas production. The natural gas industry in the state continues to expand due to low levels of consumption and development of pipeline systems that facilitate transport to consumers in California and the Midwest.
Oil production in Wyoming only accounts for about 3 percent of U.S. production. However, Wyoming's oil shale
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitut ...
deposits contain one fourth of global shale oil reserves, or about 300 billion barrels. Oil shale is not currently an economically recoverable source of energy, as current technology is unable to extract the shale efficiently, but these reserves could pave the way for further development in the state.
Energy development in Wyoming has generated well-deserved attention, as the state has been able to maintain a relatively stable economy throughout the current recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
. While economic growth has proven beneficial in many aspects, it has also adversely impacted the environment of the least populous U.S. state, affecting the quality of air, water, soil and wildlife. Recently, concentration on degradation of air quality and damage to wildlife habitat has been emphasized by environmental activists.
Air pollution
Development in Wyoming's oil and gas industry is transforming what has historically been some of the cleanest air in the nation to some of the mostpolluted
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
. Production of natural gas contributes to heightened ozone levels. Ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
is a molecule consisting of three oxygen atoms that is harmful to animals when present in the lower atmosphere.Environmental Protection Agency. (2010). What is ozone?. In Air Quality Awareness. Retrieved November 29, 2011, from Winter months correlate with heightened ozone levels in the region. Temperature inversions occur when cool air on the ground covered by a layer of warmer air trap volatile organic compounds and nitrous oxides in the lower atmosphere, whose interactions create ozone. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), winter 2010 saw ozone pollution levels in the Upper Green River Green River may refer to:
Rivers
Canada
* Green River (British Columbia), a tributary of the Lillooet River
*Green River, a tributary of the Saint John River, also known by its French name of Rivière Verte
*Green River (Ontario), a tributary of ...
Basin of Sublette County, Wyoming surpass the worst days of any major U.S. city.
Water pollution
Cows often graze on public land. Their manure pollutes rivers with '' E. coli'' and '' Salmonella''. In 2015, the Wyoming Legislature declared trespassing to collect data a crime with Senate File 12 as well as making the action a civil violation with Senate File 80. This penalizes scientists and journalists who are studying pollution.Health effects
Excessive ozone levels are harmful to human health, especially in children and elderly people. Effects include lung damage, worsenedasthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
, reduced lung capacity
Lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air in the lungs at different phases of the respiratory cycle.
The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air.
Tidal breathing is normal, resting breathin ...
, and increased premature deaths. More commonly reported effects include watery eyes, bloody noses, and breathlessness. In winter 2010, Wyoming issued 10 warnings for citizens to remain indoors in order to avoid spikes in ozone pollution.Bleizeffer, D. (2011, September 13). Wyoming governor, industry won't promise an ozone-free Pinedale. In Ozone Dilemma. Retrieved November 29, 2011, from
CURED lawsuit
Sublette County-based organization Citizens United for Responsible Energy Development (CURED), represented by environmental firmEarthjustice
Earthjustice (originally Sierra Club Legal Defense Fund) is a nonprofit public interest organization based in the United States dedicated to litigating environmental issues. Headquartered in San Francisco, it has 14 regional offices across the Un ...
, served the EPA with intent to file lawsuit in early October 2011 unless the Upper Green River Basin be formally designated as a nonattainment area, or one that does not comply with current national standards set by the Clean Air Act. Designation as a nonattainment area would initiate efforts to restore ozone levels to those in agreement with the Clean Air Act, ensuring that citizens' health is not at risk. Former Wyoming Governor Dave Freudenthal advised that the Upper Green River Basin be designated as a region that exceeds national standards for acceptable ozone levels in 2009. Failure of the EPA to formally recognize the Upper Green River Basin as a nonattainment area is what instigates CURED's threat to sue.
Wildlife
Gray wolf
The gray wolf was once the most widespread mammal in the northern hemisphere with home ranges exceeding .Eradication
In the 1800s, grazing opportunities for domesticated livestock increased. In Montana from 1867 to 1890 cattle numbers rose from 67000 to 1.1 million and sheep from 300000 to 2.2 million. With the reduction of wild hoofed prey, wolves turned to cattle and sheep for prey. Predation of livestock was a common rationale behind wolf elimination. Additionally, wolves had a negative view by the majority of the population during that time. Even Theodore Roosevelt, pioneer of conservation described the wolf as a “beast of waste and desolation.” Wolves were killed by hunting, trapping, snaring and poisoning. Bounties on wolf pelts were offered by state governments and livestock associations. In 1915 the U.S. Federal government established the Division of Rodent and Predator Control Which further augmented wolf eradication. This pursuit of wolves combined with habitat loss to drive wolves out of most areas across North America. Wyoming, Idaho, Montana and Yellowstone National Park had reached total wolf eradication by the 1930s.
Protection and reintroduction
The gray wolf was provided protection under the Endangered Species Act (ESA) in 1974. ESA protection made it illegal to kill wolves or destroy their habitats. Listing wolves under the ESA also initiated the production of a recovery plan. The recovery originally planned for wolf recovery through natural wolf dispersal from Canada but was later modified. In 1994 U.S. Fish and Wildlife submitted a report to congress recommending wolves be reestablished in Idaho and Yellowstone National Park as nonessential experimental populations. In March 1995 3 groups of 6, 5 and 3 wolves were released into Yellowstone National Park. This release marked the beginning of a successful reintroduction effort coordinated with multiple wildlife agencies from multiple U.S. States and Canadian Provinces. A total of 31 wolves were released in Yellowstone National Park.Proposed removal from ESA
The Gray wolf in Wyoming is on the verge of being removed from the Endangered Species Act. Removal has been approved by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Secretary of the Interior Ken Salazar and Wyoming Game and Fish. The wolf management plan that has been agreed upon by all parties requires a minimum of 100 wolves including ten breeding pairs in Wyoming. Currently there are 1650 wolves and 110 breeding pairs in Wyoming Idaho and Montana. Wolf numbers have exceeded recovery goals for the past 11 years. U.S. Fish and Wildlife will continue to collaborate with Wyoming Game and Fish following delisting from the ESA. Delisting will also allow Wyoming to implement a wolf trophy hunting season for wolves outside Yellowstone National Park. Tactics used during the removal process have been highly political. The Casper Star Tribune reported that Wyoming SenatorJohn Barrasso
John Anthony Barrasso III ( ; born July 21, 1952) is an American physician and politician serving as the senior United States senator from Wyoming, a seat he has held since 2007. A member of the Republican Party, he served in the Wyoming State ...
placed a hold on a senate vote on the nomination of Daniel Ashe as the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Director. Barrasso lifted the hold following a commitment from Secretary of Interior Ken Salazar to “aggressively pursue a solution” to the wolf delisting dispute.
Arguments and organizations for delisting
Groups for delisting include, Wyoming Game and Fish, Wyoming Governor Matt Mead, hunting public, hunting outfitters, Congressional Sportsmen's Foundation (CSF), National Rifle Association (NRA), Safari Club International (SCI), Rocky Mountain Elk Foundation (RMEF), American Sheep Industry Association and National Cattlemen's Beef Association. The primary argument for delisting is that wolf population numbers are well above recovery levels. This recovery indicates that the wolves are ready to be managed at a state level. Several groups believe that high wolf numbers are detrimental to elk and moose populations sharing the same habitat. Other conservation groups want wolf management at the state level so that stakeholders have more say in management decisions.Arguments and organizations against delisting
Earlier attempts in 2008 and 2009 to delist the Gray Wolf were prevented with lawsuits from the Sierra Club. There are various groups against removing the gray wolf. Groups opposing delisting include Defenders of Wildlife, Western Wildlife Conservancy, Sierra Club and others. Arguments against delisting wolves include fear of overexploitation through trophy hunting, and a population crash. Idaho, Montana and Wyoming all plan to have a trophy game season for wolves following delisting. In addition to a trophy season, wolves found outside the trophy area of Wyoming may be shot as a predator, no license required. Additionally, several groups worry that removal from ESA could undermine authority of the endangered species act.Grizzly bear
Grizzly bear
The grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), also known as the North American brown bear or simply grizzly, is a population or subspecies of the brown bear inhabiting North America.
In addition to the mainland grizzly (''Ursus arctos horri ...
populations are expanding across the state under the protection of the federal Endangered Species Act (ESA). Management of the grizzly bear population includes relocation. Large carnivore biologists use this management tool to minimize conflicts between humans and grizzly bears. In 2021, state officials requested the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to remove grizzly bears from ESA protections in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem
The Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem (GYE) is one of the last remaining large, nearly intact ecosystems in the northern temperate zone of the Earth. It is located within the northern Rocky Mountains, in areas of northwestern Wyoming, southwestern M ...
which includes northwestern Wyoming, southwestern Montana, and eastern Idaho. State management would minimize human disruption and maximize hunting opportunities while meeting the goals set by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Pine beetle
Wyoming faces a range of ecological risks but perhaps none greater than the current infestation of pine beetle populations across the coniferous forests of the state and surrounding regions. The problem is extensive, far-reaching, and almost all encompassing. Steps are being taken to prevent further spread of the infestation but in expert opinions those steps are coming too little too late. In addition, there is an entire future forest that will be threatened by these beetles andclimate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
Infestation
TheMountain pine beetle
The mountain pine beetle (''Dendroctonus ponderosae'') is a species of bark beetle native to the forests of western North America from Mexico to central British Columbia. It has a hard black exoskeleton, and measures approximately , about the siz ...
typically attacks in the late summer and lay larva in the trees that survive under the bark until the next summer. During the summer infestation, the beetle produces a blue fungus that at epidemic levels usually destroys even healthy trees. Trees that have been affected are marked by brown pine needles and a bluish hue to the inside of their bark. In a typical climate large amounts of the beetle populations are killed during the days in the middle of winter when the temperature falls to minus 30 for weeks at a time. Today these temperatures are not being seen in forests, allowing pine beetles to survive the winter and come back in greater populations the next summer. In some instances, however, the temperatures are staying so warm the beetles are allowed time for two eating cycles causing even further devastation to tree populations.Department of Agriculture, Forest Service. Bark Beetle Fact Sheet .://www. Fs. Usda. Gov/internet/fse_documents/stelprdb5337223. Pdf Distribution
Currently in Wyoming it is estimated that nearly have been infected and across the United States that number is above 40 million acres. The beetles usually attack the Lodgepole Pine populations but because the epidemic is at such a monumental scale the beetles are attacking any coniferous tree including:Ponderosa Pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the ...
, Limber Pine
''Pinus flexilis'', the limber pine, is a species of pine tree-the family Pinaceae that occurs in the mountains of the Western United States, Mexico, and Canada. It is also called Rocky Mountain white pine.
A limber pine in Eagle Cap Wildernes ...
, Douglas Fir, Subalpine Fir
''Abies lasiocarpa'', the subalpine fir or Rocky Mountain fir, is a western North American fir tree.
Description
''Abies lasiocarpa'' is a medium-sized evergreen conifer with a very narrow conic crown, growing to tall, exceptionally , with a t ...
, Silver Fir
Silver fir is a common name for several trees and may refer to:
*''Abies alba
''Abies alba'', the European silver fir or silver fir, is a fir native to the mountains of Europe, from the Pyrenees north to Normandy, east to the Alps and the Car ...
, Spruce, and Cedar
Cedar may refer to:
Trees and plants
*''Cedrus'', common English name cedar, an Old-World genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae
*Cedar (plant), a list of trees and plants known as cedar
Places United States
* Cedar, Arizona
* ...
trees. Through the next ten years it is estimated 100,000 trees will fall daily in forests across the country due to pine beetle infestations.
Causes and prevention
In the early 1800s settlers mismanaged forests in the hopes of preventing fires but only allowed stand densities to reach critical levels that allowed beetles to easily spread from one tree to the next. In addition rising global temperature have allowed these beetle populations to grow and thrive at unheard of rates. Lastly a multi-year drought that extended from the mid-1990s to the early 2000s made trees weak and susceptible to attacks. The Southeastern region of Wyoming is the most infected region. Experts already predict by the year 2012 90% of the trees in these regions will be dead or infected. Steps are, however, being taken to prevent further infection and distribution. Throughout the region the local forest service is safely cutting these trees in an attempt to keep beetle populations at bay and to prevent the risk of falling trees in heavily traveled areas of the forest. With the future of the forests in mind forest services are also working on forest recovery. To do this they are replanting/-seeding areas of the forest to create a diverse and manageable environment for the future ecology of the area. This recovery process also entails a resiliency aspect that will allow future trees to be protected from pine beetle infestations by reducing stand densities.
Ecological effect
This combination of mismanaged forests and deadfall caused by pine beetle adds up to an inevitable conclusion that fires will destroy these forests. These fire risks and falling trees caused by the beetle infestation have the ability to affect over 3,700 miles of roads, 1,300 miles of trails, and 69 miles of transmission and distribution power lines. Consequently, it is important that the forest service manages these falling trees by cutting certain sections of forest down to aid in the safety of these areas. This catastrophe will severely impact the wildlife of the region. Many animal species rely on these forests for both predation and climate protection. American Elk populations will likely decrease due to the loss of protection as will American Marten populations due to the Marten's reliance on thick, heavily forested areas to hunt. Pine squirrel populations will likely experience the most dramatic decrease because the squirrels rely on pine seeds to survive the harsh winters. Other animal populations that will be effected include the Northern goshawk and the snowshoe hare as their habitats are destroyed and their nutrition resources disappear.Future forests
If global climate simulators prove correct, then in fifty years, when these forests are returning, the heavily temperature effected pine beetle populations could potentially be even stronger and in regions today protected by the colder climates at higher elevations. The predicted 2.5 degree Celsius temperature increase will allow the beetles to further migrate into regions of massive Canadian forests and into the eastern United States that had once been protected by the vast plains of Middle America. Current studies show the pine beetle populations beginning to slow. The 2010 mortality rate of trees was a quarter of what it had been the two previous years. This may sound like good news but in reality it means the beetles are simply running out of trees to infect.Sage grouse
 Dwindling sage grouse populations have sparked heated debate over Wyoming's natural resource industry. The PAPA covers a large portion of the sage grouse's habitat. The area consists of about 200,000 acres of land, much of it covered with sagebrush, the grouse's landscape it requires to survive. The three largest operators in the PAPA are Ultra Resources, Shell Rocky Mountain Production, LLC and Questar Exploration and Production Company. Together these companies funded a five-year sage grouse study examining the impact of natural gas development on the birds’ winter habitat, at a cost of $1.4 million. According to the Greater sage-grouse winter habitat selection 2009 report, the study results suggested that the sage grouse were avoiding industry activity areas with truck traffic, but not avoiding well sites with pipelines, or liquid gathering systems installed. A smaller operator in the PAPA, Devon Energy, reported that oil and gas companies pledged $60 million in 2007 to monitor the sage grouse and its habitat in the vicinities of their well sites.
Wyoming spent at least half a million dollars in 2010 solely to examine and redefine the map of the core areas of sage grouse habitat. In an August 2011 press release from the USDA, Agriculture secretary
Dwindling sage grouse populations have sparked heated debate over Wyoming's natural resource industry. The PAPA covers a large portion of the sage grouse's habitat. The area consists of about 200,000 acres of land, much of it covered with sagebrush, the grouse's landscape it requires to survive. The three largest operators in the PAPA are Ultra Resources, Shell Rocky Mountain Production, LLC and Questar Exploration and Production Company. Together these companies funded a five-year sage grouse study examining the impact of natural gas development on the birds’ winter habitat, at a cost of $1.4 million. According to the Greater sage-grouse winter habitat selection 2009 report, the study results suggested that the sage grouse were avoiding industry activity areas with truck traffic, but not avoiding well sites with pipelines, or liquid gathering systems installed. A smaller operator in the PAPA, Devon Energy, reported that oil and gas companies pledged $60 million in 2007 to monitor the sage grouse and its habitat in the vicinities of their well sites.
Wyoming spent at least half a million dollars in 2010 solely to examine and redefine the map of the core areas of sage grouse habitat. In an August 2011 press release from the USDA, Agriculture secretary Tom Vilsack
Thomas James Vilsack (; born December 13, 1950) is an American politician serving as the 32nd United States Secretary of Agriculture in the Biden administration. He previously served in the role from 2009 to 2017 during the Obama administration. ...
disclosed that an additional 21.8 million will be spent to conserve sage grouse habitat in the form of government subsidies to farmers.
Despite the sage grouse population having declined 90% in the past hundred years, and despite the loss of about half of their habitat in that same time, reports claim that efforts by state governments and the oil and gas industry have managed to keep the numbers stable, in localized areas, in the past decade. Those actions prevented the bird from being listed as endangered or threatened.
Wyoming toad
 The
The Wyoming toad
The Wyoming toad or Baxter's toad (''Anaxyrus baxteri'') is an extremely rare amphibian that exists only in captivity and within Mortenson Lake National Wildlife Refuge in Wyoming in the United States. The Wyoming toad was listed as an endanger ...
''Anaxyrus baxteri'' (formerly known as ''Bufo baxteri''), is an extremely rare amphibian restricted to the Albany County. The toad was initially considered a subspecies of the Canadian toad but found later to be a separate species. The adult is, on average, 2.2 inches in length and the color varies from brown to gray (often with a greenish tint) accompanied with darker blotches. A very distinctive feature of the species is the 'bony hump' between the eyes as a result of fused cranial crests. The toad was a common sight in the Laramie Basin up until the population crash that occurred in the mid-1970s. Originally, the toad occupied a geographical range of about 2330 km², and lived in floodplains or on shores of lakes & ponds, but eventually was only found at the Mortenson Lake National Wildlife Refuge. The species has been critically endangered since 1984 and became totally extinct in the wild in 1991 (also listed as such under the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species).
Causes of decline
The primary cause of the decline of the Wyoming toad is the chytrid fungus ''Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
''Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' ( ), also known as ''Bd'' or the amphibian chytrid fungus, is a fungus that causes the disease chytridiomycosis in amphibians.
Since its discovery in 1998 by Lee Berger, the disease devastated amphibian popula ...
'' (Db), which is affecting amphibian populations worldwide. The fungus has been shown, in numerous studies, to cause disease in many different amphibian species and has been found in captive Wyoming Toad populations as well. Scientists have discovered through retrospective analysis that the fungus was present on the natural habitat of the Wyoming Toad as early as 1989 at least, and speculate that the fungus might have been responsible for the initial population crash, which still remains unknown. Other important environmental issues contributing to the decline include agro-chemicals that used on farms and ranches. Chemicals such as pesticides, herbicides, agricultural hormones and fertilizers, have been observed to directly alter the physiological development of the toads in some cases, and indirectly stress the amphibians, weakening their resistance to the Chrytrid fungus. Because chemicals are usually tested individually, the ‘legal’ dosages of many agro-chemicals, which were considered to be harmless before, are now observed to be rather dangerous in combination with one another or with other factors already present such as the Chytrid fungus. Habitat destruction and global climate change are also affecting the Wyoming Toad or other amphibian populations but to a somewhat lesser extent.
Ecological consequences
The first major concern with regards to the population decline is the possible extinction of the species. The species is not only totally extinct in the wild for 2 decades, but even its populations in captivity are also declining. Due to their low number, there is a rather elevated rate of inbreeding, making the gene pool of the population small, and decreasing the likelihood to evolve resistance against pathogens including the Chytrid fungus. Aside from the possible extinction of the toad, scientists are also worried that the population decline might lead to unforeseen chain effects in the ecosystem. Since the Wyoming Toad is an amphibian, which occupies a niche in both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, its absence might lead to trophic cascades in the ecosystem, such as its preys increasing in number and affecting other species. Amphibians such as the Wyoming Toad are furthermore good indicators ofecosystem health
Ecosystem health is a metaphor used to describe the condition of an ecosystem.Rapport, David (1998). "Defining ecosystem health." Pages 18-33 in Rapport, D.J. (ed.) (1998). ''Ecosystem Health.'' Blackwell Scientific. Ecosystem condition can vary ...
, and their disappearance would not only signify the degradation of the environment but would also render assessment of the natural habitats harder.
Conservation
 Several agencies such as the Wyoming Game and Fish, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services, and the Cheyenne Mountain Zoo are currently working on saving the species. The primary focus is breeding the toad in captivity and releasing tadpoles in the wild as an attempt to restore the previous populations. No reproduction has been recorded in the wild so far, and it seems that the species are procreating successfully only in captivity. The reason why the Toads are not doing as well in nature remains unknown. Even though the species is protected under the Endangered Species Act, professionals working with the toad also argue that the situation is not well known enough to the public, and believe that the Wyoming Toads deserve more attention.
Several agencies such as the Wyoming Game and Fish, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services, and the Cheyenne Mountain Zoo are currently working on saving the species. The primary focus is breeding the toad in captivity and releasing tadpoles in the wild as an attempt to restore the previous populations. No reproduction has been recorded in the wild so far, and it seems that the species are procreating successfully only in captivity. The reason why the Toads are not doing as well in nature remains unknown. Even though the species is protected under the Endangered Species Act, professionals working with the toad also argue that the situation is not well known enough to the public, and believe that the Wyoming Toads deserve more attention.
Habitat loss
The infrastructure ofnatural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
development includes wells, pipelines, roads, and other components that damage wildlife through direct habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
, deterioration of habitat and displacement. Population spikes associated with industry growth result in urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
, as demand for living space increases, further reducing habitat available to wildlife. Additionally, road and pipeline construction divide habitat, resulting in greater automobile related fatalities.
Development of the Pinedale Anticline Project Area (PAPA) has impacted several species of big game dependent on western Wyoming for winter habitat, most notably pronghorn
The pronghorn (, ) (''Antilocapra americana'') is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed, hoofed) mammal indigenous to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is known colloquially in North America as the American a ...
, mule deer
The mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') is a deer indigenous to western North America; it is named for its ears, which are large like those of the mule. Two subspecies of mule deer are grouped into the black-tailed deer.
Unlike the related whi ...
, elk, bighorn sheep
The bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis'') is a species of sheep native to North America. It is named for its large horns. A pair of horns might weigh up to ; the sheep typically weigh up to . Recent genetic testing indicates three distinct subspec ...
and moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
. Growth of the Pinedale Anticline gas field has also compromised winter habitat and mating grounds for the Greater Sage Grouse
Sage-grouse are grouse belonging to the bird genus ''Centrocercus.'' The genus includes two species: the Gunnison grouse (''Centrocercus minimus'') and the greater sage-grouse (''Centrocercus urophasianus''). These birds are distributed throug ...
, a game bird species indigenous to western North America and present candidate for the endangered species list.
See also
* Wyoming Department of Environmental QualityReferences
Further reading
* *Cheyenne Mountain Zoo. 2011. Wyoming Toad. ''Amphibians and Reptiles'' Retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20111114051549/http://www.cmzoo.org/animalsPlants/amphibReptiles/?s=1 * * * * *National Biological Information Infrastructure. 2011. Focus on Amphibians. ''Plants, Animals & Other Organisms''. Retrieved from: https://web.archive.org/web/20111209195832/http://www.nbii.gov/portal/server.pt/community/amphibians/201 *Oltmans, S., Schnell, R., Johnson, B., Pétron, G., Mefford, T., & Neely, R. 2014. Anatomy of wintertime ozone associated with oil and natural gas extraction activity in Wyoming and Utah. ''Elementa''. Retrieved from http://elementascience.org/article/info:doi/10.12952/journal.elementa.000024 *Pelzer, J. (2011, June 28). Salazar, fish and wildlife service nominee to discuss wolf delisting in Wyoming visit. Casper star-tribune. Retrieved from http://trib.com/news/state-and-regional/article_6a6bbcc1-75bb-527c-8178-558f8ffbd14b.html * *Savage, A. 2006. Origin and Spread of the Frog Chytrid. ''Cornell Mushroom Blog, Cornell University''. Retrieved from: http://blog.mycology.cornell.edu/?p=104 *Spencer, B., & Callaway, D. 2000. Wyoming Toad 98 Fact Sheet. ''American Zoo and Aquarium Association'' Retrieved from: http://www.nagonline.net/Fact%20Sheet%20pdf/AZA%20-%20Wyoming%20Toad%20Species%20Survival%20Plan.pdf * *U.S. Fish and Wildlife, Office of Communications. (2011). U.s. fish and wildlife service proposes gray wolf delisting and. Retrieved from U.S. Fish and Wildlife website: http://www.fws.gov/mountain-prairie/species/mammals/wolf/wyoming-102011/WY-Wolf-pdelisting-news-release.pdf *Wyoming Game and Fish. (2011). Wyoming gray wolf management plan. Retrieved from Wyoming game and Fish Commission website: https://web.archive.org/web/20111018225239/http://gf.state.wy.us/downloads/pdf/wolfplan2011/2011-09-14_FinalApprovedWolfMgmtPlan.pdf *Wyoming Game and Fish Department. 2011. Wyoming Toad-Anaxyrus baxteri. ''Species Account, Amphibians''. Retrieved from:http://gf.state.wy.us/downloads/pdf/SWAP/Amphibians/WyomingToad.pdf *Zumbo, J. Yellowstone National Park, (2011). Wildlife-wolves. Retrieved from Yellowstone Media website: http://www.yellowstonenationalpark.com/wolves.htm *Protecting wolves in the greater yellowstone ecosystem. (2009, August 31). Retrieved from https://web.archive.org/web/20111226174736/http://wyoming.sierraclub.org/issues/wolves/index.htmlExternal links
*http://www.fws.gov/mountain-prairie/species/mammals/wolf/wyoming-102011/WY-Wolf-pdelisting-news-release.pdf *http://www.fws.gov/mountain-prairie/species/mammals/wolf/ *https://web.archive.org/web/20111018225239/http://gf.state.wy.us/downloads/pdf/wolfplan2011/2011-09-14_FinalApprovedWolfMgmtPlan.pdf *http://trib.com/news/state-and-regional/article_6a6bbcc1-75bb-527c-8178-558f8ffbd14b.html *http://www.yellowstonenationalpark.com/wolves.htm * *{{Cite journal , jstor = 3783320, volume=24, issue = 3, pages=402–413, title=Reintroducing the Gray Wolf to Central Idaho and Yellowstone National Park , journal=Wildlife Society Bulletin , last1 = Bangs, first1 = Edward E, last2 = Fritts, first2 = Steven H, year = 1996 *https://web.archive.org/web/20111226174736/http://wyoming.sierraclub.org/issues/wolves/index.html *http://www.epa.gov/aboutepa/states/wy.html *http://deq.state.wy.us/ *https://web.archive.org/web/20111122060428/http://gf.state.wy.us/index.asp *https://web.archive.org/web/20111119210728/http://www.wma-minelife.com/ Environmental issues in WyomingWyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the s ...