Energy in Croatia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Energy in Croatia describes
Energy in Croatia describes
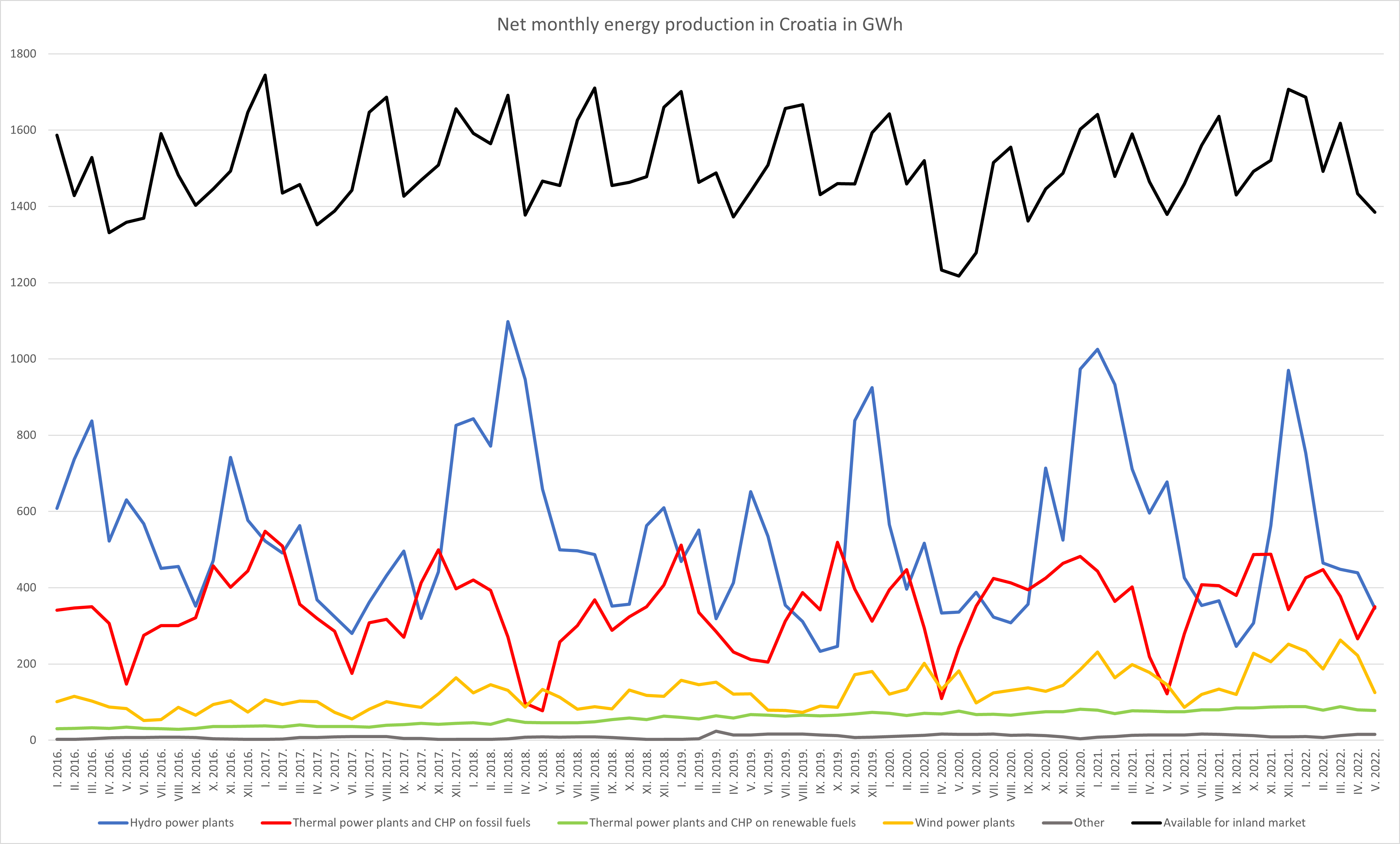 Total installed capacity of generating objects built in Croatia amounts to 3,557 MW, 2,166 MW of which is hydropower and renewable sources share and 1,391 MW comes from thermal and nuclear power plants.
In 2020, domestic production amounted to 13,731 GWh, which was 68% of total domestic demand. Remaining 32% was covered through trade.
Total consumption equaled 14,683 GWh, a 5.6% increase from 2020.
Total installed capacity of generating objects built in Croatia amounts to 3,557 MW, 2,166 MW of which is hydropower and renewable sources share and 1,391 MW comes from thermal and nuclear power plants.
In 2020, domestic production amounted to 13,731 GWh, which was 68% of total domestic demand. Remaining 32% was covered through trade.
Total consumption equaled 14,683 GWh, a 5.6% increase from 2020.
 Energy in Croatia describes
Energy in Croatia describes energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
and electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
production, consumption and import in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
.
As of 2021, Croatia imported about 52.9% of the total energy consumed annually: 80% of its oil demand, 67% of its gas, 32.5% of its electricity, and 100% of its coal needs.
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
satisfies its electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
needs largely from hydro
Hydro from Ancient Greek word ὕδωρ (húdōr), meaning ''water''.
Hydro may also refer to:
Energy technologies
* Water-derived power or energy:
** Hydropower, derived from water
** Hydroelectricity, in electrical form
* "Hydro", AC mains ...
and thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
power plants, and partly from the Krško nuclear power plant
The Krško Nuclear Power Plant ( sl, Jedrska elektrarna Krško, JEK, or , NEK, ; hr, Nuklearna elektrana Krško) is located in Vrbina in the Municipality of Krško, Slovenia. The plant was connected to the power grid on October 2, 1981 and went ...
, which is co-owned by Croatian and Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
n state-owned power companies. Renewable energies account for approximately 28.5% of Croatia’s energy mix.
Electricity
''Hrvatska elektroprivreda
Hrvatska elektroprivreda (HEP Group) is a national power company in Croatia which has been engaged in electricity production, transmission and distribution for more than one century, and with heat supply and gas distribution for the past few dec ...
'' (HEP) is the national energy company charged with production, transmission and distribution of electricity.
Production
 Total installed capacity of generating objects built in Croatia amounts to 3,557 MW, 2,166 MW of which is hydropower and renewable sources share and 1,391 MW comes from thermal and nuclear power plants.
In 2020, domestic production amounted to 13,731 GWh, which was 68% of total domestic demand. Remaining 32% was covered through trade.
Total consumption equaled 14,683 GWh, a 5.6% increase from 2020.
Total installed capacity of generating objects built in Croatia amounts to 3,557 MW, 2,166 MW of which is hydropower and renewable sources share and 1,391 MW comes from thermal and nuclear power plants.
In 2020, domestic production amounted to 13,731 GWh, which was 68% of total domestic demand. Remaining 32% was covered through trade.
Total consumption equaled 14,683 GWh, a 5.6% increase from 2020.
Hydropower
Croatia has 28 hydropower plants of which 2 are reversible, 2 small size and 1pumped storage
Pumping may refer to:
* The operation of a pump, for moving a liquid from one location to another
**The use of a breast pump for extraction of milk
* Pumping (audio), a creative misuse of dynamic range compression
* Pumping (computer systems), th ...
. They are distributed in three production areas: North, West and South with one independent plant, and are HEP's most important source of renewable energy.
Wind energy
Most of Croatian wind energy is produced by companies in private ownership for difference of other types of energy production. Out of 25 wind firms only one is owned by HEP (VE Korlat) while others are mainly individually owned.Thermal energy
There are 7 thermal power plants of which 4 are alsoheating plant
A heating plant, also called a physical plant, or steam plant, generates thermal energy in the form of steam for use in district heating applications. Unlike combined heat and power installations which produce thermal energy as a by-produc ...
s and one is combined cycle power plant
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turb ...
. Additionally, the first geothermal power plant was opened in 2019, but there are projects and potential for new ones.
Bioenergy
Five biopower plants are now located in Croatia and they are also used for heating purposes.Nuclear energy
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
has no nuclear power plants on its territory, but co-owns the Krško Nuclear Power Plant
The Krško Nuclear Power Plant ( sl, Jedrska elektrarna Krško, JEK, or , NEK, ; hr, Nuklearna elektrana Krško) is located in Vrbina in the Municipality of Krško, Slovenia. The plant was connected to the power grid on October 2, 1981 and went ...
together with Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
. The Krško plant was built in the era of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
on the territory of present-day Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
. Planned decommissioning is by 2043.
Solar energy
In 2014, HEP built nine solar power plants on the roofs of business buildings. The power plants are located in the office building at the headquarters of HEP in Zagreb and the buildings of the HEP Distribution System Operator. Solar power plants have the status of a privileged producer of electricity, which enables the sale of produced electricity to HROTE at a preferential price. Since 2018, Hrvatska elektroprivreda has started building integrated solar power plants according to the concept of a customer with its own production. This model enables a significant reduction in costs for own consumption of electricity. Most of the produced energy is consumed in the buildings themselves, while the rest of the energy is delivered to the distribution network. HEP's first non-integrated power plant was SE Kaštelir, purchased in 2019 from a private producer, and the first independently built was SE Vis, commissioned in 2020.Transmission
Croatian transmission grid consists of lines on three different rated voltage levels, namely 400, 220 and 110 kV. Total length of high-voltage lines is while length of medium and low voltage lines is . The grid was often the target of attacks during Croatian War of Independence, resulting in frequent black-outs during the period. Since then, the grid has been repaired, and reconnected tosynchronous grid of Continental Europe
The synchronous grid of Continental Europe (also known as Continental Synchronous Area; formerly known as the UCTE grid) is the largest synchronous electrical grid (by connected power) in the world. It is interconnected as a single phase-locked ...
synchronous zones 1 and 2, making it an important transit system again.
Distribution
Under the 2004 Energy law, customers in Croatia are allowed to choose their preferred distributor of electricity. However, HEP Operator distribucijskog sustava or HEP-ODS (a Hrvatska elektroprivreda subsidiary) remains the largest distributor to both industry and households. Its distribution grid is long, with 26 859 transformers installed, totaling 23,421 MVA of power. In 2021 there were 2,132,002 customers, 95.8% of which were households.Development projects
Hydropower
With the implementation of the project HE Senj 2, HEP intends to use the remaining hydro potential in the Lika and Gacka basins by upgrading the existing hydropower system. The project involves the construction of a large reservoir and additional capacity in order to transfer production to the top of the daily chart. This will enable the capacity to inject high regulatory power into the power system with flexible hydro units ready for rapid power change. The construction of the hydroelectric power plant will cost 3.4 billion kuna and will have an installed capacity of 412 MW, while the construction deadline is 2028.Wind energy
In July 2022, the Spanish company Acciona Energia announced an investment of one hundred million euros in the construction of two wind farms. One will be built in the vicinity ofSplit
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
, and the other between Šibenik
Šibenik () is a historic city in Croatia, located in central Dalmatia, where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea. Šibenik is a political, educational, transport, industrial and tourist center of Šibenik-Knin County, and is also the ...
and Knin
Knin (, sr, link=no, Книн, it, link=no, Tenin) is a city in the Šibenik-Knin County of Croatia, located in the Dalmatian hinterland near the source of the river Krka, an important traffic junction on the rail and road routes between Zagr ...
and will contain 16 wind turbines with a production of 203 GWh of clean electricity per year. The projects named Opor and Boraja 2 will be sufficient to supply 60 thousand households, and the propellers will start spinning at these locations in 2024, after a year and a half of construction and testing. This will avoid the annual emission of 135,000 tons of CO2. In 2013, the same company built the Jelinak wind park worth 48 million euros.
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) will grant a loan of EUR 43 million to the company Kunovac, jointly owned by the funds Taaleri Energia SolarWind II and ENCRO Kunovac, for the construction and operation of two onshore wind farms in the Zadar region. Zagrebačka banka
Zagrebačka banka d.d. is the largest bank in Croatia, owned by UniCredit group of Italy. It was the first Croatian bank to become fully privatised in 1989 and the first one to be listed at the Zagreb Stock Exchange in 1995. It is one of 24 compan ...
and Croatian bank for reconstruction and development
Croatian Bank for Reconstruction and Development ( hr, Hrvatska banka za obnovu i razvitak, HBOR) is Croatia's national development bank. Its task is the promotion of the development of the Croatian economy by extending loans, insuring export trans ...
will participate in the financing with a total loan amount of 126 million euros, and the total network capacity of the two power plants is 111 megawatts, which is enough to power 85,000 households.
In January 2023, the Greek energy company EuroEnergy announced that it was taking over the 114 MW wind farm project in Lika-Senj County
Lika-Senj County (, hr, Ličko-senjska županija) is a county in Croatia that includes most of the Lika region and some northern coastline of the Adriatic near the town of Senj, including the northern part of the Pag island. Its center is Go ...
. The acquisition reserves the right to expand with an additional 70.5 MW of wind capacity, subject to grid upgrades that can increase production. The value of the project is EUR 150 million and will be realized in the area of Udbina
Udbina is a village and a municipality in historical Krbava, in the Lika region of Croatia. It is administratively a part of the Lika-Senj County.
Geography
Udbina is located in the large karst field called Krbava. It is approximately 45 kilomet ...
.
The action plan for renewable energy sources at sea is the first comprehensive study that looks at the possibilities of renewable energy development in the Adriatic, and it was financed by the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development. The study considered two technologies: wind farms (stationary and floating) and floating solar farms. Through a spatial analysis of numerous ecological and other technical parameters, the experts came up with data on the possibility of RES development in five zones with an area of 1,260 square kilometers, of which 204 km2 is within the territorial sea. It has been calculated that a 25 GW RES power plant could be installed on that surface. If the area where the medium impact on the landscape is assessed is added to that area, the possible area for RES increases to an additional 1,602 km2 and 44 GW. The development of offshore wind farms in these zones depends on concession agreements between INA and the Republic of Croatia. Also, if hydrocarbon exploitation areas in the central and southern Adriatic are added to that area, a possible 26,000 square kilometers for floating wind power plants and solar power plants will be reached, due to greater depth.
Thermal power
In December 2019, the project of building a new high-efficiency combi-cogeneration unit KKE EL-TO Zagreb began, electric power 150 MW. The construction lasts for three years, and this project will replace part of the dilapidated and obsolete units at the EL-TO Zagreb location. It is expected for a unit to start working in the summer of 2023.Nuclear power
In 1978, the Adriatic island of Vir was selected as a location for a future nuclear power plant, but these plans were abandoned. According to reports, since 2009 Croatia has been discussing the option of building a nuclear power plant withAlbania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, in a location on the shore of Shkodër Lake, on the border with Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
. In April 2009 the Croatian government denied that any agreement had been signed.
In a 2012 poll among 447 Croatian citizens, who were asked "Do you think it is justified to use nuclear energy for the production of electricity?", 42% answered "yes" and 44% answered "no".
In 2021 the Slovenian government has issued an energy permit to GEN Energija
GEN energija, d.o.o. is a state-owned power company in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to t ...
for the planning and construction of the second unit of the Krško Nuclear Power Plant,followed by a statement by the Minister of Economy and Sustainable Development of Croatia Tomislav Ćorić
Tomislav Ćorić (born 17 November 1979) is a Croatian politician.
See also
*Cabinet of Andrej Plenković I
*Cabinet of Andrej Plenković II
The Fifteenth Government of the Republic of Croatia ( hr, Petnaesta Vlada Republike Hrvatske) is t ...
that Croatia "will not look benevolently at the construction of the new bloc". In March 2022, Plenković confirmed Croatia's readiness to enter the project of building the second block of the Krško NPP.
Solar power
As of 2021, Croatia had 100 MW of solar power, providing 0.4% of electricity. The potential for solar energy in Croatia is estimated at 6.8 GW, of which 5.3 GW would be accounted for by utility-scale photovoltaic plants and 1.5 GW by rooftop solar systems. Croatia plans to install 1.5 GW of solar capacity by 2024. The totalsolar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovolta ...
grid-connected capacity in Croatia was 109 MW as 2022.
In May 2023, Acciona Energy announced the construction of the largest solar power plant in Croatia. The new power plant will be spread over three million square meters of rugged state land and will have a capacity of 150 MW, which is enough to meet the needs of around 100,000 households. Its official name is SE Promina.
Battery storage
In September 2022, theEuropean Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
approved state support in the amount of 19.8 million euros for the project of building a large-capacity battery system. The project will be built in Šibenik, and will enter into operation in 2023 with a capacity of 10 MW, and ultimately the capacity will be 50 MW.
See also
* Wind power in Croatia *Industry of Croatia
Industry of Croatia plays an important role in the Economy of Croatia, country's economy. It has a longstanding tradition based since the 19th century on agriculture, forestry and mining. Many industrial branches developed at that time, like wood i ...
Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Energy In Croatia