Dredgers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Dredging is the
Dredging is the


 These operate by sucking through a long tube like some
These operate by sucking through a long tube like some

 This is a bar or blade which is pulled over the seabed behind any suitable ship or boat. It has an effect similar to that of a
This is a bar or blade which is pulled over the seabed behind any suitable ship or boat. It has an effect similar to that of a
 Fishing dredges are used to collect various species of
Fishing dredges are used to collect various species of
 As of June 2018, the largest dredger in Asia is "'' MV Tian Kun Hao''", a 140 metres long dredger constructed in China, with a capacity of 6,000 cubic meters per hour. An even larger dredger, retired in 1980, was the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers '' Essayons'', which was long. The Mallard II, a clamshell dredger that maintains
As of June 2018, the largest dredger in Asia is "'' MV Tian Kun Hao''", a 140 metres long dredger constructed in China, with a capacity of 6,000 cubic meters per hour. An even larger dredger, retired in 1980, was the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers '' Essayons'', which was long. The Mallard II, a clamshell dredger that maintains
dredge hoses
too. There are a few different types of dredge hoses that differ in terms of working pressure, float-ability, armored or not etc. Suction hoses, discharge armored hoses and self-floating hoses are some of the popular types engineered for transporting and discharging dredge materials. Some even had the pipes or hoses customised to exact dredging needs etc. Other times, it is pumped into
File:Dredge in the Port of Oakland with San Francisco in the background.JPG , Grab (clamshell) dredge ''Njord'' of the Manson Construction Co. fleet in the
Directory of Dredgers
(a close to exhaustive private collection of dredger photographs)
Dredging and Spoil Disposal Policy
(from the Government of Australia, Australian Government)
The Art of Dredging
(Knowledge sharing)
International Association of Dredging Companies
Knowledge centre
World of Boats (EISCA) Collection ~ Isambard Kingdom Brunel's Bertha
{{Authority control Dredging, * Engineering vehicles Coastal construction Nautical terminology Coastal engineering de:Baggerschiff
 Dredging is the
Dredging is the excavation
Excavation may refer to:
* Excavation (archaeology)
* Excavation (medicine)
* ''Excavation'' (The Haxan Cloak album), 2013
* ''Excavation'' (Ben Monder album), 2000
* ''Excavation'' (novel), a 2000 novel by James Rollins
* '' Excavation: A Mem ...
of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess of water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils is good enough to prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic condition ...
, navigability, and commercial use; constructing dams, dikes, and other controls for streams and shorelines; and recovering valuable mineral deposits or marine life having commercial value. In all but a few situations the excavation is undertaken by a specialist floating plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
, known as a dredger.
Dredging is carried out in many different locations and for many different purposes, but the main objectives are usually to recover material of value or use, or to create a greater depth of water. Dredges have been classified as suction or mechanical.
Dredging has significant environmental impacts: it can disturb marine sediments, leading to both short- and long-term water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. ...
, destroy important seabed ecosystems, and can release human-sourced toxins captured in the sediment.
Description
Dredging isexcavation
Excavation may refer to:
* Excavation (archaeology)
* Excavation (medicine)
* ''Excavation'' (The Haxan Cloak album), 2013
* ''Excavation'' (Ben Monder album), 2000
* ''Excavation'' (novel), a 2000 novel by James Rollins
* '' Excavation: A Mem ...
carried out underwater or partially underwater, in shallow waters or ocean waters. It keeps waterways and ports navigable, and assists coastal protection, land reclamation and coastal redevelopment, by gathering up bottom sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
s and transporting it elsewhere. Dredging can be done to recover materials of commercial value; these may be high value minerals or sediments such as sand and gravel that are used by the construction industry.
Dredging is a four-part process: loosening the material, bringing the material to the surface (together extraction), transportation and disposal.
The extract can be disposed of locally or transported by barge or in a liquid suspension in pipelines. Disposal can be to infill sites, or the material can be used constructively to replenish eroded sand that has been lost to coastal erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landwar ...
, or constructively create sea-walls, building land or whole new landforms such as viable islands in coral atoll
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secr ...
s.
History
Ancient authors refer to harbour dredging. The seven arms of theNile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
were channelled and wharfs built at the time of the pyramids (4000 BC), there was extensive harbour building in the eastern Mediterranean from 1000 BC and the disturbed sediment layers gives evidence of dredging. At Marseille, dredging phases are recorded from the third century BC onwards, the most extensive during the first century AD. The remains of three dredging boats have been unearthed; they were abandoned at the bottom of the harbour during the first and second centuries AD.
The Banu Musa Brothers during the Muslim Golden Age in while working at the Bayt-Al-Hikmah (house of wisdom) in Baghdad, designed an original invention in their book named ‘book of ingenious devices’ A grab machine that that does not appear in any earlier Greek works. The grab they described was used to extract objects from underwater, and recover objects from the beds of streams.
During the renaissance Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on ...
drew a design for a drag dredger.
Dredging machines have been used during the construction of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popula ...
from the late 1800s to present day expansions and maintenance. The completion of the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
in 1914, the most expensive U.S. engineering project at the time, relied extensively on dredging.


Purposes
*Capital dredging: dredging carried out to create a newharbour
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is ...
, berth or waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary ...
, or to deepen existing facilities in order to allow larger ships access. Because capital works usually involve hard material or high-volume works, the work is usually done using a cutter suction dredge or large trailing suction hopper dredge; but for rock works, drilling and blasting along with mechanical excavation may be used.
*Land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamat ...
: dredging to mine sand, clay or rock from the seabed and using it to construct new land elsewhere. This is typically performed by a cutter-suction dredge or trailing suction hopper dredge. The material may also be used for flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
or erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is d ...
control.
*Maintenance: dredging to deepen or maintain navigable waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary ...
s or channels
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
which are threatened to become silted with the passage of time, due to sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
ed sand and mud, possibly making them too shallow for navigation. This is often carried out with a trailing suction hopper dredge. Most dredging is for this purpose, and it may also be done to maintain the holding capacity of reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contr ...
s or lakes.
*Harvesting materials: dredging sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
for elements like gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
, diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, b ...
s or other valuable trace substances. Hobbyists examine their dredged matter to pick out items of potential value, similar to the hobby of metal detecting.
* Fishing dredging is a technique for catching certain species of edible clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve molluscs. The word is often applied only to those that are edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the seafloor or riverbeds. Clams have two shel ...
s and crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all th ...
s. In Louisiana and other American states, with salt water estuaries that can sustain bottom oyster beds, oysters are raised and harvested. A heavy rectangular metal scoop is towed astern of a moving boat with a chain bridle attached to a cable. This drags along the bottom scooping up oysters. It is periodically winched aboard and the catch is sorted and bagged for shipment.
* Preparatory: dredging work and excavation for future bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
s, pier
Seaside pleasure pier in Brighton, England. The first seaside piers were built in England in the early 19th century.">England.html" ;"title="Brighton, England">Brighton, England. The first seaside piers were built in England in the early 19th ...
s or docks or wharves
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more berths (mooring location ...
, This is often to build the foundations.
* Winning construction materials: dredging sand and gravels from offshore licensed areas for use in construction industry, principally for use in concrete. This very specialist industry is focused in NW Europe, it uses specialized trailing suction hopper dredgers self discharging the dry cargo ashore. Land based old river beddings can be processed in this manner too.
* Contaminant
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
Wi ...
remediation: to reclaim areas affected by chemical spills, storm water surges (with urban runoff
Urban runoff is surface runoff of rainwater, landscape irrigation, and car washing created by urbanization. Impervious surfaces (roads, parking lots and sidewalks) are constructed during land development. During rain , storms and other precip ...
), and other soil contaminations, including silt from sewage sludge
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater. The term " septage" also refers to sludge from simple wastewater treatment but is connected to s ...
and from decayed matter, like wilted plants. Disposal becomes a proportionally large factor in these operations.
* Flood prevention: dredging increases the channel depth and therefore increase a channel's capacity for carrying water.
Other
*Beach nourishment
Beach nourishment (also referred to as beach renourishment, beach replenishment, or sand replenishment) describes a process by which sediment, usually sand, lost through longshore drift or erosion is replaced from other sources. A wider beach ...
: this is mining sand offshore and placing on a beach to replace sand eroded by storms or wave action. This enhances the recreational and protective function of the beach, which are also eroded by human activity. This is typically performed by a cutter-suction dredge or trailing suction hopper dredge.
* Peat extraction
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficient c ...
: ''dredging poles'' or ''dredge hauls'' were used on the back of small boats to manually dredge the beds of peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and ...
- moor waterways. The extracted peat was used as a fuel. This tradition is now more or less obsolete. The tools are now significantly changed.
* Removing rubbish and debris: often done in combination with maintenance dredging, this process removes non-natural matter from the bottoms of rivers and canals and harbours. Law enforcement agencies sometimes need to use a 'drag' to recover evidence or corpses from beneath the water.
* Anti-eutrophication: A kind of contaminant remediation, dredging is an expensive option for the remediation of eutrophied (or de-oxygenated) water bodies; one of the causes is like mentioned above, sewage sludge
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater. The term " septage" also refers to sludge from simple wastewater treatment but is connected to s ...
. However, as artificially elevated phosphorus levels in the sediment aggravate the eutrophication process, controlled sediment removal is occasionally the only option for the reclamation of still waters.
* Seabed mining: is a possible future use, recovering natural metal ore nodules from the sea's deepest troughs.
Types
Suction dredgers
 These operate by sucking through a long tube like some
These operate by sucking through a long tube like some vacuum cleaner
A vacuum cleaner, also known simply as a vacuum or a hoover, is a device that causes suction in order to remove dirt from floors, upholstery, draperies, and other surfaces. It is generally electrically driven.
The dirt is collected by either a ...
s but on a larger scale.
A plain suction dredger has no tool at the end of the suction pipe to disturb the material.
Trailing suction
A trailing suction hopper dredger (TSHD) trails its suction pipe when working. The pipe, which is fitted with adredge drag head
{{unreferenced, date=July 2018
A dredge drag head is used by a trailing suction hopper dredger to collect sand from the sea floor.
The dredge drag head is a steel structure that is connected to the dredger by a suction pipe. Supported by the g ...
, loads the dredge spoil into one or more hoppers in the vessel.
When the hoppers are full, the TSHD sails to a disposal area and either dumps the material through doors in the hull or pumps the material out of the hoppers. Some dredges also self-offload using drag buckets and conveyors.
the largest trailing suction hopper dredgers in the world were Jan De Nul
Jan De Nul Group is a Belgian family-owned company, with the financial headquarters in Luxembourg, that provides services relating to the construction and maintenance of maritime infrastructure on an international basis. Its main focus is dredging ...
's ''Cristobal Colon'' (launched 4 July 2008) and her sister ship ''Leiv Eriksson'' (launched 4 September 2009). Main design specs for the ''Cristobal Colon'' and the '' Leiv Eriksson'' are: 46,000 cubic metre hopper and a design dredging depth of 155 m. Next largest is ''HAM 318'' (Van Oord
Royal Van Oord is a Dutch maritime contracting company that specializes in dredging, land reclamation and constructing man made islands. Royal Van Oord has undertaken many projects throughout the world, including land reclamation, dredging and beac ...
) with its 37,293 cubic metre hopper and a maximum dredging depth of 101 m.
Cutter-suction
A cutter-suction dredger's (CSD) suction tube has a cutting mechanism at the suction inlet. The cutting mechanism loosens the bed material and transports it to the suction mouth. The dredged material is usually sucked up by a wear-resistant centrifugal pump and discharged either through a pipe line or to a barge. Cutter-suction dredgers are most often used in geological areas consisting of hard surface materials (for example gravel deposits or surface bedrock) where a standard suction dredger would be ineffective. They can, if sufficiently powerful, be used instead of underwater blasting. As of 2018, the most powerful cutter-suction dredger in the world isDEME
In Ancient Greece, a deme or ( grc, δῆμος, plural: demoi, δημοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and ear ...
's ''Spartacus'', which is scheduled to enter service in 2019.
Auger suction
The auger dredge system functions like a cutter suction dredger, but the cutting tool is a rotatingArchimedean screw
The Archimedes screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest hydraulic machines. Using Archimedes screws as water pumps (Archimedes screw pump (ASP) or screw pump) dates bac ...
set at right angles to the suction pipe. Mud Cat invented the auger dredge in the 1970s.
Jet-lift
These use theVenturi effect
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section (or choke) of a pipe. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the 18th century Italian physicist, Giovanni Battista ...
of a concentrated high-speed stream of water to pull the nearby water, together with bed material, into a pipe.
Air-lift
Anairlift
An airlift is the organized delivery of supplies or personnel primarily via military transport aircraft.
Airlifting consists of two distinct types: strategic and tactical. Typically, strategic airlifting involves moving material long distan ...
is a type of small suction dredge. It is sometimes used like other dredges. At other times, an airlift is handheld underwater by a diver. It works by blowing air into the pipe, and that air, being lighter than water, rises inside the pipe, dragging water with it.
Mechanical dredgers
Some bucket dredgers and grab dredgers are powerful enough to rip out coral to make a shipping channel throughcoral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of Colony (biology), colonies of coral polyp (zoology), polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, wh ...
s.

Bucket dredgers
Abucket
A bucket is typically a watertight, vertical cylinder or truncated cone or square, with an open top and a flat bottom, attached to a semicircular carrying handle called the ''bail''.
A bucket is usually an open-top container. In contrast, a ...
dredger is equipped with a bucket dredge, which is a device that picks up sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
by mechanical means, often with many circulating buckets attached to a wheel or chain
A chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. ...
.
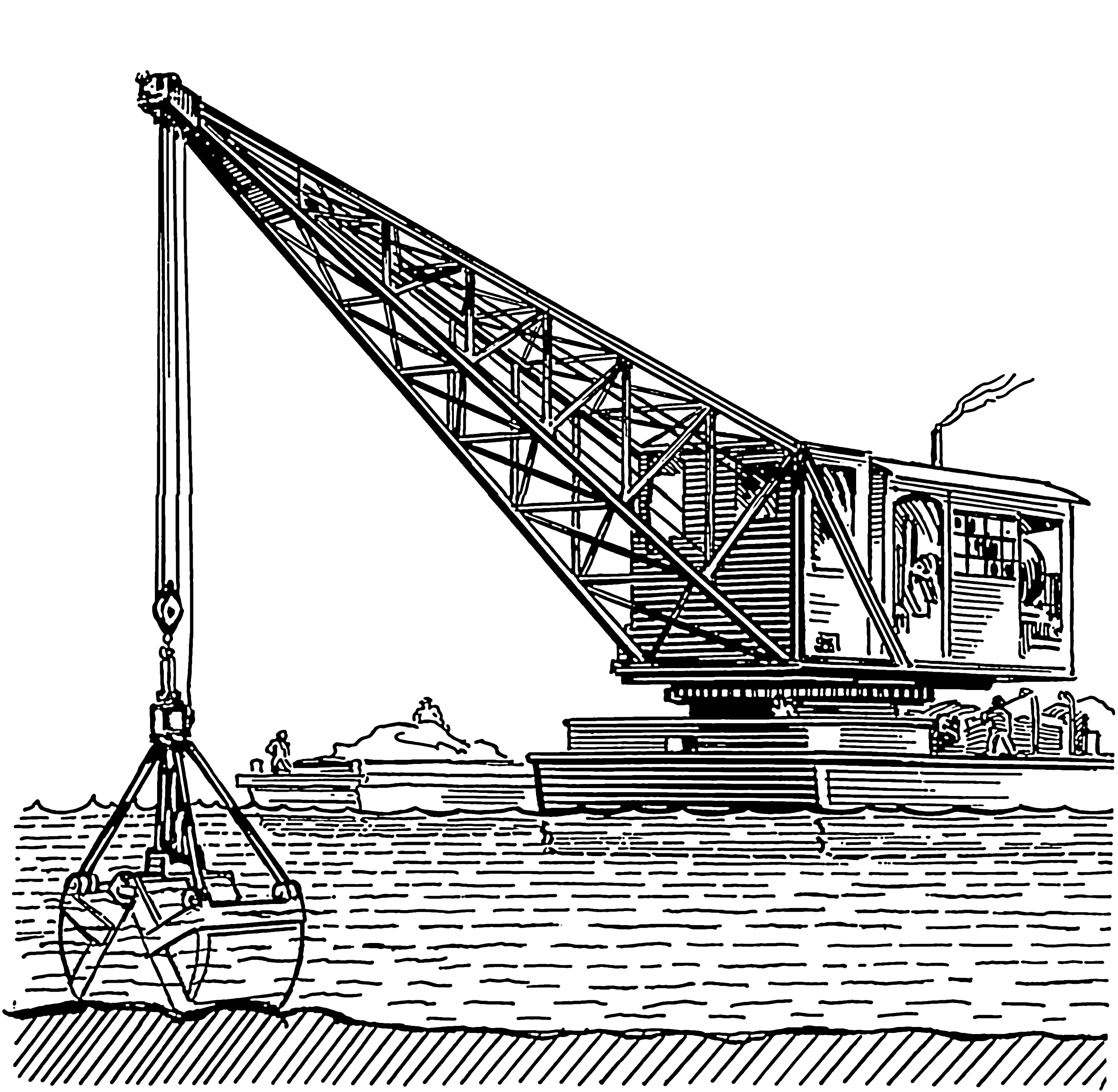
Grab dredgers
A grab dredger picks up seabed material with a clam shell bucket, which hangs from an onboard crane or a crane barge, or is carried by a hydraulic arm, or is mounted like on adragline
A dragline excavator is a piece of heavy equipment used in civil engineering and surface mining.
Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting cranes, and the heavy units which have to be built on-site. ...
. This technique is often used in excavation of bay mud
Bay mud consists of thick deposits of soft, unconsolidated silty clay, which is saturated with water; these soil layers are situated at the bottom of certain estuaries, which are normally in temperate regions that have experienced cyclical glac ...
. Most of these dredges are crane barges with spuds, steel piles that can be lowered and raised to position the dredge.
Backhoe/dipper dredgers
A backhoe/dipper dredger has abackhoe
A backhoe—also called rear actor or back actor—is a type of excavating equipment, or digger, consisting of a digging bucket on the end of a two-part articulated arm. It is typically mounted on the back of a tractor or front loader, the latt ...
like on some excavator
Excavators are heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels. They are a natural progression fr ...
s. A crude but usable backhoe dredger can be made by mounting a land-type backhoe excavator on a pontoon. The six largest backhoe dredgers in the world are currently the Vitruvius, the Mimar Sinan, Postnik Yakovlev (Jan De Nul), the Samson (DEME), the Simson and the Goliath (Van Oord). They featured barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. ...
-mounted excavators. Small backhoe dredgers can be track-mounted and work from the bank of ditches. A backhoe dredger is equipped with a half-open shell. The shell is filled moving towards the machine. Usually dredged material is loaded in barges. This machine is mainly used in harbours and other shallow water.
Excavator dredge attachments
The excavator dredge attachment uses the characteristics of cutter-suction dredgers, consisting of cutter heads and a suction pump for transferring material. These hydraulic attachments mount onto the boom arm of an excavator allowing an operator to maneuver the attachment along the shoreline and in shallow water for dredging.
Bed leveler
 This is a bar or blade which is pulled over the seabed behind any suitable ship or boat. It has an effect similar to that of a
This is a bar or blade which is pulled over the seabed behind any suitable ship or boat. It has an effect similar to that of a bulldozer
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large, motorized machine equipped with a metal blade to the front for pushing material: soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous track ...
on land. The chain-operated steam dredger ''Bertha
Bertha is a female Germanic name, from Old High German ''berhta'' meaning "bright one". It was usually a short form of Anglo Saxon names ''Beorhtgifu'' meaning "bright gift" or ''Beorhtwynn'' meaning "bright joy".
The name occurs as a theonym, s ...
'', built in 1844 to a design by Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one ...
and was the oldest operational steam vessel in Britain, was of this type.
Krabbelaar
This is an early type of dredger which was formerly used in shallow water in the Netherlands. It was a flat-bottomed boat with spikes sticking out of its bottom. As tide current pulled the boat, the spikes scraped seabed material loose, and the tide current washed the material away, hopefully to deeper water. ''Krabbelaar'' is the Dutch word for "scratcher".Water injection
A water injection dredger uses a small jet to inject water under low pressure (to prevent the sediment from exploding into the surrounding waters) into the seabed to bring the sediment in suspension, which then becomes aturbidity current
A turbidity current is most typically an underwater current of usually rapidly moving, sediment-laden water moving down a slope; although current research (2018) indicates that water-saturated sediment may be the primary actor in the process. T ...
, which flows away down slope, is moved by a second burst of water from the WID or is carried away in natural currents. Water injection results in a lot of sediment in the water which makes measurement with most hydrographic equipment (for instance: singlebeam echosounders) difficult.
Pneumatic
These dredgers use a chamber with inlets, out of which the water is pumped with the inlets closed. It is usually suspended from a crane on land or from a small pontoon or barge. Its effectiveness depends on depth pressure.Snagboat
Asnagboat
A snagboat is a river boat, resembling a barge with superstructure for crew accommodations, and deck-mounted cranes and hoists for removing snags and other obstructions from rivers and other shallow waterways.
USA
During the American Civil ...
is designed to remove big debris such as dead trees and parts of trees from North America waterways.
Amphibious
Some of these are any of the above types of dredger, which can operate normally, or by extending legs, also known as spuds, so it stands on the seabed with its hull out of the water. Some forms can go on land. Some of these are land-type backhoe excavators whose wheels are on long hinged legs so it can drive into shallow water and keep its cab out of water. Some of these may not have a floatable hull and, if so, cannot work in deep water.Oliver Evans
Oliver Evans (September 13, 1755 – April 15, 1819) was an American inventor, engineer and businessman born in rural Delaware and later rooted commercially in Philadelphia. He was one of the first Americans building steam engines and an advoca ...
(1755–1819) in 1804 invented the Oruktor Amphibolos, an amphibious dredger which was America's first steam-powered road vehicle.
Submersible
These are usually used to recover useful materials from the seabed. Many of them travel oncontinuous track
Continuous track is a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle ...
. A unique variant is intended to walk on legs on the seabed.
Fishing
 Fishing dredges are used to collect various species of
Fishing dredges are used to collect various species of clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve molluscs. The word is often applied only to those that are edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the seafloor or riverbeds. Clams have two shel ...
s, scallop
Scallop () is a common name that encompasses various species of marine bivalve mollusks in the taxonomic family Pectinidae, the scallops. However, the common name "scallop" is also sometimes applied to species in other closely related families ...
s, oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not ...
s or mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which ...
s from the seabed. Some dredges are also designed to catch crabs, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and conch. These dredges have the form of a scoop made of chain mesh, and are towed by a fishing boat
A fishing vessel is a boat or ship used to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Many different kinds of vessels are used in commercial, artisanal and recreational fishing.
The total number of fishing vessels in the world in 2016 was ...
. Clam-specific dredges can utilize hydraulic injection to target deeper into the sand. Dredging can be destructive to the seabed and some scallop dredging has been replaced by collecting via scuba diving
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface air supply. The name "scuba", an acronym for " Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus", was coined by Chr ...
.
Notable individual dredgers
levee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastli ...
s in San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water f ...
, has operated continuously since being built in 1936.
Dredge monitoring software
Dredgers are often equipped with dredge monitoring software to help the dredge operator position the dredger and monitor the current dredge level. The monitoring software often usesReal Time Kinematic
Real-time kinematic positioning (RTK) is the application of surveying to correct for common errors in current satellite navigation (GNSS) systems. It uses measurements of the phase of the signal's carrier wave in addition to the information cont ...
satellite navigation to accurately record where the machine has been operating and to what depth the machine has dredged to.
Transportation and disposal of materials
French hopper dredger ''Daniel Laval'' at work on the Seine estuary (2018) In a "hopper dredger", the dredged materials end up in a large onboard hold called a "hopper." A suction hopper dredger is usually used for maintenance dredging. A hopper dredge usually has doors in its bottom to empty the dredged materials, but some dredges empty their hoppers by splitting the two-halves of their hulls on large hydraulic hinges. Either way, as the vessel dredges, excess water in the dredged materials is spilled off as the heavier solids settle to the bottom of the hopper. This excess water is returned to the sea to reduce weight and increase the amount of solid material (or slurry) that can be carried in one load. When the hopper is filled withslurry
A slurry is a mixture of denser solids suspended in liquid, usually water. The most common use of slurry is as a means of transporting solids or separating minerals, the liquid being a carrier that is pumped on a device such as a centrifugal p ...
, the dredger stops dredging and goes to a dump site and empties its hopper.
Some hopper dredges are designed so they can also be emptied from above using pumps if dump sites are unavailable or if the dredge material is contaminated. Sometimes the slurry of dredgings and water is pumped straight into pipes which deposit it on nearby land. These pipes are also commonly known adredge hoses
too. There are a few different types of dredge hoses that differ in terms of working pressure, float-ability, armored or not etc. Suction hoses, discharge armored hoses and self-floating hoses are some of the popular types engineered for transporting and discharging dredge materials. Some even had the pipes or hoses customised to exact dredging needs etc. Other times, it is pumped into
barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. ...
s (also called scow
A scow is a smaller type of barge. Some scows are rigged as sailing scows. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, scows carried cargo in coastal waters and inland waterways, having an advantage for navigating shallow water or small harbours. S ...
s), which deposit it elsewhere while the dredge continues its work.
A number of vessels, notably in the UK and NW Europe de-water the hopper to dry the cargo to enable it to be discharged onto a quayside 'dry'. This is achieved principally using self discharge bucket wheel, drag scraper or excavator via conveyor systems.
When contaminated (toxic) sediments are to be removed, or large volume inland disposal sites are unavailable, dredge slurries are reduced to dry solids via a process known as dewatering. Current dewatering techniques employ either centrifuges, geotube containers, large textile based filters or polymer flocculant/congealant based apparatus.
In many projects, slurry dewatering is performed in large inland settling pits, although this is becoming less and less common as mechanical dewatering techniques continue to improve.
Similarly, many groups (most notable in east Asia) are performing research towards utilizing dewatered sediments for the production of concretes and construction block, although the high organic content (in many cases) of this material is a hindrance toward such ends.
The proper management of contaminated sediments is a modern-day issue of significant concern. Because of a variety of maintenance activities, thousands of tonnes of contaminated sediment are dredged worldwide from commercial ports and other aquatic areas at high level of industrialization. Dredged material can be reused after appropriate decontamination. A variety of processes has been proposed and tested at different scales of application ( technologies for environmental remediation). Once decontaminated, the material could well suit the building industry, or could be used for beach nourishment.
Environmental impacts
Dredging can create disturbance toaquatic ecosystem
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem formed by surrounding a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The t ...
s, often with adverse impacts. In addition, dredge spoils may contain toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a sub ...
chemicals that may have an adverse effect on the disposal area; furthermore, the process of dredging often dislodges chemicals residing in benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning " ...
substrates and injects them into the water column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-D ...
.
The activity of dredging can create the following principal impacts to the environment:
* Release of toxic chemicals (including heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals are generally defined as ...
and PCB) from bottom sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
s into the water column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-D ...
.Bridges, T S., Gustavson, K. E., Schroeder, P., Ells, S. J., & Hayes, D. (2010). Dredging processes and remedy effectiveness: Relationship to the 4 Rs of environmental dredging. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 6 (4), 619-630.
* Collection of heavy metal lead left by fishing, bullets, 98% mercury reclaimed atural occurring and left over from gold rush era
* Short term increases in turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids ...
, which can affect aquatic species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
and interfere with spawning
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aquat ...
. Suction dredging activity is allowed only during non-spawning time frames set by fish and game (in-water work periods).
* Secondary impacts to marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found ...
productivity from sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the ...
and general changes in wetland chemistry after dredging.
* Tertiary impacts to avifauna
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight s ...
which may prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill ...
upon contaminated aquatic organisms.
* Secondary impacts to aquatic and benthic organisms' metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
and mortality
* Possible contamination of dredge spoils sites
* Changes to the topography by the creation of "spoil islands" from the accumulated spoil.
* Releases toxic compound Tributyltin
Tributyltin (TBT) is an umbrella term for a class of organotin compounds which contain the (C4H9)3 Sn group, with a prominent example being tributyltin oxide. For 40 years TBT was used as a biocide in anti-fouling paint, commonly known as bott ...
, a popular biocide
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a sli ...
used in anti-fouling paint
Anti-fouling paint is a specialized category of coatings applied as the outer (outboard) layer to the hull of a ship or boat, to slow the growth of and facilitate detachment of subaquatic organisms that attach to the hull and can affect a vess ...
banned in 2008, back into the water.
The nature of dredging operations and possible environmental impacts cause the industry to be closely regulated and a requirement for comprehensive regional environmental impact assessments with continuous monitoring. The U.S. Clean Water Act
The Clean Water Act (CWA) is the primary federal law in the United States governing water pollution. Its objective is to restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters; recognizing the responsibiliti ...
requires that any discharge of dredged or fill materials into "waters of the United States," including wetlands, is forbidden unless authorized by a permit issued by the Army Corps of Engineers. As a result of the potential impacts to the environment, dredging is restricted to licensed areas only with vessel activity monitored closely using automatic GPS systems.
Major dredging companies
According to aRabobank
Rabobank (; full name: ''Coöperatieve Rabobank U.A.'') is a Dutch multinational banking and financial services company headquartered in Utrecht, Netherlands. The group comprises 89 local Dutch Rabobanks (2019), a central organisation (Raboban ...
outlook report in 2013, the largest dredging companies in the world are in order of size, based on dredging sales in 2012
* China Harbour Engineering
China Harbour Engineering Company Ltd (CHEC) is an engineering contractor and a subsidiary of China Communications Construction Company (CCCC), providing infrastructure construction, such as marine engineering, dredging and reclamation, road and ...
(China)
* Jan De Nul
Jan De Nul Group is a Belgian family-owned company, with the financial headquarters in Luxembourg, that provides services relating to the construction and maintenance of maritime infrastructure on an international basis. Its main focus is dredging ...
(Belgium)
* DEME
In Ancient Greece, a deme or ( grc, δῆμος, plural: demoi, δημοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and ear ...
(Belgium)
* Royal Boskalis Westminster
Royal Boskalis Westminster N.V. is a Dutch dredging and heavylift company that provides services relating to the construction and maintenance of maritime infrastructure internationally. The company has one of the world's largest dredging fleets, ...
(Netherlands)
* Van Oord Dredging and Marine Contractors (Netherlands)
* National Marine Dredging Company
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
(United Arab Emirates)
* Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (United States)
Notable dredging companies in North America
* Manson Construction Co. (United States)
Notable dredging companies in South Asia
* Dredging Corporation of India
*Adani Ports & SEZ
Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (Adani Ports & SEZ; also APSEZ) formerly known as Mundra Port and Special Economic Zone Limited, is an Indian port operator. APSEZ represents a large network of ports with India's largest SEZ at Mu ...
(India)
Images
Port of Oakland
The Port of Oakland is a major container ship facility located in Oakland, California, in the San Francisco Bay. It was the first major port on the Pacific Coast of the United States to build terminals for container ships. As of 2011 it was the f ...
, California
Image:Dredge No-4 (1).JPG, The excavator of a Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
dredge.
Image:Lakes Entrance Dredger April Hamer.JPG, ''April Hamer'' at Lakes Entrance
Lakes Entrance is a seaside resort and fishing port in eastern Victoria, Australia. It is situated approximately east of Melbourne, near a managed, artificial channel connecting the Gippsland Lakes to Bass Strait. At the 2016 census, Lakes Ent ...
, Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
Australia
Image:OrisantDredger.jpg, The ''Orisant'' a trailing suction dredger in the port of IJmuiden, Netherlands
Image:Hong Kong dredger123.jpg, Grab dredging in Victoria Harbour, Hong Kong
Image:Alexander von Humboldt (empty).jpg, ''Alexander von Humboldt'' of the Jan De Nul
Jan De Nul Group is a Belgian family-owned company, with the financial headquarters in Luxembourg, that provides services relating to the construction and maintenance of maritime infrastructure on an international basis. Its main focus is dredging ...
fleet
Image:BurigangaDredge.JPG, Sand mining
Image:HR-Morris-Pipeline-Dredge.jpg, ''HR Morris'' of the Manson Construction Co. fleet, a Cutter Suction Pipeline Dredge, working on Mission Bay, San Diego, California
Image:Barge on Neva river.jpg, Dredge ship with barges on Neva River, Neva bay in Saint Petersburg, Russia
Image:Dredge ship top view - 01.JPG, Top view of a suction dredger on the Nandu River, Hainan, China
Image:Cutterhead of dredge Bill Holman Louisville Kentucky USA Ohio River mile 607 July 2002 file a2g092.jpg, Cutterhead of dredge ''Bill Holman'', Louisville, Kentucky, United States, USA, Ohio River mile 607, July 2002
File:Xcentric Ripper XR120 in a dredging work.png, Xcentric Ripper XR120 is a large jackup leg backhoe dredger
See also
* Chemistry of wetland dredging * Dredge ball joint, connection between 2 pipes that are used to transport mixture of water and sand from a dredger to the discharging area * Dredge drag head * Long_Island_Sound#Dumping_of_dredged_sediment, Dumping of dredged sediment in Long Island Sound * Navigability * Peace in Africa (ship), ''Peace in Africa'' (ship), a diamond-mining dredger * Queen of the Netherlands (ship), ''Queen of the Netherlands'' (ship), a big dredger * River engineering for inland dredging and other river management systems * WT Preston, asnagboat
A snagboat is a river boat, resembling a barge with superstructure for crew accommodations, and deck-mounted cranes and hoists for removing snags and other obstructions from rivers and other shallow waterways.
USA
During the American Civil ...
* Foreign Dredge Act of 1906, a US law banning foreign-built and foreign-owned dredges from operating in US waters
* Gold dredge
References
External links
Directory of Dredgers
(a close to exhaustive private collection of dredger photographs)
Dredging and Spoil Disposal Policy
(from the Government of Australia, Australian Government)
The Art of Dredging
(Knowledge sharing)
International Association of Dredging Companies
Knowledge centre
World of Boats (EISCA) Collection ~ Isambard Kingdom Brunel's Bertha
{{Authority control Dredging, * Engineering vehicles Coastal construction Nautical terminology Coastal engineering de:Baggerschiff