Dendi Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Dendi (or Dandi, Dendiganda) was a former province of the
Worldstatesmen
African KingdomsTimeline of West African History
{{Sahelian kingdoms States and territories established in 1591 Songhai Empire Countries in precolonial Africa History of Niger States and territories disestablished in 1901 Muslim empires Former kingdoms
Songhai Empire
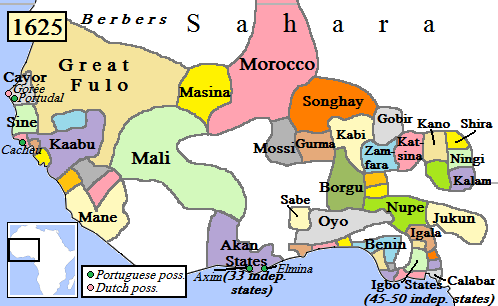
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical ...
. Its centers today are the cities of Gaya in Niger, Kamba in Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
and Malanville
Malanville is a city, arrondissement and commune in the Alibori Department of northeastern Benin, located across the River Niger from Niger. It is known as a centre of cross-border trade and has a major market. Malanville is also a centre for rice ...
in Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
Dendi Kingdom
Under the Songhai empire, Dendi had been the easternmost province, governed by the prestigious ''Dendi-fari'' ("governor of the eastern front"). Some of theAskia dynasty The Askiya dynasty, also known as the Askia dynasty, ruled the Songhai Empire at the height of that state's power. It was founded in 1493 by Askia Mohammad I, a general of the Songhai Empire who usurped the Sonni dynasty. The Askiya ruled from Gao ...
and its followers fled to here after the defeated by the invading Saadi dynasty
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, السعديون, translit=as-saʿdiyyūn) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was l ...
of Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
at the Battle of Tondibi
The Battle of Tondibi was the decisive confrontation in the 16th-century invasion of the Songhai Empire by the army of the Saadi dynasty in Morocco. Though vastly outnumbered, the Moroccan forces under Judar Pasha defeated the Songhai Askia Ish ...
and at another battle seven months later. There, they resisted Moroccan Invaders and maintained the tradition of the Songhai with the same Askia rulers and its newly established capital as Lulami
Lulami (also Loulami) was the capital of the Dendi of the Songhai Empire. It was established by Askia Nuh, son of Askia Dawud and it is from here the Songhai resistance against Morocco continued. In 1639 during the reign of Askia Ismail, the Mo ...
. The first ruler who was Askia Ishaq II
Askia Ishaq II was ruler of the Songhai Empire from 1588 to 1591.
Ishaq came to power in a long dynastic struggle following the death of the long-ruling Askia Daoud. Sensing the Empire's weakness, Moroccan Sultan Ahmad I al-Mansur Saadi dispatch ...
was deposed by his brother Muhammad Gao, who was in turn murdered on the order of the Moroccan pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, gener ...
. The Moroccans then appointed Sulayman
Sulayman (Arabic: سُلِيمَان ''sulaymān'') is an Arabic name of the Biblical king and Islamic prophet Solomon meaning "man of peace", derived from the Hebrew name Shlomo.
The name Sulayman is a diminutive of the name Salman (سَلْ ...
as puppet king ruling the Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesDjenné
Djenné ( Bambara: ߘߖߋߣߣߋ tr. Djenne; also known as Djénné, Jenné and Jenne) is a Songhai people town and an urban commune in the Inland Niger Delta region of central Mali. The town is the administrative centre of the Djenné Cercle, on ...
and Gao
Gao , or Gawgaw/Kawkaw, is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an impor ...
. South of Tillaberi the Songhai resistance against Morocco continued under Askia Nuh
Askia Nuh was a ruler of the Dendi Kingdom, the rump state of the Songhai Empire. He was a son of Askia Dawud and established his capital at Lulami, from where Songhai resistance to the Saadi Moroccans continued.
Conflict with the Saadi dynasty
A ...
, a son of Askia Dawud
Askia Daoud (also Askia Dāwūd, Askiya Dawud) was the ruler of the Songhai Empire from 1549 to 1582. Daoud came to power unopposed following the death of his brother Askia Ishaq I in 1549. The Empire continued to expand under Daoud's peaceful rul ...
. He established his capital at Lulami
Lulami (also Loulami) was the capital of the Dendi of the Songhai Empire. It was established by Askia Nuh, son of Askia Dawud and it is from here the Songhai resistance against Morocco continued. In 1639 during the reign of Askia Ismail, the Mo ...
.

Conflict with the Saadi dynasty
After the Moroccans had Askia Sulayman appointed as their puppet the pasha,Mahmud ibn Zarqun
Mahmud is a transliteration of the male Arabic given name (), common in most parts of the Islamic world. It comes from the Arabic triconsonantal root Ḥ-M-D, meaning ''praise'', along with ''Muhammad''.
Siam Mahmud
*Mahmood (singer) (born 19 ...
, attempted to conquer the remaining smaller Songhai kingdoms Which was now centred in south-western Niger. Askia Nuh resisted the invasion by a costly warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
lasting two years. In 1594 Mahmud was forced to discontinue the war and retreated, just to be killed in the same year by Dogon
Dogon may refer to:
*Dogon people, an ethnic group living in the central plateau region of Mali, in West Africa
*Dogon languages, a small, close-knit language family spoken by the Dogon people of Mali
*''Dogon A.D.'', an album by saxophonist Julius ...
, with whom Nuh was probably allied. The new pasha called Mansur
Mansour ( ar, منصور, Manṣūr); also spelled Mounsor, Monsur (Bengali), Mansoor, Manser, Mansur, Mansyur (Indonesian) or Mensur (Turkish), is a male Arabic name that means "He who is victorious", from the Arabic root '' naṣr'' (نصر), m ...
continued the war against the Songhai and again Nuh resorted to guerilla warfare. This situation lasted until 1599, when Nuh's followers became tired of the war and deposed him in favor of his brother Harun
Harun, also transliterated as Haroon or Haroun ( ar, هارون, ) is a common male given name of Arabic origin, related to the Hebrew name of the Prophet Aaron. Both are most likely of Ancient Egyptian origin, from ''aha rw'', meaning "warrior li ...
.
In 1609, the city of Djenné
Djenné ( Bambara: ߘߖߋߣߣߋ tr. Djenne; also known as Djénné, Jenné and Jenne) is a Songhai people town and an urban commune in the Inland Niger Delta region of central Mali. The town is the administrative centre of the Djenné Cercle, on ...
revolted against the Saadi pashas with the support of the Songhai. The Saadi were eventually able to regain the city, but with a lack of support from their homeland, they soon abandoned the area, leaving it to Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern A ...
and Fulbe
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. ...
nomads.
In 1612, Askia al-Amin came to power. His short reign of six years was followed by the rule of Askiya Dawud. Dawud killed many people during his reign including relatives and members of the military. His brother, Isma'il, fled to Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou;
Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrativ ...
and sought Saadi support to overthrow al-Amin. Isma'il returned to Songhai and deposed his brother in 1639. Upon attempting to send the foreign army back, he was deposed and replaced by a ruler that the pashas felt would be easier to deal with. This ruler was eventually removed by the Songhai people.
Decline
The Dendi Kingdom lasted for the next two and a half centuries witnessing increasingly unstable reigns, coups and counter-coups. When France entered the region, the empire was defensively unprepared. In 1901, the French deposed the last askia of Dendi, ending Songhai's control of either Mali or Niger until independence. Askia Rulers of Dendi (18th Century-Early 20th Century) *Askia Hanga (1700–1761) *Askia Samsu Beri (1761–1779) *Askia Hargani (1779–1793) *Askia Fodi Mayrumfa (1793) (1st time) *Askiak Samsu Keyna (1793–1798) *Fodi Mayrumfa (2nd time) *Askia Tomo (1805–1823) *Askia Bassaru Missi Ize (1823–1842) *Askia Bumi "Kodama Komi" (1842–1845) *Askia Koyze Baba (1845–1864) *Koyze Baba Baki (1864–1865) *Askia Wankoy (1865–1868) *Askia Bigo Farma (1868–1882) *Askia Dauda (1882–1887) *Askia Malla (1887–1901)Culture
The main ethnic groups in Dendi are the Tyenga, Zarma,Songhai proper
The Songhai proper (Songhay, Sangwai or Sonrai) are an ethnic group in the northwestern corner of Niger's Tillaberi Region, an area historically known in the country as '' Songhai''. They are a subgroup of the broader Songhai group. Even thoug ...
, Hausa people
The Hausa ( autonyms for singular: Bahaushe ( m), Bahaushiya ( f); plural: Hausawa and general: Hausa; exonyms: Ausa; Ajami: ) are the largest native ethnic group in Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the second most spoken language ...
, Bariba and the Fulbe
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. ...
. In the pre-colonial era, the Songhai, who migrated from the fallen Songhai empire, held political rule while the Tyenga, who had been the older residents mainly derived their power from their practice of Bori (a pre-Islamic traditional cult). These two ethic groups; the Songhai and the Tyenga mixed to form a new distinct ethnic group, the Dendi people
The Dendi are an ethnic group located in Benin, Niger, Nigeria and northern Togo mainly in the plains of the Niger River. They are part of the Songhai people. Derived from the Songhay language, the term "Dendi" translates to "down the river." Th ...
. They speak the Dendi Songhai dialect.
Like Birni-N'Konni
Birni-N'Konni (also Birnin-Konni or shortened to Konni/Bkonni) is a town in the Tahoua Region of Niger, lying immediately north of the border of Nigeria and west of seasonal Maggia River. It is an important market town and transport hub and as o ...
and Dogondoutchi
Dongondoutchi ("High Hill", also nicknamed Doutchi) is a commune in Niger. It is located about 300 km east of the capital Niamey and 40 km from the Nigerian border. It lies on national route 1 which links the capital to the towns of ...
, Dendi was a center of the Bori obsession cult, which almost completely disappeared as a result of Islamization by the mid-1950s. Merchants who moved from other regions made this region in the border triangle an important trading center in the second half of the 20th century where agricultural products such as rice, millet and corn from other regions are traded.
See also
*Askiya dynasty The Askiya dynasty, also known as the Askia dynasty, ruled the Songhai Empire at the height of that state's power. It was founded in 1493 by Askia Mohammad I, a general of the Songhai Empire who usurped the Sonni dynasty. The Askiya ruled from Gao ...
*Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical ...
*List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
The following is a list of Sunni Muslim dynasties.
Asia
Middle East Arabian Peninsula
* Banu Wajih (926–965)
*Sharif of Mecca (967–1925)
* Al Uyuniyun (1076–1253)
*Sulaymanids (1063–1174)
*Mahdids (1159–1174)
*Kathiri (Hadhramaut) ( ...
Sources
Worldstatesmen
Notes
References
* *External links
African Kingdoms
{{Sahelian kingdoms States and territories established in 1591 Songhai Empire Countries in precolonial Africa History of Niger States and territories disestablished in 1901 Muslim empires Former kingdoms