Debt crisis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Debt crisis is a situation in which a government (nation, state/province, county, or city etc.) loses the ability of paying back its governmental 
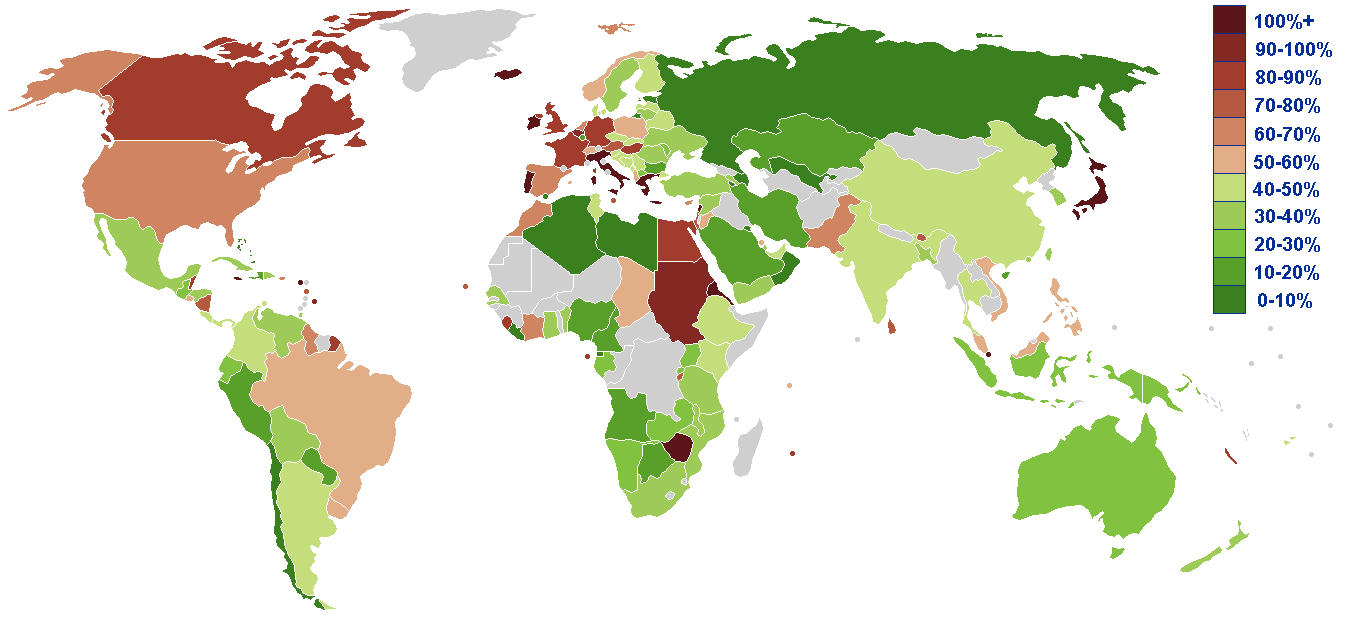 A debt crisis can also refer to a general term for a proliferation of massive
A debt crisis can also refer to a general term for a proliferation of massive
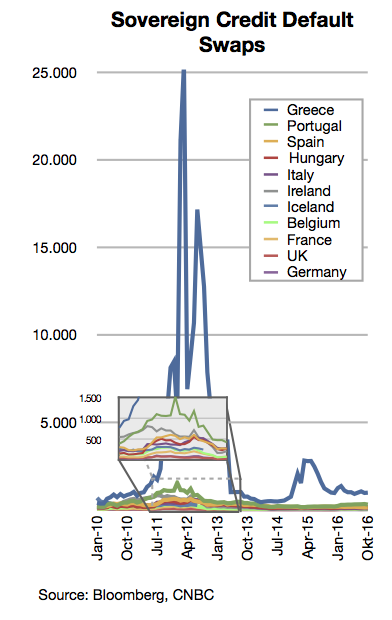 In 2007 the
In 2007 the
Mark Brown and Alex Chambers, Euromoney, September 2005 This allowed the sovereigns to mask their deficit and debt levels through a combination of techniques, including inconsistent accounting, off-balance-sheet transactions, and the use of complex currency and credit derivatives structures. From late 2009 on, after Greece's newly elected,
 2011 July – November - The debt crisis deepens. All three main credit ratings agencies cut Greece's to a level associated with substantial risk of default. In November 2011, Greece faced with a storm of criticism over his referendum plan, Mr Papandreou withdraws it and then announces his resignation.
2011 July – November - The debt crisis deepens. All three main credit ratings agencies cut Greece's to a level associated with substantial risk of default. In November 2011, Greece faced with a storm of criticism over his referendum plan, Mr Papandreou withdraws it and then announces his resignation.
 2012 February - December - The second bailout programme was ratified in February 2012. A total of was to be transferred in regular tranches through December 2014. The recession worsened and the government continued to dither over bailout program implementation. In December 2012 the Troika provided Greece with more debt relief, while the IMF extended an extra €8.2bn of loans to be transferred from January 2015 to March 2016.
2014 - In 2014 the outlook for the Greek economy was optimistic. The government predicted a structural surplus in 2014, opening access to the private lending market to the extent that its entire financing gap for 2014 was covered via private bond sales.
2015 June – July - The Greek parliament approved the referendum with no interim bailout agreement. Many Greeks continued to withdraw cash from their accounts fearing that capital controls would soon be invoked. On 13 July, after 17 hours of negotiations, Eurozone leaders reached a provisional agreement on a third bailout programme, substantially the same as their June proposal. Many financial analysts, including the largest private holder of Greek debt, private equity firm manager, Paul Kazarian, found issue with its findings, citing it as a distortion of net debt position.
2017 - The Greek finance ministry reported that the government's debt load is now €226.36 billion after increasing by €2.65 billion in the previous quarter. In June 2017, news reports indicated that the "crushing debt burden" had not been alleviated and that Greece was at the risk of defaulting on some payments.
2018 - Greek successfully exited (as declared) the bailouts on 20 August 2018.
2012 February - December - The second bailout programme was ratified in February 2012. A total of was to be transferred in regular tranches through December 2014. The recession worsened and the government continued to dither over bailout program implementation. In December 2012 the Troika provided Greece with more debt relief, while the IMF extended an extra €8.2bn of loans to be transferred from January 2015 to March 2016.
2014 - In 2014 the outlook for the Greek economy was optimistic. The government predicted a structural surplus in 2014, opening access to the private lending market to the extent that its entire financing gap for 2014 was covered via private bond sales.
2015 June – July - The Greek parliament approved the referendum with no interim bailout agreement. Many Greeks continued to withdraw cash from their accounts fearing that capital controls would soon be invoked. On 13 July, after 17 hours of negotiations, Eurozone leaders reached a provisional agreement on a third bailout programme, substantially the same as their June proposal. Many financial analysts, including the largest private holder of Greek debt, private equity firm manager, Paul Kazarian, found issue with its findings, citing it as a distortion of net debt position.
2017 - The Greek finance ministry reported that the government's debt load is now €226.36 billion after increasing by €2.65 billion in the previous quarter. In June 2017, news reports indicated that the "crushing debt burden" had not been alleviated and that Greece was at the risk of defaulting on some payments.
2018 - Greek successfully exited (as declared) the bailouts on 20 August 2018.
 Several thousand homeless and jobless Argentines found work as '' cartoneros'', cardboard collectors. An estimate in 2003 had 30,000 to 40,000 people scavenging the streets for cardboard to sell to recycling plants. Such desperate measures were common because of the unemployment rate, nearly 25%.
Argentine agricultural products were rejected in some international markets for fear that they might have been damaged by the chaos. The US Department of Agriculture put restrictions on Argentine food and drug exports.
Several thousand homeless and jobless Argentines found work as '' cartoneros'', cardboard collectors. An estimate in 2003 had 30,000 to 40,000 people scavenging the streets for cardboard to sell to recycling plants. Such desperate measures were common because of the unemployment rate, nearly 25%.
Argentine agricultural products were rejected in some international markets for fear that they might have been damaged by the chaos. The US Department of Agriculture put restrictions on Argentine food and drug exports.
 2005
2005
''Global Waves of Debt: Causes and Consequences''
Edited by M. Ayhan Kose, Peter Nagle, Franziska Ohnsorge, and Naotaka Sugawara.
debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
. When the expenditures
An expense is an item requiring an outflow of money, or any form of fortune in general, to another person or group as payment for an item, service, or other category of costs. For a tenant, rent is an expense. For students or parents, tuition is ...
of a government are more than its tax revenues
Tax revenue is the income that is collected by governments through taxation. Taxation is the primary source of government revenue. Revenue may be extracted from sources such as individuals, public enterprises, trade, royalties on natural resourc ...
for a prolonged period, the government may enter into a debt crisis. Various forms of governments finance their expenditures
An expense is an item requiring an outflow of money, or any form of fortune in general, to another person or group as payment for an item, service, or other category of costs. For a tenant, rent is an expense. For students or parents, tuition is ...
primarily by raising money
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money ar ...
through taxation
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, o ...
. When tax revenues
Tax revenue is the income that is collected by governments through taxation. Taxation is the primary source of government revenue. Revenue may be extracted from sources such as individuals, public enterprises, trade, royalties on natural resourc ...
are insufficient, the government can make up the difference by issuing debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
.
public debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
relative to tax revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive rev ...
s, especially in reference to Latin American countries during the 1980s, the United States and the European Union since the mid-2000s, and the Chinese debt crises of 2015.
Debt wall
Hitting the debt wall is a dire financial situation that can occur when anation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective identity of a group of people understood as defined by th ...
depends on foreign debt and/or investment to subsidize their budget and then commercial deficits
The government budget balance, also alternatively referred to as general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the overall difference between government revenues and spending. A positive balance is called a ''g ...
stop being the recipient of foreign capital flows. The lack of foreign capital flows reduces the demand for the local currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general ...
. The increased supply of currency coupled with an increased demand then causes a significant devaluation
In macroeconomics and modern monetary policy, a devaluation is an official lowering of the value of a country's currency within a fixed exchange-rate system, in which a monetary authority formally sets a lower exchange rate of the national curre ...
of the currency. This hurts the industrial base of the country since it can no longer afford to buy those imported supplies needed for production. Further, any obligations in foreign currency are now significantly more expensive to service both for the government and businesses.
This same concept has also been applied to personal debt. Specifically it has been applied to students who get in over their heads with student loans to finance their education.
Current and recent debt crises
Europe
European debt crisis
TheEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an debt crisis is a crisis affecting several eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU pol ...
countries since the end of 2009. Member states affected by this crisis were unable to repay their government debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
or to bail out indebted financial institutions without the assistance of third-parties (namely the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
, European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
, and the European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the prime component of the monetary Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's most important centra ...
). The causes of the crisis included high-risk lending and borrowing practices, burst real estate bubble
A real-estate bubble or property bubble (or housing bubble for residential markets) is a type of economic bubble that occurs periodically in local or global real-estate markets, and typically follow a land boom. A land boom is the rapid increa ...
s, and hefty deficit spending
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit; the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget ...
. As a result, investors have reduced their exposure to European investment products, and the value of the Euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
has decreased.
 In 2007 the
In 2007 the global financial crisis
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Global'' (Paul van Dyk album), 2003
* ''Global'' (Bunji Garlin album), 2007
* ''Global'' (Humanoid album), 1989
* ''Global'' (Todd Rundgren album), 2015
* Bruno ...
began with a crisis in the subprime mortgage
In finance, subprime lending (also referred to as near-prime, subpar, non-prime, and second-chance lending) is the provision of loans to people in the United States who may have difficulty maintaining the repayment schedule. Historically, subpri ...
market in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, and developed into a full-blown international banking crisis with the collapse of the investment bank Lehman Brothers
Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. ( ) was an American global financial services firm founded in 1847. Before filing for bankruptcy in 2008, Lehman was the fourth-largest investment bank in the United States (behind Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, ...
on 15 September 2008. The crisis was nonetheless followed by a global economic downturn, the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
. The European debt crisis
The European debt crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis or the European sovereign debt crisis, is a multi-year debt crisis that took place in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until the mid to late 2010s. Several eurozone me ...
, a crisis in the banking system of the European countries using the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
, followed later.
In sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
markets of PIIGS (Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
) created unprecedented funding pressure that spread to the national banks of the euro-zone countries and the European Central Bank (ECB) in 2010. The PIIGS announced strong fiscal reforms and austerity measures, but toward the end of the year, the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
once again suffered from stress.
Causes
The eurozone crisis resulted from the structural problem of the eurozone and a combination of complex factors, including the globalisation of finance, easy credit conditions during the 2002–2008 period that encouraged high-risk lending and borrowing practices, thefinancial crisis of 2007–08
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of f ...
, international trade imbalances, real estate bubble
A real-estate bubble or property bubble (or housing bubble for residential markets) is a type of economic bubble that occurs periodically in local or global real-estate markets, and typically follow a land boom. A land boom is the rapid increa ...
s that have since burst; the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
of 2008–2012, fiscal policy choices related to government revenues and expenses, and approaches used by states to bail out troubled banking industries and private bondholders, assuming private debt burdens or socializing losses.
In 1992, members of the European Union signed the Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve member states of the European Communities, it announced "a new stage in the ...
, under which they pledged to limit their deficit spending
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit; the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget ...
and debt levels. However, in the early 2000s, some EU member states were failing to stay within the confines of the Maastricht criteria and turned to securitising future government revenues to reduce their debts and/or deficits, sidestepping best practice and ignoring international standards."How Europe's Governments have Enronized their debts"Mark Brown and Alex Chambers, Euromoney, September 2005 This allowed the sovereigns to mask their deficit and debt levels through a combination of techniques, including inconsistent accounting, off-balance-sheet transactions, and the use of complex currency and credit derivatives structures. From late 2009 on, after Greece's newly elected,
PASOK
The Panhellenic Socialist Movement ( el, Πανελλήνιο Σοσιαλιστικό Κίνημα, Panellínio Sosialistikó Kínima, ), known mostly by its acronym PASOK, (; , ) is a social-democratic political party in Greece. Until 2012, it ...
government stopped masking its true indebtedness and budget deficit, fears of sovereign default
A sovereign default is the failure or refusal of the
government of a sovereign state to pay back its debt in full when due. Cessation of due payments (or receivables) may either be accompanied by that government's formal declaration that it wi ...
s in certain European states
The list below includes all entities falling even partially under any of the various common definitions of Europe, geographical or political. Fifty generally recognised sovereign states, Kosovo with limited, but substantial, international reco ...
developed in the public, and the government debt of several states was downgraded. The crisis subsequently spread to Ireland and Portugal, while raising concerns about Italy, Spain, and the European banking system, and more fundamental imbalances within the eurozone.
Other European debt crises
Greek debt crisis
Timeline of Greek debt crisis
2009 December - One of the world's three leading rating agencies downgrades Greece's credit rating amid fears the government could default on its ballooning debt. PM Papandrou announces programme of tough public spending cuts. 2010 January–March - Two more rounds of tough austerity measures are announced by government, and government faces mass protests and strikes. 2010 April–May - The deficit was estimated that up to 70% of Greek government bonds were held by foreign investors, primarily banks. After publication of GDP data which showed an intermittent period of recession starting in 2007, credit rating agencies then downgraded Greek bonds to junk status in late April 2010. On 1 May 2010, the Greek government announced a series of austerity measures. 2011 July – November - The debt crisis deepens. All three main credit ratings agencies cut Greece's to a level associated with substantial risk of default. In November 2011, Greece faced with a storm of criticism over his referendum plan, Mr Papandreou withdraws it and then announces his resignation.
2011 July – November - The debt crisis deepens. All three main credit ratings agencies cut Greece's to a level associated with substantial risk of default. In November 2011, Greece faced with a storm of criticism over his referendum plan, Mr Papandreou withdraws it and then announces his resignation.
 2012 February - December - The second bailout programme was ratified in February 2012. A total of was to be transferred in regular tranches through December 2014. The recession worsened and the government continued to dither over bailout program implementation. In December 2012 the Troika provided Greece with more debt relief, while the IMF extended an extra €8.2bn of loans to be transferred from January 2015 to March 2016.
2014 - In 2014 the outlook for the Greek economy was optimistic. The government predicted a structural surplus in 2014, opening access to the private lending market to the extent that its entire financing gap for 2014 was covered via private bond sales.
2015 June – July - The Greek parliament approved the referendum with no interim bailout agreement. Many Greeks continued to withdraw cash from their accounts fearing that capital controls would soon be invoked. On 13 July, after 17 hours of negotiations, Eurozone leaders reached a provisional agreement on a third bailout programme, substantially the same as their June proposal. Many financial analysts, including the largest private holder of Greek debt, private equity firm manager, Paul Kazarian, found issue with its findings, citing it as a distortion of net debt position.
2017 - The Greek finance ministry reported that the government's debt load is now €226.36 billion after increasing by €2.65 billion in the previous quarter. In June 2017, news reports indicated that the "crushing debt burden" had not been alleviated and that Greece was at the risk of defaulting on some payments.
2018 - Greek successfully exited (as declared) the bailouts on 20 August 2018.
2012 February - December - The second bailout programme was ratified in February 2012. A total of was to be transferred in regular tranches through December 2014. The recession worsened and the government continued to dither over bailout program implementation. In December 2012 the Troika provided Greece with more debt relief, while the IMF extended an extra €8.2bn of loans to be transferred from January 2015 to March 2016.
2014 - In 2014 the outlook for the Greek economy was optimistic. The government predicted a structural surplus in 2014, opening access to the private lending market to the extent that its entire financing gap for 2014 was covered via private bond sales.
2015 June – July - The Greek parliament approved the referendum with no interim bailout agreement. Many Greeks continued to withdraw cash from their accounts fearing that capital controls would soon be invoked. On 13 July, after 17 hours of negotiations, Eurozone leaders reached a provisional agreement on a third bailout programme, substantially the same as their June proposal. Many financial analysts, including the largest private holder of Greek debt, private equity firm manager, Paul Kazarian, found issue with its findings, citing it as a distortion of net debt position.
2017 - The Greek finance ministry reported that the government's debt load is now €226.36 billion after increasing by €2.65 billion in the previous quarter. In June 2017, news reports indicated that the "crushing debt burden" had not been alleviated and that Greece was at the risk of defaulting on some payments.
2018 - Greek successfully exited (as declared) the bailouts on 20 August 2018.
Greek debt restructuring
It stands out in the history of sovereign defaults. Greek debt restructuring of 2012 achieved very large debt relief – with minimal financial disruption, using a combination of new legal techniques, exceptionally large cash incentives, and official sector pressure on key creditors. But it did so at a cost. The timing and design of the restructuring left money on the table from the perspective of Greece, set precedents and created a large risk for taxpayer – particularly in its very generous treatment of holdout creditors – that are likely to make future debt restructurings in Europe more difficult.Effects
To take considerations that the most characteristic feature of the Greek social landscape in the current crisis is the steep rise in joblessness. Theunemployment rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refere ...
had fluctuated around the 10 per cent mark in the first half of the previous decade. It then began to fall until May 2008, when unemployment figures reached their lowest level for over a decade (325,000 workers or 6.6 per cent of the labour force). While job losses involved an unusually high number of workers, loss of earnings for those still in employment was also significant. Average real gross earnings for employees have lost more ground since the onset of the crisis than they gained in the nine years before that.
In February 2012, it was reported that 20,000 Greeks had been made homeless during the preceding year, and that 20 per cent of shops in the historic city centre of Athens were empty.
* Irish financial crisis
* Portuguese economic crisis
Latin America
Argentine debt crisis
Background
Argentina's turbulent economic history: Argentina has a history of chronic economic, monetary and political problems. Economic reforms of the 1990s. In 1989, Carlos Menem became president. After some fumbling, he adopted a free-market approach that reduced the burden of government by privatizing, deregulating, cutting some tax rates, and reforming the state. The centerpiece of Menem's policies was the Convertibility Law, which took effect on 1 April 1991. Argentina's reforms were faster and deeper than any country of the time outside the former communist bloc. Real GDP grew more than 10 percent a year in 1991 and 1992, before slowing to a more normal rate of slightly below 6 percent in 1993 and 1994. The1998–2002 Argentine great depression
The Argentine Great Depression was an economic depression in Argentina, which began in the third quarter of 1998 and lasted until the second quarter of 2002. It followed the fifteen years stagnation and a brief period of free-market reforms.
...
was an economic depression
An economic depression is a period of carried long-term economical downturn that is result of lowered economic activity in one major or more national economies. Economic depression maybe related to one specific country were there is some economic ...
in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, which began in the third quarter of 1998 and lasted until the second quarter of 2002. It almost immediately followed the 1974–1990 Great Depression after a brief period of rapid economic growth.
Effects
Debt restructuring history
 2005
2005 Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
was one of the largest single investors in Argentine bonds following these developments, which bought a total of more than $5 billion in restructured Argentine bonds from 2005 to 2007. Between 2001 and 2006, Venezuela was the largest single buyer of Argentina's debt. In 2005 and 2006, Banco Occidental de Descuento
Banco Occidental de Descuento (BOD) (English: ''Western Discount Bank'') (WDB) was a Venezuelan bank. With around 6.6% of the Venezuelan market, it was Venezuela's fifth-largest bank in 2009.
The owner of BOD is the Grupo Financiero BOD (English: ...
and Fondo Común, owned by Venezuelan bankers Victor Vargas Irausquin and Victor Gill Ramirez respectively, bought most of Argentina's outstanding bonds and resold them on to the market. The banks bought $100 million worth of Argentine bonds and resold the bonds for a profit of approximately $17 million. People who criticize Vargas have said that he made a $1 billion "backroom deal" with swaps of Argentine bonds as a sign of his friendship with Chavez. The ''Financial Times'' interviewed financial analysts in the United States who said that the banks profited from the resale of the bonds; the Venezuelan government did not profit.
Bondholders who had accepted the 2005 swap (three out of four did so) saw the value of their bonds rise 90% by 2012, and these continued to rise strongly during 2013.
2010 On 15 April 2010, the debt exchange was re-opened to bondholders who rejected the 2005 swap; 67% of these latter accepted the swap, leaving 7% as holdouts. Holdouts continued to put pressure on the government by attempting to seize Argentine assets abroad, and by suing to attach future Argentine payments on restructured debt to receive better treatment than cooperating creditors.
The government reached an agreement in 2005 by which 76% of the defaulted bonds were exchanged for other bonds at a nominal value of 25 to 35% of the original and at longer terms. A second debt restructuring in 2010 brought the percentage of bonds out of default to 93%, but some creditors have still not been paid. Foreign currency denominated debt thus fell as a percentage of GDP from 150% in 2003 to 8.3% in 2013.
U.S. interventions
The U.S. foreign policy known as the Roosevelt Corollary asserted that the United States would intervene on behalf of European countries to avoid those countries intervening militarily to press their interests, including repayment of debts. This policy was used to justify interventions in the early 1900s in Venezuela, Cuba, Nicaragua, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic (1916–1924).North America
*United States debt-ceiling crisis of 2011
The 2011 United States debt-ceiling crisis was a stage in the ongoing political debate in the United States Congress about the appropriate level of government spending and its effect on the national debt and deficit. The debate centered on th ...
* United States debt-ceiling crisis of 2013
* Puerto Rican debt crisis (2015-present)
See also
*Debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
* Debt of developing countries
The debt of developing countries usually refers to the external debt incurred by governments of developing countries.
There have been several historical episodes of governments of developing countries borrowing in quantities beyond their abilit ...
* Government debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit oc ...
* List of countries by credit rating
* List of countries by net international investment position __FORCETOC__
The net international investment position (NIIP) is the difference in the external financial assets and liabilities of a country. External debt of a country includes government debt and private debt. External assets publicly and privat ...
* List of countries by public debt
Below is a list of countries and territories by government debt , public debt (also called government debt or sovereign debt). ''Gross'' government debt is government financial liabilities that are debt instruments. A ''debt instrument'' is a f ...
* Monetary sovereignty
* Odious debt
* Sovereign default
A sovereign default is the failure or refusal of the
government of a sovereign state to pay back its debt in full when due. Cessation of due payments (or receivables) may either be accompanied by that government's formal declaration that it wi ...
* State (polity)
A state is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory. There is no undisputed definition of a state. One widely used definition comes from the German sociologist Max Weber: a "st ...
* Tax
* World debt
Further reading
* World Bank, 2019''Global Waves of Debt: Causes and Consequences''
Edited by M. Ayhan Kose, Peter Nagle, Franziska Ohnsorge, and Naotaka Sugawara.
References
{{Financial crises Government debt Financial crises