Cumbric language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cumbric is an extinct
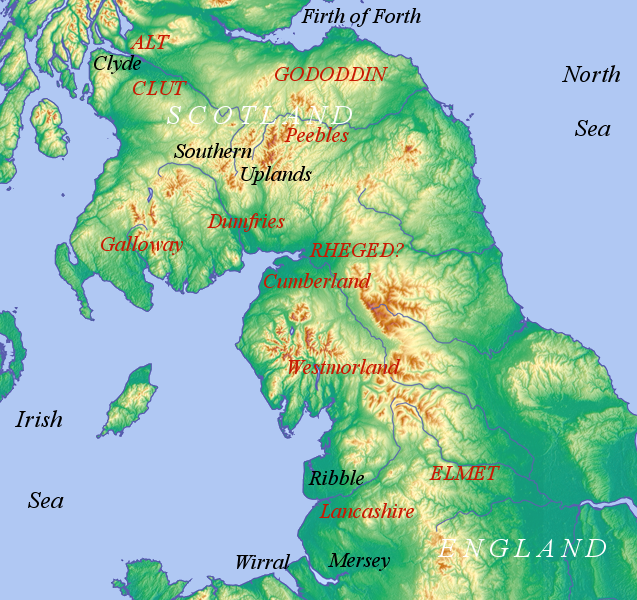 The Latinate term
The Latinate term
 The evidence from Cumbric comes almost entirely through secondary sources, since no known contemporary written records of the language survive. The majority of evidence comes from place names of the north of England and the south of Scotland. Other sources include the personal names of Strathclyde Britons in Scottish, Irish, and Anglo-Saxon sources, and a few Cumbric words surviving into the
The evidence from Cumbric comes almost entirely through secondary sources, since no known contemporary written records of the language survive. The majority of evidence comes from place names of the north of England and the south of Scotland. Other sources include the personal names of Strathclyde Britons in Scottish, Irish, and Anglo-Saxon sources, and a few Cumbric words surviving into the
Cumbric.org - Language and History
h2>
Celtic language
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves ...
of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
in the ''Hen Ogledd
Hen Ogledd (), meaning the Old North, is the historical region that was inhabited by the Celtic Britons, Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages, now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands, alongside the fello ...
'' or "Old North", in Northern England
Northern England, or the North of England, refers to the northern part of England and mainly corresponds to the Historic counties of England, historic counties of Cheshire, Cumberland, County Durham, Durham, Lancashire, Northumberland, Westmo ...
and the southern Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( or , ; , ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland.
The region is characterised by its relatively flat or gently rolling terrain as opposed to the mountainous landscapes of the Scottish Highlands. This area includes ci ...
. It was closely related to Old Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, ha ...
and the other Brittonic languages
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; ; ; and ) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic languages; the other is Goidelic. It comprises the extant languages Breton, Cornish, and Welsh. The name ''Brythonic'' ...
. Place-name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales are a series of valleys, or Dale (landform), dales, in the Pennines, an Highland, upland range in England. They are mostly located in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of North Yorkshire, but extend into C ...
. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (, "valley of the River Clyde, Clyde"), also known as Cumbria, was a Celtic Britons, Brittonic kingdom in northern Britain during the Scotland in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages. It comprised parts of what is now southern Scotland an ...
into the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
.
Problems with terminology
Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reconstructed Brittonic meaning "fellow countrymen"). The Welsh and the Cumbric-speaking people of what are now southern Scotland and northern England probably felt they were actually one ethnic group. Old Irish speakers called them "Britons", , or . The Norse called them . In Latin, the terms and were Latinised asCambria
Cambria is a name for Wales, being the Latinised form of the Welsh name for the country, . The term was not in use during the Roman period (when Wales had not come into existence as a distinct entity) or the early medieval period. After the ...
and Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancash ...
respectively. In Medieval Latin, the English term Welsh became ("of Wales"), while the term referred to Cumbrians ("of Cumbria").Forbes, A. P. (1874) ''Lives of St. Ninian and St. Kentigern: compiled in the twelfth century'' However, in Scots, a Cumbric speaker seems to have been called – from the Scots "Welsh".
 The Latinate term
The Latinate term Cambria
Cambria is a name for Wales, being the Latinised form of the Welsh name for the country, . The term was not in use during the Roman period (when Wales had not come into existence as a distinct entity) or the early medieval period. After the ...
is often used for Wales; nevertheless, the ''Life of St Kentigern'' ( 1200) by Jocelyn of Furness has the following passage:
John T. Koch defined the specifically Cumbric region as "the area approximately between the line of the River Mersey
The River Mersey () is a major river in North West England. Its name derives from Old English and means "boundary river", possibly referring to its having been a border between the ancient kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria. For centuries it h ...
and the Forth-Clyde Isthmus", but went on to include evidence from the Wirral Peninsula
The Wirral Peninsula (), known locally as the Wirral, is a peninsula in North West England. The roughly rectangular peninsula is about long and wide, and is bounded by the Dee Estuary to the west, the Mersey Estuary to the east, and Liverpo ...
in his discussion and did not define its easterly extent. Kenneth H. Jackson described Cumbric as "the Brittonic dialect of Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish ...
, Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland''R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref>) is an area of North West England which was Historic counties of England, historically a county. People of the area ...
, northern Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to ...
, and south-west Scotland" and went on to define the region further as being bound in the north by the Firth of Clyde, in the south by the River Ribble and in the east by the Southern Scottish Uplands and the Pennine Ridge. The study Brittonic Language in the Old North by Alan G. James, concerned with documenting place- and river-names as evidence for Cumbric and the pre-Cumbric Brittonic dialects of the region ''Yr Hen Ogledd'', considered Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond (; ) is a freshwater Scottish loch which crosses the Highland Boundary Fault (HBF), often considered the boundary between the lowlands of Central Scotland and the Highlands.Tom Weir. ''The Scottish Lochs''. pp. 33-43. Published by ...
the northernmost limit of the study with the southernmost limits being Liverpool Bay
Liverpool Bay is a bay of the Irish Sea between northeast Wales, Cheshire, Lancashire and Merseyside to the east of the Irish Sea. The bay is a classic example of a region of freshwater influence. Liverpool Bay has historically suffered from redu ...
and the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Trent, Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms ...
, although a few more southerly place-names in Cheshire and, to a lesser extent, Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands of England. It borders Greater Manchester, West Yorkshire, and South Yorkshire to the north, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south-east, Staffordshire to the south a ...
and Staffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation ''Staffs''.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England. It borders Cheshire to the north-west, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, ...
were also included.
Available evidence
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
in southwest Scotland as legal terms. Although the language is long extinct, traces of its vocabulary arguably have persisted into the modern era in the form of " counting scores" and in a handful of dialectal words.
From this scanty evidence, little can be deduced about the singular characteristics of Cumbric, not even the name by which its speakers referred to it. However, linguists generally agree that Cumbric was a Western Brittonic language closely related to Welsh and, more distantly, to Cornish and Breton.
Around the time of the battle described in the poem ''Y Gododdin
''Y Gododdin'' () is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia ...
'', c. 600, Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic (; ; ), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, is a Celtic language historically spoken in Britain and Brittany from which evolved the later and modern Brittonic languages.
It is a form of Insular Cel ...
is believed to have been transitioning into its daughter languages: Cumbric in North Britain, Old Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, ha ...
in Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
, and Southwestern Brittonic, the ancestor of Cornish and Breton. Kenneth Jackson concludes that the majority of changes that transformed British into Primitive Welsh belong to the period from the middle of the fifth to the end of the sixth century. This involved syncope and the loss of final syllables. If the poem ultimately dates to this time, it would have originally been written in an early form of Cumbric, the usual name for the Brythonic speech of the Hen Ogledd; Jackson suggested the name "Primitive Cumbric" for the dialect spoken at the time. However, scholars date the poem to between the 7th and the early 11th centuries, and the earliest surviving manuscript of it dates to the 13th, written in Old Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, ha ...
and Middle Welsh
Middle Welsh (, ) is the label attached to the Welsh language of the 12th to 15th centuries, of which much more remains than for any earlier period. This form of Welsh developed directly from Old Welsh ().
Literature and history
Middle Welsh is ...
.
Place names
Cumbric place-names occur in Scotland south of the firths of Forth and Clyde. Brittonic names north of this line arePictish
Pictish is an extinct Brittonic Celtic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from late antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geog ...
. Cumbric names are also found commonly in the historic county of Cumberland and in bordering areas of Northumberland. They are less common in Westmorland, east Northumberland, and Durham, with some in Lancashire and the adjoining areas of North and West Yorkshire. Approaching Cheshire, late Brittonic placenames are probably better characterised as Welsh rather than as Cumbric. As noted below, however, any clear distinction between Cumbric and Welsh is difficult to prove. Many Brittonic place-names remain in these regions which should not be described as Cumbric, such as Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
, Manchester
Manchester () is a city and the metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester, England. It had an estimated population of in . Greater Manchester is the third-most populous metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.92&nbs ...
, Wigan
Wigan ( ) is a town in Greater Manchester, England. The town is midway between the two cities of Manchester, to the south-east, and Liverpool, to the south-west. It is the largest settlement in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan and is its ad ...
and York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
, because they were coined in a period before Brittonic split into Cumbric and its sister dialects.
Some of the principal towns and cities of the region have names of Cumbric origin, including:
*Bathgate
Bathgate ( or , ) is a town in West Lothian, Scotland, west of Livingston, Scotland, Livingston and adjacent to the M8 motorway (Scotland), M8 motorway. Nearby towns are Linlithgow, Livingston, and West Calder. A number of villages fall under ...
, West Lothian: meaning 'boar wood' (Welsh 'wild boar' + 'forest, wood').
* Bryn, Metropolitan Borough of Wigan: from the word meaning "hill" (W. ''bryn'').
* Carlisle, Cumberland: recorded as in the Roman period; the word 'fort' was added later.Ekwall, E. (1960) ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place-names'', 4th ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press. The Welsh form is derived by regular sound changes from the Romano-British name.
*Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
, Scotland: widely believed to derive from words cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language.
Because language change can have radical effects on both the s ...
with glas 'green' and the Welsh gae, 'field' (possibly that below Glasgow Cathedral
Glasgow Cathedral () is a parish church of the Church of Scotland in Glasgow, Scotland. It was the cathedral church of the Archbishop of Glasgow, and the mother church of the Archdiocese of Glasgow and the province of Glasgow, from the 12th ...
).
*Lanark
Lanark ( ; ; ) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, located 20 kilometres to the south-east of Hamilton, South Lanarkshire, Hamilton. The town lies on the River Clyde, at its confluence with Mouse Water. In 2016, the town had a populatio ...
, Lanarkshire: from the equivalent of Welsh ' glade, clearing'.
* Penicuik, Midlothian: from words meaning 'hill of the cuckoo
Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae ( ) family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes ( ). The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals, and anis. The coucals and anis are somet ...
' (W. ).
* Penrith, Westmorland & Furness: meaning 'chief ford' (Welsh 'head, chief' + 'ford').
Several supposed Cumbric elements occur repeatedly in place names of the region. The following table lists some of them according to the modern Welsh equivalent:
Some Cumbric names have historically been replaced by Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
, Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
, or Scots equivalents, and in some cases the different forms occur in the historical record.
*Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
occurs in early Welsh texts as and in medieval Scottish records as (Gaelic ), all meaning 'fort of Eidyn'.
*Falkirk
Falkirk ( ; ; ) is a town in the Central Lowlands of Scotland, historically within the county of Stirlingshire. It lies in the Forth Valley, northwest of Edinburgh and northeast of Glasgow.
Falkirk had a resident population of 32,422 at the ...
similarly has several alternative medieval forms meaning 'speckled church': etc. from Cumbric (Welsh ); etc. from Gaelic (modern Gaelic ); etc. from Scots (in turn from Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
).
* Kirkintilloch began as a Cumbric name recorded as in the 10th century, but was partly replaced by the Gaelic words 'head' + 'hillock' later on (plus 'church' from Scots again).
* Kinneil derives from Gaelic 'head of the [Antonine] Wall' but it was recorded by Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
as (Welsh ), and by Bede
Bede (; ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, Bede of Jarrow, the Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable (), was an English monk, author and scholar. He was one of the most known writers during the Early Middle Ages, and his most f ...
as , which appears to be a merger of Cumbric and Gaelic.
Derivatives of Common Brittonic ''*magno'', such as Welsh ''maen'' and Cornish ''men'', mean "stone", particularly one with a special purpose or significance. In the Cumbric region, the word "Man" frequently occurs in geographical names associated with standing stones (most notably the Old Man of Coniston
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
* Old, Northamptonshire, England
* Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, ...
) and it is possible, albeit "hard to say" according to Alan G. James, if the Cumbric reflex ''*main'' had any influence on these.
Counting systems
Among the evidence that Cumbric might have influenced local English dialects are a group ofcounting
Counting is the process of determining the number of elements of a finite set of objects; that is, determining the size of a set. The traditional way of counting consists of continually increasing a (mental or spoken) counter by a unit for ever ...
systems, or scores, recorded in various parts of northern England. Around 100 of these systems have been collected since the 18th century; the scholarly consensus is that these derive from a Brittonic language closely related to Welsh.Filppula, Klemola, & Paulasto, pp. 102–105. Though they are often referred to as "sheep-counting numerals", most recorded scores were not used to count sheep, but in knitting
Knitting is a method for production of textile Knitted fabric, fabrics by interlacing yarn loops with loops of the same or other yarns. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done Hand knitting, by hand or Knitting machi ...
or for children's games
This is a list of games that are played by children. Traditional children's games do not include commercial products such as board games but do include games which require props such as hopscotch or marbles (toys go in List of toys unless the toy ...
or nursery rhyme
A nursery rhyme is a traditional poem or song for children in Britain and other European countries, but usage of the term dates only from the late 18th/early 19th century. The term Mother Goose rhymes is interchangeable with nursery rhymes.
Fr ...
s. These scores are often suggested to represent a survival from medieval Cumbric, a theory first popularized in the 19th century. However, later scholars came to reject this idea, suggesting instead that the scores were later imports from either Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
or Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, but in light of the dearth of evidence one way or another, Markku Filppula, Juhani Klemola, and Heli Paulasto posit that it remains plausible that the counting systems are indeed of Cumbric origin.
Cumbric, in common with other Brythonic languages, used a vigesimal
A vigesimal ( ) or base-20 (base-score) numeral system is based on 20 (number), twenty (in the same way in which the decimal, decimal numeral system is based on 10 (number), ten). ''wikt:vigesimal#English, Vigesimal'' is derived from the Latin a ...
counting system, i.e. numbering up to twenty, with intermediate numbers for ten and fifteen. Therefore, after numbering one to ten, numbers follow the format one-and-ten, two-and-ten etc. to fifteen, then one-and-fifteen, two-and-fifteen to twenty. The dialect words for the numbers themselves show much variation across the region. (see chart)
Scots and English
A number of words occurring in the Scots language and Northern English dialects have been proposed as being of possible Brittonic origin. Ascertaining the real derivation of these words is far from simple, due in part to the similarities between some cognates in the Brittonic andGoidelic languages
The Goidelic ( ) or Gaelic languages (; ; ) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historically formed a dialect continuum stretching from Ireland through the Isle o ...
and the fact that borrowing took place in both directions between these languages.
Another difficulty lies with other words which were taken into Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
, as in many cases it is impossible to tell whether the borrowing is directly from Brittonic or not (e.g. ''Brogat'', ''Crag'', below). The following are possibilities:
* ''Bach'' – 'cowpat' (cf. Welsh 'dung', Gaelic )
* ''Baivenjar'' – 'mean fellow' (Welsh 'scoundrel')
* ''Brat'' – 'apron'. The word appears in Welsh (with meanings 'rag, cloth' and 'pinafore'), Scots and northern English dialects, but may be an Old English borrowing from Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic (, Ogham, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ; ; or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic languages, Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from 600 to 900. The ...
.
* ''Brogat'' – a type of mead
Mead (), also called honey wine, and hydromel (particularly when low in alcohol content), is an alcoholic beverage made by fermenting honey mixed with water, and sometimes with added ingredients such as fruits, spices, grains, or hops. The alco ...
(Welsh ' bragget' – also found in Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for '' The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He ...
)
* ''Coble'' – a type of small, flat-bottomed boat (also in Northeast England), akin to Welsh '' ceubal'' 'a hollow' and Latin '' caupulus''; distinct from the round-bottomed coracle.
* ''Crag'' – 'rocks'. Either from Brittonic (Welsh ) or Goidelic (Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
).
* ''Croot'' – 'small boy' (Welsh , Gaelic 'small person', 'humpback/hunchback')
* ''Croude'' – a type of small harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or ...
or lyre
The lyre () (from Greek λύρα and Latin ''lyra)'' is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute family of instruments. In organology, a ...
(as opposed to the larger ; Welsh 'bowed lyre', later 'fiddle
A fiddle is a Bow (music), bowed String instrument, string musical instrument, most often a violin or a bass. It is a colloquial term for the violin, used by players in all genres, including European classical music, classical music. Althou ...
', Gaelic )
* ''Lum'' – Scottish word for 'chimney' (Middle Welsh
Middle Welsh (, ) is the label attached to the Welsh language of the 12th to 15th centuries, of which much more remains than for any earlier period. This form of Welsh developed directly from Old Welsh ().
Literature and history
Middle Welsh is ...
)
Equivalence with Old Welsh
The linguistic term Cumbric is defined according to geographical rather than linguistic criteria: that is, it refers to the variety of Brittonic spoken within a particular region of North Britain and implies nothing about that variety except that it was geographically distinct from other varieties. This has led to a discussion about the nature of Cumbric and its relationship with other Brittonic languages, in particular withOld Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, ha ...
.
Linguists appear undecided as to whether Cumbric should be considered a separate language, or a dialect of Old Welsh. Koch calls it a dialect but goes on to say that some of the place names in the Cumbric region "clearly reflect a developed medieval language, much like Welsh, Cornish or Breton". Jackson also calls it a dialect but points out that "to call it Pr mitiveW lshwould be inaccurate",Jackson, K. H. (1956): Language and History in Early Britain, Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press so clearly views it as distinct in some meaningful respect.
It has been suggested that Cumbric was more closely aligned to the Pictish language
Pictish is an extinct Brittonic Celtic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from late antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geo ...
than to Welsh, though there is considerable debate regarding the classification of that language. On the basis of place name evidence it has also been proposed that all three languages were very similar. In all probability, the "Cumbric" of Lothian more nearly resembled the "Pictish" of adjacent Fife than the Welsh dialects spoken over 300 miles away in Dyfed and accordingly, Alan G. James has argued that all 3 languages may have formed a continuum.
The whole question is made more complex because there is no consensus as to whether any principled distinction can be made between languages and dialects.
Below, some of the proposed differences between Cumbric and Old Welsh are discussed.
Retention of Brittonic ''*rk''
In Welsh, Cornish, and Breton, the Common Brittonic cluster ''*rk'' was spirantized to (Welsh ''rch'', Cornish ''rgh'', Breton ''rc'h'') but a number of place names appear to show Cumbric retained the stop in this position.Lanark
Lanark ( ; ; ) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, located 20 kilometres to the south-east of Hamilton, South Lanarkshire, Hamilton. The town lies on the River Clyde, at its confluence with Mouse Water. In 2016, the town had a populatio ...
and Lanercost are thought to contain the equivalent of Welsh ''llannerch'' 'clearing'.Mills, A.D. (2003): Oxford Dictionary of British Place Names, Oxford: OUP
There is evidence to the contrary, however, including the place names Powmaughan and Maughanby (containing Welsh ''Meirchion'') and the word ''kelchyn'' (related to Welsh ''cylch''). Jackson concludes that the change of Common Brittonic ''*rk'' > "''may'' have been somewhat later in Cumbric".
Retention of Brittonic ''*mb''
There is evidence to suggest that the consonant cluster ''mb'' remained distinct in Cumbric later than the time it was assimilated to ''mm'' in Welsh, Cornish, and Breton. The cluster remains in: * Old English ''Cumbraland'' "land of Cumbrians" (from Common Brittonic ''*kombrogi'', whence Welsh ''Cymru'' "Wales" also originates). * ''Crombocwater'' and ''Crombokwatre'', two 14th-century records of Crummock Water and ''Crombok'' an 1189 record for Crummack Dale inYorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the ...
(from Common Brittonic ''*Crumbāco-'' "curved one" (W ''crwm'' "curved")).
* Cam Beck, the name of a stream in north Cumbria recorded as ''Camboc'' (1169) and believed to be from Common Brittonic ''*Cambāco-'' "crooked stream" (W ''cam'', CB ''kamm'').
* Crimple Beck, Yorkshire, which is said to derive from Common Brittonic. ''*Crumbopull-'' "crooked pool". Here the ''b'' is assumed to have survived late enough to cause provection.
Jackson notes that only in the north does the cluster appear in place names borrowed after ''circa'' 600AD and concludes that it may have been a later dialectal survival here.
Syncope
Jackson notes the legal term ''galnys'', equivalent to Welsh ''galanas
''Galanas'' in Welsh law was a payment made by a Kin punishment, killer and his family to the family of his or her victim. It is similar to éraic in Ireland and the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon weregild.
Definition
The details of galanas were lai ...
'', may show syncope of internal syllables to be a feature of Cumbric. Further evidence is wanting, however.
Devoicing
JamesJames, A. G. (2008): 'A Cumbric Diaspora?' in Padel and Parsons (eds.) A Commodity of Good Names: essays in honour of Margaret Gelling, Shaun Tyas: Stamford, pp 187–203 mentions that devoicing appears to be a feature of many Cumbric place names. Devoicing of word final consonants is a feature of modern Breton and, to an extent, Cornish. WatsonWatson, W. J. (1926): History of the Celtic Place-Names of Scotland, Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press notes initial devoicing in Tinnis Castle (in Drumelzier) (compare Welsh ''dinas'' 'fortress, city') as an example of this, which can also be seen in the CornishTintagel
Tintagel () or Trevena (, meaning ''Village on a Mountain'') is a civil parishes in England, civil parish and village situated on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village and nearby Tintagel Castle ...
, ''din'' 'fort'. Also notable are the different English names of two Welsh towns named ''Dinbych'' ('little fort'); Denbigh
Denbigh ( ; ) is a market town and a community (Wales), community in Denbighshire, Wales. It was the original county town of the Denbighshire (historic), historic county of Denbighshire created in 1536. Denbigh's Welsh name () translates to ...
and Tenby
Tenby () is a seaside town and community (Wales), community in the county of Pembrokeshire, Wales. It lies within Carmarthen Bay.
Notable features include of sandy beaches and the Pembrokeshire Coast Path, the 13th-century Tenby Town Walls, me ...
.
There is also a significant number of place names which do not support this theory. Devoke Water and Cumdivock (< ''Dyfoc'', according to Ekwall) and Derwent (< Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic (; ; ), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, is a Celtic language historically spoken in Britain and Brittany from which evolved the later and modern Brittonic languages.
It is a form of Insular Cel ...
''Derwentiō'') all have initial . The name Calder (< Brit. ''*Caletodubro-'') in fact appears to show a voiced Cumbric consonant where Welsh has ''Calettwr'' by provection, which Jackson believes reflects an earlier stage of pronunciation. Jackson also notes that Old English had no internal or final , so would be borrowed with by sound substitution. This can be seen in names with ''c, k, ck'' (e.g. Cocker < Brittonic ''*'', Eccles < Brittonic ''eglēsia'').
Loss of
The Cumbric personal names Gospatrick, Gososwald and Gosmungo meaning 'servant of St...' (Welsh, Cornish, Breton ''gwas'' 'servant, boy') and the Galloway dialect word ''gossock'' 'short, dark haired inhabitant of Wigtownshire' (W. ''gwasog'' 'a servant') apparently show that the Cumbric equivalent of Welsh and Cornish ''gwas'' & B ''gwaz'' 'servant' was ''*gos''. Jackson suggests that it may be a survival of the originalProto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the hypothetical ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly Linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed throu ...
form of the word in –o- (i.e. ''*uɸo-sto'').
This idea is disputed by the ''Dictionary of the Scots Language''; and the occurrence in Gospatrick's Writ of the word ''wassenas'' 'dependants', thought to be from the same word ''gwas'', is evidence against Jackson's theory. Koch notes that the alternation between ''gwa-'' and ''go-'' is common among the Brittonic languages and does not amount to a systematic sound change in any of them.
Thomas Clancy opined that the royal feminine personal name in Life of Kentigern, ''Languoreth'', demonstrates the presence of /gw/ Cumbric.
It is noteworthy that the toponym ''Brenkibeth'' in Cumberland (now Burntippet; possibly ''bryn'', "hill" + ''gwyped'', "gnats") may display this syllable anglicized as ''-k-''. The name, however, may not be Brittonic at all, and instead be of Scandinavian origin.
Semantics of ''Penn''
In the ''Book of Aneirin
The Book of Aneirin () is a late 13th century Welsh manuscript containing Old and Middle Welsh poetry attributed to the late 6th century Northern Brythonic poet, Aneirin, who is believed to have lived in present-day Scotland.
The manuscript is ...
'', a poem entitled '' " Peis Dinogat" '' (possibly set in the Lake District
The Lake District, also known as ''the Lakes'' or ''Lakeland'', is a mountainous region and National parks of the United Kingdom, national park in Cumbria, North West England. It is famous for its landscape, including its lakes, coast, and mou ...
of Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancash ...
), contains a usage of the word ''penn'' "head" (attached to the names of several animals hunted by the protagonist), that is unique in medieval Welsh literature and may, according to Koch, reflect Cumbric influence (" ferring to a single animal in this way is otherwise found only in Breton, and we have no evidence that the construction ever had any currency in the present-day Wales"). The relevant lines are:
:Pan elei dy dat ty e vynyd
:Dydygei ef penn ywrch penn gwythwch penn hyd
:Penn grugyar vreith o venyd
:Penn pysc o rayadyr derwennyd
Translated as:
: When your father went to hemountain
: He brought a head of buck, head of wild pig, head of stag
: Head of speckled grouse from hemountain
: Head of fish from hefalls of Derwent
The form ''derwennydd'' however, is at odds with the absence of the ending ''-ydd'' noted below.
It is to be noted, however, that such semantics are probably archaisms, and rather than being features diagnostic of linguistic distinctiveness, are more likely to be legacies of features once common to all Brittonic speech.
Definite article
The modern Brittonic languages have different forms of thedefinite article
In grammar, an article is any member of a class of dedicated words that are used with noun phrases to mark the identifiability of the referents of the noun phrases. The category of articles constitutes a part of speech.
In English, both "the" ...
: Welsh ''yr, -'r, y'', Cornish ''an'', and Breton ''an, ar, al''. These are all taken to derive from an unstressed form of the Common Brittonic demonstrative
Demonstratives (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) are words, such as ''this'' and ''that'', used to indicate which entities are being referred to and to distinguish those entities from others. They are typically deictic, their meaning ...
''*sindos'', altered by assimilation (compare the Gaelic articles). Throughout Old Welsh the article is ''ir'' (or ''-r'' after a vowel), but there is evidence in Cumbric for an article in ''-n'' alongside one in ''-r''. Note the following:
*Tallentire, Cumbria (''Talentir'' 1200–25): 'brow/end of the land' (Welsh ''tal y tir'')
*Triermain, Cumbria (''Trewermain, Treverman'' c 1200): 'homestead at the stone' (Welsh ''tre(f) y maen'')
*Treales, Lancashire (''Treueles'' 1086): possibly 'village of the court' (Welsh ''tre(f) y llys''). But note Treflys
Treflys is a community in the county of Powys, Wales, and is 49.9 miles (80.4 km) from Cardiff and 154.4 miles (248.5 km) from London. In 2011 the population of Treflys was 484 with 15.1% of them able to speak Welsh. It is in the histor ...
, Powys
Powys ( , ) is a Principal areas of Wales, county and Preserved counties of Wales, preserved county in Wales. It borders Gwynedd, Denbighshire, and Wrexham County Borough, Wrexham to the north; the English Ceremonial counties of England, ceremo ...
which has no article.
*Pen-y-Ghent, Yorkshire (''Penegent'' 1307): 'hill of the border country' (Welsh ''pen y gaint''). The final element is disputed. Ekwall says it is identical to Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
(< Br ''*Kantion''), which is related to Welsh ''cant'' 'rim, border', though Mills gives 'coastal district' or 'land of the hosts or armies' for the county.
*Traquair, Borders (''Treverquyrd'' 1124): 'homestead on the River Quair' (Welsh ''tre(f) y Quair'').Mackay, George (2002): Scottish Place Names, New Lanark: Lomond Books
*Penicuik, Midlothian
Midlothian (; ) is registration county, lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area and one of 32 council areas of Scotland used for local government. Midlothian lies in the east-central Lowlands, bordering the City of Edinburgh council ar ...
(''Penicok'' 1250): 'hill of the cuckoo' (Welsh ''pen y cog'')
*Liscard, Wirral Peninsula
The Wirral Peninsula (), known locally as the Wirral, is a peninsula in North West England. The roughly rectangular peninsula is about long and wide, and is bounded by the Dee Estuary to the west, the Mersey Estuary to the east, and Liverpo ...
(''Lisenecark'' 1260): possibly 'court of the rock' (Welsh ''llys y garreg''), but also suggested is Irish ''lios na carraige'' of identical meaning.
Absence of ''-ydd''
Of all the names of possible Cumbric derivation, few are more certain thanCarlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England.
Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its pro ...
and Derwent which can be directly traced back to their Romano-British recorded forms ''Luguvalium'' and ''Derventio''.
The modern and medieval forms of Carlisle (''Luel'' c1050, ''Cardeol'' 1092, ''Karlioli'' c1100 (in the Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidi ...
genitive case
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive ca ...
), ''Cærleoil'' 1130) and Derwent (''Deorwentan stream'' c890 (Old English), ''Derewent'') suggest derivations from Br *''Luguvaljon'' and ''*Derwentjō''. But the Welsh forms ''Caerliwelydd'' and ''Derwennydd'' are derived from alternative forms ''*Luguvalijon, *Derwentijō'' which gave the ''-ydd'' ending. This appears to show a divergence between Cumbric and Welsh at a relatively early date.
If this was an early dialectal variation, it can't be applied as a universal sound law, as the equivalent of W ''mynydd'' 'mountain' occurs in a number of Cumbric names with the spirant intact: E.g. Mindrum (''Minethrum'' 1050) from 'mountain ridge' (Welsh ''mynydd trum''). It might also be noted that Medieval Welsh forms of ''Caerliwelydd''
and ''Derwennydd'' both occur in poems of supposed Cumbrian origin whose rhyme and metre would be disrupted if the ending were absent.
Of additional relevance is that Guto Rhys demonstrated "some robust proof" of the presence of the ''-ydd'' ending in the closely aligned Pictish language
Pictish is an extinct Brittonic Celtic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from late antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geo ...
.
Use of the name element ''Gos-''
One particularly distinctive element of Cumbric is the repeated use of the element or (W. 'boy, lad; servant, attendant') in personal names, followed by the name of a saint. The practice is reminiscent of Gaelic names such as ''Maol Choluim'' "Malcolm" and ''Gille Crìosd'' "Gilchrist", which haveScottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
(Old Irish 'bald, tonsured; servant') and ('servant, lad', < Old Irish 'a youth').
The most well-known example of this Cumbric naming practice is ''Gospatric'', which occurs as the name of several notable Anglo-Scottish noblemen in the 11th and 12th centuries. Other examples, standardised from original sources, include ''Gosmungo'' ( Saint Mungo), ''Gososwald'' (Oswald of Northumbria
Oswald (; c 604 – 5 August 641/642Bede gives the year of Oswald's death as 642. However there is some question of whether what Bede considered 642 is the same as what would now be considered 642. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and H ...
) and ''Goscuthbert'' (Cuthbert
Cuthbert of Lindisfarne () ( – 20 March 687) was a saint of the early Northumbrian church in the Hiberno-Scottish mission, Celtic tradition. He was a monk, bishop and hermit, associated with the monastery, monasteries of Melrose Abbey#Histo ...
).Koch, J. T. (1983) 'The Loss of Final Syllables and Loss of Declension in Brittonic' in ulletin of the Board of Celtic Studies 30: 214-220/ref>
Date of extinction
It is impossible to give an exact date of the extinction of Cumbric. However, there are some pointers which may give a reasonably accurate estimate. In the mid-11th century, some landowners still bore what appear to be Cumbric names. Examples of such landowners are Dunegal (Dyfnwal), lord of Strathnith orNithsdale
Nithsdale (), also known as Strathnith, Stranith or Stranit, is the strath or dale (landform), dale of the River Nith in southern Scotland. Nithsdale was one of the medieval provinces of Scotland. The provinces gradually lost their administrat ...
; Moryn (Morien), lord of Cardew and Cumdivock near Carlisle; and Eilifr (Eliffer), lord of Penrith.Phythian-Adams, Charles (1996): Land of the Cumbrians, Aldershot: Scolar Press
There is a village near Carlisle called Cumwhitton (earlier Cumquinton). This appears to contain the Norman name Quinton, affixed to a cognate of the Welsh ''cwm'', meaning valley.Armstrong, A. M., Mawer, A., Stenton, F. M. and Dickens, B. (1952) The Place-Names of Cumberland. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. There were no Normans in this area until 1069 at the earliest.
In the Battle of the Standard in 1138, the Cumbrians are noted as a separate ethnic group. Given that their material culture was very similar to their Gaelic and Anglian neighbours, it is arguable that what set them apart was still their language. Also the castle at Castle Carrock – Castell Caerog – dates from around 1160–1170. Barmulloch, earlier Badermonoc (Cumbric "monk's dwelling"), was given to the church by Malcolm IV of Scotland
Malcolm IV (; ), nicknamed Virgo, "the Maiden" (between 23 April and 24 May 1141 – 9 December 1165) was King of Scotland from 1153 until his death. He was the eldest son of Henry, Earl of Huntingdon and Northumbria (died 1152) and Ada de War ...
between 1153 and 1165.
A more controversial point is the surname Wallace. It means "Welshman". It is possible that all the Wallaces in the Clyde area were medieval immigrants from Wales, but given that the term was also used for local Cumbric-speaking Strathclyde Welsh, it seems equally, if not more, likely that the surname refers to people who were seen as being "Welsh" due to their Cumbric language.
Surnames in Scotland were not inherited before 1200 and not regularly until 1400. Sir William Wallace (known in Gaelic as Uilleam Breatnach – namely William the Briton or Welshman) came from the Renfrew area – itself a Cumbric name. Wallace slew the sheriff of Lanark (also a Cumbric name) in 1297. Even if he had inherited the surname from his father, it is possible that the family spoke Cumbric within memory in order to be thus named.
There are also some historical pointers to a continuing separate ethnic identity. Prior to being crowned king of Scotland in 1124, David I was invested with the title Prince of the Cumbrians. William the Lion
William the Lion (), sometimes styled William I (; ) and also known by the nickname ; e.g. Annals of Ulster, s.a. 1214.6; Annals of Loch Cé, s.a. 1213.10. ( 1142 – 4 December 1214), reigned as King of Alba from 1165 to 1214. His almost 49 ...
between 1173 and 1180 made an address to his subjects, identifying the Cumbrians as a separate group. This does not prove that any of them still spoke Cumbric at this time.
The legal documents in the Lanercost Cartulary, dating from the late 12th century, show witnesses with Norman French or English names, and no obvious Cumbric names. Though these people represent the upper classes, it seems significant that by the late 12th century in the Lanercost area, Cumbric is not obvious in these personal names.Todd, J. M. (ed.) (1991) The Lanercost Cartulary, Carlisle: CWAAS In 1262 in Peebles, jurymen in a legal dispute over peat cutting also have names which mostly appear Norman French or English,Chambers, W. (1864) A History of Peebleshire, Edinburgh: W & M Chambers but possible exceptions are Gauri Pluchan, Cokin Smith and Robert Gladhoc, where ''Gladhoc'' has the look of an adjectival noun similar to Welsh "gwladog" = "countryman".Prifysgol Cymru. (2002) Geiriadur Prifysgol Cymru: Caerdydd: Gwasg Prifysgol Cymru In the charters of Wetherall Priory near Carlisle there is a monk called Robert Minnoc who appears as a witness to 8 charters dating from around 1260.Prescott, J. E. (ed.) (1897) Register of Wetheral Priory, Carlisle: CWAAS His name is variously spelled Minnoc/Minot/Mynoc and it is tempting to see an equivalent of the Welsh "mynach" – "Robert the Monk" here.
Given that in other areas which have given up speaking Celtic languages, the upper classes have generally become Anglicised before the peasantry, it is not implausible that the peasantry continued to speak Cumbric for at least a little while after. Around 1200 there is a list of the names of men living in the area of Peebles
Peebles () is a town in the Scottish Borders, Scotland. It was historically a royal burgh and the county town of Peeblesshire. According to the United Kingdom census, 2011, 2011 census, the population was 8,376 and the estimated population in ...
. Amongst them are Cumbric names such as Gospatrick: servant or follower of Saint Patrick
Saint Patrick (; or ; ) was a fifth-century Romano-British culture, Romano-British Christian missionary and Archbishop of Armagh, bishop in Gaelic Ireland, Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Irelan ...
, Gosmungo: servant of Saint Mungo, Guososwald: servant of Oswald of Northumbria
Oswald (; c 604 – 5 August 641/642Bede gives the year of Oswald's death as 642. However there is some question of whether what Bede considered 642 is the same as what would now be considered 642. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and H ...
and Goscubrycht: servant of Cuthbert
Cuthbert of Lindisfarne () ( – 20 March 687) was a saint of the early Northumbrian church in the Hiberno-Scottish mission, Celtic tradition. He was a monk, bishop and hermit, associated with the monastery, monasteries of Melrose Abbey#Histo ...
. Two of the saints – Oswald and Cuthbert — are from Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
showing influence on Cumbric not found in Welsh.
In 1305 Edward I of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 1254 ...
prohibited the '' Leges inter Brettos et Scottos''.Barrow, G. W. S. (2005) Robert Bruce & the Community of the Realm of Scotland, Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press The term Brets or Britons refers to the native, traditionally Cumbric speaking people of southern Scotland and northern England as well as the Pictish speakers in Northern Scotland.
It seems that Cumbric could well have survived into the middle of the 12th century as a community language and even lasted into the 13th on the tongues of the last remaining speakers. Certain areas seem to be particularly dense in Cumbric place-names even down to very minor features. The two most striking of these are around Lanercost east of Carlisle and around Torquhan south of Edinburgh. If the 1262 names from Peebles do contain traces of Cumbric personal names then we can imagine Cumbric dying out between 1250 and 1300 at the very latest.
See also
* Cumbrian dialect * Cumbrian toponymy * Kenneth H. Jackson *Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (, "valley of the River Clyde, Clyde"), also known as Cumbria, was a Celtic Britons, Brittonic kingdom in northern Britain during the Scotland in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages. It comprised parts of what is now southern Scotland an ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
Cumbric.org - Language and History
h2>
Reconstuctions
* https://spns.org.uk/resources/blitonConstructed languages
* {{Authority control Languages attested from the 6th century Languages extinct in the 12th century Western Brittonic languages Extinct Celtic languages Extinct languages of Scotland Languages of the United Kingdom Unsolved problems in linguistics History of Cumbria History of the Scottish Borders Medieval languages Languages of England Languages of Scotland North West England Hen Ogledd