Collar bone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped
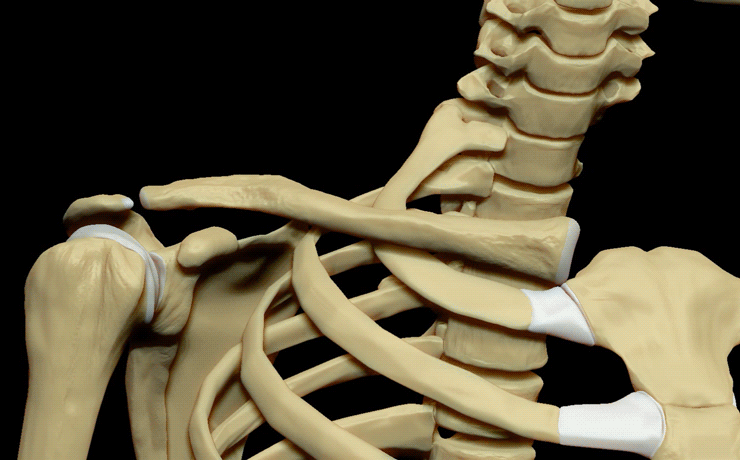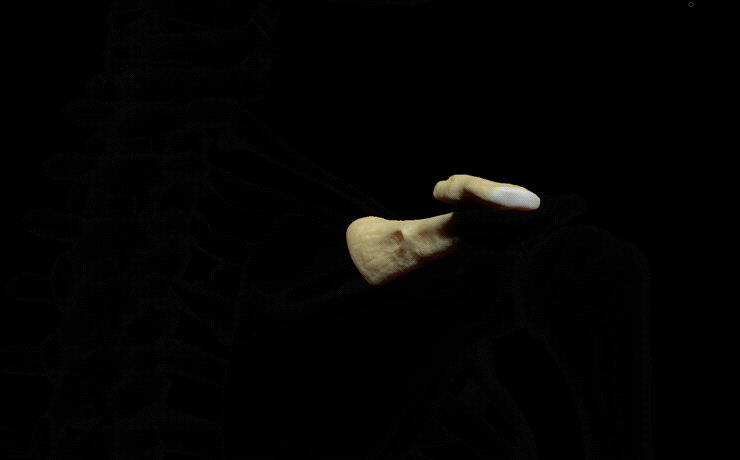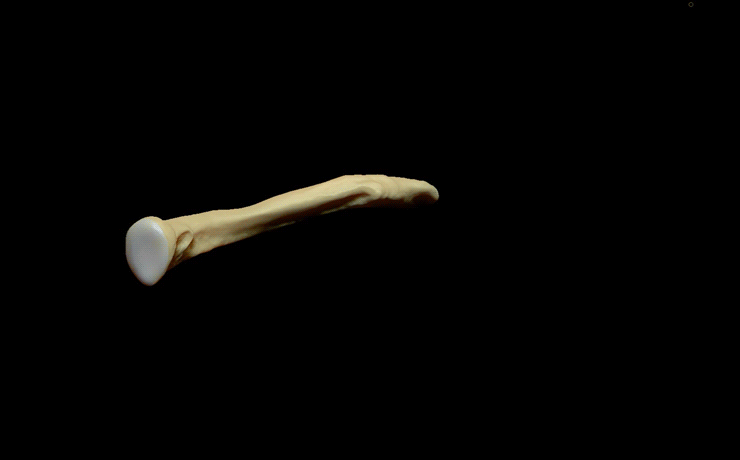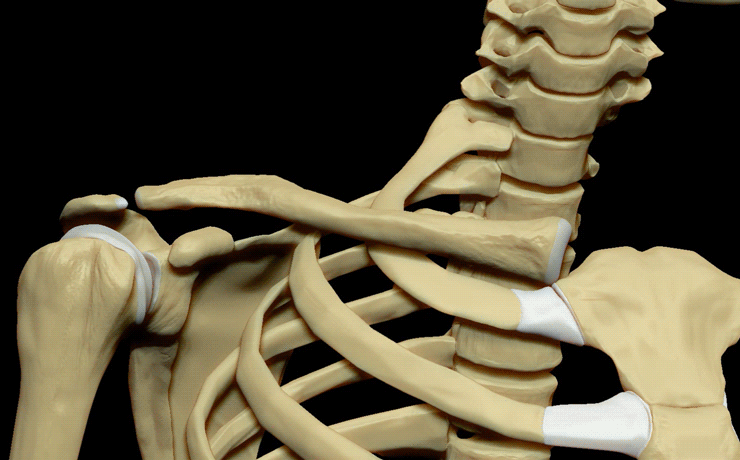
Clavicle
- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School {{Authority control Skeletal system Upper limb anatomy Shoulder
long bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities ...
approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut
A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension.
Human anatomy
Part of the functionality o ...
between the shoulder blade
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either ...
and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists ...
. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit.
Structure
The collarbone is a thin doubly curvedlong bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities ...
that connects the arm to the trunk
Trunk may refer to:
Biology
* Trunk (anatomy), synonym for torso
* Trunk (botany), a tree's central superstructure
* Trunk of corpus callosum, in neuroanatomy
* Elephant trunk, the proboscis of an elephant
Computing
* Trunk (software), in rev ...
of the body. Located directly above the first rib
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a ...
, it acts as a strut to keep the scapula in place so that the arm can hang freely. At its rounded medial end (sternal end), it articulates with the manubrium
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. S ...
of the sternum (breastbone) at the sternoclavicular joint
The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a synovial saddle joint between the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle, as well as the first rib. The joint possesses a joint capsule, and an articular disk, and is reinfo ...
. At its flattened lateral end (acromial end), it articulates with the acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The ...
, a process of the scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eith ...
(shoulder blade), at the acromioclavicular joint.
The rounded medial region (sternal region) of the shaft has a long curve laterally and anteriorly along two-thirds of the entire shaft. The flattened lateral region (acromial region) of the shaft has an even larger posterior curve to articulate with the acromion of the scapula. The medial region is the longest clavicular region as it takes up two-thirds of the entire shaft. The lateral region is both the widest clavicular region and thinnest clavicular region. The lateral end has a rough inferior surface that bears a ridge, the trapezoid line, and a slight rounded projection, the conoid tubercle (above the coracoid process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with t ...
). These surface features are attachment sites for muscles and ligaments of the shoulder.
It can be divided into three parts: medial end, lateral end, and shaft.
Medial end
The medial end is also known as the sternal end. It is quadrangular and articulates with the clavicular notch of the manubrium of the sternum to form the sternoclavicular joint. The articular surface extends to the inferior aspect for articulation with the first costal cartilage.Lateral end
The lateral end is also known as the acromial end. It is flat from above downward. It bears a facet that articulates with the shoulder to form the acromioclavicular joint. The area surrounding the joint gives an attachment to the joint capsule. The anterior border is concave forward and the posterior border is convex backward.Shaft
The shaft is divided into two main regions, the medial region, and the lateral region. The medial region is also known as the sternal region, it is the longest clavicular region as it takes up two-thirds of the entire shaft. The lateral region is also known as the acromial region, it is both the widest clavicular region and thinnest clavicular region.
Lateral region of the shaft
The lateral region of the shaft has two borders and two surfaces. * the anterior border is concave forward and gives origin to the deltoid muscle. * the posterior border is convex and gives attachment to thetrapezius muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the ...
.
* the inferior surface has a ridge called the trapezoid line and a tubercle; the conoid tubercle for attachment with the trapezoid and the conoid ligament, part of the coracoclavicular ligament that serves to connect the collarbone with the coracoid process of the scapula.
Development
The collarbone is the first bone to begin the process ofossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in ...
(laying down of minerals onto a preformed matrix) during development of the embryo, during the fifth and sixth weeks of gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pr ...
. However, it is one of the last bones to finish ossification at about 21–25 years of age. Its lateral end is formed by intramembranous ossification
Intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal system by which rudimentary bone tissue is created.
Intramembranous ossification i ...
while medially it is formed by endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system by which bone tissue is produced. Unlike intramembranous ossification, the other process by which bone tissue is produced ...
. It consists of a mass of cancellous bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and ...
surrounded by a compact bone shell. The cancellous bone forms via two ossification centres, one medial and one lateral, which fuse later on. The compact forms as the layer of fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs ...
covering the bone stimulate the ossification of adjacent tissue. The resulting compact bone is known as a periosteal collar.
Even though it is classified as a long bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities ...
, the collarbone has no medullary cavity ( marrow cavity) like other long bones, though this is not always true. It is made up of spongy cancellous bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and ...
with a shell of compact bone. It is a dermal bone
A dermal bone or investing bone or membrane bone is a bony structure derived from intramembranous ossification forming components of the vertebrate skeleton including much of the skull, jaws, gill covers, shoulder girdle and fin spines rays ( le ...
derived from elements originally attached to the skull.
Variation
The shape of the clavicle varies more than most other long bones. It is occasionally pierced by a branch of the supraclavicular nerve. In males the clavicle is usually longer and larger than in females. A study measuring 748 males and 252 females saw a difference in collarbone length between age groups 18–20 and 21–25 of about for males and females respectively. The left clavicle is usually longer and weaker than the right clavicle. The collarbones are sometimes partly or completely absent incleidocranial dysostosis
Cleidocranial dysostosis (CCD), also called cleidocranial dysplasia, is a birth defect that mostly affects the bones and teeth. The collarbones are typically either poorly developed or absent, which allows the shoulders to be brought close togeth ...
.
The levator claviculae muscle
In human anatomy, the levator claviculae is a very rare accessory muscle, accessory and Human vestigiality, vestigial skeletal muscle in the posterior triangle of the neck. It originates on the transverse processes of the upper cervical vertebrae ...
, present in 2–3% of people, originates on the transverse processes of the upper cervical vertebrae and is inserted in the lateral half of the clavicle.
Functions
The collarbone serves several functions: * It serves as a rigid support from which the scapula and free limb suspended; an arrangement that keeps the upper limb away from the thorax so that the arm has maximum range of movement. Acting as a flexible, crane-like strut, it allows the scapula to move freely on the thoracic wall. * Covering thecervicoaxillary canal The cervicoaxillary canal is the passageway that extends between the neck and the upper extremities through which the long thoracic nerve and other structures pass.Cervicoaxillary Canal -- Medical DefinitionCervicoaxillary Canal -- Medical Definitio ...
, it protects the neurovascular bundle that supplies the upper limb.
* Transmits physical impacts from the upper limb to the axial skeleton
The axial skeleton is the part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk of a vertebrate. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of six parts; the skull (22 bones), also the ossicles of the middle ...
.
Muscle
Muscles and ligaments that attach to the collarbone include:Clinical significance
* Acromioclavicular dislocation ("AC Separation") * Degeneration of the clavicle *Osteolysis
Osteolysis is an active resorption of bone matrix by osteoclasts and can be interpreted as the reverse of ossification. Although osteoclasts are active during the natural formation of healthy bone the term "osteolysis" specifically refers to a pa ...
* Sternoclavicular dislocations
A vertical line drawn from the mid-clavicle called the mid-clavicular line is used as a reference in describing cardiac apex beat during medical examination. It is also useful for evaluating an enlarged liver, and for locating the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although ...
which is between the mid-clavicular line and the transpyloric plane.
Collarbone fracture
Clavicle fractures (colloquially, a broken collarbone) occur as a result of injury or trauma. The most common type of fractures occur when a person falls horizontally on the shoulder or with an outstretched hand. A direct hit to the collarbone will also cause a break. In most cases, the direct hit occurs from the lateral side towards the medial side of the bone. The most common site of fracture is the junction between the two curvatures of the bone, which is the weakest point. This results in the sternocleidomastoid muscle lifting the medial aspect superiorly, which can result in perforation of the overlying skin.Other animals
The clavicle first appears as part of the skeleton in primitivebony fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartil ...
, where it is associated with the pectoral fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as se ...
; they also have a bone called the cleithrum. In such fish, the paired clavicles run behind and below the gills on each side, and are joined by a solid symphysis on the fish's underside. They are, however, absent in cartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. ...
and in the vast majority of living bony fish, including all of the teleost
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Tele ...
s.
The earliest tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s retained this arrangement, with the addition of a diamond-shaped interclavicle between the base of the clavicles, although this is not found in living amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
s. The cleithrum disappeared early in the evolution of reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalia ...
s, and is not found in any living amniote
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are dis ...
s, but the interclavicle is present in most modern reptiles, and also in monotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals ( Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brai ...
s. In modern forms, however, there are a number of variations from the primitive pattern. For example, crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian stage) and are the closest livin ...
s and salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s lack clavicles altogether (although crocodilians do retain the interclavicle), while in turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked t ...
s, they form part of the armoured plastron.
The interclavicle is absent in marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in ...
s and placental mammals. In many mammals, the clavicles are also reduced, or even absent, to allow the scapula greater freedom of motion, which may be useful in fast-running animals.
Though a number of fossil hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
(humans and chimpanzees) clavicles have been found, most of these are mere segments offering limited information on the form and function of the pectoral girdle. One exception is the clavicle of AL 333x6/9 attributed to ''Australopithecus afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would no ...
'' which has a well-preserved sternal end. One interpretation of this specimen, based on the orientation of its lateral end and the position of the deltoid attachment area, suggests that this clavicle is distinct from those found in extant apes (including humans), and thus that the shape of the human shoulder dates back to less than . However, analyses of the clavicle in extant primates suggest that the low position of the scapula in humans is reflected mostly in the curvature of the medial portion of the clavicle rather than the lateral portion. This part of the bone is similar in ''A. afarensis'' and it is thus possible that this species had a high shoulder position similar to that in modern humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
.
In dinosaurs
Indinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s the main bones of the pectoral girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of ...
were the scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eith ...
(shoulder blade) and the coracoid, both of which directly articulated with the clavicle. The clavicle was present in saurischian dinosaurs but largely absent in ornithischian dinosaurs. The place on the scapula where it articulated with the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a r ...
(upper bone of the forelimb) is the called the glenoid. The clavicles fused in some theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
dinosaurs to form a furcula, which is the equivalent to a wishbone.Martin, A.J. (2006). Introduction to the Study of Dinosaurs. Second Edition. Oxford, Blackwell Publishing. pg. 299-300. .
In birds, the clavicles and interclavicle have fused to form a single Y-shaped bone, the furcula or "wishbone" which evolved from the clavicles found in coelurosaurian theropods.
Additional media
See also
* Clavicle fractureReferences
External links
Clavicle
- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School {{Authority control Skeletal system Upper limb anatomy Shoulder