Colestilan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Colestilan ( INN, trade name BindRen) is a medication that acts as a phosphate binder and bile acid sequestrant. It is an ion-exchange resin, is an orally administered bile acid sequestrant that is being developed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for the treatment of hypercholesterolaemia and hyperphosphataemia. It has been launched in Japan for hypercholesterolaemia. For the treatment of hyperphosphataemia, it is launched in Austria, Germany, the Czech Republic, Portugal and the United Kingdom, is registered in the EU. Phase III development in paediatric patients with hyperphosphataemia associated with chronic kidney disease was underway in the UK and Germany. However, the company discontinued the development. In addition, the phase II development in type-2 diabetes mellitus and phase I development in hyperphosphataemia, in Japan, was also discontinued by the company.
Phase III development for hyperphosphataemia was previously underway in the US. However, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma discontinued development in this market. Colestilan was also investigated in phase III trials in Europe and Asia for hypercholesterolaemia. However, as of March 2015, no recent reports of development have been identified for the drug in this indication
Clinical use
Colestilan is used for the treatment of hyperphosphataemia (too high phosphate concentrations in the blood serum) in patients undergoingdialysis Dialysis may refer to:
*Dialysis (chemistry), a process of separating molecules in solution
**Electrodialysis, used to transport salt ions from one solution to another through an ion-exchange membrane under the influence of an applied electric pote ...
, including peritoneal dialysis.
Contraindications
Colestilan is contraindicated in patients with bowel obstruction.Interactions
The substance can inhibit the resorption of other drugs, as well as fat soluble vitamins ( A, D, E, K) and folate, from the gut. Resulting lower blood levels can be clinically problematic with immunosuppressant andantiepileptic
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
drugs.
Adverse effects
Adverse effects include gastrointestinal problems such as constipation, as well as vitamin and calcium deficiency. Vitamin K deficiency sometimes causes gastrointestinal bleeding.Chemistry and mechanism of action
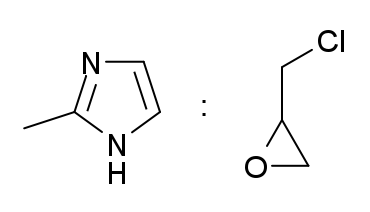
Colestilan is a cross-linked copolymer of2-methylimidazole
2-Methylimidazole is an organic compound that is structurally related to imidazole with the chemical formula CH3C3H2N2H. It is a white or colorless solid that is highly soluble in polar organic solvents and water. It is a precursor to a range of d ...
and epichlorohydrin
Epichlorohydrin (abbreviated ECH) is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organi ...
and works as an anion exchanger resin with affinity to phosphate, bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Primary b ...
anions and urate. It binds these anions in the gut and removes them from the enterohepatic circulation. Colestilan is not absorbed from the gut, but is excreted together with the bound anions.

Notes and references
{{Lipid modifying agents Phosphate binders Bile acid sequestrants