|
Hyperphosphataemia
Hyperphosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is an elevated level of phosphate in the blood. Most people have no symptoms while others develop calcium deposits in the soft tissue. Often there is also low calcium levels which can result in muscle spasms. Causes include kidney failure, pseudohypoparathyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, diabetic ketoacidosis, tumor lysis syndrome, and rhabdomyolysis. Diagnosis is generally based on a blood phosphate levels of greater than 1.46 mmol/L (4.5 mg/dL). Levels may appear falsely elevated with high blood lipid levels, high blood protein levels, or high blood bilirubin levels. Treatment may include eating a phosphate low diet and antacids, like calcium carbonate, that bind phosphate. Occasionally intravenous normal saline or dialysis may be used. How commonly it occurs is unclear. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms include ectopic calcification, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and renal osteodystrophy. Abnormal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophosphatemia
Hypophosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a low level of phosphate in the blood. Symptoms may include weakness, trouble breathing, and loss of appetite. Complications may include seizures, coma, rhabdomyolysis, or softening of the bones. Causes include alcohol use disorder, refeeding in those with malnutrition, recovery from diabetic ketoacidosis, burns, hyperventilation, and certain medications. It may also occur in the setting of hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism, and Cushing syndrome. It is diagnosed based on a blood phosphate concentration of less than 0.81 mmol/L (2.5 mg/dL). When levels are below 0.32 mmol/L (1.0 mg/dL) it is deemed to be severe. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Phosphate may be given by mouth or by injection into a vein. Hypophosphatemia occurs in about 2% of people within hospital and 70% of people in the intensive care unit (ICU). Signs and symptoms * Muscle dysfunction and weakness – This occurs in major muscles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
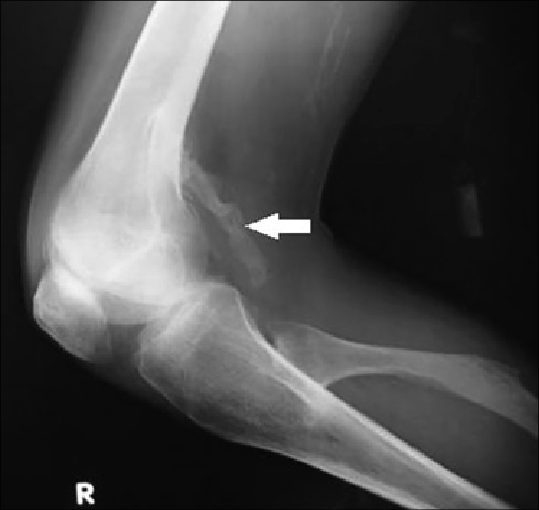
Ectopic Calcification
Ectopic calcification is a pathologic deposition of calcium salts in tissues or bone growth in soft tissues. This can be a symptom of hyperphosphatemia. Formation of osseous tissue in soft tissues such as the lungs, eyes, arteries, or other organs is known as ectopic calcification, dystrophic calcification, or ectopic ossification. Causes Absorption of calcium salts normally occurs in bony tissues and is facilitated by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D. However, increased amounts of parathyroid hormone in the blood result in the deposit of calcium in soft tissues. This can be an indication of hyperparathyroidism, arteriosclerosis, or trauma to tissues. Calcification of muscle can occur after traumatic injury and is known as myositis ossificans. It can be recognized by muscle tenderness and loss of stretch in the affected area. To reduce the risk of calcification after an injury, initiate what is commonly known as "RICE" (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). Diagnosis Typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
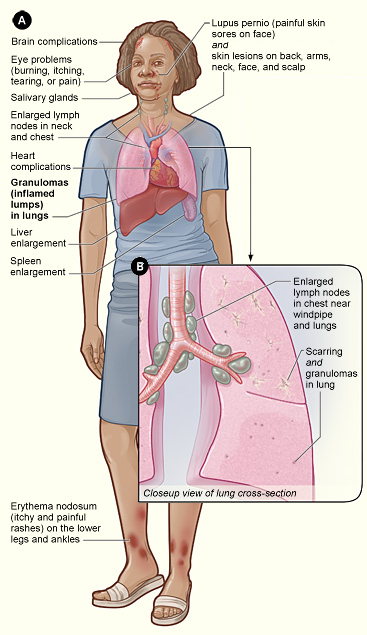
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and brain. Any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected though. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no, or only mild, symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, large lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs and symptoms, which may be supported by tissue biopsy, biopsy. Findings that make i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervitaminosis A
Hypervitaminosis A refers to the toxic effects of ingesting too much preformed vitamin A (retinyl esters, retinol, and retinal). Symptoms arise as a result of altered bone metabolism and altered metabolism of other fat-soluble vitamins. Hypervitaminosis A is believed to have occurred in early humans, and the problem has persisted throughout human history. Toxicity results from ingesting too much preformed vitamin A from foods (such as fish liver or animal liver), supplements, or prescription medications and can be prevented by ingesting no more than the recommended daily amount. Diagnosis can be difficult, as serum retinol is not sensitive to toxic levels of vitamin A, but there are effective tests available. Hypervitaminosis A is usually treated by stopping intake of the offending food(s), supplement(s), or medication. Most people make a full recovery. High intake of provitamin carotenoids (such as beta-carotene) from vegetables and fruits does not cause hypervitaminosis A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervitaminosis D
Vitamin D toxicity, or hypervitaminosis D is the toxic state of an excess of vitamin D. The normal range for blood concentration is 20 to 50 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). However, the toxic state is known to be a value of 100 ng/ml or more in a clinical setting. Signs and symptoms An excess of vitamin D causes abnormally high blood concentrations of calcium, which can cause overcalcification of the bones, soft tissues, heart and kidneys. In addition, hypertension can result. Symptoms of vitamin D toxicity may include the following: * Dehydration * Vomiting * Diarrhea * Decreased appetite * Irritability * Constipation * Fatigue * Muscle weakness * Metastatic calcification of the soft tissues * Insomnia Symptoms of vitamin D toxicity appear several months after excessive doses of vitamin D are administered. In almost every case, a low-calcium diet combined with corticosteroid drugs will allow for a full recovery within a month. It is possible that some of the symptoms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany (involuntary muscle contraction), and several other symptoms. It is a very rare disease. The condition can be inherited, but it is also encountered after thyroid or parathyroid gland surgery, and it can be caused by immune system-related damage as well as a number of rarer causes. The diagnosis is made with blood tests, and other investigations such as genetic testing depending on the results. The primary treatment of hypoparathyroidism is calcium and vitamin D supplementation. Calcium replacement or vitamin D can ameliorate the symptoms but can increase the risk of kidney stones and chronic kidney disease. Additionally, injectable medications such as recombinant human parathyroid hormone or teriparatide may be given by injection to replace the missing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Insufficiency
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include (in chronological order) high blood pressure (often related to activation of the renin–angiotensin system system), bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization. Causes of chronic kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis, and polycystic kidney disease. Risk factors include a family history of chronic kidney disease. Diagnosis is by blood tests to measure the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and a urine test to measure albumin. Ultrasound or kidney biopsy may be performed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Kidney Disease-mineral And Bone Disorder
Chronic kidney disease–mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) is one of the many complications associated with chronic kidney disease. It represents a systemic disorder of mineral and bone metabolism due to CKD manifested by either one or a combination of the following: * Abnormalities of calcium, phosphorus (phosphate), parathyroid hormone, or vitamin D metabolism * Abnormalities in bone turnover, mineralization, volume, linear growth, or strength * Vascular or other soft-tissue calcification CKD-MBD explains, at least in part, the high morbidity and mortality of CKD patients, linking kidney and bone disease with cardiovascular complications. It is a matter of discussion whether CKD-MBD may be considered a real syndrome or not. CKD-MBD broadens the "old" concept of " renal osteodystrophy", which now should be restricted to describing the ''bone pathology'' associated with CKD. Thus, renal osteodystrophy is currently considered ''one'' measure of the skeletal component of the sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy/adynamic bone disease is currently defined as an alteration of bone morphology in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is one measure of the skeletal component of the systemic disorder of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). The term "renal osteodystrophy" was coined in 1943, 60 years after an association was identified between bone disease and kidney failure. The traditional types of renal osteodystrophy have been defined on the basis of turnover and mineralization as follows: 1) mild, slight increase in turnover and normal mineralization; 2) osteitis fibrosa, increased turnover and abnormal mineralization; 3) osteomalacia, decreased turnover and abnormal mineralization; 4) adynamic, decreased turnover and acellularity; and, 5) mixed, increased turnover with abnormal mineralization. A Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes report has suggested that bone biopsies in patients with CKD should be characterized by determining bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands ( primary hyperparathyroidism) or as response to external stimuli (secondary hyperparathyroidism). Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism are caused by inappropriately normal or elevated blood calcium leaving the bones and flowing into the blood stream in response to increased production of parathyroid hormone. In healthy people, when blood calcium levels are high, parathyroid hormone levels should be low. With long-standing hyperparathyroidism, the most common symptom is kidney stones. Other symptoms may include bone pain, weakness, depression, confusion, and increased urination. Both primary and secondary may result in osteoporosis (weakening of the bones). In 80% of cases, primary hyperparathyroidism is due to a single benign tumor known as a parathyroid adenoma. Most of the remainder are due to several of these adenomas. Very rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
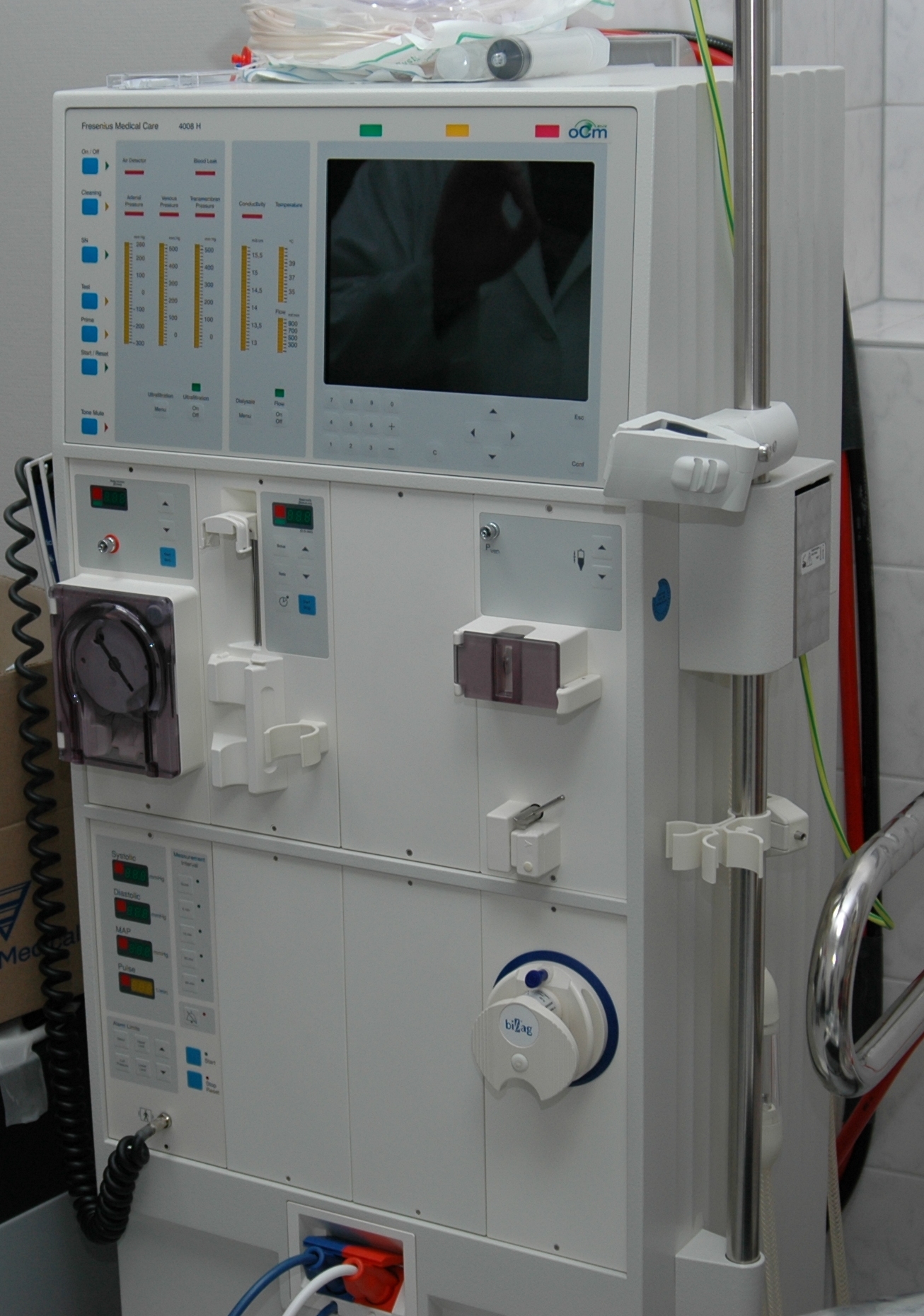
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis (from Greek , , 'dissolution'; from , , 'through', and , , 'loosening or splitting') is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney disease, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is 10–15% of normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Saline
Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, acidosis, and high blood sodium. In those with long-standing low blood sodium, excessive use may result in osmotic demyelination syndrome. Saline is in the crystalloid family of medications. It is most commonly used as a sterile 9 g of salt per litre (0.9%) solution, known as normal saline. Higher and lower concentrations may also occasionally be used. Saline is acidic, with a pH of 5.5 (due mainly to dissolved carbon dioxide). The medical use of saline began around 1831. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, sodium was the 274th most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |