Ectopic calcification on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ectopic calcification is a pathologic deposition of 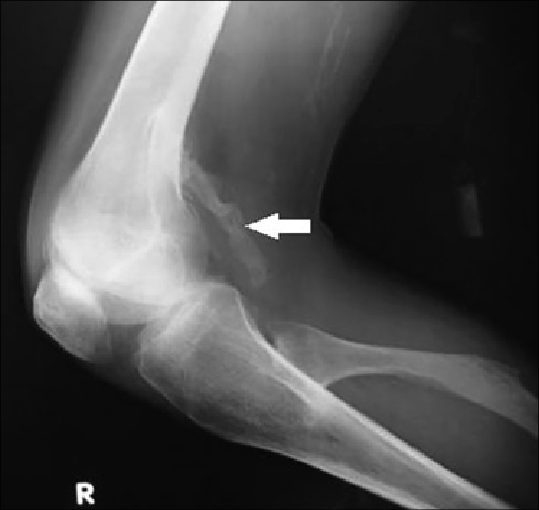
calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
salts in tissues or bone growth in soft tissues. This can be a symptom of hyperphosphatemia
Hyperphosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is an elevated level of phosphate in the blood. Most people have no symptoms while others develop calcium deposits in the soft tissue. Often there is also low calcium levels which can r ...
. Formation of osseous tissue in soft tissues such as the lungs, eyes, arteries, or other organs is known as ectopic calcification, dystrophic calcification, or ectopic ossification.

Causes
Absorption of calcium salts normally occurs in bony tissues and is facilitated byparathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine.
PTH influences bone re ...
and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
. However, increased amounts of parathyroid hormone in the blood result in the deposit of calcium in soft tissues. This can be an indication of hyperparathyroidism, arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is the thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of Artery, arteries. This process gradually restricts the blood flow to one's organs and tissues and can lead to severe health risks brought on by atherosclerosis ...
, or trauma to tissues.
Calcification of muscle can occur after traumatic injury and is known as myositis ossificans
Myositis ossificans comprises two syndromes characterized by heterotopic ossification (calcification) of muscle. The World Health Organization, 2020, has grouped myositis ossificans together with fibro-osseous pseudotumor of digits as a single spe ...
. It can be recognized by muscle tenderness and loss of stretch in the affected area. To reduce the risk of calcification after an injury, initiate what is commonly known as "RICE
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
" (rest, ice, compression, and elevation).Diagnosis
Typically, the diagnosis of extra-skeletal ectopic calcification is quite straightforward. A physical examination of a suspected area with calcified deposits palpates as hard and rough. To confirm, the calcified tissues can be seen on an x-ray.Prognosis
Ectopic ossification of the heart valves is an indicator of future heart problems, hyperparathyroidism, andnecrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
of tissues.
See also
*Subepidermal calcified nodule
Subepidermal calcified nodule is a type of Calcinosis cutis. It's a cutaneous condition characterized by calcification of the skin resulting from the deposition of calcium and phosphorus, occurring most frequently as one or a few skin lesions on th ...
References
{{reflist Inborn errors of metal metabolism