CERN Neutrinos to Gran Sasso on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
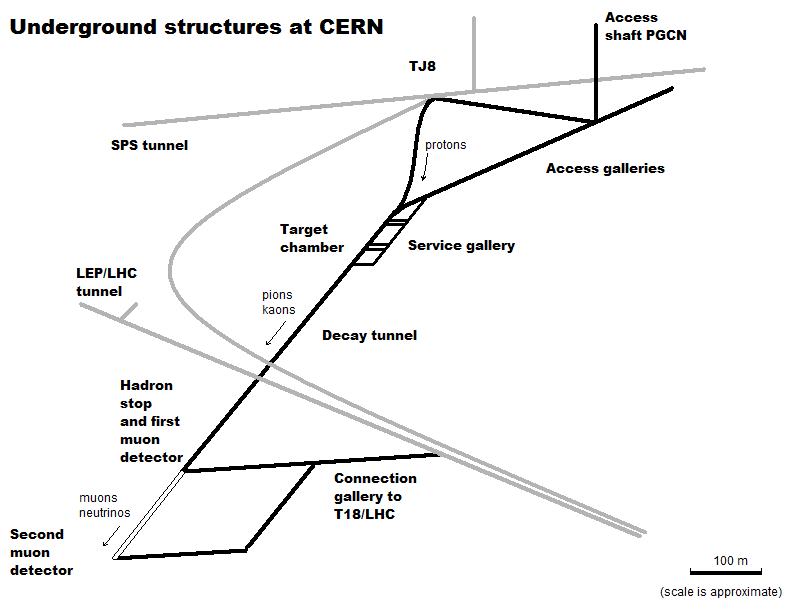 The CERN Neutrinos to Gran Sasso (CNGS) project was a physics project of the
The CERN Neutrinos to Gran Sasso (CNGS) project was a physics project of the
Official CNGS project website
Official OPERA experiment website
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cngs CERN experiments Neutrino experiments International science experiments
 The CERN Neutrinos to Gran Sasso (CNGS) project was a physics project of the
The CERN Neutrinos to Gran Sasso (CNGS) project was a physics project of the European Organization for Nuclear Research
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Gene ...
(CERN). The aim of the project was to analyse the hypothesis of neutrino oscillation by directing a beam
Beam may refer to:
Streams of particles or energy
*Light beam, or beam of light, a directional projection of light energy
**Laser beam
*Particle beam, a stream of charged or neutral particles
**Charged particle beam, a spatially localized grou ...
of neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
s from CERN's facilities to the detector of the OPERA experiment
The Oscillation Project with Emulsion-tRacking Apparatus (OPERA) was an instrument used in a scientific experiment for detecting tau neutrinos from muon neutrino oscillations. The experiment is a collaboration between CERN in Geneva, Switzerla ...
at the Gran Sasso National Laboratory
Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS) is the largest underground research center in the world. Situated below Gran Sasso mountain in Italy, it is well known for particle physics research by the INFN. In addition to a surface portion of the ...
(LNGS), located in the Gran Sasso
Gran Sasso d'Italia (; ) is a massif in the Apennine Mountains of Italy. Its highest peak, Corno Grande (2,912 metres), is the highest mountain in the Apennines, and the second-highest mountain in Italy outside the Alps. The mountain lies wit ...
mountain in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
. The CNGS facility was housed in a tunnel which diverged from one of the SPS–LHC transfer tunnels, at the Franco
Franco may refer to:
Name
* Franco (name)
* Francisco Franco (1892–1975), Spanish general and dictator of Spain from 1939 to 1975
* Franco Luambo (1938–1989), Congolese musician, the "Grand Maître"
Prefix
* Franco, a prefix used when ref ...
–Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
border near Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaki ...
. It used the Super Proton Synchrotron
The Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) is a particle accelerator of the synchrotron type at CERN. It is housed in a circular tunnel, in circumference, straddling the border of France and Switzerland near Geneva, Switzerland.
History
The SPS was de ...
(SPS) accelerator as a source of high-energy proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
s.
History
Approval for the CNGS project was signed by the CERN Council in December 1999, with civil engineering on the project starting the following September. Construction of the tunnels and service caverns was completed in mid-2004, with equipment installation completed in summer 2005 and commissioning being carried out throughout spring 2006. The firstproton beam
A charged particle beam is a spatially localized group of electrically charged particles that have approximately the same position, kinetic energy (resulting in the same velocity), and direction. The kinetic energies of the particles are much ...
was sent to the target on 11 July 2006, with the CNGS facility being approved for physics operations on 18 August 2006. CNGS ceased operation in 2012. The tunnel was then repurposed for the AWAKE
Wakefulness is a daily recurring brain state and state of consciousness in which an individual is conscious and engages in coherent cognitive and behavioral responses to the external world.
Being awake is the opposite of being asleep, in which ...
experiment, which became operational in 2016.
Function
Aproton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
beam was taken from the SPS at and is made to collide with a graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large ...
target within the CNGS tunnel. The resulting particles, most importantly kaons
KAON (Karlsruhe ontology) is an ontology infrastructure developed by the University of Karlsruhe and the Research Center for Information Technologies in Karlsruhe.
Its first incarnation was developed in 2002 and supported an enhanced version of ...
and pions
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more gene ...
among many other particles, were then focused by magnetic lens
thumb
thumb
A subtype of a magnetic lens ( quadrupole magnet) in the Maier-Leibnitz laboratory, Munich
A magnetic lens is a device for the focusing or deflection of moving charged particles, such as electrons or ions, by use of the magnetic Lor ...
ing and travelled down the CNGS tunnel in a vacuum tube. These particles are naturally unstable, and their decay products include muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As wi ...
s and muon neutrino
The muon neutrino is an elementary particle which has the symbol () and zero electric charge. Together with the muon it forms the second generation of leptons, hence the name muon neutrino. It was discovered in 1962 by Leon Lederman, Melvin Schwar ...
s. All particles except neutrinos (protons, muons, pion, kaon...) stop near the end of the tunnel. The neutrinos continue their flight unaffected, as they rarely interact with matter. The number of muons was measured at this point, which gave an indication of the beam's profile and intensity. This beam then passed through the crust of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
and it is expected that during flight some of the muon neutrinos convert into other neutrino types such as tau neutrinos. Once the beam arrived at Gran Sasso, the OPERA
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
and ICARUS
In Greek mythology, Icarus (; grc, Ἴκαρος, Íkaros, ) was the son of the master craftsman Daedalus, the architect of the labyrinth of Crete. After Theseus, king of Athens and enemy of Minos, escaped from the labyrinth, King Minos suspe ...
experiments were used to detect the neutrinos.
Results
The first candidates for neutrino oscillation to tau neutrinos were announced in May 2010 by the OPERA experiment. In total five tau neutrinos were observed, consistent with the expectations from the theory of neutrino oscillation. On 22 September 2011, the OPERA collaboration garnered international attention when they released apreprint
In academic publishing, a preprint is a version of a scholarly or scientific paper that precedes formal peer review and publication in a peer-reviewed scholarly or scientific journal. The preprint may be available, often as a non-typeset versio ...
reporting the Faster-than-light neutrino anomaly
In 2011, the OPERA experiment mistakenly observed neutrinos appearing to travel faster than light. Even before the source of the error was discovered, the result was considered anomalous because speeds higher than that of light in vacuum are g ...
, wherein neutrinos were measured to be travelling, on average, at faster-than-light
Faster-than-light (also FTL, superluminal or supercausal) travel and communication are the conjectural propagation of matter or information faster than the speed of light (). The special theory of relativity implies that only particles with zero ...
speed. On 24 February 2012, the team said they had discovered two problems with their previous test, muddying the validity of the previous result. The preprint has been modified to account for these facts, and indeed the measurement of the neutrino speed, there reported, agrees with the velocity of the light.
References
External links
Official CNGS project website
Official OPERA experiment website
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cngs CERN experiments Neutrino experiments International science experiments