The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an
anti-foreign,
anti-colonial, and
anti-Christian
Anti-Christian sentiment or Christophobia constitutes opposition or objections to Christians, the Christian religion, and/or its practices. Anti-Christian sentiment is sometimes referred to as Christophobia or Christianophobia, although these terms ...
uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
, by the
Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (), known as the "Boxers" in English because many of its members had practised
Chinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts, often called by the umbrella terms kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (), are multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to comm ...
, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing".
After the
Sino-Japanese War of 1895, villagers in
North China
North China, or Huabei () is a geographical region of China, consisting of the provinces of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Part of the larger region of Northern China (''Beifang''), it lies north of the Qinling–Hu ...
feared the expansion of
foreign spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898 Northern China experienced several natural disasters, including the
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, Boxers spread violence across
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in His ...
and the
North China Plain
The North China Plain or Huang-Huai-Hai Plain () is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin formed in the late Paleogene and Neogene and then modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. It is the largest alluvial plain of China. The plain is border ...
, destroying foreign property such as railroads and attacking or murdering Christian missionaries and
Chinese Christians
Christianity in China has been present since at least the 3rd century, and it has gained a significant amount of influence during the last 200 years.
While Christianity may have existed in China before the 3rd century, evidence of its existe ...
. The events came to a head in June 1900 when Boxer fighters, convinced they were invulnerable to foreign weapons, converged on Beijing with the slogan "Support the Qing government and exterminate the foreigners."
Diplomats, missionaries, soldiers and some Chinese Christians took refuge in the diplomatic
Legation Quarter
The Peking Legation Quarter was the area in Peking (Beijing), China where a number of foreign legations were located between 1861 and 1959. In the Chinese language, the area is known as ''Dong Jiaomin Xiang'' (), which is the name of the ''hutong ...
. An
Eight Nation Alliance of American, Austro-Hungarian, British, French, German, Italian, Japanese and Russian troops moved into China to lift the siege and on June 17 stormed the
Dagu Fort
The Taku Forts or Dagu Forts, also called the Peiho Forts are forts located by the Hai River (Peiho River) estuary in the Binhai New Area, Tianjin, in northeastern China. They are located southeast of the Tianjin urban center.
History
The f ...
, at
Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
. The
Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi ( ; mnc, Tsysi taiheo; formerly romanised as Empress Dowager T'zu-hsi; 29 November 1835 – 15 November 1908), of the Manchu Yehe Nara clan, was a Chinese noblewoman, concubine and later regent who effectively controlled ...
, who had initially been hesitant, now supported the Boxers and on June 21, issued an
Imperial Decree declaring war on the invading powers. Chinese officialdom was split between those supporting the Boxers and those favouring conciliation, led by
Prince Qing
Prince Qing of the First Rank (Manchu: ; ''hošoi fengšen cin wang''), or simply Prince Qing, was the title of a princely peerage used in China during the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1636–1912). It was also one of the 12 "iron-cap" princely pe ...
. The supreme commander of the Chinese forces, the Manchu General
Ronglu
Ronglu (6 April 1836 – 11 April 1903), courtesy name Zhonghua, was a Manchu political and military leader of the late Qing dynasty. He was born in the Guwalgiya clan, which was under the Plain White Banner of the Manchu Eight Banners. ...
(Junglu), later claimed he acted to protect the foreigners. Officials in the
southern provinces
The Southern Provinces ( ar, الأقاليم الجنوبية, Al-Aqalim al-Janubiyah, french: Provinces du Sud) or Moroccan Sahara ( ar, الصحراء المغربية, Assahra al-Maghribiya, french: Sahara marocain) are the terms used by th ...
ignored the imperial order to fight against foreigners.
The
Eight-Nation Alliance
The Eight-Nation Alliance was a multinational military coalition that invaded northern China in 1900 with the stated aim of relieving the foreign legations in Beijing, then besieged by the popular Boxer militia, who were determined to remove fo ...
, after initially being turned back by the Imperial Chinese military and Boxer militia, brought 20,000 armed troops to China. They defeated the Imperial Army in Tianjin and arrived in Beijing on August 14, relieving the
fifty-five day siege of the Legations. Plunder of the capital and the surrounding countryside ensued, along with
summary execution
A summary execution is an execution in which a person is accused of a crime and immediately killed without the benefit of a full and fair trial. Executions as the result of summary justice (such as a drumhead court-martial) are sometimes includ ...
of those suspected of being Boxers in retribution. The
Boxer Protocol
The Boxer Protocol was signed on September 7, 1901, between the Qing Empire of China and the Eight-Nation Alliance that had provided military forces (including Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, Russia, and the Un ...
of September 7, 1901, provided for the execution of government officials who had supported the Boxers, provisions for foreign troops to be stationed in Beijing, and 450 million
s of silver— more than the government's annual
tax revenue
Tax revenue is the income that is collected by governments through taxation. Taxation is the primary source of government revenue. Revenue may be extracted from sources such as individuals, public enterprises, trade, royalties on natural resour ...
—to be paid as
indemnity
In contract law, an indemnity is a contractual obligation of one Party (law), party (the ''indemnitor'') to Financial compensation, compensate the loss incurred by another party (the ''indemnitee'') due to the relevant acts of the indemnitor or ...
over the course of the next 39 years to the eight nations involved. The Qing dynasty's handling of the Boxer Rebellion further weakened their control over China, and led the dynasty to attempt
major governmental reforms in the aftermath.
Historical background
Origins of the Boxers
The Righteous and Harmonious Fists (Yihequan) arose in the inland sections of the northern coastal province of
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in His ...
, a region which had long been plagued by social unrest, religious sects, and martial societies. American Christian missionaries were probably the first people who referred to the well-trained, athletic young men as the "Boxers", because of the martial arts which they practised and the weapons training which they underwent. Their primary practice was a type of
spiritual possession
Spirit possession is an unusual or altered state of consciousness and associated behaviors purportedly caused by the control of a human body by spirits, ghosts, demons, or gods. The concept of spirit possession exists in many cultures and re ...
which involved the whirling of
sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
s, violent prostrations, and the chanting of incantations to deities.

The opportunities to fight against Western encroachment and colonisation were especially attractive to unemployed village men, many of whom were teenagers. The tradition of possession and invulnerability went back several hundred years but took on special meaning against the powerful new weapons of the West. The Boxers, armed with rifles and swords, claimed supernatural invulnerability against cannons, rifle shots, and knife attacks. The Boxer groups popularly claimed that millions of soldiers would descend out of
Heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
to assist them in purifying China of foreign oppression.
In 1895, despite ambivalence toward their heterodox practices,
Yuxian, a Manchu who was then prefect of
Caozhou
Caozhou or Cao Prefecture () was a '' zhou'' (prefecture) in imperial China centering on modern Heze or Cao County in Shandong, China. It existed (intermittently) from the 6th century to 1913.
Geography
Under the Sui, Cao Prefecture included Yua ...
and would later become provincial governor, cooperated with the
Big Swords Society
The Big Swords Society () or Great Knife Society was a traditional peasant group most noted for the killing of two German Catholic missionaries at the Juye Incident in 1897 at Zhang Jia Village where the missionaries were ambushed in their sleep ...
, whose original purpose was to fight bandits. The German Catholic missionaries of the
Society of the Divine Word
The Society of the Divine Word ( la, Societas Verbi Divini), abbreviated SVD and popularly called the Verbites or the Divine Word Missionaries, and sometimes the Steyler Missionaries, is a Catholic Church, Catholic clerical religious congregation ...
had built up their presence in the area, partially by taking in a significant portion of converts who were "in need of protection from the law". On one occasion in 1895, a large bandit gang defeated by the Big Swords Society claimed to be Catholics to avoid prosecution. "The line between Christians and bandits became increasingly indistinct", remarks
Paul Cohen
Paul Joseph Cohen (April 2, 1934 – March 23, 2007) was an American mathematician. He is best known for his proofs that the continuum hypothesis and the axiom of choice are independent from Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, for which he was award ...
.
Some missionaries such as George Stenz also used their privileges to intervene in lawsuits. The Big Swords responded by attacking Catholic properties and
burning
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
them. As a result of diplomatic pressure in the capital, Yuxian executed several Big Sword leaders, but did not punish anyone else. More martial secret societies started emerging after this.
The early years saw a variety of village activities, not a broad movement with a united purpose. Martial folk-religious societies such as the
Baguadao (Eight Trigrams) prepared the way for the Boxers. Like the Red Boxing school or the
Plum Flower Boxers, the Boxers of Shandong were more concerned with traditional social and moral values, such as filial piety, than with foreign influences. One leader, Zhu Hongdeng (Red Lantern Zhu), started as a wandering healer, specialising in skin ulcers, and gained wide respect by refusing payment for his treatments. Zhu claimed descent from
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
emperors, since his surname was the surname of the Ming imperial family. He announced that his goal was to "Revive the Qing and destroy the foreigners" ("扶清滅洋 ''fu Qing mie yang''").
The enemy was seen as foreign influence. They decided the "primary devils" were the Christian missionaries whilst the "secondary devils" were the Chinese converts to Christianity, which both had either to repent, be driven out or killed.
Causes of the conflict and the unrest
Escalating tensions caused Chinese to turn against "foreign devils" who scrambled for power in the late 19th century. The Western success at controlling China, growing anti-imperialist sentiment, and extreme weather conditions, sparked the movement. A drought followed by floods in Shandong province in 1897–1898 forced farmers to flee to cities and seek food.
A major cause of discontent in north China was missionary activity. The
Treaty of Tientsin
The Treaty of Tientsin, also known as the Treaty of Tianjin, is a collective name for several documents signed at Tianjin (then romanized as Tientsin) in June 1858. The Qing dynasty, Russian Empire, Second French Empire, United Kingdom, and t ...
(Tianjin) and the
Convention of Peking
The Convention of Peking or First Convention of Peking is an agreement comprising three distinct treaties concluded between the Qing dynasty of China and Great Britain, France, and the Russian Empire in 1860. In China, they are regarded as amo ...
, signed in 1860 after the
Second Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Sino War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a colonial war lasting from 1856 to 1860, which pitted the British Empire#Britain's imperial ...
, had granted foreign missionaries the freedom to preach anywhere in China and to buy land on which to build churches. On 1 November 1897, a band of armed men who were perhaps members of the
Big Swords Society
The Big Swords Society () or Great Knife Society was a traditional peasant group most noted for the killing of two German Catholic missionaries at the Juye Incident in 1897 at Zhang Jia Village where the missionaries were ambushed in their sleep ...
stormed the residence of a German missionary from the
Society of the Divine Word
The Society of the Divine Word ( la, Societas Verbi Divini), abbreviated SVD and popularly called the Verbites or the Divine Word Missionaries, and sometimes the Steyler Missionaries, is a Catholic Church, Catholic clerical religious congregation ...
and killed two priests. This attack is known as the
Juye Incident
The Juye Incident (, german: Juye Vorfall) refers to the killing of two German Catholic missionaries, Richard Henle and Franz Xaver Nies, of the Society of the Divine Word, in Juye County Shandong Province, China in the night of 1–2 Novemb ...
.
When
Kaiser Wilhelm II received news of these murders, he dispatched the
German East Asia Squadron to occupy
Jiaozhou Bay
The Jiaozhou Bay (; german: Kiautschou Bucht, ) is a bay located in the prefecture-level city of Qingdao (Tsingtau), China.
The bay has historically been romanized as Kiaochow, Kiauchau or Kiao-Chau in English and Kiautschou in German.
Geogra ...
on the southern coast of the Shandong peninsula.
In December 1897, Wilhelm II declared his intent to seize territory in China, which triggered a "scramble for
concessions" by which Britain, France, Russia and Japan also secured their own
sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
in China. Germany gained exclusive control of developmental loans, mining, and railway ownership in Shandong province. Russia gained influence of all territory north of the
Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand Li (unit), ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against Eurasian noma ...
,
plus the previous tax exemption for trade in
Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
and
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
, economic powers similar to Germany's over
Fengtian Fengtian (; postal: Fengtien; Manchu: ''Abkai imiyangga fu'') is:
* Shenyang, largest city and provincial capital of Liaoning province, which was formerly administered under Fengtian Fu, which was abolished in 1910
* Liaoning, the province formerl ...
,
Jilin
Jilin (; Postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three Provinces of China, provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea (Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, R ...
and
Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () Postal romanization, formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a Provinces of China, province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is th ...
provinces. France gained influence of
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
, most of
Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam ...
and
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
provinces, Japan over
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its ...
province. Britain gained influence of the whole
Yangtze River Valley
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
(defined as all provinces adjoining the Yangtze river as well as
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is a ...
and
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Ji ...
provinces
), parts of Guangdong and Guangxi provinces and part of
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
.
Only Italy's request for
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Ji ...
province was declined by the Chinese government.
These do not include the lease and
concession territories
Concession may refer to:
General
* Concession (contract) (sometimes called a concession agreement), a contractual right to carry on a certain kind of business or activity in an area, such as to explore or develop its natural resources or to operat ...
where the foreign powers had full authority. The Russian government militarily occupied their zone, imposed their law and schools, seized mining and logging privileges, settled their citizens, and even established their municipal administration on several cities.

In October 1898, a group of Boxers attacked the Christian community of Liyuantun village where a temple to the
Jade Emperor
The Jade Emperor or Yudi ( or , ') in Chinese culture, traditional religions and myth is one of the representations of the first god ( '). In Daoist theology he is the assistant of Yuanshi Tianzun, who is one of the Three Pure Ones, the th ...
had been converted into a Catholic church. Disputes had surrounded the church since 1869, when the temple had been granted to the Christian residents of the village. This incident marked the first time the Boxers used the slogan "Support the Qing, destroy the foreigners" ("扶清滅洋 ''fu Qing mie yang''") that later characterised them.
The "Boxers" called themselves the "Militia United in Righteousness" for the first time one year later, at the
Battle of Senluo Temple (October 1899), a clash between Boxers and Qing government troops. By using the word "Militia" rather than "Boxers", they distanced themselves from forbidden martial arts sects, and tried to give their movement the legitimacy of a group that defended orthodoxy.
Aggression toward missionaries and Christians drew sharp responses from diplomats protecting their nationals. In 1899, the French minister in Beijing helped the missionaries to obtain an edict granting official status to every order in the Roman Catholic hierarchy, enabling local priests to support their people in legal or family disputes and bypass the local officials. After the German government took over Shandong, many Chinese feared that the foreign missionaries and possibly all Christian activities were imperialist attempts at "carving the melon", i.e., to colonise China piece by piece. A Chinese official expressed the animosity towards foreigners succinctly, "Take away your missionaries and your opium and you will be welcome."
The early growth of the Boxer movement coincided with the
Hundred Days' Reform
The Hundred Days' Reform or Wuxu Reform () was a failed 103-day national, cultural, political, and educational reform movement that occurred from 11 June to 22 September 1898 during the late Qing dynasty. It was undertaken by the young Guangxu E ...
(11 June – 21 September 1898), in which progressive Chinese officials, with support from Protestant missionaries, persuaded the
Guangxu Emperor
The Guangxu Emperor (14 August 1871 – 14 November 1908), personal name Zaitian, was the tenth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the ninth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign lasted from 1875 to 1908, but in practice he ruled, w ...
to institute sweeping reforms. This alienated many conservative officials, whose opposition led
Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi ( ; mnc, Tsysi taiheo; formerly romanised as Empress Dowager T'zu-hsi; 29 November 1835 – 15 November 1908), of the Manchu Yehe Nara clan, was a Chinese noblewoman, concubine and later regent who effectively controlled ...
to intervene and reverse the reforms. The failure of the reform movement disillusioned many educated Chinese and thus further weakened the Qing government. The empress seized power and placed the reformist emperor under house arrest.
The national crisis was widely perceived as caused by "foreign aggression" inside. Even though afterwards a majority of Chinese were extremely grateful for the actions of the alliance.
At the time, the Qing government was extremely corrupt, common people often faced extortions from government officials and the government offered no protection from the violent actions of the Boxers.
Boxer War
Intensifying crisis

In January 1900, with a majority of conservatives in the imperial court, Empress Dowager Cixi changed her position on the Boxers, and issued edicts in their defence, causing protests from foreign powers. In spring 1900, the Boxer movement spread rapidly north from Shandong into the countryside near Beijing. Boxers burned Christian churches, killed Chinese Christians and intimidated Chinese officials who stood in their way. American Minister
Edwin H. Conger cabled Washington, "the whole country is swarming with hungry, discontented, hopeless idlers."
On 30 May the diplomats, led by British Minister
Claude Maxwell MacDonald
Colonel Sir Claude Maxwell MacDonald, (12 June 1852 – 10 September 1915) was a British soldier and diplomat, best known for his service in China and Japan.
Early life
MacDonald was born the son of Mary Ellen MacDonald (''nee'' Dougan) and Ma ...
, requested that foreign soldiers come to Beijing to defend the legations. The Chinese government reluctantly acquiesced, and the next day a multinational force of 435 navy troops from eight countries debarked from warships and travelled by train from
Dagu (Taku) to Beijing. They set up defensive perimeters around their respective missions.
On 5 June 1900, the railway line to Tianjin was cut by Boxers in the countryside and Beijing was isolated. On 11 June, at
Yongding gate, the secretary of the Japanese legation, Sugiyama Akira, was
attacked and killed by the soldiers of General
Dong Fuxiang
Dong Fuxiang (1839–1908), courtesy name Xingwu (), was a Chinese general who lived in the late Qing dynasty. He was born in the Western Chinese province of Gansu. He commanded an army of Hui soldiers, which included the later Ma clique gene ...
, who were guarding the southern part of the Beijing walled city. Armed with
Mauser
Mauser, originally Königlich Württembergische Gewehrfabrik ("Royal Württemberg Rifle Factory"), was a German arms manufacturer. Their line of bolt-action rifles and semi-automatic pistols has been produced since the 1870s for the German arm ...
rifles but wearing traditional uniforms, Dong's troops had threatened the foreign Legations in the fall of 1898 soon after arriving in Beijing, so much that
United States Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through com ...
had been called to Beijing to guard the legations. The German
Kaiser
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly ap ...
Wilhelm II
, house = Hohenzollern
, father = Frederick III, German Emperor
, mother = Victoria, Princess Royal
, religion = Lutheranism (Prussian United)
, signature = Wilhelm II, German Emperor Signature-.svg
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor ...
was so alarmed by the Chinese Muslim troops that he requested the
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
Abdul Hamid II
Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, عبد الحميد ثانی, Abd ül-Hamid-i Sani; tr, II. Abdülhamid; 21 September 1842 10 February 1918) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 31 August 1876 to 27 April 1909, and the last sultan to ...
of the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
to find a way to stop the Muslim troops from fighting.
The Caliph agreed to the Kaiser's request and sent Enver Pasha (not to be confused with the
future Young Turk leader) to China in 1901, but the rebellion was over by that time.
On 11 June, the first Boxer was seen in the Legation Quarter. The German Minister,
Clemens von Ketteler
Clemens August Freiherr von Ketteler (22 November 1853 – 20 June 1900) was a German career diplomat. He was killed during the Boxer Rebellion.
Early life and career
Ketteler was born at Münster in western Germany on 22 November 1853 into ...
, and German soldiers captured a Boxer boy and inexplicably executed him. In response, thousands of Boxers burst into the walled city of Beijing that afternoon and burned many of the Christian churches and cathedrals in the city, burning some victims alive. American and British missionaries took refuge in the Methodist Mission and an attack there was repulsed by American Marines. The soldiers at the British Embassy and German Legations shot and killed several Boxers, alienating the Chinese population of the city and nudging the Qing government towards support of the Boxers.
The Muslim Gansu braves and Boxers, along with other Chinese, then attacked and killed Chinese Christians around the legations in revenge for foreign attacks on Chinese.
Seymour Expedition

As the situation grew more violent, the Eight Powers authorities at Dagu dispatched a second multinational force to Beijing on 10 June 1900. This force of 2,000 sailors and marines was under the command of Vice-Admiral
Edward Seymour RN, the largest contingent being British. The force moved by train from Dagu to Tianjin with the agreement of the Chinese government, but the railway had been severed between Tianjin and Beijing. Seymour resolved to continue forward by rail to the break and repair the railway, or progress on foot from there if necessary, as it was only 120 km from Tianjin to Beijing. When Seymour left Tianjin and started toward Beijing, it angered the imperial court.
The court then replaced Prince Qing at the Zongli Yamen, with Manchu Prince Duan, a member of the imperial
Aisin Gioro
The House of Aisin-Gioro was a Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin dynasty (1616–1636), the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), and Manchukuo (1932–1945) in the history of China. Under the Ming dynasty, members of the Aisin Gioro clan served as ch ...
clan (foreigners called him a "Blood Royal"), who was extremely anti-foreigner and pro-Boxer. He soon ordered the Imperial army to attack the foreign forces. Confused by conflicting orders from Beijing, General
Nie Shicheng let Seymour's army pass by in their trains.

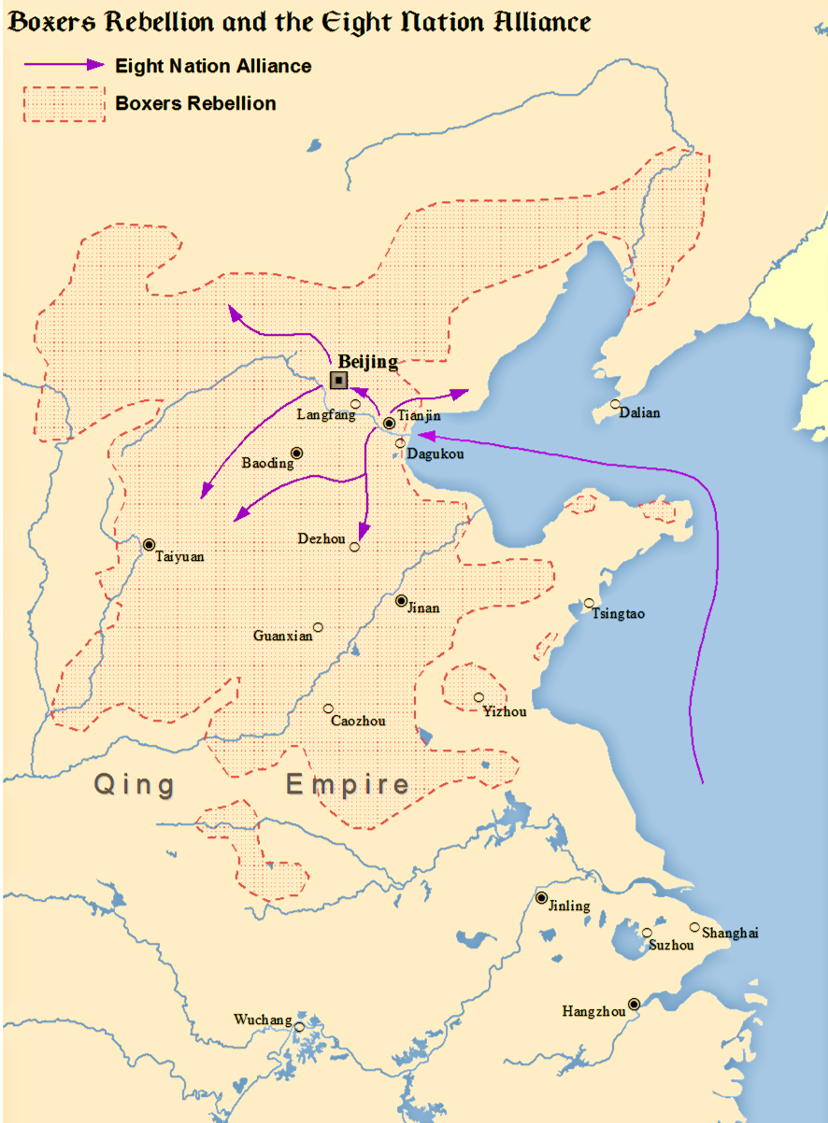
After leaving Tianjin, the force quickly reached
Langfang
Langfang () is a prefecture-level city of Hebei Province, which was known as Tianjin Prefecture until 1973. It was renamed Langfang Prefecture after Tianjin became a municipality and finally upgraded into a prefecture-level city in 1988. Lang ...
, but the railway was destroyed there. Seymour's engineers tried to repair the line, but the force found itself surrounded, as the railway in both behind directions was destroyed. They were attacked from all sides by Chinese irregulars and Imperial troops. Five thousand of Dong Fuxiang's "
Gansu Braves" and an unknown number of "Boxers" won a costly but major victory over Seymour's troops at the
Battle of Langfang on 18 June. Seymour then retreated from Langfang. The force was constantly fired upon by cavalry, and artillery bombarded their positions. It was reported that the Chinese artillery was superior, since the force had not brought much artillery with them, thinking they could easily sweep through Chinese resistance.
The Seymour force could not locate the Chinese artillery, which was raining shells upon their positions.
Chinese troops employed mining, engineering, flooding, and simultaneous attacks. The Chinese also employed pincer movements, ambushes, and sniping with some success against the foreigners.

On 18 June, Seymour learned of attacks on the Legation Quarter in Beijing, and decided to continue advancing, this time along the
Beihe Beihe may refer to the following locations in China:
* Beihe, Leizhou (北和镇), town in Guangdong
* Beihe, Dingxing County (北河镇), town in Hebei
* Beihe Township (北河乡), Xingtang County, Hebei
{{geodis ...
river, toward
Tongzhou, from Beijing. By 19 June, the force was halted by progressively stiffening resistance, and started to retreat southward along the river with over 200 wounded. They loaded all their wounded and remaining supplies on four commandeered
junks
A junk (Chinese: 船, ''chuán'') is a type of Chinese sailing ship with fully battened sails. There are two types of junk in China: northern junk, which developed from Chinese river boats, and southern junk, which developed from Austronesian ...
, which they pulled along with ropes from the riverbanks.
The force was now very low on food, ammunition, and medical supplies. They happened upon
the Great Xigu Arsenal, a hidden Qing munitions cache of which the Eight Powers had had no knowledge until then. They immediately captured and occupied it, discovering
Krupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krupp ...
field guns and rifles with millions of rounds of ammunition, along with millions of pounds of rice and ample medical supplies.
There they dug in and awaited rescue. A Chinese servant slipped through the Boxer and Imperial lines, reached Tianjin, and informed the Eight Powers of Seymour's predicament. His force was surrounded by Imperial troops and Boxers, attacked nearly around the clock, and at the point of being overrun. The Eight Powers sent a relief column from Tianjin of 1,800 men (900 Russian troops from
Port Arthur, 500 British seamen, and other assorted troops). On 25 June the relief column reached Seymour. The Seymour force now destroyed the Arsenal: they spiked the captured field guns and set fire to any munitions that they could not take (an estimated £3 million worth). The Seymour force and the relief column marched back to Tientsin, unopposed, on 26 June. Seymour's casualties during the expedition were 62 killed and 228 wounded.
Conflicting attitudes within the Qing imperial court

Meanwhile, in Beijing, on 16 June, Empress Dowager Cixi summoned the imperial court for a mass audience and addressed the choice between using the Boxers to evict the foreigners from the city and seeking a diplomatic solution. In response to a high official who doubted the efficacy of the Boxers, Cixi replied that both sides of the debate at the imperial court realised that popular support for the Boxers in the countryside was almost universal and that suppression would be both difficult and unpopular, especially when foreign troops were on the march.
Two factions were active during this debate. On one side were anti-foreigners who viewed foreigners as invasive and imperialistic and evoked a nativist populism. They advocated taking advantage of the Boxers to achieve the expulsion of foreign troops and foreign influences. The pro-foreigners on the other hand advanced rapprochement with foreign governments, seeing the Boxers as superstitious and ignorant.
The event that tilted the Qing imperial government irrevocably toward support of the Boxers and war with the foreign powers was the attack of foreign navies on the
Dagu Forts near Tianjin, on 17 June 1900.
Siege of the Beijing legations

On 15 June, Qing imperial forces deployed electric
mines in the
Beihe River
The Hai River (海河, lit. "Sea River"), also known as the Peiho, ("White River"), or Hai Ho, is a Chinese river connecting Beijing to Tianjin and the Bohai Sea.
The Hai River at Tianjin is formed by the confluence of five watercourses: the S ...
(Peiho) to prevent the Eight-Nation Alliance from sending ships to attack.
With a difficult military situation in Tianjin and a total breakdown of communications between Tianjin and Beijing, the allied nations took steps to reinforce their military presence significantly. On 17 June they took the Dagu Forts commanding the approaches to Tianjin, and from there brought increasing numbers of troops on shore. When Cixi received an ultimatum that same day demanding that China surrender total control over all its military and financial affairs to foreigners, she defiantly stated before the entire
Grand Council, "Now they
he Powershave started the aggression, and the extinction of our nation is imminent. If we just fold our arms and yield to them, I would have no face to see our ancestors after death. If we must perish, why don't we fight to the death?"
It was at this point that Cixi began to blockade the legations with the armies of the
Peking Field Force
The Peking Field Force was a modern-armed military unit that defended the Chinese imperial capital Beijing in the last decades of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912).
The Force was founded in 1862, two years after the humiliating capture of Beijing and ...
, which began the siege. Cixi stated that "I have always been of the opinion, that the allied armies had been permitted to escape too easily
in 1860. Only a united effort was then necessary to have given China the victory. Today, at last, the opportunity for revenge has come", and said that millions of Chinese would join the cause of fighting the foreigners since the Manchus had provided "great benefits" on China.
On receipt of the news of the attack on the
Dagu Fort
The Taku Forts or Dagu Forts, also called the Peiho Forts are forts located by the Hai River (Peiho River) estuary in the Binhai New Area, Tianjin, in northeastern China. They are located southeast of the Tianjin urban center.
History
The f ...
s on 19 June, Empress Dowager Cixi immediately sent an order to the legations that the diplomats and other foreigners depart Beijing under escort of the Chinese army within 24 hours.
The next morning, diplomats from the besieged legations met to discuss the Empress's offer. The majority quickly agreed that they could not trust the Chinese army. Fearing that they would be killed, they agreed to refuse the Empress's demand. The German Imperial Envoy, Baron
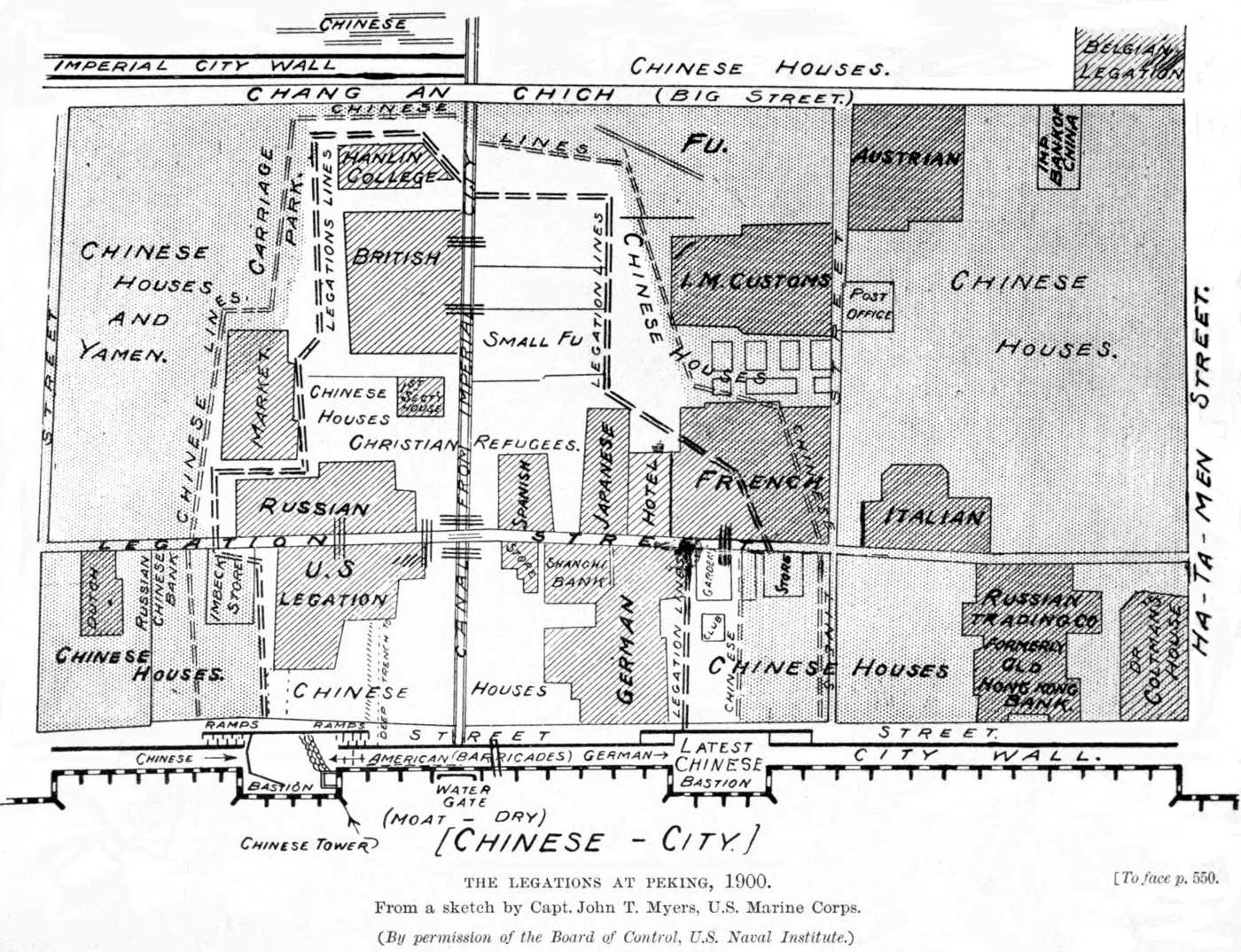
Klemens Freiherr von Ketteler, was infuriated with the actions of the Chinese army troops and determined to take his complaints to the royal court. Against the advice of the fellow foreigners, the baron left the legations with a single aide and a team of porters to carry his sedan chair. On his way to the palace, von Ketteler was killed on the streets of Beijing by a Manchu captain. His aide managed to escape the attack and carried word of the baron's death back to the diplomatic compound. At this news, the other diplomats feared they also would be murdered if they left the legation quarter and they chose to continue to defy the Chinese order to depart Beijing. The legations were hurriedly fortified. Most of the foreign civilians, which included a large number of missionaries and businessmen, took refuge in the British legation, the largest of the diplomatic compounds. Chinese Christians were primarily housed in the adjacent palace (Fu) of
Prince Su, who was forced to abandon his property by the foreign soldiers.

On 21 June, Empress Dowager Cixi declared war against all foreign powers. Regional governors in the south, who commanded substantial modernised armies, such as
Li Hongzhang
Li Hongzhang, Marquess Suyi ( zh, t=李鴻章; also Li Hung-chang; 15 February 1823 – 7 November 1901) was a Chinese politician, general and diplomat of the late Qing dynasty. He quelled several major rebellions and served in important ...
at
Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ente ...
,
Yuan Shikai
Yuan Shikai (; 16 September 1859 – 6 June 1916) was a Chinese military and government official who rose to power during the late Qing dynasty and eventually ended the Qing dynasty rule of China in 1912, later becoming the Emperor of China. H ...
in Shandong,
Zhang Zhidong
Zhang Zhidong () (4 September 18375 October 1909) was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Qing dynasty. Along with Zeng Guofan, Li Hongzhang and Zuo Zongtang, Zhang Zhidong was one of the four most famous officials of the late Qing ...
at
Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the ninth-most populous Chinese city a ...
and
Liu Kunyi
Liu Kunyi () (January21, 1830October6, 1902) was a Chinese official who came to prominence during the government suppression of the Taiping Rebellion and was active in the following Self-Strengthening Movement in the second half of the ninetee ...
at
Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
, formed the
Mutual Defense Pact of the Southeastern Provinces
The Mutual Defense Pact of the Southeastern Provinces () was an agreement reached in the summer of 1900 during the Boxer Rebellion by Qing dynasty governors of the provinces in southern, eastern and central China when the Eight-Nation Alliance inv ...
.
They refused to recognise the imperial court's declaration of war, which they declared a ''luan-ming'' (illegitimate order) and withheld knowledge of it from the public in the south. Yuan Shikai used his own forces to suppress Boxers in Shandong, and Zhang entered into negotiations with the foreigners in Shanghai to keep his army out of the conflict. The neutrality of these provincial and regional governors left the majority of Chinese military forces out of the conflict.
The legations of the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, Austria-Hungary, Spain, Belgium, the Netherlands, the United States, Russia and Japan were located in the
Beijing Legation Quarter
The Peking Legation Quarter was the area in Peking (Beijing), China where a number of foreign legations were located between 1861 and 1959. In the Chinese language, the area is known as ''Dong Jiaomin Xiang'' (), which is the name of the ''hutong ...
south of the
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrifi ...
. The Chinese army and Boxer irregulars besieged the Legation Quarter from 20 June to 14 August 1900. A total of 473 foreign civilians, 409 soldiers, marines and sailors from eight countries, and about 3,000 Chinese Christians took refuge there. Under the command of the British minister to China,
Claude Maxwell MacDonald
Colonel Sir Claude Maxwell MacDonald, (12 June 1852 – 10 September 1915) was a British soldier and diplomat, best known for his service in China and Japan.
Early life
MacDonald was born the son of Mary Ellen MacDonald (''nee'' Dougan) and Ma ...
, the legation staff and military guards defended the compound with small arms, three machine guns, and one old muzzle-loaded cannon, which was nicknamed the ''International Gun'' because the barrel was British, the carriage Italian, the shells Russian and the crew American. Chinese Christians in the legations led the foreigners to the cannon and it proved important in the defence. Also under siege in Beijing was the
Northern Cathedral (''Beitang'') of the Catholic Church. The Beitang was defended by 43 French and Italian soldiers, 33 Catholic foreign priests and nuns, and about 3,200 Chinese Catholics. The defenders suffered heavy casualties from lack of food and from mines which the Chinese exploded in tunnels dug beneath the compound. The number of Chinese soldiers and Boxers besieging the Legation Quarter and the Beitang is unknown.
Manchu Prince
Zaiyi
Zaiyi (; Manchu: ; ''dzai-i''; 26 August 1856 – 10 January 1923),Edward J.M. Rhoads, ''Manchus & Han: Ethnic Relations and Political Power in Late Qing and Early Republican China, 1861–1928'', University of Washington Press, 2001 better ...
's Manchu
bannermen in the
Tiger and Divine Corps led attacks against the Catholic cathedral church. Manchu official Qixiu
啟秀 also led attacks against the cathedral.

On 22 and 23 June, Chinese soldiers and Boxers set fire to areas north and west of the British Legation, using it as a "frightening tactic" to attack the defenders. The nearby
Hanlin Academy
The Hanlin Academy was an academic and administrative institution of higher learning founded in the 8th century Tang China by Emperor Xuanzong in Chang'an.
Membership in the academy was confined to an elite group of scholars, who performed se ...
, a complex of courtyards and buildings that housed "the quintessence of Chinese scholarship ... the oldest and richest library in the world", caught fire. Each side blamed the other for the destruction of the invaluable books it contained.
After the failure to burn out the foreigners, the Chinese army adopted an anaconda-like strategy. The Chinese built barricades surrounding the Legation Quarter and advanced, brick by brick, on the foreign lines, forcing the foreign legation guards to retreat a few feet at a time. This tactic was especially used in the Fu, defended by Japanese and Italian sailors and soldiers, and inhabited by most of the Chinese Christians. Fusillades of bullets, artillery and firecrackers were directed against the Legations almost every night—but did little damage. Sniper fire took its toll among the foreign defenders. Despite their numerical advantage, the Chinese did not attempt a direct assault on the Legation Quarter although in the words of one of the besieged, "it would have been easy by a strong, swift movement on the part of the numerous Chinese troops to have annihilated the whole body of foreigners ... in an hour." American missionary
Frank Gamewell
Frank or Franks may refer to:
People
* Frank (given name)
* Frank (surname)
* Franks (surname)
* Franks, a medieval Germanic people
* Frank, a term in the Muslim world for all western Europeans, particularly during the Crusades - see Farang
C ...
and his crew of "fighting parsons" fortified the Legation Quarter, but impressed Chinese Christians to do most of the physical labour of building defences.
The Germans and the Americans occupied perhaps the most crucial of all defensive positions: the Tartar Wall. Holding the top of the tall and wide wall was vital. The German barricades faced east on top of the wall and west were the west-facing American positions. The Chinese advanced toward both positions by building barricades even closer. "The men all feel they are in a trap", said the American commander, Capt.
John T. Myers, "and simply await the hour of execution." On 30 June, the Chinese forced the Germans off the Wall, leaving the American Marines alone in its defence. In June 1900, one American described the scene of 20,000 Boxers storming the walls:
At the same time, a Chinese barricade was advanced to within a few feet of the American positions and it became clear that the Americans had to abandon the wall or force the Chinese to retreat. At 2 am on 3 July, 56 British, Russian and American marines and sailors, under the command of Myers, launched an assault against the Chinese barricade on the wall. The attack caught the Chinese sleeping, killed about 20 of them, and expelled the rest of them from the barricades. The Chinese did not attempt to advance their positions on the Tartar Wall for the remainder of the siege.
Sir Claude MacDonald said 13 July was the "most harassing day" of the siege. The Japanese and Italians in the Fu were driven back to their last defence line. The Chinese detonated a mine beneath the French Legation pushing the French and Austrians out of most of the French Legation. On 16 July, the most capable British officer was killed and the journalist
George Ernest Morrison was wounded. But American Minister
Edwin Hurd Conger
Edwin Hurd Conger (March 7, 1843 – May 18, 1907) was an American Civil War soldier, lawyer, banker, Iowa congressman, and United States diplomat. As the United States' minister to China during the Boxer Rebellion, Conger, his family, and ...
established contact with the Chinese government and on 17 July, an armistice was declared by the Chinese. More than 40% of the legation guards were dead or wounded. The motivation of the Chinese was probably the realisation that an allied force of 20,000 men had landed in China and retribution for the siege was at hand.
Officials and commanders at cross purposes

The Manchu General
Ronglu
Ronglu (6 April 1836 – 11 April 1903), courtesy name Zhonghua, was a Manchu political and military leader of the late Qing dynasty. He was born in the Guwalgiya clan, which was under the Plain White Banner of the Manchu Eight Banners. ...
concluded that it was futile to fight all of the powers simultaneously and declined to press home the siege. The Manchu
Zaiyi
Zaiyi (; Manchu: ; ''dzai-i''; 26 August 1856 – 10 January 1923),Edward J.M. Rhoads, ''Manchus & Han: Ethnic Relations and Political Power in Late Qing and Early Republican China, 1861–1928'', University of Washington Press, 2001 better ...
(Prince Duan), an anti-foreign friend of
Dong Fuxiang
Dong Fuxiang (1839–1908), courtesy name Xingwu (), was a Chinese general who lived in the late Qing dynasty. He was born in the Western Chinese province of Gansu. He commanded an army of Hui soldiers, which included the later Ma clique gene ...
, wanted artillery for Dong's troops to destroy the legations. Ronglu blocked the transfer of artillery to Zaiyi and Dong, preventing them from attacking. Ronglu forced Dong Fuxiang and his troops to pull back from completing the siege and destroying the legations, thereby saving the foreigners and making diplomatic concessions. Ronglu and Prince Qing sent food to the legations, and used their Manchu Bannermen to attack the Muslim Gansu Braves ("Kansu Braves" in the spelling of the time) of Dong Fuxiang and the Boxers who were besieging the foreigners. They issued edicts ordering the foreigners to be protected, but the Gansu warriors ignored it, and fought against Bannermen who tried to force them away from the legations. The Boxers also took commands from Dong Fuxiang. Ronglu also deliberately hid an Imperial Decree from General
Nie Shicheng. The Decree ordered him to stop fighting the Boxers because of the foreign invasion, and also because the population was suffering. Due to Ronglu's actions, General Nie continued to fight the Boxers and killed many of them even as the foreign troops were making their way into China. Ronglu also ordered Nie to protect foreigners and save the railway from the Boxers. Because parts of the Railway were saved under Ronglu's orders, the foreign invasion army was able to transport itself into China quickly. General Nie committed thousands of troops against the Boxers instead of against the foreigners. Nie was already outnumbered by the Allies by 4,000 men. General Nie was blamed for attacking the Boxers, as Ronglu let Nie take all the blame. At the
Battle of Tianjin (Tientsin), General Nie decided to sacrifice his life by walking into the range of Allied guns.
 Xu Jingcheng
Xu Jingcheng, who had served as the Qing Envoy to many of the same states under siege in the Legation Quarter, argued that "the evasion of extraterritorial rights and the killing of foreign diplomats are unprecedented in China and abroad." Xu and five other officials urged Empress Dowager Cixi to order the repression of Boxers, the execution of their leaders, and a diplomatic settlement with foreign armies. The Empress Dowager, outraged, sentenced Xu and the five others to death for "willfully and absurdly petitioning the Imperial Court" and "building subversive thought." They were executed on 28 July 1900 and their severed heads placed on display at
Caishikou Execution Grounds
Caishikou Execution Grounds (), also known as Vegetable Market Execution Ground, was an important execution ground in Beijing during the Qing Dynasty. It was located at the crossroads of Xuanwumen Outer Street and Luomashi Street. The exact locat ...
in Beijing.

Reflecting this vacillation, some Chinese soldiers were quite liberally firing at foreigners under siege from its very onset. Cixi did not personally order imperial troops to conduct a siege, and on the contrary had ordered them to protect the foreigners in the legations. Prince Duan led the Boxers to loot his enemies within the imperial court and the foreigners, although imperial authorities expelled Boxers after they were let into the city and went on a looting rampage against both the foreign and the Qing imperial forces. Older Boxers were sent outside Beijing to halt the approaching foreign armies, while younger men were absorbed into the Muslim Gansu army.
With conflicting allegiances and priorities motivating the various forces inside Beijing, the situation in the city became increasingly confused. The foreign legations continued to be surrounded by both Qing imperial and Gansu forces. While Dong Fuxiang's Gansu army, now swollen by the addition of the Boxers, wished to press the siege, Ronglu's imperial forces seem to have largely attempted to follow Empress Dowager Cixi's decree and protect the legations. However, to satisfy the conservatives in the imperial court, Ronglu's men also fired on the legations and let off firecrackers to give the impression that they, too, were attacking the foreigners. Inside the legations and out of communication with the outside world, the foreigners simply fired on any targets that presented themselves, including messengers from the imperial court, civilians and besiegers of all persuasions. Dong Fuxiang was denied artillery held by Ronglu which stopped him from levelling the legations, and when he complained to Empress Dowager Cixi on 23 June, she dismissively said that "Your tail is becoming too heavy to wag." The Alliance discovered large amounts of unused Chinese
Krupp artillery and shells after the siege was lifted.
The armistice, although occasionally broken, endured until 13 August when, with an allied army led by the British
Alfred Gaselee
General Sir Alfred Gaselee, , (3 June 1844 – 29 March 1918) was a soldier who served in the Indian Army.
Early life
Gaselee was born at Little Yeldham, Essex, the eldest son of the Reverend John Gaselee, rector of Little Yeldham, and his ...
approaching Beijing to relieve the siege, the Chinese launched their heaviest fusillade on the Legation Quarter. As the foreign army approached, Chinese forces melted away.
Gaselee Expedition
Foreign navies started building up their presence along the northern China coast from the end of April 1900. Several international forces were sent to the capital, with varying success, and the Chinese forces were ultimately defeated by the
Eight-Nation Alliance
The Eight-Nation Alliance was a multinational military coalition that invaded northern China in 1900 with the stated aim of relieving the foreign legations in Beijing, then besieged by the popular Boxer militia, who were determined to remove fo ...
of
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
,
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
,
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
,
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, the United Kingdom and the United States. Independent of the alliance, the Netherlands dispatched three cruisers in July to protect its citizens in Shanghai.
British Lieutenant-General
Alfred Gaselee
General Sir Alfred Gaselee, , (3 June 1844 – 29 March 1918) was a soldier who served in the Indian Army.
Early life
Gaselee was born at Little Yeldham, Essex, the eldest son of the Reverend John Gaselee, rector of Little Yeldham, and his ...
acted as the commanding officer of the Eight-Nation Alliance, which eventually numbered 55,000. The main contingent was composed of Japanese (20,840), Russian (13,150), British (12,020), French (3,520), U.S. (3,420), German (900), Italian (80), Austro-Hungarian (75) and anti-Boxer Chinese troops. The "First Chinese Regiment" (
Weihaiwei Regiment
The 1st Chinese Regiment, or the Weihaiwei Regiment, was a British Army Regiment formed and disbanded in British Weihaiwei. The "First Chinese Regiment", which was praised for its performance, consisted of Chinese rank and file serving under Brit ...
) which was praised for its performance, consisted of Chinese collaborators serving in the British military.
Notable events included the seizure of the
Dagu Forts commanding the approaches to Tianjin and the boarding and capture of four Chinese destroyers by British Commander
Roger Keyes
Admiral of the Fleet Roger John Brownlow Keyes, 1st Baron Keyes, (4 October 1872 – 26 December 1945) was a British naval officer.
As a junior officer he served in a corvette operating from Zanzibar on slavery suppression missions. Ea ...
. Among the foreigners besieged in Tianjin was a young American mining engineer named
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Gre ...
, who would go on to become the 31st President of the United States.
[Hoover, Herbert C. (1952). ''The Memoirs of Herbert Hoover Years of Adventure 1874–1920''. London: Hollis & Carter. p. 47-54]
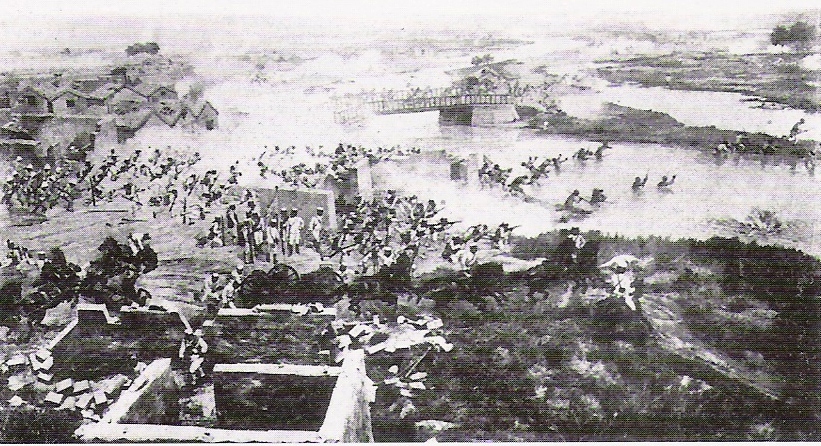


The international force finally captured
Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
on 14 July. The international force suffered its heaviest casualties of the Boxer Rebellion in the
Battle of Tianjin. With Tianjin as a base, the international force marched from Tianjin to Beijing, about 120 km, with 20,000 allied troops. On 4 August, there were approximately 70,000 Qing imperial troops and anywhere from 50,000 to 100,000 Boxers along the way. The allies only encountered minor resistance, fighting battles at
Beicang and
Yangcun. At Yangcun, the
14th Infantry Regiment of the U.S. and British troops led the assault. The weather was a major obstacle. Conditions were extremely humid with temperatures sometimes reaching . These high temperatures and insects plagued the Allies. Soldiers became dehydrated and horses died. Chinese villagers killed Allied troops who searched for wells.
The heat killed Allied soldiers, who foamed at the mouth. The tactics along the way were gruesome on either side. Allied soldiers beheaded already dead Chinese corpses, bayoneted or beheaded live Chinese civilians, and raped Chinese girls and women.
[.] Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
s were reported to have killed Chinese civilians almost automatically and Japanese kicked a Chinese soldier to death. The Chinese responded to the Alliance's atrocities with similar acts of violence and cruelty, especially towards captured Russians.
Lieutenant
Smedley Butler
Major general (United States), Major General Smedley Darlington Butler (July 30, 1881June 21, 1940), nicknamed the "Maverick Marine", was a senior United States Marine Corps Officer (armed forces), officer who fought in the Philippine–American ...
saw the remains of two Japanese soldiers nailed to a wall, who had their tongues cut off and their eyes gouged. Lieutenant Butler was wounded during the expedition in the leg and chest, later receiving the
Brevet Medal
The Marine Corps Brevet Medal, also known as the Brevet Medal, was a military decoration of the United States Marine Corps; it was created in 1921 as a result of Marine Corps Order Number 26. The decoration was a one-time issuance and retroactive ...
in recognition for his actions.

The international force reached Beijing on 14 August. Following the defeat of Beiyang army in the
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the p ...
, the Chinese government had invested heavily in modernising the imperial army, which was equipped with modern
Mauser
Mauser, originally Königlich Württembergische Gewehrfabrik ("Royal Württemberg Rifle Factory"), was a German arms manufacturer. Their line of bolt-action rifles and semi-automatic pistols has been produced since the 1870s for the German arm ...
repeater rifles and
Krupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krupp ...
artillery. Three modernised divisions consisting of Manchu
Bannermen protected the Beijing Metropolitan region. Two of them were under the command of the anti-Boxer
Prince Qing
Prince Qing of the First Rank (Manchu: ; ''hošoi fengšen cin wang''), or simply Prince Qing, was the title of a princely peerage used in China during the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1636–1912). It was also one of the 12 "iron-cap" princely pe ...
and Ronglu, while the anti-foreign Prince Duan commanded the ten-thousand-strong
Hushenying, or "Tiger Spirit Division", which had joined the Gansu Braves and Boxers in attacking the foreigners. It was a Hushenying captain who had assassinated the German diplomat Ketteler. The Tenacious Army under Nie Shicheng received Western style training under German and Russian officers in addition to their modernised weapons and uniforms. They effectively resisted the Alliance at the
Battle of Tientsin
The Battle of Tientsin, or the Relief of Tientsin, occurred on 13–14 July 1900, during the Boxer Rebellion in Northern China. A multinational military force, representing the Eight-Nation Alliance, rescued a besieged population of foreign nat ...
before retreating and astounded the Alliance forces with the accuracy of their artillery during the siege of the Tianjin concessions (the artillery shells failed to explode upon impact due to corrupt manufacturing). The Gansu Braves under Dong Fuxiang, which some sources described as "ill disciplined", were armed with modern weapons but were not trained according to Western drill and wore traditional Chinese uniforms. They led the defeat of the Alliance at Langfang in the Seymour Expedition and were the most ferocious in besieging the Legations in Beijing. Some
Banner
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Als ...
forces were given modernised weapons and Western training, becoming the Metropolitan Banner forces, which were decimated in the fighting. Among the Manchu dead was the father of the writer
Lao She
Shu Qingchun (3 February 189924 August 1966), known by his pen name Lao She, was a Chinese novelist and dramatist. He was one of the most significant figures of 20th-century Chinese literature, and is best known for his novel '' Rickshaw Boy'' ...
.
The British won the race among the international forces to be the first to reach the besieged Legation Quarter. The U.S. was able to play a role due to the presence of U.S. ships and troops stationed in
Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
since the U.S. conquest of the Philippines during the
Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
and the subsequent
Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
. In the U.S. military, the action in the Boxer Rebellion was known as the
China Relief Expedition
The China Relief Expedition was an expedition in China undertaken by the United States Armed Forces to rescue United States citizens, European nationals, and other foreign nationals during the latter years of the Boxer Rebellion, which lasted ...
.
United States Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through com ...
scaling the walls of Beijing is an iconic image of the Boxer Rebellion.

The British Army reached the legation quarter on the afternoon of 14 August and relieved the Legation Quarter. The Beitang was relieved on 16 August, first by Japanese soldiers and then, officially, by the French.
Evacuation of the Qing imperial court from Beijing to Xi'an

In the early hours of 15 August, just as the Foreign Legations were being relieved, Empress Dowager Cixi, dressed in the padded blue cotton of a farm woman, the Guangxu Emperor, and a small retinue climbed into three wooden ox carts and escaped from the city covered with rough blankets. Legend has it that the Empress Dowager then either ordered that the Guangxu Emperor's favourite concubine,
Consort Zhen
Imperial Noble Consort Keshun (27 February 1876 – 15 August 1900), of the Manchu Bordered Red Banner Tatara clan, was a consort of the Guangxu Emperor. She was five years his junior. She was known to foreigners as the Pearl Concubine. Legend ...
, be thrown down a well in the Forbidden City or tricked her into drowning herself. The journey was made all the more arduous by the lack of preparation, but the Empress Dowager insisted this was not a retreat, rather a "tour of inspection." After weeks of travel, the party arrived in
Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
in
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
province, beyond protective mountain passes where the foreigners could not reach, deep in Chinese Muslim territory and protected by the Gansu Braves. The foreigners had no orders to pursue the Empress Dowager, so they decided to stay put.
Russian invasion of Manchuria

The Russian Empire and the Qing Dynasty had maintained a long peace, starting with the
Treaty of Nerchinsk
The Treaty of Nerchinsk () of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River ...
in 1689, but Russian forces took advantage of Chinese defeats to impose the
Aigun Treaty
The Treaty of Aigun (Russian: Айгунский договор; ) was an 1858 treaty between the Russian Empire and the Qing dynasty that established much of the modern border between the Russian Far East and China by ceding much of Manchuria ( ...
of 1858 and the
Treaty of Peking
The Convention of Peking or First Convention of Peking is an agreement comprising three distinct treaties concluded between the Qing dynasty of China and Great Britain, France, and the Russian Empire in 1860. In China, they are regarded as ...
of 1860 which ceded formerly Chinese territory in Manchuria to Russia, much of which is held by Russia to the present day (
Primorye
Primorsky Krai (russian: Приморский край, r=Primorsky kray, p=prʲɪˈmorskʲɪj kraj), informally known as Primorye (, ), is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, located in the Far East region of the country and is a part of t ...
). The Russians aimed for control over the
Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China (Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
for navigation, and the all-weather ports of
Dairen
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the ...
and
Port Arthur in the
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
peninsula. The rise of Japan as an Asian power provoked Russia's anxiety, especially in light of expanding Japanese influence in
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
. Following Japan's victory in the
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the p ...
of 1895, the
Triple Intervention
The Tripartite Intervention or was a diplomatic intervention by Russia, Germany, and France on 23 April 1895 over the harsh terms of the Treaty of Shimonoseki imposed by Japan on the Qing dynasty of China that ended the First Sino-Japanese War. ...
of Russia, Germany and France forced Japan to return the territory won in Liaodong, leading to a de facto Sino-Russian alliance.
Local Chinese in Manchuria were incensed at these Russian advances and began to harass Russians and Russian institutions, such as the
Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, russian: Китайско-Восточная железная дорога, or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (als ...
. In June 1900, the Chinese bombarded the town of
Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благове́щенск, p=bləgɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, meaning ''City of the Annunciation'') is a city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. It is located at the confluence of the Amur and the Zeya Rivers, o ...
on the Russian side of the Amur. The Czar's government used the pretext of Boxer activity to move some 200,000 troops into the area to
crush the Boxers. The Chinese used arson to destroy a bridge carrying a railway and a barracks on 27 July. The
Boxers destroyed railways and cut lines for telegraphs and burned the Yantai mines.
By 21 September, Russian troops took
Jilin
Jilin (; Postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three Provinces of China, provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea (Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, R ...
and Liaodong, and by the end of the month completely occupied Manchuria, where their presence was a major factor leading to the
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
.
The Chinese
Honghuzi bandits of Manchuria, who had fought alongside the Boxers in the war, did not stop when the Boxer rebellion was over, and continued guerrilla warfare against the Russian occupation up to the
Russo-Japanese war
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
when the Russians were defeated by Japan.
Massacre of missionaries and Chinese Christians

Orthodox, Protestant, and Catholic missionaries and their Chinese parishioners were massacred throughout northern China, some by Boxers and others by government troops and authorities. After the declaration of war on Western powers in June 1900, Yuxian, who had been named governor of
Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-leve ...
in March of that year, implemented a brutal anti-foreign and anti-Christian policy. On 9 July, reports circulated that he had executed forty-four foreigners (including women and children) from missionary families whom he had invited to the provincial capital
Taiyuan
Taiyuan (; ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; also known as (), ()) is the capital and largest city of Shanxi Province, People's Republic of China. Taiyuan is the political, economic, cultural and international exchange center of Shanxi Province. ...
under the promise to protect them. Although the purported
eyewitness accounts have recently been questioned as improbable, this event became a notorious symbol of Chinese anger, known as the
Taiyuan Massacre. The
Baptist Missionary Society
BMS World Mission is a Christian missionary society founded by Baptists from England in 1792. It was originally called the Particular Baptist Society for the Propagation of the Gospel Amongst the Heathen, but for most of its life was known as th ...
, based in England, opened its mission in Shanxi in 1877. In 1900 all its missionaries there were killed, along with all 120 converts. By the summer's end, more foreigners and as many as 2,000 Chinese Christians had been put to death in the province. Journalist and historical writer Nat Brandt has called the massacre of Christians in Shanxi "the greatest single tragedy in the history of Christian evangelicalism."
During the Boxer Rebellion as a whole, a total of 136 Protestant missionaries and 53 children were killed, and 47 Catholic priests and nuns, 30,000 Chinese Catholics, 2,000 Chinese Protestants, and 200 to 400 of the 700 Russian Orthodox Christians in Beijing were estimated to have been killed. Collectively, the Protestant dead were called the
China Martyrs of 1900. 222 of Russian Christian
Chinese Martyrs including
St. Metrophanes were
locally canonised as
New Martyrs on 22 April 1902, after
Archimandrite
The title archimandrite ( gr, ἀρχιμανδρίτης, archimandritēs), used in Eastern Christianity, originally referred to a superior abbot (''hegumenos'', gr, ἡγούμενος, present participle of the verb meaning "to lead") whom ...
Innocent (Fugurovsky), head of the Russian Orthodox Mission in China, solicited the
Most Holy Synod
The Most Holy Governing Synod (russian: Святѣйшій Правительствующій Сѵнодъ, Святейший Правительствующий Синод) was the highest governing body of the Russian Orthodox Church betwee ...
to perpetuate their memory. This was the first local canonisation for more than two centuries. The Boxers went on to murder Christians across 26 prefectures.
Aftermath
Occupation, looting, and atrocities
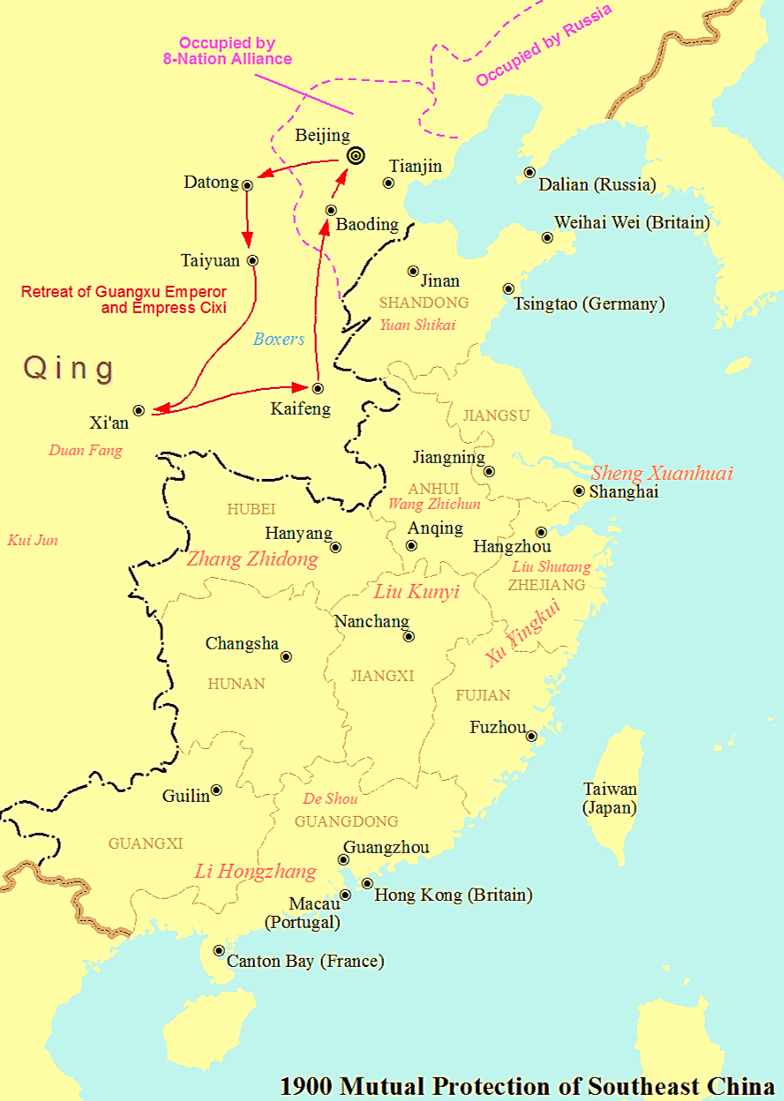
The Eight Nation Alliance occupied Zhili province while Russia occupied Manchuria, but the rest of China was not occupied due to the actions of several Han governors who formed the
Mutual Protection of Southeast China that refused to obey the declaration of war and kept their armies and provinces out of the war. Zhang Zhidong told Everard Fraser, the Hankou-based British consul general, that he despised Manchus in order that the Eight Nation Alliance would not occupy provinces under the Mutual Defense Pact.

Beijing, Tianjin and Zhili province were occupied for more than one year by the international expeditionary force under the command of German General
Alfred Graf von Waldersee
Alfred Ludwig Heinrich Karl Graf von Waldersee (8 April 1832 in Potsdam5 March 1904 in Hanover) was a German field marshal ('' Generalfeldmarschall'') who became Chief of the Imperial German General Staff.
Born into a prominent military famil ...
. The Americans and British paid General
Yuan Shikai
Yuan Shikai (; 16 September 1859 – 6 June 1916) was a Chinese military and government official who rose to power during the late Qing dynasty and eventually ended the Qing dynasty rule of China in 1912, later becoming the Emperor of China. H ...
and his army (the
Right Division) to help the Eight Nation Alliance suppress the Boxers. Yuan Shikai's forces killed tens of thousands of people in their anti-Boxer campaign in Zhili Province and Shandong after the Alliance captured Beijing.
The majority of the hundreds of thousands of people living in inner Beijing during the Qing were Manchus and
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
bannermen from the Eight Banners after they were moved there in 1644, when Han Chinese were expelled.
Sawara Tokusuke, a Japanese journalist, wrote in "Miscellaneous Notes about the Boxers" about the rapes of Manchu and Mongol banner girls. A daughter and wife of Mongol banner noble Chongqi
崇绮 of the
Alute clan were allegedly gang raped. Other relatives, including his son, Baochu, killed themselves after he killed himself on 26 August 1900.
Contemporary British and American observers levelled their greatest criticism at German, Russian, and Japanese troops for their ruthlessness and willingness to execute Chinese of all ages and backgrounds, sometimes burning and killing entire village populations. The German force arrived too late to take part in the fighting, but undertook punitive expeditions to villages in the countryside. Kaiser Wilhelm II on 27 July, during departure ceremonies for the German relief force, in a
speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
included an impromptu but intemperate reference to the
Hun
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
invaders of continental Europe, which would later be resurrected by British propaganda to mock Germany during the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
:
One newspaper called the aftermath of the siege a "carnival of ancient loot", and others called it "an orgy of looting" by soldiers, civilians and missionaries. These characterisations called to mind the
sacking of the Summer Palace in 1860. Each nationality accused the others of being the worst looters. An American diplomat,
Herbert G. Squiers, filled several railway carriages with loot and artefacts. The British Legation held loot auctions every afternoon and proclaimed, "Looting on the part of British troops was carried out in the most orderly manner." However, one British officer noted, "It is one of the unwritten
laws of war
The law of war is the component of international law that regulates the conditions for initiating war ('' jus ad bellum'') and the conduct of warring parties (''jus in bello''). Laws of war define sovereignty and nationhood, states and territ ...
that a city which does not surrender at the last and is taken by storm is looted." For the rest of 1900–1901, the British held loot auctions everyday except Sunday in front of the main-gate to the British Legation. Many foreigners, including
Sir Claude Maxwell MacDonald and Lady Ethel MacDonald and
George Ernest Morrison of ''
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ( ...
'', were active bidders among the crowd. Many of these looted items ended up in Europe. The Catholic
Beitang or North Cathedral was a "salesroom for stolen property."
The American commander General
Adna Chaffee
Adna Romanza Chaffee (April 14, 1842 – November 1, 1914) was a lieutenant general in the United States Army. Chaffee took part in the American Civil War and Indian Wars, played a key role in the Spanish–American War, and fought in the Boxe ...
banned looting by American soldiers, but the ban was ineffectual.

Some but by no means all Western missionaries took an active part in calling for retribution. To provide restitution to missionaries and Chinese Christian families whose property had been destroyed,
William Ament, a missionary of
American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions
The American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions (ABCFM) was among the first American Christian missionary organizations. It was created in 1810 by recent graduates of Williams College. In the 19th century it was the largest and most imp ...
, guided American troops through villages to punish those he suspected of being Boxers and confiscate their property. When
Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has pr ...
read of this expedition, he wrote a scathing essay,
"To the Person Sitting in Darkness", that attacked the "Reverend bandits of the American Board," especially targeting Ament, one of the most respected missionaries in China. The controversy was front-page news during much of 1901. Ament's counterpart on the distaff side was British missionary Georgina Smith, who presided over a neighbourhood in Beijing as judge and jury.
While one historical account reported that Japanese troops were astonished by other Alliance troops raping civilians, others noted that Japanese troops were 'looting and burning without mercy', and that Chinese 'women and girls by hundreds have committed suicide to escape a worse fate at the hands of Russian and Japanese brutes.' Roger Keyes, who commanded the British destroyer ''
Fame'' and accompanied the Gaselee Expedition, noted that the Japanese had brought their own "regimental wives" (prostitutes) to the front to keep their soldiers from raping Chinese civilians.
''
The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was f ...
'' journalist
E. J. Dillon
Emile Joseph Dillon (21 March 1854 – 9 June 1933) was an Irish author, journalist and linguist.
Biography
He was born on 21 March 1854 in Dublin, Ireland, the son of an Irish father and an English mother.
Dillon initially trained for the ...
stated that he witnessed the mutilated corpses of Chinese women who were raped and killed by the Alliance troops. The French commander dismissed the rapes, attributing them to "gallantry of the French soldier." A foreign journalist, George Lynch, said "there are things that I must not write, and that may not be printed in England, which would seem to show that this Western civilisation of ours is merely a veneer over savagery."
Many
Manchu Bannermen supported the Boxers and shared their anti-foreign sentiment. Bannermen had been devastated in the
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the p ...
in 1895 and Banner armies were destroyed while resisting the invasion. In the words of historian
Pamela Crossley
Pamela K Crossley (born 18 November 1955) is a historian of modern China, northern Asia, and global history and is the Charles and Elfriede Collis Professor of History, Dartmouth College. She is a founding appointment of the Dartmouth Society of ...
, their living conditions went "from desperate poverty to true misery."
When thousands of Manchus fled south from
Aigun
Aigun (; Manchu language, Manchu: ''aihūn hoton''; ) was a historic China, Chinese Town (China), town in northern Manchuria, situated on the right bank of the Amur River, some south (downstream) from the central urban area of Heihe (which is a ...
during the fighting in 1900, their cattle and horses were stolen by Russian Cossacks who then burned their villages and homes to ashes. Manchu Banner armies were destroyed while resisting the invasion, many annihilated by Russians. Manchu Shoufu killed himself during the battle of Peking and the Manchu
Lao She
Shu Qingchun (3 February 189924 August 1966), known by his pen name Lao She, was a Chinese novelist and dramatist. He was one of the most significant figures of 20th-century Chinese literature, and is best known for his novel '' Rickshaw Boy'' ...
's father was killed by western soldiers in the battle as the Manchu banner armies of the Center Division of the Guards Army,
Tiger Spirit Division and
Peking Field Force
The Peking Field Force was a modern-armed military unit that defended the Chinese imperial capital Beijing in the last decades of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912).
The Force was founded in 1862, two years after the humiliating capture of Beijing and ...
in the Metropolitan banners were slaughtered by the western soldiers. The Inner city Legation Quarters and Catholic cathedral (
Church of the Saviour, Beijing) were both attacked by Manchu bannermen. Manchu bannermen were slaughtered by the Eight Nation Alliance all over Manchuria and Beijing because most of the Manchu bannermen supported the Boxers.The clan system of the Manchus in Aigun was obliterated by the despoliation of the area at the hands of the Russian invaders. There were 1,266 households including 900
Daurs
The Daur people (Khalkha Mongolian: Дагуур, ''Daguur''; ) are a Mongolic people in Northeast China. The Daur form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognised in the People's Republic of China. They numbered 131,992 according to the la ...
and 4,500 Manchus in
Sixty-Four Villages East of the River
The Sixty-Four Villages East of the River were a group of Manchu, Daur and Han-inhabited villages located on the left (north) bank of the Amur River (Heilong Jiang) opposite of Heihe, and on the east bank of Zeya River opposite of Blagovesh ...
and
Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благове́щенск, p=bləgɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, meaning ''City of the Annunciation'') is a city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. It is located at the confluence of the Amur and the Zeya Rivers, o ...
until the
committed by Russian Cossack soldiers. Many Manchu villages were burned by Cossacks in the massacre according to Victor Zatsepine.
Manchu royals, officials and officers like
Yuxian, Qixiu
啟秀,
Zaixun, Prince Zhuang
Zaixun (24 January 1853 – 21 February 1901), formally known as Prince Zhuang, was a Manchu prince of the Qing dynasty. He is best known for his involvement in the Boxer Rebellion.
Life
Zaixun was born in the Aisin Gioro clan as the second son ...
and Captain
Enhai (En Hai) were executed or forced to commit suicide by the Eight Nation Alliance. Manchu official Gangyi's
剛毅 execution was demanded, but he already died.
[ (]Draft History of Qing
The ''Draft History of Qing'' () is a draft of the official history of the Qing dynasty compiled and written by a team of over 100 historians led by Zhao Erxun who were hired by the Beiyang government of the Republic of China. The draft was publ ...
Volume 465) Japanese soldiers arrested Qixiu before he was executed. Zaixun, Prince Zhuang was forced to commit suicide on 21 February 1901. They executed Yuxian on 22 February 1901. On 31 December 1900 German soldiers beheaded the Manchu captain Enhai for killing
Clemens von Ketteler
Clemens August Freiherr von Ketteler (22 November 1853 – 20 June 1900) was a German career diplomat. He was killed during the Boxer Rebellion.
Early life and career
Ketteler was born at Münster in western Germany on 22 November 1853 into ...
.
Reparations
After the capture of Peking by the foreign armies, some of Empress Dowager Cixi's advisers advocated that the war be carried on, arguing that China could have defeated the foreigners as it was disloyal and traitorous people within China who allowed Beijing and Tianjin to be captured by the Allies, and that the interior of China was impenetrable. They also recommended that Dong Fuxiang continue fighting. The Empress Dowager Cixi was practical, however, and decided that the terms were generous enough for her to acquiesce when she was assured of her continued reign after the war and that China would not be forced to cede any territory.
On 7 September 1901, the Qing imperial court agreed to sign the "
Boxer Protocol
The Boxer Protocol was signed on September 7, 1901, between the Qing Empire of China and the Eight-Nation Alliance that had provided military forces (including Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, Russia, and the Un ...
" also known as Peace Agreement between the Eight-Nation Alliance and China. The protocol ordered the execution of 10 high-ranking officials linked to the outbreak and other officials who were found guilty for the slaughter of foreigners in China.
Alfons Mumm (Freiherr von Schwarzenstein),
Ernest Satow
Sir Ernest Mason Satow, (30 June 1843 – 26 August 1929), was a British scholar, diplomat and Japanologist.
Satow is better known in Japan than in Britain or the other countries in which he served, where he was known as . He was a key fig ...
and
Komura Jutaro signed on behalf of Germany, Britain and Japan, respectively.
China was fined
war reparations
War reparations are compensation payments made after a war by one side to the other. They are intended to cover damage or injury inflicted during a war.
History
Making one party pay a war indemnity is a common practice with a long history.
...
of 450,000,000
s of fine silver (≈ @ 1.2 ozt/tael) for the loss that it caused. The reparation was to be paid by 1940, within 39 years, and would be 982,238,150 taels with interest (4 per cent per year) included. To help meet the payment it was agreed to increase the existing tariff from an actual 3.18 to 5 per cent, and to tax hitherto duty-free merchandise. The sum of reparation was estimated by the Chinese population (roughly 450 million in 1900), to let each Chinese pay one tael. Chinese custom income and salt taxes guaranteed the reparation. China paid 668,661,220 taels of silver from 1901 to 1939, equivalent in 2010 to ≈US$61 billion on a purchasing power parity basis.
[Hsu, 481]
A large portion of the reparations paid to the United States was diverted to pay for the education of Chinese students in U.S. universities under the
Boxer Indemnity Scholarship Program
The Boxer Indemnity Scholarship Program () was a scholarship program for Chinese students to be educated in the United States, funded by the . In 1908, the U.S. Congress passed a bill to return to China the excess of Boxer Indemnity, amounting to ...
. To prepare the students chosen for this program an institute was established to teach the English language and to serve as a preparatory school. When the first of these students returned to China they undertook the teaching of subsequent students; from this institute was born
Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University (; abbr. THU) is a national public research university in Beijing, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education.
The university is a member of the C9 League, Double First Class University Plan, Projec ...
. Some of the reparation due to Britain was later earmarked for a similar program.

The
China Inland Mission
OMF International (formerly Overseas Missionary Fellowship and before 1964 the China Inland Mission) is an international and interdenominational Evangelical Christian missionary society with an international centre in Singapore. It was founded in ...
lost more members than any other missionary agency:
58 adults and 21 children were killed. However, in 1901, when the allied nations were demanding compensation from the Chinese government,
Hudson Taylor
James Hudson Taylor (; 21 May 1832 – 3 June 1905) was a British Baptist Christian missionary to China and founder of the China Inland Mission (CIM, now OMF International). Taylor spent 51 years in China. The society that he began was respons ...
refused to accept payment for loss of property or life in order to demonstrate the meekness and gentleness of Christ to the Chinese.
The Belgian Catholic vicar apostolic of Ordos, Msgr. Alfons Bermyn wanted foreign troops garrisoned in
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, but the Governor refused. Bermyn petitioned the Manchu
Enming to send troops to
Hetao where Prince Duan's Mongol troops and General
Dong Fuxiang
Dong Fuxiang (1839–1908), courtesy name Xingwu (), was a Chinese general who lived in the late Qing dynasty. He was born in the Western Chinese province of Gansu. He commanded an army of Hui soldiers, which included the later Ma clique gene ...
's Muslim troops allegedly threatened Catholics. It turned out that Bermyn had created the incident as a hoax.
Western Catholic missionaries forced Mongols to give up their land to Han Chinese Catholics as part of the Boxer indemnities according to Mongol historian Shirnut Sodbilig. Mongols had participated in attacks against Catholic missions in the Boxer rebellion.
The Qing government did not capitulate to all the foreign demands. The Manchu governor Yuxian, was executed, but the imperial court refused to execute the Han Chinese General Dong Fuxiang, although he had also encouraged the killing of foreigners during the rebellion.
Empress Dowager Cixi intervened when the Alliance demanded him executed and Dong was only cashiered and sent back home.
Instead, Dong lived a life of luxury and power in "exile" in his home province of Gansu.
Upon Dong's death in 1908, all honours which had been stripped from him were restored and he was given a full military burial.
Long-term consequences
The European great powers ceased their ambitions of colonising China since they had learned from the Boxer rebellions that the best way to deal with China was through the ruling dynasty, rather than directly with the Chinese people (a sentiment embodied in the adage: "The people are afraid of officials, the officials are afraid of foreigners, and the foreigners are afraid of the people") (), and they even briefly assisted the Qing in their war against the Japanese to prevent Japanese domination in the region.

Concurrently, the period marks the decline of European great power interference in Chinese affairs, with the Japanese replacing the Europeans as the dominant power for their lopsided involvement in the war against the Boxers as well as their victory in the
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the p ...
. With the toppling of the Qing that followed and the rise of the Nationalist
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Ta ...
, European sway in China was reduced to symbolic status. After replacing Russian influence in the southern half of Inner Manchuria as a result of the
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
, Japan came to dominate Asian affairs militarily and culturally with many of the Chinese scholars also educated in Japan, the most prominent example being
Sun Yat-Sen
Sun Yat-sen (; also known by several other names; 12 November 1866 – 12 March 1925)Singtao daily. Saturday edition. 23 October 2010. section A18. Sun Yat-sen Xinhai revolution 100th anniversary edition . was a Chinese politician who serve ...
, who would later found the Nationalist
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Ta ...
in China.
In October 1900, Russia occupied the provinces of Manchuria,
a move that threatened
Anglo-American hopes of maintaining the country's openness to commerce under the
Open Door Policy
The Open Door Policy () is the United States diplomatic policy established in the late 19th and early 20th century that called for a system of equal trade and investment and to guarantee the territorial integrity of Qing China. The policy wa ...
.
Japan's clash with Russia over
Liaodong
The Liaodong Peninsula (also Liaotung Peninsula, ) is a peninsula in southern Liaoning province in Northeast China, and makes up the southwestern coastal half of the Liaodong region. It is located between the mouths of the Daliao River (the ...
and other provinces in eastern Manchuria, because of the Russian refusal to honour the terms of the Boxer protocol that called for their withdrawal, led to the
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
when two years of negotiations broke down in February 1904. The Russian Lease of the Liaodong (1898) was confirmed. Russia was ultimately defeated by an increasingly confident Japan.
Besides the compensation,
Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi ( ; mnc, Tsysi taiheo; formerly romanised as Empress Dowager T'zu-hsi; 29 November 1835 – 15 November 1908), of the Manchu Yehe Nara clan, was a Chinese noblewoman, concubine and later regent who effectively controlled ...
reluctantly started some reforms, despite her previous views. Known as the
New Policies, which started in 1901, the
imperial examination
The imperial examination (; lit. "subject recommendation") refers to a civil-service examination system in Imperial China, administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the state bureaucracy. The concept of choosing bureaucrats by ...
system for government service was eliminated, and the system of
education through Chinese classics was replaced with a
European liberal system that led to a university degree. Along with the formation of new military and police organisations, the reforms also simplified central bureaucracy and made a start at revamping taxation policies.
After the deaths of Cixi and the
Guangxu Emperor
The Guangxu Emperor (14 August 1871 – 14 November 1908), personal name Zaitian, was the tenth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the ninth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign lasted from 1875 to 1908, but in practice he ruled, w ...
in 1908, the
prince regent
A prince regent or princess regent is a prince or princess who, due to their position in the line of succession, rules a monarchy as regent in the stead of a monarch regnant, e.g., as a result of the sovereign's incapacity (minority or illne ...
Zaifeng (Prince Chun), the Guangxu Emperor's brother, launched further reforms.
The effect on China was a weakening of the dynasty and its national defence capabilities. The government structure was temporarily sustained by the Europeans. Behind the international conflict, internal ideological differences between northern Chinese anti-foreign royalists and southern Chinese anti-Qing revolutionists were further deepened. The scenario in the last years of the Qing dynasty gradually escalated into a chaotic
warlord era in which the most powerful northern warlords were hostile towards the southern revolutionaries, who overthrew the Qing monarchy in 1911. The rivalry was not fully resolved until the northern warlords were defeated by the Kuomintang's 1926–28
Northern Expedition
The Northern Expedition was a military campaign launched by the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT), also known as the "Chinese Nationalist Party", against the Beiyang government and other regional warlords in 1926. The ...
. Prior to the final defeat of the Boxer Rebellion, all anti-Qing movements in the previous century, such as the
Taiping Rebellion
The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive rebellion and civil war that was waged in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Han, Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It last ...
, had been successfully suppressed by the Qing.
The historian
Walter LaFeber
Walter Fredrick LaFeber (August 30, 1933March 9, 2021) was an American academic who served as the Andrew H. and James S. Tisch Distinguished University Professor in the Department of History at Cornell University. Previous to that he served as t ...
has argued that President
William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until his assassination in 1901. As a politician he led a realignment that made his Republican Party largely dominant in t ...
's decision to send 5,000 American troops to quell the rebellion marks "the origins of modern presidential war powers":
Arthur M. Schlesinger, Jr.
Arthur Meier Schlesinger Jr. (; born Arthur Bancroft Schlesinger; October 15, 1917 – February 28, 2007) was an American historian, social critic, and public intellectual. The son of the influential historian Arthur M. Schlesinger Sr. and a s ...
, concurred and wrote,
In the
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific T ...
, when the Japanese asked the Muslim general
Ma Hongkui
Ma Hongkui (,
Xiao'erjing: ; March 14, 1892 – January 14, 1970) was a prominent warlord in China during the Republic of China era, ruling the province of Ningxia. His rank was lieutenant general. His courtesy name was Shao-yun (少雲 ...
to defect and become head of a Muslim puppet state, he responded that his relatives had been killed during the Battle of Peking, including his uncle
Ma Fulu
Ma Fulu ( Chinese: 马福禄, Pinyin: Mǎ Fúlù, Xiao'erjing: ; 1854 – 1900), a Chinese Muslim, was the son of General Ma Qianling and the brother of Ma Fucai, Ma Fushou and Ma Fuxiang. He was a middle born son.
In 1880, Ma Fulu went to Be ...
. Since Japanese troops made up most of the Alliance forces, there would be no co-operation with the Japanese.
Controversies and changing views of the Boxers
From the beginning, views differed as to whether the Boxers were better seen as anti-imperialist, patriotic and
proto-nationalist, or as "uncivilized" irrational and futile opponents of inevitable change. The historian
Joseph Esherick, comments that "confusion about the Boxer Uprising is not simply a matter of popular misconceptions" since "there is no major incident in China's modern history on which the range of professional interpretation is as great".
The Boxers drew condemnation from those who wanted to modernise China on
Western models of civilisation.
Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen (; also known by several other names; 12 November 1866 – 12 March 1925)Singtao daily. Saturday edition. 23 October 2010. section A18. Sun Yat-sen Xinhai revolution 100th anniversary edition . was a Chinese politician who serve ...
, the founding father of the
Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeas ...
and of the
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Ta ...
(Chinese Nationalist Party), at the time worked to overthrow the Qing but believed that government spread rumours that "caused confusion among the populace" and stirred up the Boxer Movement. He delivered "scathing criticism" of the Boxers' "anti-foreignism and obscurantism". Sun praised the Boxers for their "spirit of resistance" but called them "bandits". Students studying in Japan were ambivalent. Some stated that while the uprising originated from the ignorant and stubborn people, their beliefs were brave and righteous and could be transformed into a force for independence.
After the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1911, nationalistic Chinese became more sympathetic to the Boxers. In 1918, Sun praised their fighting spirit and said that the Boxers were courageous and fearless in fighting to the death against the Alliance armies, specifically the
Battle of Yangcun
The Battle of Yangcun was a battle during the march of Eight-Nation Alliance forces from Tianjin to Beijing during the Boxer Rebellion. The Alliance forces defeated the Qing and were able to continue their march towards Peking.
Background
On ...
. Chinese liberals such as
Hu Shih
Hu Shih (; 17 December 1891 – 24 February 1962), also known as Hu Suh in early references, was a Chinese diplomat, essayist, literary scholar, philosopher, and politician. Hu is widely recognized today as a key contributor to Chinese libera ...
, who called on China to modernise, still condemned the Boxers for their irrationality and barbarity. The leader of the
New Culture Movement
The New Culture Movement () was a movement in China in the 1910s and 1920s that criticized classical Chinese ideas and promoted a new Chinese culture based upon progressive, modern and western ideals like democracy and science. Arising out of ...
,
Chen Duxiu
Chen Duxiu ( zh, t=陳獨秀, w=Ch'en Tu-hsiu; 8 October 187927 May 1942) was a Chinese revolutionary socialist, educator, philosopher and author, who co-founded the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) with Li Dazhao in 1921. From 1921 to 1927, he ...
, forgave the "barbarism of the Boxer... given the crime foreigners committed in China" and contended that it was those "subservient to the foreigners" that truly "deserved our resentment."

In other countries, views of the Boxers were complex and contentious.
Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has pr ...
said that "the Boxer is a patriot. He loves his country better than he does the countries of other people. I wish him success." The Russian writer
Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich TolstoyTolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; russian: link=no, Лев Николаевич Толстой,In Tolstoy's day, his name was written as in pre-refor ...
also praised the Boxers and accused Nicholas II of Russia and Wilhelm II of Germany of being chiefly responsible for the lootings, rapes, murders and the "Christian brutality" of the Russian and Western troops. The Russian revolutionary
Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
mocked the Russian government's claim that it was protecting Christian civilisation: "Poor Imperial Government! So Christianly unselfish, and yet so unjustly maligned! Several years ago it unselfishly seized Port Arthur, and now it is unselfishly seizing Manchuria; it has unselfishly flooded the frontier provinces of China with hordes of contractors, engineers, and officers, who, by their conduct, have roused to indignation even the Chinese, known for their docility." The Russian newspaper ''Amurskii Krai'' criticised the killing of innocent civilians and charged that "restraint", "civilization" and "culture," instead of "racial hatred" and "destruction," would have been more becoming of a "civilized Christian nation." The paper asked, "What shall we tell civilized people? We shall have to say to them: 'Do not consider us as brothers anymore. We are mean and terrible people; we have killed those who hid at our place, who sought our protection.'"
Even some American churchmen spoke out in support of the Boxers. In 1912, the evangelist Rev. Dr.
George F. Pentecost said that the Boxer uprising was a
The Indian Bengali
Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore (; bn, রবীন্দ্রনাথ ঠাকুর; 7 May 1861 – 7 August 1941) was a Bengali polymath who worked as a poet, writer, playwright, composer, philosopher, social reformer and painter. He resh ...
attacked the European colonialists.
A number of Indian soldiers in the
British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which cou ...
sympathised with the cause of the Boxers, and in 1994 the
Indian military returned a bell looted by British soldiers in the Temple of Heaven to China.

The events also left a longer impact. Historian
Robert Bickers
Robert A. Bickers (born 1964) is a British historian of modern China and colonialism. He is currently a professor of history at the University of Bristol. Bickers is the author of six books and editor or co-editor of three more.
Biography
Bor ...
, noted that for the
British government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_est ...
, the Boxer Rebellion served as the "equivalent of the
Indian 'mutiny'", and the events of the rebellion influenced the idea of the
Yellow Peril
The Yellow Peril (also the Yellow Terror and the Yellow Specter) is a racial color metaphor that depicts the peoples of East and Southeast Asia as an existential danger to the Western world. As a psychocultural menace from the Eastern world ...
among the British public. Later events, he adds, such as the
Chinese Nationalist Revolution in the 1920s and even the activities of the
Red Guards
Red Guards () were a mass student-led paramilitary social movement mobilized and guided by Chairman Mao Zedong in 1966 through 1967, during the first phase of the Cultural Revolution, which he had instituted.Teiwes According to a Red Guard lead ...
of the 1960s were perceived as being in the shadow of the Boxers.
In Taiwan and Hong Kong, history textbooks often present the Boxer as irrational, but in
Mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the China, People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming Island, Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territorie ...
, the central government textbooks described the Boxer movement as an anti-imperialist, patriotic peasant movement that failed by the lack of leadership from the modern working class, and they described the international army as an invading force. In recent decades, however, large-scale projects of village interviews and explorations of archival sources have led historians in China to take a more nuanced view. Some non-Chinese scholars, such as Joseph Esherick, have seen the movement as anti-imperialist, but others hold that the concept "nationalistic" is
anachronistic
An anachronism (from the Greek , 'against' and , 'time') is a chronological inconsistency in some arrangement, especially a juxtaposition of people, events, objects, language terms and customs from different time periods. The most common type ...
because the Chinese nation had not been formed, and the Boxers were more concerned with regional issues. Paul Cohen's recent study includes a survey of "the Boxers as myth," which shows how their memory was used in changing ways in 20th-century China from the
New Culture Movement
The New Culture Movement () was a movement in China in the 1910s and 1920s that criticized classical Chinese ideas and promoted a new Chinese culture based upon progressive, modern and western ideals like democracy and science. Arising out of ...
to the
Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goa ...
.
In recent years, the Boxer question has been debated in the People's Republic of China. In 1998, the critical scholar
Wang Yi argued that the Boxers had features in common with the extremism of the
Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goa ...
. Both events had the external goal of "liquidating all harmful pests" and the domestic goal of "eliminating bad elements of all descriptions" and that the relation was rooted in "cultural obscurantism." Wang explained to his readers the changes in attitudes towards the Boxers from the condemnation of the
May Fourth Movement
The May Fourth Movement was a Chinese anti-imperialist, cultural, and political movement which grew out of student protests in Beijing on May 4, 1919. Students gathered in front of Tiananmen (The Gate of Heavenly Peace) to protest the Chin ...
to the approval expressed by
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also Romanization of Chinese, romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the List of national founde ...
during the Cultural Revolution. In 2006,
Yuan Weishi, a professor of philosophy at
Zhongshan University
Sun Yat-sen University (, abbreviated SYSU and colloquially known in Chinese as Zhongda), also known as Zhongshan University, is a national key public research university located in Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. It was founded in 1924 by and nam ...
in Guangzhou, wrote that the Boxers by their "criminal actions brought unspeakable suffering to the nation and its people! These are all facts that everybody knows, and it is a national shame that the Chinese people cannot forget." Yuan charged that history textbooks had been lacking in neutrality by presenting the Boxer Uprising as a "magnificent feat of patriotism" and not the view that most Boxer rebels were violent. In response, some labelled Yuan Weishi a "traitor" (
Hanjian
In Chinese culture, the word ''hanjian'' () is a pejorative term for a traitor to the Han Chinese state and, to a lesser extent, Han ethnicity. The word ''hanjian'' is distinct from the general word for traitor, which could be used for any cou ...
).
Terminology
The name "Boxer Rebellion", concludes
Joseph W. Esherick Joseph W. Esherick (Chinese name: , born 1942) is an emeritus professor of modern Chinese history at the University of California, San Diego. He is the holder of thHwei-chih and Julia Hsiu Chair in Chinese Studies Esherick is a graduate of Harvard ...
, a contemporary historian, is truly a "misnomer", for the Boxers "never rebelled against the Manchu rulers of China and their Qing dynasty" and the "most common Boxer slogan, throughout the history of the movement, was 'support the Qing, destroy the Foreign,' where 'foreign' clearly meant the foreign religion, Christianity, and its Chinese converts as much as the foreigners themselves." He adds that only after the movement was suppressed by the Allied Intervention did the foreign powers and influential Chinese officials both realise that the Qing would have to remain as the government of China in order to maintain order and collect taxes in order to pay the indemnity. Therefore, in order to
save face for the Empress Dowager and the members of the imperial court, all argued that the Boxers were rebels and that the only support which the Boxers received from the imperial court came from a few Manchu princes. Esherick concludes that the origin of the term "rebellion" was "purely political and opportunistic", but it has had a remarkable staying power, particularly in popular accounts.
On 6 June 1900, ''The Times'' of London used the term "rebellion" in quotation marks, presumably to indicate its view that the rising was actually instigated by Empress Dowager Cixi. The historian Lanxin Xiang refers to the uprising as the "so called 'Boxer Rebellion,'" and he also states that "while peasant rebellion was nothing new in Chinese history, a war against the world's most powerful states was." Other recent Western works refer to the uprising as the "Boxer Movement", the "Boxer War" or the Yihetuan Movement, while Chinese studies refer to it as the 义和团运动 (Yihetuan yundong), that is, the "Yihetuan Movement." In his discussion of the general and legal implications of the terminology involved, the German scholar Thoralf Klein notes that all of the terms, including the Chinese terms, are "posthumous interpretations of the conflict." He argues that each term, whether it be "uprising", "rebellion" or "movement" implies a different definition of the conflict. Even the term "Boxer War", which has frequently been used by scholars in the West, raises questions. Neither side made a formal declaration of war. The imperial edicts on June 21 said that hostilities had begun and directed the regular Chinese army to join the Boxers against the Allied armies. This was a de facto declaration of war. The Allied troops behaved like soldiers who were mounting a punitive expedition in colonial style, rather than soldiers who were waging a declared war with legal constraints. The Allies took advantage of the fact that China had not signed "The Laws and Customs of War on Land", a key document signed at the 1899
Hague Peace Conference
The Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were amon ...
. They argued that China had violated provisions that they themselves ignored.
There is also a difference in terms referring to the combatants. The first reports which came from China in 1898 referred to the village activists as the "Yihequan", (Wade–Giles: I Ho Ch'uan). The earliest use of the term "Boxer" is contained in a letter which was written in Shandong in September 1899 by missionary Grace Newton. The context of the letter makes it clear that when it was written, "Boxer" was already a well-known term, probably coined by
Arthur H. Smith or Henry Porter, two missionaries who were also residing in Shandong. Smith says in his 1902 book that the name
Later representations
By 1900, many new forms of media had matured, including illustrated newspapers and magazines, postcards, broadsides, and advertisements, all of which presented images of the Boxers and the invading armies. The rebellion was covered in the foreign illustrated press by artists and photographers. Paintings and prints were also published including Japanese woodblocks. In the following decades, the Boxers were a constant subject of comment. A sampling includes:
* In the Polish play ''
The Wedding'' by
Stanisław Wyspiański
Stanisław Mateusz Ignacy Wyspiański (; 15 January 1869 – 28 November 1907) was a Polish playwright, painter and poet, as well as interior and furniture designer. A patriotic writer, he created a series of symbolic, national dramas withi ...
, first published on 16 March 1901, even before the rebellion was finally crushed, the character of Czepiec asks the Journalist (''Dziennikarz'') one of the best-known questions in the history of Polish literature: ''"Cóż tam, panie, w polityce? Chińczyki trzymają się mocno!?'' (''"How are things in politics, Mister? Are the Chinese holding out firmly!?"'').
*
Liu E, ''
The Travels of Lao Can
''The Travels of Lao Can'' () is a novel by Liu E (1857-1909), written between 1903 and 1904 and published in 1907 to wide acclaim. Thinly disguising his own views in those of Lao Can, the physician hero, Liu describes the rise of the Boxers in t ...
'' sympathetically shows an honest official trying to carry out reforms and depicts the Boxers as sectarian rebels.
*
G. A. Henty, ''With the Allies to Pekin, a Tale of the Relief of the Legations'' (New York: Scribners, 1903; London: Blackie, 1904). Juvenile fiction by a widely read author depicts the Boxers as "a mob of ruffians."
* A false or forged diary, ''Diary of his Excellency Ching-Shan: Being a Chinese Account of the Boxer Troubles'', including text written by
Edmund Backhouse, who claimed he recovered the document from a burnt building. It is suspected that Backhouse falsified the document, as well as other stories because he was prone to tell tales dubious in nature, including claims of nightly visits to the
Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi ( ; mnc, Tsysi taiheo; formerly romanised as Empress Dowager T'zu-hsi; 29 November 1835 – 15 November 1908), of the Manchu Yehe Nara clan, was a Chinese noblewoman, concubine and later regent who effectively controlled ...
.
* In
Hergé
Georges Prosper Remi (; 22 May 1907 – 3 March 1983), known by the pen name Hergé (; ), from the French pronunciation of his reversed initials ''RG'', was a Belgian cartoonist. He is best known for creating ''The Adventures of Tintin'', ...
's ''
The Adventures of Tintin
''The Adventures of Tintin'' (french: Les Aventures de Tintin ) is a series of 24 bande dessinée#Formats, ''bande dessinée'' albums created by Belgians, Belgian cartoonist Georges Remi, who wrote under the pen name Hergé. The series was one ...
'' comic ''
The Blue Lotus'', Tintin's Chinese friend
Chang Chong-Chen
Chang Chong-Chen (french: Tchang Tchong-Jen) is a fictional character in ''The Adventures of Tintin'', the comics series by Belgian cartoonist Hergé. Although Chang and Tintin only know each other for a short time, they form a deep bond whic ...
when they first meet, after Tintin saves the boy from drowning, the boy asks Tintin why he saved him from drowning as, according to Chang's uncle who fought in the Rebellion, all white people were wicked.
* The novel ''
Moment in Peking
''Moment in Peking'' is a novel originally written in English by Chinese author Lin Yutang. The novel, Lin's first, covers the turbulent events in China from 1900 to 1938, including the Boxer Uprising, the Republican Revolution of 1911, the Wa ...
'' (1939), by
Lin Yutang
Lin Yutang ( ; October 10, 1895 – March 26, 1976) was a Chinese inventor, linguist, novelist, philosopher, and translator. His informal but polished style in both Chinese and English made him one of the most influential writers of his generati ...
, opens during the Boxer Rebellion, and provides a child's-eye view of the turmoil through the eyes of the protagonist.
* ''
Tulku
A ''tulku'' (, also ''tülku'', ''trulku'') is a reincarnate custodian of a specific lineage of teachings in Tibetan Buddhism who is given empowerments and trained from a young age by students of his or her predecessor.
High-profile examples ...
'', a 1979 children's novel by
Peter Dickinson
Peter Malcolm de Brissac Dickinson OBE FRSL (16 December 1927 – 16 December 2015) was an English author and poet, best known for children's books and detective stories.
Dickinson won the annual Carnegie Medal from the Library Association ...
, includes the effects of the Boxer Rebellion on a remote part of China.
* ''
The Diamond Age or, A Young Lady's Illustrated Primer'' (New York, 1996), by
Neal Stephenson
Neal Town Stephenson (born October 31, 1959) is an American writer known for his works of speculative fiction. His novels have been categorized as science fiction, historical fiction, cyberpunk, postcyberpunk, and baroque.
Stephenson's work e ...
, includes a quasi-historical re-telling of the Boxer Rebellion as an integral component of the novel
* The novel ''
The Palace of Heavenly Pleasure
''The Palace of Heavenly Pleasure'' is a 2003 novel by Adam Williams. The book was first published on November 25, 2004 through Thomas Dunne Books. The book is set during 1899 in China and is told through the viewpoint of multiple protagonists.
Sy ...
'' (2003), by Adam Williams, describes the experiences of a small group of foreign missionaries, traders, and railway engineers in a fictional town in northern China shortly before and during the Boxer Rebellion.
* Illusionist William Ellsworth Robinson (a.k.a.
Chung Ling Soo
William Ellsworth Robinson (April 2, 1861 – March 24, 1918) was an American magician who went by the stage name Chung Ling Soo (). He is mostly remembered today for his accidental death due to a failed bullet catch trick.
Early years
Robinso ...
) had a
bullet-catch trick entitled "Condemned to Death by the Boxers", which famously resulted in his onstage death.
* The 1963 film ''
55 Days at Peking
''55 Days at Peking'' is a 1963 American epic historical war film dramatizing the siege of the foreign legations' compounds in Peking (now known as Beijing) during the Boxer Rebellion, which took place in China from 1899 to 1901. It was produ ...
'' directed by
Nicholas Ray and starring
Charlton Heston
Charlton Heston (born John Charles Carter; October 4, 1923April 5, 2008) was an American actor and political activist.
As a Hollywood star, he appeared in almost 100 films over the course of 60 years. He played Moses in the epic film ''The Ten ...
,
Ava Gardner
Ava Lavinia Gardner (December 24, 1922 – January 25, 1990) was an American actress. She first signed a contract with Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer in 1941 and appeared mainly in small roles until she drew critics' attention in 1946 with her perform ...
and
David Niven
James David Graham Niven (; 1 March 1910 – 29 July 1983) was a British actor, soldier, memoirist, and novelist. He won the Academy Award for Best Actor for his performance as Major Pollock in '' Separate Tables'' (1958). Niven's other roles ...
.
* In 1975 Hong Kong's
Shaw Brothers
Shaw Brothers (HK) Ltd. () was the largest film production company in Hong Kong, and operated from 1925 to 2011.
In 1925, three Shaw brothers— Runje, Runme, and Runde—founded Tianyi Film Company (also called "Unique") in Shang ...
studio produced the film ''Boxer Rebellion'' () under director
Chang Cheh
Chang Cheh (; 10 February 1923 – 22 June 2002) was a Chinese filmmaker, screenwriter, lyricist and producer active in the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s. Chang Cheh directed more than 90 films in Greater China, the majority of them with the Shaw Br ...
with one of the highest budgets to tell a sweeping story of disillusionment and revenge.
* Hong Kong's
Shaw Brothers
Shaw Brothers (HK) Ltd. () was the largest film production company in Hong Kong, and operated from 1925 to 2011.
In 1925, three Shaw brothers— Runje, Runme, and Runde—founded Tianyi Film Company (also called "Unique") in Shang ...
''
Legendary Weapons of China'' (1981), director
Lau Kar Leung
Lau Kar-leung (28 July 1934 – 25 June 2013), was a Chinese actor, filmmaker, choreographer, and martial artist from Hong Kong. Lau is best known for the films he made in the 1970s and 1980s for the Shaw Brothers Studio. His most famous wor ...
. A comedy starring
Hsiao Ho (Hsiao Hou) as a disillusioned boxer of the Magic Clan who is sent to assassinate the former leader of a powerful boxer clan who refuses to dupe his students into believing they are impervious to firearms.
* There are several flashbacks to the Boxer Rebellion in the television shows ''
Buffy the Vampire Slayer
''Buffy the Vampire Slayer'' is an American supernatural drama television series created by writer and director Joss Whedon. It is based on the 1992 film of the same name, also written by Whedon, although the events of the film are not consid ...
'' and ''
Angel
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles ...
.'' During the conflict,
Spike kills his first slayer to impress
Drusilla, and
Angel
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles ...
decisively splits from
Darla.
* The film ''
Shanghai Knights
''Shanghai Knights'' is a 2003 American martial arts action comedy film. It is the sequel to '' Shanghai Noon'', and the second installment of the ''Shanghai'' film series. Directed by David Dobkin and written by Alfred Gough and Miles Millar, ...
'' (2003), starring
Jackie Chan
Fang Shilong (born 7 April 1954), known professionally in English as Jackie Chan and in Chinese as Cheng Long ( zh, c=成龍, j=Sing4 Lung4; "becoming the dragon"), is a Hong Kong actor, filmmaker, martial artist, and stuntman known for ...
and
Owen Wilson
Owen Cunningham Wilson (born November 18, 1968) is an American actor. He has had a long association with filmmaker Wes Anderson with whom he shared writing and acting credits for ''Bottle Rocket'' (1996), '' Rushmore'' (1998), and '' The Royal ...
, takes place in 1887 and features Boxers as the
henchmen
A henchman (''vernacular:'' "hencher"), is a loyal employee, supporter, or aide to some powerful figure engaged in nefarious or criminal enterprises. Henchmen are typically relatively unimportant in the organization: minions whose value lies pri ...
of the film's lead antagonist, English Lord Rathbone (
Aiden Gillen), either working as
mercenaries
A mercenary, sometimes Pseudonym, also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a memb ...
for Rathbone, or helping him as part of their support for the anti-imperialist leader Wu Chow (
Donnie Yen
Donnie Yen Chi-tan (; born 27 July 1963) is a Hong Kong actor, martial artist, and action director. Yen is one of Hong Kong's top action stars. Yen is widely credited for bringing mixed martial arts (MMA) into the mainstream Asian cinema by cho ...
), Rathbone's ally.
* ''
The Last Empress'' (Boston, 2007), by
Anchee Min
Anchee Min (; born January 14, 1957, in Shanghai, China) is a Chinese-American author who lives in San Francisco and Shanghai. Min has published two memoirs, ''Red Azalea'' and ''The Cooked Seed: A Memoir'', and six historical novels. Her ficti ...
, describes the long reign of the
Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi ( ; mnc, Tsysi taiheo; formerly romanised as Empress Dowager T'zu-hsi; 29 November 1835 – 15 November 1908), of the Manchu Yehe Nara clan, was a Chinese noblewoman, concubine and later regent who effectively controlled ...
in which the siege of the legations is one of the climactic events in the novel.
*
Mo, Yan. ''Sandalwood Death.'' The viewpoint of villagers during Boxer Uprising.
* The pair of
graphic novel
A graphic novel is a long-form, fictional work of sequential art. The term ''graphic novel'' is often applied broadly, including fiction, non-fiction, and anthologized work, though this practice is highly contested by comic scholars and industry ...
s by
Gene Luen Yang
Gene Luen Yang (Chinese Traditional: 楊謹倫, Simplified: 杨谨伦, Pinyin: ''Yáng Jǐnlún''; born August 9, 1973) is an American cartoonist. He is a frequent lecturer on the subjects of graphic novels and comics, at comic book conventions a ...
, with color by Lark Pien, ''
Boxers and Saints
''Boxers'' and ''Saints'' are two companion graphic novel volumes written and illustrated by Gene Luen Yang, and colored by Lark Pien. The publisher First Second Books released them on September 10, 2013. Together the two volumes have around 500 ...
,'' describes the "bands of foreign missionaries and soldiers" who "roam the countryside bullying and robbing Chinese peasants." In Boxers, Little Bao, "harnessing the powers of ancient Chinese gods", recruits an army of Boxers, "commoners trained in
kung fu
Chinese martial arts, often called by the umbrella terms kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (), are multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to commo ...
who fight to free China from 'foreign devils.'"
['' Boxers and Saints'' (First Second Books, 2013]
WorldCat
/ref> In Saints, Four-Sister a.k.a. Vibiana learns of the Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
faith, but was killed by Bao.
* The 2013 video game ''BioShock Infinite
''BioShock Infinite'' is a first-person shooter video game developed by Irrational Games and published by 2K Games. The third installment in the BioShock (series), ''BioShock'' series, ''Infinite'' was released worldwide for the Microsoft Window ...
'' featured the Boxer Rebellion as a major historical moment for the floating city of Columbia. Columbia, to rescue American hostages during the rebellion, opened fire upon the city of Peking and burned it to the ground. These actions resulted in the United States recalling Columbia, which led to its secession from the Union.
* The Boxer Rebellion is the historical backdrop for the episode titled "Kung Fu Crabtree" (Season 7, Episode 16, aired 24 March 2014) of the television series ''Murdoch Mysteries
''Murdoch Mysteries'' is a Canadian television drama series that premiered on Citytv on January 20, 2008, and currently airs on CBC. The series is based on characters from the ''Detective Murdoch'' novels by Maureen Jennings and stars Yannick ...
,'' in which Chinese officials visit Toronto in 1900 in search of Boxers who have fled from China.
See also
* Battle of Peking (1900)
The Battle of Peking, or historically the Relief of Peking, was the battle fought on 14–15 August 1900 in Peking, in which the Eight-Nation Alliance relieved the siege of the Peking Legation Quarter during the Boxer Rebellion. From 20 June 1 ...
* Boxer Indemnity Scholarship Program
The Boxer Indemnity Scholarship Program () was a scholarship program for Chinese students to be educated in the United States, funded by the . In 1908, the U.S. Congress passed a bill to return to China the excess of Boxer Indemnity, amounting to ...
* Century of humiliation
* China Relief Expedition
The China Relief Expedition was an expedition in China undertaken by the United States Armed Forces to rescue United States citizens, European nationals, and other foreign nationals during the latter years of the Boxer Rebellion, which lasted ...
* Donghak Rebellion, an anti-foreign, proto-nationalist uprising in pre-Japanese Korea
* Gengzi Guobian Tanci
* Imperial Decree on events leading to the signing of Boxer Protocol
* List of 1900–1930 publications on the Boxer Rebellion List of 1900-1930 publications on Boxer Rebellion is a list of Chinese language publications on the nature of Boxer Rebellion during the early 20th century. The list includes pamphlets, books, local county journals, and other publications.
Books
* ...
* Xishiku Cathedral
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
* David D. Buck
"Review", ''The China Quarterly''
173 (2003): 234–237. calls this a strong "revisionist" account.
*
*
Excerpt
*
*
*
* ; British title: ''Besieged in Peking: The Story of the 1900 Boxer Rising'' (London: Constable, 1999); popular history.
*
*
*
Further reading
General accounts and analysis
In addition to those used in the notes and listed under References, general accounts can be found in such textbooks as Jonathan Spence, ''In Search of Modern China'', pp.230–235; Keith Schoppa, ''Revolution and Its Past'', pp. 118–123; and Immanuel Hsu, Ch 16, "The Boxer Uprising", in ''The Rise of Modern China'' (1990).
* Bickers, Robert A., and R. G. Tiedemann, eds., ''The Boxers, China, and the World''. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield, 2007. .
* Bickers, Robert A. ''The Scramble for China: Foreign Devils in the Qing Empire, 1800–1914'' (London: Allen Lane, 2011)
online review
* Buck, David D. "Recent Studies of the Boxer Movement", ''Chinese Studies in History'' 20 (1987). Introduction to a special issue of the journal devoted to translations of recent research on the Boxers in the People's Republic.
* Der Ling, Princess (1928). ''Old Buddha'', Dodd, Mead & Company. Chapters XXXII-XXXVIII.
* Harrison, Henrietta. "Justice on Behalf of Heaven" ''History Today'' (Sep 2000), Vol. 50 Issue 9, pp 44–51 online; popular history.
* Knüsel, Ariane. "Facing the Dragon: Teaching the Boxer Uprising Through Cartoons." ''History Teacher'' 50.2 (2017): 201–226
online
* Shan, Patrick Fuliang (2018). ''Yuan Shikai: A Reappraisal'', The University of British Columbia Press. .
* Purcell, Victor (1963). ''The Boxer Uprising: A background study''
online edition
*
* Wu, Jiarui. "Ramifications of Two Divergent Paths: A Comparative Study of 1900 and 2020 Crises in China." ''Advances in Historical Studies'' 11.1 (2022): 1–14. online
Missionary experience and personal accounts
* Bell, P, and Clements, R, (2014). ''Lives from a Black Tin Box'' The story of the Xinzhou martyrs, Shanxi Province.
* Brandt, Nat (1994). ''Massacre in Shansi.'' Syracuse University Press
Syracuse University Press, founded in 1943, is a university press that is part of Syracuse University. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses.
History
SUP was formed in August 1943 when president William P. Tolley pro ...
. . The story of the Oberlin missionaries at Taigu, Shanxi.
* Clark, Anthony E. (2015). ''Heaven in Conflict: Franciscans and the Boxer Uprising in Shanxi.'' Seattle and London: University of Washington Press.
* Hsia, R. Po-chia. "Christianity and Empire: The Catholic Mission in Late Imperial China." ''Studies in Church History'' 54 (2018): 208–224.
* Price, Eva Jane. ''China Journal, 1889–1900: An American Missionary Family During the Boxer Rebellion,'' (1989). . Review: Susanna Ashton, "Compound Walls: Eva Jane Price's Letters from a Chinese Mission, 1890–1900." ''Frontiers'' 1996 17(3): 80–94. . The journal of the events leading up to the deaths of the Price family.
* Sharf, Frederic A., and Peter Harrington (2000). ''China 1900: The Eyewitnesses Speak''. London: Greenhill. . Excerpts from German, British, Japanese, and American soldiers, diplomats and journalists.
* Sharf, Frederic A., and Peter Harrington (2000). ''China 1900: The Artists' Perspective''. London: Greenhill.
* Tiedemann, R.G. "Boxers, Christians and the culture of violence in north China" ''Journal of Peasant Studies'' (1998) 25:4 pp 150–160, DOI: 10.1080/03066159808438688
* Tiedemann, R.G. ''Reference Guide to Christian Missionary Societies in China: From the Sixteenth to the Twentieth Century'' (East Gate Books, 2009)
Allied intervention, the Boxer War, and the aftermath
* Bodin, Lynn E. and Christopher Warner. ''The Boxer Rebellion''. London: Osprey, Men-at-Arms Series 95, 1979. (pbk.) Illustrated history of the military campaign.
*
* Hevia, James L. "Leaving a Brand on China: Missionary Discourse in the Wake of the Boxer Movement", ''Modern China'' 18.3 (1992): 304–332.
* Hevia, James L. "A Reign of Terror: Punishment and Retribution in Beijing and its Environs", Chapter 6, in ''English Lessons: The Pedagogy of Imperialism in Nineteenth Century China'' (Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2003), pp. 195–240.
* Hunt, Michael H. "The American Remission of the Boxer Indemnity: A Reappraisal", ''Journal of Asian Studies'' 31 (Spring 1972): 539–559.
* Hunt, Michael H. "The Forgotten Occupation: Peking, 1900–1901", ''Pacific Historical Review'' 48.4 (November 1979): 501–529.
* Langer, William. ''The Diplomacy of Imperialism 1890–1902'' (2nd ed. 1950), pp. 677–709.
Contemporary accounts and sources
* . A contemporary account.
*
* E. H. Edwards, ''Fire and Sword in Shansi: The Story of the Martyrdom of Foreigners and Chinese Christians'' (New York: Revell, 1903)
* Isaac Taylor Headland, ''Chinese Heroes; Being a Record of Persecutions Endured by Native Christians in the Boxer Uprising'' (New York, Cincinnati: Eaton & Mains; Jennings & Pye, 1902).
* Arnold Henry Savage Landor
Arnold Henry Savage Landor (2 June 1865 – 26 December 1924) was an English painter, explorer, writer, and anthropologist. Landor wrote in an often witty style.
Life and career
Arnold H. S. Landor was born to Charles Savage Landor in Fl ...
, ''China and the Allies'' (New York: Scribner's, 1901). 01008198 Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
China and the Allies
* Pierre Loti, ''The Last Days of Pekin'' (Boston: Little, Brown and Co., 1902): tr. of ''Les Derniers Jours De Pékin'' (Paris: Lévy, 1900).
* W. A. P. Martin, ''The Siege in Peking, China against the World'' (New York: F. H. Revell company, 1900).
* Putnam Weale, Bertram Lenox, (1907). ''Indiscreet Letters from Peking: Being the Notes of an Eyewitness, Which Set Forth in Some Detail, From Day to Day, The Real Story of the Siege and Sack of a Distressed Capital in 1900– The Year of Great Tribulation.'' Dodd, Mead
Free ebook
Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital libr ...
.
* Arthur H. Smith, ''China in Convulsion'' (New York: F. H. Revell, 2 vols. 1901). Internet Archiv
Volume IVolume II
An account of the Boxers and the siege by a missionary who had lived in a North China village.
External links
Lost in the Gobi Desert: Hart retraces great-grandfather's footsteps
William & Mary News Story, 3 January 2005.
September 1900 San Francisco Newspaper
200 Photographs in Library of Congress online Collection
*
*
* ttps://archive.org/details/proceedingstent00berngoog Proceedings of the Tenth Universal Peace Congress, 1901
Pictures from the Siege of Peking
from the Caldwell Kvaran archives
an excerpt of Pierre Loti's ''Les Derniers Jours de Pékin'' (1902).
Documents of the Boxer Rebellion (China Relief Expedition), 1900–1901
National Museum of the U.S. Navy (Selected Naval Documents).
* Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
br>"Boxer Rebellion" Books, films, and audio
{{Authority control
Wars involving the United States
1899 in China
1899 in Christianity
1900 in China
1900 in Christianity
1901 in China
1901 in Christianity
Anti-Christian sentiment in Asia
Anti-imperialism in Asia
Attacks on diplomatic missions in China
Battles involving the princely states of India
Chinese nationalism
Chinese Taoists
Conflicts involving the German Empire
Eight Banners
History of the Royal Marines
Looting
Persecution of Christians
Rebellions in the Qing dynasty
Shamanism
United States Marine Corps in the 18th and 19th centuries
United States Marine Corps in the 20th century
Wars involving France
Wars involving Germany
Wars involving Italy
Wars involving Japan
Wars involving the Habsburg Monarchy
Wars involving the Russian Empire
Wars involving the United Kingdom
 The Righteous and Harmonious Fists (Yihequan) arose in the inland sections of the northern coastal province of
The Righteous and Harmonious Fists (Yihequan) arose in the inland sections of the northern coastal province of  The opportunities to fight against Western encroachment and colonisation were especially attractive to unemployed village men, many of whom were teenagers. The tradition of possession and invulnerability went back several hundred years but took on special meaning against the powerful new weapons of the West. The Boxers, armed with rifles and swords, claimed supernatural invulnerability against cannons, rifle shots, and knife attacks. The Boxer groups popularly claimed that millions of soldiers would descend out of
The opportunities to fight against Western encroachment and colonisation were especially attractive to unemployed village men, many of whom were teenagers. The tradition of possession and invulnerability went back several hundred years but took on special meaning against the powerful new weapons of the West. The Boxers, armed with rifles and swords, claimed supernatural invulnerability against cannons, rifle shots, and knife attacks. The Boxer groups popularly claimed that millions of soldiers would descend out of  In October 1898, a group of Boxers attacked the Christian community of Liyuantun village where a temple to the
In October 1898, a group of Boxers attacked the Christian community of Liyuantun village where a temple to the  In January 1900, with a majority of conservatives in the imperial court, Empress Dowager Cixi changed her position on the Boxers, and issued edicts in their defence, causing protests from foreign powers. In spring 1900, the Boxer movement spread rapidly north from Shandong into the countryside near Beijing. Boxers burned Christian churches, killed Chinese Christians and intimidated Chinese officials who stood in their way. American Minister Edwin H. Conger cabled Washington, "the whole country is swarming with hungry, discontented, hopeless idlers."
On 30 May the diplomats, led by British Minister
In January 1900, with a majority of conservatives in the imperial court, Empress Dowager Cixi changed her position on the Boxers, and issued edicts in their defence, causing protests from foreign powers. In spring 1900, the Boxer movement spread rapidly north from Shandong into the countryside near Beijing. Boxers burned Christian churches, killed Chinese Christians and intimidated Chinese officials who stood in their way. American Minister Edwin H. Conger cabled Washington, "the whole country is swarming with hungry, discontented, hopeless idlers."
On 30 May the diplomats, led by British Minister  As the situation grew more violent, the Eight Powers authorities at Dagu dispatched a second multinational force to Beijing on 10 June 1900. This force of 2,000 sailors and marines was under the command of Vice-Admiral Edward Seymour RN, the largest contingent being British. The force moved by train from Dagu to Tianjin with the agreement of the Chinese government, but the railway had been severed between Tianjin and Beijing. Seymour resolved to continue forward by rail to the break and repair the railway, or progress on foot from there if necessary, as it was only 120 km from Tianjin to Beijing. When Seymour left Tianjin and started toward Beijing, it angered the imperial court.
The court then replaced Prince Qing at the Zongli Yamen, with Manchu Prince Duan, a member of the imperial
As the situation grew more violent, the Eight Powers authorities at Dagu dispatched a second multinational force to Beijing on 10 June 1900. This force of 2,000 sailors and marines was under the command of Vice-Admiral Edward Seymour RN, the largest contingent being British. The force moved by train from Dagu to Tianjin with the agreement of the Chinese government, but the railway had been severed between Tianjin and Beijing. Seymour resolved to continue forward by rail to the break and repair the railway, or progress on foot from there if necessary, as it was only 120 km from Tianjin to Beijing. When Seymour left Tianjin and started toward Beijing, it angered the imperial court.
The court then replaced Prince Qing at the Zongli Yamen, with Manchu Prince Duan, a member of the imperial  After leaving Tianjin, the force quickly reached
After leaving Tianjin, the force quickly reached  On 18 June, Seymour learned of attacks on the Legation Quarter in Beijing, and decided to continue advancing, this time along the
On 18 June, Seymour learned of attacks on the Legation Quarter in Beijing, and decided to continue advancing, this time along the  Meanwhile, in Beijing, on 16 June, Empress Dowager Cixi summoned the imperial court for a mass audience and addressed the choice between using the Boxers to evict the foreigners from the city and seeking a diplomatic solution. In response to a high official who doubted the efficacy of the Boxers, Cixi replied that both sides of the debate at the imperial court realised that popular support for the Boxers in the countryside was almost universal and that suppression would be both difficult and unpopular, especially when foreign troops were on the march.
Two factions were active during this debate. On one side were anti-foreigners who viewed foreigners as invasive and imperialistic and evoked a nativist populism. They advocated taking advantage of the Boxers to achieve the expulsion of foreign troops and foreign influences. The pro-foreigners on the other hand advanced rapprochement with foreign governments, seeing the Boxers as superstitious and ignorant.
The event that tilted the Qing imperial government irrevocably toward support of the Boxers and war with the foreign powers was the attack of foreign navies on the Dagu Forts near Tianjin, on 17 June 1900.
Meanwhile, in Beijing, on 16 June, Empress Dowager Cixi summoned the imperial court for a mass audience and addressed the choice between using the Boxers to evict the foreigners from the city and seeking a diplomatic solution. In response to a high official who doubted the efficacy of the Boxers, Cixi replied that both sides of the debate at the imperial court realised that popular support for the Boxers in the countryside was almost universal and that suppression would be both difficult and unpopular, especially when foreign troops were on the march.
Two factions were active during this debate. On one side were anti-foreigners who viewed foreigners as invasive and imperialistic and evoked a nativist populism. They advocated taking advantage of the Boxers to achieve the expulsion of foreign troops and foreign influences. The pro-foreigners on the other hand advanced rapprochement with foreign governments, seeing the Boxers as superstitious and ignorant.
The event that tilted the Qing imperial government irrevocably toward support of the Boxers and war with the foreign powers was the attack of foreign navies on the Dagu Forts near Tianjin, on 17 June 1900.

 On 15 June, Qing imperial forces deployed electric mines in the
On 15 June, Qing imperial forces deployed electric mines in the  On 21 June, Empress Dowager Cixi declared war against all foreign powers. Regional governors in the south, who commanded substantial modernised armies, such as
On 21 June, Empress Dowager Cixi declared war against all foreign powers. Regional governors in the south, who commanded substantial modernised armies, such as  On 22 and 23 June, Chinese soldiers and Boxers set fire to areas north and west of the British Legation, using it as a "frightening tactic" to attack the defenders. The nearby
On 22 and 23 June, Chinese soldiers and Boxers set fire to areas north and west of the British Legation, using it as a "frightening tactic" to attack the defenders. The nearby  The Manchu General
The Manchu General  Xu Jingcheng, who had served as the Qing Envoy to many of the same states under siege in the Legation Quarter, argued that "the evasion of extraterritorial rights and the killing of foreign diplomats are unprecedented in China and abroad." Xu and five other officials urged Empress Dowager Cixi to order the repression of Boxers, the execution of their leaders, and a diplomatic settlement with foreign armies. The Empress Dowager, outraged, sentenced Xu and the five others to death for "willfully and absurdly petitioning the Imperial Court" and "building subversive thought." They were executed on 28 July 1900 and their severed heads placed on display at
Xu Jingcheng, who had served as the Qing Envoy to many of the same states under siege in the Legation Quarter, argued that "the evasion of extraterritorial rights and the killing of foreign diplomats are unprecedented in China and abroad." Xu and five other officials urged Empress Dowager Cixi to order the repression of Boxers, the execution of their leaders, and a diplomatic settlement with foreign armies. The Empress Dowager, outraged, sentenced Xu and the five others to death for "willfully and absurdly petitioning the Imperial Court" and "building subversive thought." They were executed on 28 July 1900 and their severed heads placed on display at  Reflecting this vacillation, some Chinese soldiers were quite liberally firing at foreigners under siege from its very onset. Cixi did not personally order imperial troops to conduct a siege, and on the contrary had ordered them to protect the foreigners in the legations. Prince Duan led the Boxers to loot his enemies within the imperial court and the foreigners, although imperial authorities expelled Boxers after they were let into the city and went on a looting rampage against both the foreign and the Qing imperial forces. Older Boxers were sent outside Beijing to halt the approaching foreign armies, while younger men were absorbed into the Muslim Gansu army.
With conflicting allegiances and priorities motivating the various forces inside Beijing, the situation in the city became increasingly confused. The foreign legations continued to be surrounded by both Qing imperial and Gansu forces. While Dong Fuxiang's Gansu army, now swollen by the addition of the Boxers, wished to press the siege, Ronglu's imperial forces seem to have largely attempted to follow Empress Dowager Cixi's decree and protect the legations. However, to satisfy the conservatives in the imperial court, Ronglu's men also fired on the legations and let off firecrackers to give the impression that they, too, were attacking the foreigners. Inside the legations and out of communication with the outside world, the foreigners simply fired on any targets that presented themselves, including messengers from the imperial court, civilians and besiegers of all persuasions. Dong Fuxiang was denied artillery held by Ronglu which stopped him from levelling the legations, and when he complained to Empress Dowager Cixi on 23 June, she dismissively said that "Your tail is becoming too heavy to wag." The Alliance discovered large amounts of unused Chinese Krupp artillery and shells after the siege was lifted.
The armistice, although occasionally broken, endured until 13 August when, with an allied army led by the British
Reflecting this vacillation, some Chinese soldiers were quite liberally firing at foreigners under siege from its very onset. Cixi did not personally order imperial troops to conduct a siege, and on the contrary had ordered them to protect the foreigners in the legations. Prince Duan led the Boxers to loot his enemies within the imperial court and the foreigners, although imperial authorities expelled Boxers after they were let into the city and went on a looting rampage against both the foreign and the Qing imperial forces. Older Boxers were sent outside Beijing to halt the approaching foreign armies, while younger men were absorbed into the Muslim Gansu army.
With conflicting allegiances and priorities motivating the various forces inside Beijing, the situation in the city became increasingly confused. The foreign legations continued to be surrounded by both Qing imperial and Gansu forces. While Dong Fuxiang's Gansu army, now swollen by the addition of the Boxers, wished to press the siege, Ronglu's imperial forces seem to have largely attempted to follow Empress Dowager Cixi's decree and protect the legations. However, to satisfy the conservatives in the imperial court, Ronglu's men also fired on the legations and let off firecrackers to give the impression that they, too, were attacking the foreigners. Inside the legations and out of communication with the outside world, the foreigners simply fired on any targets that presented themselves, including messengers from the imperial court, civilians and besiegers of all persuasions. Dong Fuxiang was denied artillery held by Ronglu which stopped him from levelling the legations, and when he complained to Empress Dowager Cixi on 23 June, she dismissively said that "Your tail is becoming too heavy to wag." The Alliance discovered large amounts of unused Chinese Krupp artillery and shells after the siege was lifted.
The armistice, although occasionally broken, endured until 13 August when, with an allied army led by the British 
 The international force finally captured
The international force finally captured  The international force reached Beijing on 14 August. Following the defeat of Beiyang army in the
The international force reached Beijing on 14 August. Following the defeat of Beiyang army in the  The British Army reached the legation quarter on the afternoon of 14 August and relieved the Legation Quarter. The Beitang was relieved on 16 August, first by Japanese soldiers and then, officially, by the French.
The British Army reached the legation quarter on the afternoon of 14 August and relieved the Legation Quarter. The Beitang was relieved on 16 August, first by Japanese soldiers and then, officially, by the French.
 In the early hours of 15 August, just as the Foreign Legations were being relieved, Empress Dowager Cixi, dressed in the padded blue cotton of a farm woman, the Guangxu Emperor, and a small retinue climbed into three wooden ox carts and escaped from the city covered with rough blankets. Legend has it that the Empress Dowager then either ordered that the Guangxu Emperor's favourite concubine,
In the early hours of 15 August, just as the Foreign Legations were being relieved, Empress Dowager Cixi, dressed in the padded blue cotton of a farm woman, the Guangxu Emperor, and a small retinue climbed into three wooden ox carts and escaped from the city covered with rough blankets. Legend has it that the Empress Dowager then either ordered that the Guangxu Emperor's favourite concubine,  The Russian Empire and the Qing Dynasty had maintained a long peace, starting with the
The Russian Empire and the Qing Dynasty had maintained a long peace, starting with the  Orthodox, Protestant, and Catholic missionaries and their Chinese parishioners were massacred throughout northern China, some by Boxers and others by government troops and authorities. After the declaration of war on Western powers in June 1900, Yuxian, who had been named governor of
Orthodox, Protestant, and Catholic missionaries and their Chinese parishioners were massacred throughout northern China, some by Boxers and others by government troops and authorities. After the declaration of war on Western powers in June 1900, Yuxian, who had been named governor of  The Eight Nation Alliance occupied Zhili province while Russia occupied Manchuria, but the rest of China was not occupied due to the actions of several Han governors who formed the Mutual Protection of Southeast China that refused to obey the declaration of war and kept their armies and provinces out of the war. Zhang Zhidong told Everard Fraser, the Hankou-based British consul general, that he despised Manchus in order that the Eight Nation Alliance would not occupy provinces under the Mutual Defense Pact.
The Eight Nation Alliance occupied Zhili province while Russia occupied Manchuria, but the rest of China was not occupied due to the actions of several Han governors who formed the Mutual Protection of Southeast China that refused to obey the declaration of war and kept their armies and provinces out of the war. Zhang Zhidong told Everard Fraser, the Hankou-based British consul general, that he despised Manchus in order that the Eight Nation Alliance would not occupy provinces under the Mutual Defense Pact.
 Beijing, Tianjin and Zhili province were occupied for more than one year by the international expeditionary force under the command of German General
Beijing, Tianjin and Zhili province were occupied for more than one year by the international expeditionary force under the command of German General  Some but by no means all Western missionaries took an active part in calling for retribution. To provide restitution to missionaries and Chinese Christian families whose property had been destroyed, William Ament, a missionary of
Some but by no means all Western missionaries took an active part in calling for retribution. To provide restitution to missionaries and Chinese Christian families whose property had been destroyed, William Ament, a missionary of  The
The  Concurrently, the period marks the decline of European great power interference in Chinese affairs, with the Japanese replacing the Europeans as the dominant power for their lopsided involvement in the war against the Boxers as well as their victory in the
Concurrently, the period marks the decline of European great power interference in Chinese affairs, with the Japanese replacing the Europeans as the dominant power for their lopsided involvement in the war against the Boxers as well as their victory in the  In other countries, views of the Boxers were complex and contentious.
In other countries, views of the Boxers were complex and contentious.  The events also left a longer impact. Historian
The events also left a longer impact. Historian