Ariobarzanes of Phrygia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ariobarzanes ( peo, *Aryābr̥zaⁿs; grc, Ἀριοβαρζάνης ; death: crucified in c. 362 BCE), sometimes known as Ariobarzanes I of Cius, was a
Ariobarzanes ( peo, *Aryābr̥zaⁿs; grc, Ἀριοβαρζάνης ; death: crucified in c. 362 BCE), sometimes known as Ariobarzanes I of Cius, was a
viii. 8
Aristotle
v. 10
/ref>Brosius 2006, p. 29
Politics
', H. Rackham (translator),
Bibliotheca
', C. H. Oldfather (translator), Cambridge, MA - London, (1989) * *McGing, Brian C. (1986) "The Kings of Pontus: Some Problems of Identity and Date,". Rheinisches Museum für Philologie, vol. 129 (1986), pp 248..259. *Nepos, Cornetlius (1866)
', John Selby Watson (translator), (1886) * Smith, William (editor); ''
"Ariobarzanes I"

 Ariobarzanes ( peo, *Aryābr̥zaⁿs; grc, Ἀριοβαρζάνης ; death: crucified in c. 362 BCE), sometimes known as Ariobarzanes I of Cius, was a
Ariobarzanes ( peo, *Aryābr̥zaⁿs; grc, Ἀριοβαρζάνης ; death: crucified in c. 362 BCE), sometimes known as Ariobarzanes I of Cius, was a Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
of Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
and military commander, leader of an independence revolt, and the first known of the line of rulers of the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
town of Cius
Cius (; grc-gre, Kίος or Κῖος ''Kios''), later renamed Prusias on the Sea (; la, Prusias ad Mare) after king Prusias I of Bithynia, was an ancient Greek city bordering the Propontis (now known as the Sea of Marmara), in Bithynia and i ...
from which were eventually to stem the kings of Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
in the 3rd century BCE.
Ariobarzanes was apparently a cadet member of the Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
dynasty, possibly son of Pharnabazus II
Pharnabazus II (Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', grc-gre, Φαρνάβαζος ; ruled 413-374 BC) was a Persian soldier and statesman, and Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of Pharnaces II of Phrygia and grandson of Pharnabazus I ...
, and part of the Pharnacid dynasty
The Pharnacid dynasty was a Persian dynasty that ruled the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid Dynasty from the 5th until the 4th century BCE. It was founded by Artabazus, son of satrap Pharnaces I (younger brother of Hystasp ...
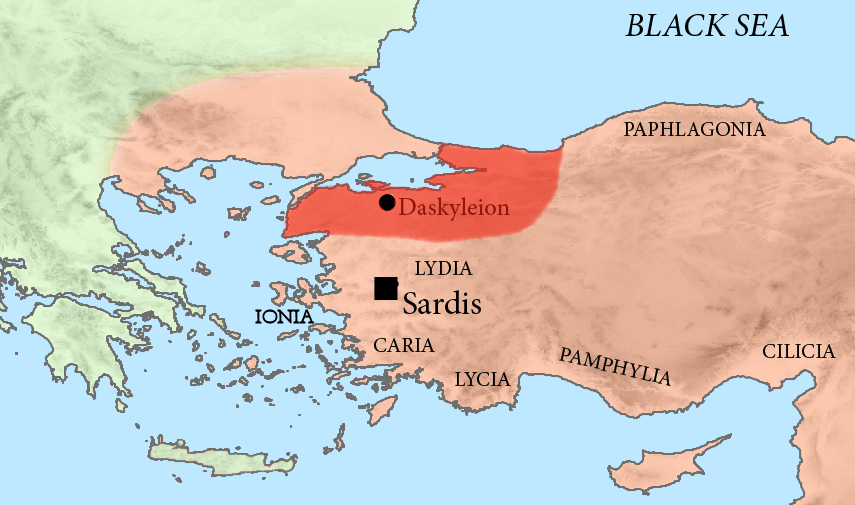
which had settled to hold Dascylium
Dascylium, Dascyleium, or Daskyleion ( grc, Δασκύλιον, Δασκυλεῖον), also known as Dascylus, was a town in Anatolia some inland from the coast of the Propontis, at modern Ergili, Turkey. Its site was rediscovered in 1952 and ...
of Hellespont in the 470s BCE. Cius is located near Dascylium, and Cius seemingly was a share of family holdings for the branch of Ariobarzanes.
Ariobarzanes' one predecessor was a (kinsman) named Mithradates (possibly Mithradates, Satrap of Cappadocia). The archaeologist Walther Judeich
Walther Judeich (5 October 1859, Dresden – 24 February 1942, Jena) was a German ancient historian. His grandfather on his mother's side was publisher Heinrich Brockhaus (1804–1874)."Statement based on translated text of an equivalent article at ...
claims that Ariobarzanes was that Mithradates' son, but Brian C. McGing refutes that specific filiation. Seemingly, no classical source itself calls them son and father, the filiation being a later reconstruction on basis of successorship.
Rule
Pharnabazus, Satrap of Phrygia ( fl. 413373 BCE), son of Pharnaces of Phrygia, is indicated to have shared his rule and territories with his brothers in the late 5th century BCE when Pharnabazos had recently succeeded to the position. Mithradates, Satrap of Cappadocia, might have been one of such brothers. Ariobarzanes of Cius might have also been one of those brothers. The classical sourceAppian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Hadr ...
us relates that Ariobarzanes was of a cadet line of the family of the Persian Great King Dareios (Darius the Great).
It is highly probable he is the same Ariobarzanes who, around 407 BCE, was the Persian envoy to the Greek city-states and cultivated the friendship of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
and Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
.
Ariobarzanes conducted the Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
ambassadors, in 405 BCE, to his sea-town of Cius in Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the ...
, after they had been detained three years by order of Cyrus the Younger
Cyrus the Younger ( peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ''Kūruš''; grc-gre, Κῦρος ; died 401 BC) was an Achaemenid prince and general. He ruled as satrap of Lydia and Ionia from 408 to 401 BC. Son of Darius II and Parysatis, he died in 401 BC i ...
.
Ariobarzanes was mentioned as under-satrap in Anatolia in late 5th century BCE. He then apparently succeeded his presumed kinsman (possibly elder brother) Pharnabazus (fl. 413373 BCE) as satrap of Phrygia and Lydia, assigned by Pharnabazos himself when he departed to the Persian court to marry Apama, daughter of the Persian king. Thus Ariobarzanes became the satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia
Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellēspontiakē Phrygia) or Lesser Phrygia ( grc, μικρᾶ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia) was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of t ...
, in what is now the northwest of Turkey. Pharnabazos lived well into the 370s BCE, having obtained higher positions in the Persian monarchy than merely the Phrygian satrapship.
Ariobarzanes assisted Antalcidas
Antalcidas ( grc-gre, Ἀνταλκίδας; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta.
__NOTOC__
Life
Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Spa ...
in 388 BCE.
Delphi embassy (368 BC)
He appears to have still held some high office in the Persian court in 368 BCE, as we find him, apparently on behalf of the king, sending an embassy led byPhiliscus of Abydos
Philiscus or Philiskos ( gr, Φιλίσκος) was a 4th-century Greek tyrant of the city of Abydos, on the Asian side of the Hellespont, and a hyparch ("vice-regent") and military commander of the Achaemenid satrap Ariobarzanes. He was sent by Ar ...
to Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
in that year. Both Philiscus and Ariobarzanes, as well as three of his sons, were made citizens of Athens, a remarkable honor suggesting important services rendered to the city-state.
Ariobarzanes, who is called by Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
of Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
, and by Nepos satrap of Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
, Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian ...
, and Phrygia, revolted against Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and suc ...
in 362. Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; el, Δημοσθένης, translit=Dēmosthénēs; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual prow ...
speaks of Ariobarzanes and his three sons having been lately made Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
citizens. He mentions him again in the following year and says, that the Athenians had sent Timotheus
Timotheus is a masculine male name. It is a latinized version of the Greek name (Timόtheos) mmeaning "one who honours God", from τιμή "honour" and θεός "god"., . The English version '' Timothy'' (and its variations) is a common name in ...
to his assistance; but that when the Athenian general saw that Ariobarzanes was in open revolt against the king, he refused to assist him.
Great Satraps' Revolt
When Pharnabazos' other son,Artabazos II of Phrygia
Artabazos II (in Greek Ἀρτάβαζος) (fl. 389 – 328 BC) was a Persian general and satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of the Persian satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia Pharnabazus II, and younger kinsman (most probably ...
, wanted to regain the satrapy from his brother, Ariobarzanes refused. Ultimately, in about 366 BCE, Ariobarzanes joined an unsuccessful revolt of the satraps of western Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
against the Achamenian King Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and suc ...
(Revolt of the Satraps
The Great Satraps' Revolt, or the Revolt of the Satraps (366-360 BC), was a rebellion in the Achaemenid Empire of several satraps against the authority of the Great King Artaxerxes II Mnemon. The Satraps who revolted were Datames, Ariobarzanes and ...
). Several other satraps sided with Ariobarzanes, including Mausolus
Mausolus ( grc, Μαύσωλος or , xcr, ���𐊠���𐊸𐊫𐊦 ''Mauśoλ'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by h ...
of Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionians, Ionian and Dorians, Dorian Greeks colonized the west of i ...
(briefly), Orontes I
Orontes I (Old Persian: ''*Arvanta-''; died 344 BC) was a Bactrian nobleman, who served as a military officer of the Achaemenid Empire in the first half of the 4th-century BC. He first appears in 401 BC as the satrap of the satrapy of Armenia. The ...
of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, Autophradates
Autophradates (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: , lived 4th century BC) was a Persian Satrap of Lydia, who also distinguished himself as a general in the reign of Artaxerxes III and Darius III.
Rule as a satrap of Lydia
During the reign of the Ar ...
of Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
and Datames
Datames (Old Persian: ''Dātama'' or ''Dātāma'', Aramaic: ''Tadanmu'', grc, Δατάμης, Datámēs; 407 BC – 362 BC), also known as Tarkamuwa, was an Iranian military leader, who served as the governor ( satrap) of the Achaemenid satrapy o ...
of Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revo ...
. The rebel satraps also received support from the pharaoh of Egypt, Teos
Teos ( grc, Τέως) or Teo was an ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, on a peninsula between Chytrium and Myonnesus. It was founded by Minyans from Orchomenus, Ionians and Boeotians, but the date of its foundation is unknown. Teos was ...
, as well as from some of the Greek city states, with the Spartan king Agesilaus II
Agesilaus II (; grc-gre, Ἀγησίλαος ; c. 442 – 358 BC) was king of Sparta from c. 399 to 358 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony ...
coming to their assistance with a mercenary force.
Ariobarzanes withstood a siege at Adramyttium
Adramyttium ( el, Άδραμύττιον ''Adramyttion'', Άδραμύττειον ''Adramytteion'', or Άτραμύττιον ''Atramyttion'') was an ancient city and bishopric in Aeolis, in modern-day Turkey. It was originally located at the he ...
in 366 BC, from Mausolus
Mausolus ( grc, Μαύσωλος or , xcr, ���𐊠���𐊸𐊫𐊦 ''Mauśoλ'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by h ...
of Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionians, Ionian and Dorians, Dorian Greeks colonized the west of i ...
and Autophradates
Autophradates (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: , lived 4th century BC) was a Persian Satrap of Lydia, who also distinguished himself as a general in the reign of Artaxerxes III and Darius III.
Rule as a satrap of Lydia
During the reign of the Ar ...
of Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
, until Agesilaus negotiated the besiegers' retreat.Gershevitch 1985, p. 378
Ariobarzanes was betrayed by his son Mithridates to his overlord, the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
king, who had Ariobarzanes crucified.Xenophon, ''Cyropaedia'viii. 8
Aristotle
v. 10
/ref>Brosius 2006, p. 29

Notes
Sources
*Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
, Politics
', H. Rackham (translator),
Cambridge, MA
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston ...
- London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, (1944)
*
*Demosthenes, ''Speeches'', C. A. Vince & J. H. Vince (translators), Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
—London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, (1926)
*Diodorus Siculus, Bibliotheca
', C. H. Oldfather (translator), Cambridge, MA - London, (1989) * *McGing, Brian C. (1986) "The Kings of Pontus: Some Problems of Identity and Date,". Rheinisches Museum für Philologie, vol. 129 (1986), pp 248..259. *Nepos, Cornetlius (1866)
', John Selby Watson (translator), (1886) * Smith, William (editor); ''
Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology
The ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'' (1849, originally published 1844 under a slightly different title) is an encyclopedia/biographical dictionary. Edited by William Smith, the dictionary spans three volumes and 3,700 p ...
''"Ariobarzanes I"
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, (1867)
*Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, wikt:Ξενοφῶν, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Anci ...
, ''Cyropaedia
The ''Cyropaedia'', sometimes spelled ''Cyropedia'', is a partly fictional biography of Cyrus the Great, the founder of Persia's Achaemenid Empire. It was written around 370 BC by Xenophon, the Athenian-born soldier, historian, and student of Soc ...
'', Cambridge, MA - London, (1979–83)
*Xenophon, ''Hellenica
''Hellenica'' ( grc, Ἑλληνικά) simply means writings on Greek (Hellenic) subjects. Several histories of 4th-century Greece, written in the mould of Thucydides or straying from it, have borne the conventional Latin title ''Hellenica''. Th ...
'', Cambridge, MA—London, (1985–86)
----
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ariobarzanes 01 Of Cius
5th-century BC births
5th-century BC rulers
4th-century BC deaths
Iranian rebels
Achaemenid satraps of Hellespontine Phrygia
Military leaders of the Achaemenid Empire
Pharnacid dynasty
5th-century BC Iranian people
4th-century BC Iranian people