|
Antalcidas
Antalcidas ( grc-gre, Ἀνταλκίδας; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta. __NOTOC__ Life Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Spartan king Agesilaus II. Antalcidas is first recorded at the outset of the Corinthian War. Following the end of the Peloponnesian War after the destruction of the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, Sparta had launched a series of raids against the Persian satrapies of Asia Minor. Pharnabazus, satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia, finally responded by sending the Rhodian Timocrates to bribe the other Greek city states into declaring war on Sparta. Thebes rose up in 395 BC, eventually encouraging others to join in what became known as the Corinthian War. Persia was now on friendly terms with Athens and Pharnabazus permitted their disgraced general Conon to command his fleet of Phoenician and Cypriot ships in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian War
The Corinthian War (395–387 BC) was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with Spartan imperialism in the aftermath of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), both from Athens, the defeated side in that conflict, and from Sparta's former allies, Corinth and Thebes, who had not been properly rewarded. Taking advantage of the fact that the Spartan king Agesilaus II was away campaigning in Asia against the Achaemenid Empire, Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos forged an alliance in 395 BC with the goal of ending Spartan hegemony over Greece; the allies' war council was located in Corinth, which gave its name to the war. By the end of the conflict, the allies had failed to end Spartan hegemony over Greece, although Sparta was durably weakened by the war. At first, the Spartans achieved several successes in pitched battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agesilaus II
Agesilaus II (; grc-gre, Ἀγησίλαος ; c. 442 – 358 BC) was king of Sparta from c. 399 to 358 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC). Although brave in combat, Agesilaus lacked the diplomatic skills to preserve Sparta's position, especially against the rising power of Thebes, which reduced Sparta to a secondary power after its victory at Leuctra in 371 BC. Despite the traditional secrecy fostered by the Spartiates, the reign of Agesilaus is particularly well-known thanks to the works of his friend Xenophon, who wrote a large history of Greece (the ''Hellenica'') covering the years 411 to 362 BC, therefore extensively dealing with Agesilaus' rule. Xenophon furthermore composed a panegyric biography of his friend, perhaps to clean his memory from the criticisms voiced against him. Another historical tradition—much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiribazus
Tiribazus, Tiribazos or Teribazus (Old Iranian: ''Tīrībāzu'') (c.440 BC-370 BC) was an Achaemenid satrap of Western Armenia and later satrap of Lydia in western Anatolia. Satrap of Western Armenia He was highly regarded by the Persian King Artaxerxes II, and when he was present, so Xenophon tells us, no one else had the honour of helping the sovereign to mount his horse. Until 395 BC, Tiribazus served as the hyparch of Western Armenia. Satrap of Lydia He succeeded Tithraustes as satrap of Western Asia (Sardis). He was holding this office when, in 393 BC, Antalcidas was sent to negotiate, through him, a peace for Sparta with the Persian king. In 392 BC, while the Corinthian War was being contested amongst the Greek states, Tiribazus received envoys from the major belligerents of that war, and held a conference in which a proposal for ending the war was discussed. That discussion failed, but Tiribazus, convinced that Athens was becoming a threat to Persia in the Aegean, sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II () and his mother was Parysatis. Soon after his accession, Artaxerxes II faced opposition from his younger brother Cyrus the Younger, who assembled an army composing of troops from his Lydian and Ionian satrapies as well as Greek mercenaries in his bid for the throne. The forces of the brothers clashed at Cunaxa in 401 BC, which resulted in the defeat and death of Cyrus. Following this, Artaxerxes II had to contend with several other revolts; a revolt by Evagoras I () in Cyprus between 391–380 BC, by the Phoenicians in , and most importantly, the revolts by the western satraps (known as the Great Satraps' Revolt) in the 360s and 350s BC, led by distinguished figures such as Datames, Ariobarzanes, and Autophradat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
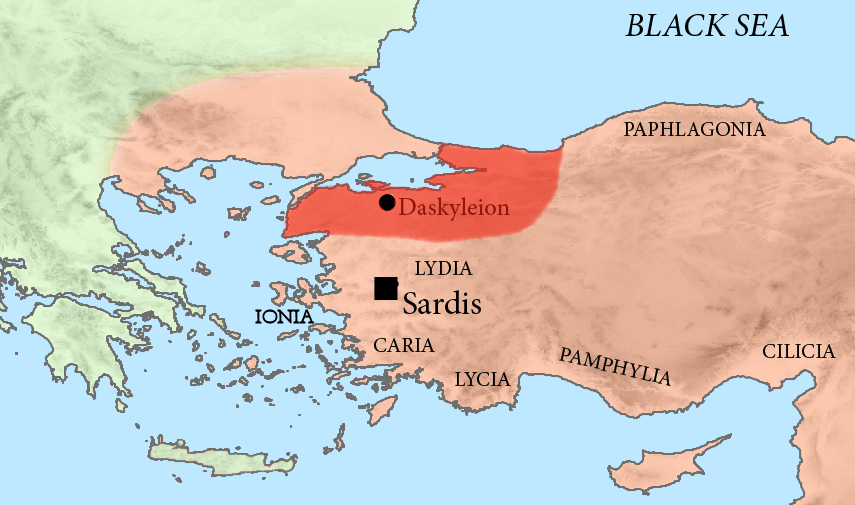
Pharnabazus II
Pharnabazus II (Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', grc-gre, Φαρνάβαζος ; ruled 413-374 BC) was a Persian soldier and statesman, and Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of Pharnaces II of Phrygia and grandson of Pharnabazus I, and great-grandson of Artabazus I. He and his male ancestors, forming the Pharnacid dynasty, had governed the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia from its headquarters at Dascylium since 478 BC. He married Apama, daughter of Artaxerxes II of Persia, and their son Artabazus also became a satrap of Phrygia. According to some accounts, his granddaughter Barsine may have become Alexander the Great's concubine. According to research by Theodor Nöldeke, he was descended from Otanes, one of the associates of Darius in the murder of Smerdis. Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia War with Sparta against Athens (c.413-404 BC) Athens was the dominant power in the Aegean in the 5th century BC, following the Greeks' victories over the Achaemenids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
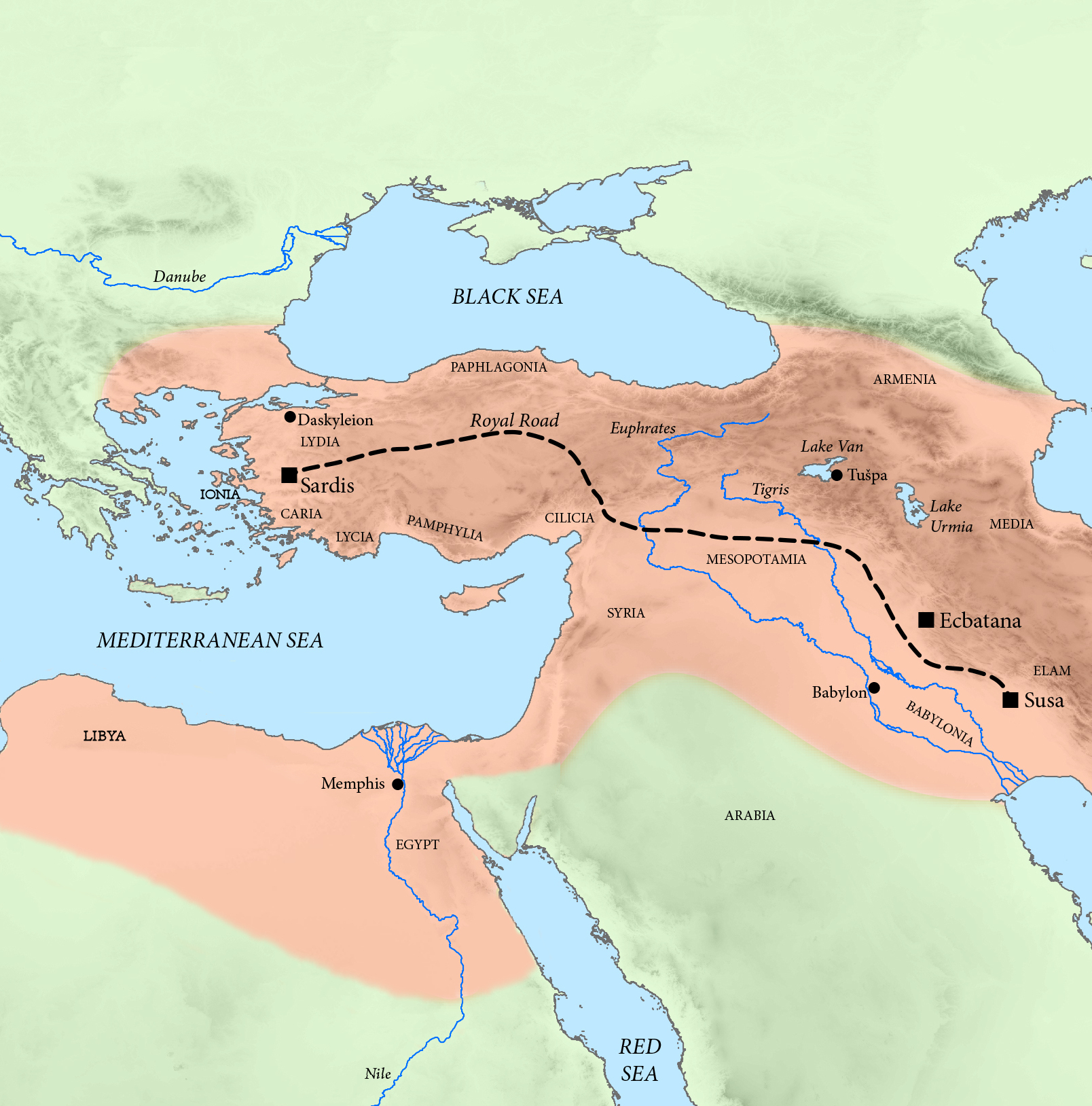
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Warfare
Warfare occurred throughout the history of Ancient Greece, from the Greek Dark Ages onward. The Greek 'Dark Ages' drew to an end as a significant increase in population allowed urbanized culture to be restored, which led to the rise of the city-states (''Poleis''). These developments ushered in the period of Archaic Greece (800–480 BC). They also restored the capability of organized warfare between these '' Poleis'' (as opposed to small-scale raids to acquire livestock and grain, for example). The fractious nature of Ancient Greek society seems to have made continuous conflict on this larger scale inevitable. Along with the rise of the city- states evolved a new style of warfare: the hoplite phalanx. Hoplites were armored infantrymen, armed with spears and shields. Seen in media, the phalanx was a formation of these soldiers with their shields locked together and spears pointed forward. The Chigi vase, dated to around 650 BC, is the earliest depiction of a hoplite in full bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city neverth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cnidus
The Battle of Cnidus ( gr, Ναυμαχία της Κνίδου) was a military operation conducted in 394 BC by the Achaemenid Empire against the Spartan naval fleet during the Corinthian War. A fleet under the joint command of Pharnabazus and former Athenian admiral, Conon, destroyed the Spartan fleet led by the inexperienced Peisander, ending Sparta's brief bid for naval supremacy. The battle outcome was a significant boost for the anti-Spartan coalition that resisted Spartan hegemony in the course of the Corinthian War. Prelude In 394 BC, King Agesilaus II of Sparta and his army were recalled from Ionia to help fight the Corinthian War. The Spartan fleet, under Peisander, also began a return to Greece, sailing out from its harbor at Cnidus with eighty-five triremes. The "Greek" vanguard of the Achaemenid fleet, referred to as such only due to its consisting of Greek mercenaries, was commanded by Conon, while the Persian satrap Pharnabazus led the main body of the forces, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Phoenicia
The history of ancient Lebanon traces the course of events related to the geographic area in the Eastern Mediterranean of what is now known as Lebanon from the beginning of antiquity to the beginning of Arab rule. Prehistoric times The earliest known settlements in Lebanon date back to earlier than 5000 BC. In Byblos, which is considered to be the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world, archaeologists have discovered remnants of prehistoric huts with crushed limestone floors, primitive weapons, and burial jars which are evidence of the Neolithic and Chalcolithic fishing communities who lived on the shore of the Mediterranean Sea over 8,000 years ago. Ancient Near East Bronze Age The area was first recorded in history around 4000 BC as a group of coastal cities and a heavily forested hinterland. It was inhabited by the Canaanites, a Semitic people, whom the Greeks called "Phoenicians" because of the purple (phoinikies) dye they sold. These early inhabitants refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eber-Nari
Eber-Nari (Akkadian, also Ebir-Nari), Abar-Nahara עבר-נהרה (Aramaic) or 'Ābēr Nahrā ( Syriac) meaning "Beyond the River" or "Across the River" in both the Akkadian and Imperial Aramaic languages of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, i.e., the Western bank of the Euphrates from a Mesopotamian and Persian viewpoint), also referred to as Transeuphratia (french: Transeuphratène) by modern scholars, was a region of Western Asia and a satrapy of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–605 BC), Neo-Babylonian Empire (612–539 BC) and Achaemenid Empire (539–332 BC). The Akkadian Eber-Nari is referred to as Athura or Athuriya in Old Persian, and Aššur in the Elamite. The Targum Onkelos lists Nineveh, Calah, Reheboth, and Resen as being in the jurisdiction of Athura. Name * akk, text=𒆳𒂊𒄵𒀀𒇉, translit=Eber-Nāri UR.e.bir.ID₂lit=trans river — i.e. the region west of the Euphrates. * — i.e. the other side of the Euphrates. * he, עבר הנהר, translit=ʿĒḇer haNāh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






_19.jpg)
.jpg)