Aqua Anio Vetus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Aqua Anio Vetus was an ancient
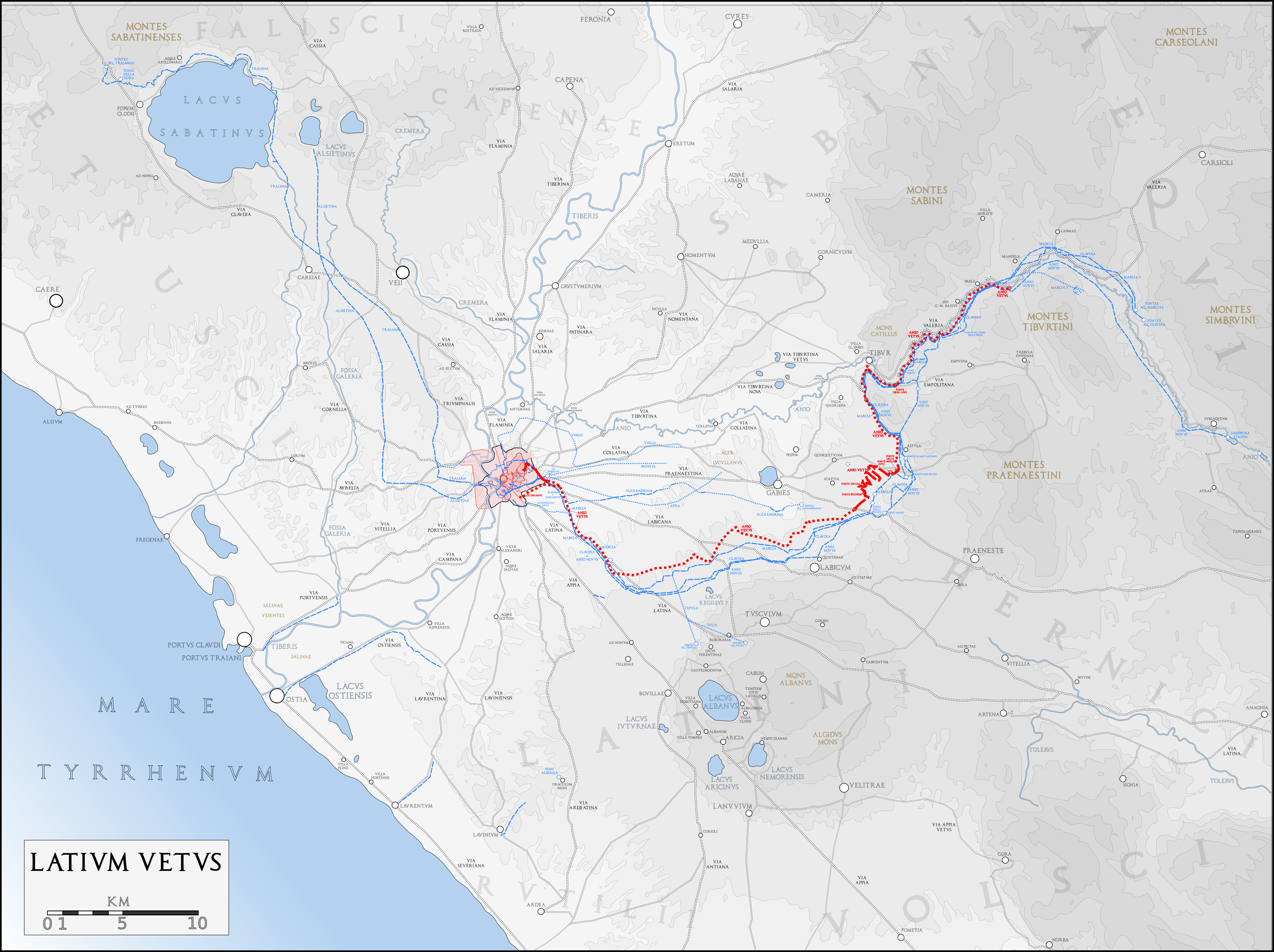
 Its source is believed to be between Vicovaro and Mandela, upstream of the gorge at
Its source is believed to be between Vicovaro and Mandela, upstream of the gorge at
Roman aqueduct
The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported min ...
, and the second oldest after the Aqua Appia
The Aqua Appia was the first Roman aqueduct, constructed in 312 BC by the co-censors Gaius Plautius Venox and Appius Claudius Caecus, the same Roman censor who also built the important Via Appia.
The Appia fed the city of Rome with an estima ...
. It was commissioned in 272 BC and funded by treasures seized after the victory against Pyrrhus of Epirus
Pyrrhus (; grc-gre, Πύρρος ; 319/318–272 BC) was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period.Plutarch. '' Parallel Lives'',Pyrrhus... He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he be ...
. Two magistrates were appointed by the Senate, the censors Manius Curius Dentatus
Manius Curius Dentatus (died 270 BC) was a Roman general and statesman noted for ending the Samnite War and for his military exploits during the Pyrrhic War. According to Pliny, he was born with teeth, thus earning the surname Dentatus, "toothed. ...
(who died five days after the assignment) and Flavius Flaccus.
The aqueduct took water from the Anio
The Aniene (; la, Aniō), formerly known as the Teverone, is a river in Lazio, Italy. It originates in the Apennines at Trevi nel Lazio and flows westward past Subiaco, Vicovaro, and Tivoli to join the Tiber in northern Rome. It formed the pr ...
river and acquired the nickname of ''Vetus'' ("old") only after the Anio Novus
Aqua Anio Novus ( Latin for "New Anio aqueduct") was an ancient Roman aqueduct. Like the Aqua Claudia, it was begun by emperor Caligula in 38 AD and completed in 52 AD by Claudius, who dedicated them both on August 1. Together with the Aqua Ani ...
was built almost three centuries later..
The Anio Vetus was an engineering masterpiece, especially considering its early date and complexity of construction. It was four times as long as the Aqua Appia
The Aqua Appia was the first Roman aqueduct, constructed in 312 BC by the co-censors Gaius Plautius Venox and Appius Claudius Caecus, the same Roman censor who also built the important Via Appia.
The Appia fed the city of Rome with an estima ...
and its source much higher. Its flow was more than twice that of the Aqua Appia and supplied water to higher elevations of the city. However, the Anio Vetus had muddy and discoloured water and probably did not supply drinking water to the Roman aristocracy.
Route

San Cosimato
The church of San Cosimato is a church located in the city of Rome, Italy. It was originally built in the 10th century in the Trastevere rione and now includes the hospital known as "Nuovo Regina Margherita." Originally, it was built as a Bene ...
. Like the Aqua Appia, its route was mainly underground.
It descended from its source along the valley to Tivoli
Tivoli may refer to:
* Tivoli, Lazio, a town in Lazio, Italy, known for historic sites; the inspiration for other places named Tivoli
Buildings
* Tivoli (Baltimore, Maryland), a mansion built about 1855
* Tivoli Building (Cheyenne, Wyoming), ...
, where it left the Anio towards the Alban Hills
The Alban Hills ( it, Colli Albani) are the caldera remains of a quiescent volcanic complex in Italy, located southeast of Rome and about north of Anzio. The high Monte Cavo forms a highly visible peak the centre of the caldera, but the hi ...
to near Gallicano
Gallicano is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Lucca in the Italian region Tuscany, located about northwest of Florence and about northwest of Lucca.
The municipality is located in Serchio Valley, on the right bank of the Serchi ...
, below Palestrina
Palestrina (ancient ''Praeneste''; grc, Πραίνεστος, ''Prainestos'') is a modern Italian city and ''comune'' (municipality) with a population of about 22,000, in Lazio, about east of Rome. It is connected to the latter by the Via Pre ...
. It crossed under the Via Latina
The Via Latina (Latin for "Latin Road") was a Roman road of Italy, running southeast from Rome for about 200 kilometers.
Route
It led from the Porta Latina in the Aurelian walls of Rome to the pass of Mount Algidus; it was important in the ear ...
near the seventh milestone and at the fourth milestone turned northwest to enter Rome.
It entered the city underground at the Porta Praenestina and terminated inside the Porta Esquilina
The Porta Esquilina (or Esquiline Gate) was a gate in the Servian Wall,Platner, S.B. and Ashby, T. ''A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome''. London: Humphrey Milford Oxford University, Press. 1929 of which the Arch of Gallienus is extant tod ...
. Only 5.8% of the Vetus' total flow supplied imperial buildings, an important difference from the Appia, which provided almost 22% to such buildings.
It had 35 ''castella'' for distribution in the city.
Three major restorations were done along with the Appia aqueduct: in 144 BC by the praetor Quintus Marcius Rex during construction of the Aqua Marcia, by adding a secondary conduit in the Casal Morena area; in 33 BC when Agrippa took control of the entire water system of the city; and between 11 and 4 BC by Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
. With this latter, an underground branch was built, the ''specus Octavianus'', that started from the current Pigneto area and followed the Via Casilina
The Via Casilina is a medieval road in Latium and Campania. It led from Rome to Casilinum (present-day Capua), to present-day Santa Maria Capua Vetere.
It was created from the fusion of two ancient Roman roads, the ''Via Latina'' and the '' Via La ...
and reached the area where the Baths of Caracalla
, alternate_name = it, Terme di Caracalla
, image = File:Baths of Caracalla, facing Caldarium.jpg
, caption = The baths as viewed from the south-west. The caldarium would have been in the front of the image
, coordinates = ...
were later built.
Other restorations in the first two centuries AD include the construction of bridges across valleys on the route to shortcut long underground diversions. These include Ponte Della Mola, which dates to Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania ...
and was built to cross a valley shortening the route by about . It is long and high with a double order of 29 arches and two single arches. The central part, for a stretch of three double arches, collapsed in 1965 and an adjacent fourth double arch was soon demolished because it was unsafe.
Other remains
Remains of the bridges Ponte Taulella, Ponte Pischero, Ponte degli Arci, and Ponte Lupo still exist.See also
*List of aqueducts in the city of Rome
This article lists ancient Roman aqueducts in the city of Rome.
Introduction
In order to meet the massive water needs of its huge population, the city of Rome was eventually supplied with 11 aqueducts by 226 AD, which were some of the city's ...
*List of aqueducts in the Roman Empire
This is a list of aqueducts in the Roman Empire. For a more complete list of known and possible Roman aqueducts and Roman bridges see List of Roman bridges.
Aqueducts in the Roman Empire
See also
* List of aqueducts
Map of Roman Aqueduct i ...
*List of Roman aqueducts by date
This is a list of aqueducts in the city of Rome listed in chronological order of their construction.
Ancient Rome
Modern Rome
* Acqua Vergine Antica
** built in 1453
** source: springs in Salone, east of Rome
** length: ; underground from ...
*Parco degli Acquedotti
The Parco degli Acquedotti is a public park to the southeast of Rome, Italy. It is part of the Appian Way Regional Park and is of approximately 240 ha.
Description
The park is named after the aqueducts that run through it. It is crossed on o ...
*Ancient Roman technology
Roman technology is the collection of antiques, skills, methods, processes, and engineering practices which supported Roman civilization and made possible the expansion of the economy and military of ancient Rome (753 BC – 476 AD).
The R ...
*Roman engineering
The ancient Romans were famous for their advanced engineering accomplishments. Technology for bringing running water into cities was developed in the east, but transformed by the Romans into a technology inconceivable in Greece. The architecture ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Ancient Roman aqueducts in Rome