Aeaea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Aeaea, Ææa or Eëä ( or ; grc, Αἰαία, Aiaíā ) was a
__NOTOC__
Aeaea, Ææa or Eëä ( or ; grc, Αἰαία, Aiaíā ) was a
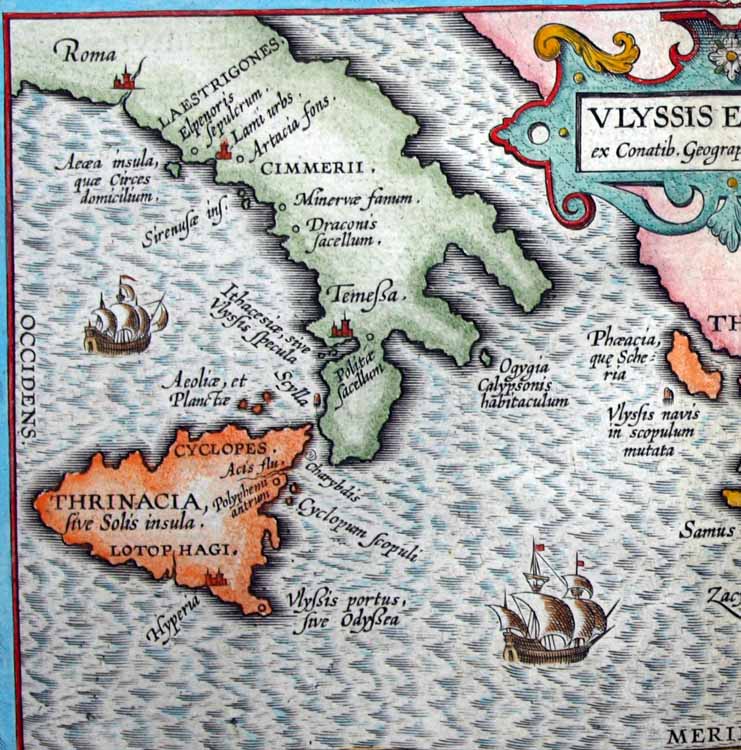
 The somewhat inconsistent geography of Homer's ''Odyssey'' is often considered more mythic than literal, but the geography of the Alexandrian scholar and poet
The somewhat inconsistent geography of Homer's ''Odyssey'' is often considered more mythic than literal, but the geography of the Alexandrian scholar and poet
 __NOTOC__
Aeaea, Ææa or Eëä ( or ; grc, Αἰαία, Aiaíā ) was a
__NOTOC__
Aeaea, Ææa or Eëä ( or ; grc, Αἰαία, Aiaíā ) was a mythological
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
island said to be the home of the goddess-sorceress Circe
Circe (; grc, , ) is an enchantress and a minor goddess in ancient Greek mythology and religion. She is either a daughter of the Titan Helios and the Oceanid nymph Perse or the goddess Hecate and Aeëtes. Circe was renowned for her vas ...
.
In Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Iliad'', ...
'', Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odys ...
tells Alcinous
In Greek mythology, Alcinous (; Ancient Greek: Ἀλκίνους or Ἀλκίνοος ''Alkínoös'' means "mighty mind") was a son of Nausithous and brother of Rhexenor. After the latter's death, he married his brother's daughter Arete who ...
that he stayed here for one year on his way home to Ithaca
Ithaca most commonly refers to:
*Homer's Ithaca, an island featured in Homer's ''Odyssey''
*Ithaca (island), an island in Greece, possibly Homer's Ithaca
*Ithaca, New York, a city, and home of Cornell University and Ithaca College
Ithaca, Ithaka ...
. He says that he could not resist the need to be on this island, not so much for Circe but so that he does not resist the pull.
Before leaving Aeaea, Odysseus was given instructions by Circe about how to cross the ocean and assisted by the North Wind to reach the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwo ...
:
Description
Homer describes Aeaea as covered with a mixture of pasture and dense woodland of oak and beech. There were high hills or bluffs from which the sea could be seen encircling the island in all directions. Circe's stone house was located in a "dense forest of trees" "in a place that could be seen from far."Location
 The somewhat inconsistent geography of Homer's ''Odyssey'' is often considered more mythic than literal, but the geography of the Alexandrian scholar and poet
The somewhat inconsistent geography of Homer's ''Odyssey'' is often considered more mythic than literal, but the geography of the Alexandrian scholar and poet Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( grc, Ἀπολλώνιος Ῥόδιος ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; la, Apollonius Rhodius; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the '' Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and ...
is more specific. In his epic ''Argonautica
The ''Argonautica'' ( el, Ἀργοναυτικά , translit=Argonautika) is a Greek epic poem written by Apollonius Rhodius in the 3rd century BC. The only surviving Hellenistic epic, the ''Argonautica'' tells the myth of the voyage of Jas ...
'', he locates the island somewhere south of ''Aethalia'' (Elba
Elba ( it, isola d'Elba, ; la, Ilva) is a Mediterranean island in Tuscany, Italy, from the coastal town of Piombino on the Italian mainland, and the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago. It is also part of the Arcipelago Toscano Nationa ...
), within view of the ''Tyrrhenian'' shore (western coast of Italy). In the same poem, Aeëtes remarks on the great distance between Colchis and Aeaea in these terms:
Aeaea was later identified by classical Roman writers with Mount Circeo
Monte Circeo or Cape Circeo ( it, Promontorio del Circeo , la, Mons Circeius) is a mountain promontory that marks the southwestern limit of the former Pontine Marshes.located on the southwest coast of Italy near San Felice Circeo. At the nor ...
on Cape Circeo (Cape Circaeum) on the western coast of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
—about 100 kilometers south of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
—which may have looked like an island due to the marshes and sea surrounding its base but which is a small peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on a ...
. It was already a peninsula according to Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary styl ...
. However, it may have been still an island in the days of Homer, with a long " lido" or sandy peninsula that gradually became attached to the mainland, in a common geological process. Archeologists have identified one cave or grotto on the cape as "Grotta della Maga Circe", the cave of Circe. A second was found on the nearby Island of Ponza
Ponza (Italian: ''isola di Ponza'' ) is the largest island of the Italian Pontine Islands archipelago, located south of Cape Circeo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is also the name of the commune of the island, a part of the province of Latina i ...
. It is believed that Circe had her summer home on Mount Circe and her winter home on Ponza, which may possibly be the island of Aeaea.
The modern Greek scholar Ioannis Kakridis
Ioannis Kakridis ( el, Ιωάννης Κακριδής) (17 November 1901 – 20 March 1992) was a Greek classical scholar and was one of the leading scholars of Homeric Poetry in the twentieth century.
He was born in Athens in 1901 and received ...
insists that any attempt at realistic identification is in vain, arguing that Homer vaguely located Aeaea somewhere in the eastern part of his world, perhaps near Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
, since Circe was the sister of Aeëtes
Aeëtes (; , ; , ), or Aeeta, was a king of Colchis in Greek mythology. The name comes from the ancient Greek word (, "eagle").
Family
Aeëtes was the son of Sun god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis, brother of Circe, Perses and Pasiphaë, ...
, king of Colchis, and because their paternal aunt the goddess Eos had her palace there.
Other hypothetical locations
Robert Graves
Captain Robert von Ranke Graves (24 July 1895 – 7 December 1985) was a British poet, historical novelist and critic. His father was Alfred Perceval Graves, a celebrated Irish poet and figure in the Gaelic revival; they were both Celt ...
(''The Greek Myths'') identifies, as Aeaea, the island of Lošinj, near the Istrian peninsula in the north Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
.
An author, Fernando Jaume, identified the “Island of Circe” with Didyme
Salina () is one of the Aeolian Islands north of Sicily, southern Italy. It is the second largest island in the archipelago.
Salina is divided between three ''comuni'': Santa Marina on the eastern coast, Malfa to the north, and Leni to the so ...
, that is, Salina, the “erratic rocks” being the “Faraglioni di Lipari”, next to the “Island of the Sirens” and the “ Hades in Sicily ”, perhaps as many evocations of the volcanism of this archipelago. The narrow beach, the forests dedicated to Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld aft ...
would be there, in Acquedolci
Tim Severin
Timothy Severin (25 September 1940 – 18 December 2020) was a British explorer, historian, and writer. Severin was noted for his work in retracing the legendary journeys of historical figures. Severin was awarded both the Founder's Meda ...
(''The Ulysses Voyage'') identifies, as Aeaea, the island of Paxos in the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including ...
near the Greek coast. The island is on the furthest west on a boundary between the sea and the river of Okeanos, which is said to encircle the earth. Drawing upon this interpretation, ''Assassin's Creed Odyssey
''Assassin's Creed Odyssey'' is a 2018 action role-playing video game developed by Ubisoft Quebec and published by Ubisoft. It is the eleventh major installment in the ''Assassin's Creed'' series and the successor to 2017's ''Assassin's Creed ...
'' uses a fictional atoll point off the coast of Paxos as the location.
Gaedl Lomen (''The Sea in the Greek Imagination'') identifies, as Aeaea the island of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
, in the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to commun ...
.
Aeaea in literature
InRichard Aldington
Richard Aldington (8 July 1892 – 27 July 1962), born Edward Godfree Aldington, was an English writer and poet, and an early associate of the Imagist movement. He was married to the poet Hilda Doolittle (H. D.) from 1911 to 1938. His 50-year w ...
's novel ''All Men are Enemies'' (1933), Aeaea is the island, "twelve hours from Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
" (obviously mythical), where his heroes meet, and love between them flourishes.
John Banville
William John Banville (born 8 December 1945) is an Irish novelist, short story writer, adapter of dramas and screenwriter. Though he has been described as "the heir to Proust, via Nabokov", Banville himself maintains that W. B. Yeats and Henry J ...
's 1993 novel ''Ghosts
A ghost is the soul or spirit of a dead person or animal that is believed to be able to appear to the living. In ghostlore, descriptions of ghosts vary widely from an invisible presence to translucent or barely visible wispy shapes, to re ...
'' has a boating party shipwrecked on an unnamed island; one character, Sophie, speculates that it is Aeaea; another says, "Yes...yes, Aeaea: you will feel at home, no doubt", a reference to Sophie's Circean nature.
"Aeaean" was an epithet of Circe
Circe (; grc, , ) is an enchantress and a minor goddess in ancient Greek mythology and religion. She is either a daughter of the Titan Helios and the Oceanid nymph Perse or the goddess Hecate and Aeëtes. Circe was renowned for her vas ...
and her paternal niece Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jaso ...
(), who were the sister and daughter of Aeëtes
Aeëtes (; , ; , ), or Aeeta, was a king of Colchis in Greek mythology. The name comes from the ancient Greek word (, "eagle").
Family
Aeëtes was the son of Sun god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis, brother of Circe, Perses and Pasiphaë, ...
, the ruler of Aea () in Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians are generally though ...
Circe's son Telegonus is likewise given this epithet. It was also a name of Calypso, who was believed to have inhabited a small island of the name of Aeaea in the straits between Italy and Sicily.Propert. iii. 10." 81
References
Sources
* {{authority control Locations in Greek mythology Geography of the Odyssey Mythological islands Circe